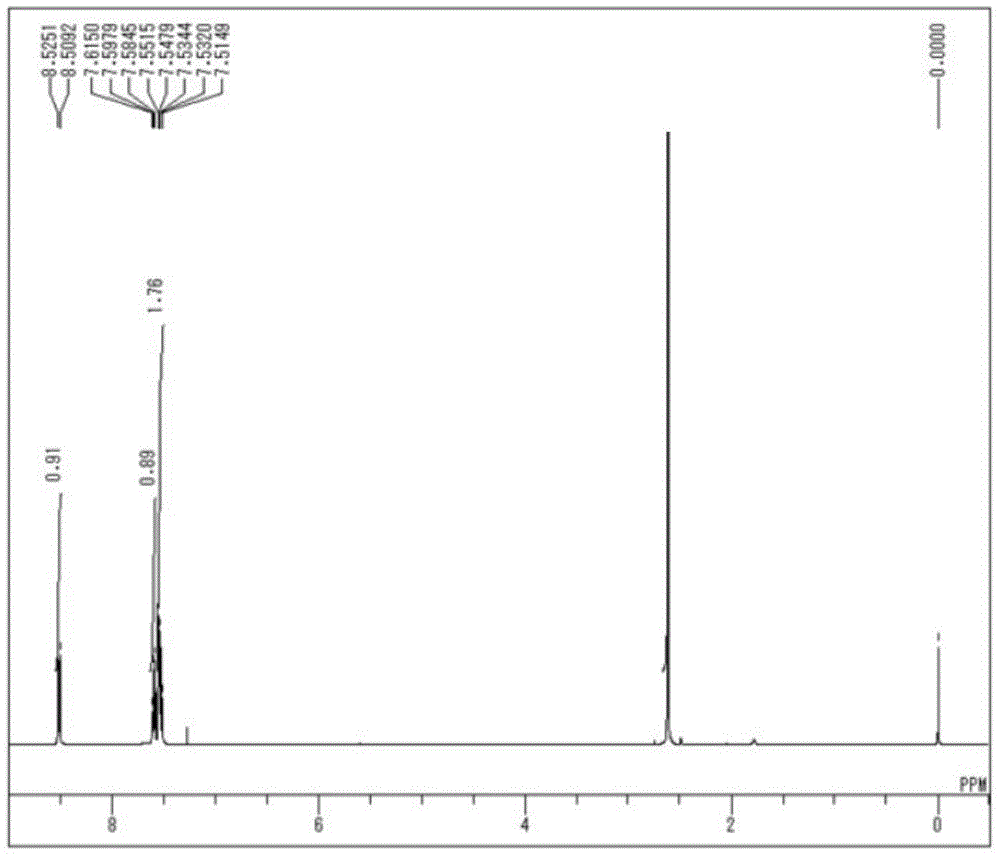
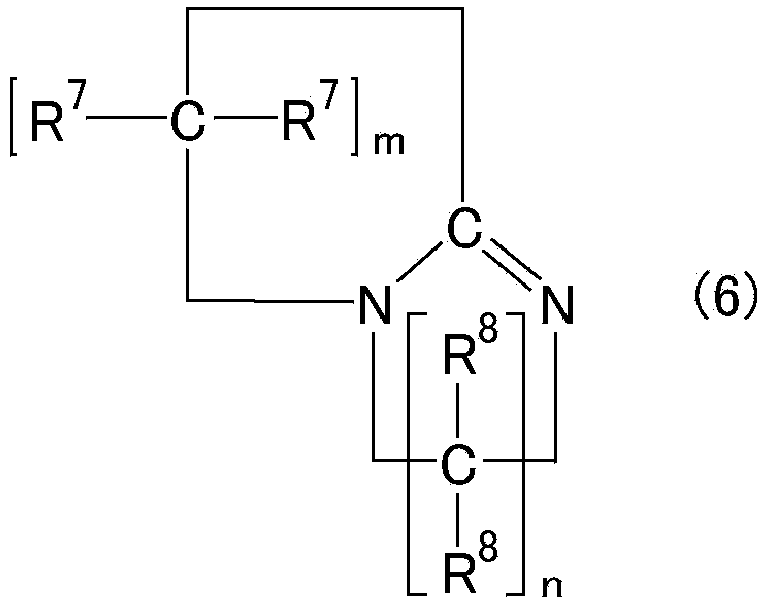
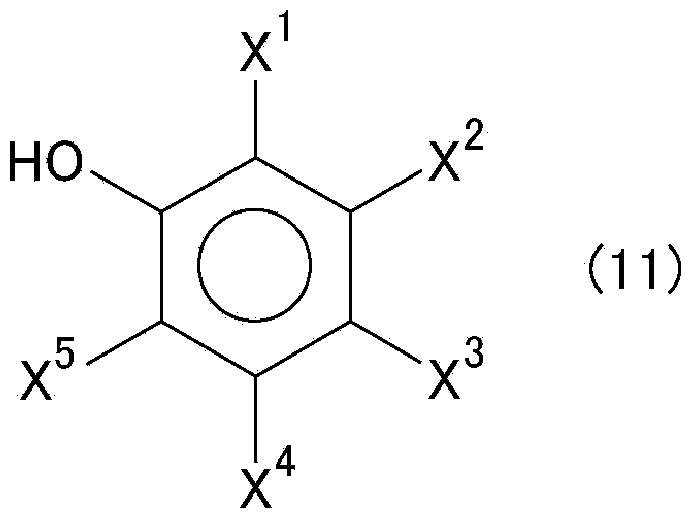
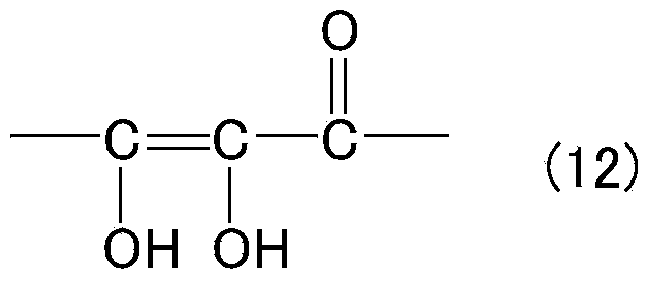
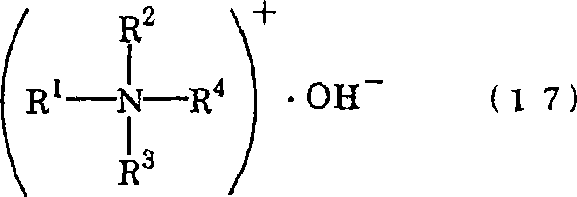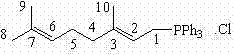Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40 results about "Dissociation reaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A dissociation reaction is a chemical reaction in which a compound breaks apart into two or more parts.
Surfactant
InactiveUS20070167343A1Efficient and advanced cleaningInhibitionNon-ionic surface-active compoundsAnionic surface-active compoundsNitrogenProton
To provide a surfactant which is obtainable by using substantially no alkali metal, has excellent readhesion prevention ability of finely-pulverized particles at the time of cleaning, and is capable of quite efficient and advanced cleaning. In the present invention, a surfactant which comprises a neutralized salt (AB1) and / or neutralized salt (AB2) is used. Neutralized salt (AB1): a neutralized salt (AB1) which comprises an acidic compound (A1) containing at least each one of an acid group (X1) of an acid having the difference of heat of formation in an acid dissociation reaction (Q1) of 3 to 200 kcal / mol and a hydrophobic group (Y) containing 1 to 36 carbon atoms, and a nitrogen-containing basic compound (B) having the difference of heat of formation in a proton addition reaction of 10 to 152 kcal / mol, wherein (X1) is at least one species selected from a sulfonic acid group, and the like. Neutralized salt (AB2): a neutralized salt (AB2) which comprises a polymer (A2) having at least one acid group (X2) within the molecule, and the nitrogen-containing basic compound (B) having the difference of heat of formation in a proton addition reaction of 10 to 152 kcal / mol.
Owner:SANYO CHEM IND LTD
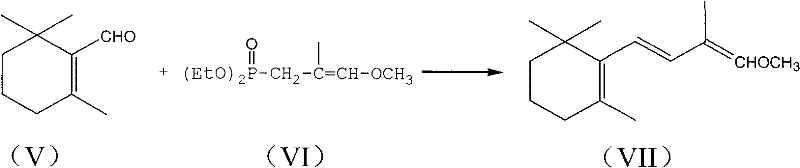
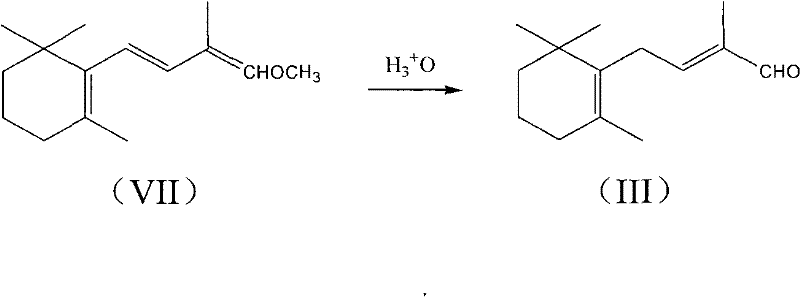
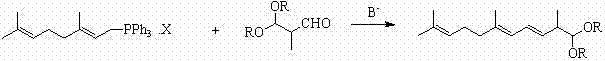
Method for preparing intermediate of vitamin A, namely tetradecanal
InactiveCN102190565AOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparation by hydrolysisEnol etherDissociation reaction
The invention provides a method for preparing an intermediate of vitamin A, namely C14-aldehyde, and an intermediate of the C14-aldehyde, namely C14 enol ether, which comprises the following steps of: (1) under the protection of inert gas, performing rearrangement dissociation reaction on C4 phosphonate at the temperature of between -40 and 30DEG C in the presence of alkali in an ether solvent ora dipolar aprotic solvent; (2) adding beta-cyclocitral, and performing Wittig-Homer condensation reaction at the temperature of between -40 and 30DEG C in the presence of alkali in the ether solvent or the dipolar aprotic solvent to obtain the C14 enol ether; and (3) under the protection of inert gas, mixing the C14 enol ether, an acid catalyst, water and a homogenous phase solvent, and performing hydrolysis reaction at the temperature of between 10 and 35DEG C with stirring to obtain the C14-aldehyde. The method has the advantages of simple process, readily available raw materials and low cost, and has great industrial value.
Owner:SHAOXING UNIVERSITY +1
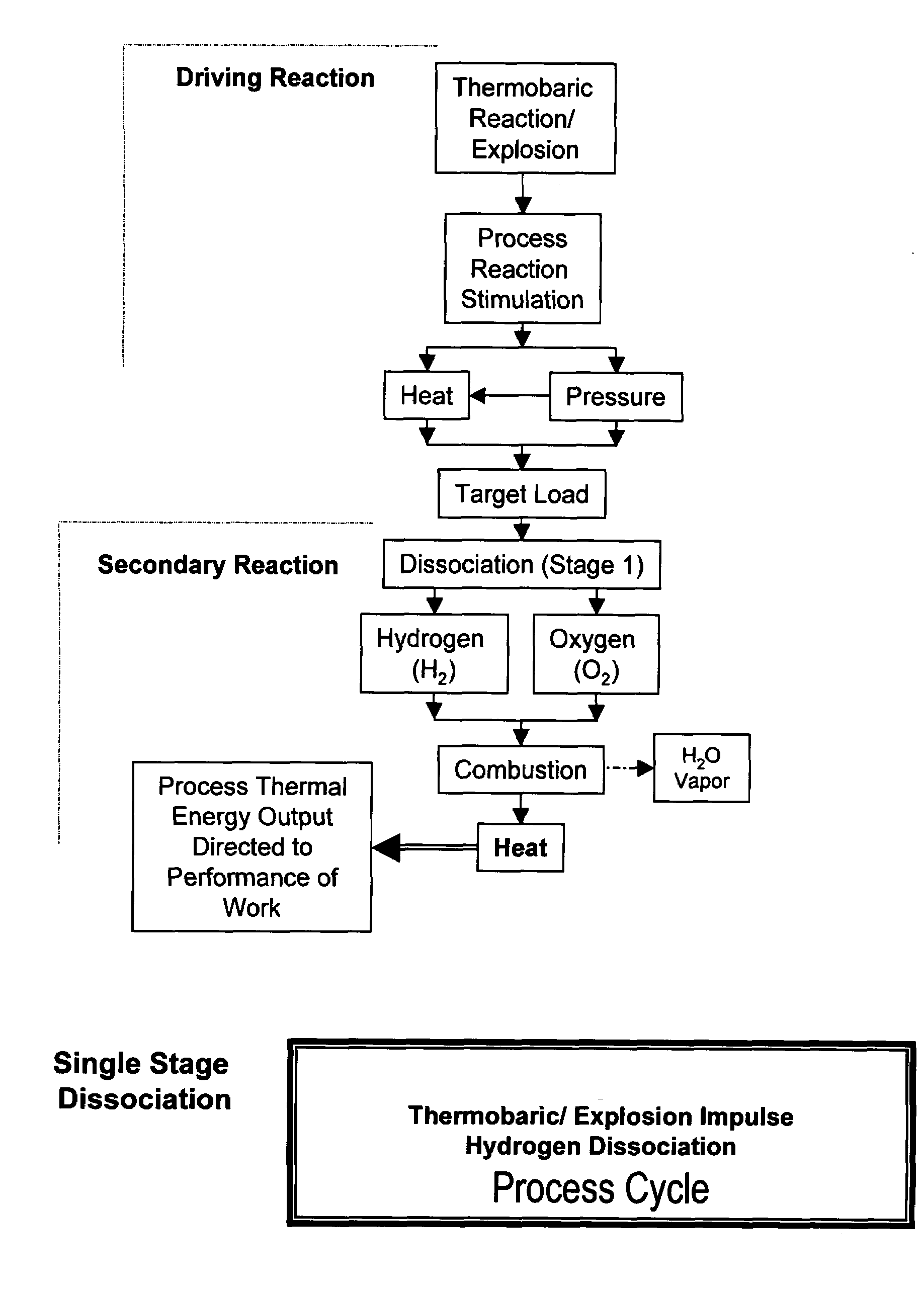
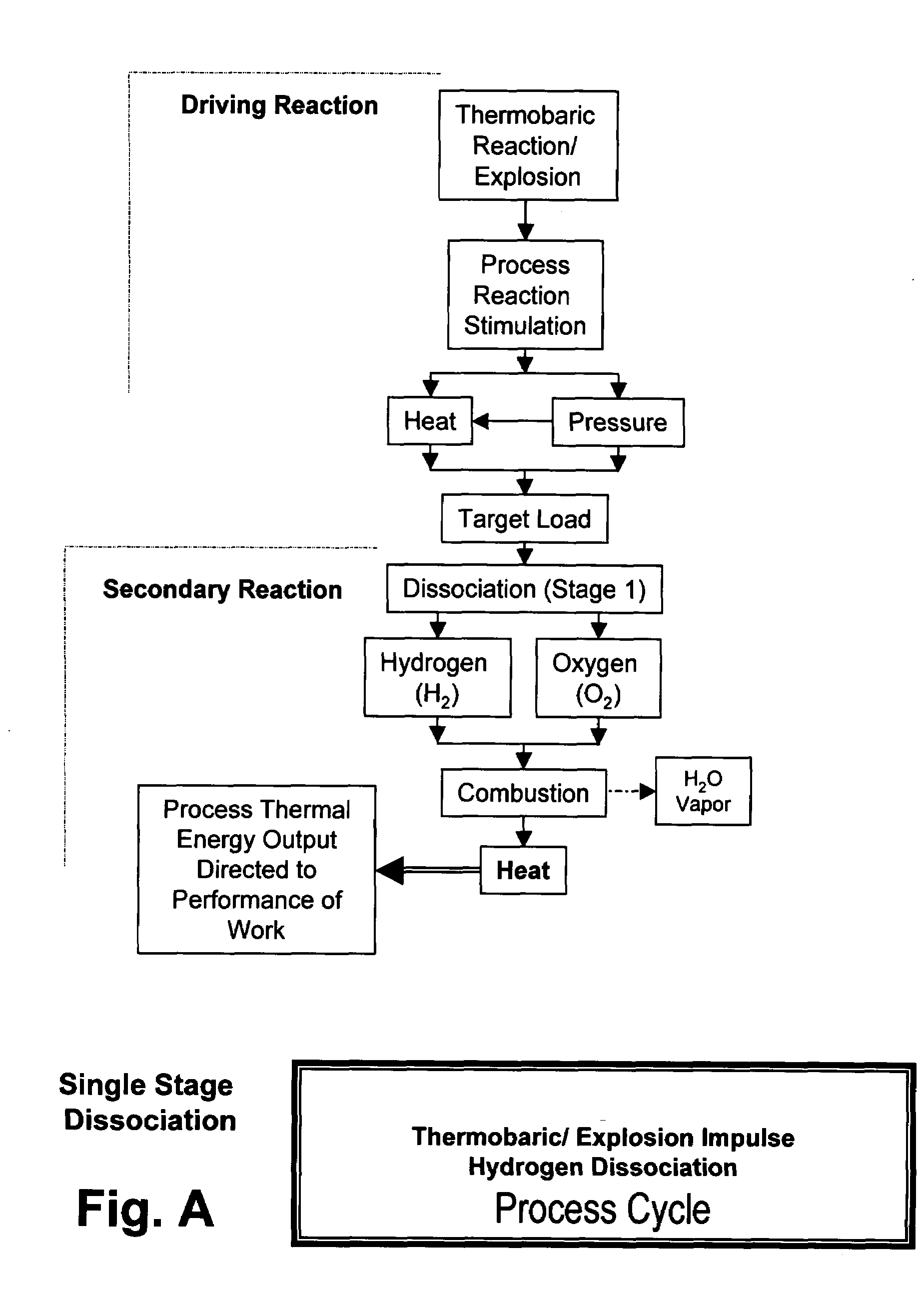
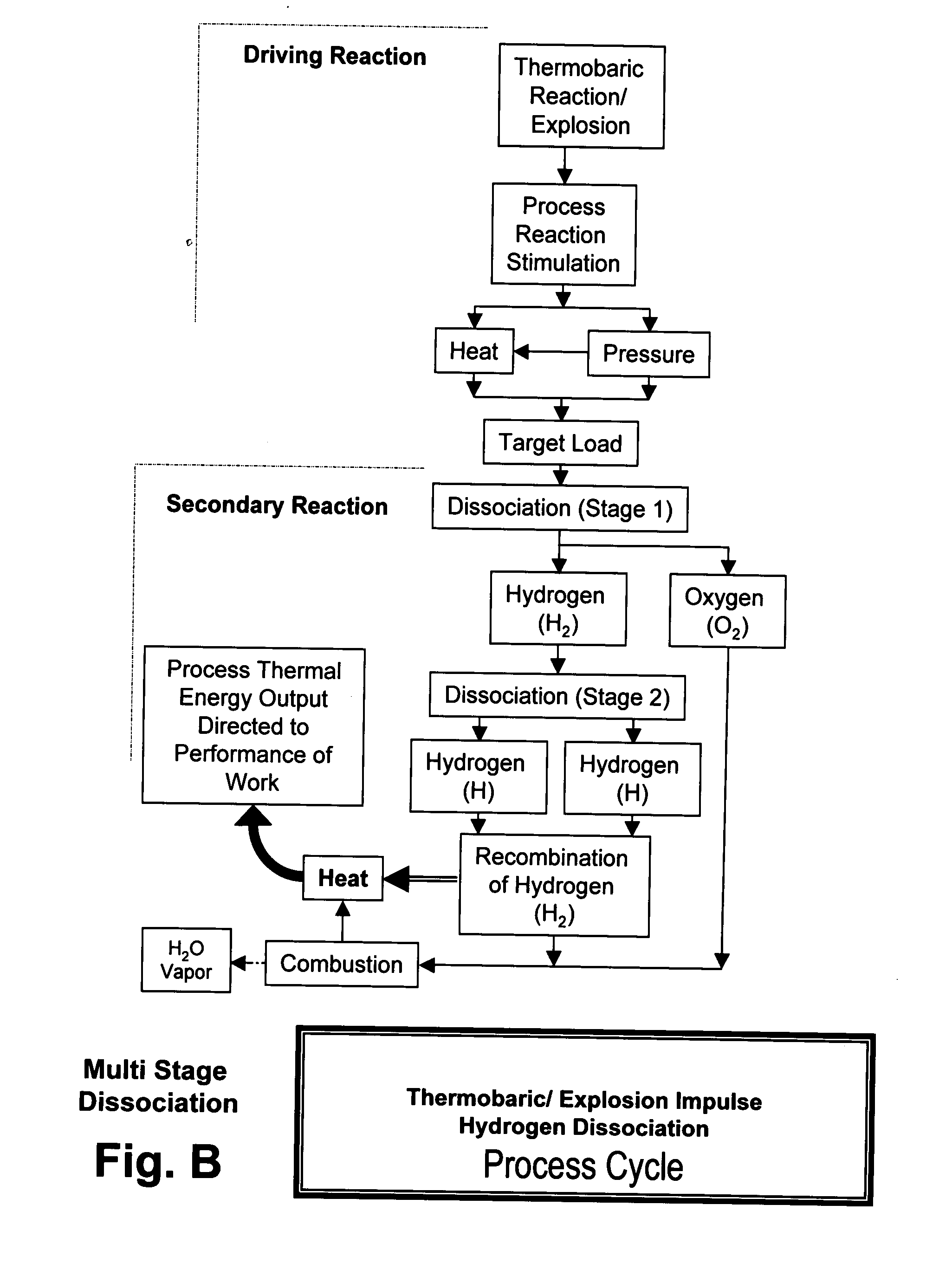
Xplogen TM: a system, method, and apparatus for generating energy from a series of dissociation reactions
InactiveUS20080223047A1Increase the Reynolds numberIncreased turbulenceOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideContinuous combustion chamberProcess systemsSteam pressure
Methods, systems, and apparatus for generating energy from a process-contained series of thermobaric reactions and / or explosion cycles are provided. The Xplogen™ energy generating system includes several embodiments for stimulating the heat and pressure release episodes, which are directed by the process system toward the task of dissociating a target substance being subjected to the hyper-stimulated pulse of energy. The target substance is thermolyzed by the pulse energy episode and the resulting dissociated gases are either quenched and captured or they are consumed in a direct thermal conversion process and are thus translated into steam pressure, and / or torque, thrust, motive force, and / or super-heat impulses. The methods and systems of the present invention include a comprehensive arrangement of process configurations and components as well as a means of operation.
Owner:OLIVER TROY LEE
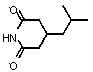
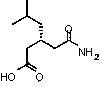
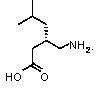
Preparation method of pregabalin
InactiveCN104140375AHigh purityEasy to operateOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationPregabalinDissociation reaction
The invention provides a preparation method of pregabalin. The preparation method comprises the following steps: performing chiral separation reaction, dissociation reaction and Hofmann degradation reaction with 3-(carbamoyl methyl)-5-methylhexanoic acid serving as raw material to prepare pregabalin, wherein a pregabalin chiral isomer generated in the process reacts under the action of an alkali reagent so as to obtain a hydrolysis product, and the hydrolysis product is hydrolyzed further and recycled to obtain the raw material 3-(carbamoyl methyl)-5-methylhexanoic acid. Compared with the prior art, the preparation method is convenient to carry out; the prepared pregabalin is high in purity; the used raw material can be recycled, so that the production cost is greatly reduced; the preparation method is favorable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:NANTONG CHANGYOO PHARMATECH CO LTD
Surfactant
InactiveCN101010421ALower zeta potentialPrevent reattachmentNon-ionic surface-active compoundsAnionic surface-active compoundsNitrogenProton
To provide a surfactant which is obtainable by using substantially no alkali metal, has excellent readhesion prevention ability of finely-pulverized particles at the time of cleaning, and is capable of quite efficient and advanced cleaning. In the present invention, a surfactant which comprises a neutralized salt (AB1) and / or neutralized salt (AB2) is used. Neutralized salt (AB1): a neutralized salt (AB1) which comprises an acidic compound (A1) containing at least each one of an acid group (X1) of an acid having the difference of heat of formation in an acid dissociation reaction (Q1) of 3 to 200 kcal / mol and a hydrophobic group (Y) containing 1 to 36 carbon atoms, and a nitrogen-containing basic compound (B) having the difference of heat of formation in a proton addition reaction of 10 to 152 kcal / mol, wherein (X1) is at least one species selected from a sulfonic acid group, and the like. Neutralized salt (AB2): a neutralized salt (AB2) which comprises a polymer (A2) having at least one acid group (X2) within the molecule, and the nitrogen-containing basic compound (B) having the difference of heat of formation in a proton addition reaction of 10 to 152 kcal / mol.
Owner:SANYO CHEM IND LTD
Method for concentrating oxygen isotope
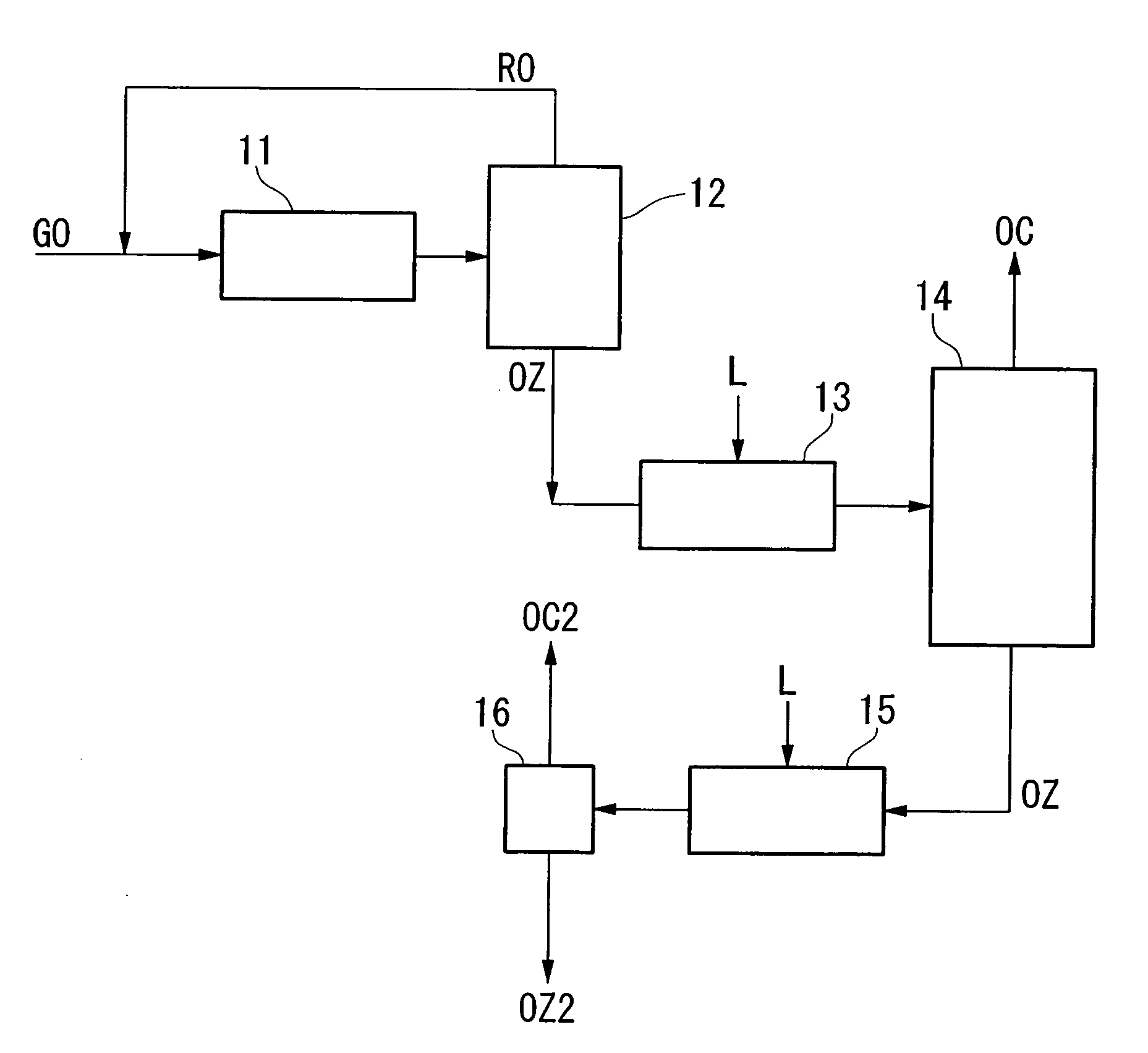
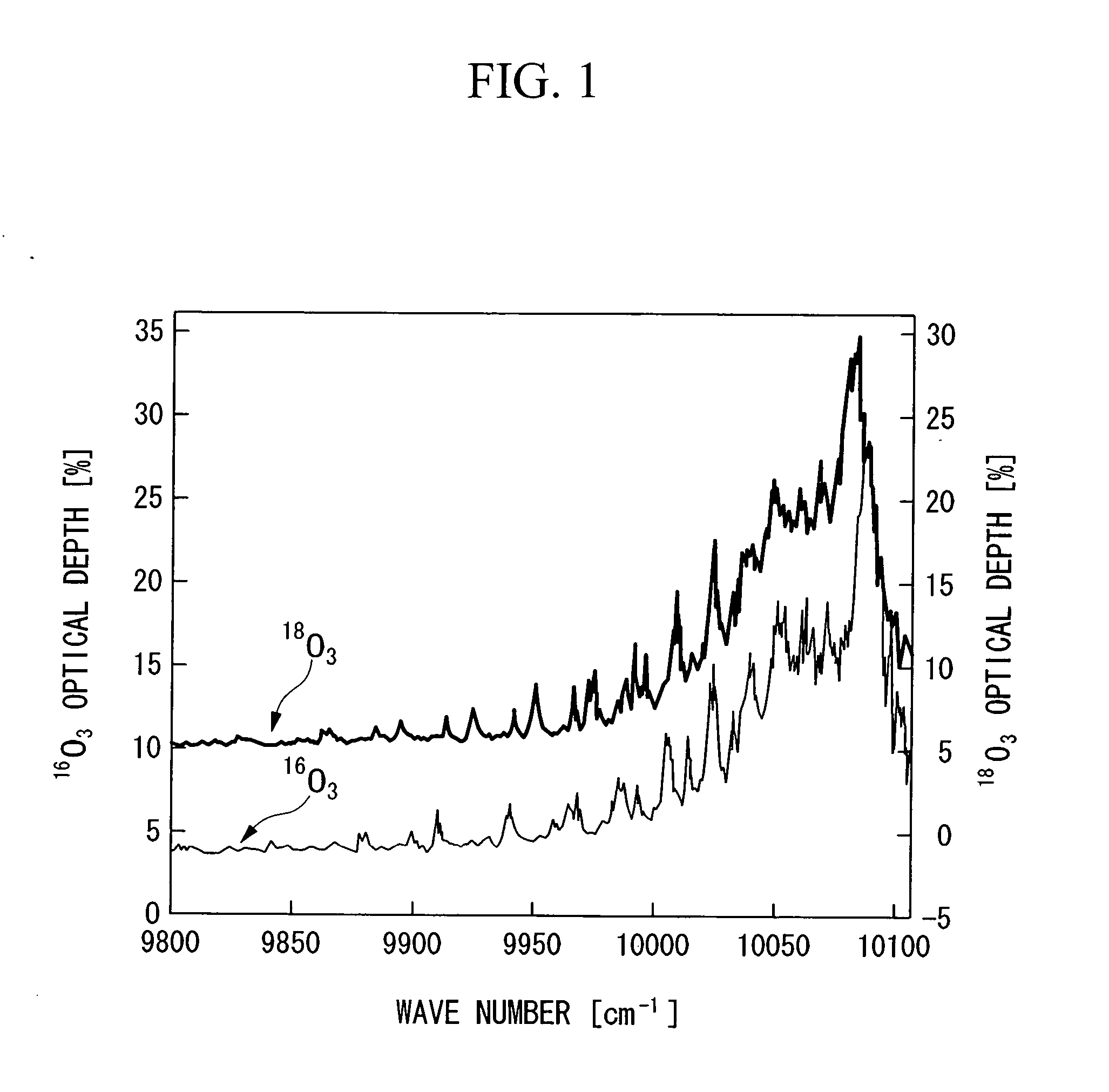
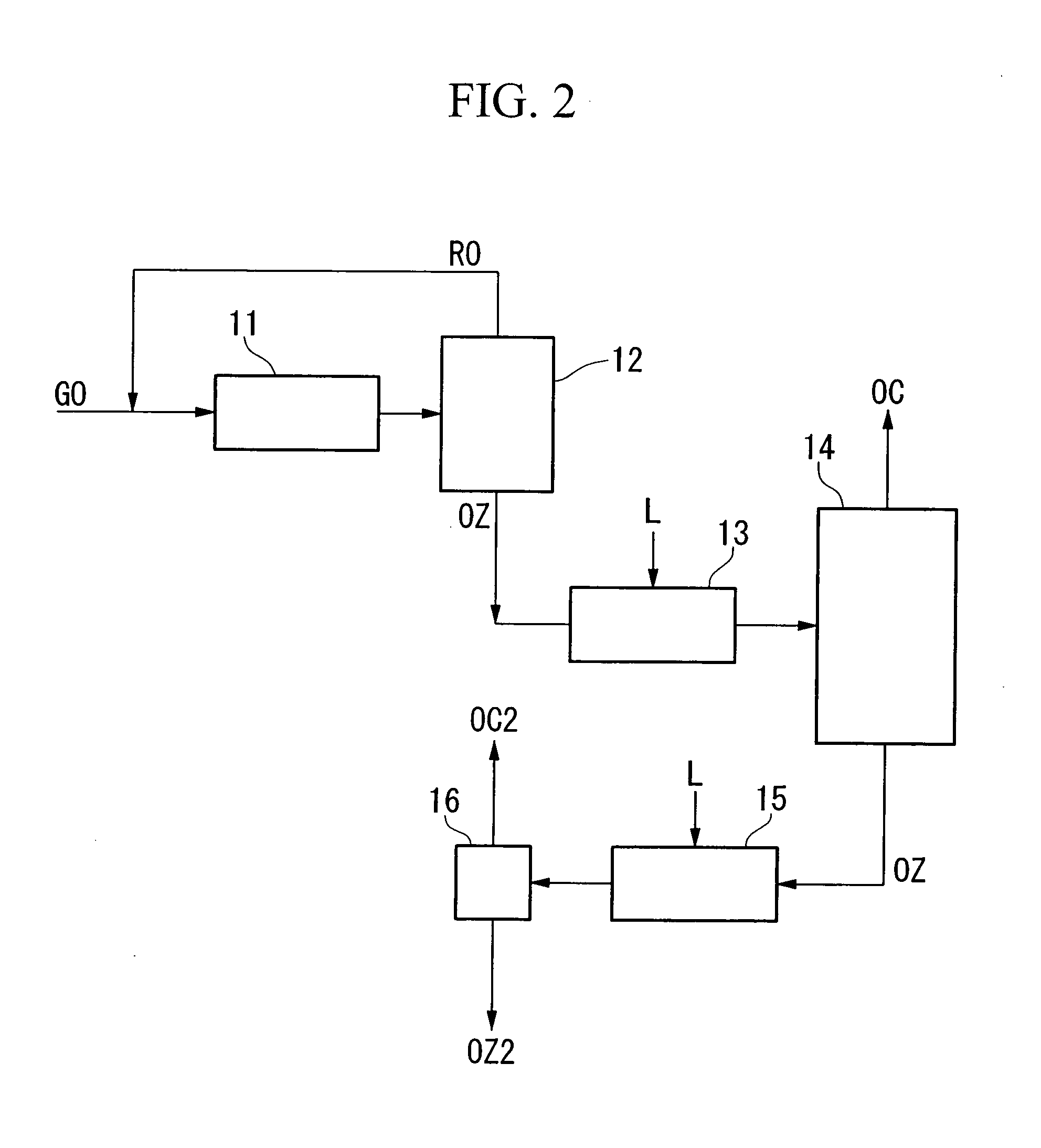
InactiveUS20060249366A1Increased concentration rateReduce ozone concentrationVapor condensationIsotope separationKryptonNoble gas
The object of the present invention is to provide an oxygen isotope concentration method capable of concentrating the stable oxygen isotopes of 17O and 18O which can be carried out using a simple device configuration. The present invention relates to a method for concentrating an oxygen isotope in separated oxygen by irradiating ozone with light, selectively dissociating an isotopomer of ozone containing an oxygen isotope in its molecule into oxygen, followed by dissociating the ozone and separating the formed oxygen from the non-dissociated ozone. The basic configuration of the device is provided with an ozone formation unit 11 that forms ozone from raw material oxygen, an ozone separation unit 12 that separates ozone formed with said ozone generation unit and raw material oxygen, an ozone photodissociation unit 13 that radiates light of a specific wavelength onto the ozone separated by said ozone separation unit 12 and selectively dissociates ozone containing an oxygen isotope in its molecule into oxygen, and an oxygen separation unit that separates the oxygen formed by dissociating ozone in said ozone photodissociation unit 13 and non-dissociated ozone to concentrate the oxygen isotope in the oxygen. The present invention also relates to a method for concentrating an oxygen isotope comprising an ozone photodissociation step, in which light is radiated onto a rare gas-ozone mixed gas containing ozone and at least one type of rare gas selected from krypton, xenon and radon to selectively dissociate ozone containing a specific oxygen isotope in its molecule into oxygen, and an oxygen isotope concentration step, in which the oxygen separated from ozone in said ozone photodissociation step is separated from non-dissociated ozone and rare gas to concentrate the oxygen isotope present in the separated oxygen. An oxygen isotope may also be concentrated in a dissociation reaction product by irradiating a gas containing a peroxide selected from hydroperoxides, (di)alkyl peroxides, peroxyacids including peracids, (di)acyl peroxides, peroxy esters, peroxycarbonates, peroxydicarbonates, diperoxycarbonates, peroxalates, cyclic peroxides, ozonides and endoperoxides, nitrite esters and nitrate esters, and selectively dissociating a peroxide containing a specific oxygen isotope in its molecule.
Owner:NIPPON SANSO CORP
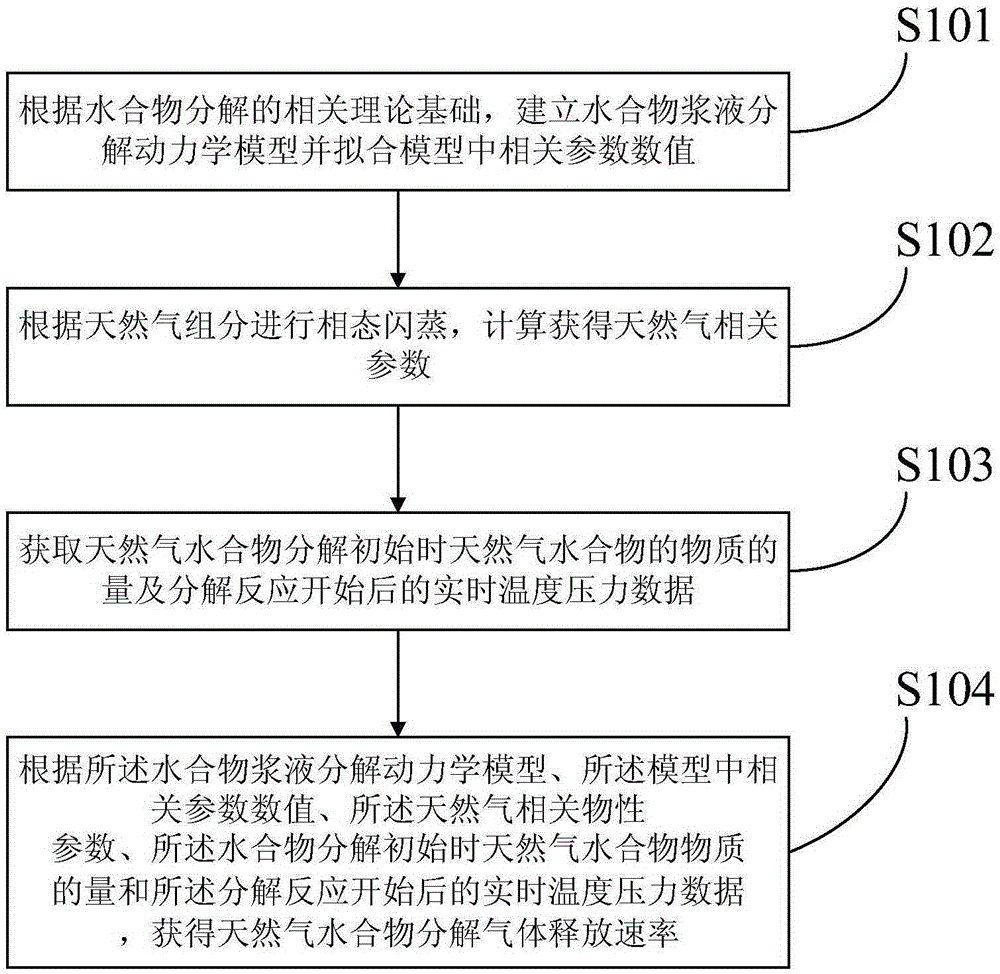
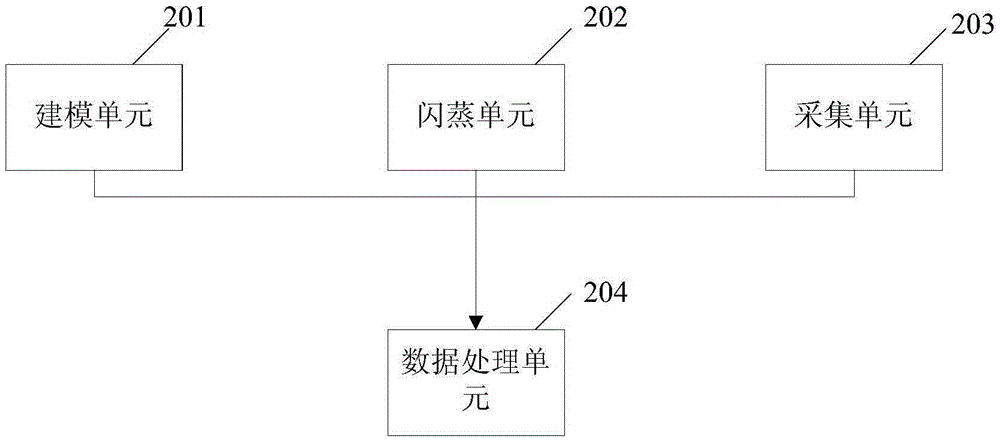
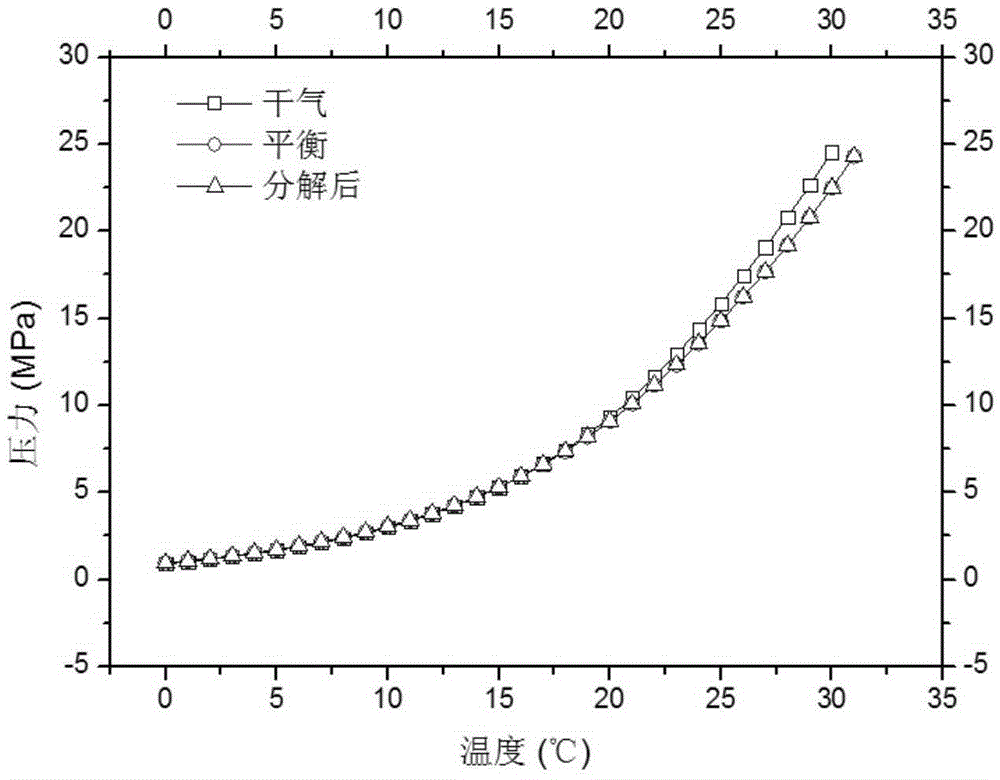
Natural gas hydrate dissociation gas release rate calculation method and apparatus
ActiveCN105426666ASafe and stable operationSpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsSlurryDissociation reaction
The invention provides a natural gas hydrate dissociation gas release rate calculation method and apparatus. The method comprises: according to a hydrate dissociation related theory basis, establishing a hydrate slurry dissociation kinetic model and fitting values of related parameters in the hydrate dissociation model; according to natural gas components, performing phase-state flash evaporation and performing calculation to obtain natural gas related parameters; obtaining an amount of substances of natural gas hydrate during initial natural gas hydrate dissociation and real-time temperature and pressure data after a dissociation reaction is performed; and according to the hydrate slurry dissociation kinetic model, the values of the related parameters in the hydrate dissociation model, the natural gas related physical parameters, the amount of the substances of the natural gas hydrate during the initial natural gas hydrate dissociation and the real-time temperature and pressure data after the dissociation reaction is performed, obtaining a natural gas hydrate dissociation gas release rate. The calculation method and apparatus are mainly applied to the aspects of natural gas hydrate mineral development, flow assurance of removal of natural gas hydrate freezing and plugging, natural gas hydrate storage and transport technology, hydrate separation and the like.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Amine-Reactive Biosensor
InactiveUS20100093106A1Material analysis by optical meansBiological testingAnalyteDissociation reaction
Described are methods, articles of manufacture, and kits for coupling an analyte-binding molecule to the surface of a biosensor through formation of amide bonds. One amide bond is formed between a first carboxyl group on a polymer and a first reflecting surface comprising an aminoalkyl moiety. A second amide bond is formed between a second carboxyl group on the polymer and an amine group on an analyte-binding molecule to be coupled. The present invention thus provides for covalent attachment of the analyte-binding molecule to the biosensor, thus providing advantages over non-covalent attachment methods of the prior art. These advantages include the ability to couple without using bio tin (which, in some instances can alter functional properties of a molecule) the ability to improve the fidelity with which a binding or dissociation reaction that takes place on the surface of the biosensor represents a solution phase reaction, and the ability to regenerate the sensor by stripping ligands from the covalently bound analyte-binding molecule.
Owner:PALL FORTEBIO
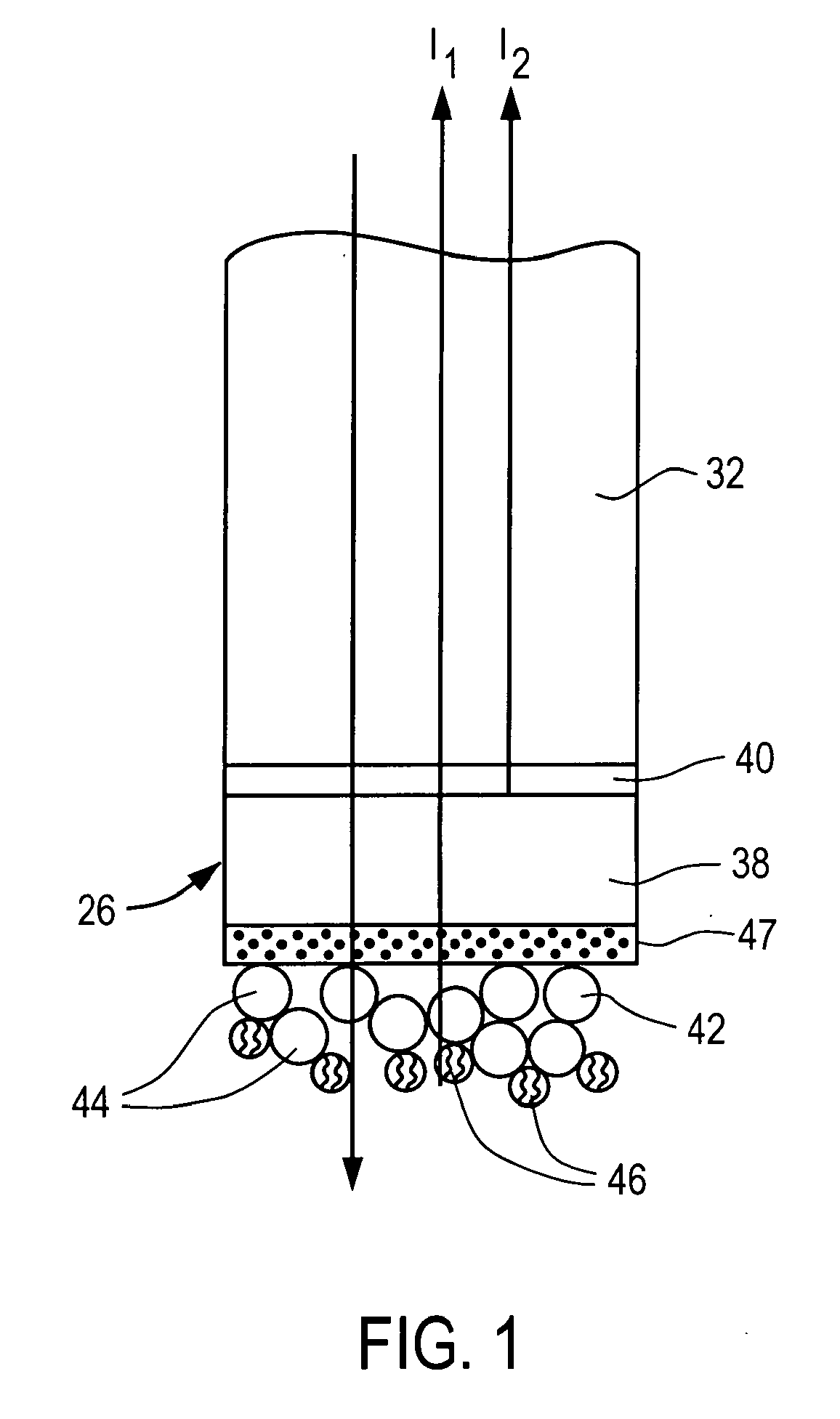
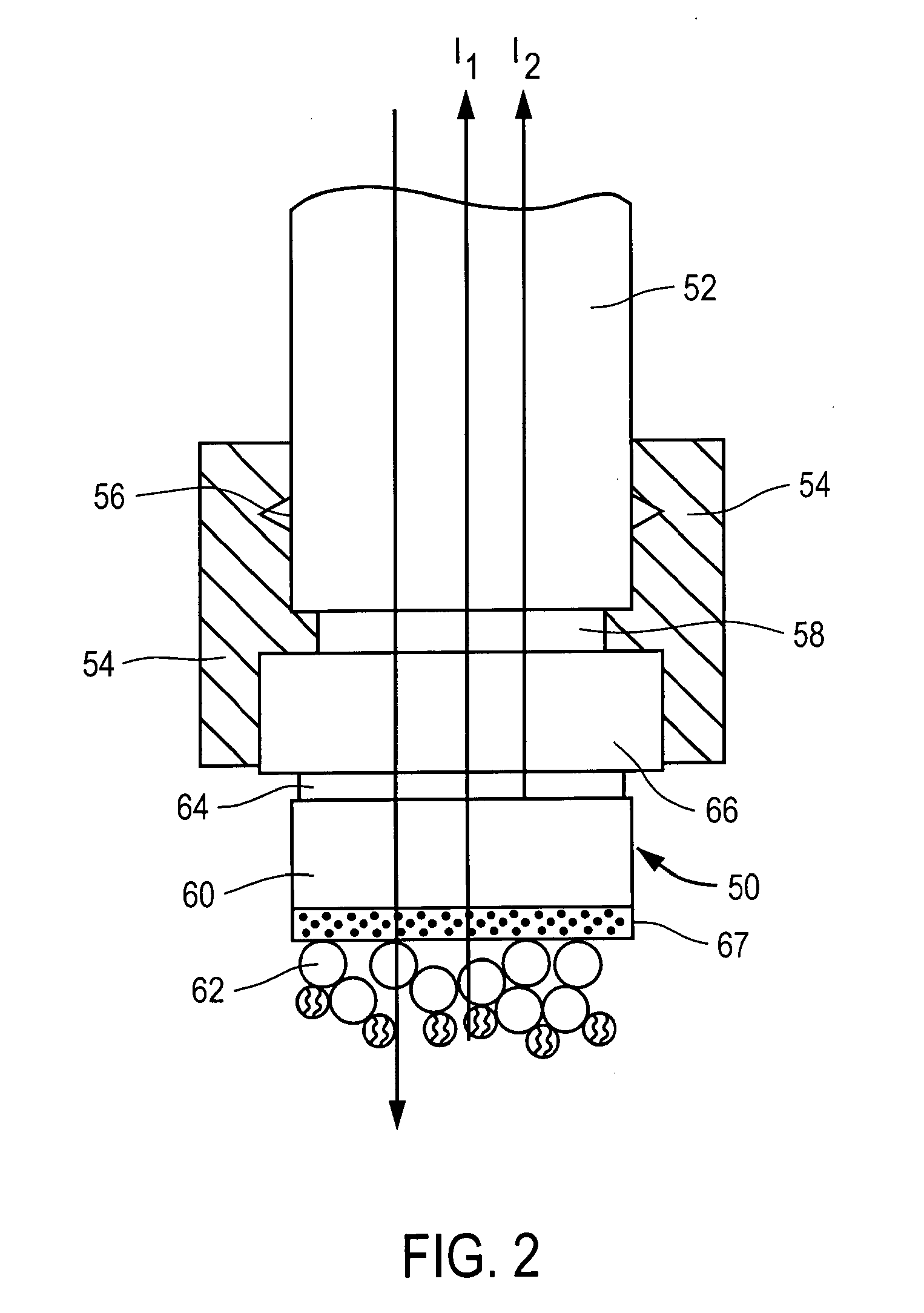
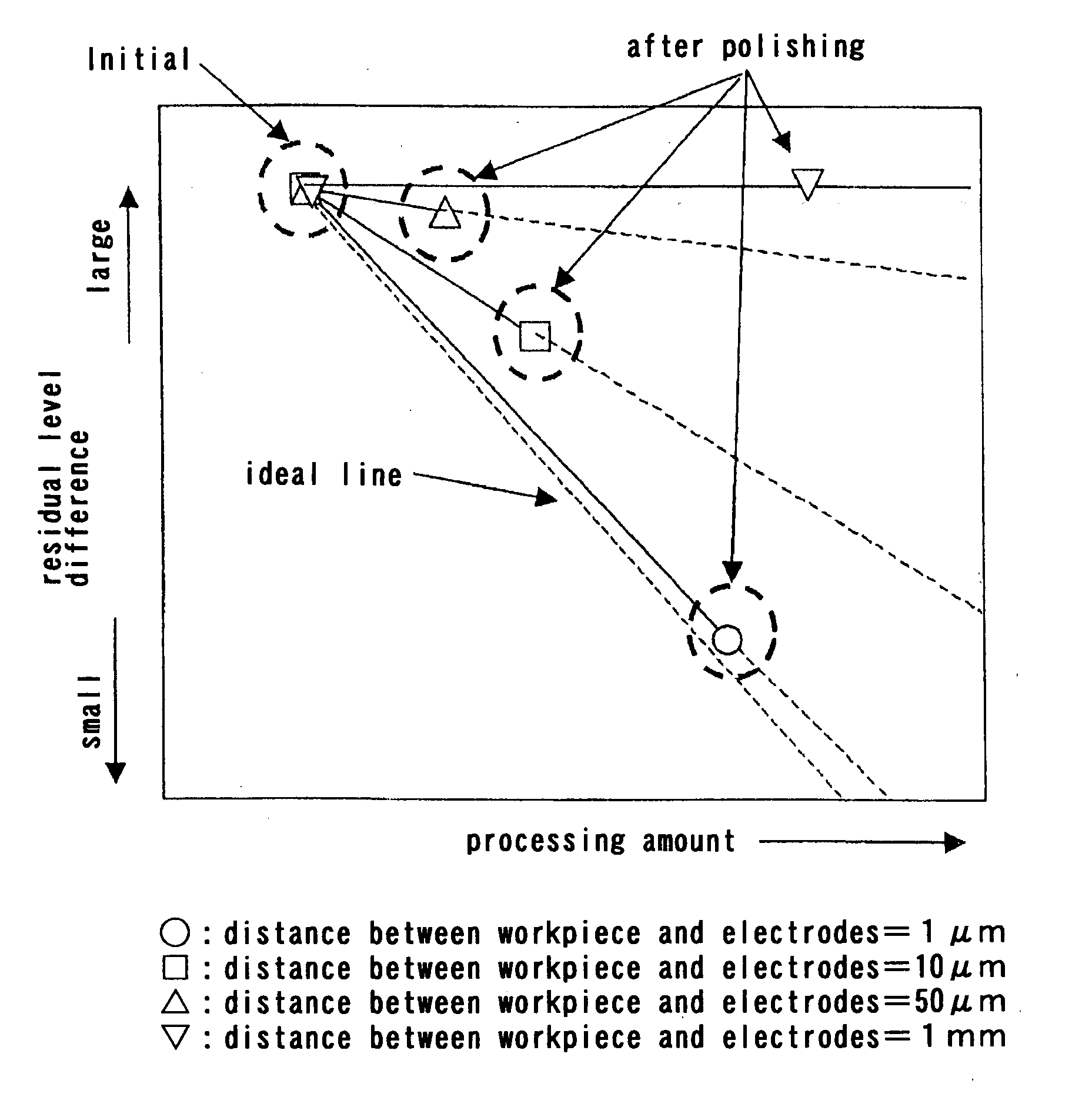
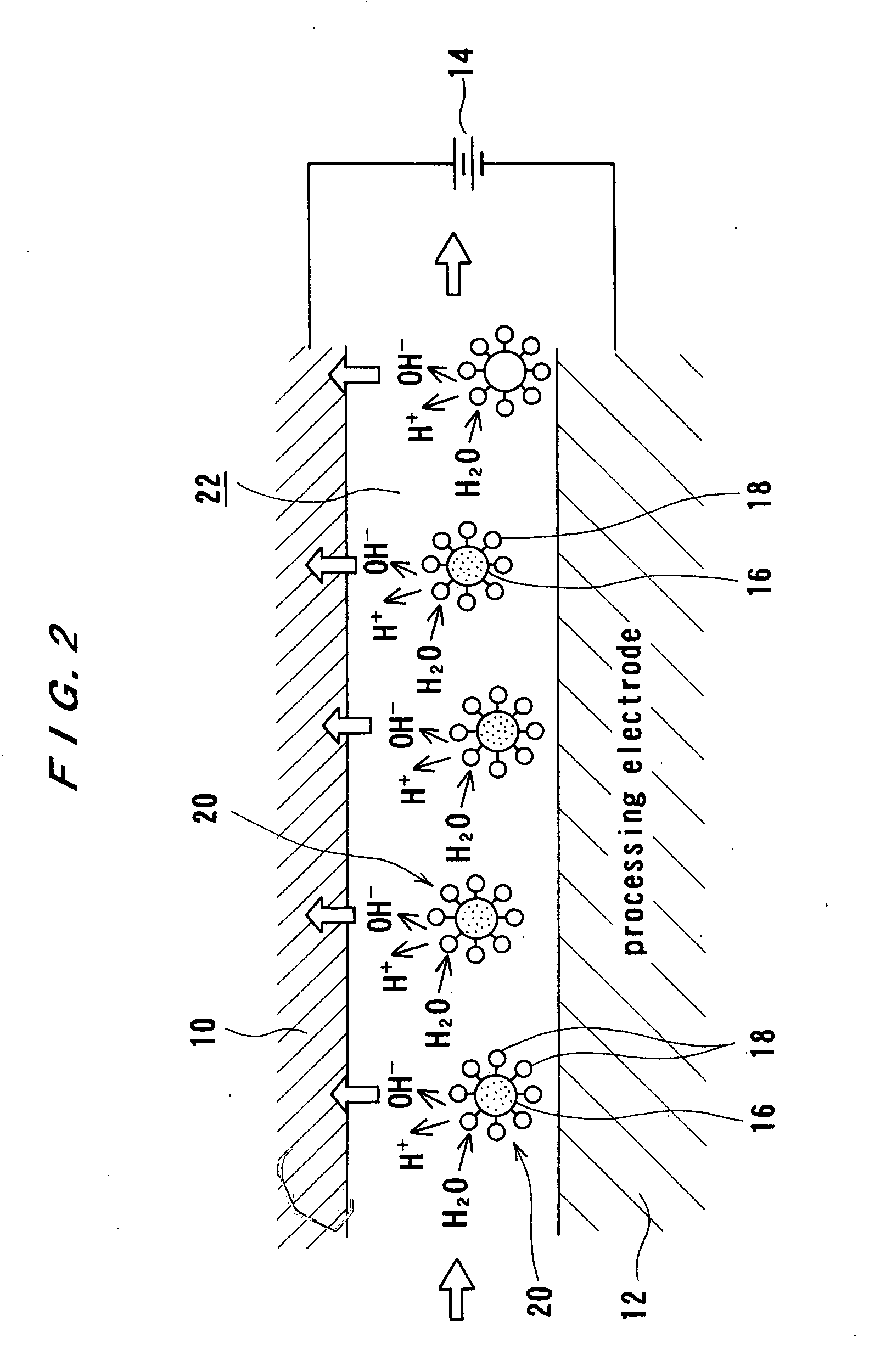
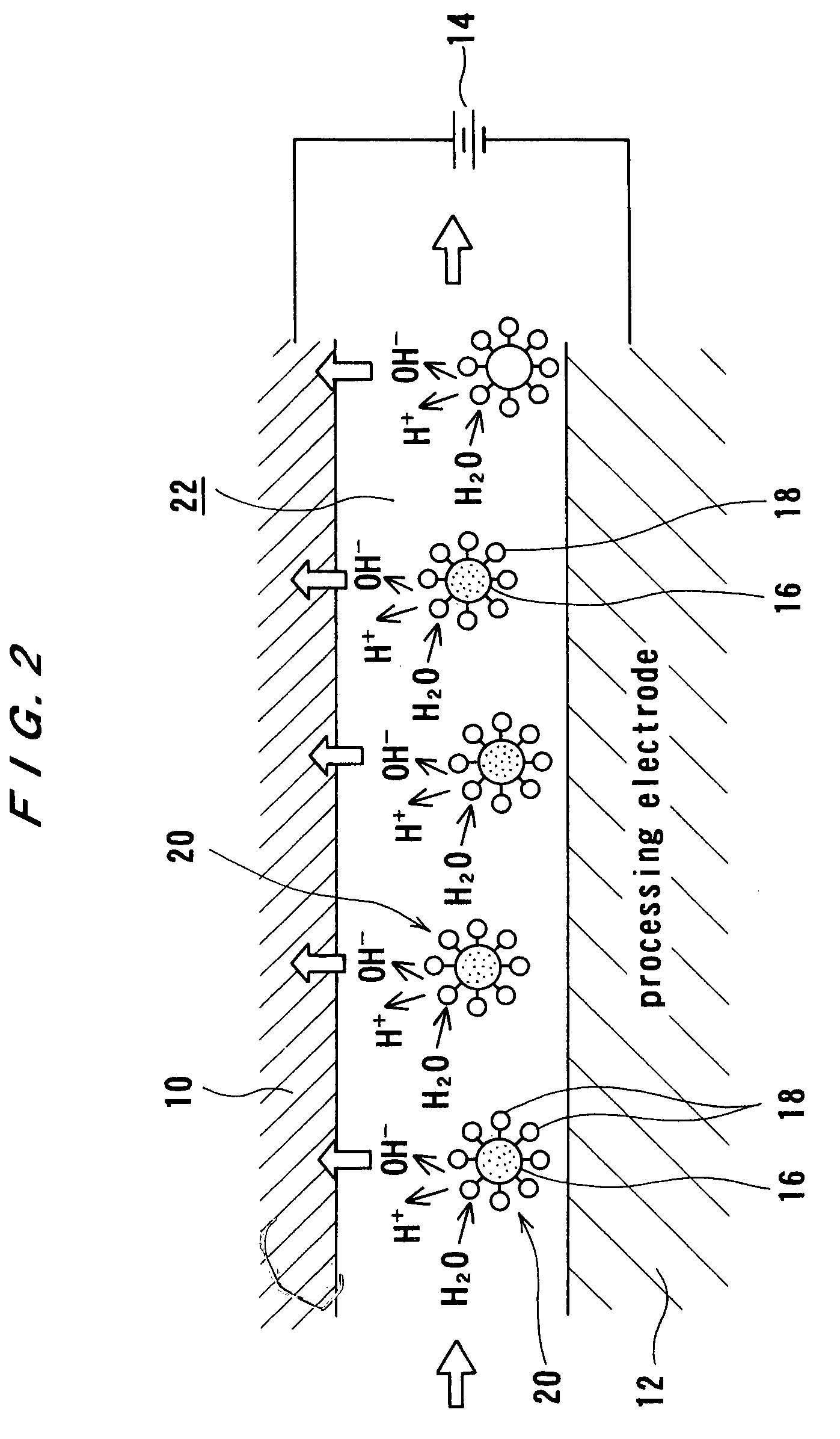
Electrolytic processing apparatus and electrolytic processing method
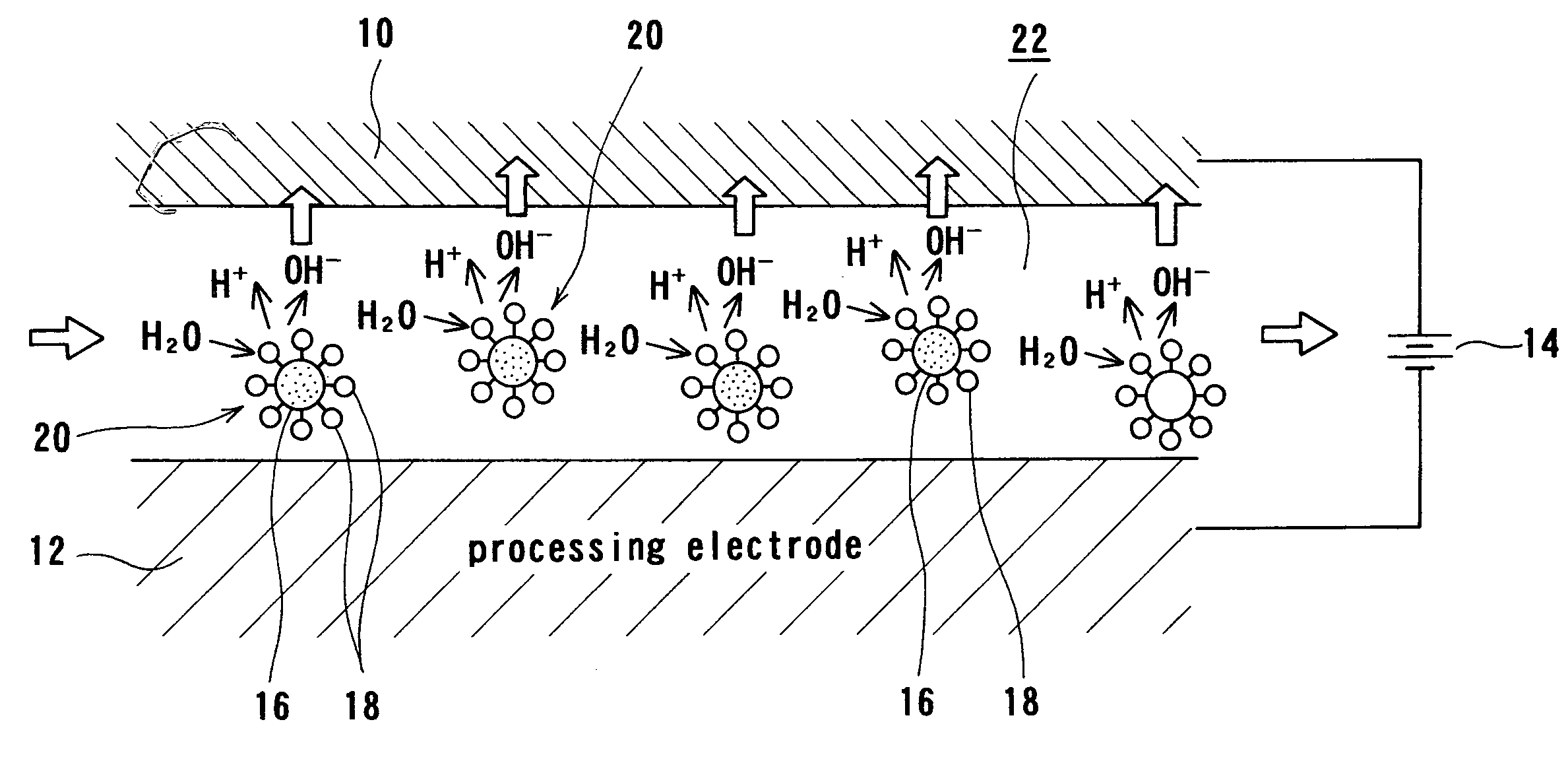
InactiveUS20050155868A1Improve efficiencyEfficient executionElectrolysis componentsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrolysisIon exchange
An electrolytic processing apparatus can increase the efficiency of the dissociation reaction of water and efficiently perform electrolytic processing, and can eliminate the need for an operation for a change of ion exchanger. The electrolytic processing apparatus includes: a processing electrode and a feeding electrode; a liquid supply section for supplying a liquid containing an ion-exchange material between the workpiece and at least one of the processing electrode and the feeding electrode; a power source for applying a voltage between the processing electrode and the feeding electrode; and a drive section for moving the workpiece and at least one of the processing electrode and the feeding electrode relative to each other; wherein electrolytic processing of the workpiece is carried out while keeping the workpiece not in contact with and close to the processing electrode at a distance of not more than 10 μm.
Owner:EBARA CORP
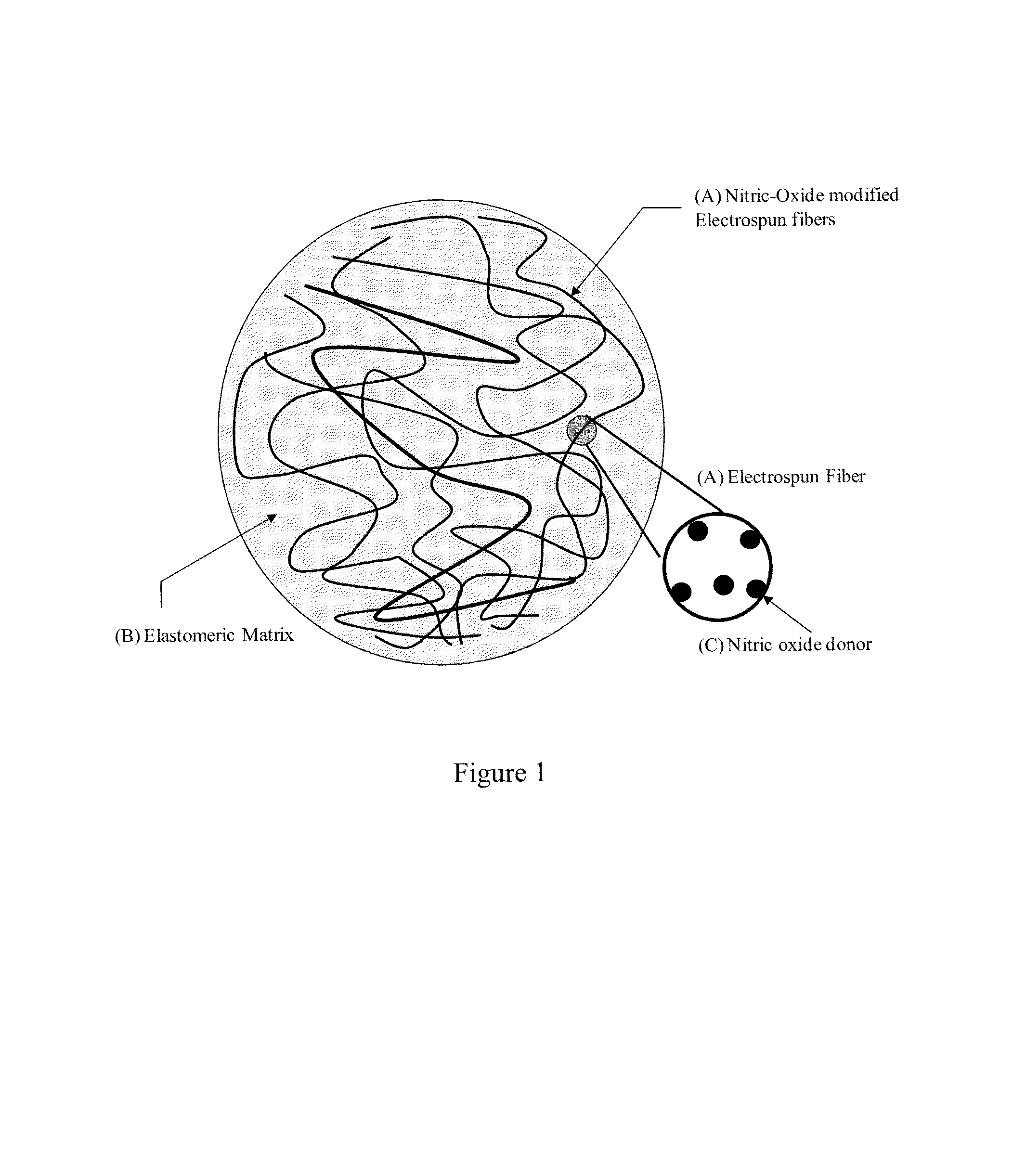
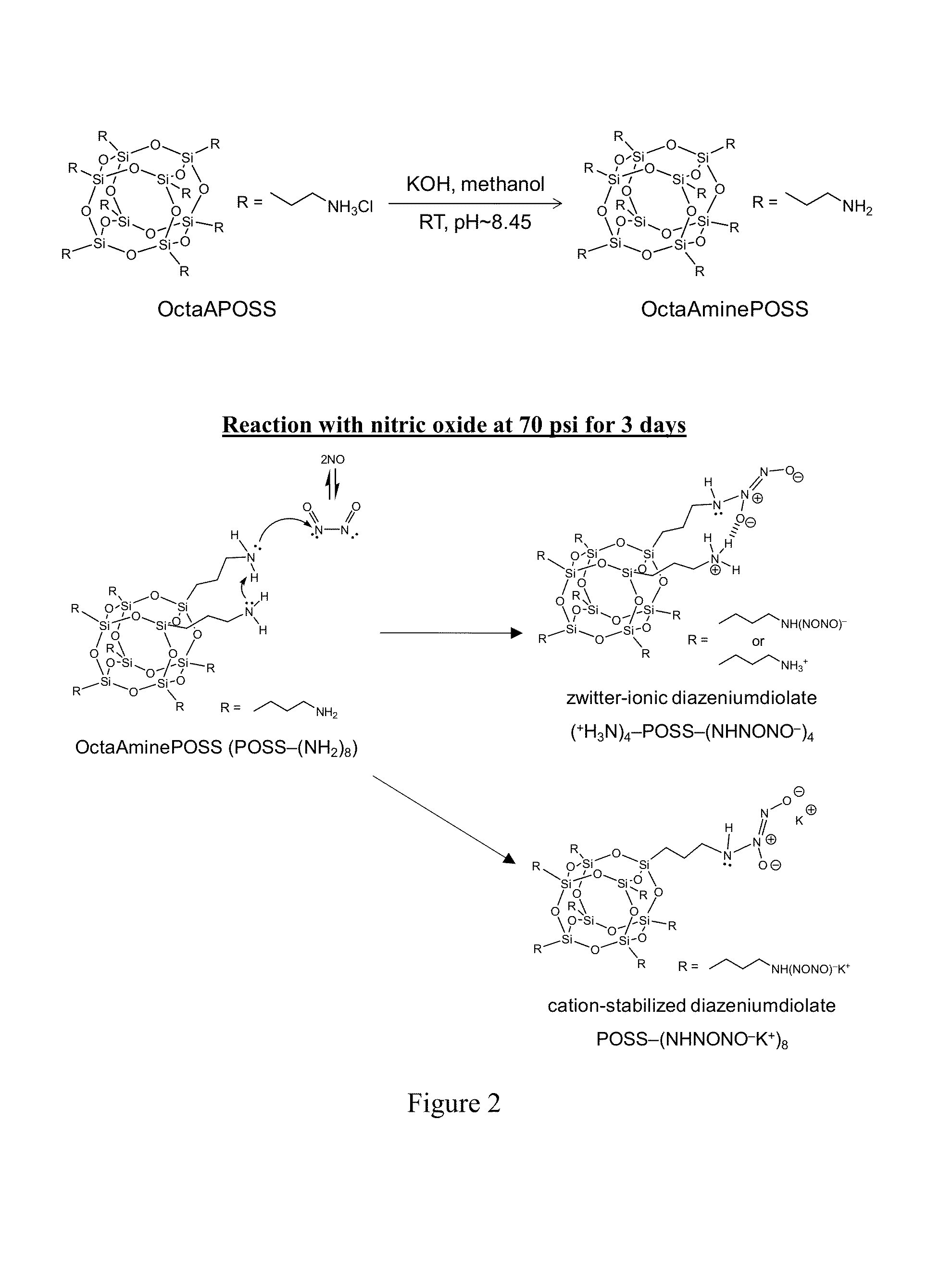
System and method for the release of nitric oxide using nanoscale media
A composite material containing polymeric nanofibers, themselves containing NO-donor molecules, imbibed with an elastomer matrix is permeable to both water and gas so that dissociation reactions in the presence of water releases NO gas in a sustained manner. The NO-donor nanofibers may be formed by synthesizing acceptable NO-donor molecules, blending such molecules in solution with PVP, PCL or PVAc, electrospinning the blend at relatively high voltage for form fiber mats, applying PDMS rubber to the fiber mat and crosslinking it. The resulting NO-releasing electrospun fiber composite may be used in medical devices such as catheters, stents, or vascular grafts, with the purpose of releasing nitric oxide within a controlled rate and for a sustained period of time, as well as other known medical applications for NO.
Owner:SYRACUSE UNIVERSITY
Plant and method for processing low-concentration high-capacity foul gas
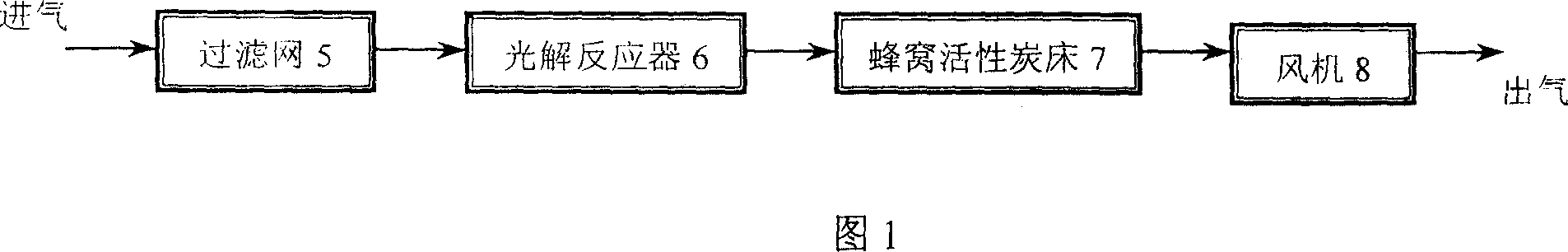
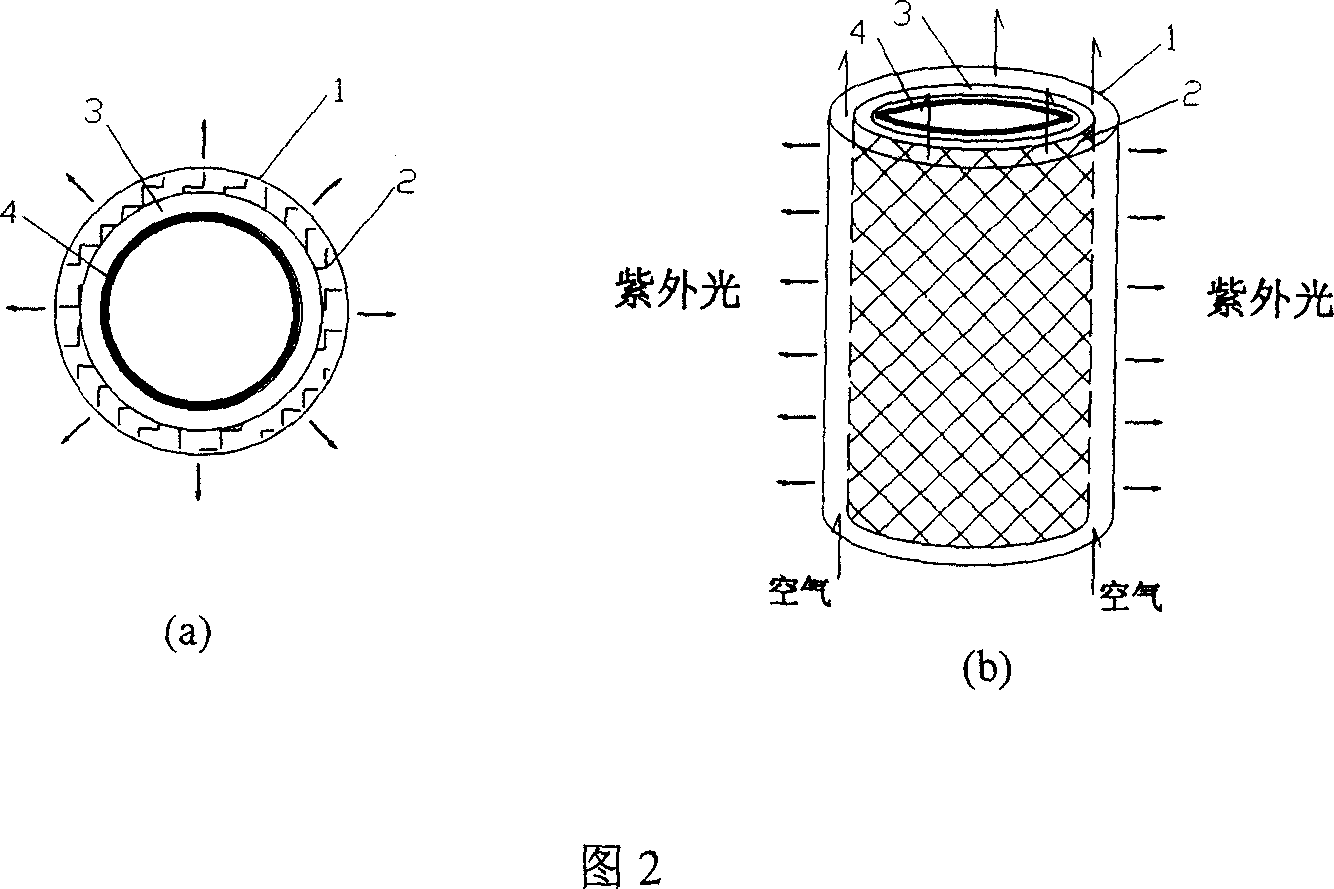
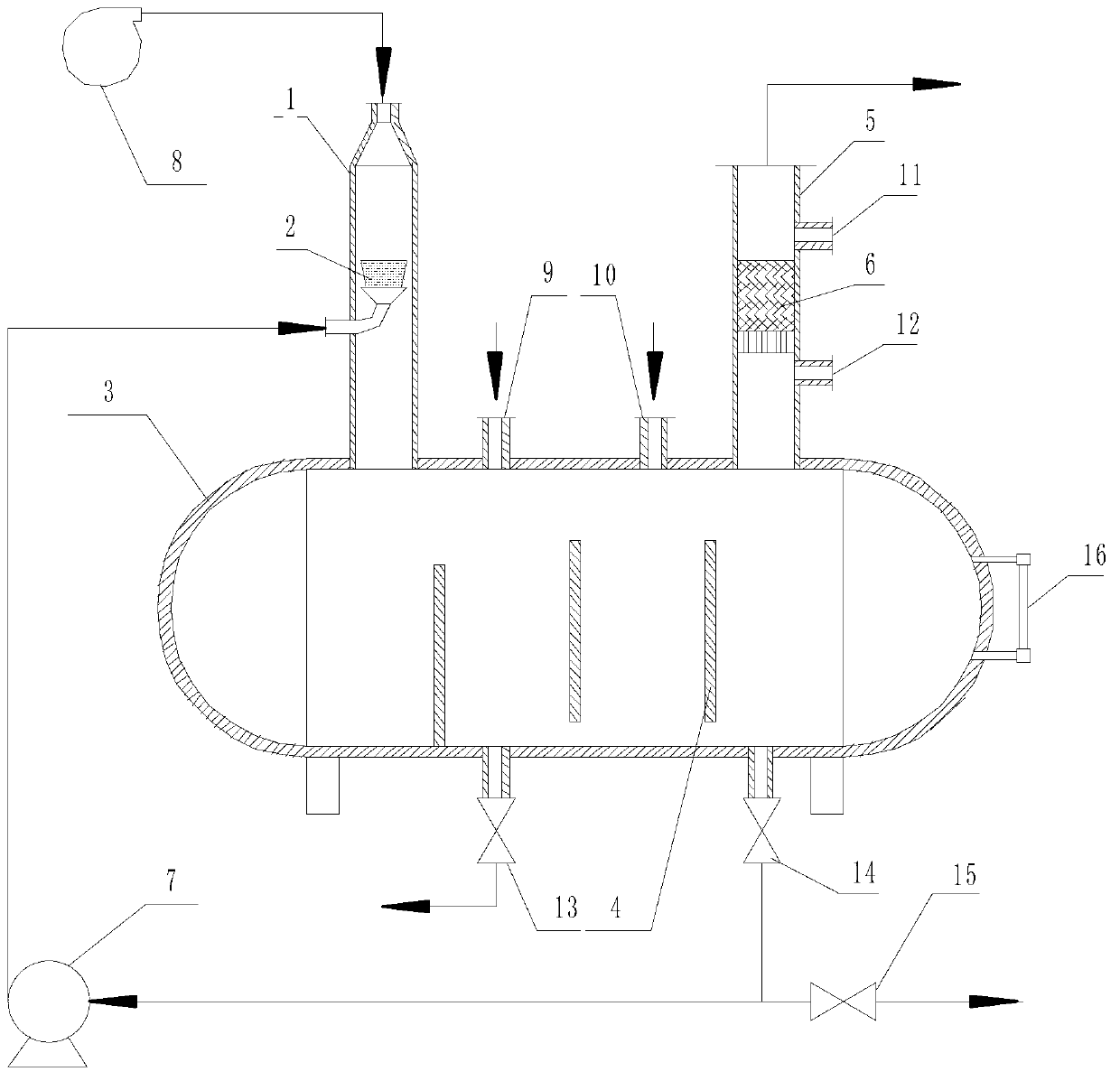
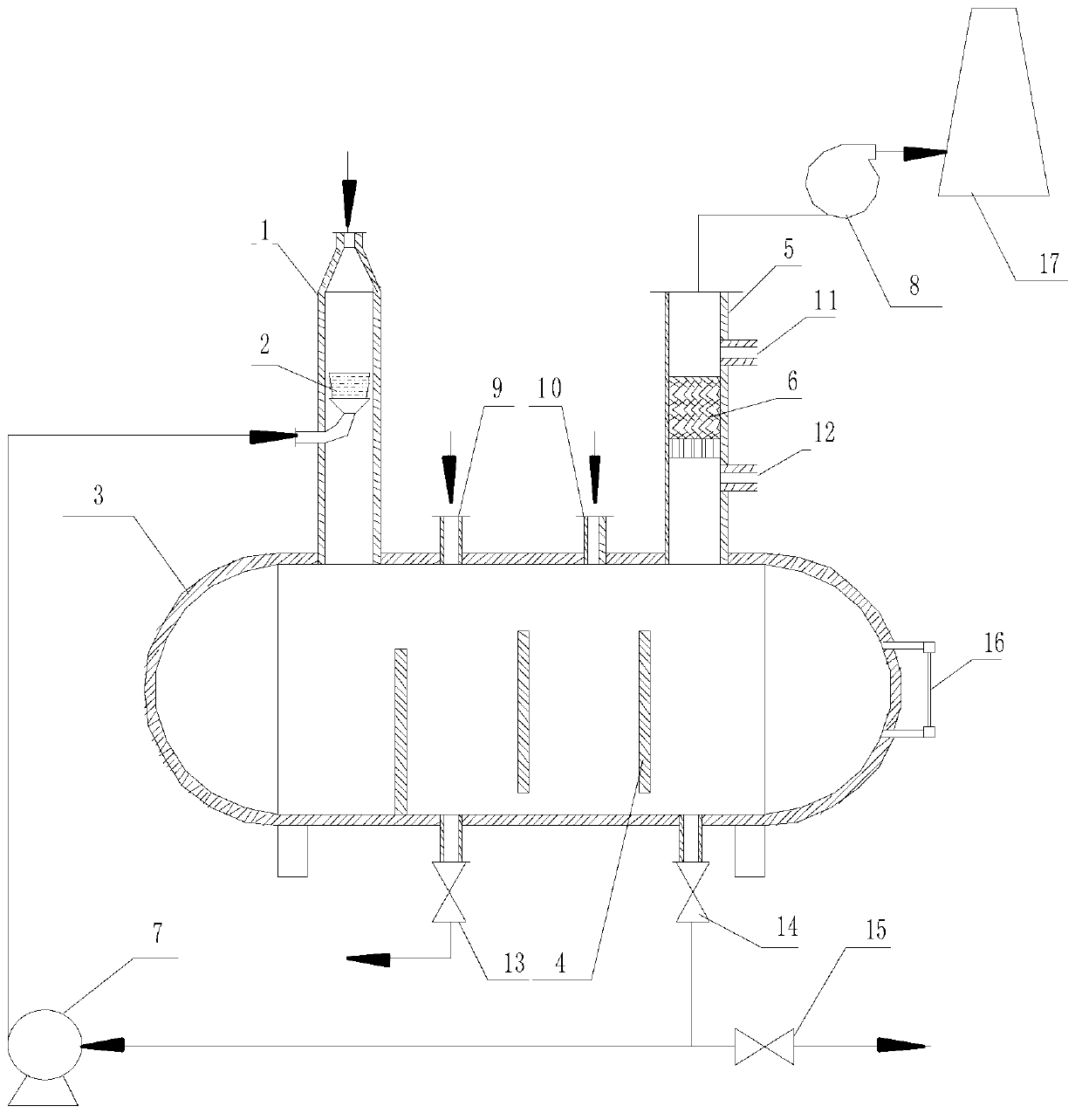
InactiveCN1319600CPrevent leakageTo achieve the purpose of eliminating odorDispersed particle separationDeodrantsUltravioletHoneycomb
The invention belongs to the technique field of treating the foul gas, which in detail is the device and process by the organic combination of the 172nm quasi-molecular ultraviolet technology and honeycomb activated char adsorption-catalytic oxidation bed. The device id formed by the order connection of filtering net, photo dissociation reactor, honey comb activated char bed and fan. The photo dissociation reactor employs the 172nm quasi-molecular ultraviolet lamp and is in hollow cylinder structure. The ozone, HO. and HO2.and other groups of high activity generated from the photo dissociation reaction; the malodorous substance not completely broke up and the oxygen in the air are all accumulated in the micro-porous structure of the activated char through the adsorption action of the activated char; oxidizing and decomposing the malodorous substance by applying the media and catalytic oxidation function of the activated char. The method in this invention can treat the foul gas of low depth and large air quantity with a high effect and in large scale.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method for measuring reaction rate coefficient in analysis utilizing total reflection attenuation
InactiveUS20070031893A1Correction coefficientRate coefficientColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological testingUltrasound attenuationDiffusion
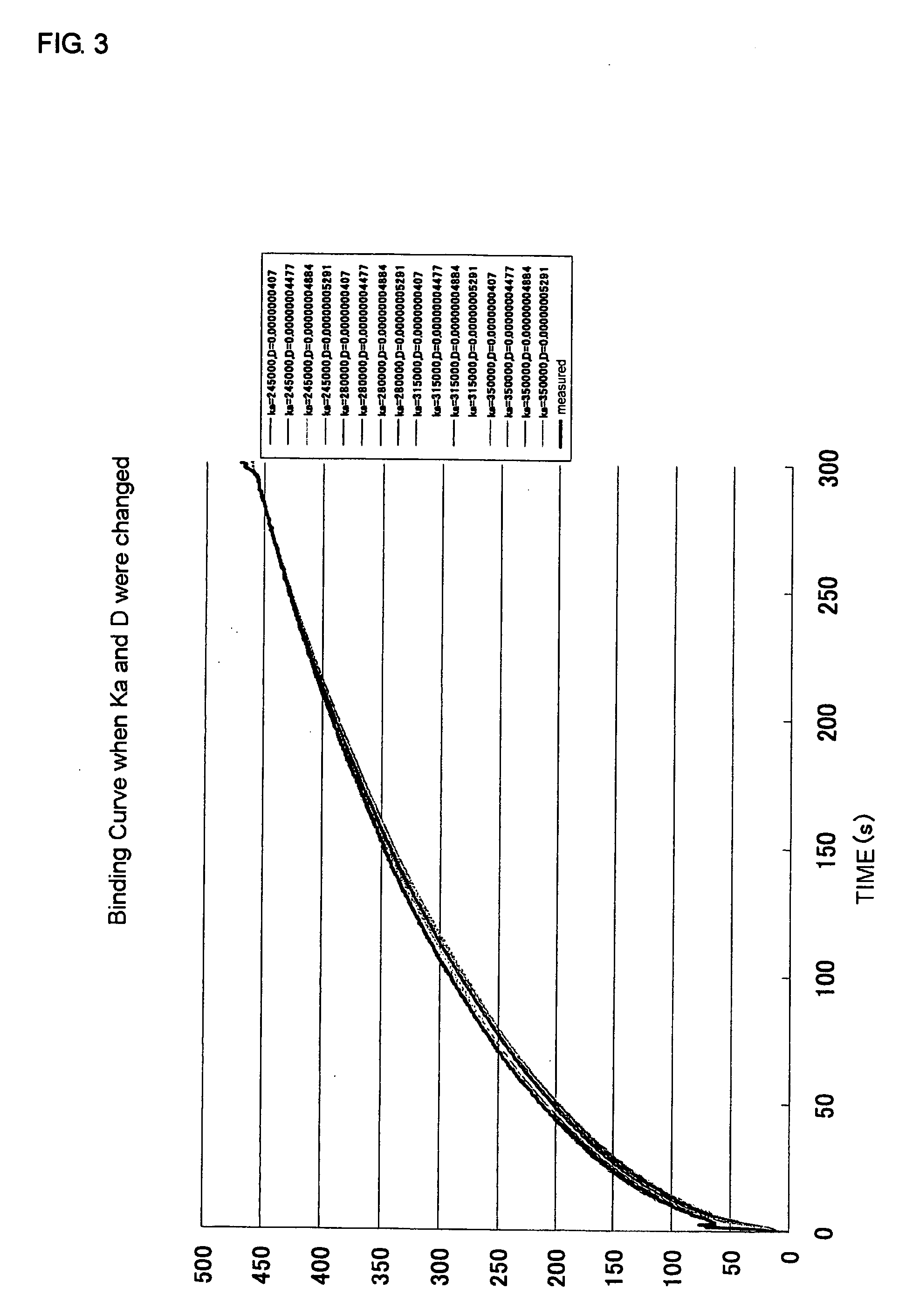
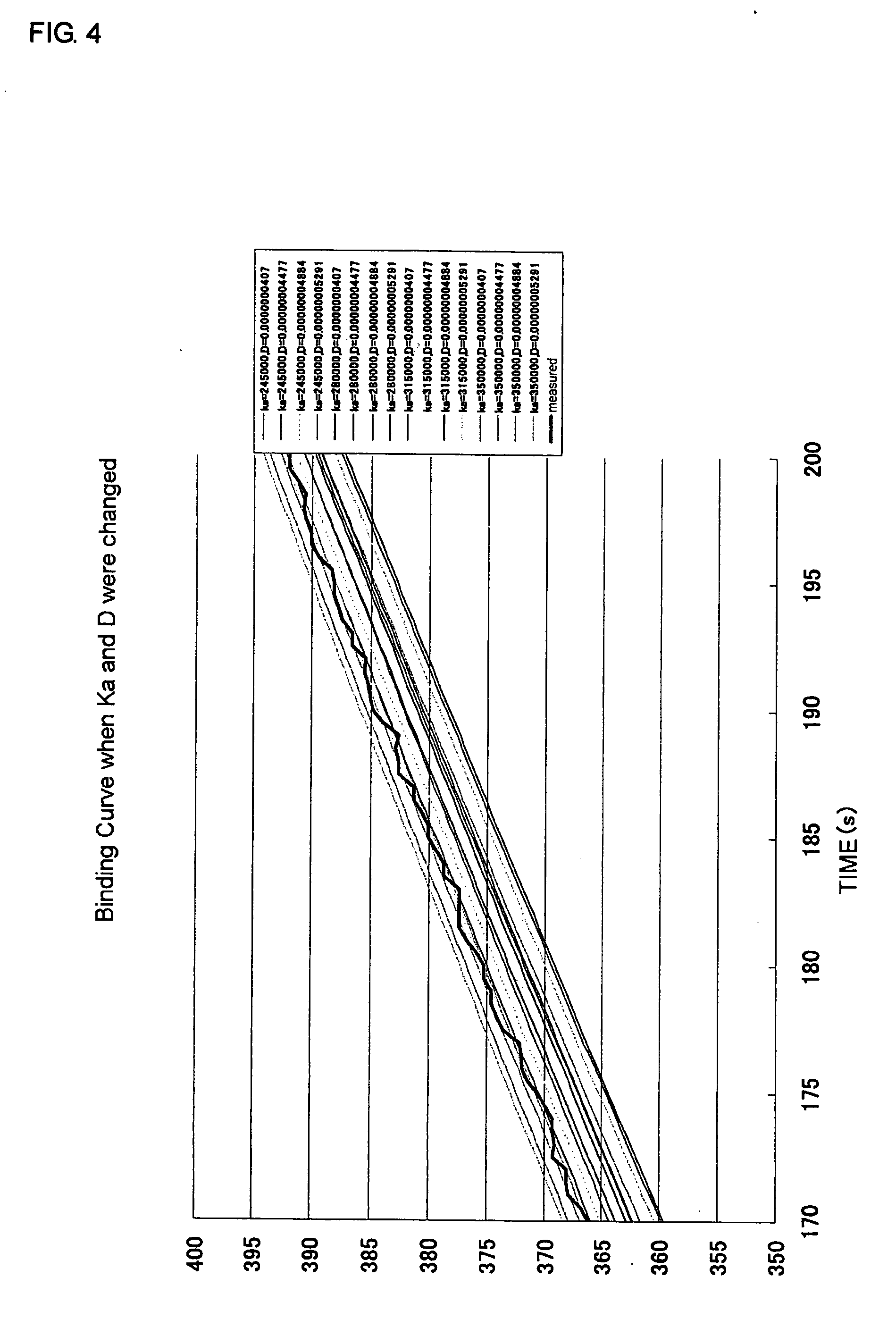
An object of the present invention is to provide a method for measuring a reaction rate coefficient in an analysis utilizing total reflection attenuation, which is capable of calculating the reaction rate coefficient speedily and accurately. The present invention provides a method for measuring adsorption rate coefficient (Ka) and diffusion coefficient (D) in a reaction between an analyte molecule immobilized on a metal surface and a molecule that interacts with the analyte molecule, by measuring an angular change in the total reflection attenuation angle (θSP) using an analysis device utilizing total reflection attenuation, which comprises (1) providing multiple simulation curves of a binding dissociation reaction for sets of variables in which adsorption rate coefficient (Ka) and diffusion coefficient (D) are each varied within a predetermined width, (2) preparing a measurement curve of the binding dissociation reaction based on an angular change in a measured total reflection attenuation angle (θSP), (3) examining the level of correspondence between the measurement curve prepared in above (2) and the multiple simulation curves of above (1), and (4) applying the adsorption rate coefficient (Ka) and diffusion coefficient (D) that were used for the preparation of the simulation curve with the highest level of correspondence to the adsorption rate coefficient (Ka) and the diffusion coefficient (D) in the reaction between the analyte molecule immobilized on the metal surface and the molecule that interacts with the analyte molecule.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Multiphase flow rotation foam separation device and waste water/ gas treatment technology using same
InactiveCN102992418AReduce removal rateCause secondary pollutionCombination devicesWater/sewage treatmentLiquid wasteChemical oxygen demand
The invention discloses a multiphase flow rotation foam separation device and a waste water / gas treatment technology using the device. The technology and the device are used for high-ammonia nitrogen sewage treatment, can be used for replacing the conventional technologies such as aerobiotic aeration, steam stripping, air stripping and the like and have the advantages that the upper limit concentration is not limited, the ammonia nitrogen removal rate is more than 95%, and the chemical oxygen demand (COD) cr removal rate is more than 98%. The device has multiple functions such as ammonia nitrogen dissociation reaction, air stripping and ammonia recovery, thus being capable of easily completing high-ammonia nitrogen waste liquid full-loop operation in a matching way and realizing 'zero emission' in deed. The device can be used for treating various industrial flue gases with high temperature, high sulfur, high humidity and high dust content, integrates the functions of cooling, desulfurating and dust removing, and has the desulfurization rate being more than 90% and the dust removal rate being more than 99%; and after multiple stages of multiphase flow rotation foam separation devices are connected in series, the effect of electric precipitation can be achieved, but the project investment and energy consumption are far lower than those of electric precipitation.
Owner:HUNAN KEYING SPECIAL ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION EQUIP & TECH
Electrolyte and preparation method as well as secondary lithium-sulfur battery using electrolyte
InactiveCN108281700AImprove conductivityFacilitate dissociation reactionSecondary cellsCyclic processUltrasound attenuation
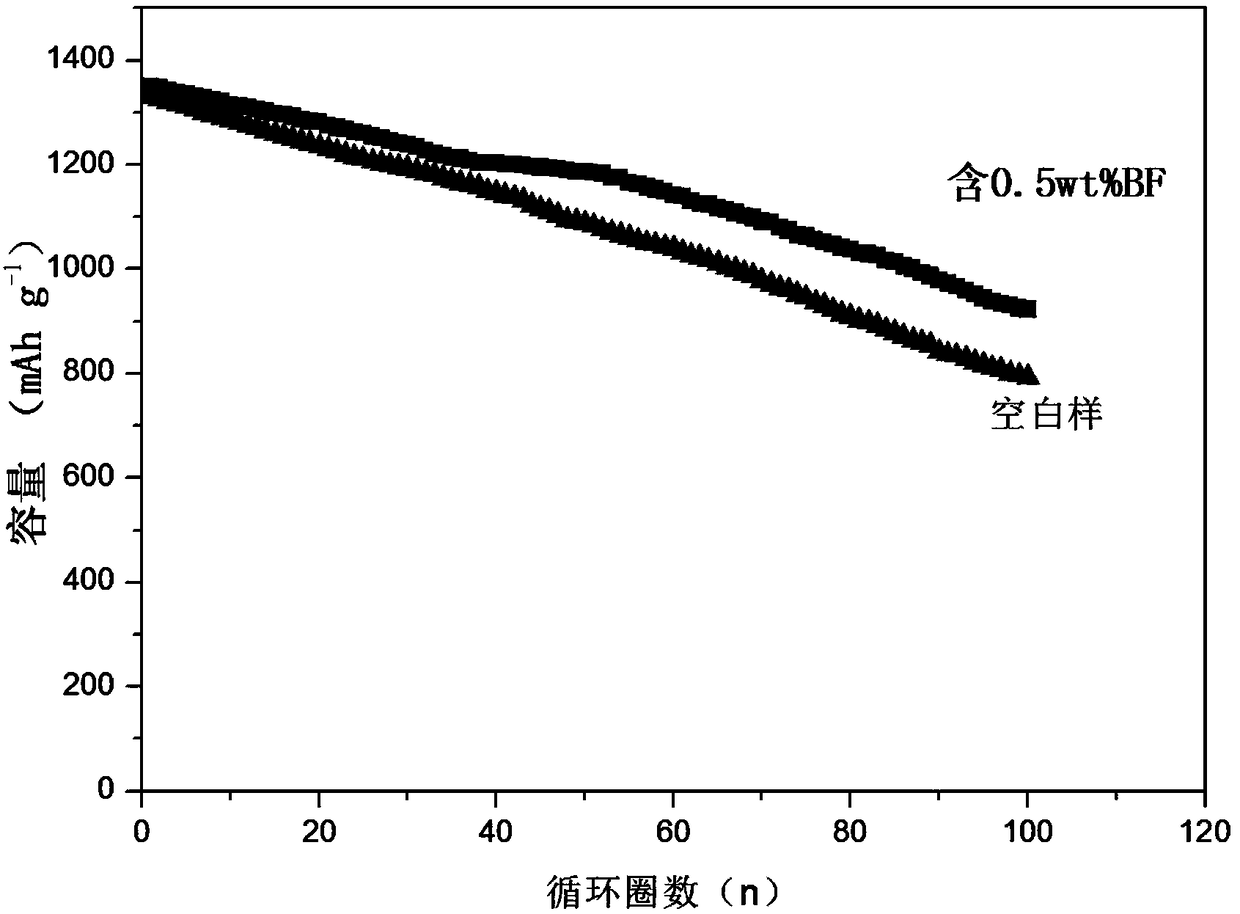
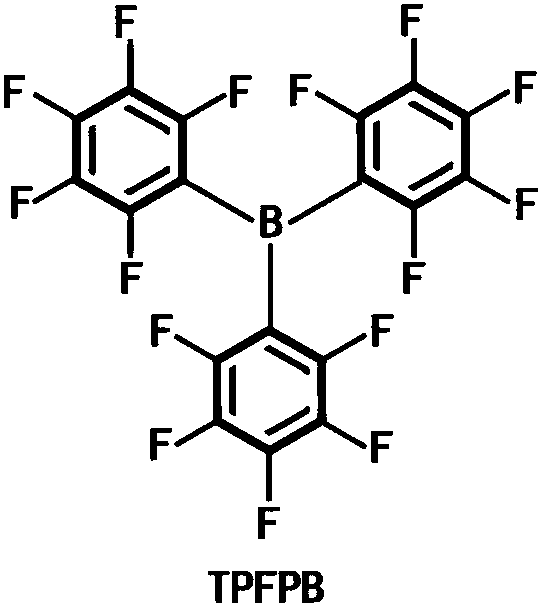
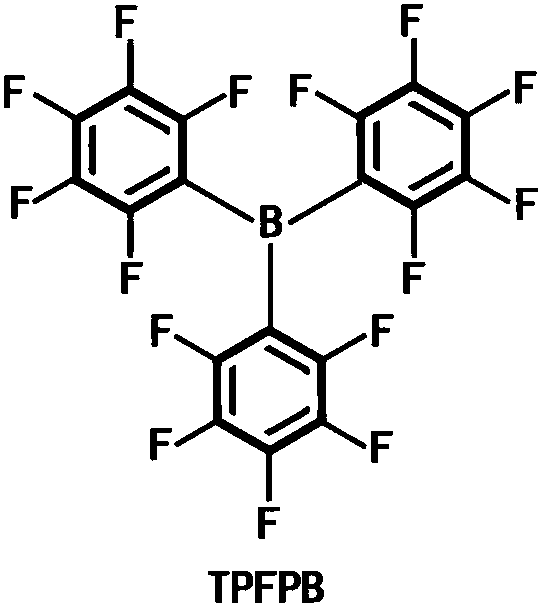
The invention discloses electrolyte and a preparation method as well as a secondary lithium-sulfur battery using the electrolyte. The electrolyte is prepared from lithium salt, an organic solvent anda functional additive, wherein the concentration of the lithium salt in the electrolyte is 0.5 to 5 mol / L, and the mass percentage of the functional additive in the electrolyte is 0.1 to 3 percent. The electrolyte is prepared by adding the lithium salt into the organic solvent and uniformly stirring the lithium salt and the organic solvent, and functional electrolyte for the secondary lithium-sulfur battery is obtained by adding the functional additive into the electrolyte and continuously stirring the components till the components are uniformly mixed. The electrolyte disclosed by the invention takes trifluoropentaphenyl borane as the functional additive which can participate in formation of a solid electrolyte phase interface (an SEI film), and can dissolve LiF to improve the conductivity of the SEI film; the trifluoropentaphenyl borane is favorable for promoting dissociation reaction of LiPF6 to adsorb free F<->, so that HF formed by trace water is reduced, and corrosion of the HF to an electrode material is reduced; capacity attenuation of a cathode material in a cyclic process is effectively suppressed, and the cycle stability and the capacity retention rate of the lithium-sulfur battery are improved.
Owner:HEFEI GUOXUAN HIGH TECH POWER ENERGY
Method for fast detecting content of fluorine ion contained in antarctic krill
InactiveCN102967646ARapid detection of fluoride ion contentMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansIon contentCoaxial probe
The invention relates to a method for fast detecting fluorine ions contained in antarctic krill, which comprises the following steps: (1) picking 1-5 grams of antarctic krill powder or fresh krill materials, placing into deionized water with the mass ratio of 1:100, refluxing and heating for 1-4 hours under the temperature of 90-100 DEG C, and then cooling to 30 DEG C for standby application; (2) determining the dielectric characteristics of an NaF deionized water solution by utilizing a coaxial probe method under the condition of 30 DEG C, and drawing and determining the standard curve: Y=13.26*(X+C) of the NaF deionized water solution under the condition of low frequency of 300-3000 MHz when the concentration of the NaF deionized water solution is 0.1-50 mg / ml; (3) filtering a solution obtained in step (1), then determining the dielectric loss ratio of the solution, introducing into the standard curve obtained in step (2), and determining and computing the content of F ions. The method disclosed by the invention obtains the characteristic relationship of fluorine ion content according to the equimolar dissociation reaction: NaF=Na++F+ of the NaF deionized water solution, thereby obtaining the fluorine ion content YF=1.296*(X-D).
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
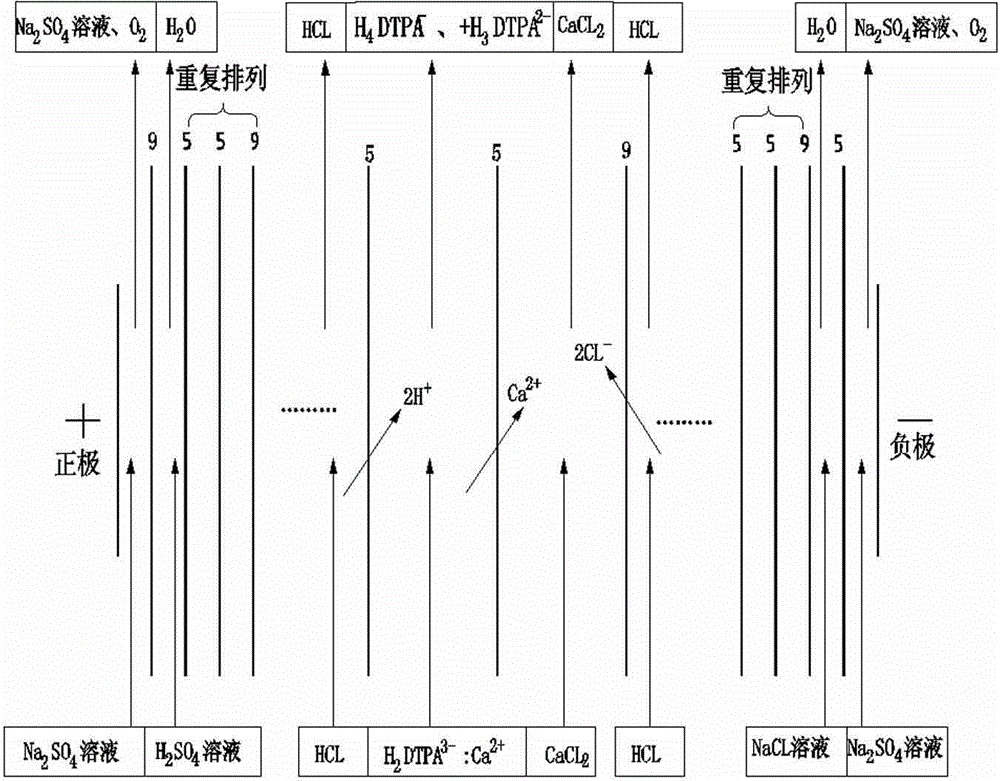
Method of separating complexing-form DTPA (diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid) and hardness ions by electrodialysis process
ActiveCN104310543AEmission reductionImprove protectionWater contaminantsDispersed particle separationResource utilizationDiethylenetriamine
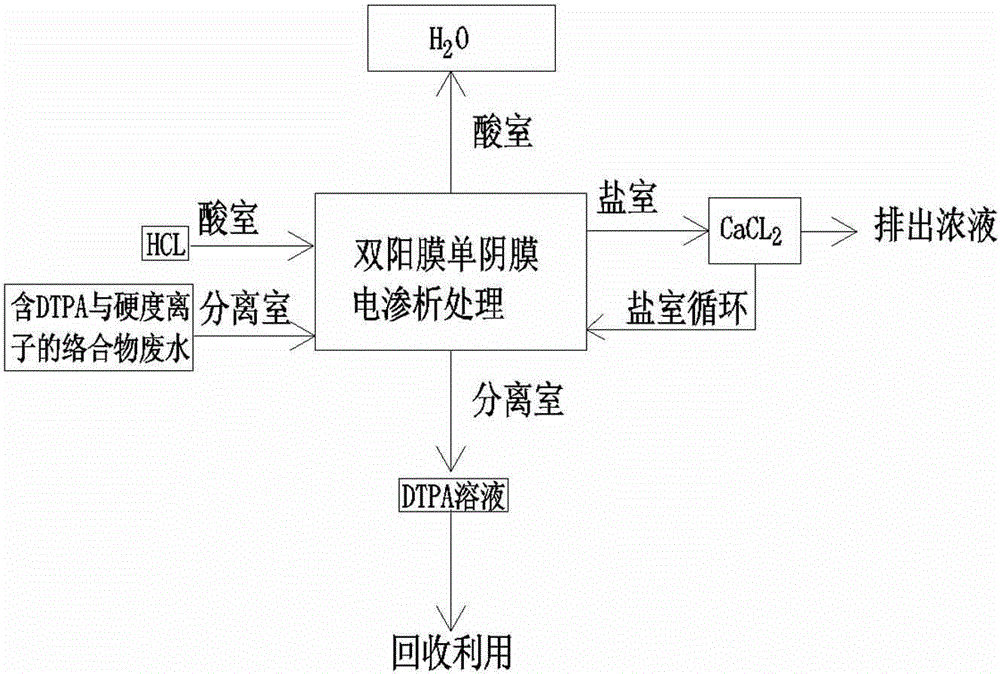
The invention discloses a method of separating complexing-form DTPA (diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid) and hardness ions by an electrodialysis process. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, filling a Na2SO4 solution into an anode chamber and a cathode chamber of an electrodialysis device, filling a sulfuric acid solution into an acid chamber, and filling a solution into a salt chamber; then, introducing wastewater containing DTPA and hardness ion complexes into a separating chamber, starting a direct-current power supply, enabling hydrogen ions in the acid chamber to selectively penetrate through a cationic membrane to enter the separating chamber, so that the pH value of the wastewater in the separating chamber is lowered to be lower than 3; enabling the DTPA and the hardness ions to generate dissociation reaction to form a free DTPA anionic group and hardness ions; enabling the hardness ions to continuously penetrate through the cationic membrane selectively to enter the salt chamber and enabling the DTPA anionic groups not to transfer towards the adjacent acid chamber and the salt chamber, and thus realizing the separation of the DTPA and the hardness ions. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for realizing large-scale industrial production, realizing the separation of the DPTA and the hardness ions, reducing the wastewater emission, facilitating the environmental protection, recycling the valuable DTPA solution and realizing the resource utilization purpose.
Owner:SHANDONG AMS ENVIRONMENTAL
Method of detecting gene
InactiveCN1388831AMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationTemperature controlHybridization reaction
A method of detecting gene whereby a gene can be detected by forming a polymer by using the PALSAR method without capturing ligated oligonucleotides or washing excessive oligonucleotides. By using a plurality of probe pairs consisting of n (n<3) base sequence regions complementary to each other, one point in one side of the complementary domain, one point in each of the both sides thereof or two or more points therein of a target gene of the above-described probe pair are preliminarily cleaved and then a hybridization reaction, a ligation reaction and a dissociation reaction are conducted under temperature control. Thus the cleaved probes are ligated to form a complete probe. By using a method of constructing a probe polymer, a double-stranded polymer is formed and thus the above-described gene is detected.
Owner:三光纯药株式会社
Method for preparing magnesium oxide fibers by ligand analysis technology
ActiveCN104404654ASolve easy pulverizationSolve the strength problemInorganic material artificial filamentsArtificial filament chemical after-treatmentFiberWater vapor
The invention relates to a method for preparing magnesium oxide fibers by a ligand analysis technology. The method comprises the following steps: putting fully dried magnesium oxide precursor fibers into an alkaline gas, alkaline steam or / and water vapor atmosphere, performing ligand analysis treatment under a condition that the temperature is higher than 100 DEG C, and performing dissociation reaction on the magnesium oxide precursor fibers to generate magnesium hydrate; enabling magnesium hydrate to be shrunk to form the magnesium oxide fibers. By the ligand analysis technology, the technical difficulties that the fibers are easy to pulverize and difficultly formed are solved; by an optimized thermal treatment program, the mechanical property of the magnesium oxide fibers can be effectively enhanced.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for preparing 2,6,10-trimethyl-1,1-dialkoxyl-3,5,9-undecatriene
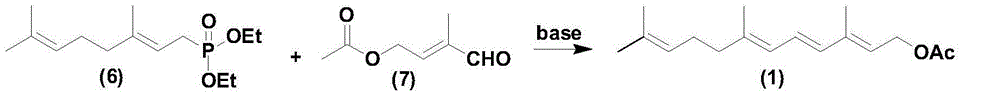
ActiveCN102311320ASimple process routeRaw materials are easy to getOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationOrganic solventLycopene
The invention relates to a method for preparing 2,6,10-trimethyl-1,1-dialkoxyl-3,5,9-undecatriene, belonging to the technical field of lycopene intermediate synthesis methods. The method comprises the following steps: (1) under the protection of inert gas and in the presence of an organic solvent and alkali, carrying out dissociation reaction on C10 triphenyl phosphonium salt at the temperature of minus 40-30 DEG C; and (2) after the dissociation reaction in the step (1) is completed, adding C4 acetal, carrying out Wittig condensation reaction at the temperature of minus 40-30 DEG C in the presence of the organic solvent and alkali so as to obtain 2,6,10-trimethyl-1,1-dialkoxyl-3,5,9-undecatriene. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of concise process route and easy obtainment of raw materials, low cost and high industrial value.
Owner:启东欧常新材料有限公司
Method of studying reactions between two or more molecules in a biological sample
InactiveUS20160274107A1Precise positioningImprove pointing accuracyBiological material analysisMicroscopesCompetitive bindingDissociation reaction
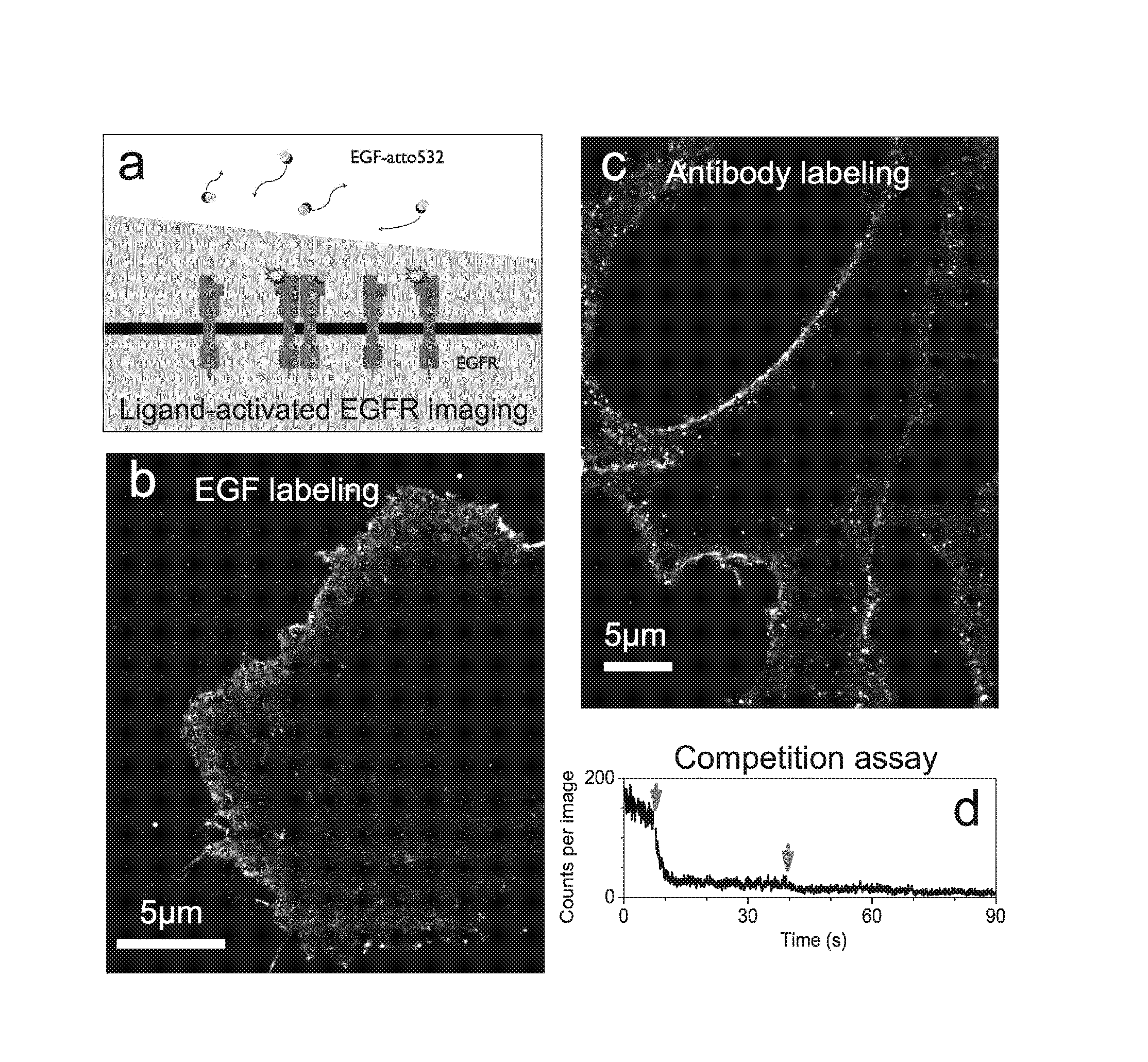
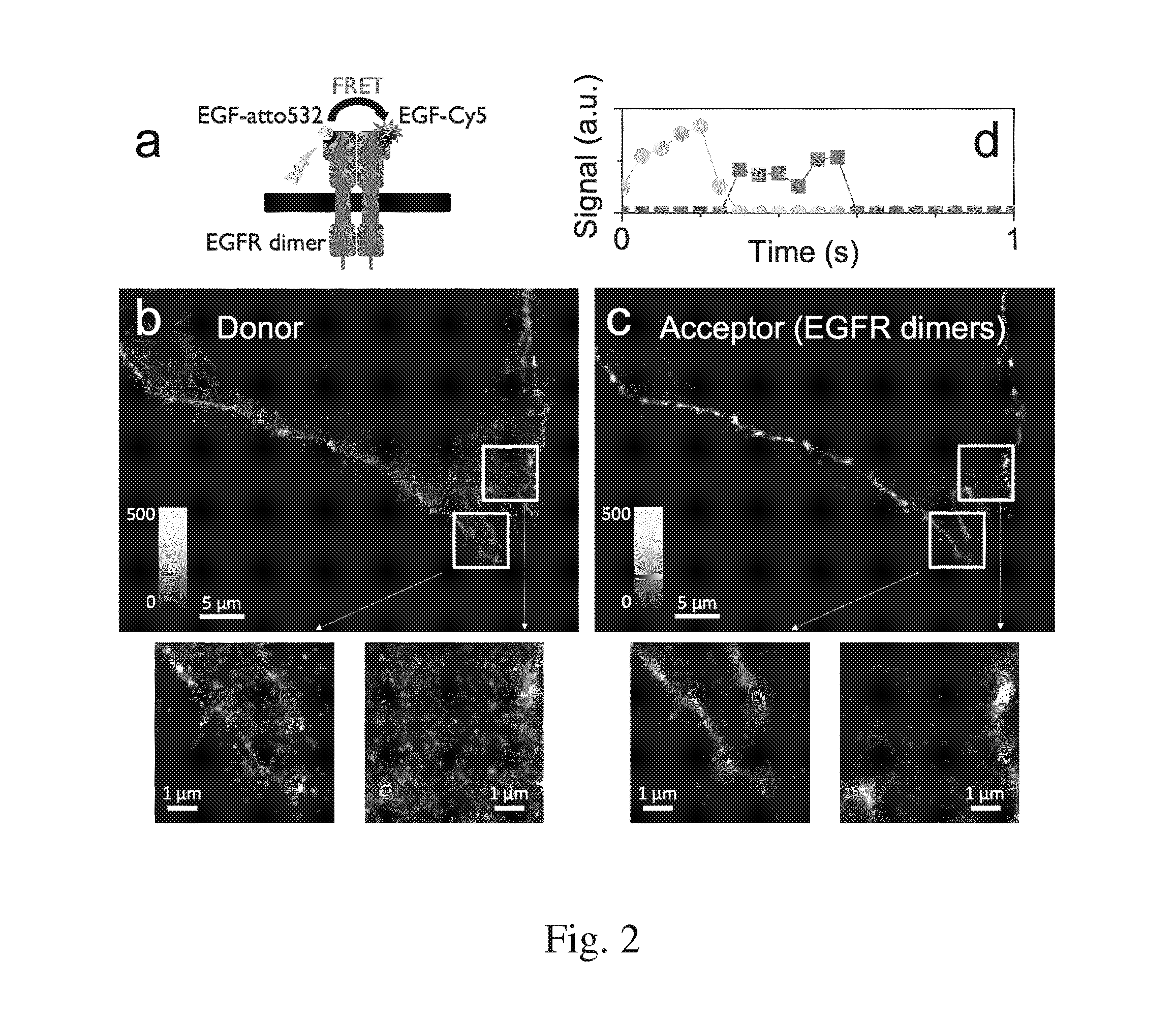
The present invention is related to a method of studying (i) binding reactions, (ii) dissociation reactions, (iii) competitive binding reactions, or (iv) association reactions between two or more molecules in a biological sample by means of super-resolution imaging, in which method the reaction as such causes an event that forms the basis for the identification and localization-based super-resolution microscopy of the reaction (FIG. 1a).
Owner:COGNET LAURENT +1
Novel diazo benzothiapyrone photosensitive protecting groups and synthesis method thereof
InactiveCN104478852AEfficient and rapid photodissociation reactionRelatively stableGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsBulk chemical productionVisibilityFluorescence
The invention discloses novel diazo benzothiapyrone photosensitive protecting groups and a synthesis method thereof. A compound disclosed by the invention can be used for protecting a phosphoric acid functional group compound. The novel benzothiapyrone photosensitive protecting groups disclosed by the invention are efficient and rapid in photo-dissociation reaction, have good relative stability under daily illumination conditions, and also have unique photosensitive structures which have response to light and can also be used for releasing potential fluorescent groups. According to the novel diazo benzothiapyrone photosensitive protecting groups disclosed by the invention, tracking and monitoring of a light control process can be facilitated, and the 'controllability' and 'visibility' of release can be achieved; and a novel research method for performing quantitative release and accumulation degree research under cell biological environments can be provided.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
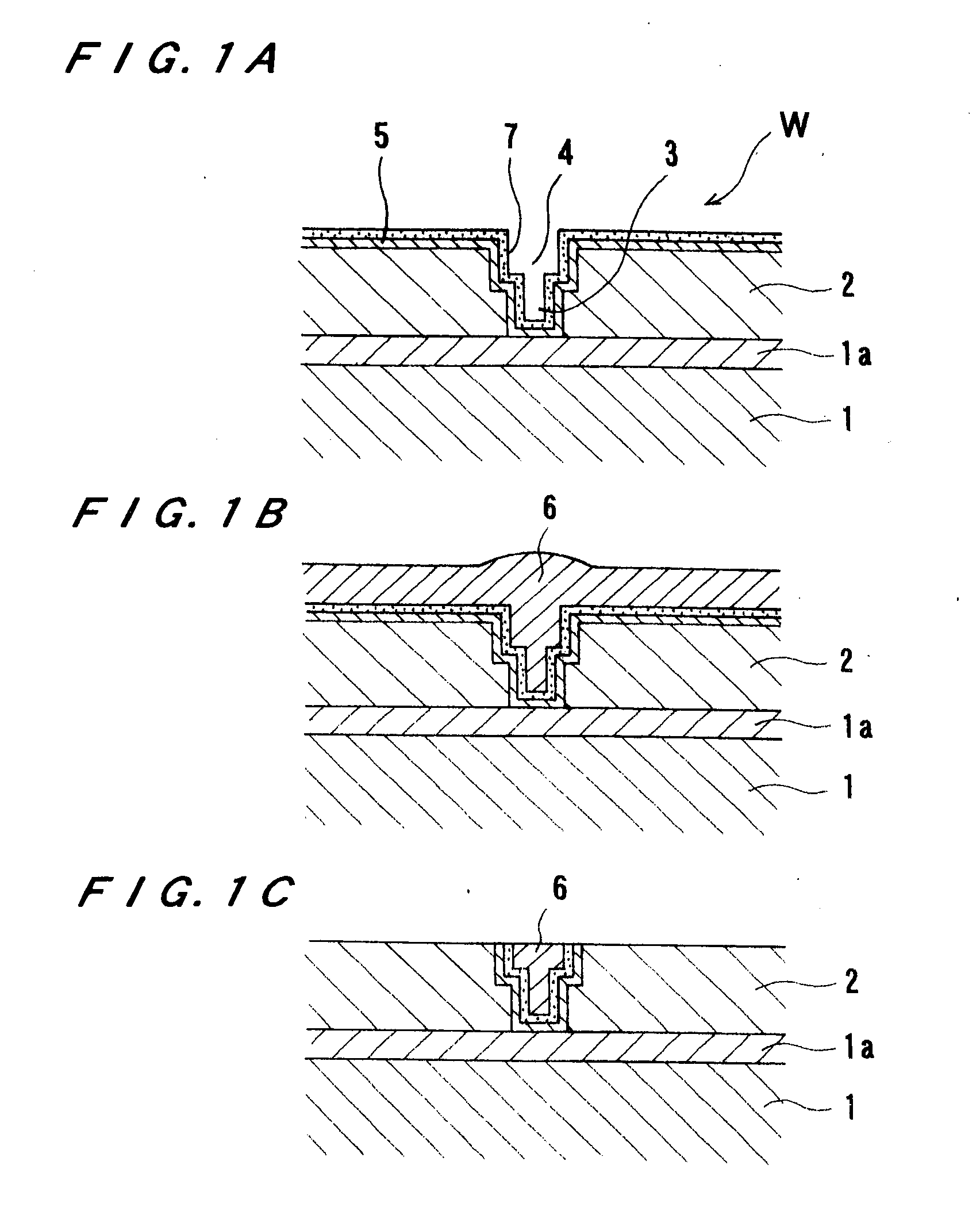
Neutral salt for use in polishing liquid, electronic material polishing liquid, polishing method, and method of manufacturing electronic materials
InactiveCN103619982AReduce adhesionEasy to removeOther chemical processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProtonationNitrogen
This invention comprises: a specific neutral salt (AB) used in a step for polishing an electronic material intermediary using a polishing pad; an electronic material polishing liquid containing said neutral salt (AB); a polishing method for polishing an electronic material intermediary using said electronic material polishing liquid; and a manufacturing method of an electronic material involving a step for polishing an electronic material intermediary with said polishing method. Here, the neutral salt (AB) is a salt of (A) an acidic compound having at least one acid radical (X) in the molecule, and (B) a nitrogen-containing basic compound having a 10-152 kcal / mol heat of formation change (Q2) in protonation reactions, wherein said neutral salt has a 3-200 kcal / mol heat of formation change (Q1) in acid dissociation reactions of the aforementioned acid radical (X). Thus provided is a material which, compared to conventional polishing liquids, results in fewer substrate defects such as scratches, which further, in a subsequent washing step, facilitates removal of polishing debris, and which further makes it possible to sustain polishing speed in the polishing step.
Owner:SANYO CHEM IND LTD
Ether bond dissociation method of phenylalkyl ether
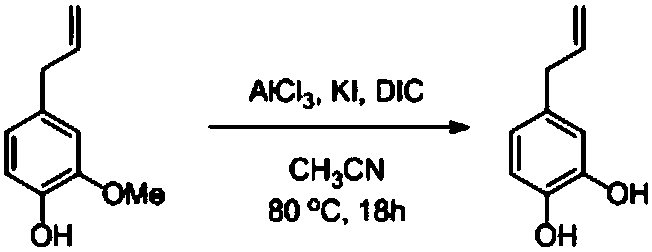
ActiveCN108516925AWide variety of sourcesLow priceOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationOrganic solventIodide
The invention discloses an ether bond dissociation method of phenylalkyl ether. The ether bond dissociation method of phenylalkyl ether includes the following steps that in organic solvent, in the presence of aluminium trihalogen, metal iodide and acid scavenging agents, phenylalkyl ether is subjected to an ether bond dissociation reaction at -20 DEG C to reflux temperature to generate phenol andderivatives thereof. The ether bond dissociation method of phenylalkyl ether is mild in condition, convenient to operate, high in yield and wide in phenylalkyl ether applicable range.
Owner:JINGCHU UNIV OF TECH
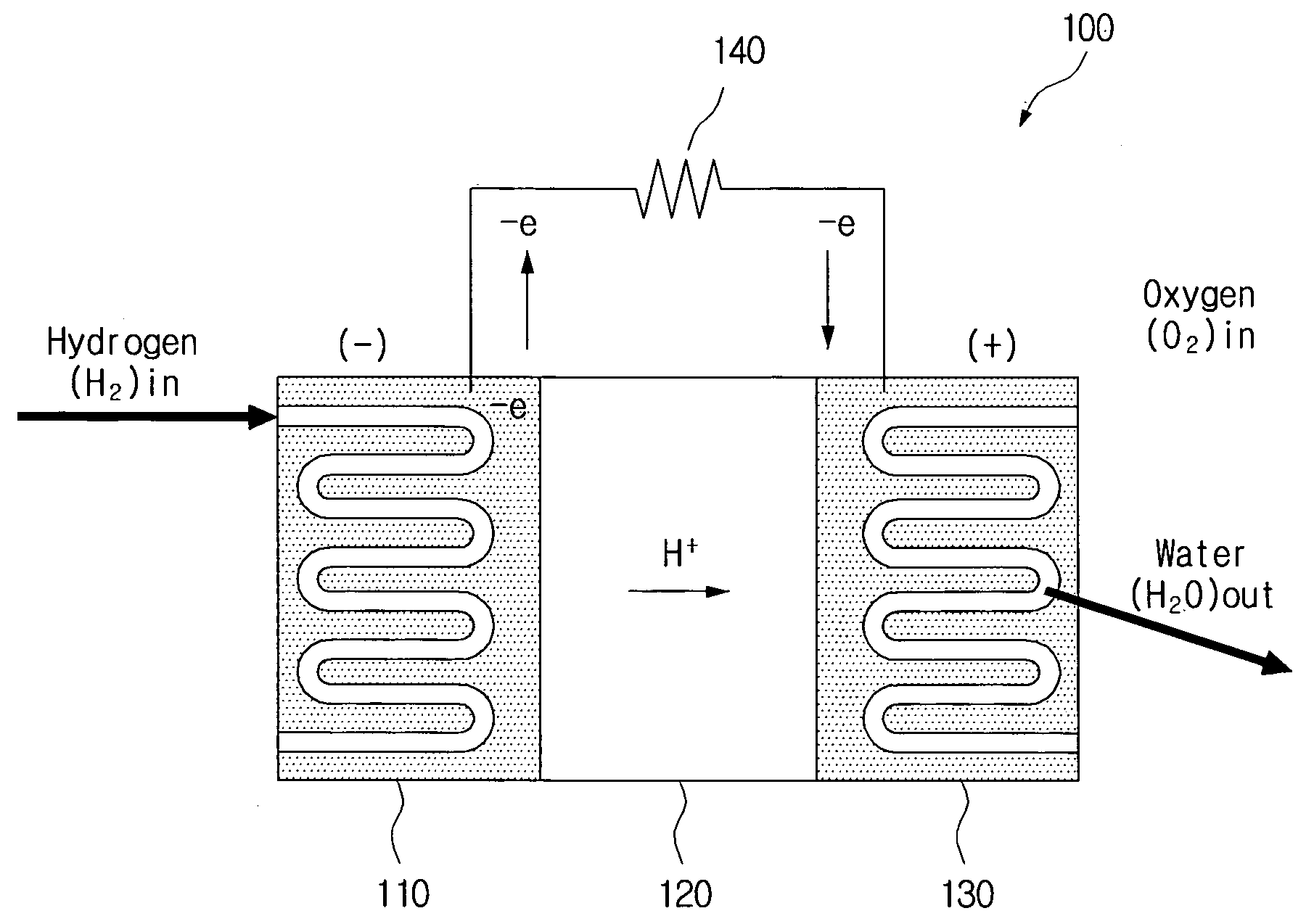
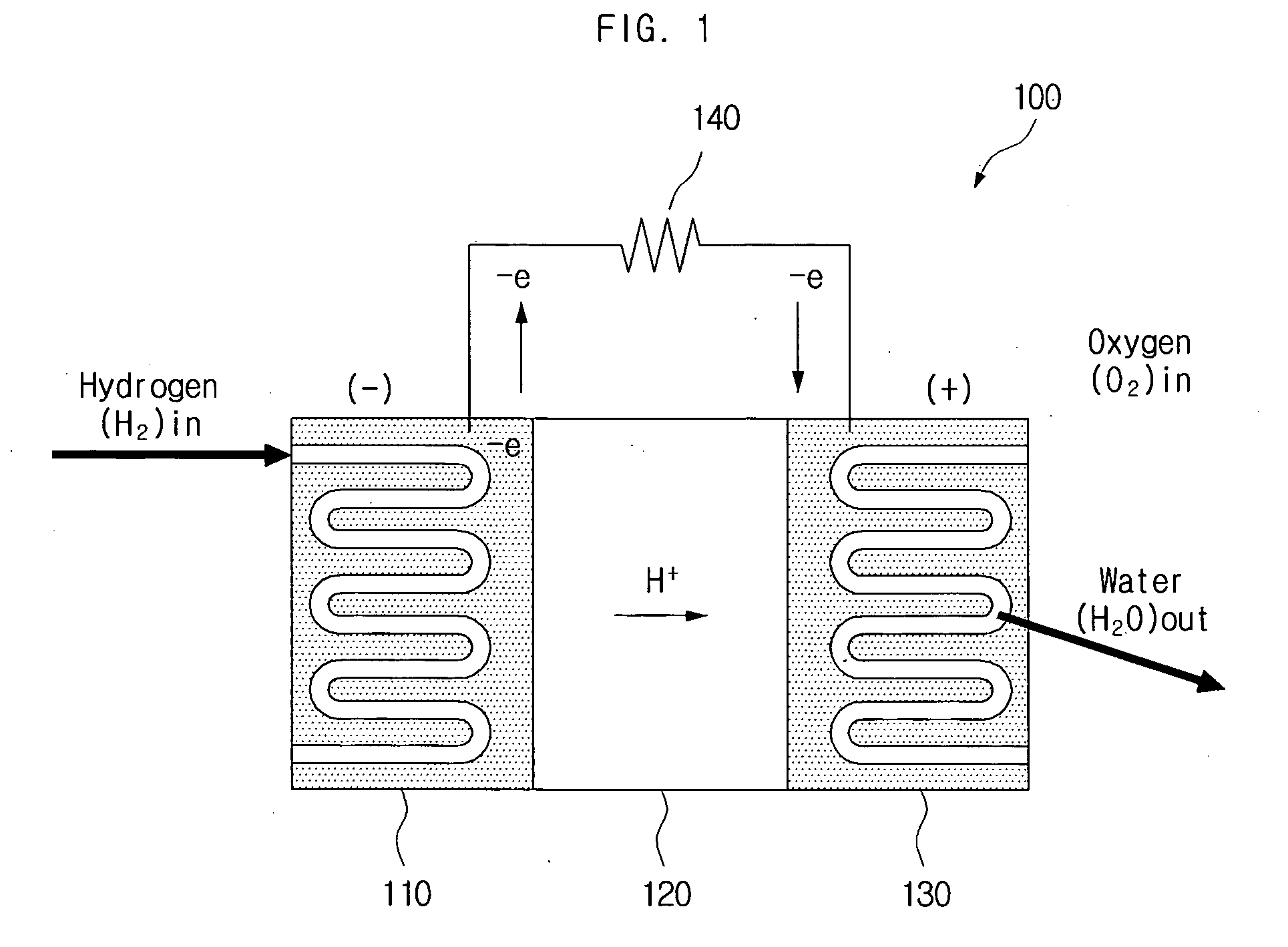
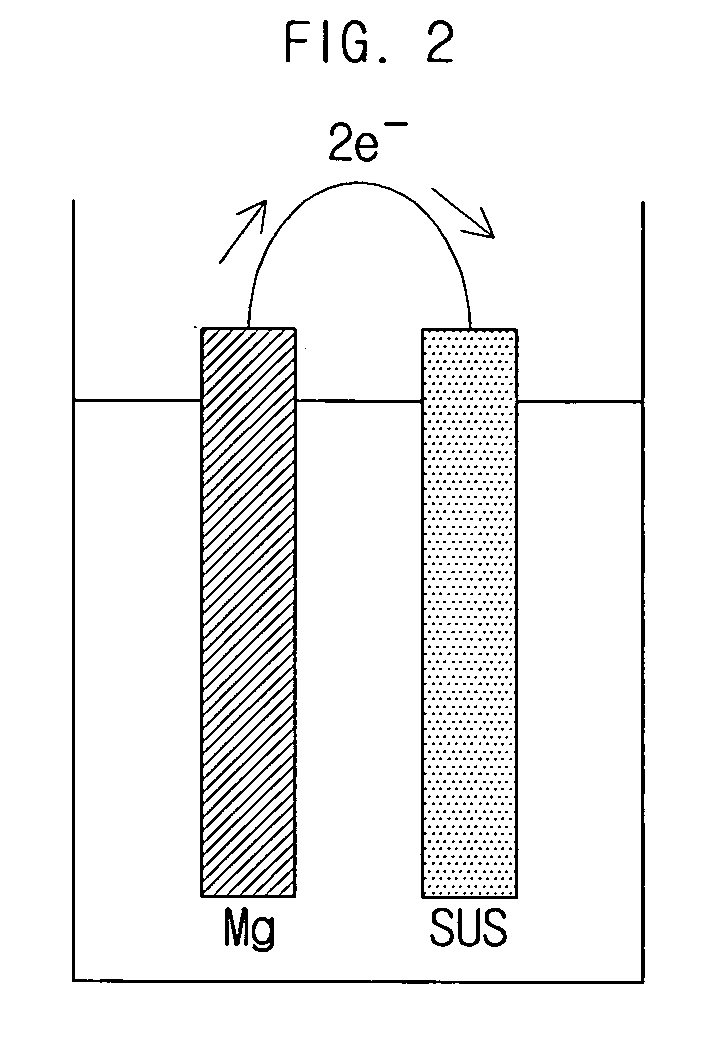
Hydrogen generating apparatus and fuel cell power generation system
InactiveUS20090011296A1Improve efficiencyPhysical/chemical process catalystsRegenerative fuel cellsFuel cellsHydrogen
A hydrogen generating apparatus and a fuel cell power generation system. An aspect of the invention provides a hydrogen generating apparatus for generating hydrogen through a dissociation reaction of an aqueous solution using electrons formed by an ionization of a metal. The hydrogen generating apparatus can include a chamber, which contains the aqueous solution, and in one side of which an outlet is formed to discharge the hydrogen; and a membrane, which is formed inside the chamber adjacent to the outlet, and which selectively permits the passage of the hydrogen. With certain embodiments of the invention, the overflowing of reagents can be prevented, for higher efficiency in the fuel cell. Because of the improvement in efficiency of the fuel cell power generation system, the volume of the system can be reduced, allowing for easier application to mobile devices.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
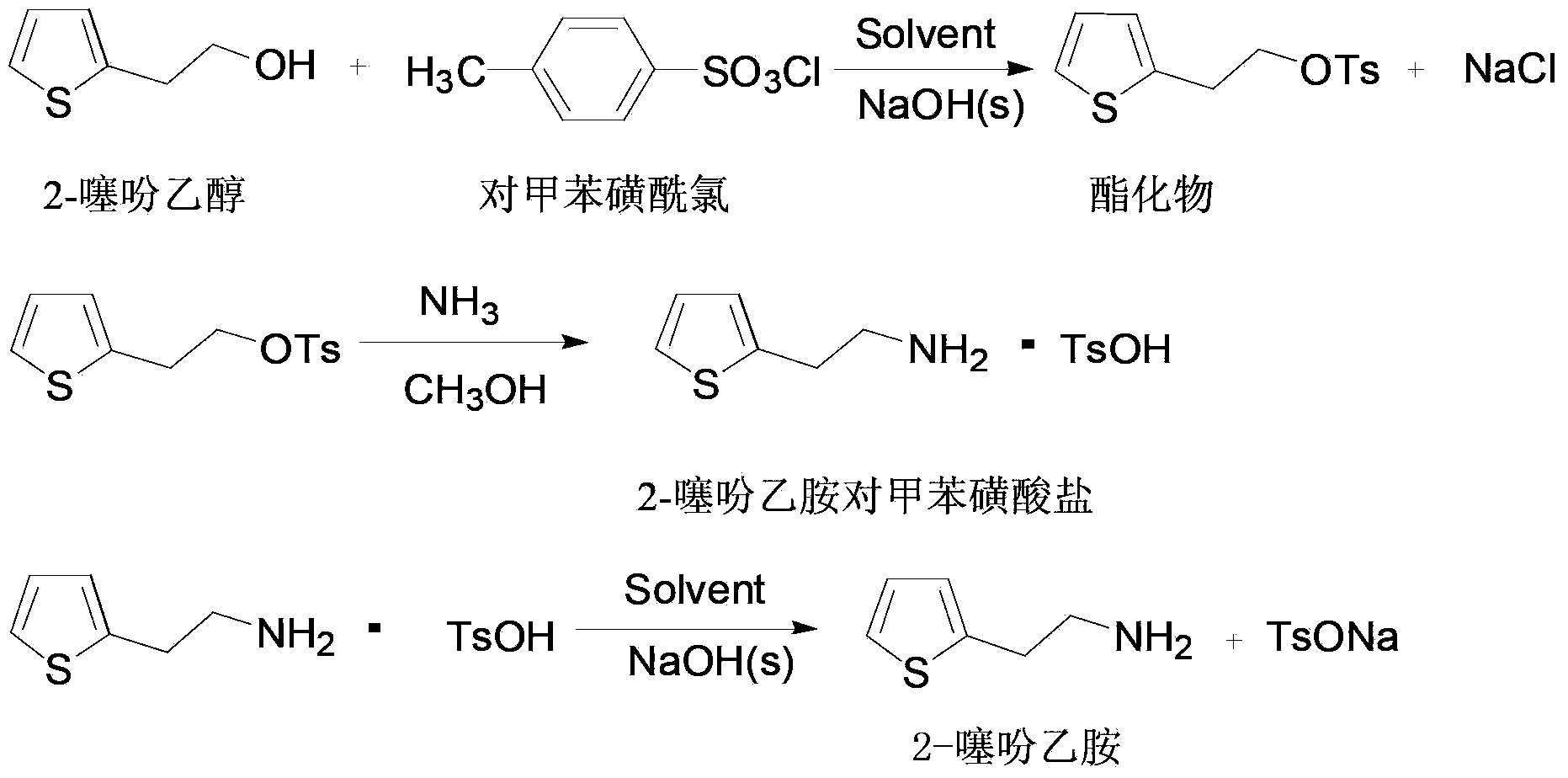
Synthetic method of 2-thiophene ethylamine
ActiveCN103351376AAchieving zero emissionsAchieve recyclingOrganic chemistryDissociation reactionEthylamine
The invention provides a synthetic method of 2-thiophene ethylamine. The synthetic method is characterized in that: the 2-thiophene ethylamine is obtained through esterification, ammonification and dissociation in non-aqueous medium by using 2-thiopheneethanol as initial raw materials. The synthetic method comprises the following steps of: (1) an esterification reaction, i.e., generating an esterified substance under the condition of solid base catalysis from 2-thiopheneethanol and p-toluenesulfonyl chloride in an organic solvent; (2) an ammonification reaction, i.e., injecting liquid ammonia into the esterified substance, pressurizing and ammonifying so as to generate 2-thienylethamino-4-toluenesulfonate; (3) a dissociation reaction, i.e., reacting the 2-thienylethamino-4-toluenesulfonate with a solid base in the organic solvent by the dissociation so as to prepare the 2-thiophene ethylamine. The whole preparation process of the 2-thiophene ethylamine is completed in the non-aqueous medium so that no waste water is discharged, solid waste materials are recycled and reused, and the purpose of green production is achieved. Besides, reaction conditions are milder, post treatment process is simpler, yield is high, and industrial production is facilitated.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LIAOYUAN PHARM CO LTD
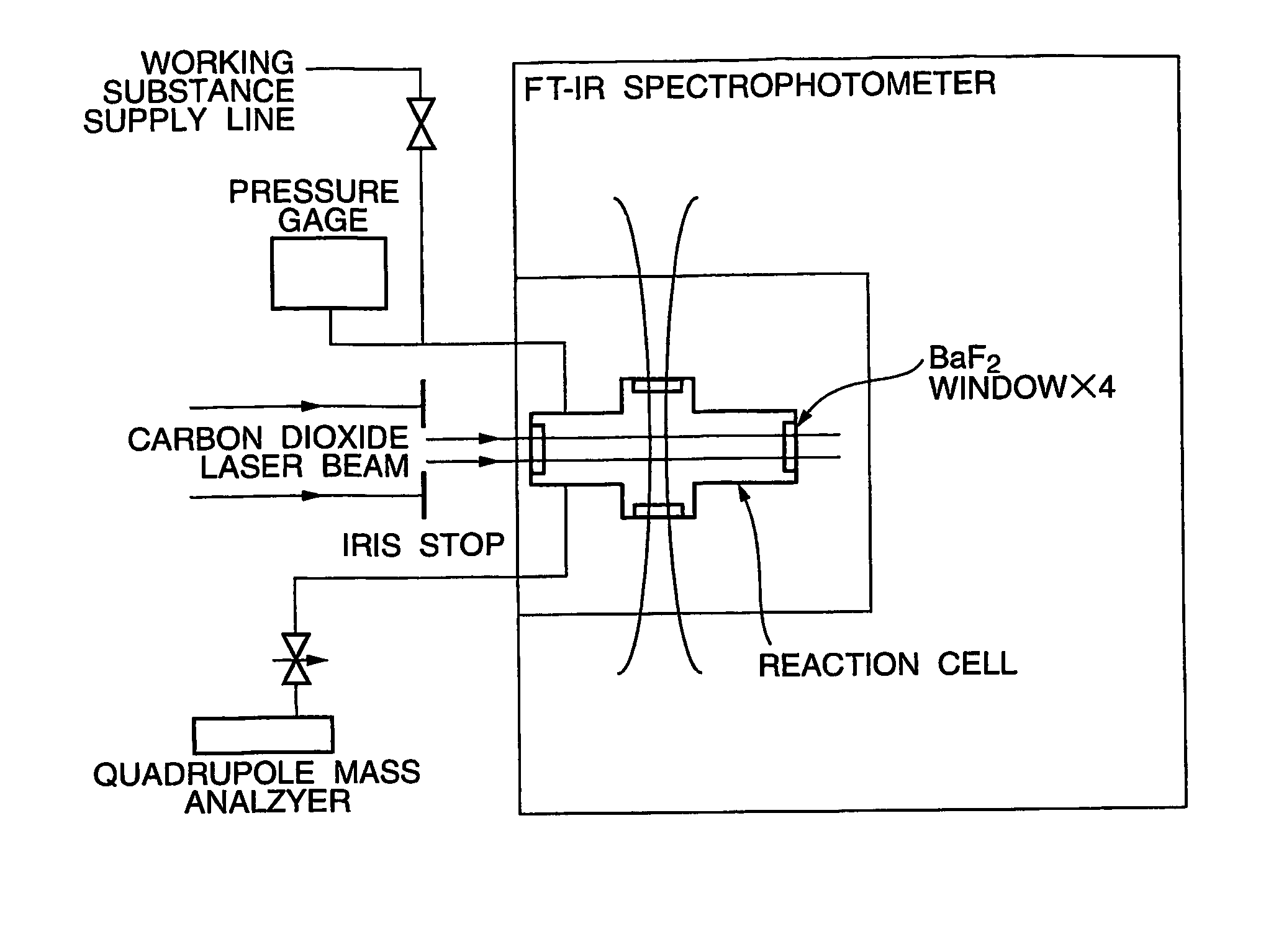
Isotope separation method and working substance for isotope separation
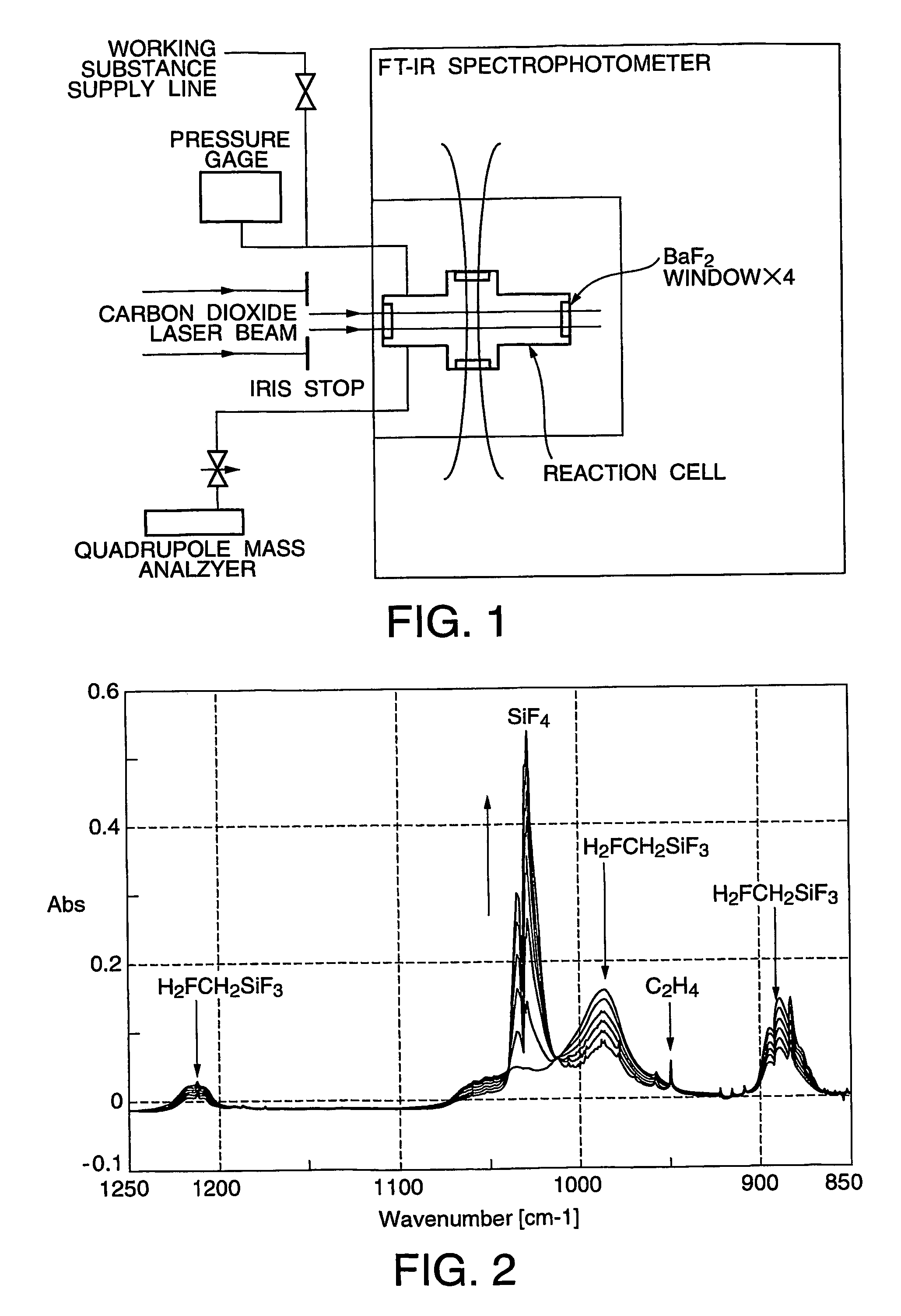
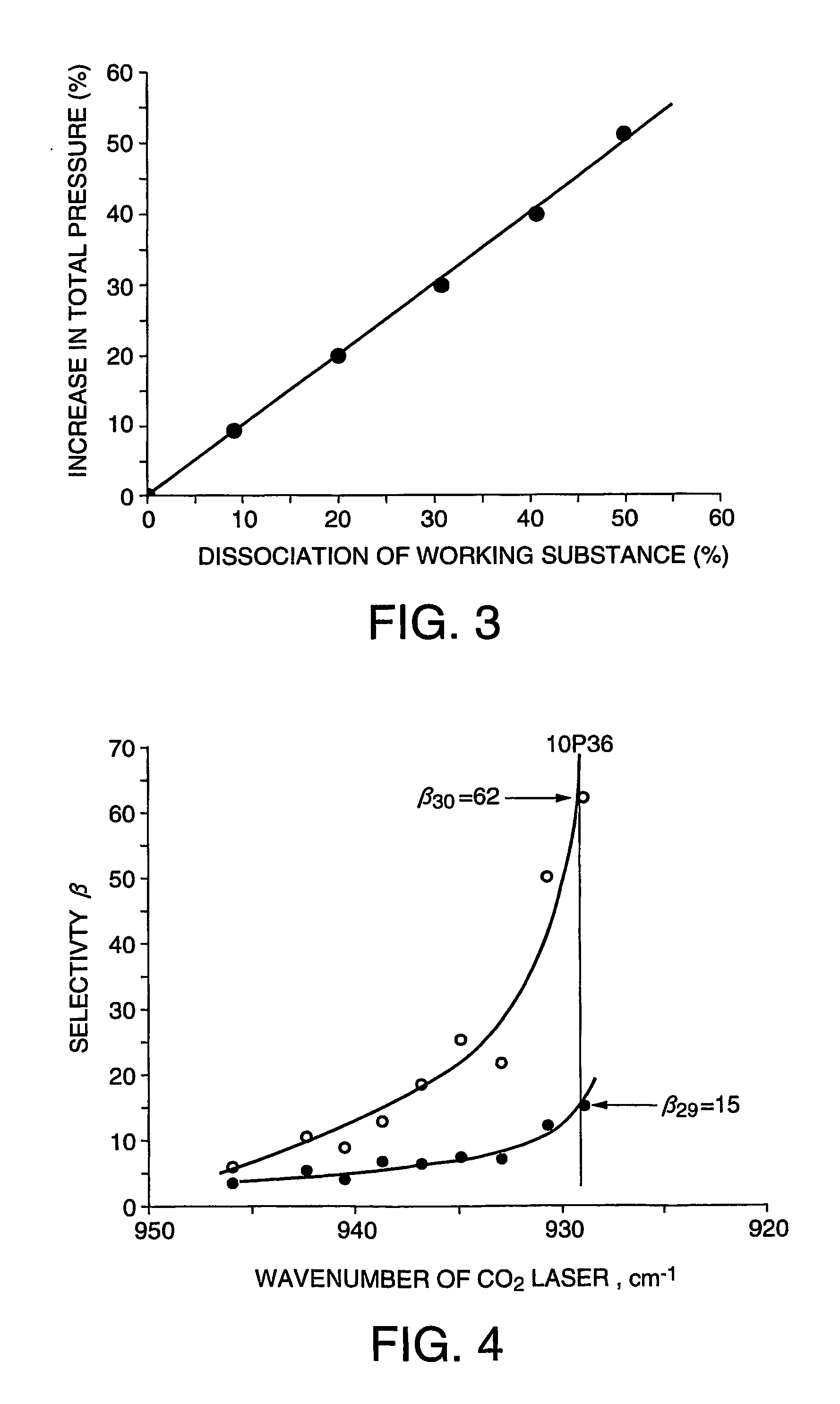
ActiveUS7307233B2Efficient separationWeaken energySilicon organic compoundsVapor condensationHalogenHydrogen atom
The present invention is directed to the provision of an isotope separation method, which can effectively prevent, without the use of a second gas, a secondary reaction and the formation of a polymer involved in a multiphoton dissociation reaction in laser isotope separation and, at the same time, can efficiently separate a target isotope with low activation energy, and a working substance for use in the isotope separation. The isotope separation method comprises the step of irradiating a working substance for isotope separation comprising a compound represented by formula SiX3-CY2-CZ3 or SiX3-CY═CZ2, wherein X, Y, and Z, which may be the same or different, represent a halogen atom, H, or an alkyl group; and at least one of Z's represents a halogen atom with the remaining Z's being H or an alkyl group, with a laser beam to dissociate only a molecule containing a particular target isotope atom, whereby the dissociation product or the nondissociation molecule is enriched with the target Si isotope atom.
Owner:KAWASAKI HEAVY IND LTD
Electrolytic processing apparatus and electrolytic processing method
InactiveUS7527723B2Improve efficiencyEfficient executionElectrolysis componentsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrolysisIon exchange
An electrolytic processing apparatus can increase the efficiency of the dissociation reaction of water and efficiently perform electrolytic processing, and can eliminate the need for an operation of a change of ion exchanger. The electrolytic processing apparatus includes: a processing electrode and a feeding electrode; a liquid supply section for supplying a liquid containing an ion-exchange material between the workpiece and at least one of the processing electrode and the feeding electrode; a power source for applying a voltage between the processing electrode and the feeding electrode; and a drive section for moving the workpiece and at least one of the processing electrode and the feeding electrode relative to each other; wherein electrolytic processing of the workpiece is carried out while keeping the workpiece not in contact with but close to the processing electrode at a distance of not more than 10 μm.
Owner:EBARA CORP
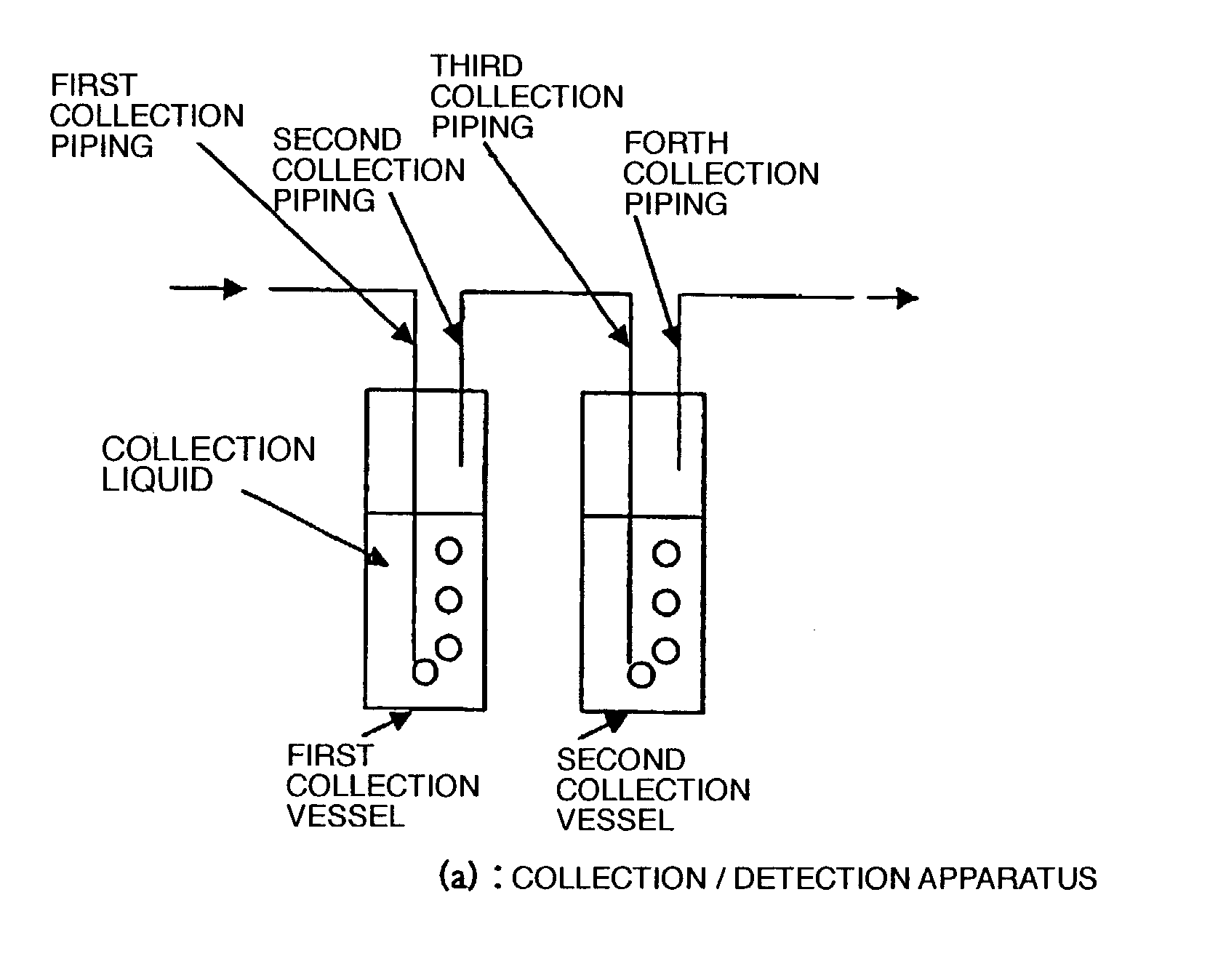
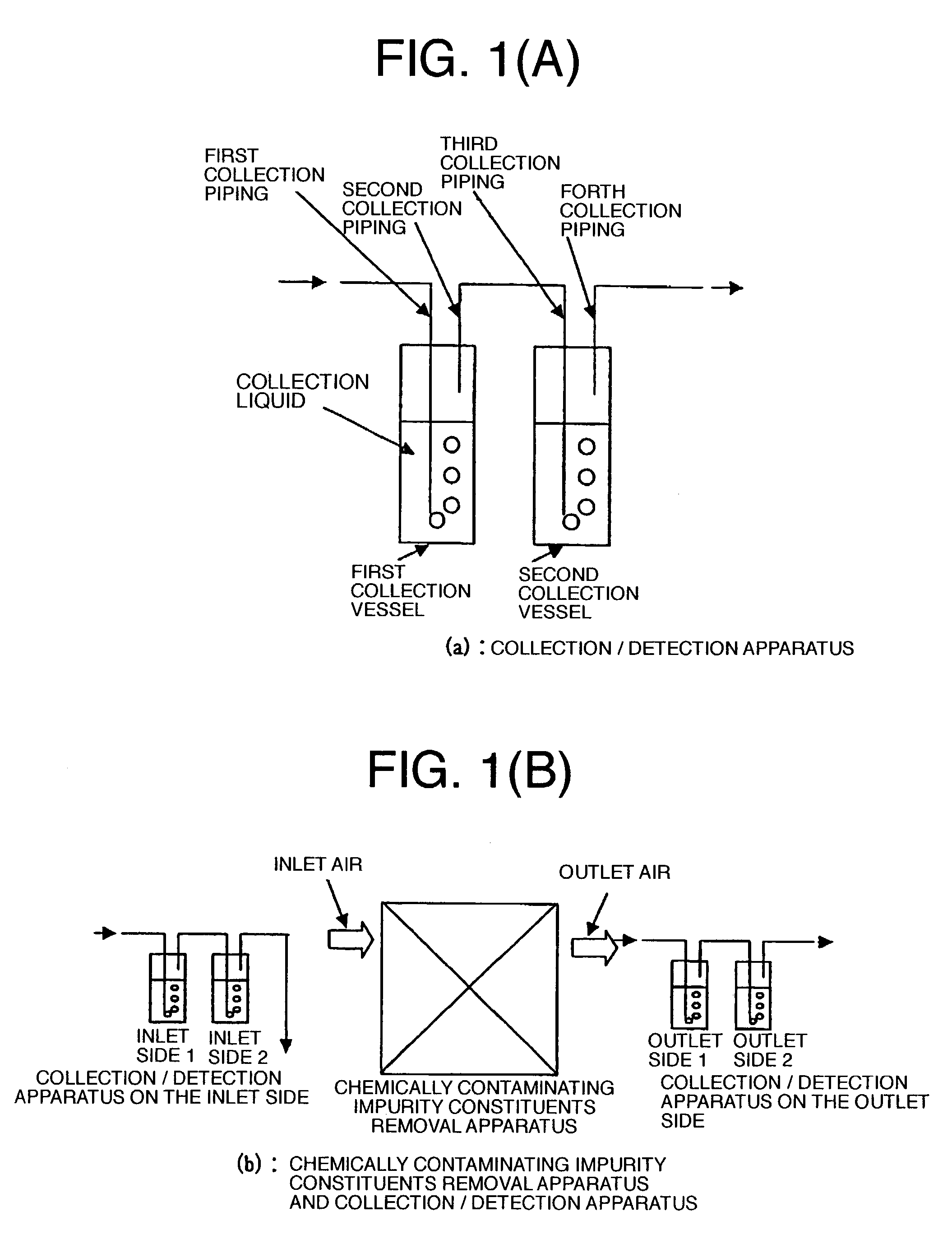
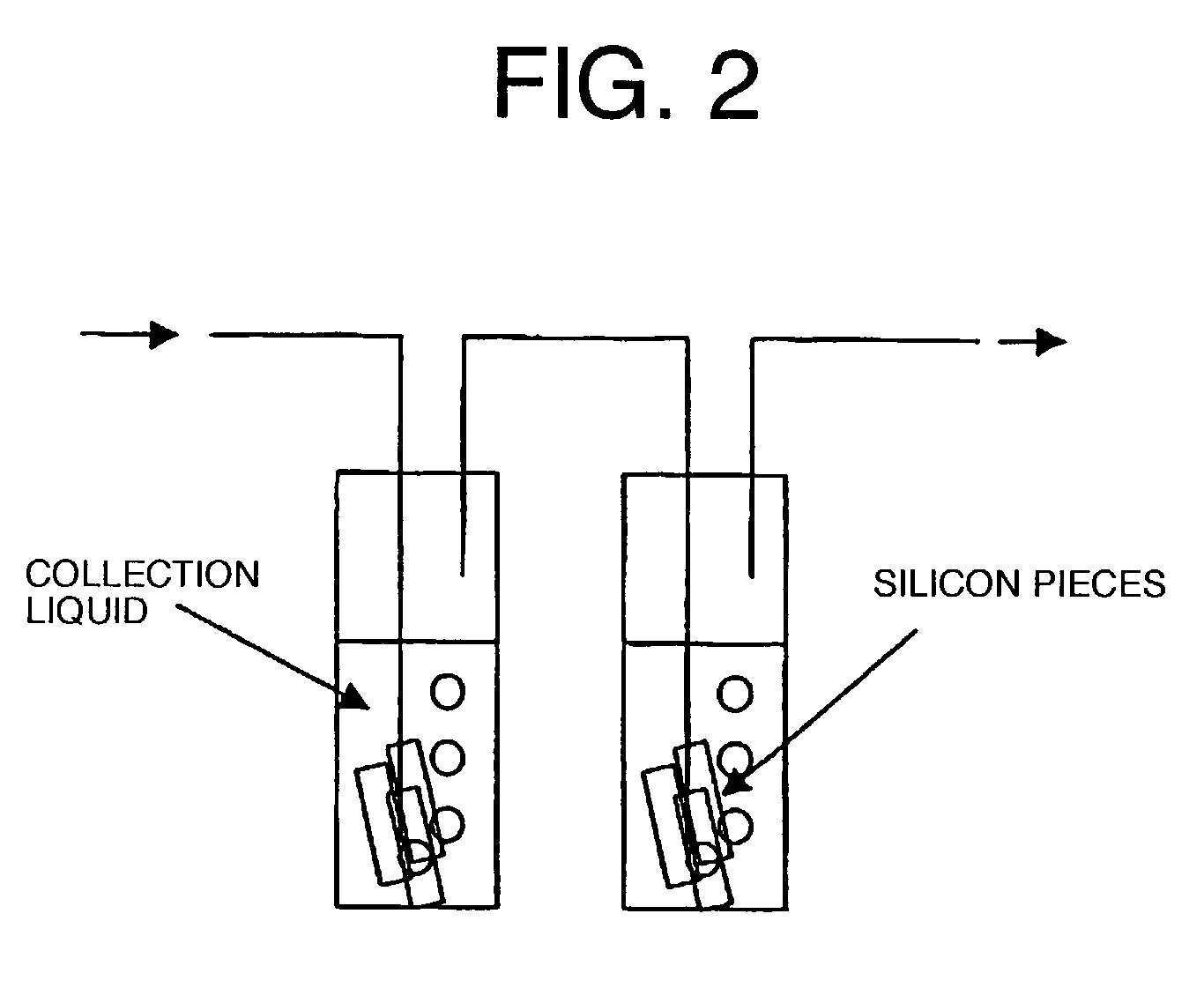
Method of collecting chemically contaminating impurity constituents contained in air
InactiveUS7332346B2High sensitivityImprove accuracyComponent separationLighting and heating apparatusSolubilityIonic composition
The method is intended to detect with high sensitivity and high accuracy chemically contaminating impurities in which there exist chemically contaminating impurity constituents of basic series, acidic series, and organic substance series, in gaseous and particle states, and constituents of compounds thereof, contained in air inside a clean room, as constituents having every property. To this end, ions composed of various cations and anions, constituting the chemically contaminating impurities in fine particle, gaseous, or molecular state, are caused to continuously undergo dissolution reaction and dissociation reaction in a solution in sequence from those constituting salts having strong solubility or strong dissociative tendency.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Preparation method and application of terpenoid 3,7,11-trimethyl-2,4,6,10-dodecatetraene-1-alcohol acetate
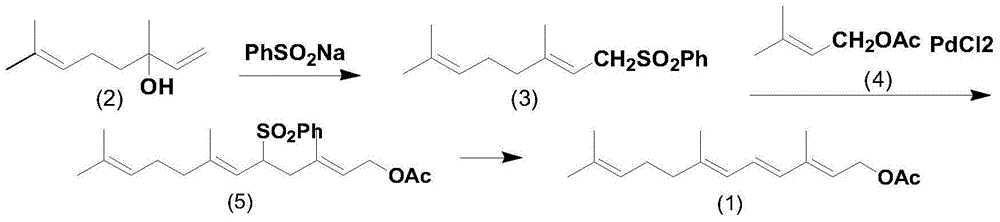
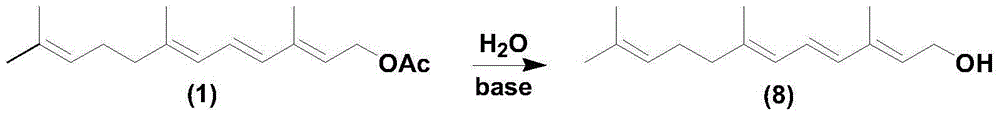
InactiveCN103553918AGood technical effectSimple process routeOxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationAcetic acidAlcohol
The invention relates to the technical field of organic synthesis and discloses a preparation method and an application of a terpenoid 3,7,11-trimethyl-2,4,6,10-dodecatetraene-1-alcohol acetate. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly carrying out dissociation reaction on C10 phosphonate at minus 40-30 DEG C in the presence of an organic solvent and an alkali under the protection of inert gases; after dissociation is completed, adding C5 aldehyde and carrying out Wittig-Horner condensation reaction at minus 40-30 DEG C in the presence of the organic solvent and the alkali. The prepared target product 3,7,11-trimethyl-2,4,6,10-dodecatetraene-1-alcohol acetate (1) is concise in process route, accessible in raw materials and low in cost and extremely has industrial value.
Owner:SHAOXING UNIVERSITY
Synthetic method of B-trichloroborazine
InactiveCN101607715BReduce volatile lossEasy to measure accuratelyGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsBoron compoundsProcess equipmentOrganic solvent
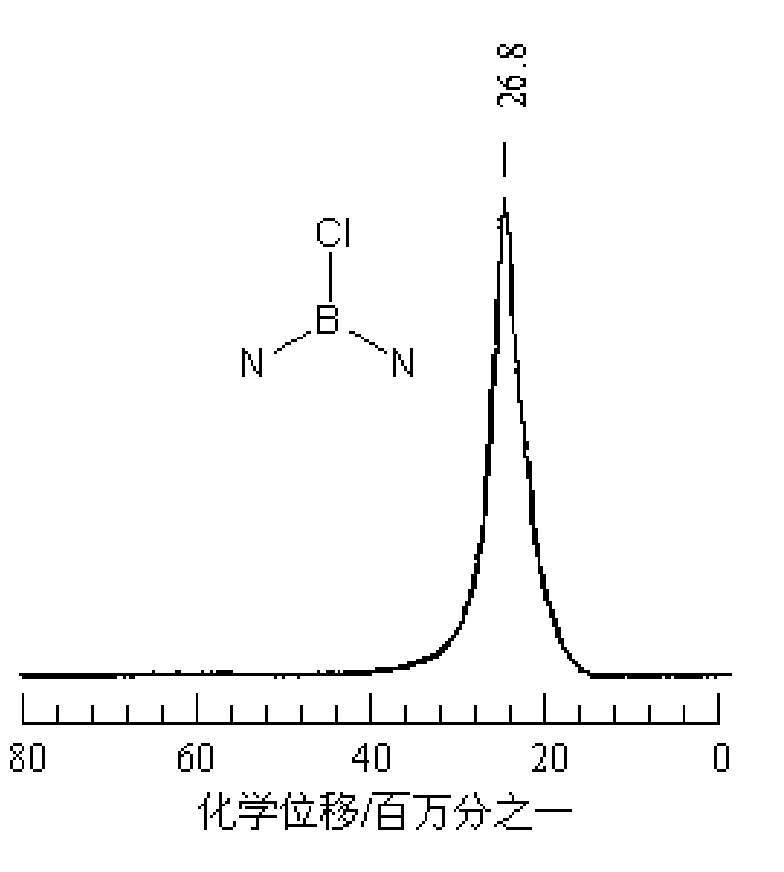
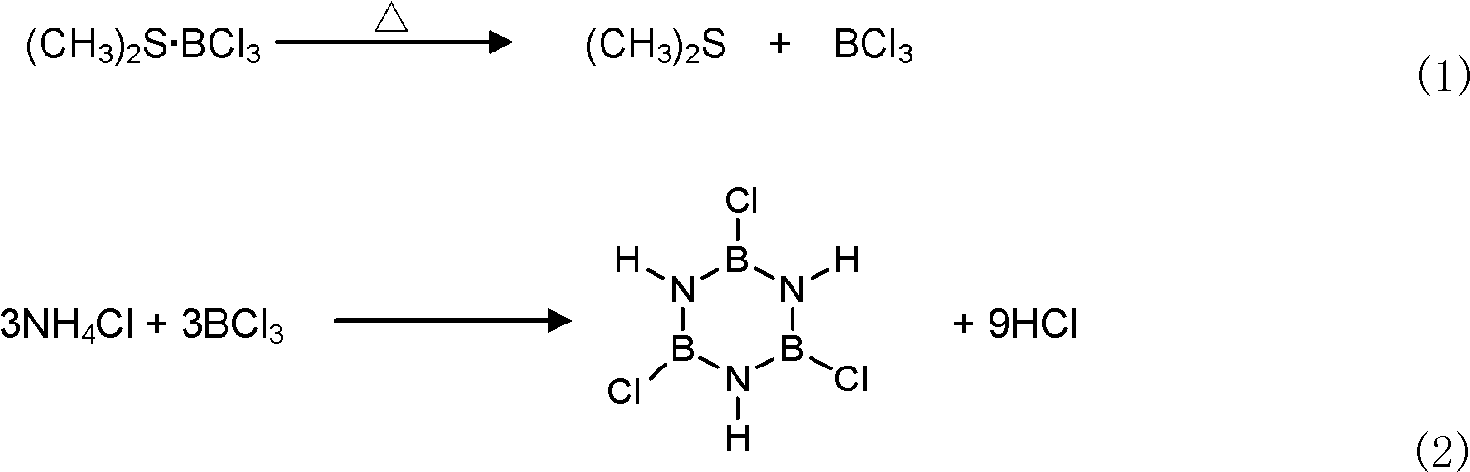
The invention discloses a synthetic method of B-trichloroborazine, which comprises the following steps of: fully and evenly mixing dimethyl sulphide boron trichloride complex and inorganic ammonium salt compound according to a mole ratio of an element B to an element N in the material of 1:1 to 3:1 and then dispersing the mixture in an organic solvent; adding the dispersed turbid liquor into a reactor with a stirring and low-temperature condensing back flow device, carrying out synthetic reaction for 10 to 20 hours under the conditions of temperature of 110 to 150 DEG C and violent stirring after vacuumization and filling dried nitrogen; carrying out condensing back flow when the temperature of the outlet end is controlled to -20 to -10 DEG C; and cooling the temperature to room temperature, filtering, recovering the organic solvent by reducing pressure and distilling, and obtaining the colourless needle crystal product. The synthetic method releases boron trichloride slowly by complex dissociation reaction of the dimethyl sulphide boron trichloride at the reaction temperature, and improves synthetic yield and boron utilization ratio, the material throwing amount is easy to accurately calculated, the technique equipment is simple and large-scale production is easy to realize.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com