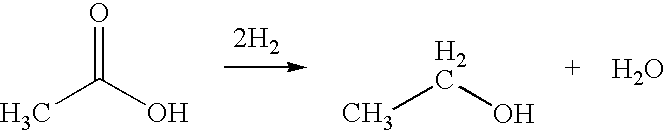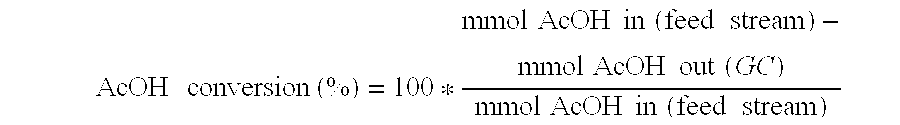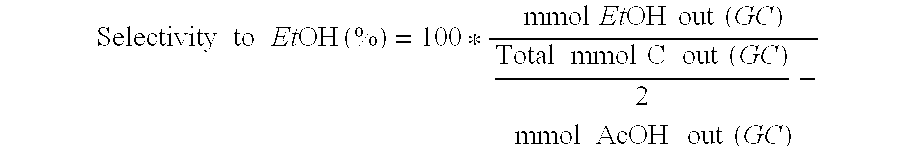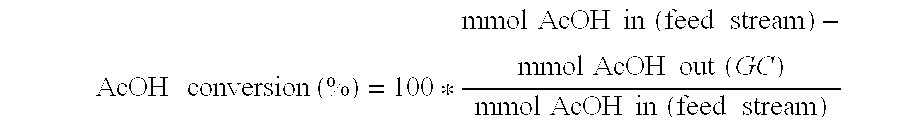Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
27070 results about "Tin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn (from Latin: stannum) and atomic number 50. Tin is a silvery metal that characteristically has a faint yellow hue. Tin, like indium, is soft enough to be cut without much force. When a bar of tin is bent, the so-called tin cry can be heard as a result of sliding tin crystals reforming; this trait is shared by indium, cadmium, and frozen mercury. Pure tin after solidifying keeps a mirror-like appearance similar to most metals. However, in most tin alloys (such as pewter) the metal solidifies with a dull gray color. Tin is a post-transition metal in group 14 of the periodic table of elements. It is obtained chiefly from the mineral cassiterite, which contains stannic oxide, SnO₂. Tin shows a chemical similarity to both of its neighbors in group 14, germanium and lead, and has two main oxidation states, +2 and the slightly more stable +4. Tin is the 49th most abundant element on Earth and has, with 10 stable isotopes, the largest number of stable isotopes in the periodic table, thanks to its magic number of protons. It has two main allotropes: at room temperature, the stable allotrope is β-tin, a silvery-white, malleable metal, but at low temperatures, it transforms into the less dense grey α-tin, which has the diamond cubic structure. Metallic tin does not easily oxidize in air.
Memory cell incorporating a chalcogenide element and method of making same
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Barrier material and process for Cu interconnect
InactiveUS20060113675A1Improved electromigration performanceImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorDiffusion barrier
A semiconductor diffusion barrier layer and its method of manufacture is described. The barrier layer includes of at least one layer of TaN, TiN, WN, TbN, VN, ZrN, CrN, WC, WN, WCN, NbN, AlN, and combinations thereof. The barrier layer may further include a metal rich surface. Embodiments preferably include a glue layer about 10 to 500 Angstroms thick, the glue layer consisting of Ru, Ta, Ti, W, Co, Ni, Al, Nb, AlCu, and a metal-rich nitride, and combinations thereof. The ratio of the glue layer thickness to the barrier layer thickness is preferably about 1 to 50. Other alternative preferred embodiments further include a conductor annealing step. The various layers may be deposited using PVD, CVD, PECVD, PEALD and / or ALD methods including nitridation and silicidation methods.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Direct and selective production of ethanol from acetic acid utilizing a platinum/tin catalyst
InactiveUS7863489B2High selectivityHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationOxygen compounds preparation by reductionCalcium silicateAcetic acid
A process for the selective production of ethanol by vapor phase reaction of acetic acid over a hydrogenating catalyst composition to form ethanol is disclosed and claimed. In an embodiment of this invention reaction of acetic acid and hydrogen over a platinum and tin supported on silica, graphite, calcium silicate or silica-alumina selectively produces ethanol in a vapor phase at a temperature of about 250° C.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
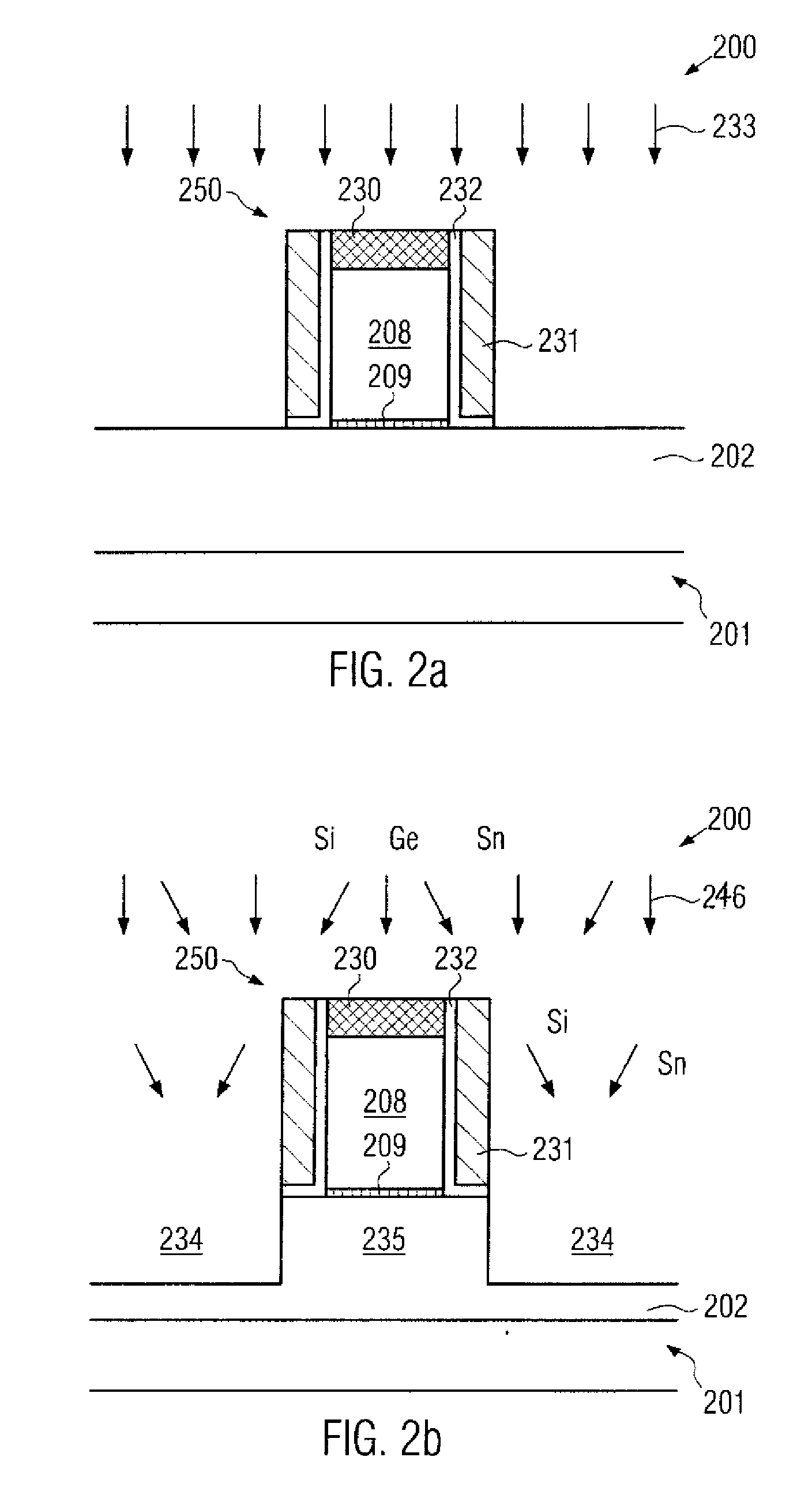
Technique for strain engineering in si-based transistors by using embedded semiconductor layers including atoms with high covalent radius
By incorporating an atomic species of increased covalent radius, which may at least partially substitute germanium, a highly efficient strain mechanism may be provided, in which the risk of stress relief due to germanium conglomeration and lattice defects may be reduced. The atomic species of increased radius, such as tin, may be readily incorporated by epitaxial growth techniques on the basis of tin hydride.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Method of manufacturing a contact interconnection layer containing a metal and nitrogen by atomic layer deposition for deep sub-micron semiconductor technology
ActiveUS7235482B2Good step coverageSafe handlingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAtomic layer depositionContamination
An atomic layer deposition method is used to deposit a TiN or TiSiN film having a thickness of about 50 nm or less on a substrat. A titanium precursor which is tetrakis(dimethylamido)titanium (TDMAT), tetrakis(diethylamido)titanium (TDEAT), or Ti{OCH(CH3)2}4 avoids halide contamination from a titanium halide precursor and is safer to handle than a titanium nitrate. After a monolayer of the titanium precursor is deposited on a substrate, a nitrogen containing reactant is introduced to form a TiN monolayer which is followed by a second purge. For TiSiN, a silicon source gas is fed into the process chamber after the TiN monolayer formation. The process is repeated several times to produce a composite layer comprised of a plurality of monolayers that fills a contact hole. The ALD method is cost effective and affords an interconnect with lower impurity levels and better step coverage than conventional PECVD or CVD processes.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
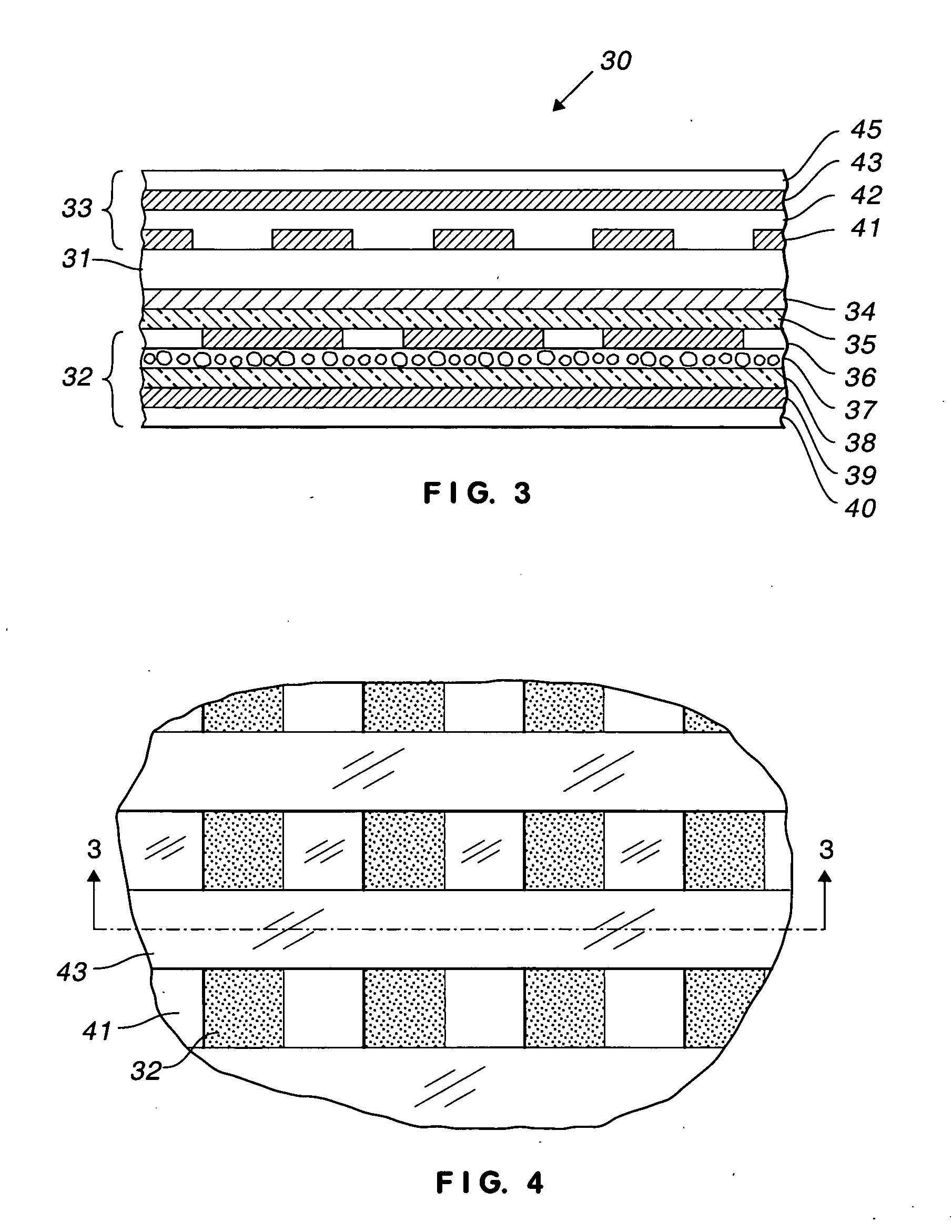
Memory cell incorporating a chalcogenide element
A memory cell incorporating a chalcogenide element and a method of making same is disclosed. In the method, a doped silicon substrate is provided with two or more polysilicon plugs to form an array of diode memory cells. A layer of silicon nitride is disposed over the plugs. Using a poly-spacer process, small pores are formed in the silicon nitride to expose a portion of the polysilicon plugs. A chalcogenide material is disposed in the pores by depositing a layer of chalcogenide material on the silicon nitride layer and planarizing the chalcogenide layer to the silicon nitride layer using CMP. A layer of TiN is next deposited over the plugs, followed by a metallization layer. The TiN and metallization layers are then masked and etched to define memory cell areas.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
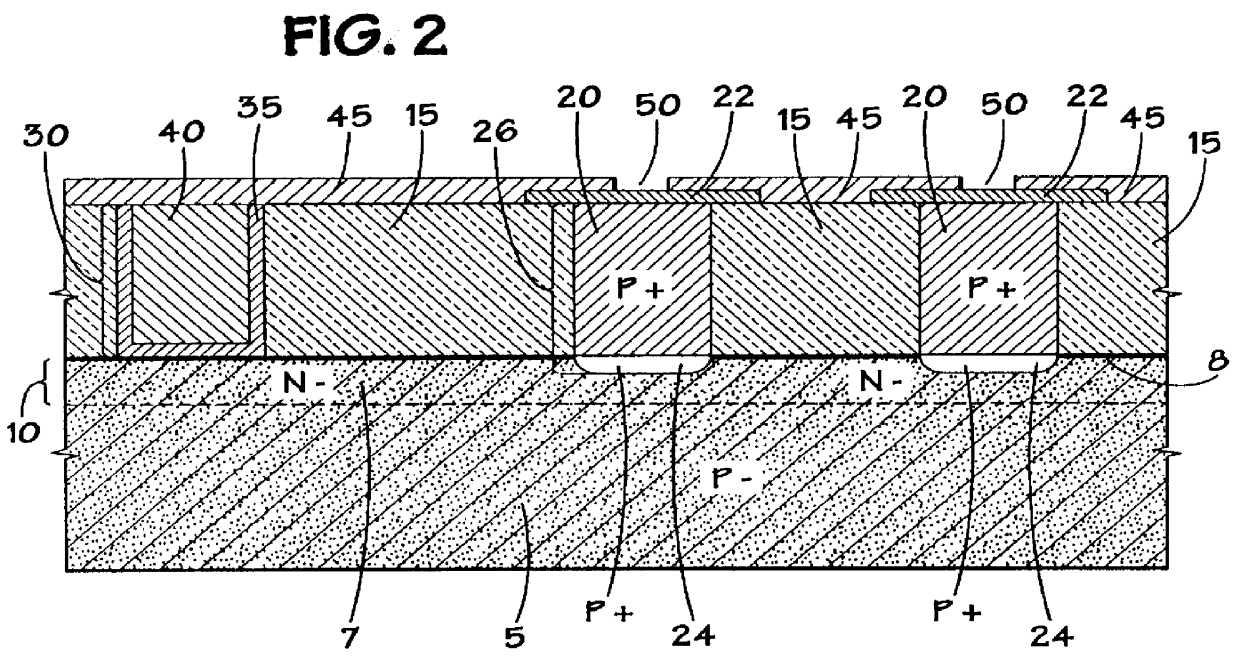
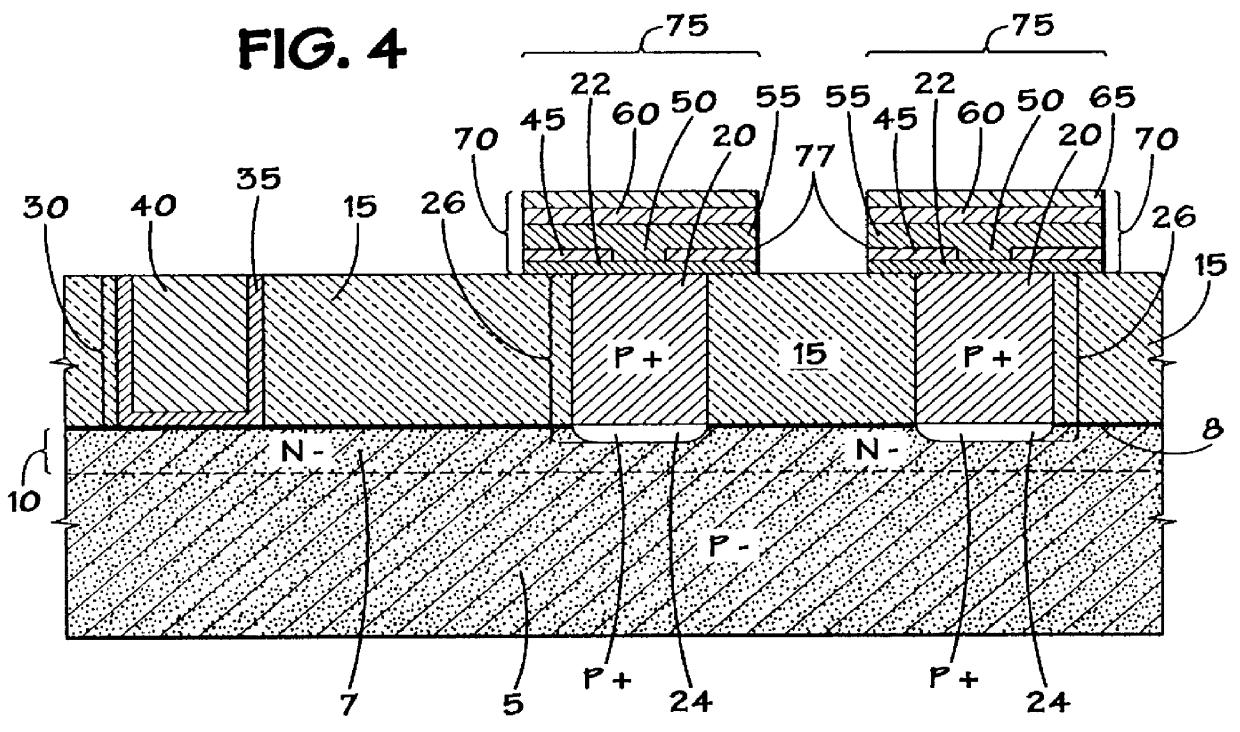
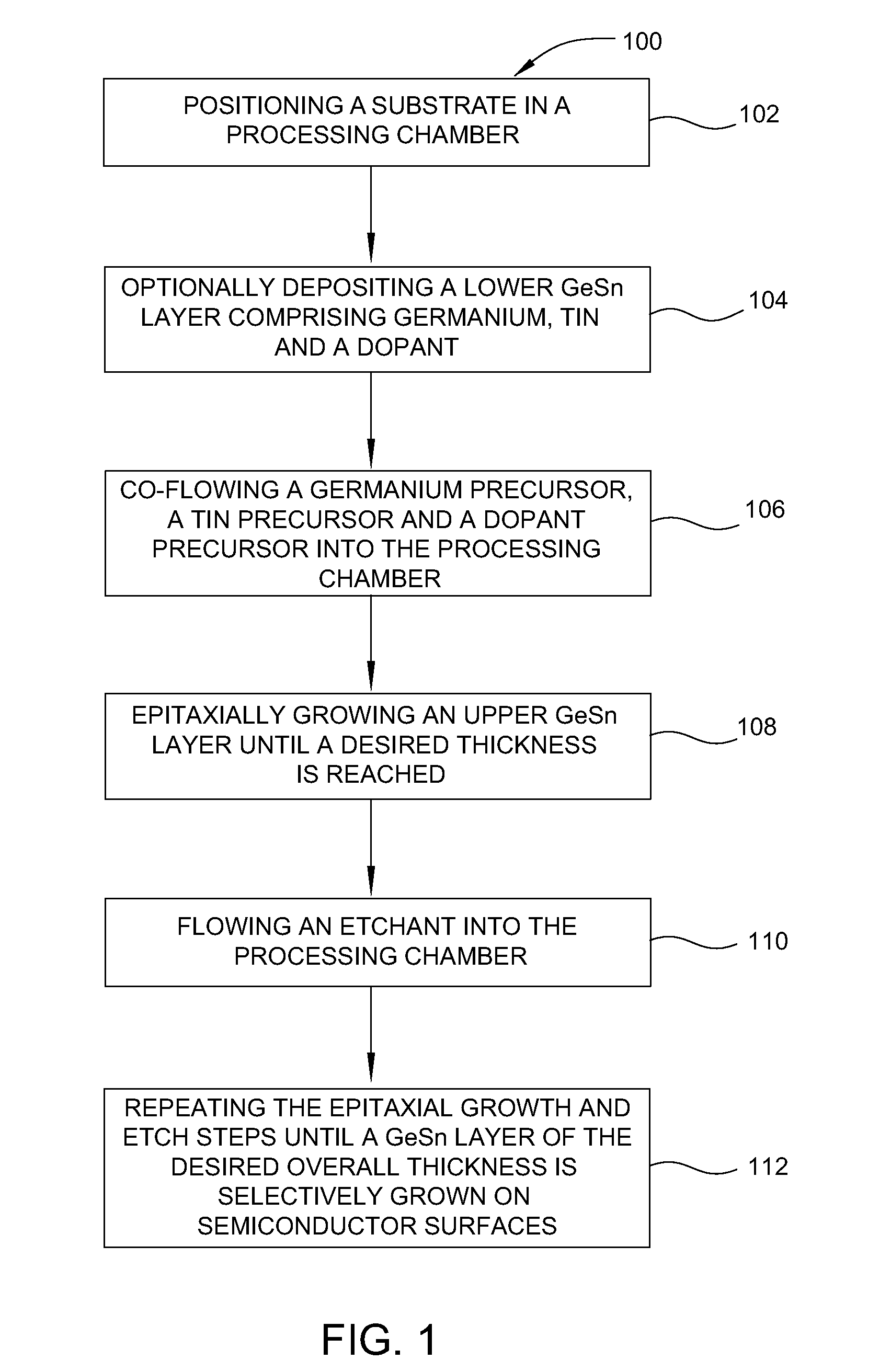
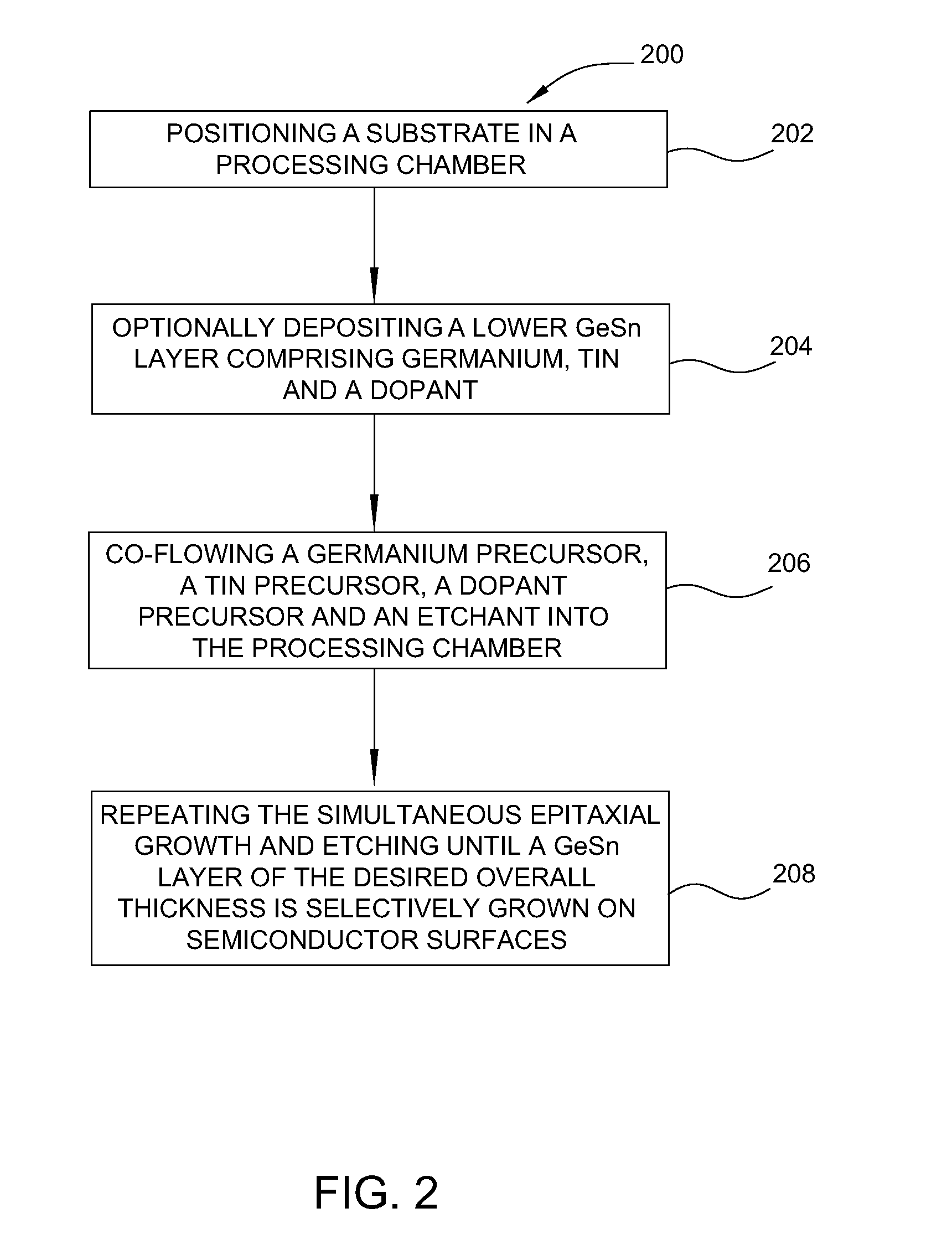
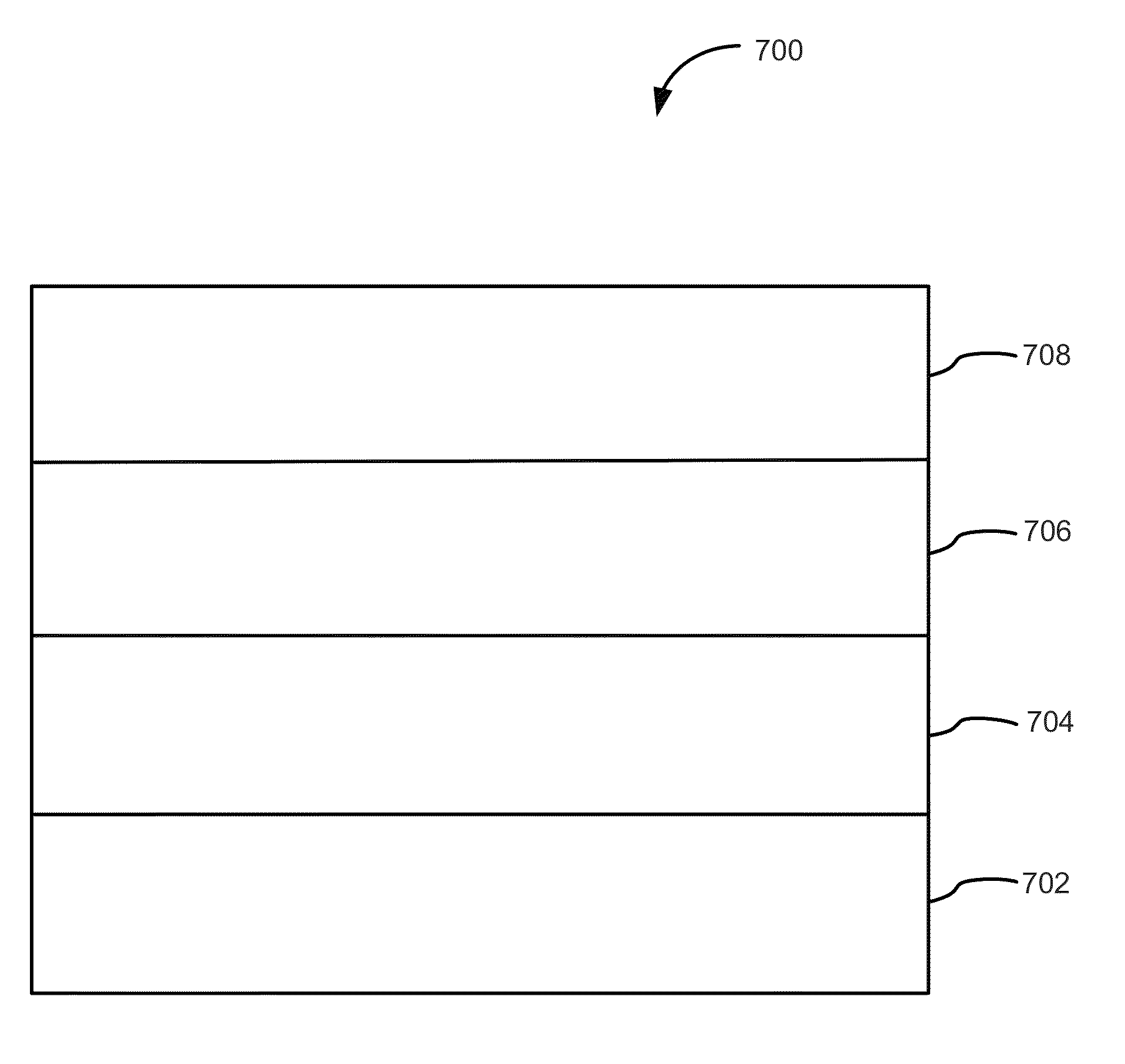
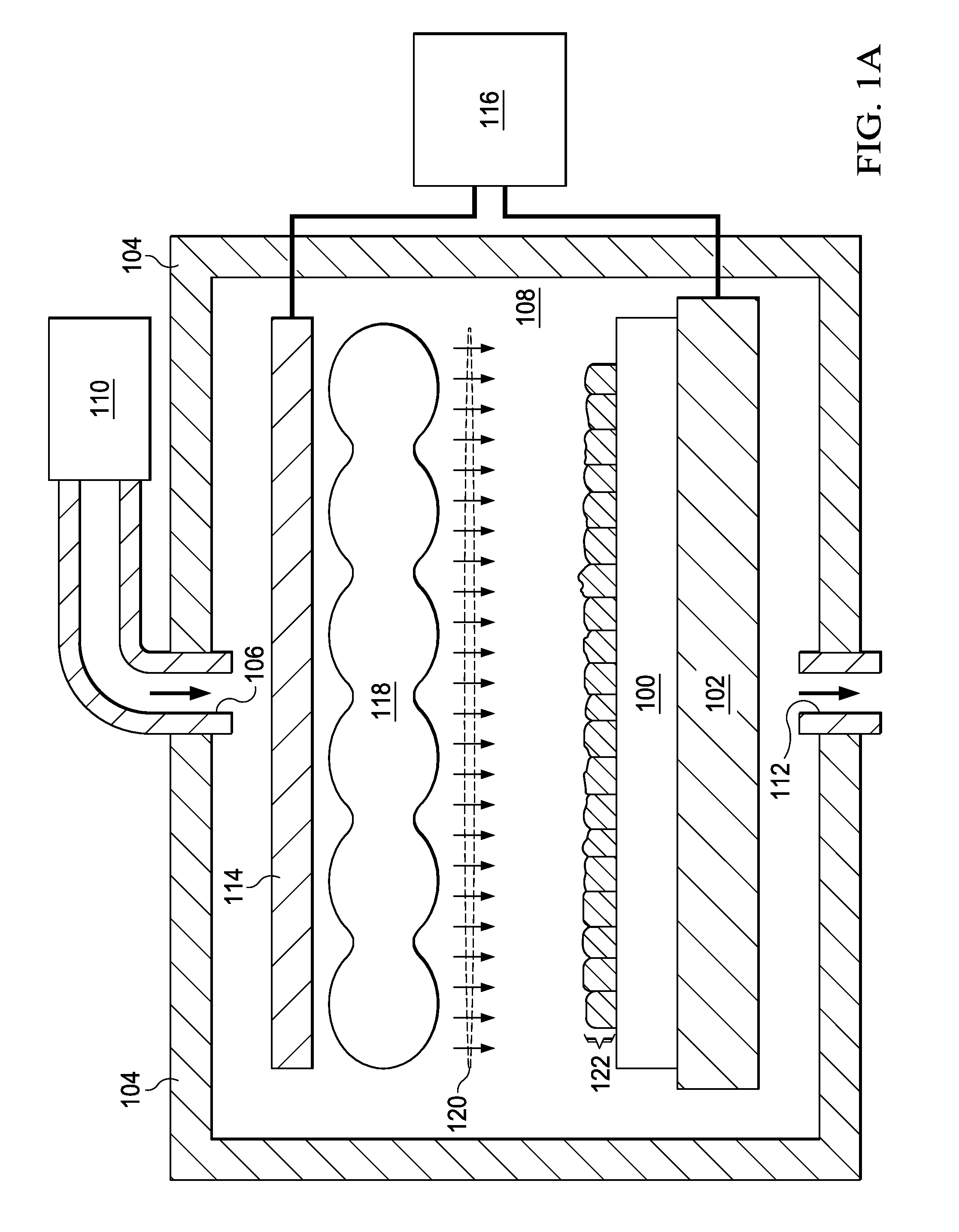
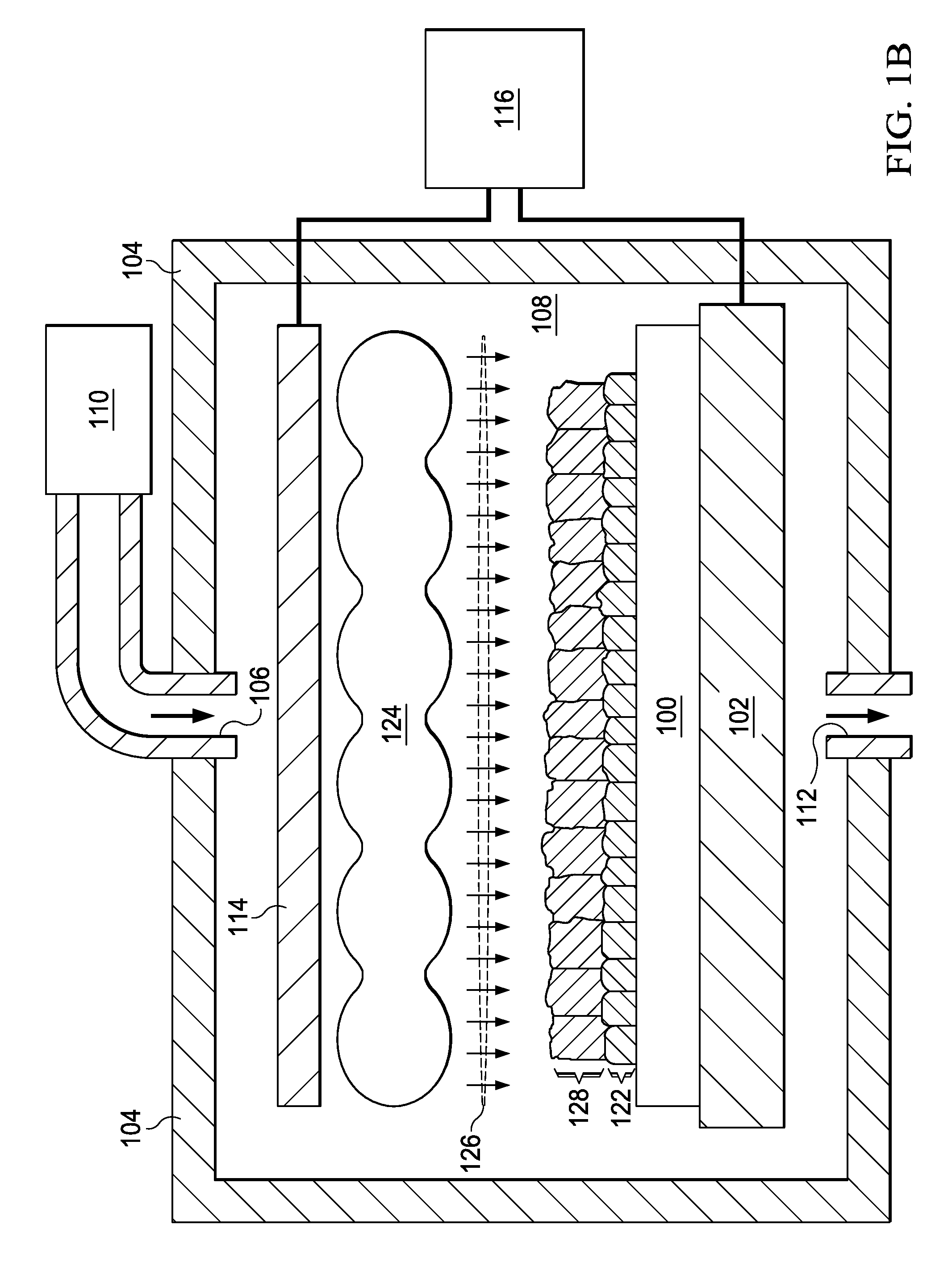
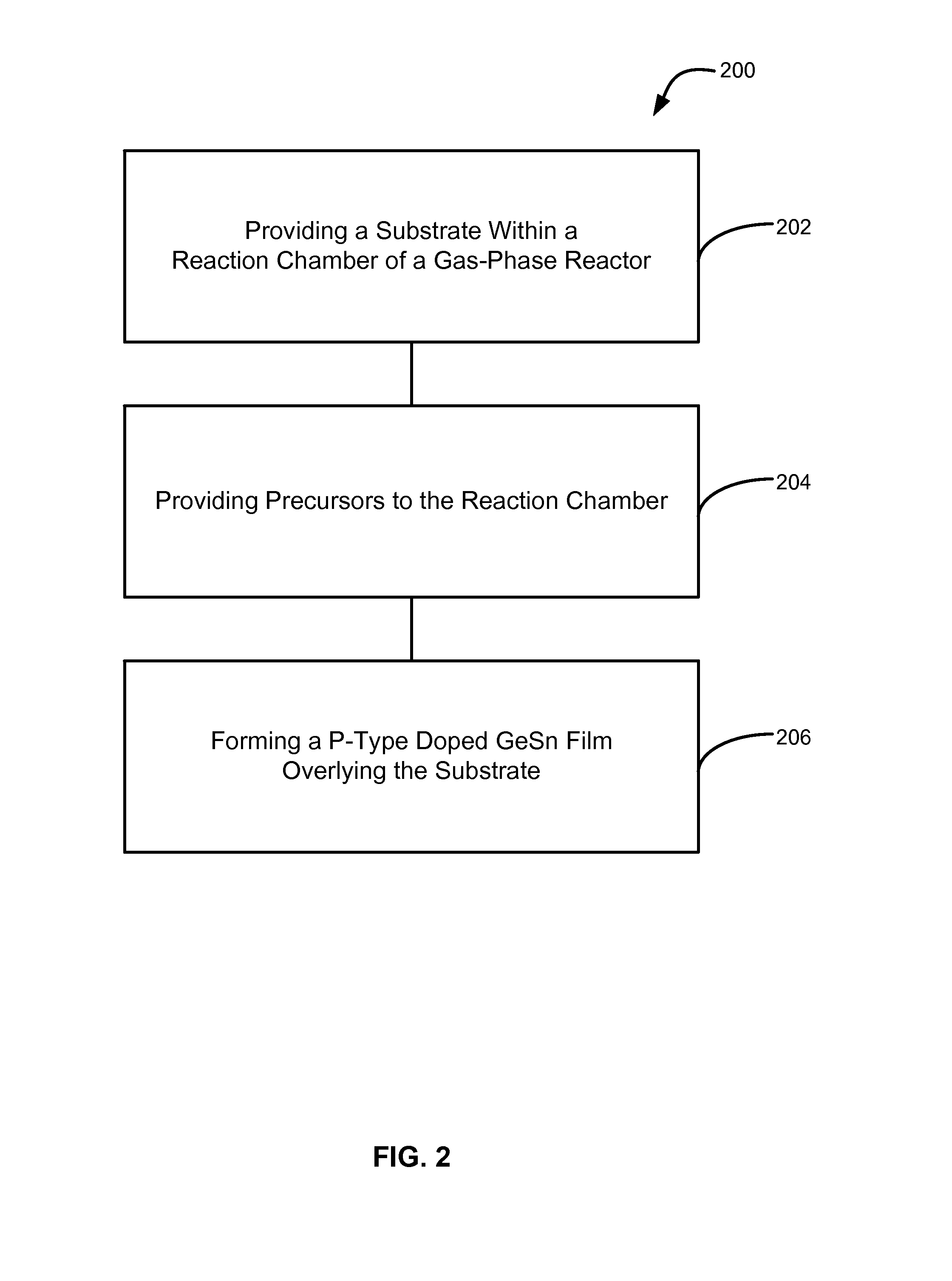
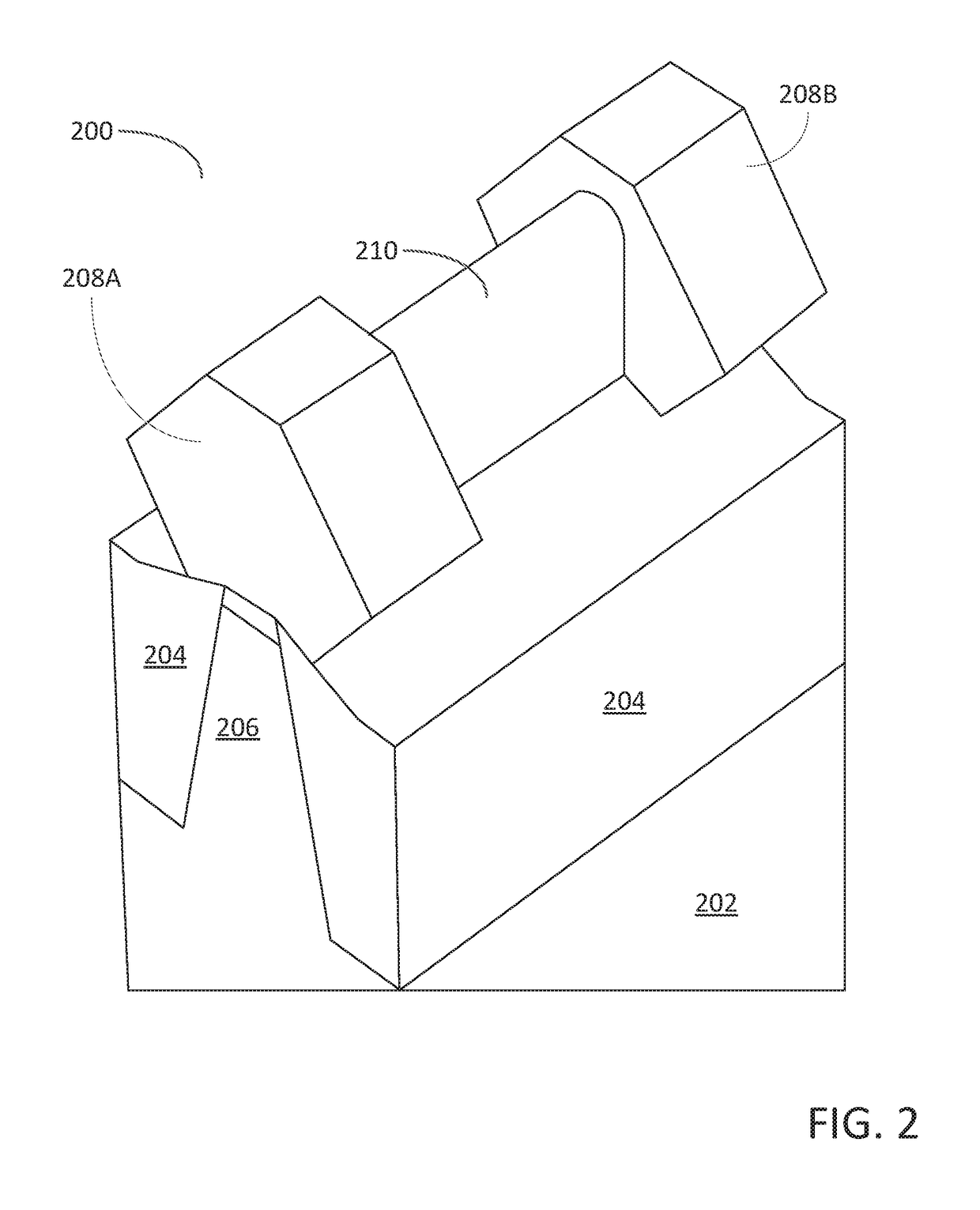
Method of epitaxial doped germanium tin alloy formation
ActiveUS20130256838A1Reduce lossesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDopantAlloy
A method for forming germanium tin layers and the resulting embodiments are described. A germanium precursor and a tin precursor are provided to a chamber, and an epitaxial layer of germanium tin is formed on the substrate. The germanium tin layer is selectively deposited on the semiconductor regions of the substrate and can include thickness regions of varying tin and dopant concentrations. The germanium tin layer can be selectively deposited by either alternating or concurrent flow of a halide gas to etch the surface of the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Methods of forming films including germanium tin and structures and devices including the films
ActiveUS9396934B2Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGermananeChemical vapor deposition
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
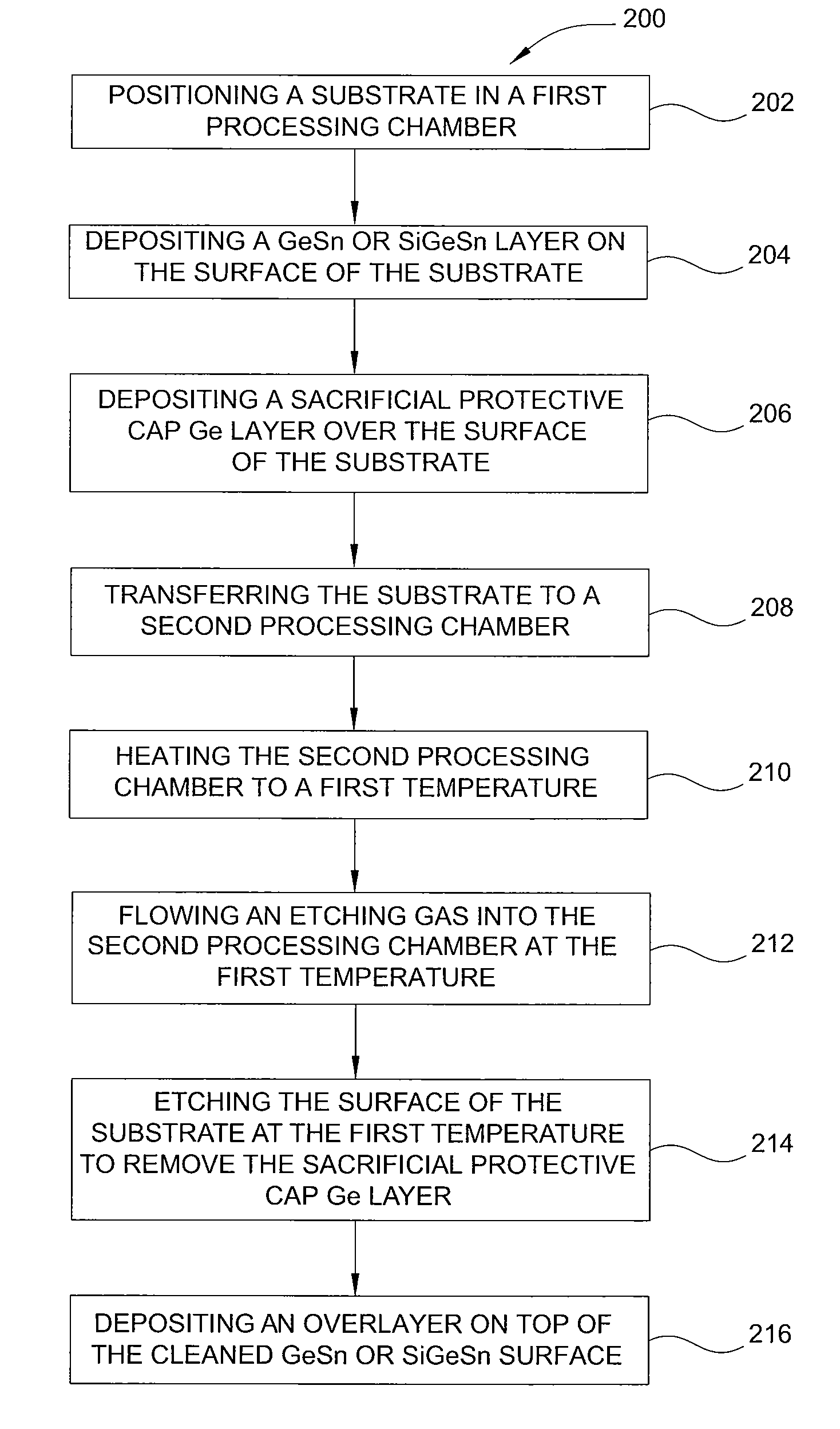
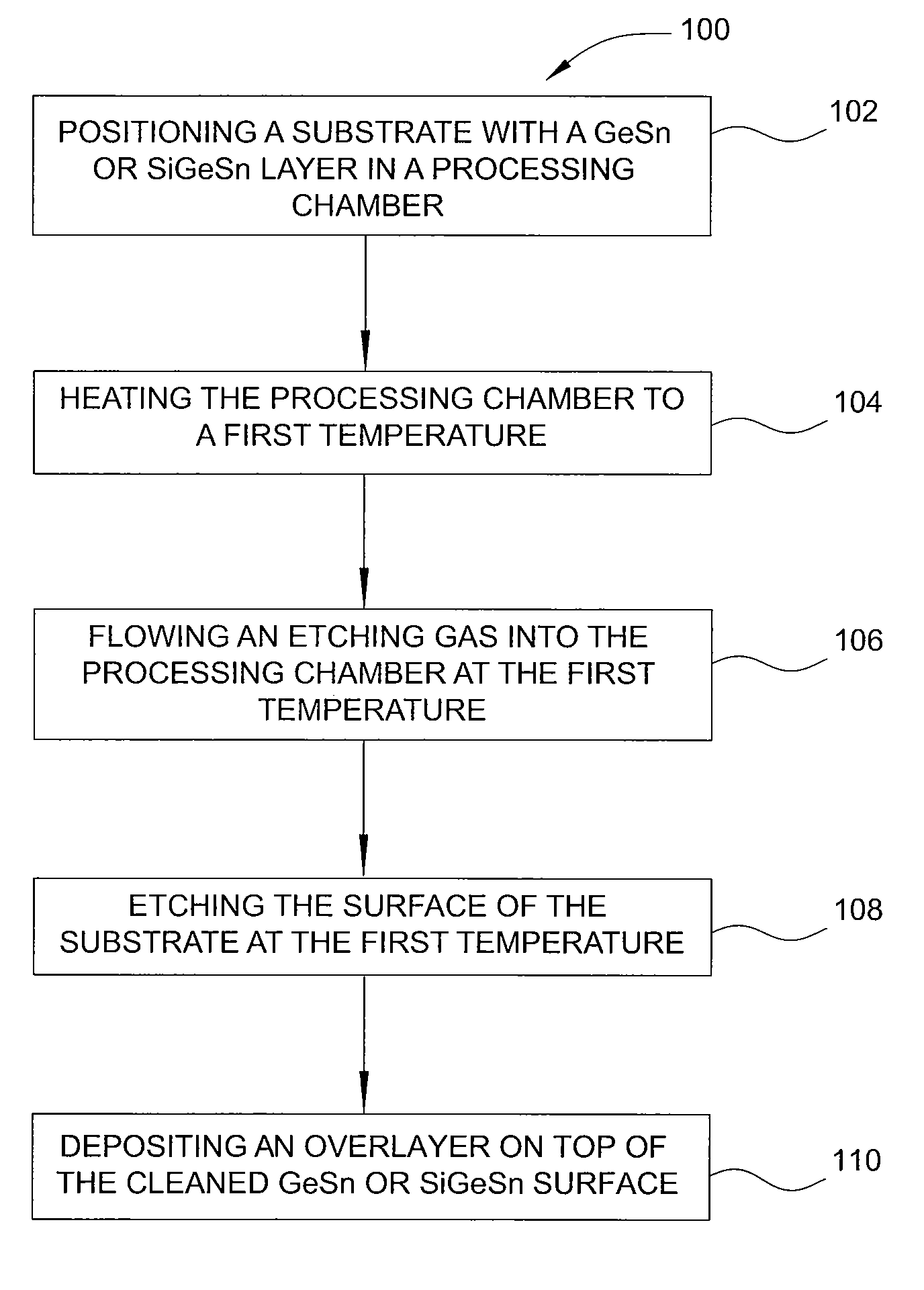
Method of epitaxial germanium tin alloy surface preparation
ActiveUS20130288480A1Increase temperatureStop the flowSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationEtchingRapid thermal annealing
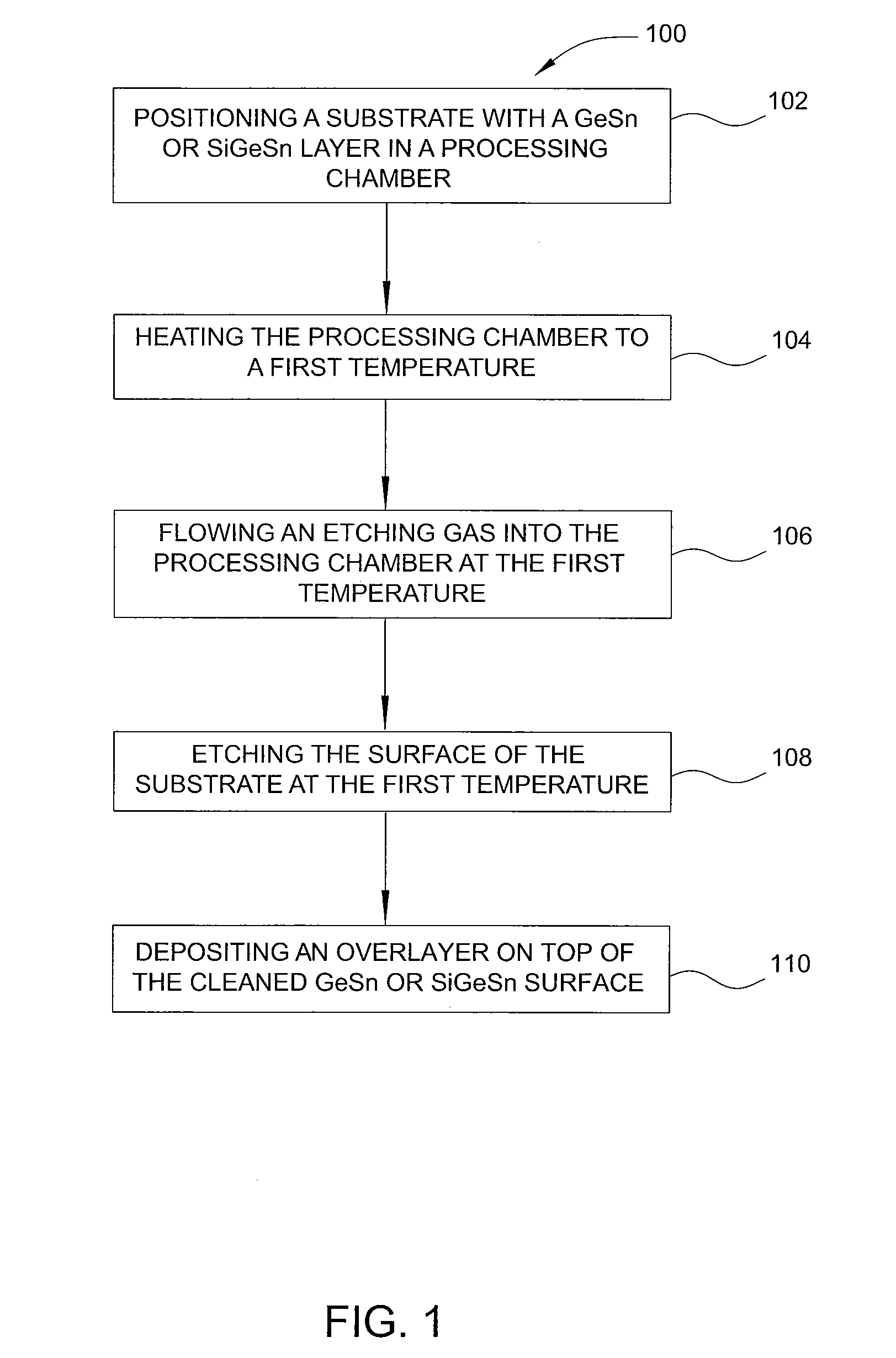
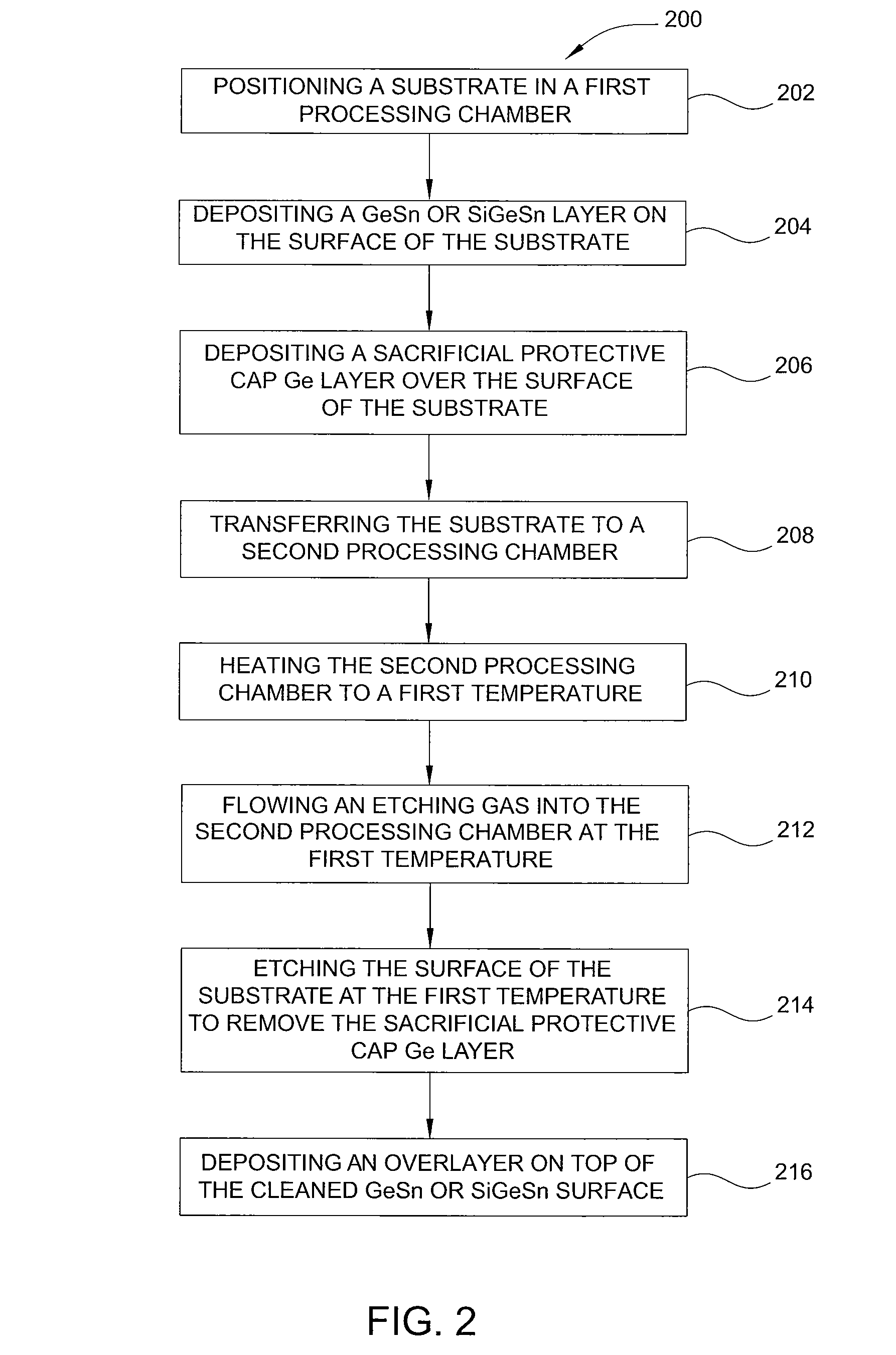
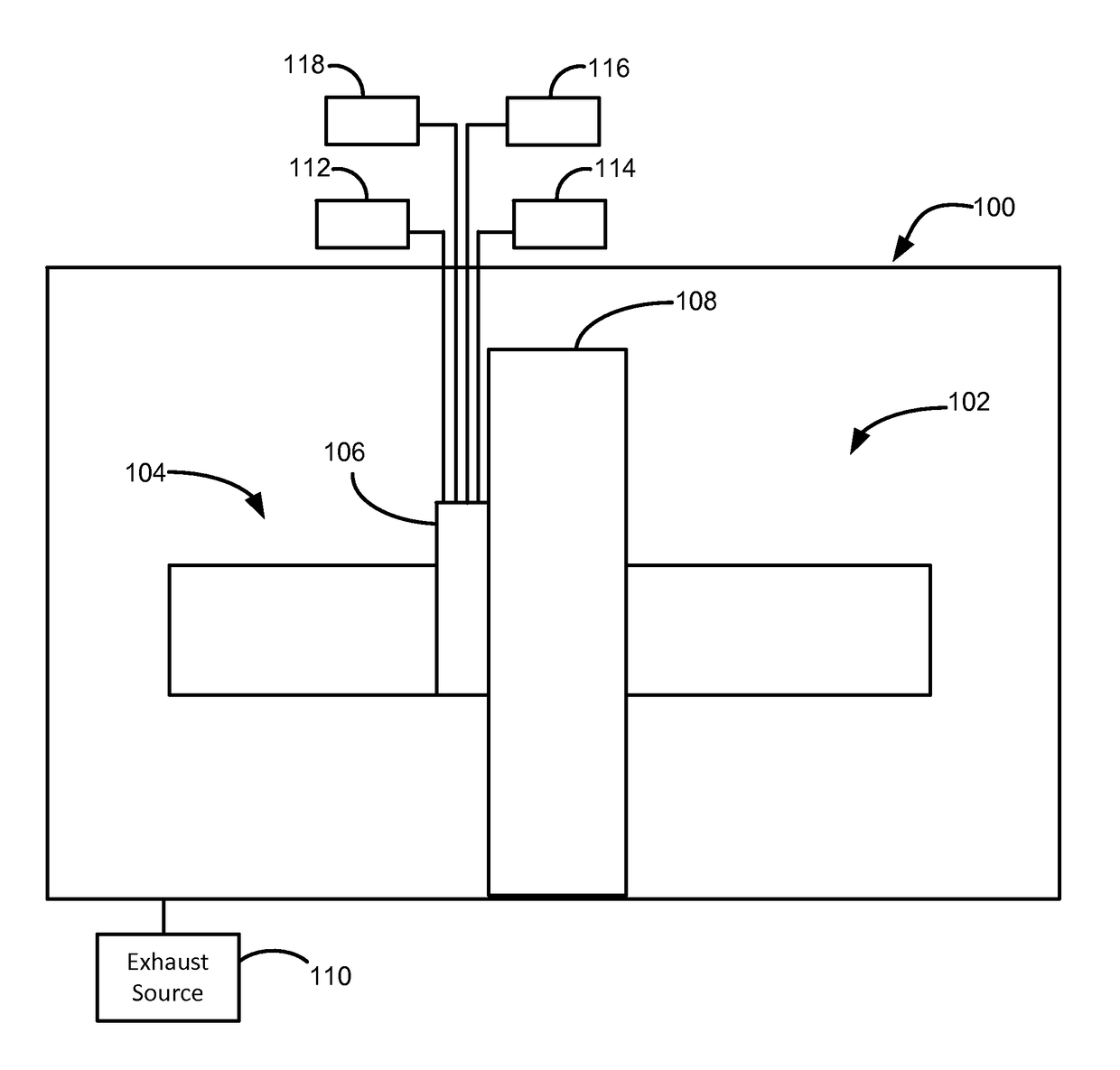
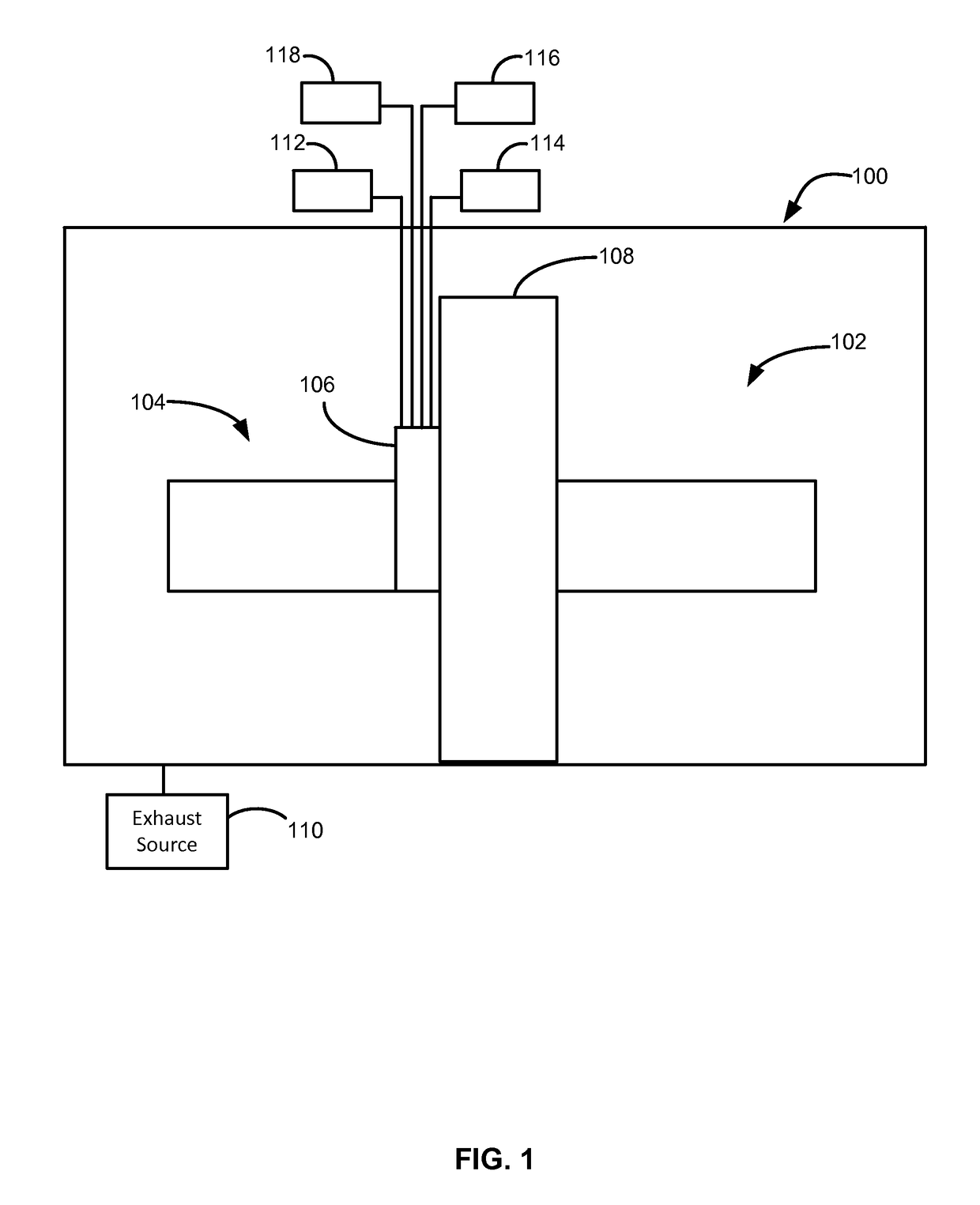
Methods of preparing a clean surface of germanium tin or silicon germanium tin layers for subsequent deposition are provided. An overlayer of Ge, doped Ge, another GeSn or SiGeSn layer, a doped GeSn or SiGeSn layer, an insulator, or a metal can be deposited on a prepared GeSn or SiGeSn layer by positioning a substrate with an exposed germanium tin or silicon germanium tin layer in a processing chamber, heating the processing chamber and flowing a halide gas into the processing chamber to etch the surface of the substrate using either thermal or plasma assisted etching followed by depositing an overlayer on the substantially oxide free and contaminant free surface. Methods can also include the placement and etching of a sacrificial layer, a thermal clean using rapid thermal annealing, or a process in a plasma of nitrogen trifluoride and ammonia gas.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
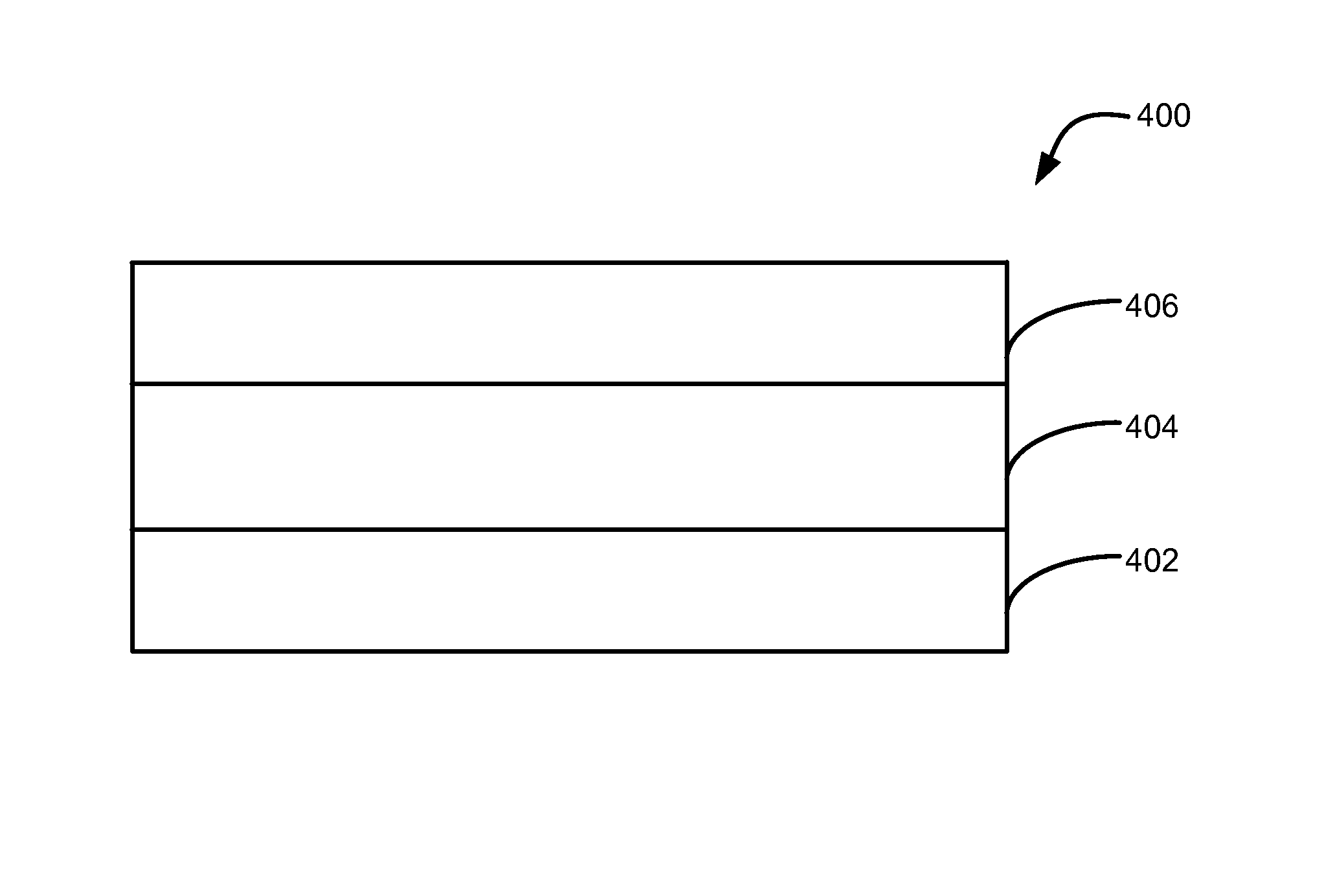
Methods of forming highly p-type doped germanium tin films and structures and devices including the films
ActiveUS9647114B2Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantP type doping
Methods of forming p-type doped germanium-tin layers, systems for forming the p-type doped germanium-tin layers, and structures including the p-type doped germanium-tin layers are disclosed. The p-type doped germanium-tin layers include an n-type dopant, which allows relatively high levels of tin and / or p-type dopant to be included into the p-type doped germanium-tin layers.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Methods of forming silicon germanium tin films and structures and devices including the films
ActiveUS9905420B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHigh volume manufacturingChemical vapor deposition
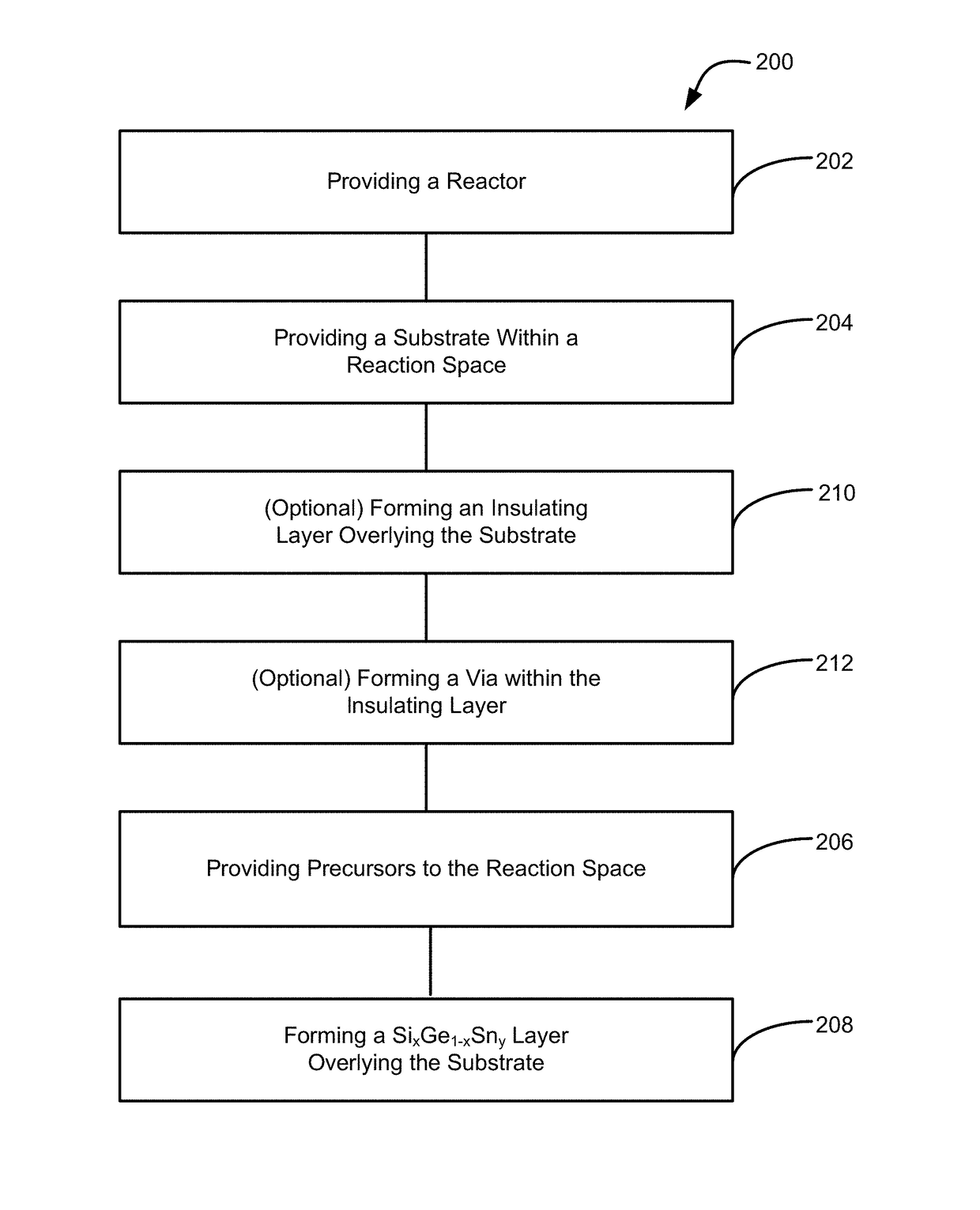
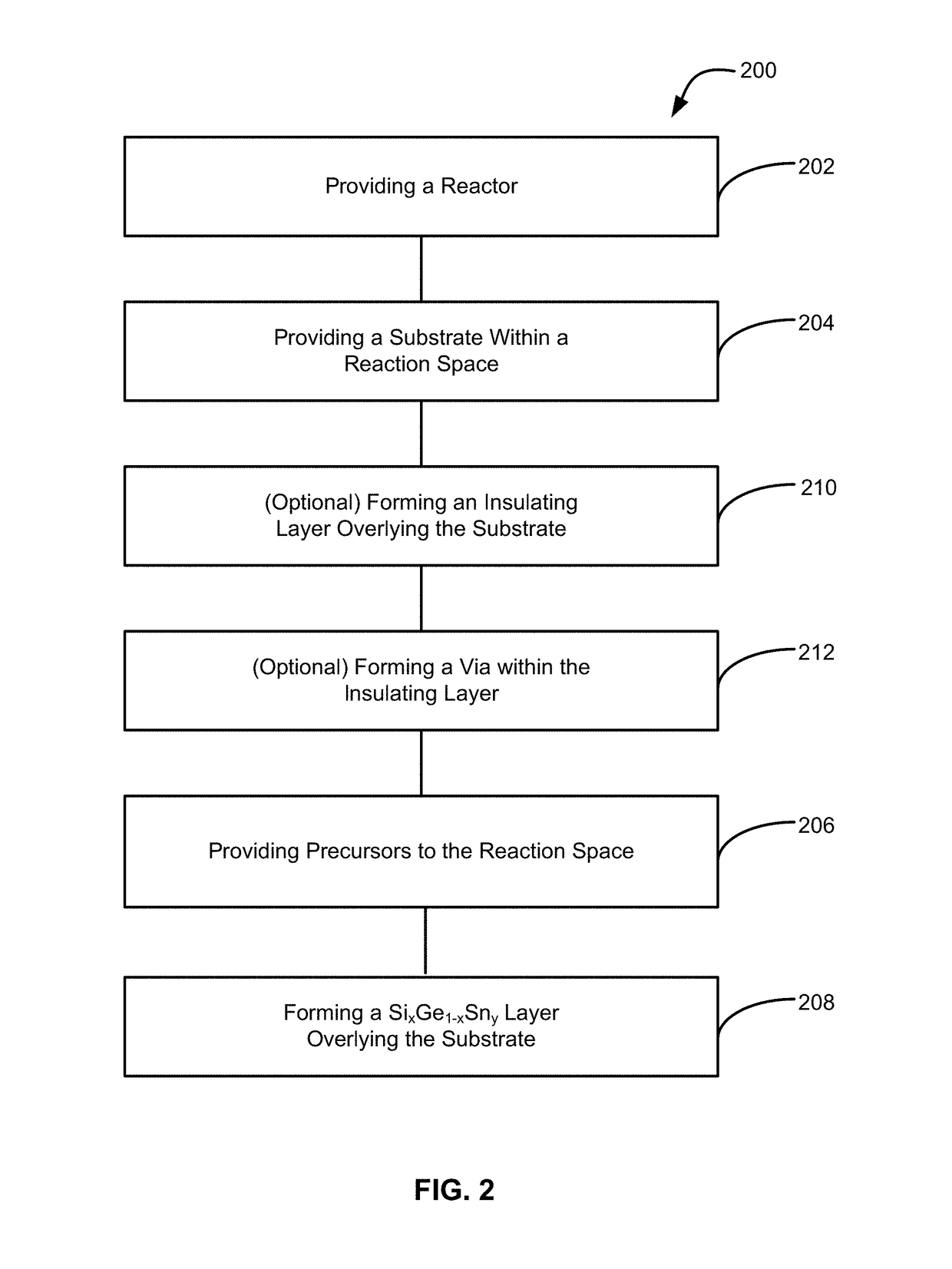
Methods of forming silicon germanium tin (SixGe1-xSny) films are disclosed. Exemplary methods include growing films including silicon, germanium and tin in an epitaxial chemical vapor deposition reactor. Exemplary methods are suitable for high volume manufacturing. Also disclosed are structures and devices including silicon germanium tin films.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
MODULATED DEPOSITION PROCESS FOR STRESS CONTROL IN THICK TiN FILMS
ActiveUS20100032842A1Liquid surface applicatorsIncorrect coupling preventionNitrogen plasmaDeposition process
A multi-layer TiN film with reduced tensile stress and discontinuous grain structure, and a method of fabricating the TiN film are disclosed. The TiN layers are formed by PVD or IMP in a nitrogen plasma. Tensile stress in a center layer of the film is reduced by increasing N2 gas flow to the nitrogen plasma, resulting in a Ti:N stoichiometry between 1:2.1 to 1:2.3. TiN films thicker than 40 nanometers without cracks are attained by the disclosed process.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
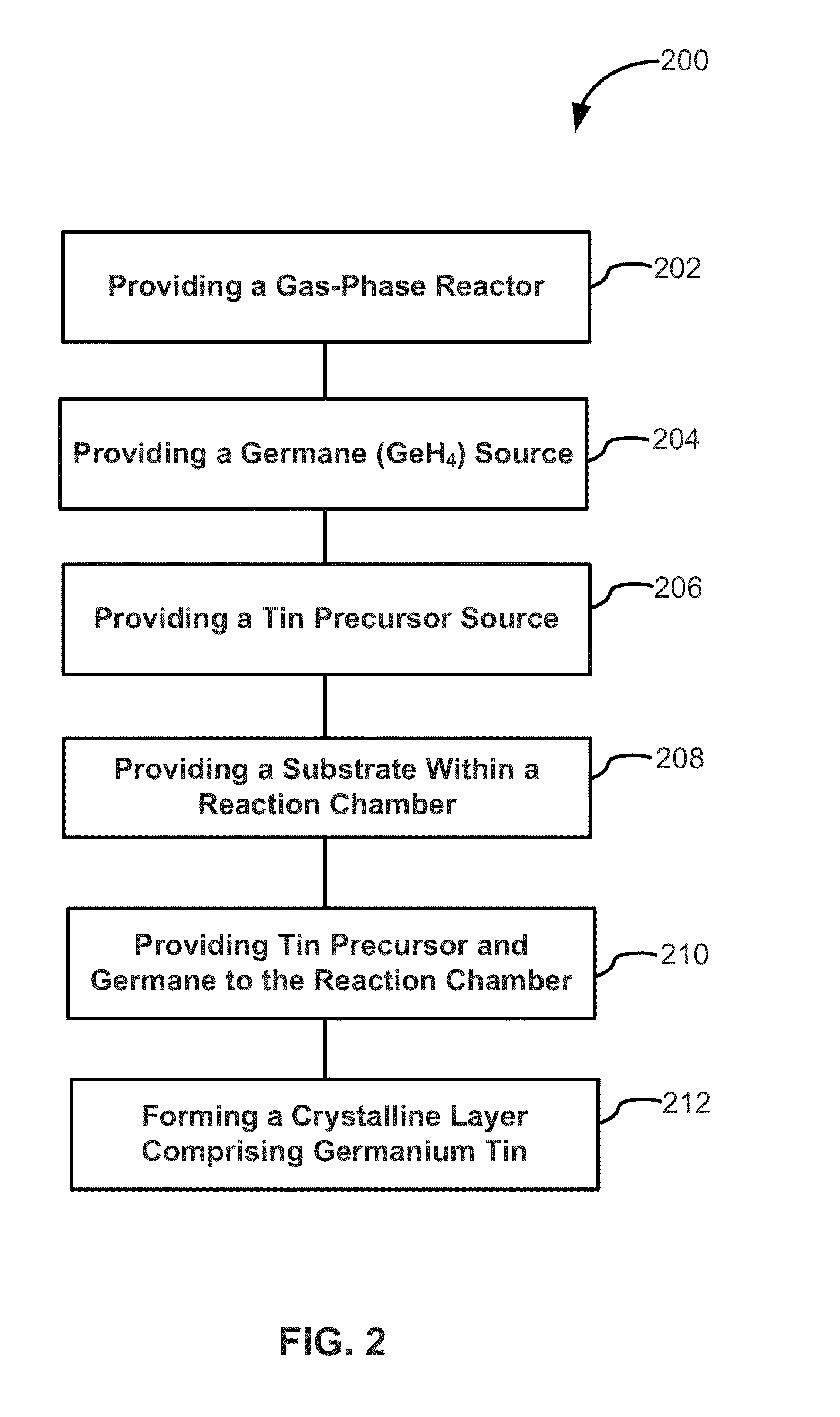
Structures and devices including germanium-tin films and methods of forming same
ActiveUS9793115B2Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor depositionGermane
Methods of forming germanium-tin films using germane as a precursor are disclosed. Exemplary methods include growing films including germanium and tin in an epitaxial chemical vapor deposition reactor, wherein a ratio of a tin precursor to germane is less than 0.1. Also disclosed are structures and devices including germanium-tin films formed using the methods described herein.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Direct and selective production of ethanol from acetic acid utilizing a platinum/tin catalyst
InactiveUS20100029995A1High selectivityHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationOxygen compounds preparation by reductionCalcium silicatePlatinum
A process for the selective production of ethanol by vapor phase reaction of acetic acid over a hydrogenating catalyst composition to form ethanol is disclosed and claimed. In an embodiment of this invention reaction of acetic acid and hydrogen over a platinum and tin supported on silica, graphite, calcium silicate or silica-alumina selectively produces ethanol in a vapor phase at a temperature of about 250° C.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Methods of forming highly p-type doped germanium tin films and structures and devices including the films
ActiveUS20170047446A1High tin contentSuitable for applicationPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantP type doping
Methods of forming p-type doped germanium-tin layers, systems for forming the p-type doped germanium-tin layers, and structures including the p-type doped germanium-tin layers are disclosed. The p-type doped germanium-tin layers include an n-type dopant, which allows relatively high levels of tin and / or p-type dopant to be included into the p-type doped germanium-tin layers.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
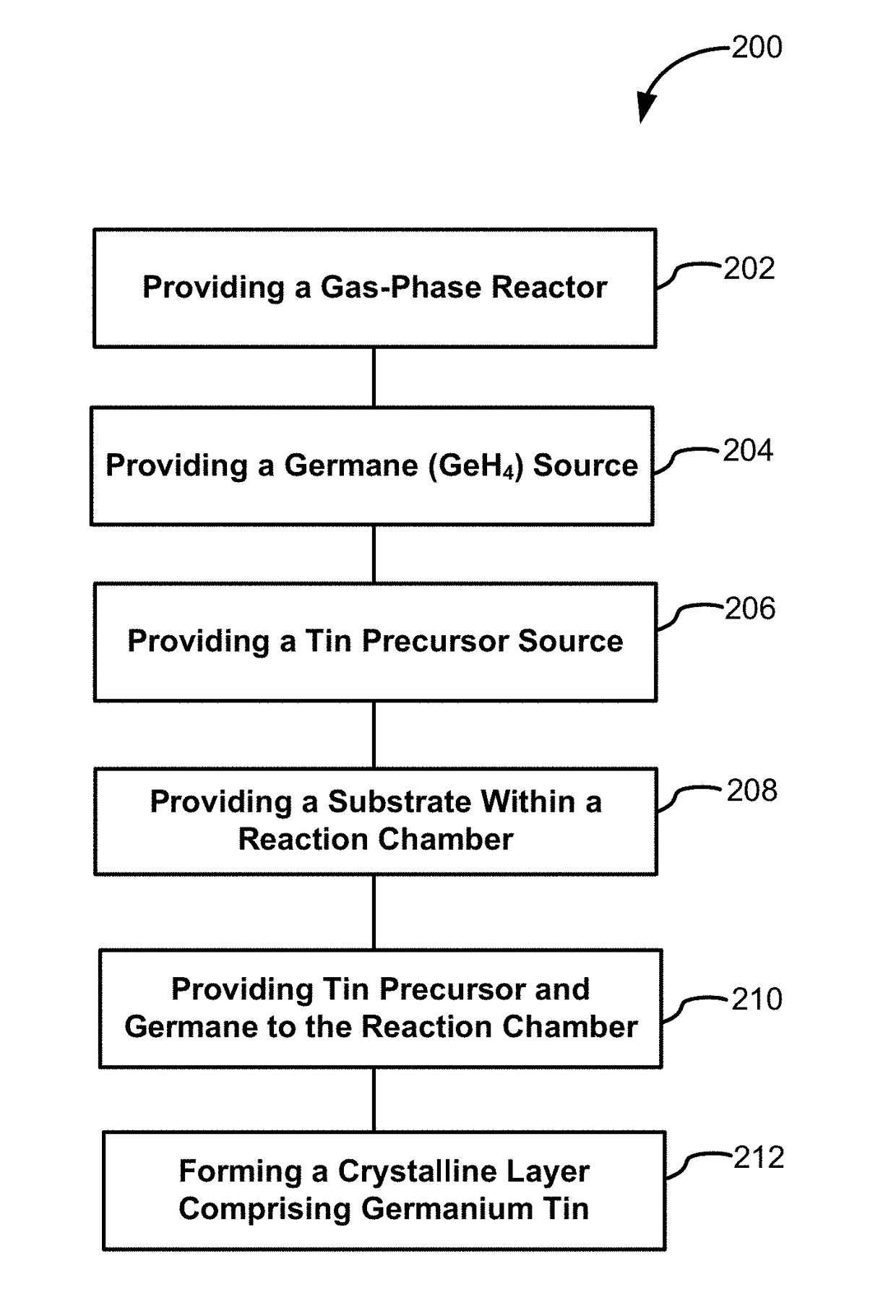
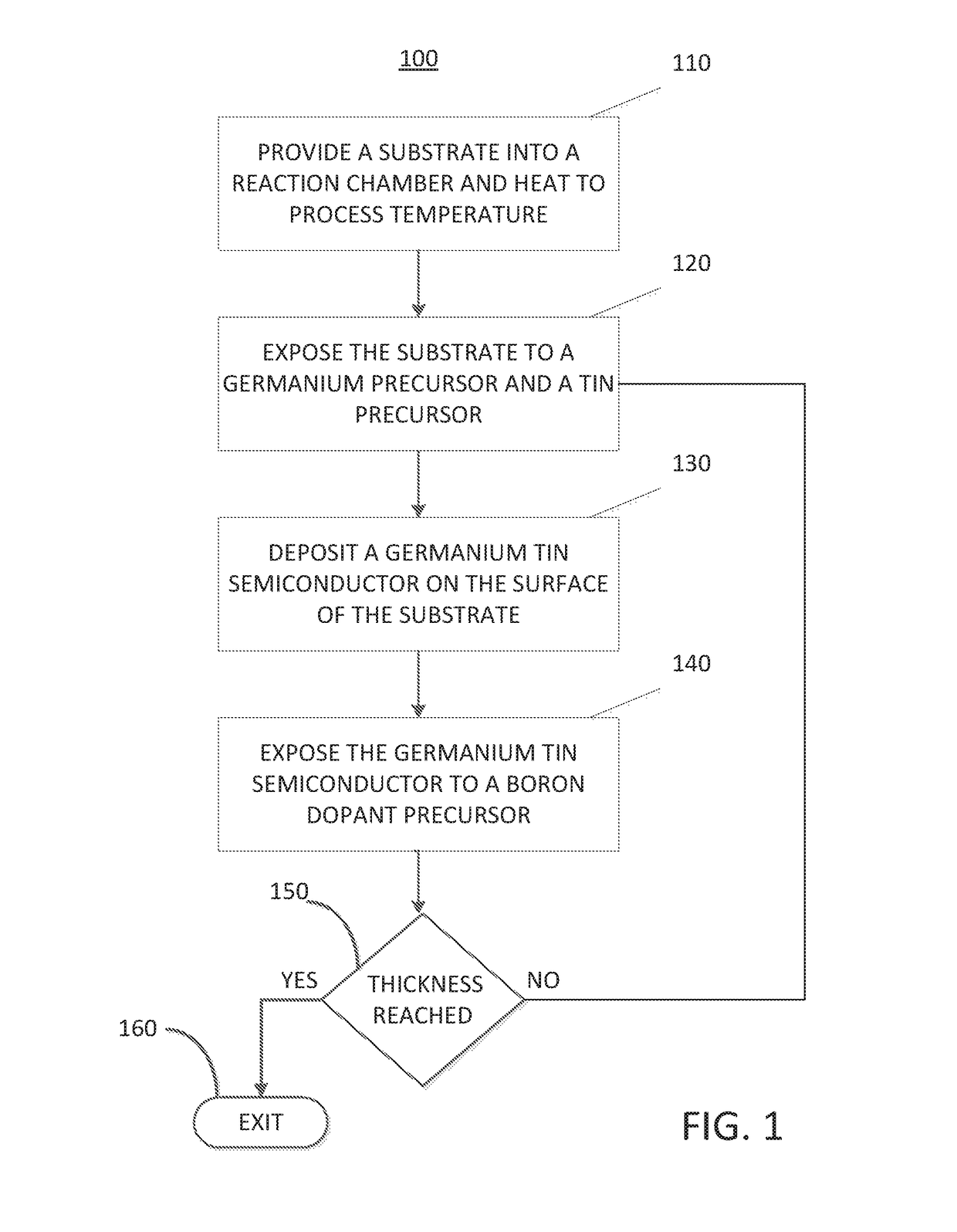
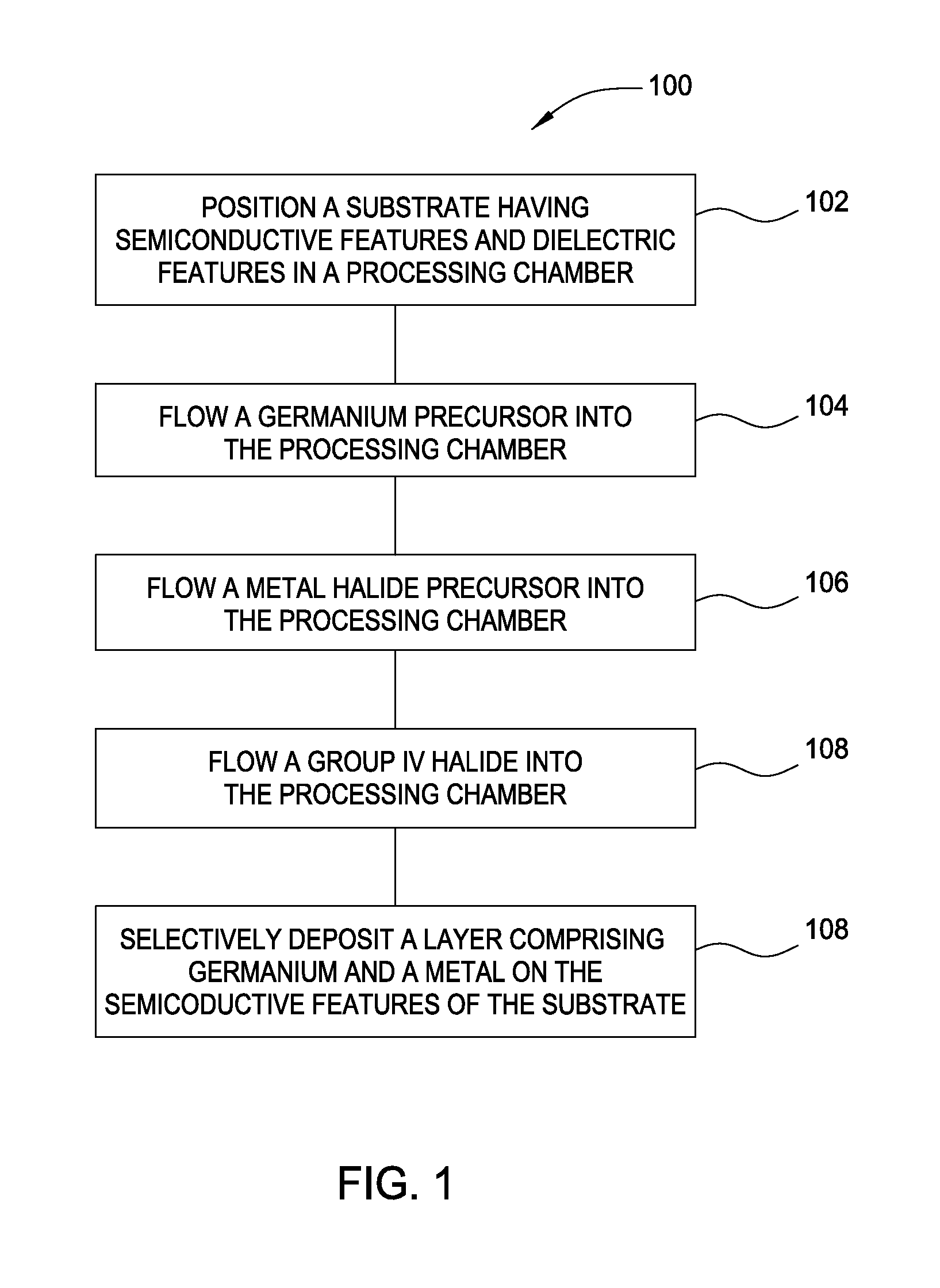
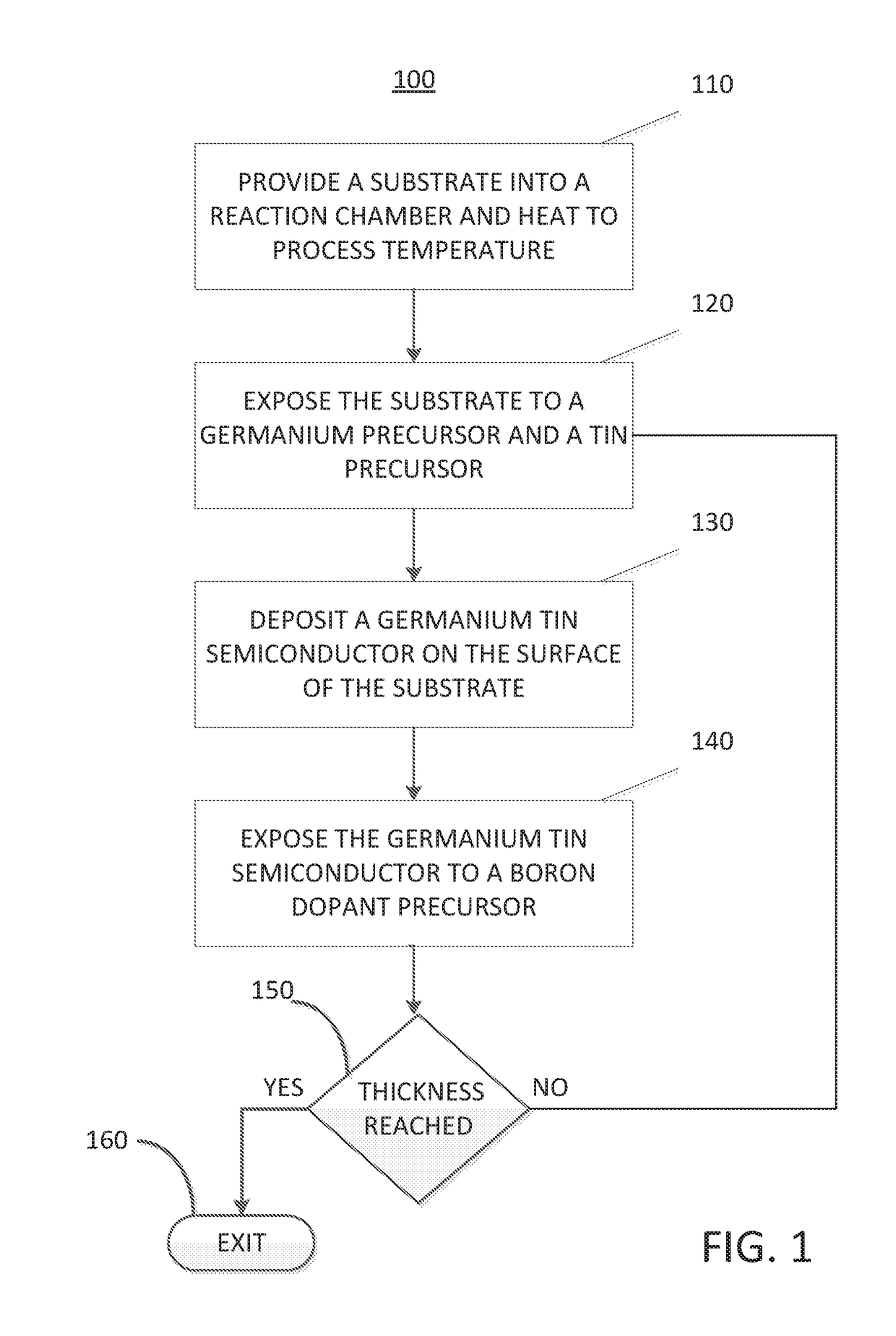
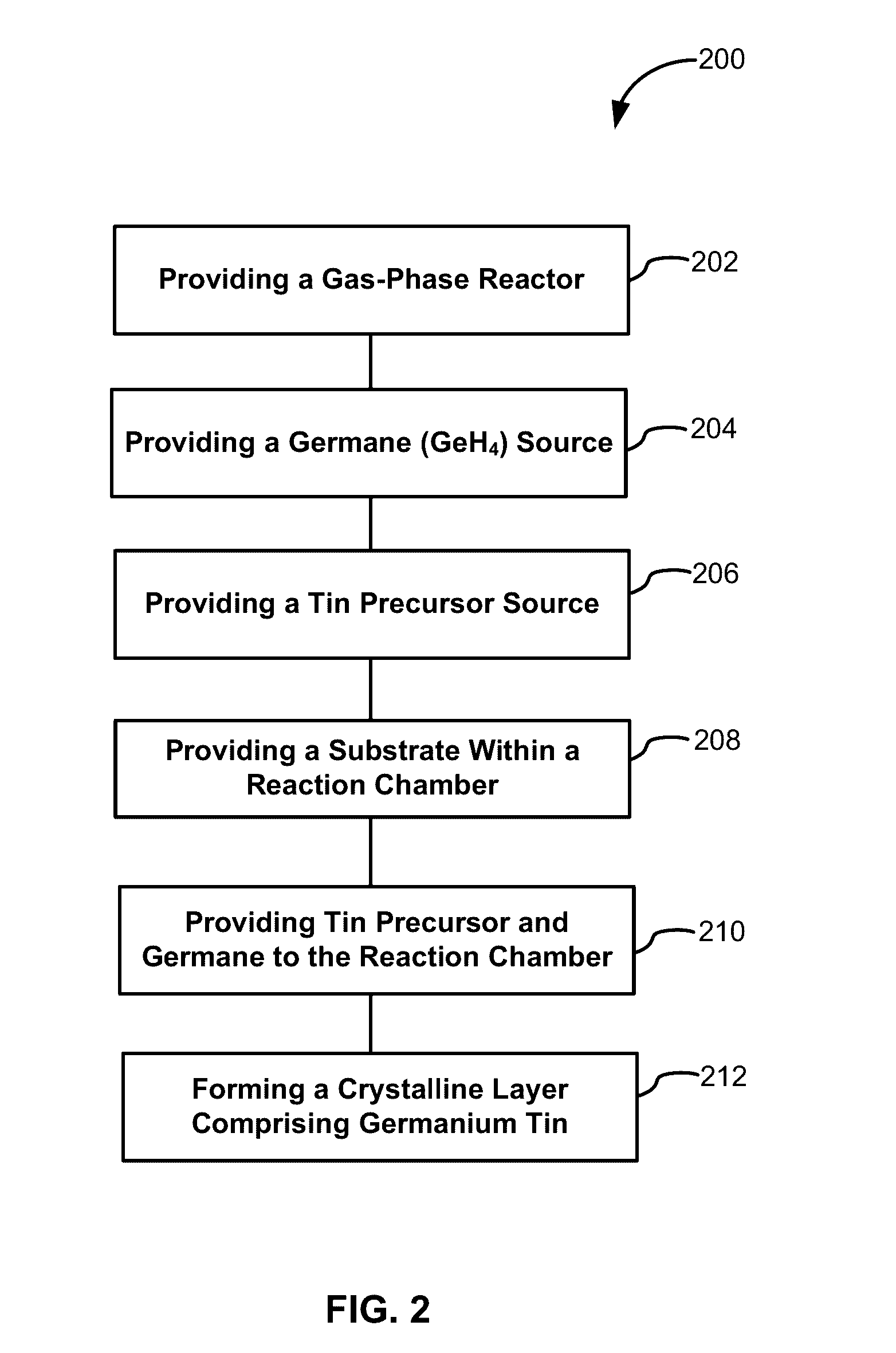
Methods for depositing a doped germanium tin semiconductor and related semiconductor device structures
ActiveUS10236177B1Polycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsDopantDeposition temperature
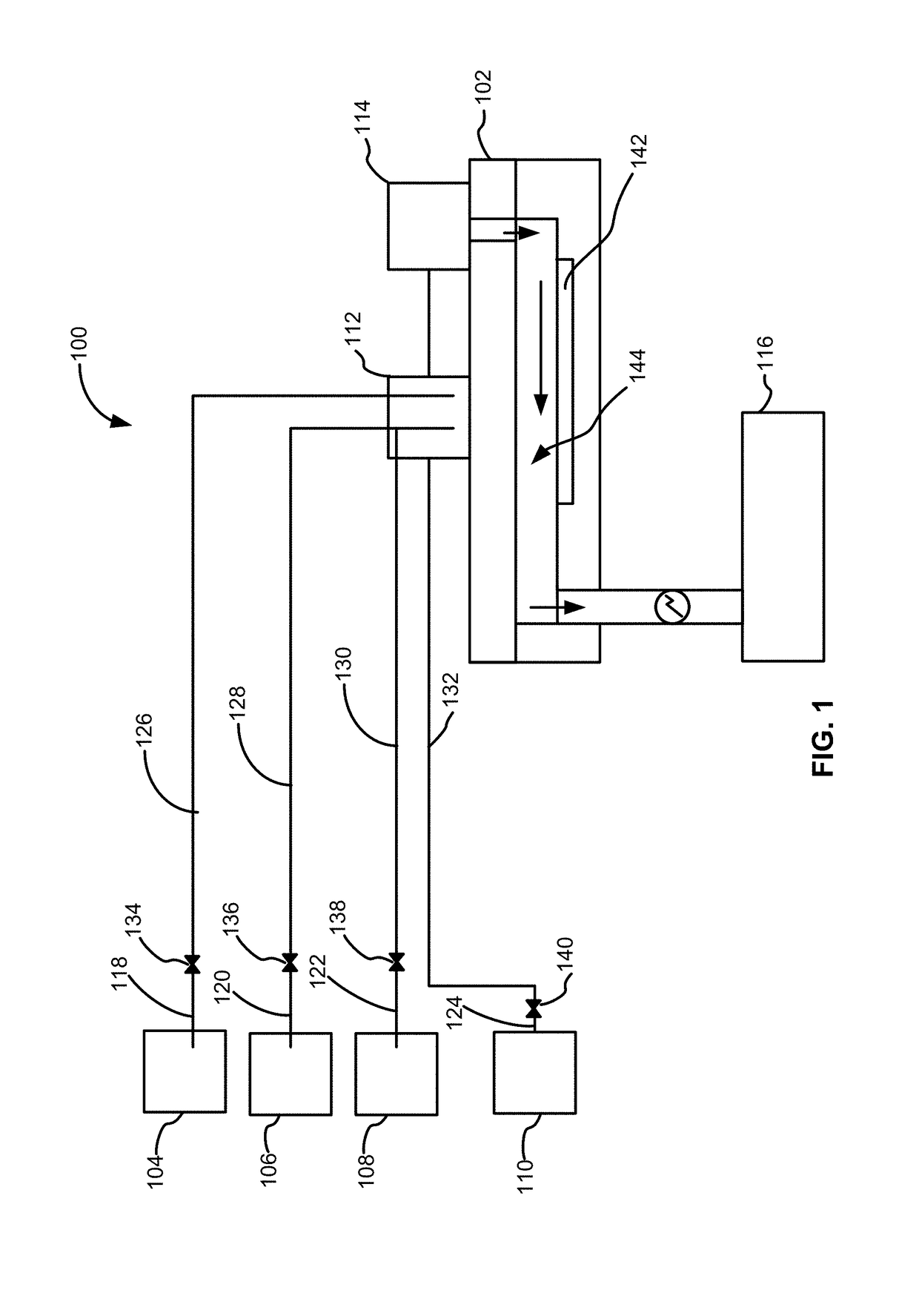
A method for depositing a germanium tin (Ge1-xSnx) semiconductor is disclosed. The method may include; providing a substrate within a reaction chamber, heating the substrate to a deposition temperature and exposing the substrate to a germanium precursor and a tin precursor. The method may further include; depositing a germanium tin (Ge1-xSnx) semiconductor on the surface of the substrate, and exposing the germanium tin (Ge1-xSnx) semiconductor to a boron dopant precursor. Semiconductor device structures including a germanium tin (Ge1-xSnx) semiconductor formed by the methods of the disclosure are also provided.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
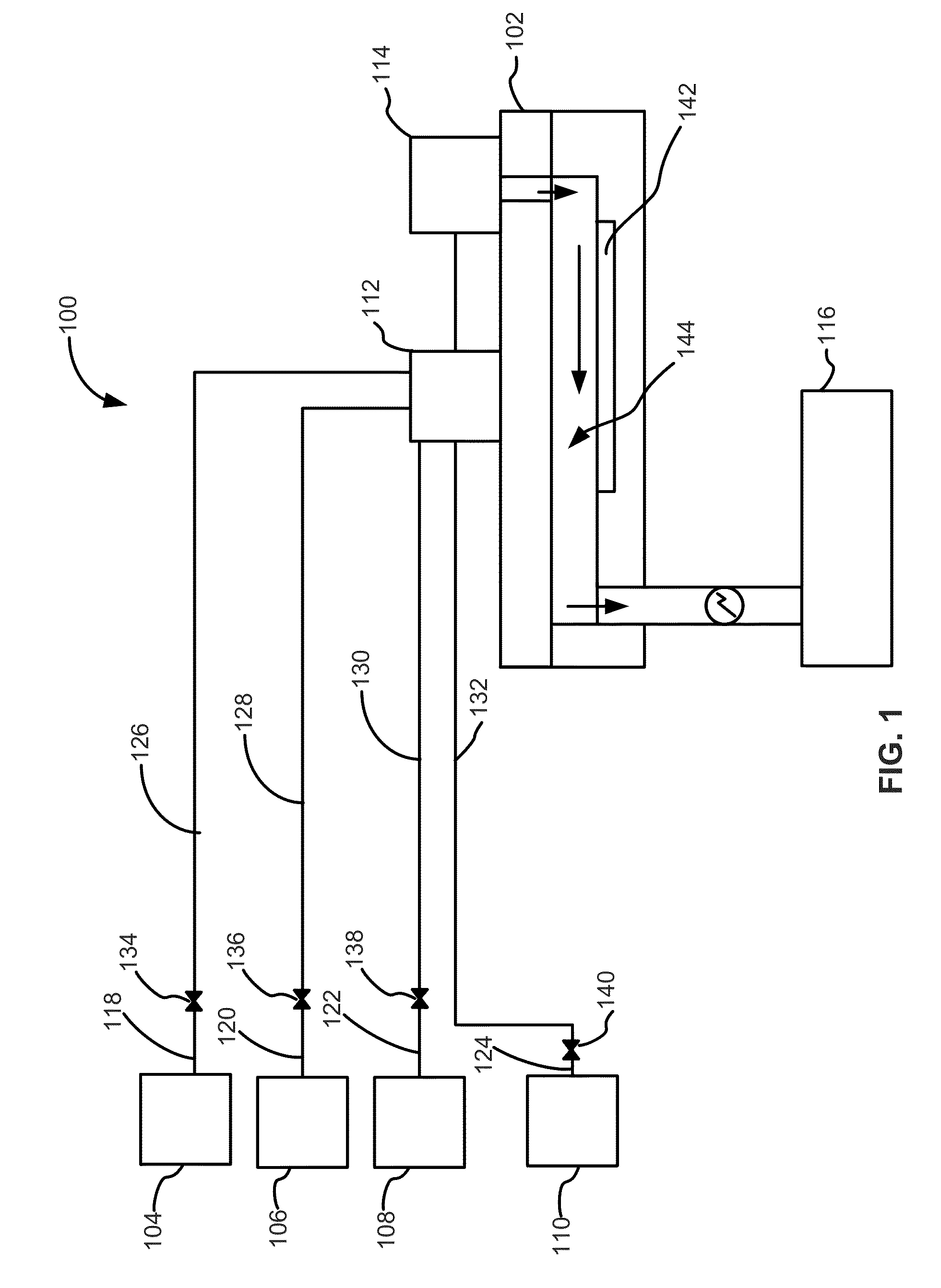
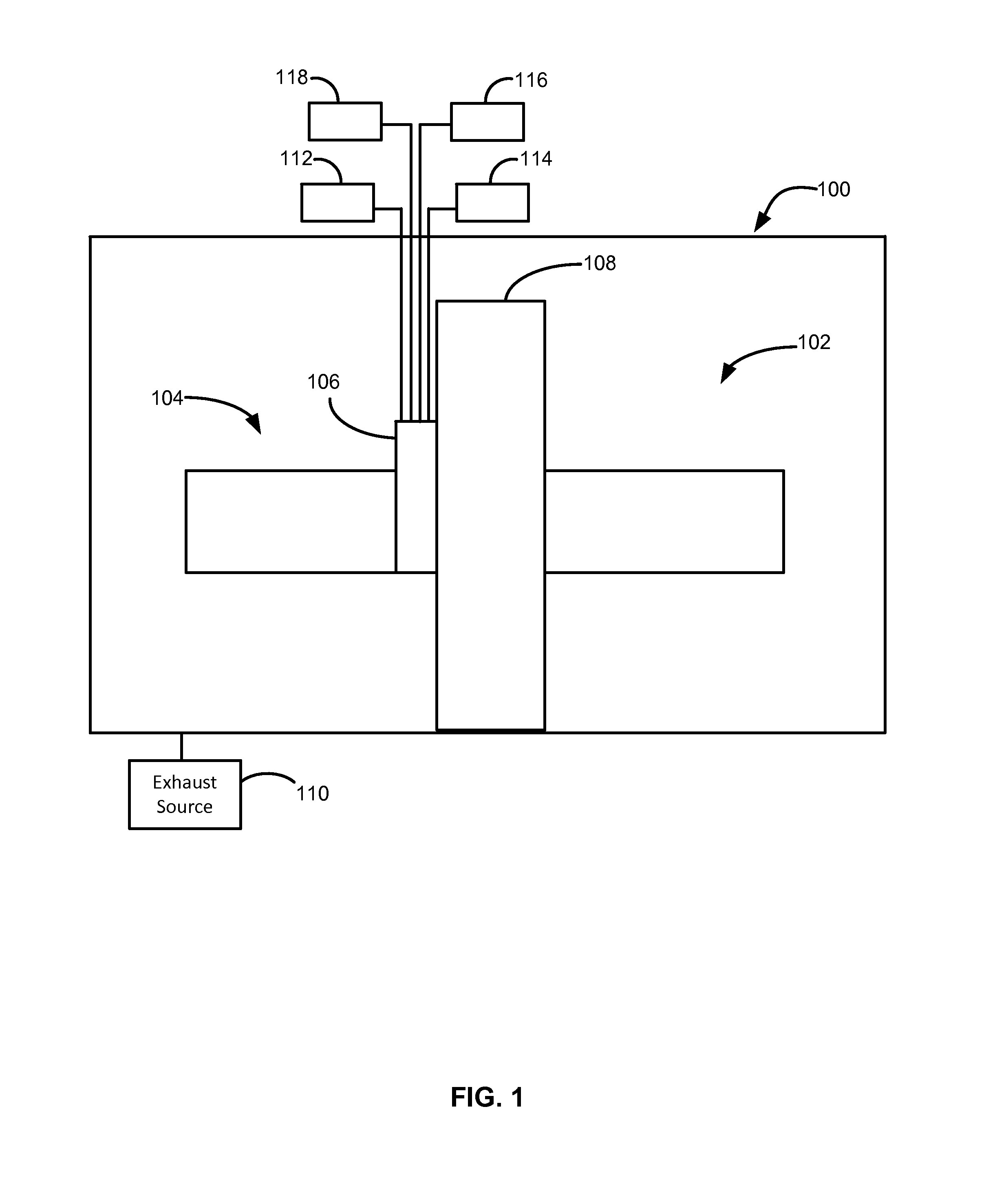
Method and apparatus for germanium tin alloy formation by thermal CVD
InactiveUS20130280891A1Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSelective depositionLiquid metal
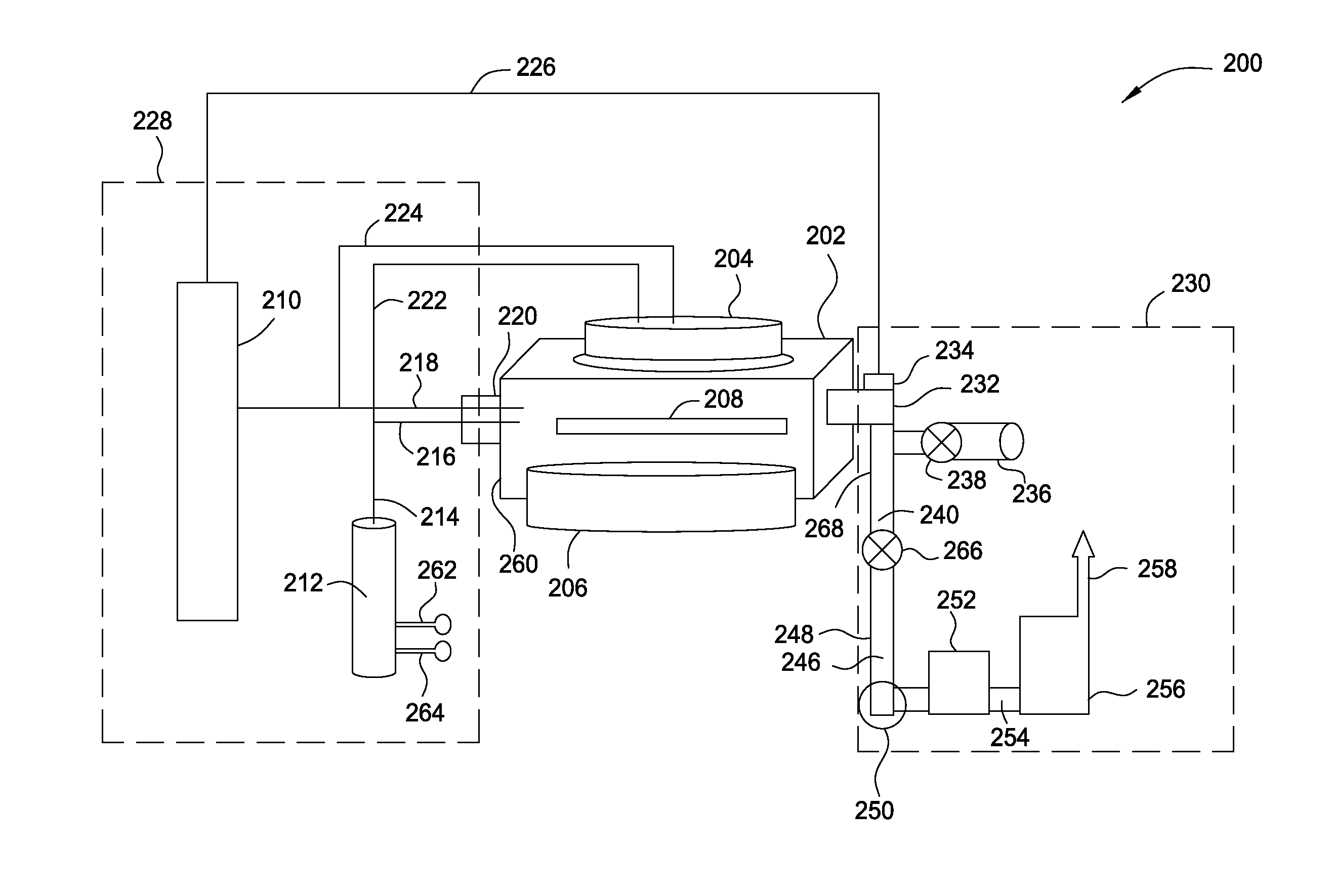
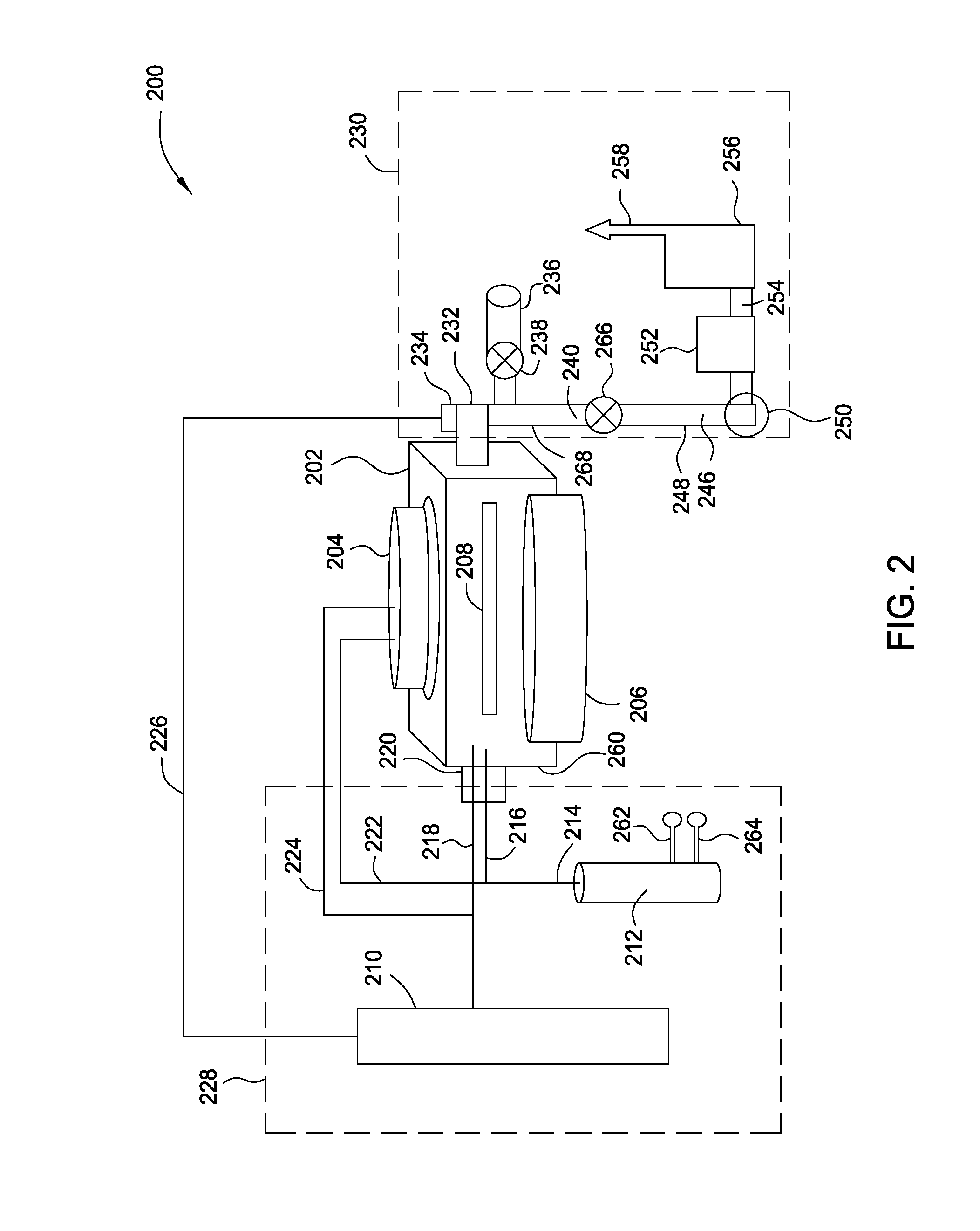
A method and apparatus for forming semiconductive semiconductor-metal alloy layers is described. A germanium precursor and a metal precursor are provided to a chamber, and an epitaxial layer of germanium-metal alloy, optionally including silicon, is formed on the substrate. The metal precursor is typically a metal halide, which may be provided by evaporating a liquid metal halide, subliming a solid metal halide, or by contacting a pure metal with a halogen gas. A group IV halide deposition control agent is used to provide selective deposition on semiconductive regions of the substrate relative to dielectric regions. The semiconductive semiconductor-metal alloy layers may be doped, for example with boron, phosphorus, and / or arsenic. The precursors may be provided through a showerhead or through a side entry point, and an exhaust system coupled to the chamber may be separately heated to manage condensation of exhaust components.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Methods for depositing a doped germanium tin semiconductor and related semiconductor device structures
ActiveUS20190067004A1Polycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsDopantDeposition temperature
A method for depositing a germanium tin (Ge1-xSnx) semiconductor is disclosed. The method may include; providing a substrate within a reaction chamber, heating the substrate to a deposition temperature and exposing the substrate to a germanium precursor and a tin precursor. The method may further include; depositing a germanium tin (Ge1-xSnx) semiconductor on the surface of the substrate, and exposing the germanium tin (Ge1-xSnx) semiconductor to a boron dopant precursor. Semiconductor device structures including a germanium tin (Ge1-xSnx) semiconductor formed by the methods of the disclosure are also provided.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method of epitaxial germanium tin alloy surface preparation
Methods of preparing a clean surface of germanium tin or silicon germanium tin layers for subsequent deposition are provided. An overlayer of Ge, doped Ge, another GeSn or SiGeSn layer, a doped GeSn or SiGeSn layer, an insulator, or a metal can be deposited on a prepared GeSn or SiGeSn layer by positioning a substrate with an exposed germanium tin or silicon germanium tin layer in a processing chamber, heating the processing chamber and flowing a halide gas into the processing chamber to etch the surface of the substrate using either thermal or plasma assisted etching followed by depositing an overlayer on the substantially oxide free and contaminant free surface. Methods can also include the placement and etching of a sacrificial layer, a thermal clean using rapid thermal annealing, or a process in a plasma of nitrogen trifluoride and ammonia gas.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
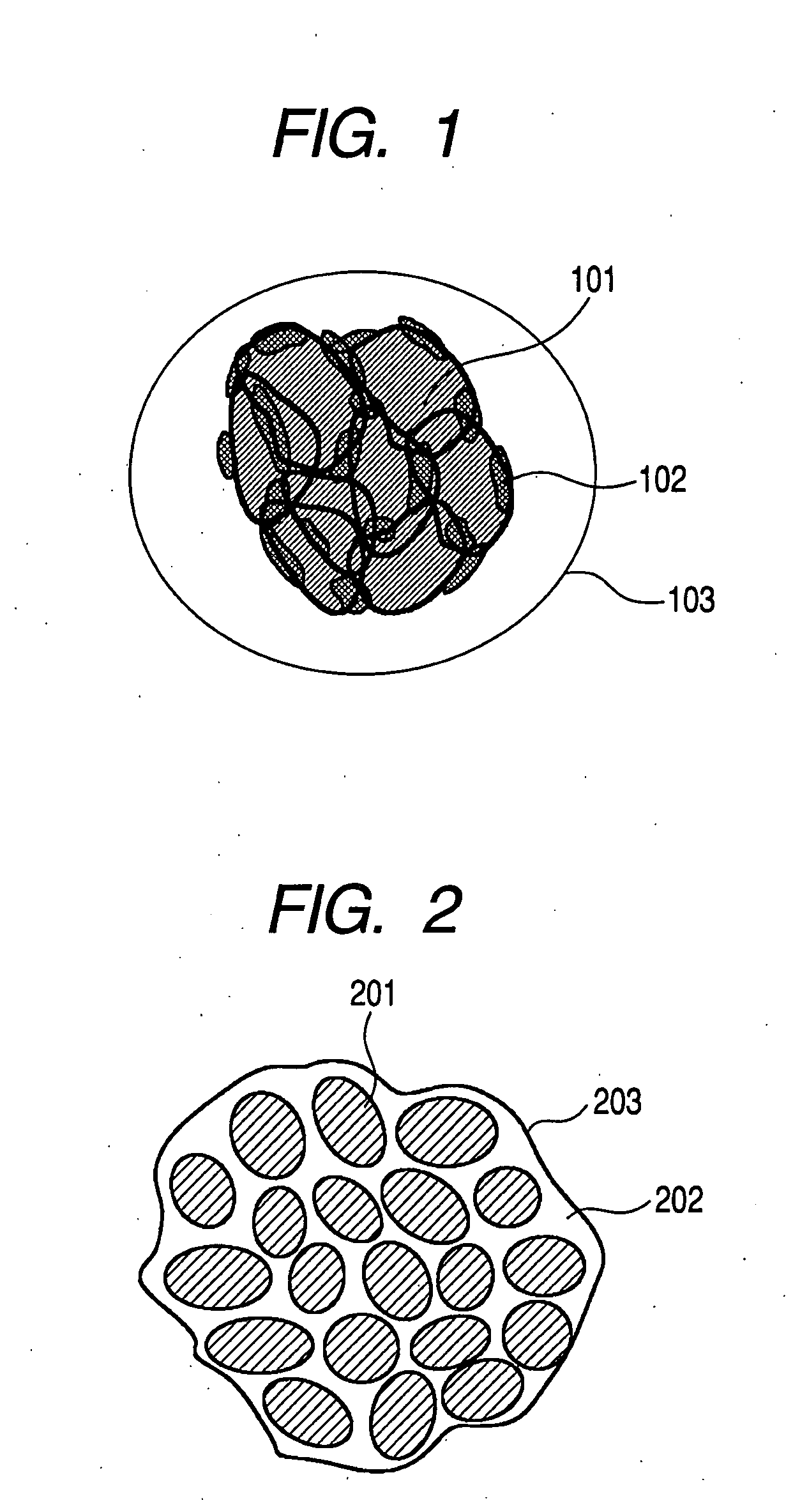
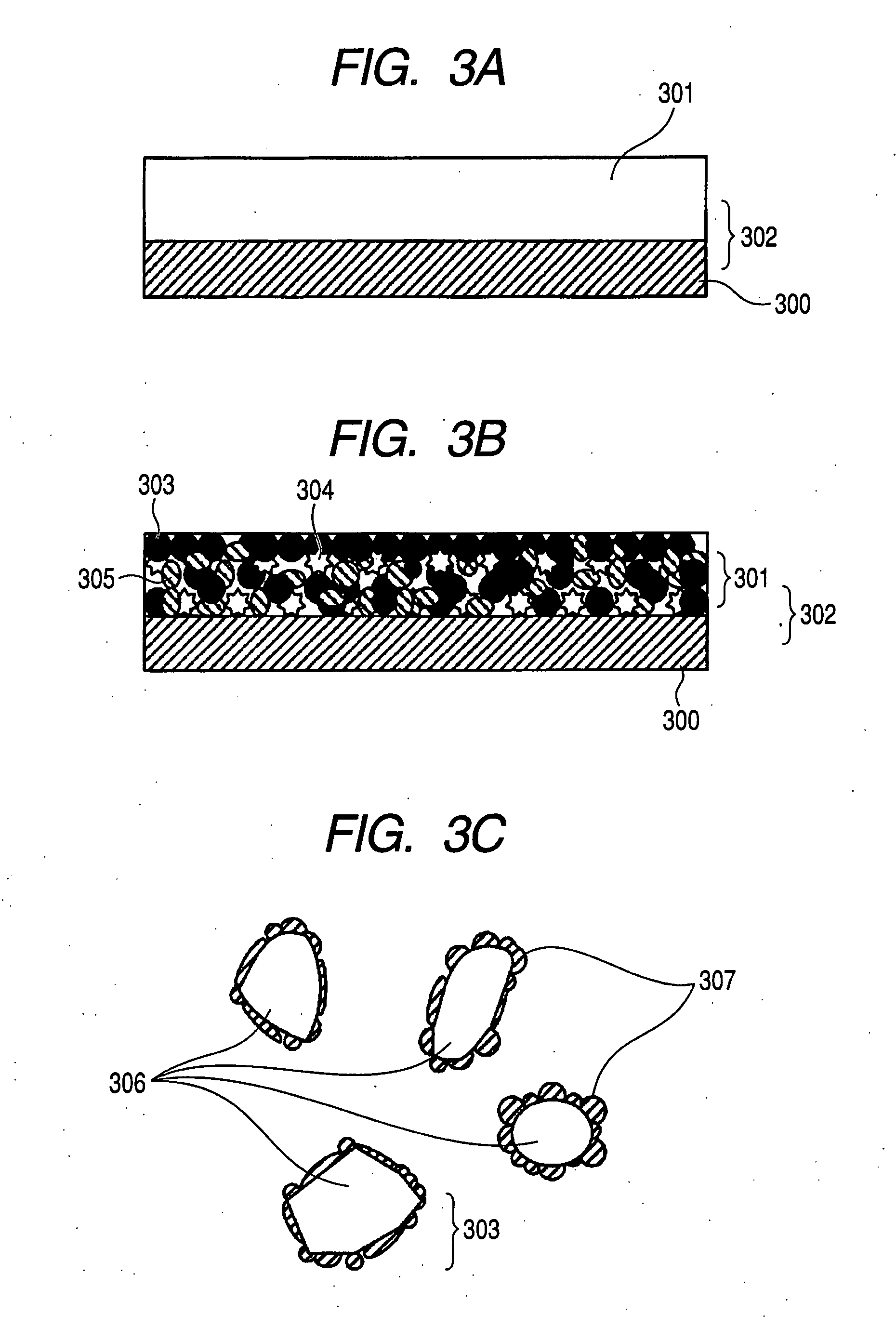
Porous silicon particulates for lithium batteries
An anode structure for lithium batteries includes nanofeatured silicon particulates dispersed in a conductive network. The particulates are preferably made from metallurgical grade silicon powder via HF / HNO3 acid treatment, yielding crystallite sizes from about 1 to 20 nm and pore sizes from about 1 to 100 nm. Surfaces of the particles may be terminated with selected chemical species to further modify the anode performance characteristics. The conductive network is preferably a carbonaceous material or composite, but it may alternatively contain conductive ceramics such as TiN or B4C. The anode structure may further contain a current collector of copper or nickel mesh or foil.
Owner:TIEGS TERRY N
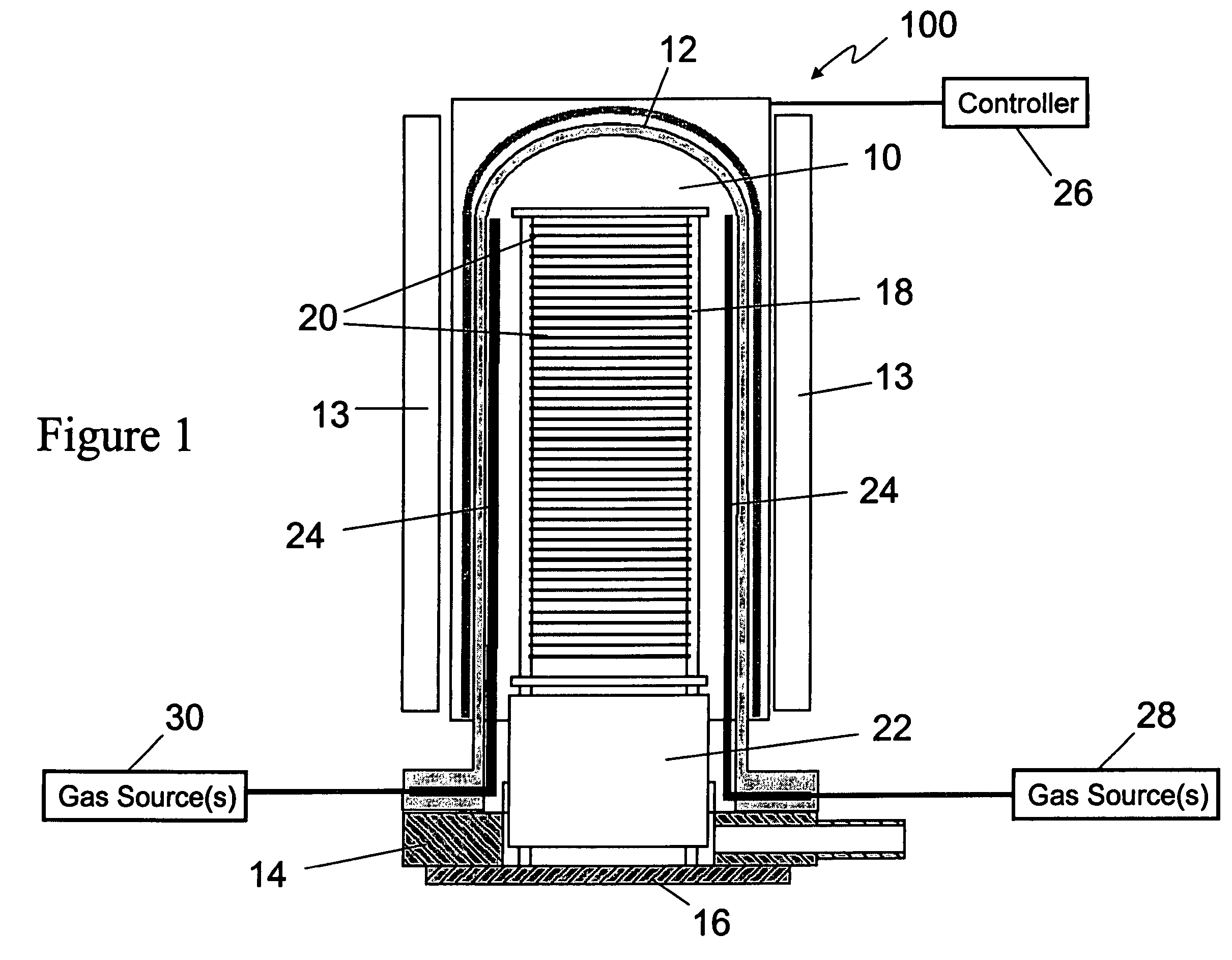
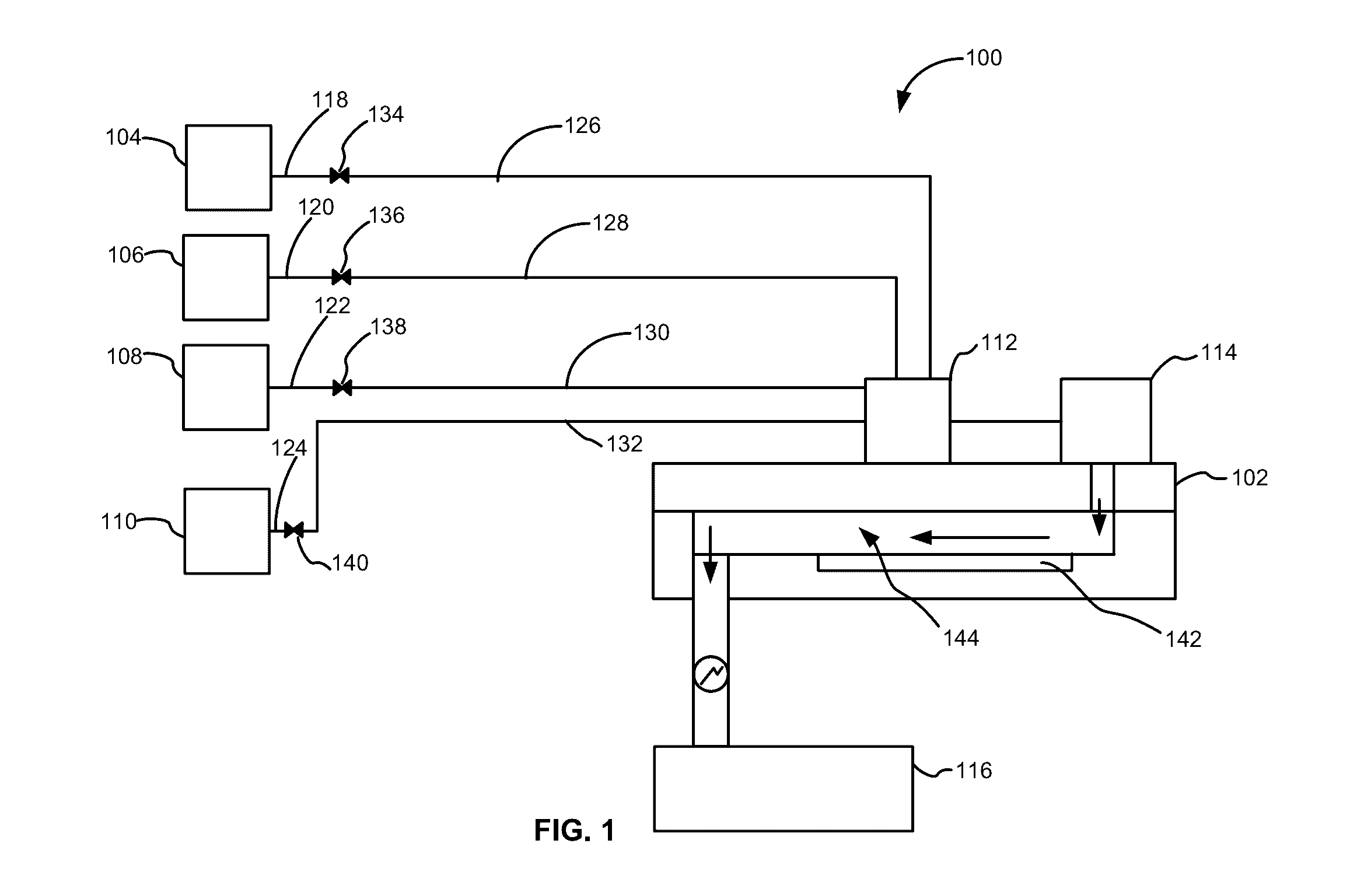
Parts for deposition reactors
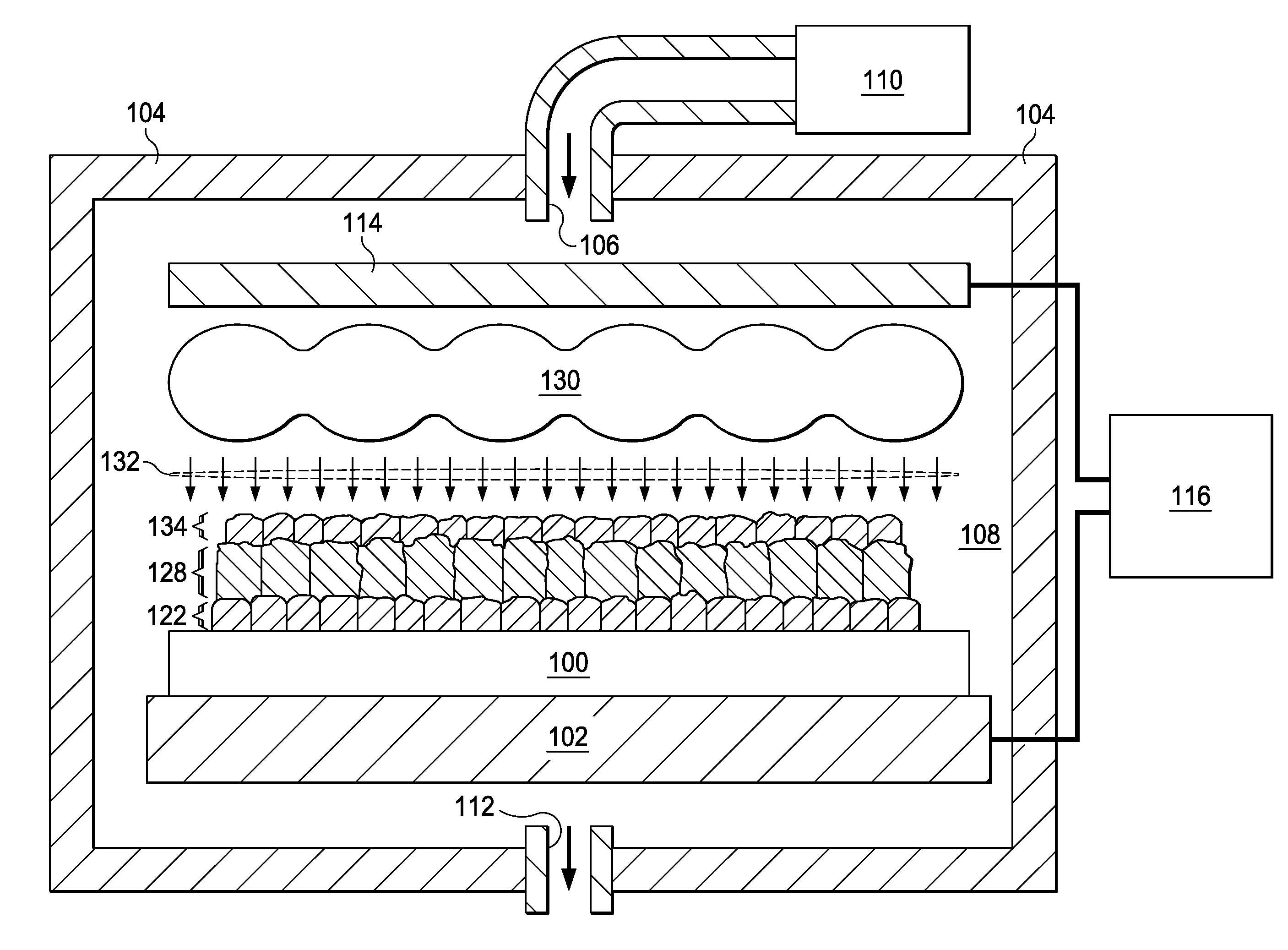
ActiveUS7674726B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingThermal expansionSemiconductor
Processing methods and internal reactor parts avoid peeling and particle generation caused by differences in the coefficients of thermal expansion (CTE's) between reactor parts and films deposited on the reactor parts in hot wall CVD chambers. Conventional materials for reactor parts have relatively low CTE's, resulting in significant CTE differences with modem films, which can be deposited on the surfaces of reactor parts during semiconductor processing. Such CTE differences can cause cracking and flaking of the deposited films, thereby leading to particle generation. Reactor parts, such as boats and pedestals, which undergo large thermal cycles even in a hot wall chamber, are made of materials having a CTE greater than about 5×10−6 K−1, in order to more closely match the CTE of deposited materials, such TiN. The decreased CTE differences decrease differences between the expansion and contraction of the reactor parts and deposited films, leading to decreased cracking, flaking and, ultimately, decreased particle generation.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Spin-transfer torque magnetic random access memory having magnetic tunnel junction with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy
A spin-torque transfer memory random access memory (STTMRAM) element includes a fixed layer formed on top of a substrate and a a tunnel layer formed upon the fixed layer and a composite free layer formed upon the tunnel barrier layer and made of an iron platinum alloy with at least one of X or Y material, X being from a group consisting of: boron (B), phosphorous (P), carbon (C), and nitride (N) and Y being from a group consisting of: tantalum (Ta), titanium (Ti), niobium (Nb), zirconium (Zr), tungsten (W), silicon (Si), copper (Cu), silver (Ag), aluminum (Al), chromium (Cr), tin (Sn), lead (Pb), antimony (Sb), hafnium (Hf) and bismuth (Bi), molybdenum (Mo) or rhodium (Ru), the magnetization direction of each of the composite free layer and fixed layer being substantially perpendicular to the plane of the substrate.
Owner:AVALANCHE TECH
Structures and devices including germanium-tin films and methods of forming same
ActiveUS20160314967A1Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor depositionGermane
Methods of forming germanium-tin films using germane as a precursor are disclosed. Exemplary methods include growing films including germanium and tin in an epitaxial chemical vapor deposition reactor, wherein a ratio of a tin precursor to germane is less than 0.1. Also disclosed are structures and devices including germanium-tin films formed using the methods described herein.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Capacitive touch sensor with integral EL backlight
InactiveUS20070165004A1Easy to optimizeInput/output processes for data processingConductive polymerAntimony tin oxide
A personal electronic device includes a programmable display and a programmable keypad, wherein at least one of the programmable display and the programmable keypad includes a capacitive touch sensor and an EL panel in a unitary structure. A conductive layer shields the capacitive touch sensor from the EL panel and can be a separate layer or be incorporated into either the capacitive sensor or the EL panel. The conductive layer includes antimony tin oxide (ATO), other conductive oxide, or a conductive polymer, such as Orgacon™ 3010.
Owner:WORLD PROPERTIES
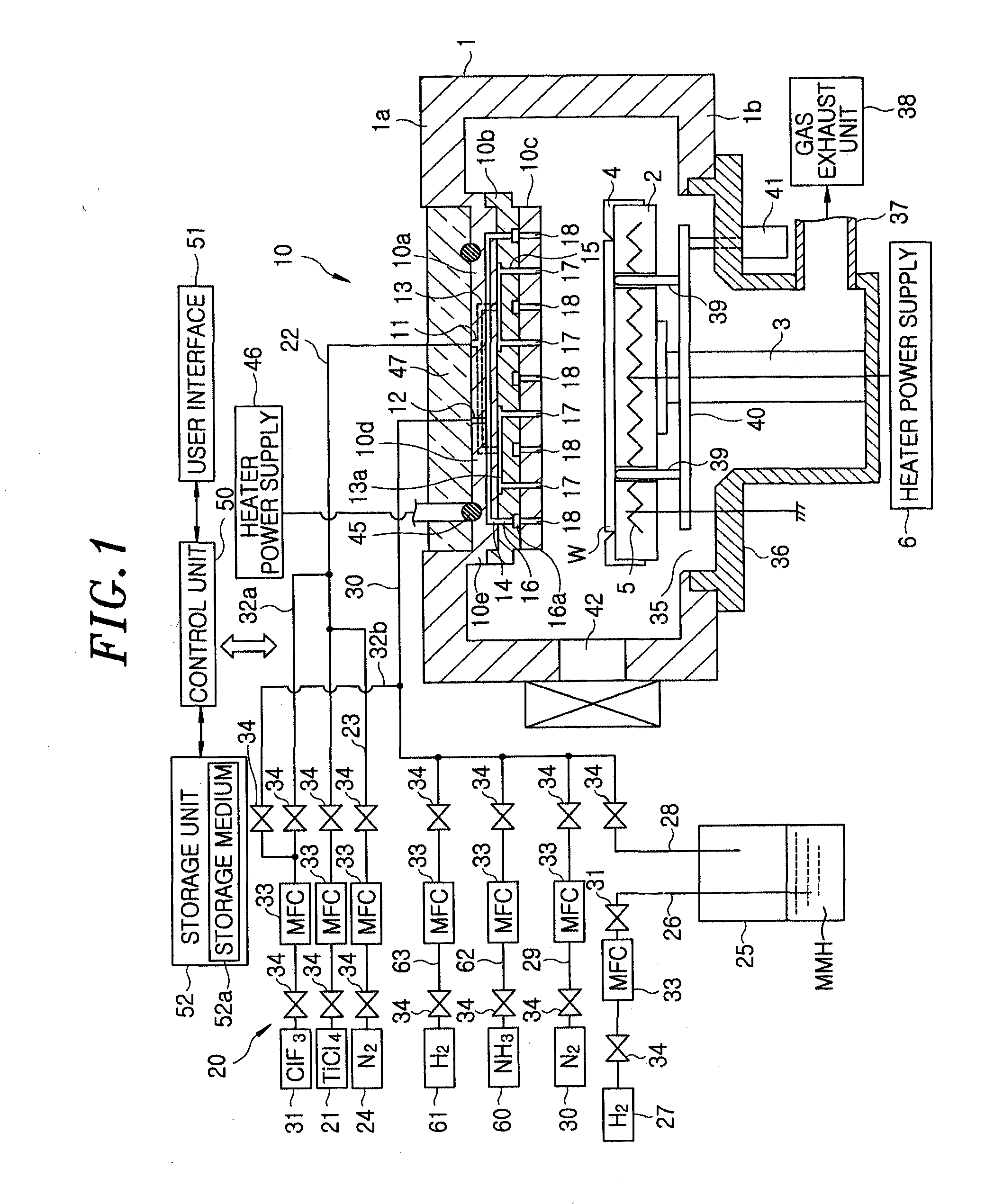
Method for forming metal nitride film
InactiveUS20120034793A1Reduce the temperatureFast film formationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringNitride
A wafer serving as a target substrate to be processed is loaded into a chamber, and an inside of the chamber is maintained under a vacuum level. Then, a TiN film is formed on the wafer by alternately supplying TiCl4 gas and MMH gas into the chamber while heating the wafer. NH3 gas is supplied in conjunction with the supply of the hydrazine compound gas.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Powder material, electrode structure using the powder material, and energy storage device having the electrode structure
InactiveUS20080003503A1Fast chargingIncrease energy densityNon-metal conductorsElectrode manufacturing processesElectrical conductorHigh energy
A powder material which can electrochemically store and release lithium ions rapidly in a large amount is provided. In addition, an electrode structure for an energy storage device which can provide a high energy density and a high power density and has a long life, and an energy storage device using the electrode structure are provided. In a powder material which can electrochemically store and release lithium ions, the surface of particles of one of silicon metal and tin metal and an alloy of any thereof is coated by an oxide including a transition metal element selected from the group consisting of W, Ti, Mo, Nb, and V as a main component. The electrode structure includes the powder material. The battery device includes a negative electrode having the electrode structure, a lithium ion conductor, and a positive electrode, and utilizes an oxidation reaction of lithium and a reduction reaction of lithium ion.
Owner:CANON KK
Lead free reduced ricochet limited penetration projectile
A frangible projectile with a specific gravity similar to a lead projectile. The projectile comprises 34-94%, by weight, binder. The binder comprises poly ether block amide resin. The projectile further comprises 6-66%, by weight, ballast. The ballast comprises at least one member selected from a group consisting of tungsten, tungsten carbide, molybdenum, tantalum, ferro-tungsten, copper, bismuth, iron, steel, brass, aluminum bronze, beryllium copper, tin, aluminum, titanium, zinc, nickel silver alloy, cupronickel and nickel. The projectile can be prepared with a particularly preferred specific gravity of 5-14 and more preferably 11-11.5.
Owner:ACCUTEC USA
Process for preparing a polymer having a 2,5-furandicarboxylate moiety within the polymer backbone and such (CO)polymers
A process for preparing a polymer having a 2,5-furandicarboxylate moiety within the polymer backbone and having a number average molecular weight of at least 10,000 (as determined by GPC based on polystyrene standards) includes a first step where a prepolymer is made having the 2,5-furandicarboxylate moiety within the polymer backbone, followed in a second step by a polycondensation reaction. In the first step a 2,5-furandicarboxylate ester is transesterified with a compound or mixture of compounds containing two or more hydroxyl groups, in the presence of a tin(IV) based transesterification catalyst. In the second step at reduced pressure and under melt conditions the prepolymer prepared in the first step is polycondensed in the presence of a tin (II) based polycondensation catalyst until the polymer is obtained. This polymer may then be subjected to Solid State Polycondensation. Polymers so produced may have a 2,5-furandicarboxylate moiety within the polymer backbone, and having a number average molecular weight of at least 20,000 (as determined by GPC based on styrene standards), and an absorbance as a 5 mg / mL solution in a dichloromethane:hexafluoroisopropanol 8:2 at 400 nm of below 0.05.
Owner:FURANIX TECH BV
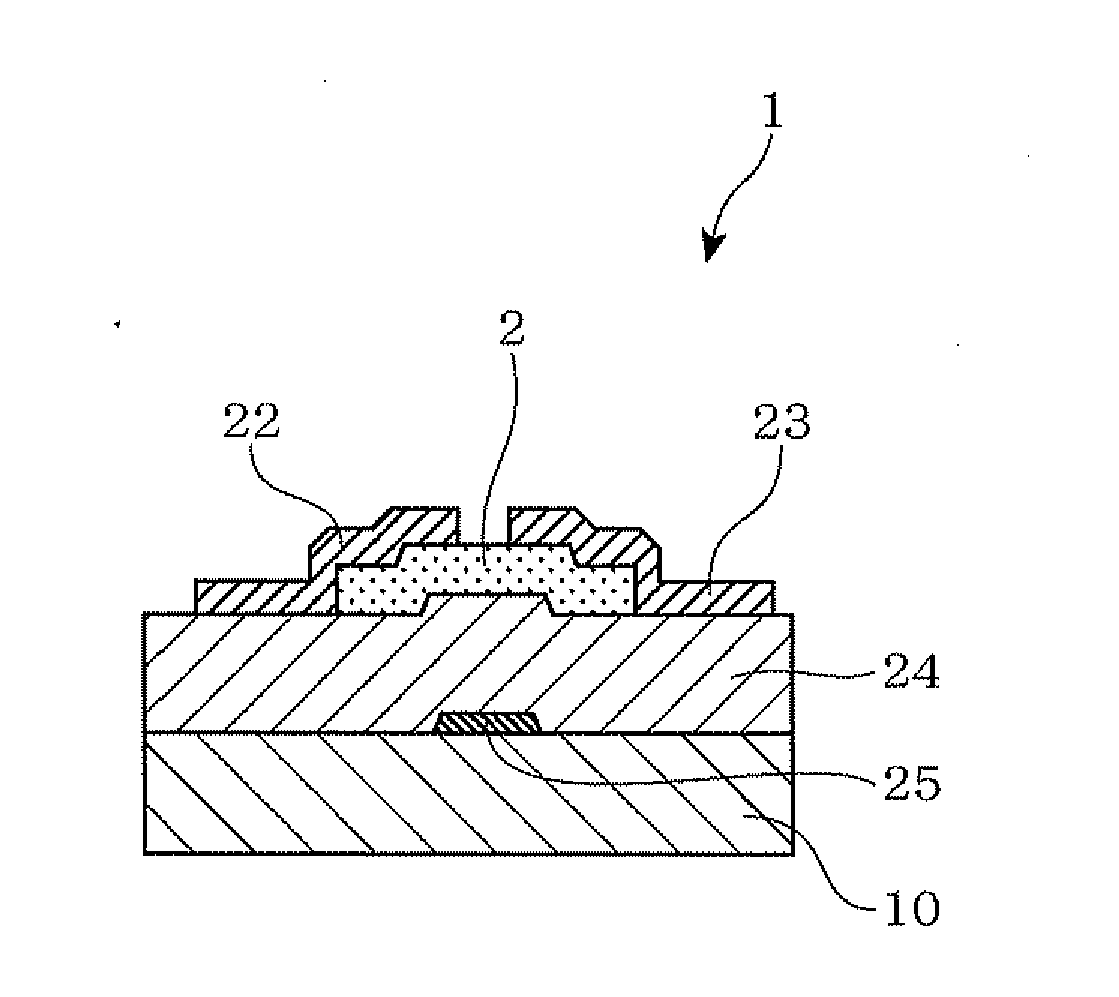
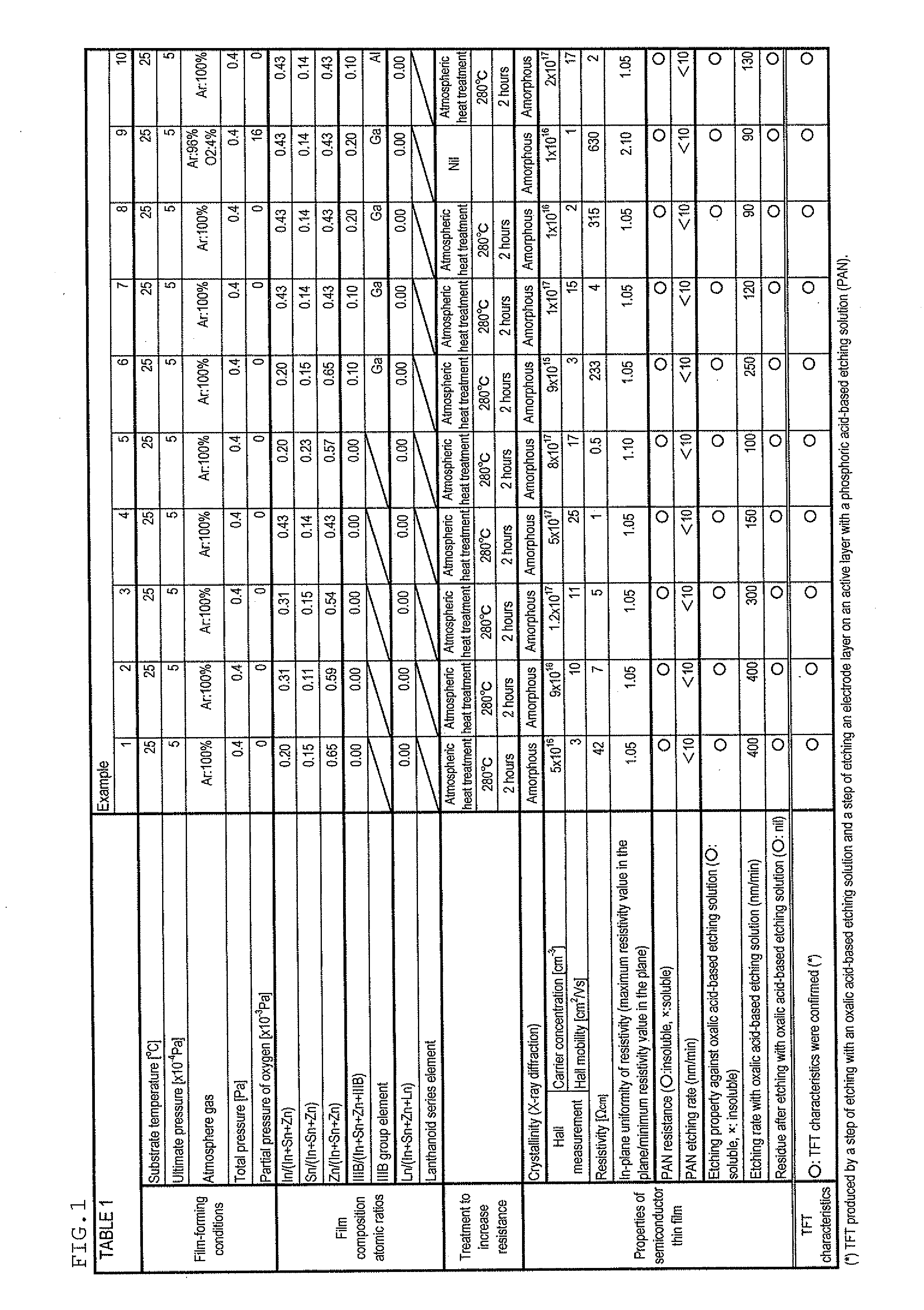
Noncrystalline oxide semiconductor thin film, process for producing the noncrystalline oxide semiconductor thin film, process for producing thin-film transistor, field-effect-transistor, light emitting device, display device, and sputtering target
ActiveUS20100155717A1Improve the immunityEasy to uniformlyCellsVacuum evaporation coatingIndiumPhosphoric acid
This invention provides an amorphous oxide semiconductor thin film, which is insoluble in a phosphoric acid-based etching solution and is soluble in an oxalic acid-based etching solution by optimizing the amounts of indium, tin, and zinc, a method of producing the amorphous oxide semiconductor thin film, etc. An image display device (1) comprises a glass substrate (10), a liquid crystal (40) as a light control element, a bottom gate-type thin film transistor (1) for driving the liquid crystal (40), a pixel electrode (30), and an opposing electrode (50). The amorphous oxide semiconductor thin film (2) in the bottom gate-type thin film transistor (1) has a carrier density of less than 10+18 cm−3, is insoluble in a phosphoric acid-based etching liquid, and is soluble in an oxalic acid-based etching liquid.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
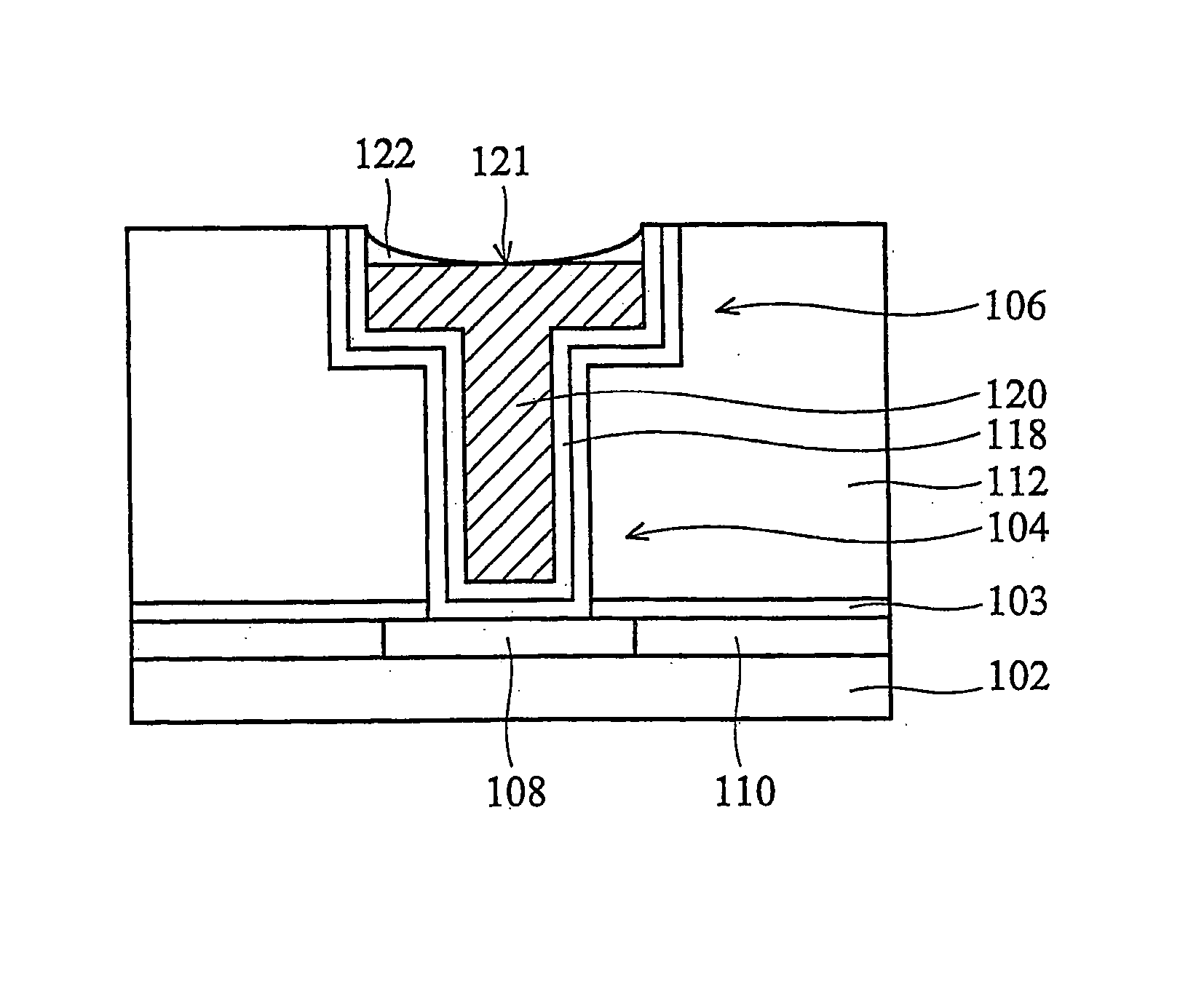
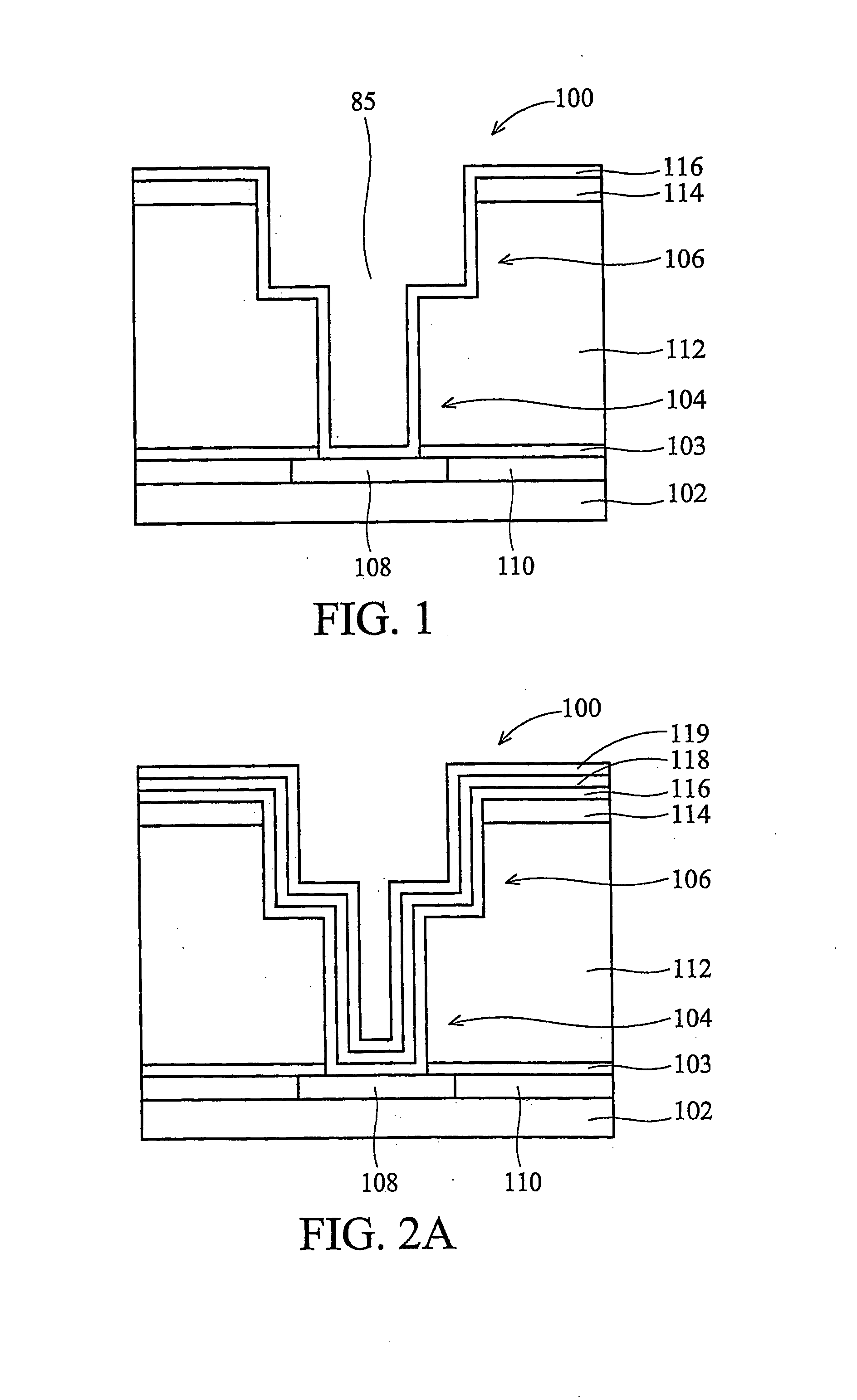
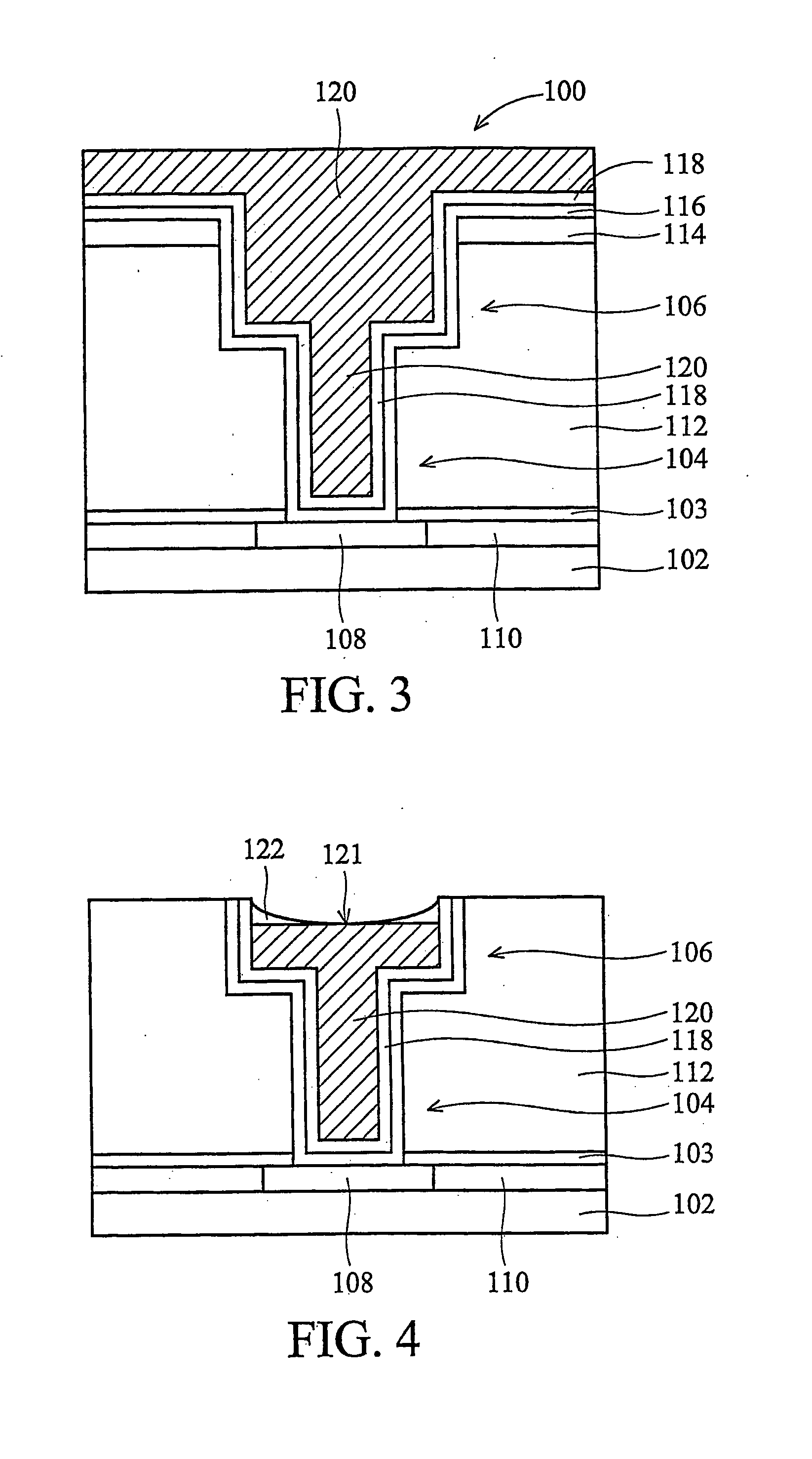
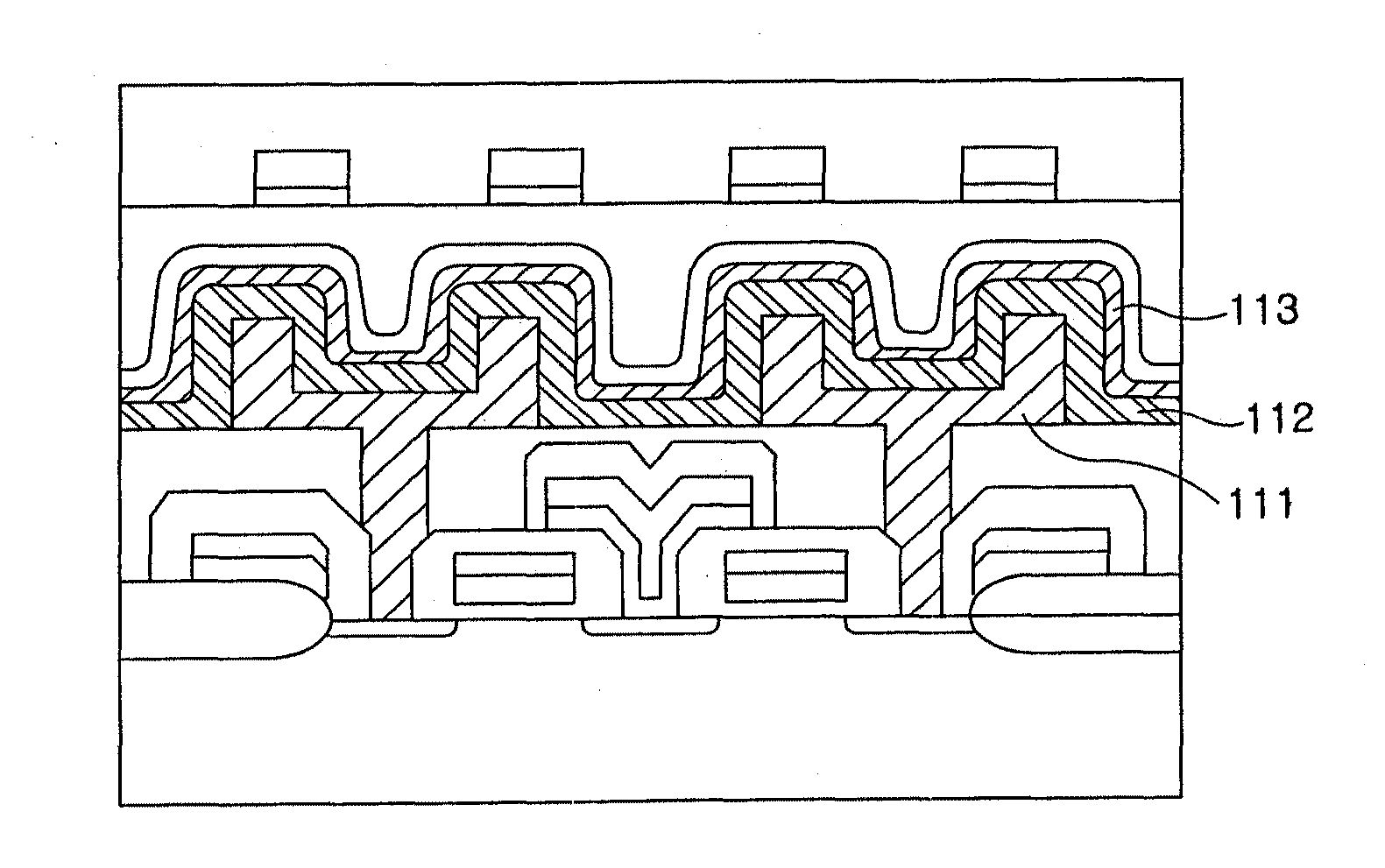
Self-align planerized bottom electrode phase change memory and manufacturing method
ActiveUS20070158645A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhase-change memoryRandom access memory
A method is described for self-aligning a bottom electrode in a phase change random access memory PCRAM device where a top electrode serves as a mask for self-aligning etching of the bottom electrode. The bottom electrode has a top surface that is planarized by chemical mechanical polishing. The top electrode also has a top surface that is planarized by chemical mechanical polishing. A bottom electrode layer like TiN is formed over a substrate and prior to the formation of a via during subsequent process steps. A first dielectric layer is formed over the bottom electrode layer, and a second dielectric layer is formed over the first dielectric layer. A via is formed at a selected section that extends through the first and second dielectric layers.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com