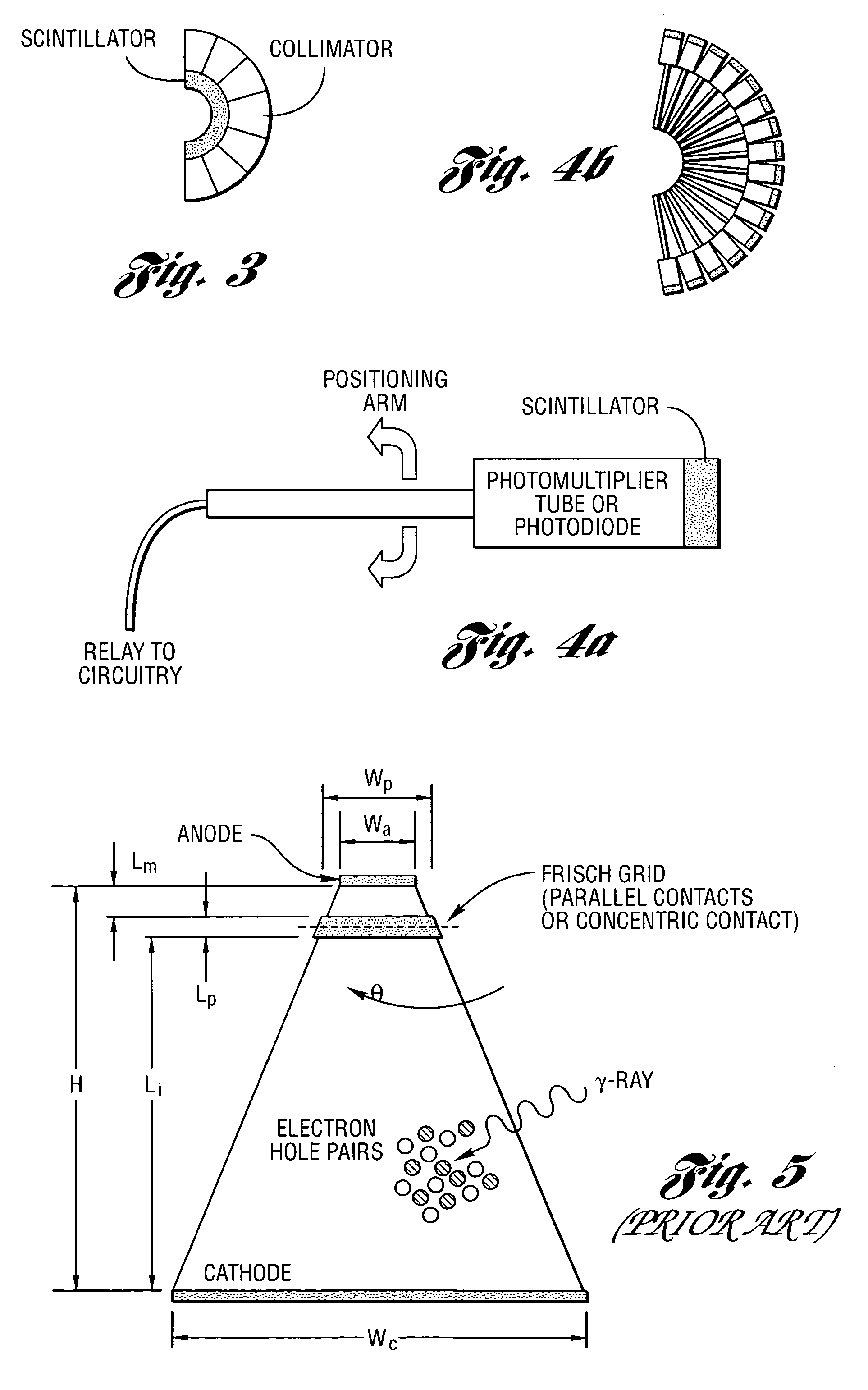
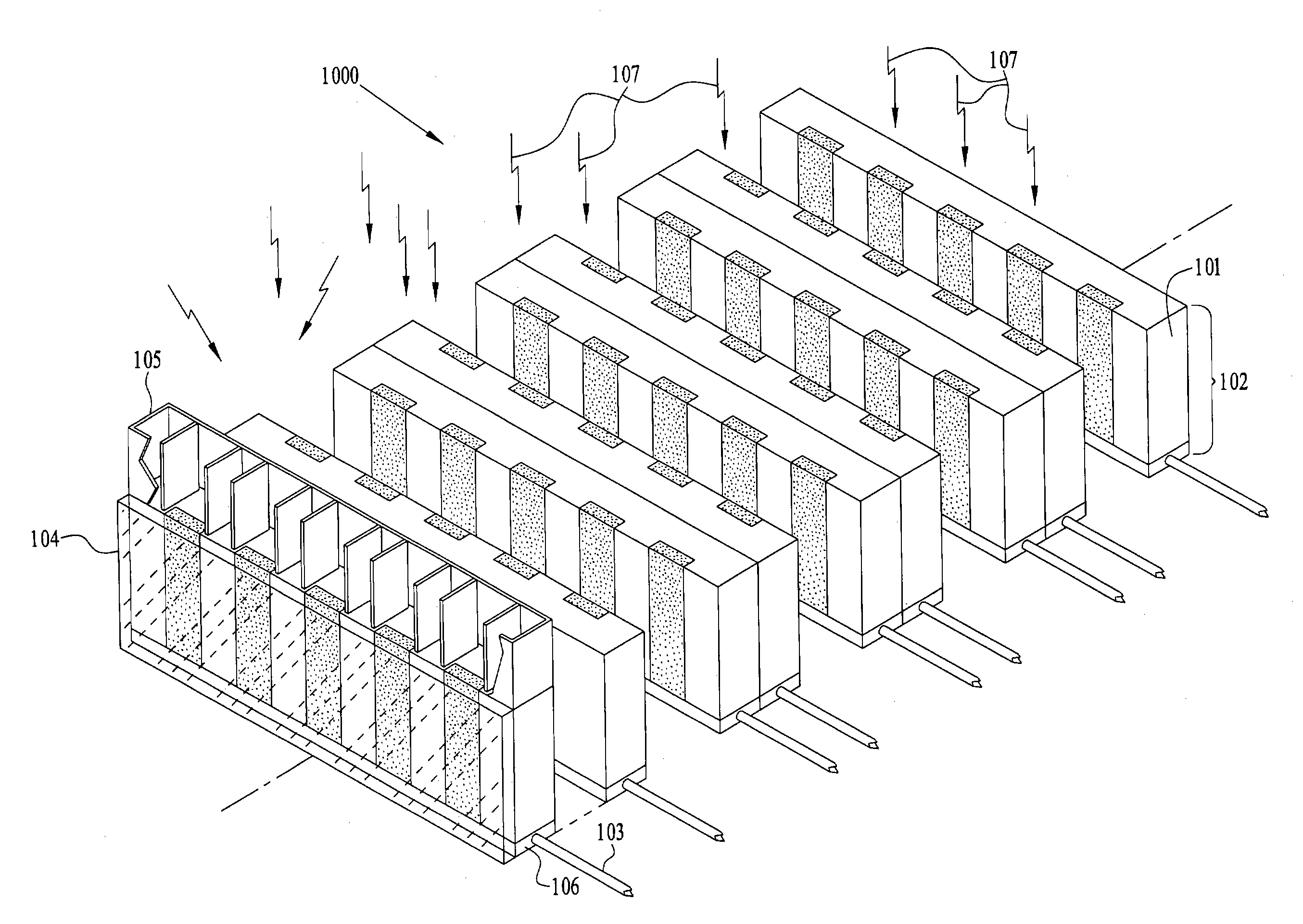
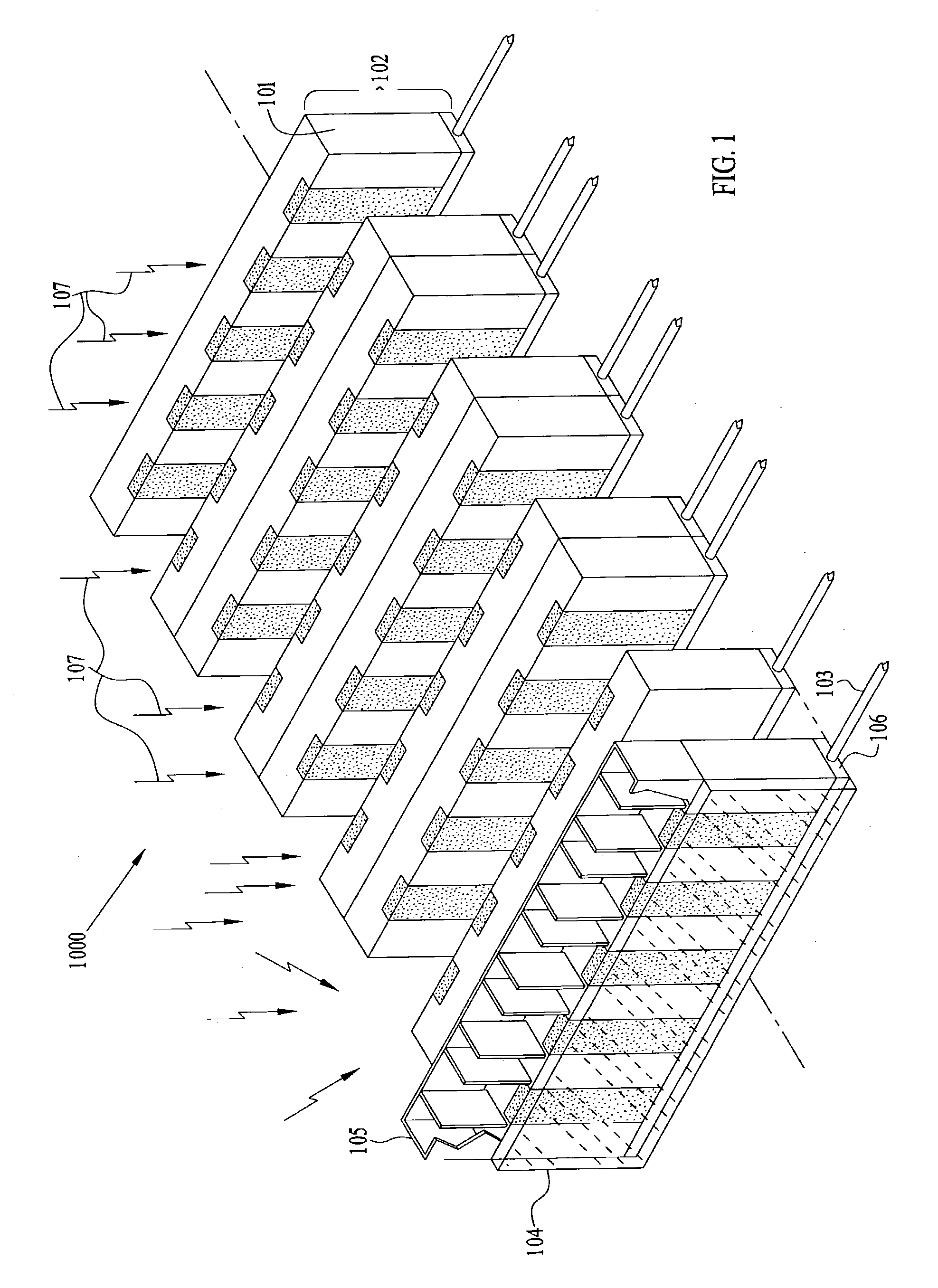
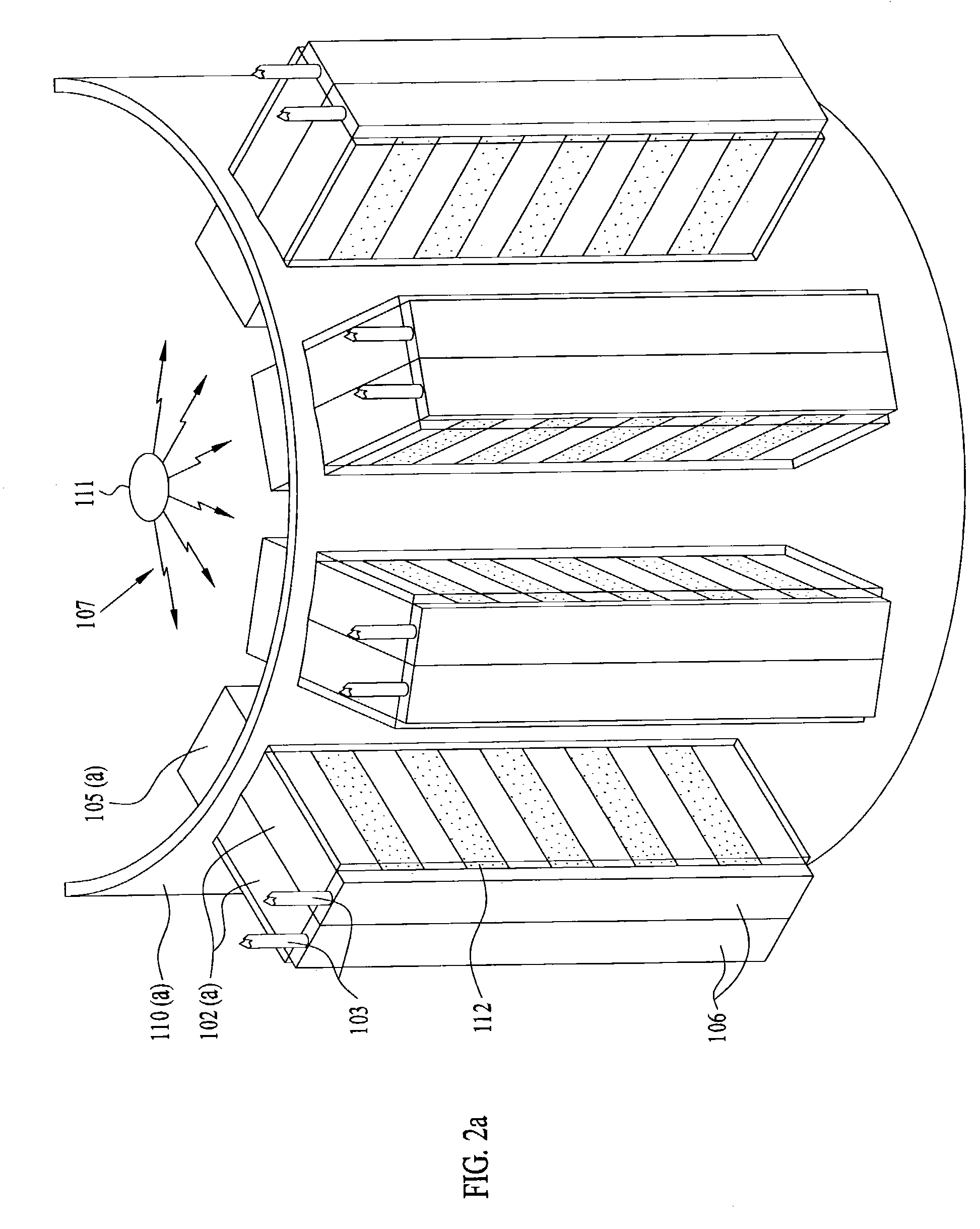
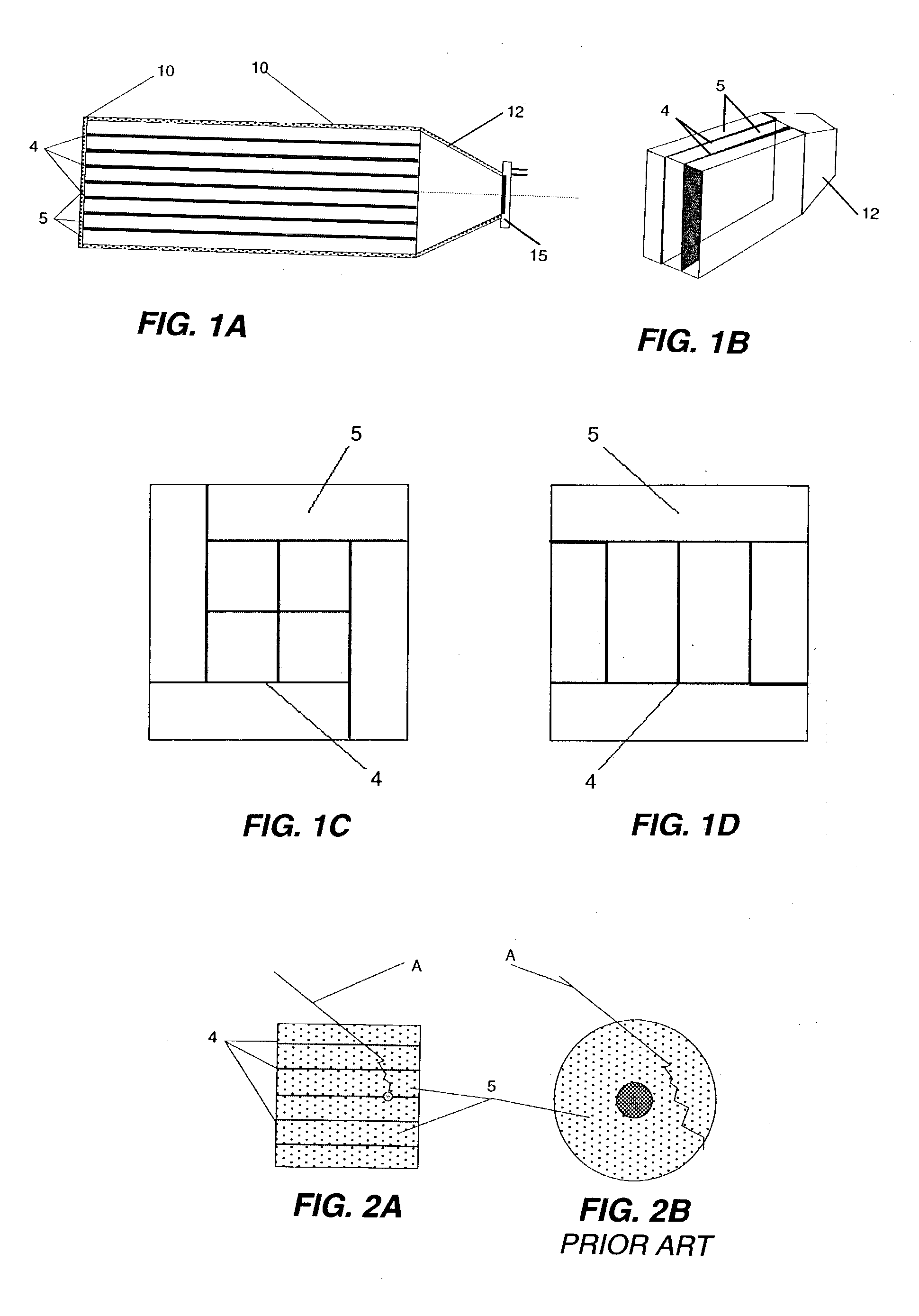
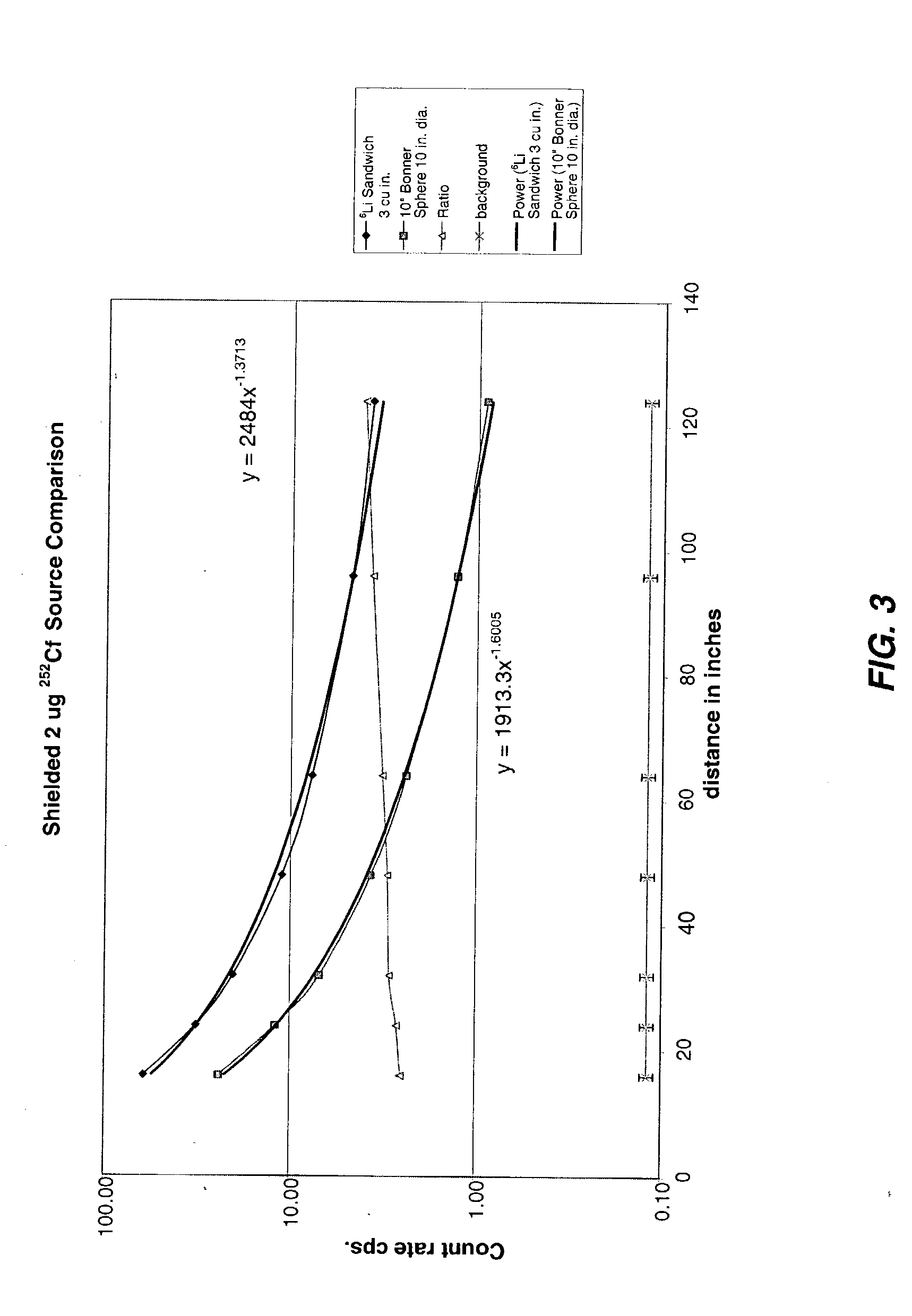
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2615 results about "Gamma ray" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A gamma ray, or gamma radiation (symbol γ or γ), is a penetrating electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves and so imparts the highest photon energy. Paul Villard, a French chemist and physicist, discovered gamma radiation in 1900 while studying radiation emitted by radium. In 1903, Ernest Rutherford named this radiation gamma rays based on their relatively strong penetration of matter; he had previously discovered two less penetrating types of decay radiation, which he named alpha rays and beta rays in ascending order of penetrating power.
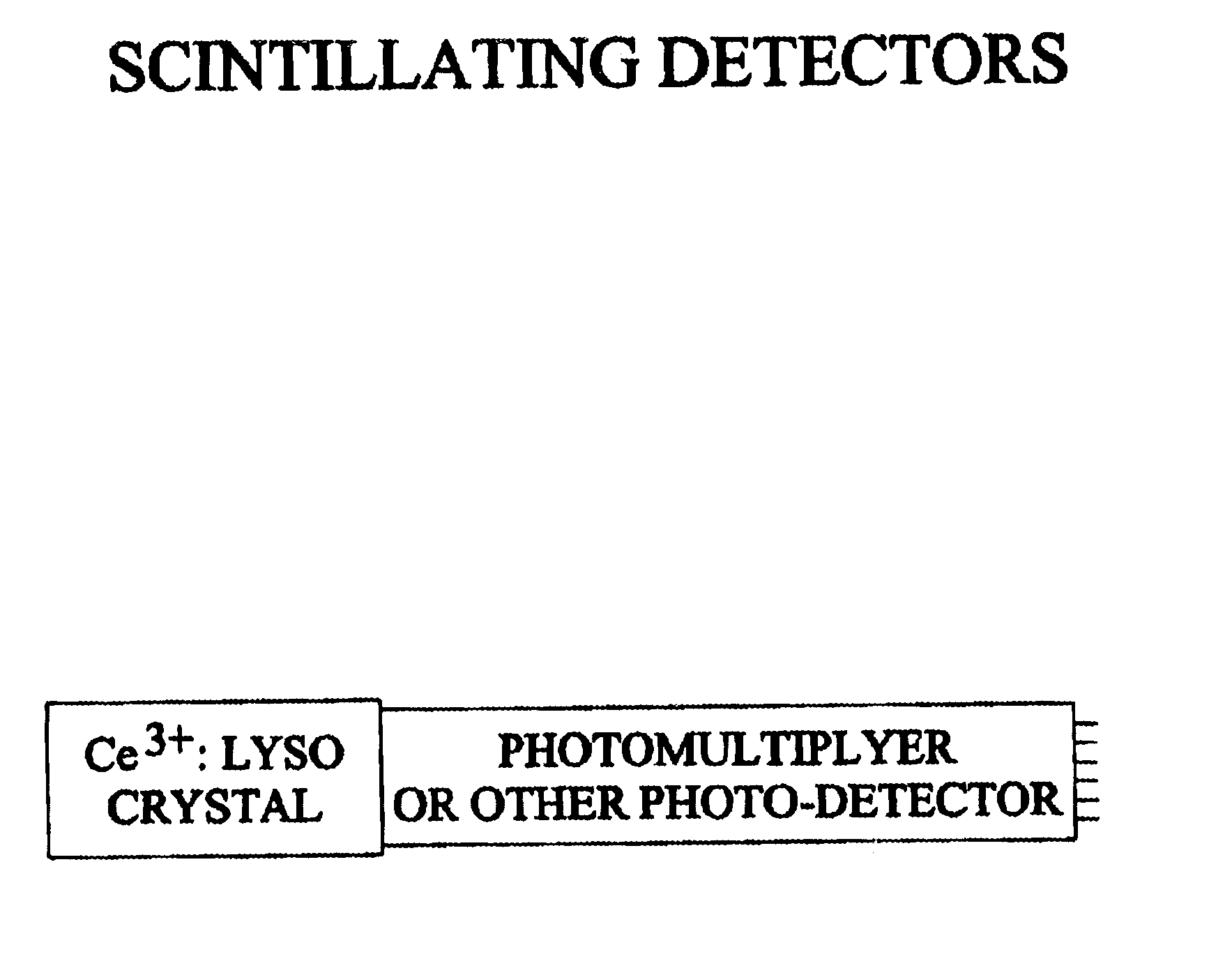
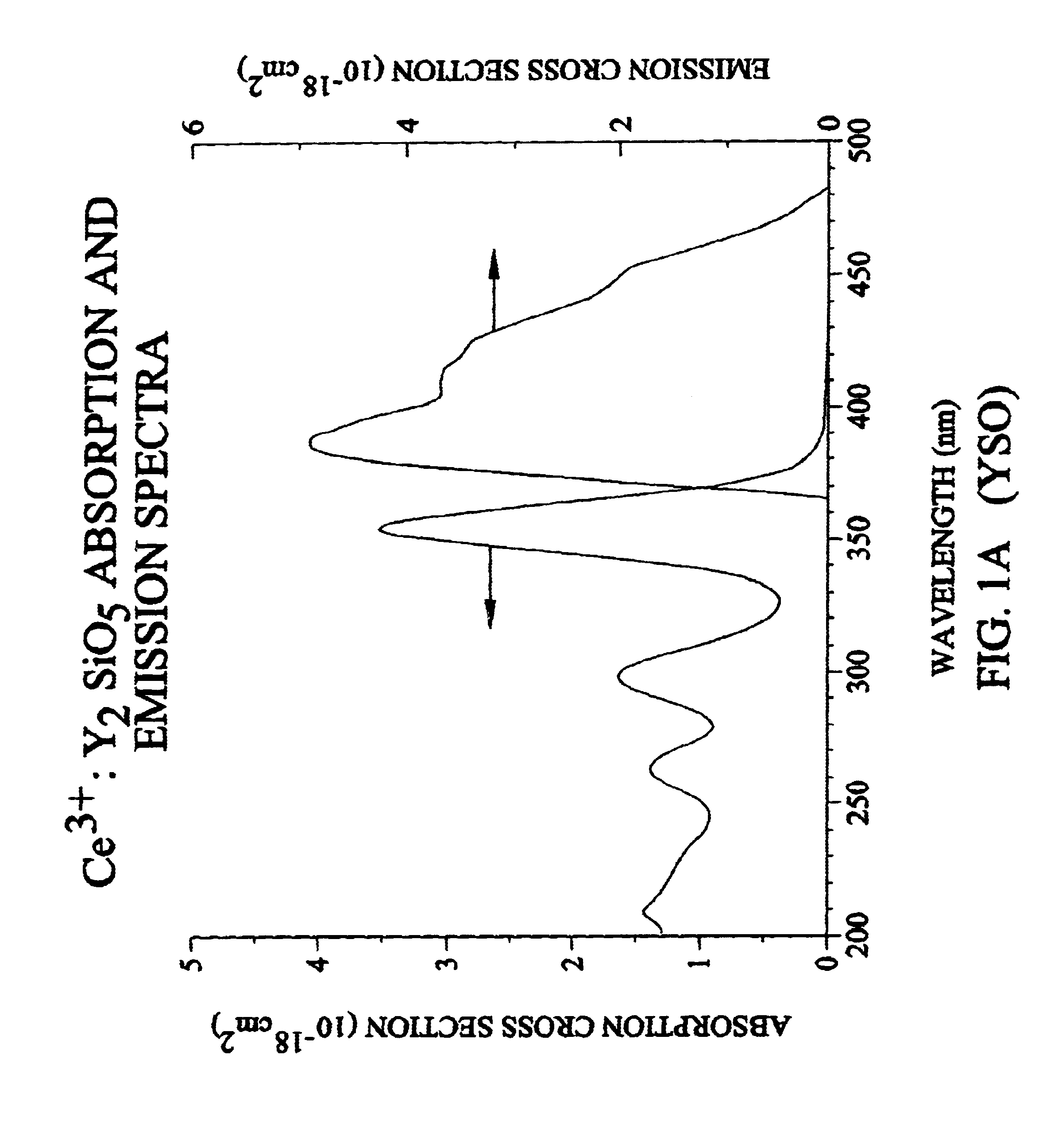
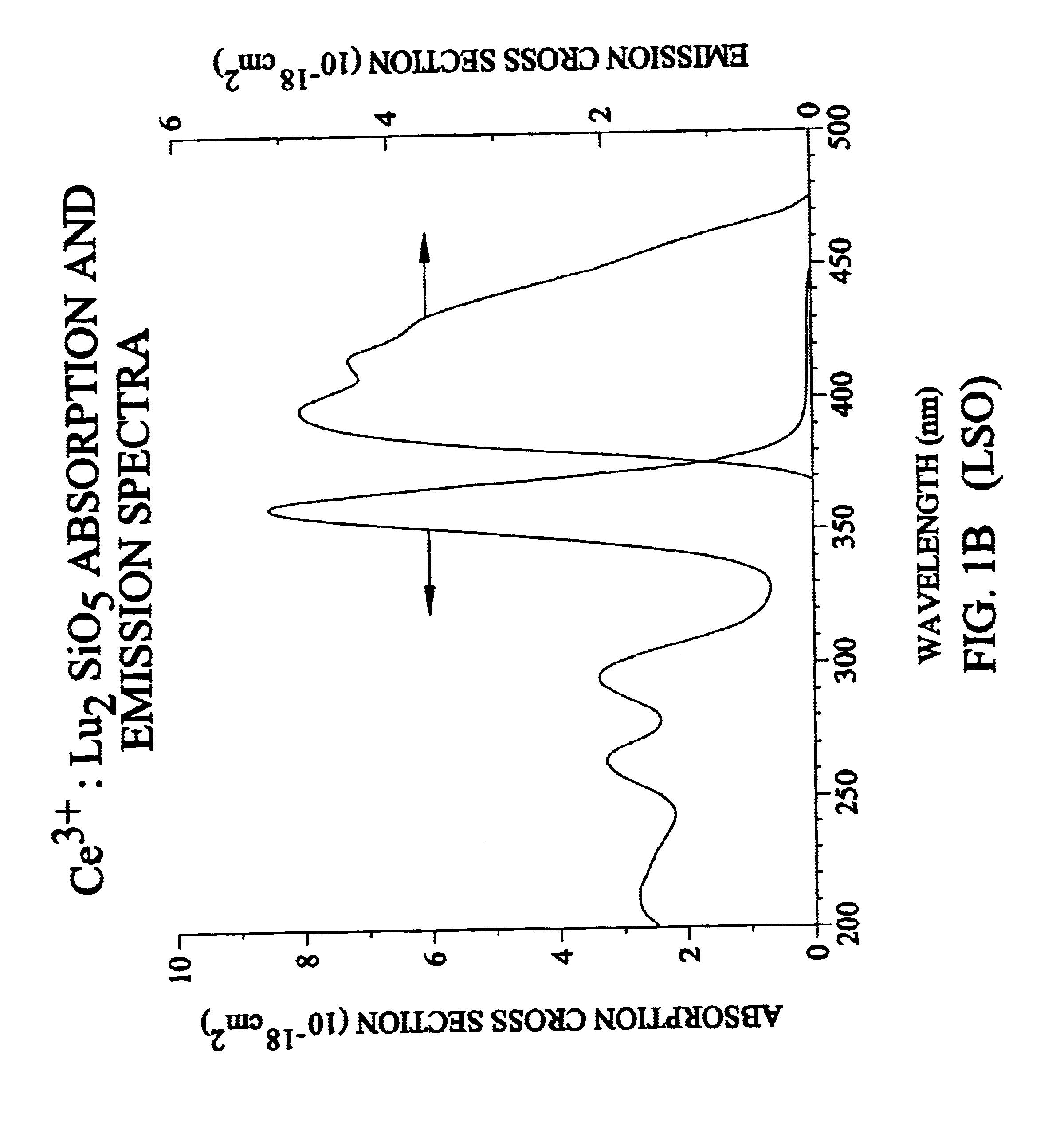
Lutetium yttrium orthosilicate single crystal scintillator detector
InactiveUS6624420B1Improve performanceMaterial analysis by optical meansLuminescent compositionsLutetiumHigh energy
A single crystal having the general composition, Ce2x(Lu1-yYy)2(1-x)SiO5 where x=approximately 0.00001 to approximately 0.05 and y=approximately 0.0001 to approximately 0.9999; preferably where x ranges from approximately 0.0001 to approximately 0.001 and y ranges from approximately 0.3 to approximately 0.8. The crystal is useful as a scintillation detector responsive to gamma ray or similar high energy radiation. The crystal as scintillation detector has wide application for the use in the fields of physics, chemistry, medicine, geology and cosmology because of its enhanced scintillation response to gamma rays, x-rays, cosmic rays and similar high energy particle radiation.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA +2
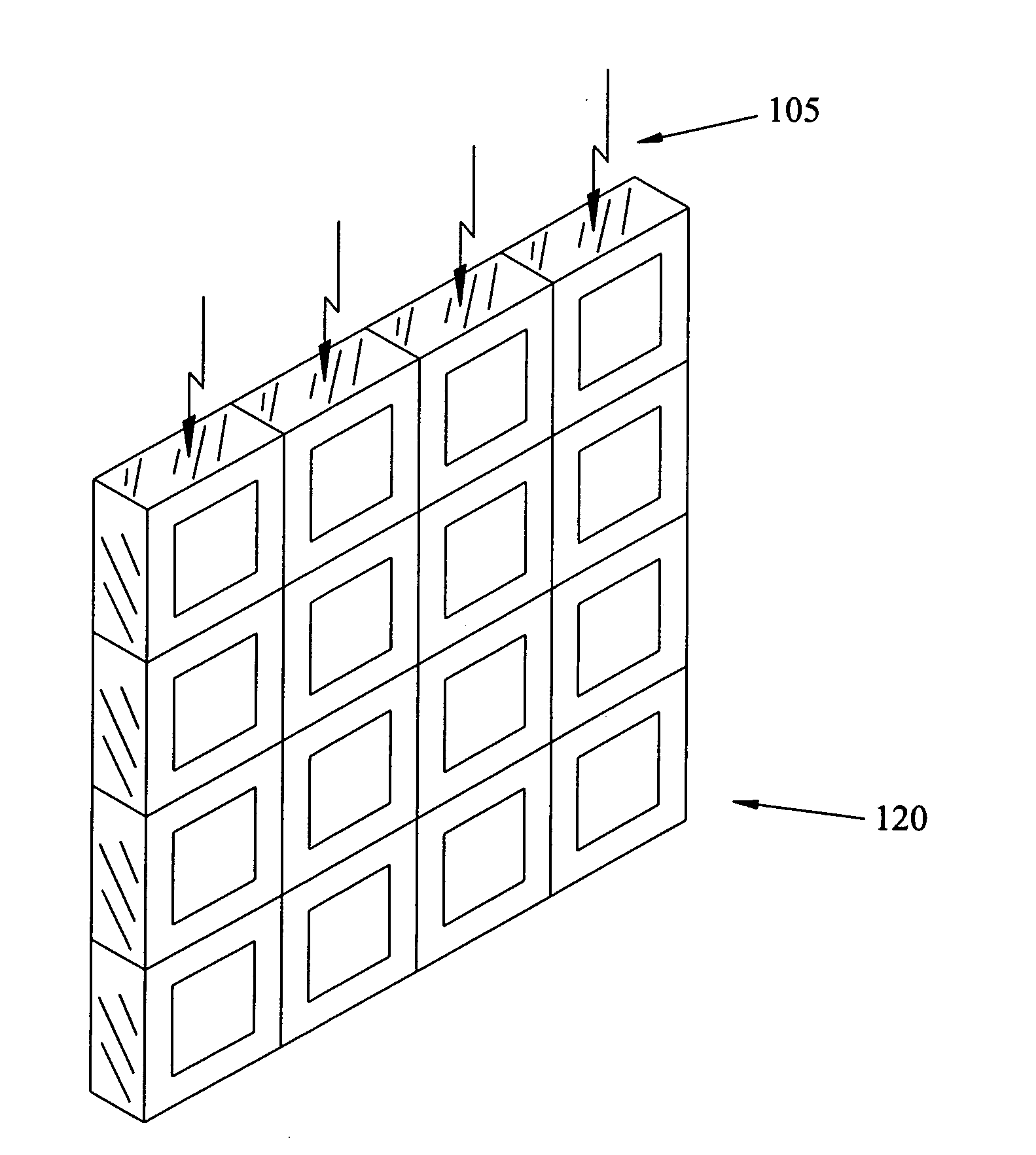
Slit and slot scan, SAR, and compton devices and systems for radiation imaging
ActiveUS20100270462A1Reduce productionReduce maintenance costsElectric discharge tubesElectroluminescent light sourcesHigh energyGas detector
The invention provides methods and apparatus for detecting radiation including x-ray photon (including gamma ray photon) and particle radiation for radiographic imaging (including conventional CT and radiation therapy portal and CT), nuclear medicine, material composition analysis, container inspection, mine detection, remediation, high energy physics, and astronomy. This invention provides novel face-on, edge-on, edge-on sub-aperture resolution (SAR), and face-on SAR scintillator detectors, designs and systems for enhanced slit and slot scan radiographic imaging suitable for medical, industrial, Homeland Security, and scientific applications. Some of these detector designs are readily extended for use as area detectors, including cross-coupled arrays, gas detectors, and Compton gamma cameras. Energy integration, photon counting, and limited energy resolution readout capabilities are described. Continuous slit and slot designs as well as sub-slit and sub-slot geometries are described, permitting the use of modular detectors.
Owner:MINNESOTA IMAGING & ENG
Radiation detectors
InactiveUS20060202125A1Thinner sliceImprove spatial resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansNanoopticsRecoil electronPhotonic bandgap
The invention consists in structuring scintillation radiation detectors as Photonic Bandgap Crystals or 3D layers of thin filaments, thus enabling extremely high spatial resolutions and achieving virtual voxellation of the radiation detector without physical separating walls. The ability to precisely measure the recoil electron track in a Compton camera enables to assess the directions of the gamma rays hitting the detector and consequently dispensing with collimators that strongly reduce the intensity of radiation detected by gamma cameras. The invention enables great enhancements of the capabilities of gamma cameras, SPECT, PET, CT and DR machines as well as their use in Homeland Security applications. Methods of fabrication of such radiation detectors are decribed.
Owner:SUHAMI AVRAHAM
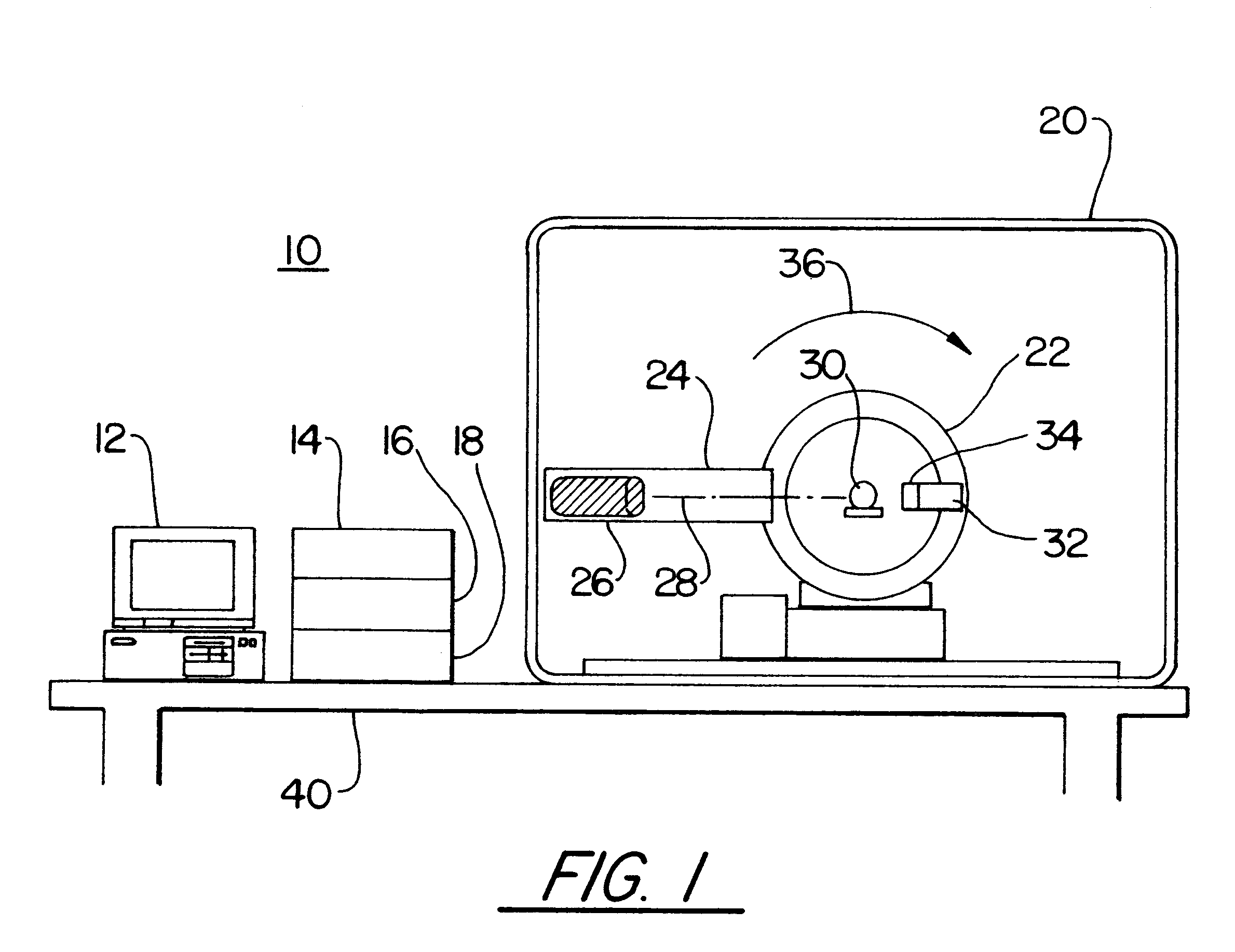
Simultaneous CT and SPECT tomography using CZT detectors
A method for simultaneous transmission x-ray computed tomography (CT) and single photon emission tomography (SPECT) comprises the steps of: injecting a subject with a tracer compound tagged with a gamma-ray emitting nuclide; directing an x-ray source toward the subject; rotating the x-ray source around the subject; emitting x-rays during the rotating step; rotating a cadmium zinc telluride (CZT) two-sided detector on an opposite side of the subject from the source; simultaneously detecting the position and energy of each pulsed x-ray and each emitted gamma-ray captured by the CZT detector; recording data for each position and each energy of each the captured x-ray and gamma-ray; and, creating CT and SPECT images from the recorded data. The transmitted energy levels of the x-rays lower are biased lower than energy levels of the gamma-rays. The x-ray source is operated in a continuous mode. The method can be implemented at ambient temperatures.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN ENERGY SYST INC
Systems and methods for hybrid scanning
InactiveUS20150085970A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingComputed tomographyX-ray
A system includes a detector and a processing unit. The detector includes multiple pixels configured to detect computed tomography (CT) events and nuclear medicine (NM) imaging events. The CT events correspond to X-rays emitted from a X-ray source through an object to be imaged, and the NM imaging events correspond to gamma rays emitted from a radiopharmaceutical that has been administered to the object. The detector is configured for photon counting detection of the CT events and the NM imaging events. The processing unit includes at least one processor and at least one memory comprising a tangible and non-transitory computer readable storage medium. The processing unit is configured to, based on corresponding energy levels of the CT events and the NM imaging events, identify CT information corresponding to the CT events and identify NM information corresponding to the NM imaging events.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST ISRAEL
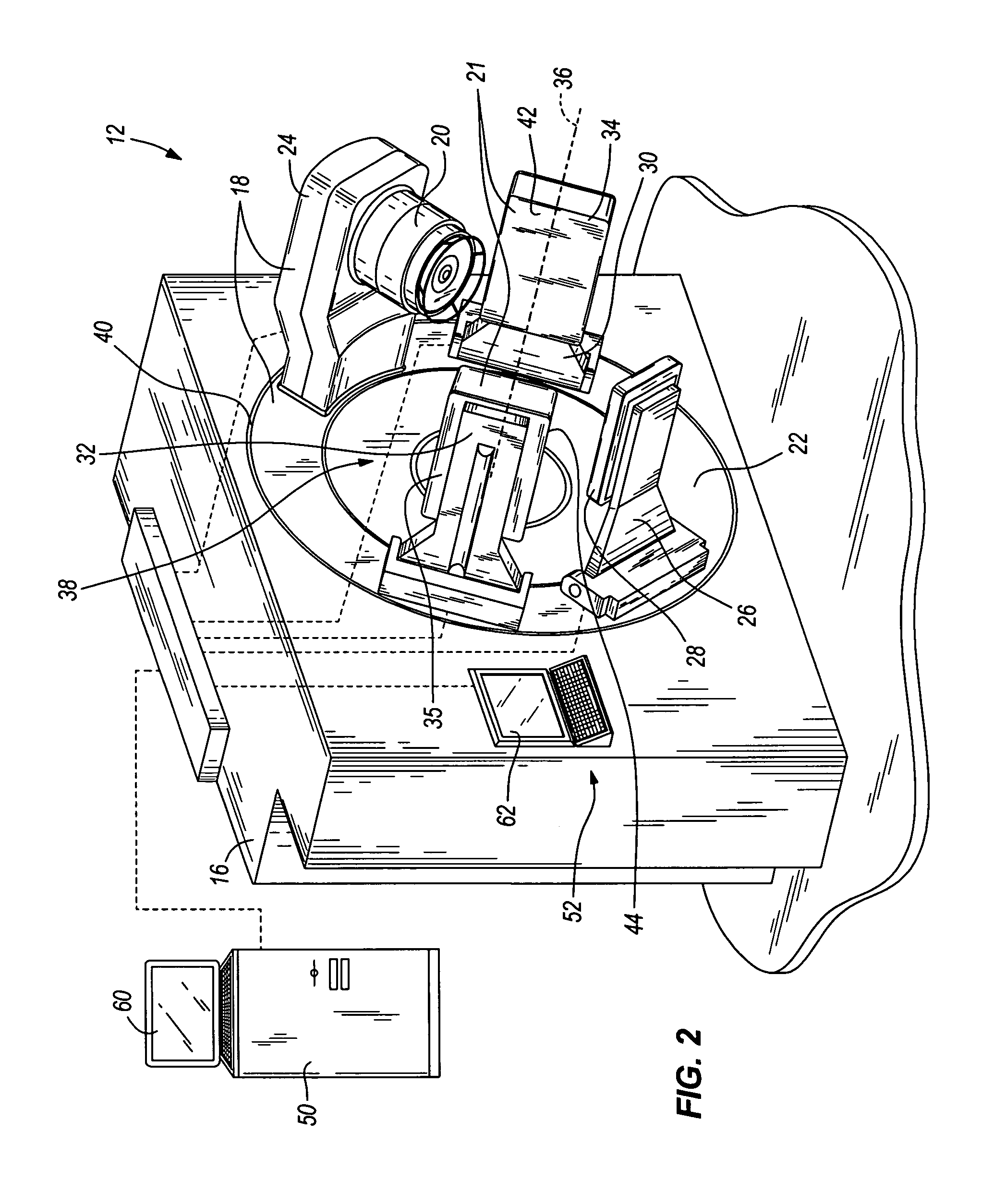
Image-guided medical intervention apparatus and method
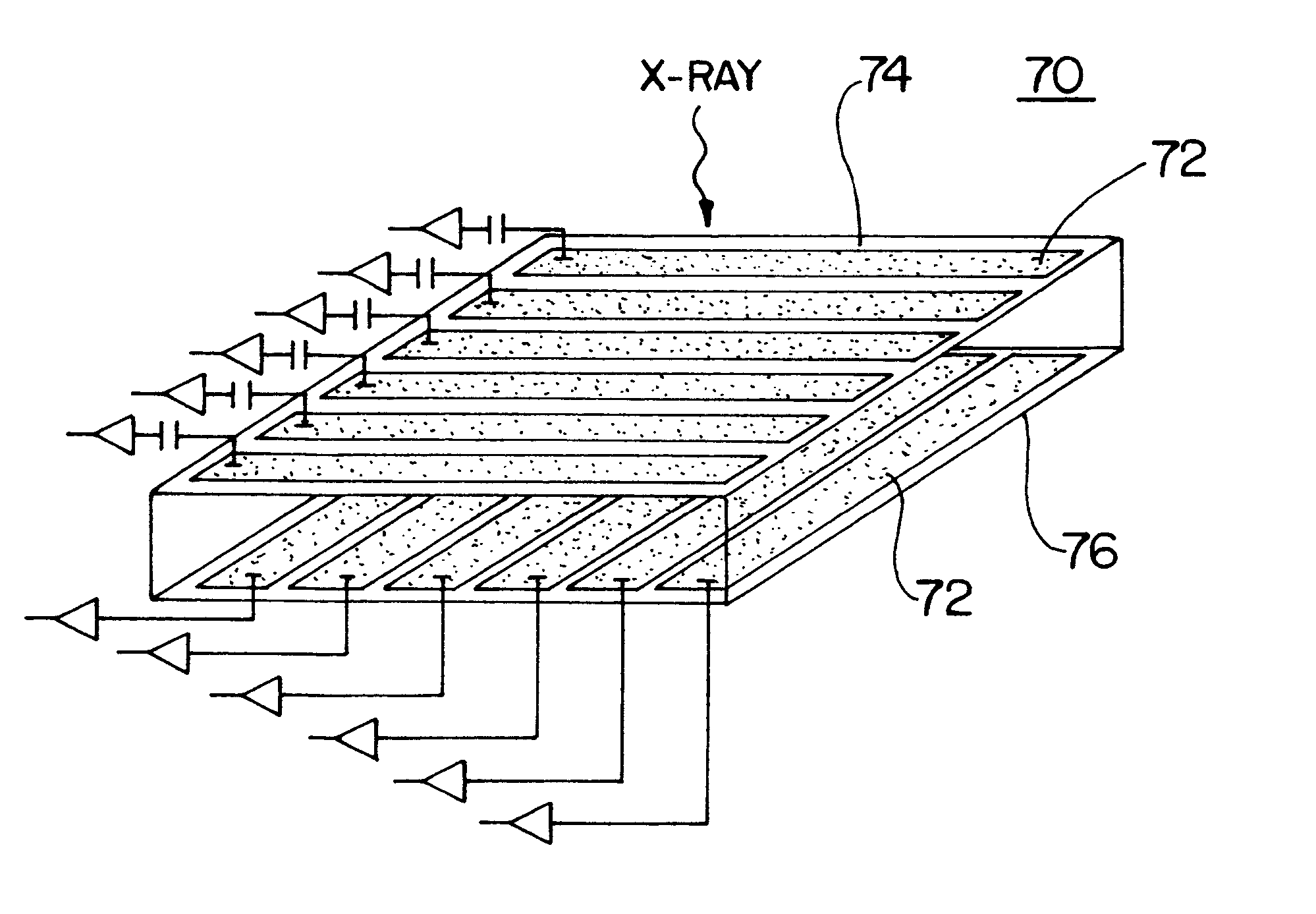
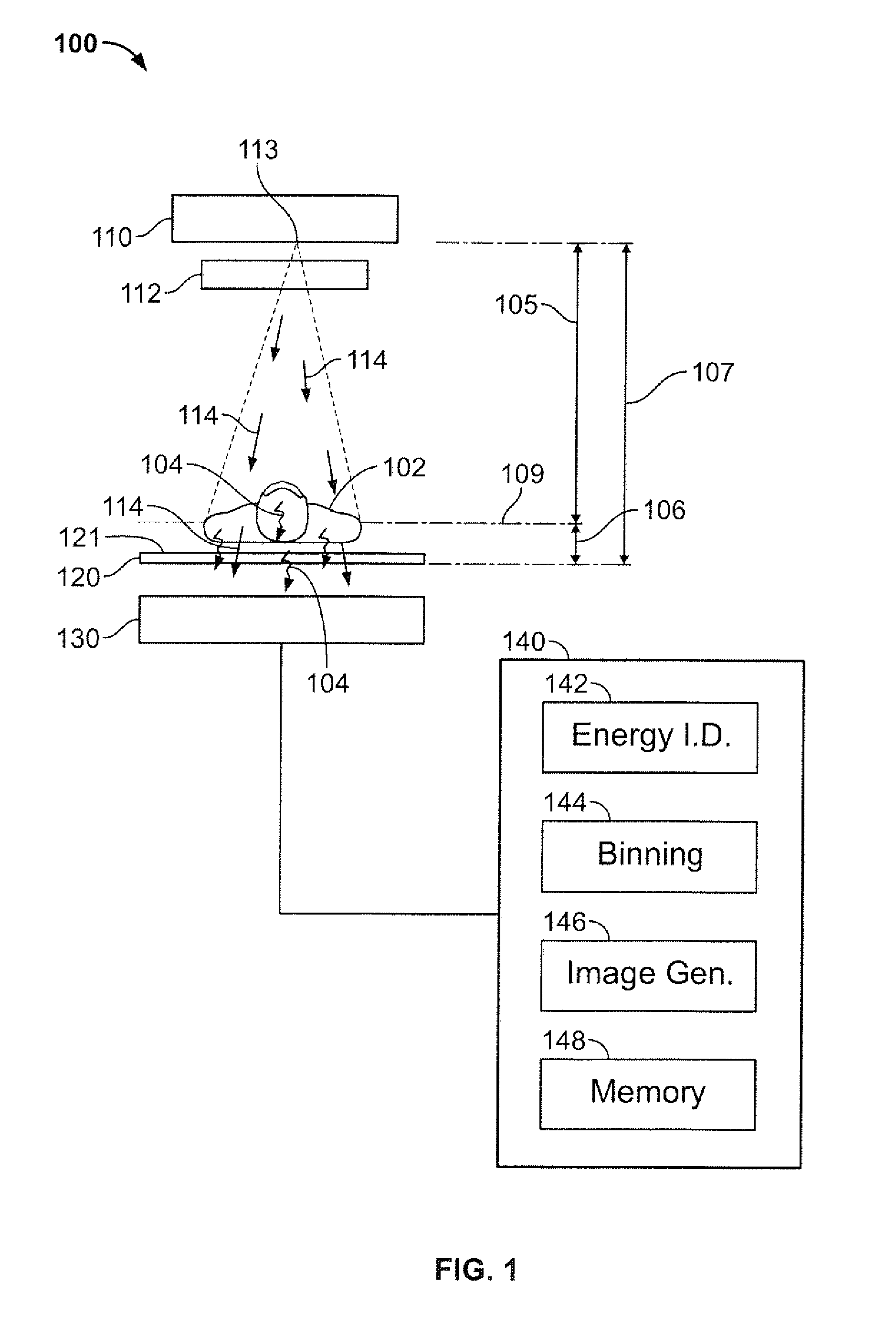
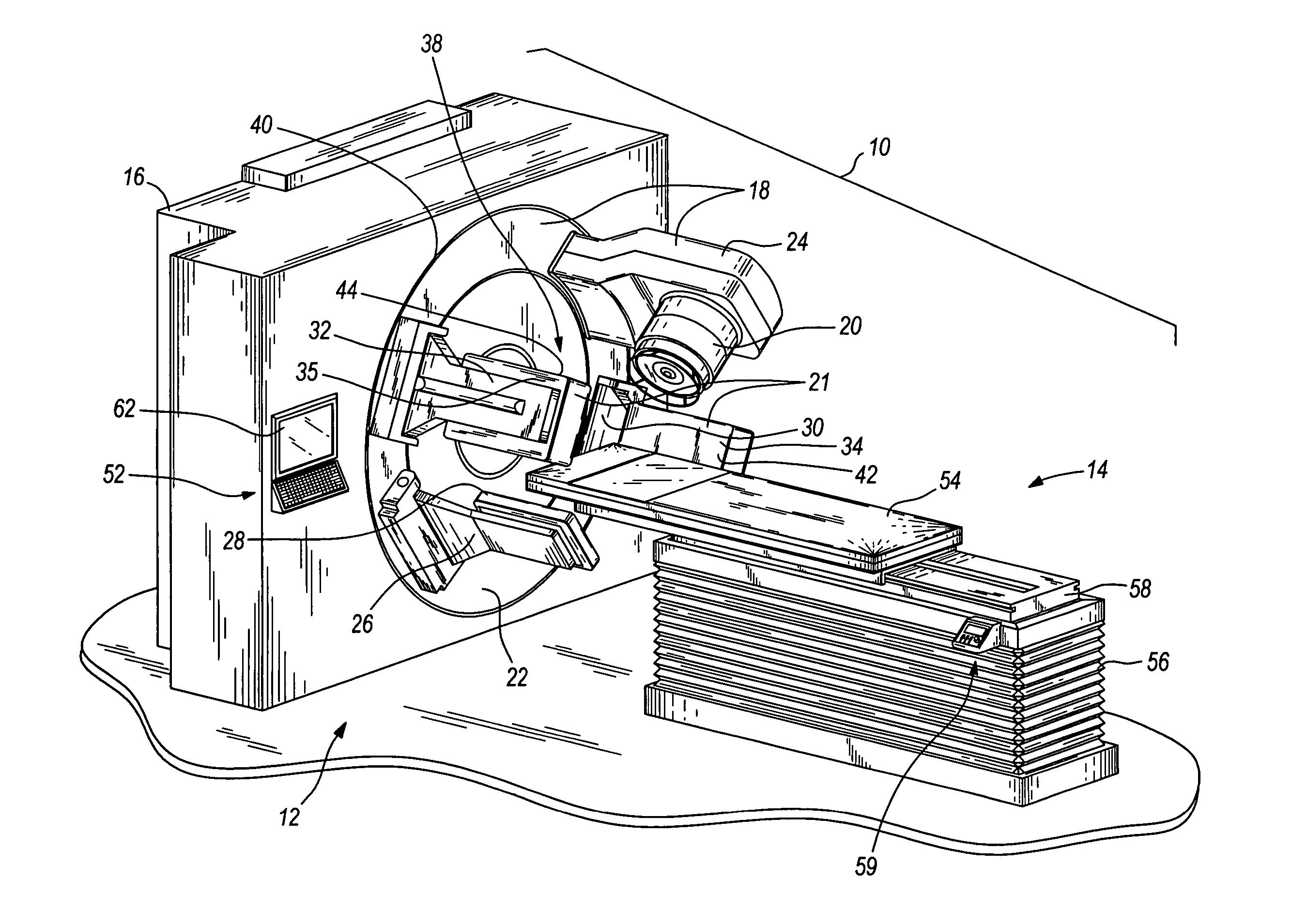
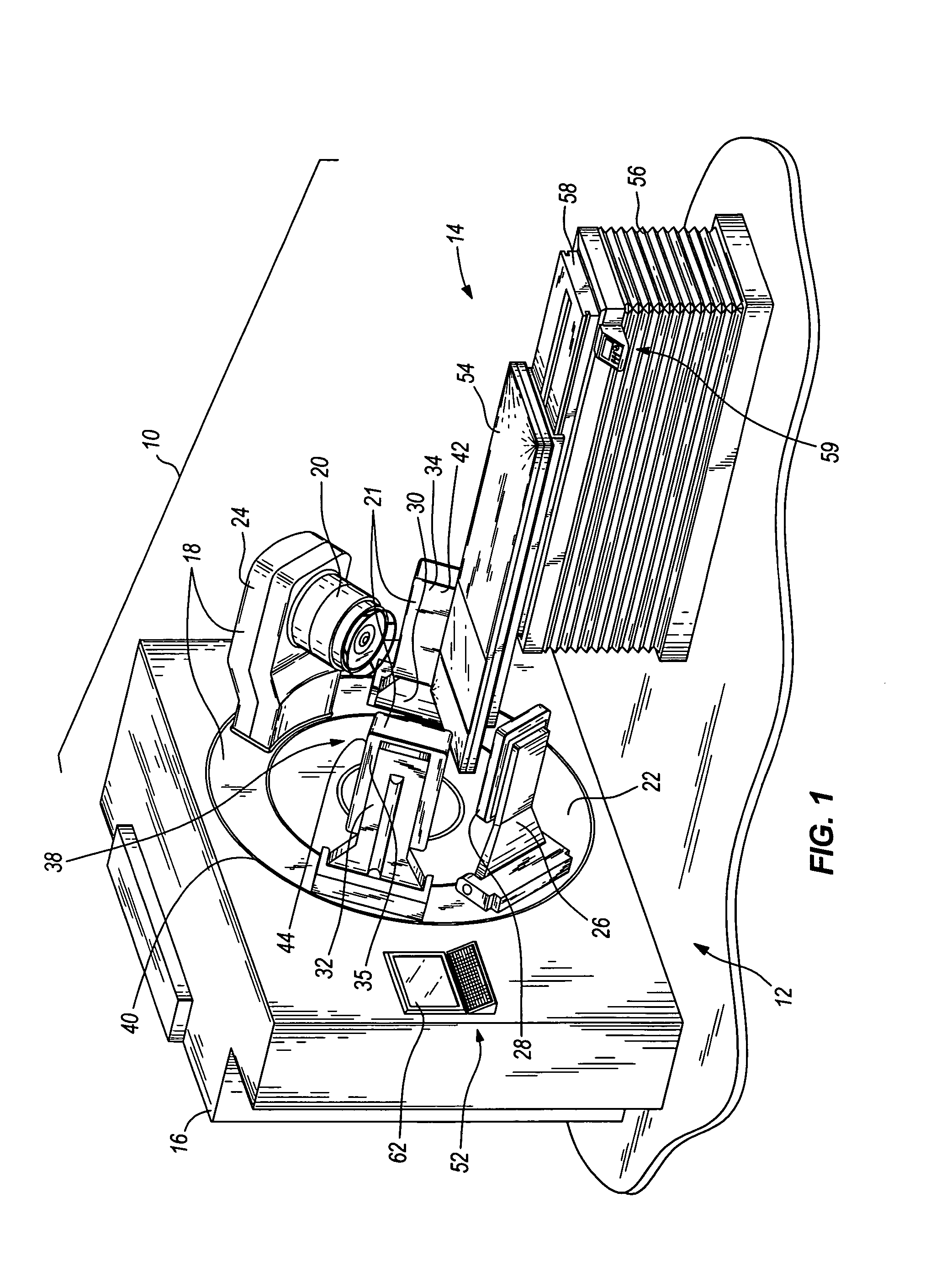
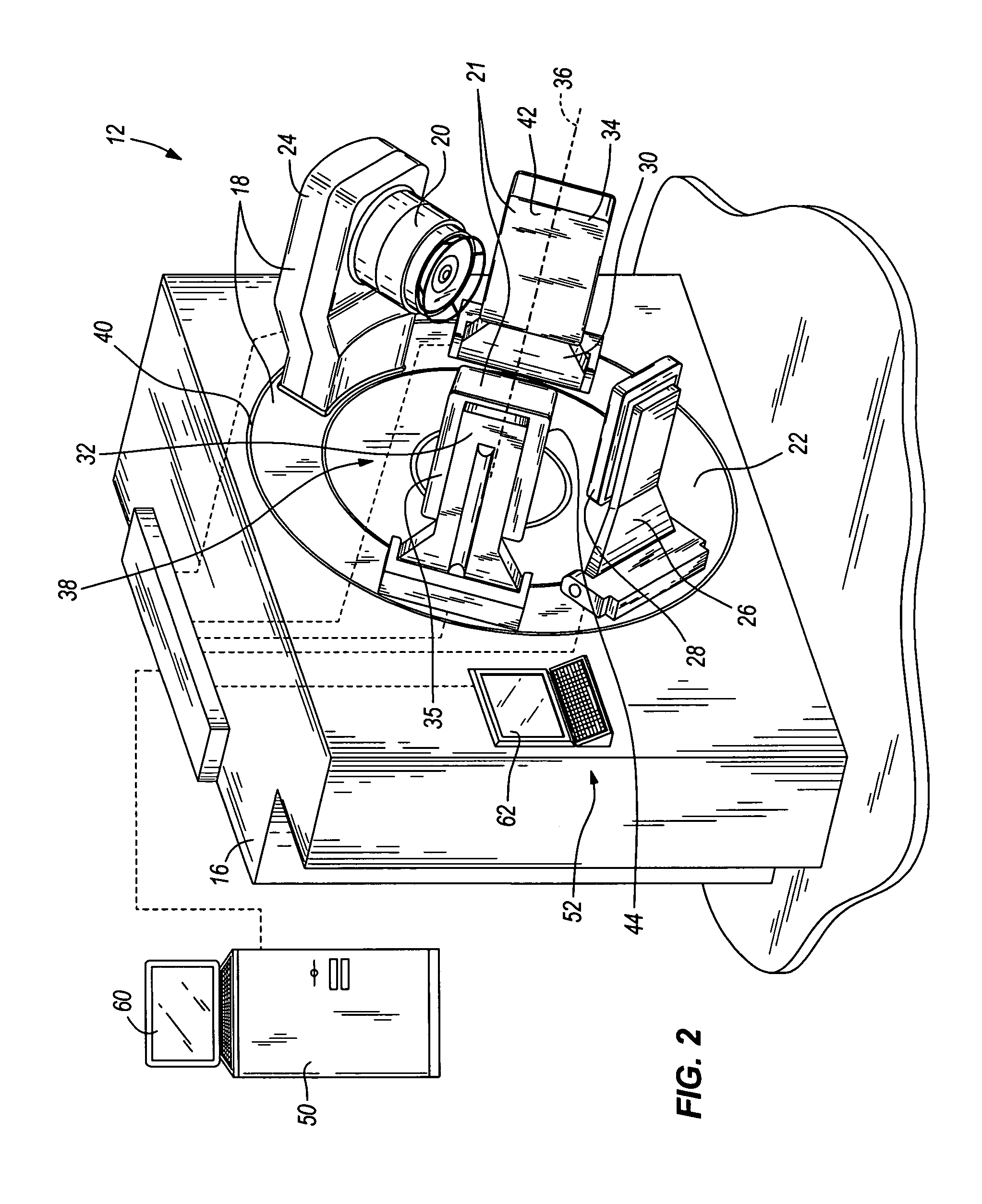
ActiveUS20060113482A1Image is differentSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansGamma rayImaging equipment
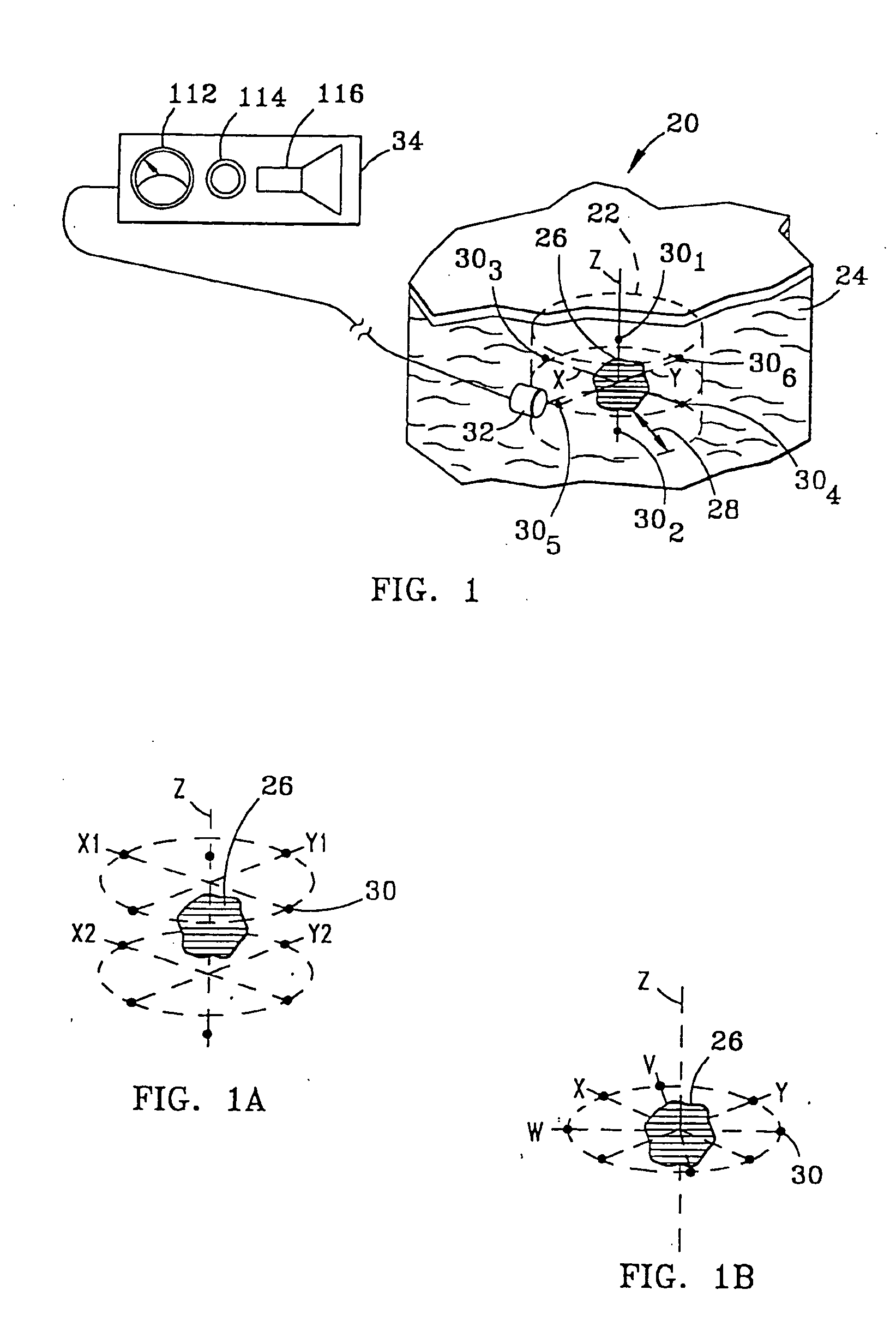
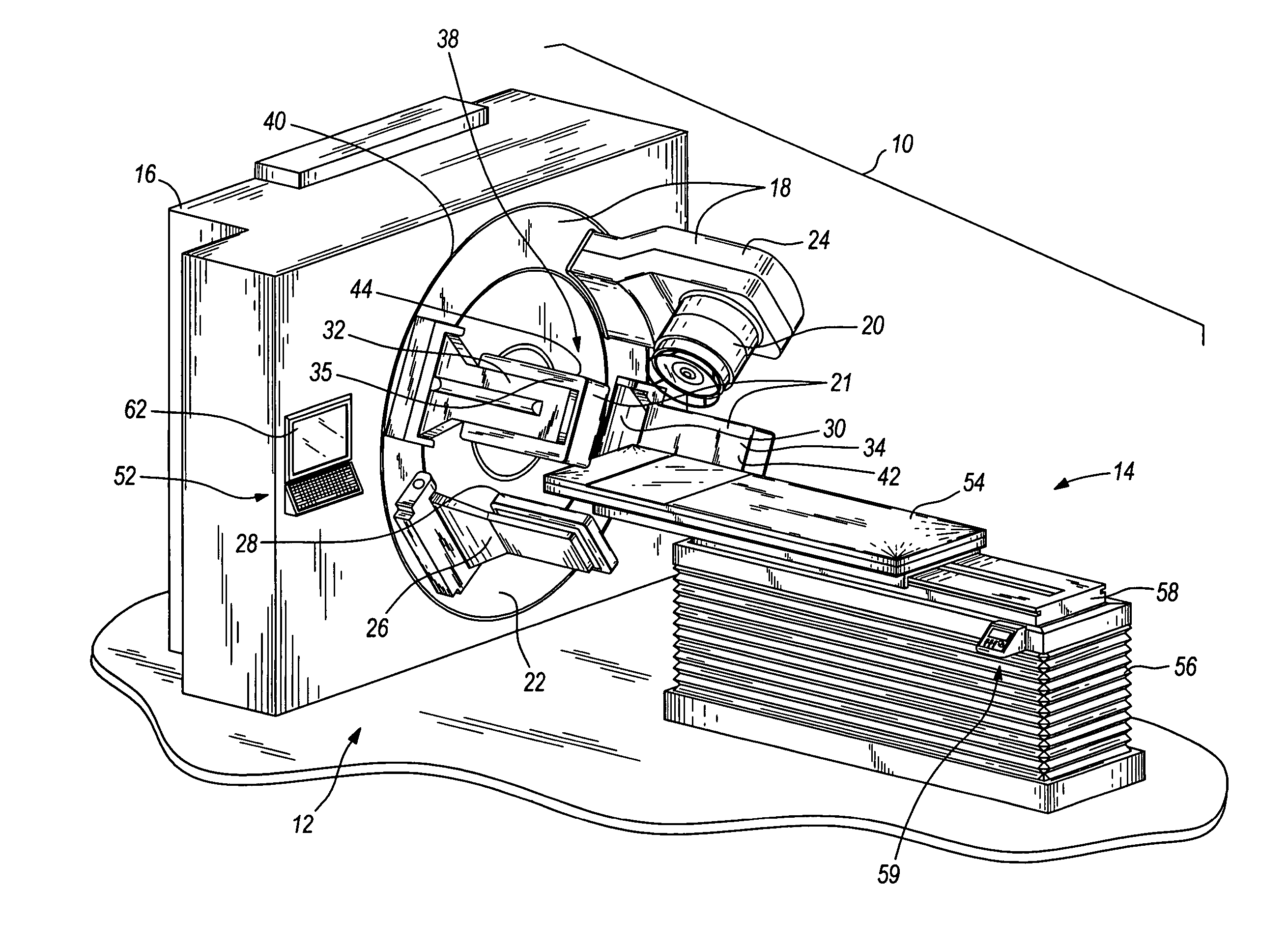
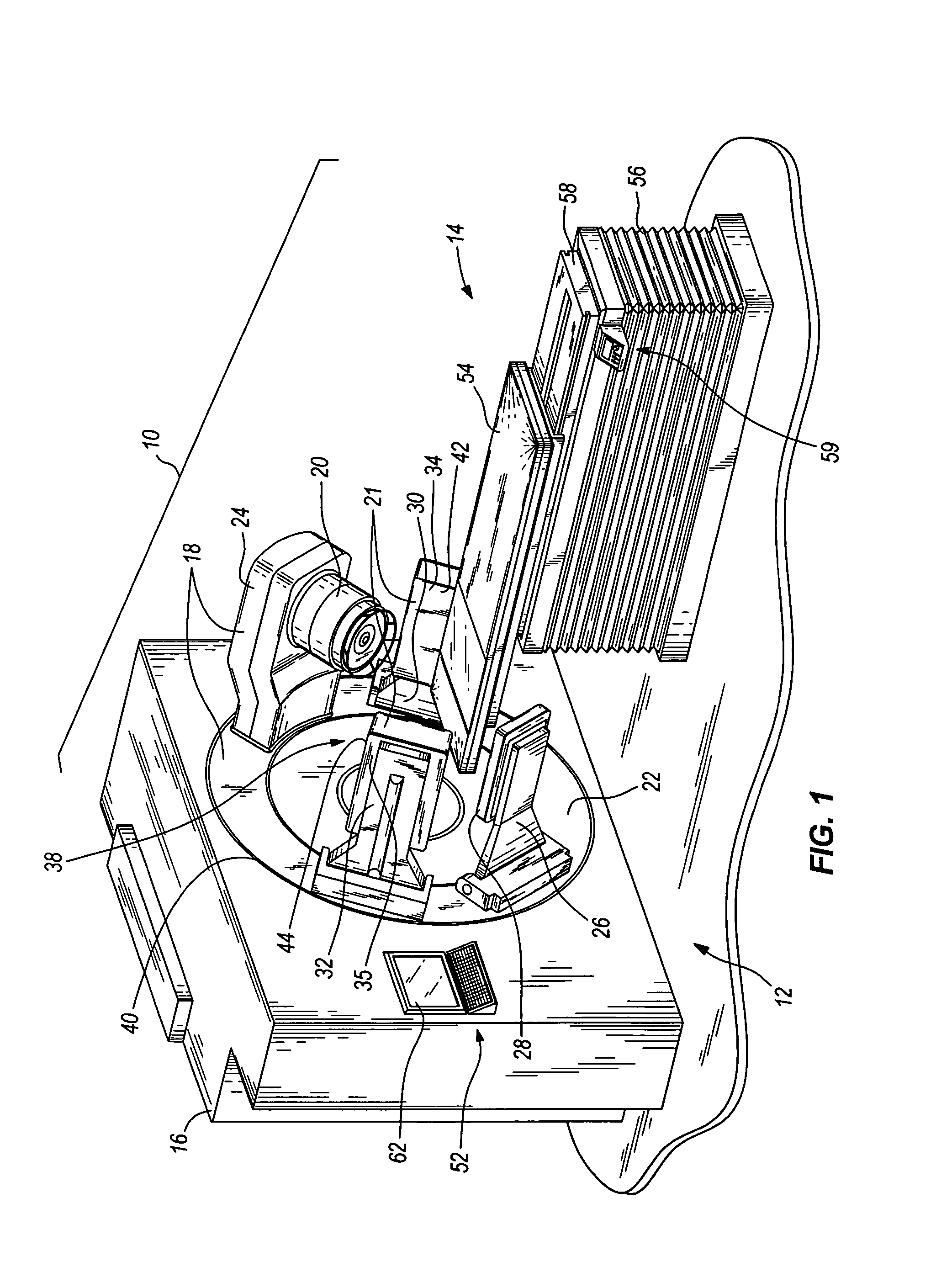
In some embodiments, an image-guided radiotherapy apparatus and method is provided in which a radiotherapy radiation source and a gamma ray photon imaging device are positioned with respect to a patient area so that a patient can be treated by a beam emitted from the radiotherapy apparatus and can have images taken by the gamma ray photon imaging device. Radiotherapy treatment and imaging can be performed substantially simultaneously and / or can be performed without moving the patient in some embodiments. The gamma ray photon imaging device can be coupled and movable with respect to any part of a building structure, can be located on a portable frame movable to and from the radiotherapy radiation source and patient, or can take other forms. In some embodiments, the gamma ray photon imaging device can be used for imaging in connection with other types of medical interventions.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Optical device for directing x-rays having a plurality of optical crystals
InactiveUS7035374B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionSoft x rayHigh energy
Devices for improving the capturing and utilization of high-energy electromagnetic radiation, for example, x-rays, gamma rays, and neutrons, for use in physical, medical, and industrial analysis and control applications are disclosed. The devices include optics having a plurality of optical crystals, for example, doubly-curved silicon or germanium crystals, arranged to optimize the capture and redirection of divergent radiation via Bragg diffraction. In one aspect, a plurality of optic crystals having varying atomic diffraction plane orientations are used to capture and focus divergent x-rays upon a target. In another aspect, a two- or three-dimensional matrix of crystals is positioned relative to an x-ray source to capture and focus divergent x-rays in three dimensions.
Owner:X-RAY OPTICAL SYSTEM INC
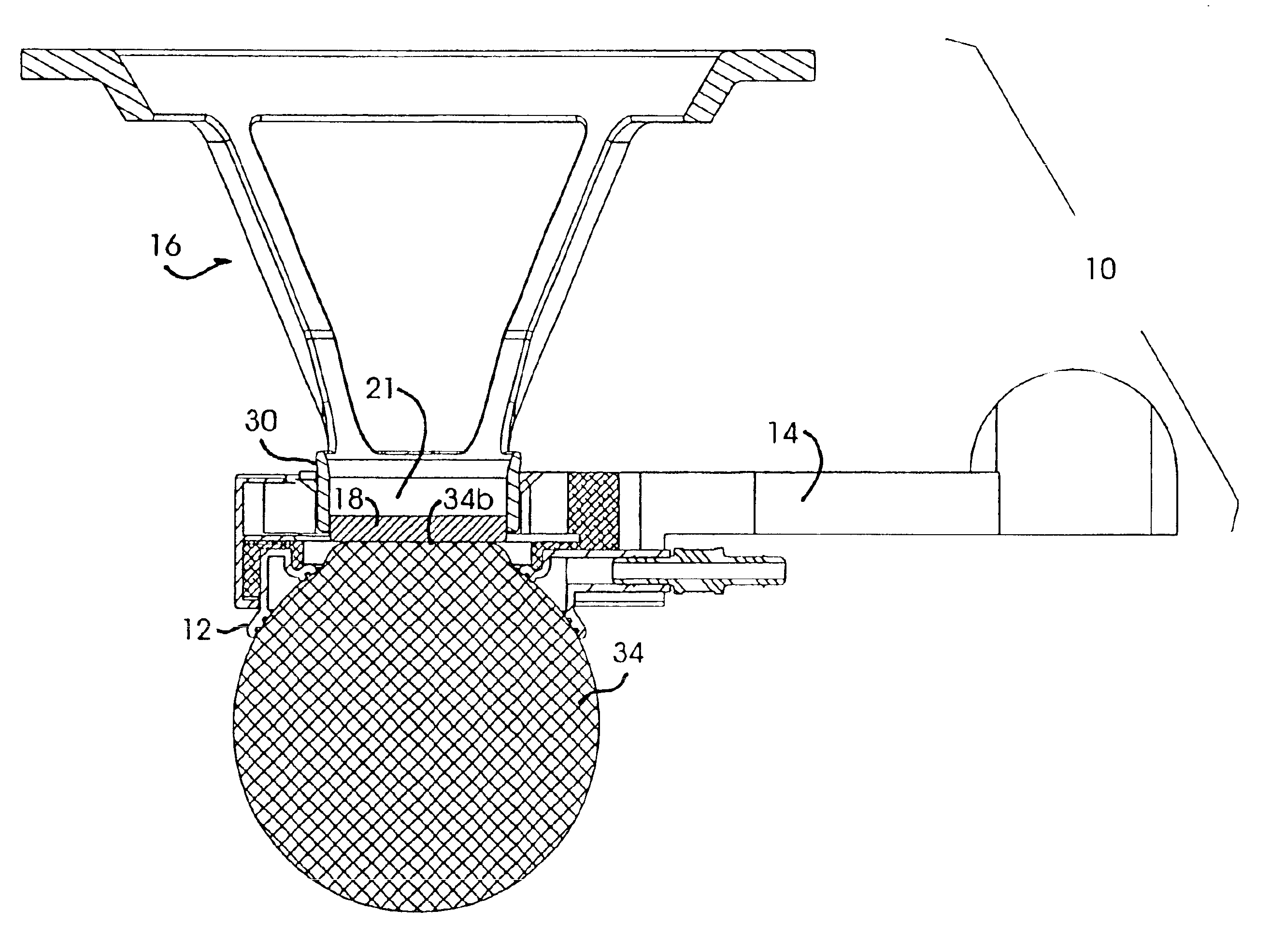
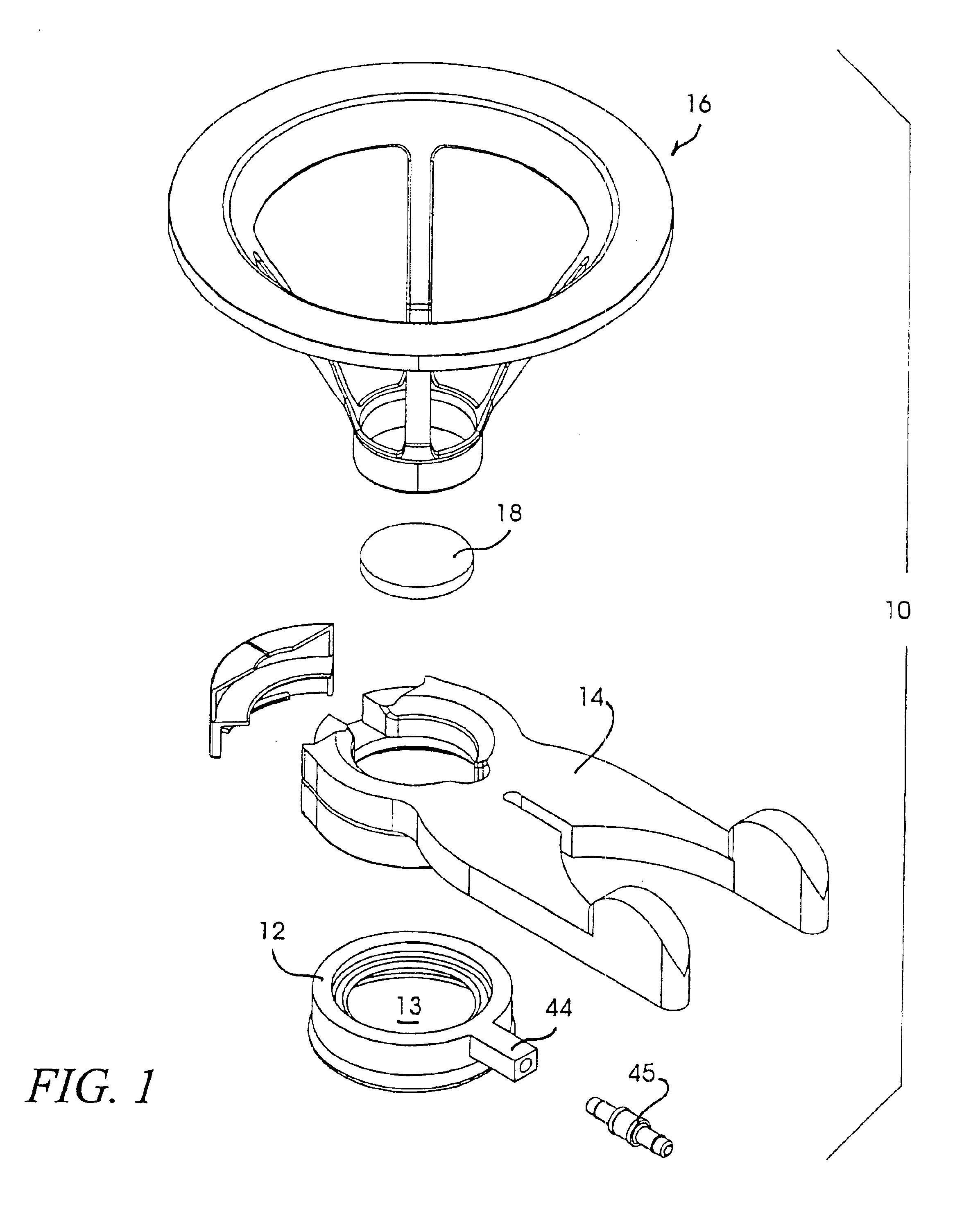
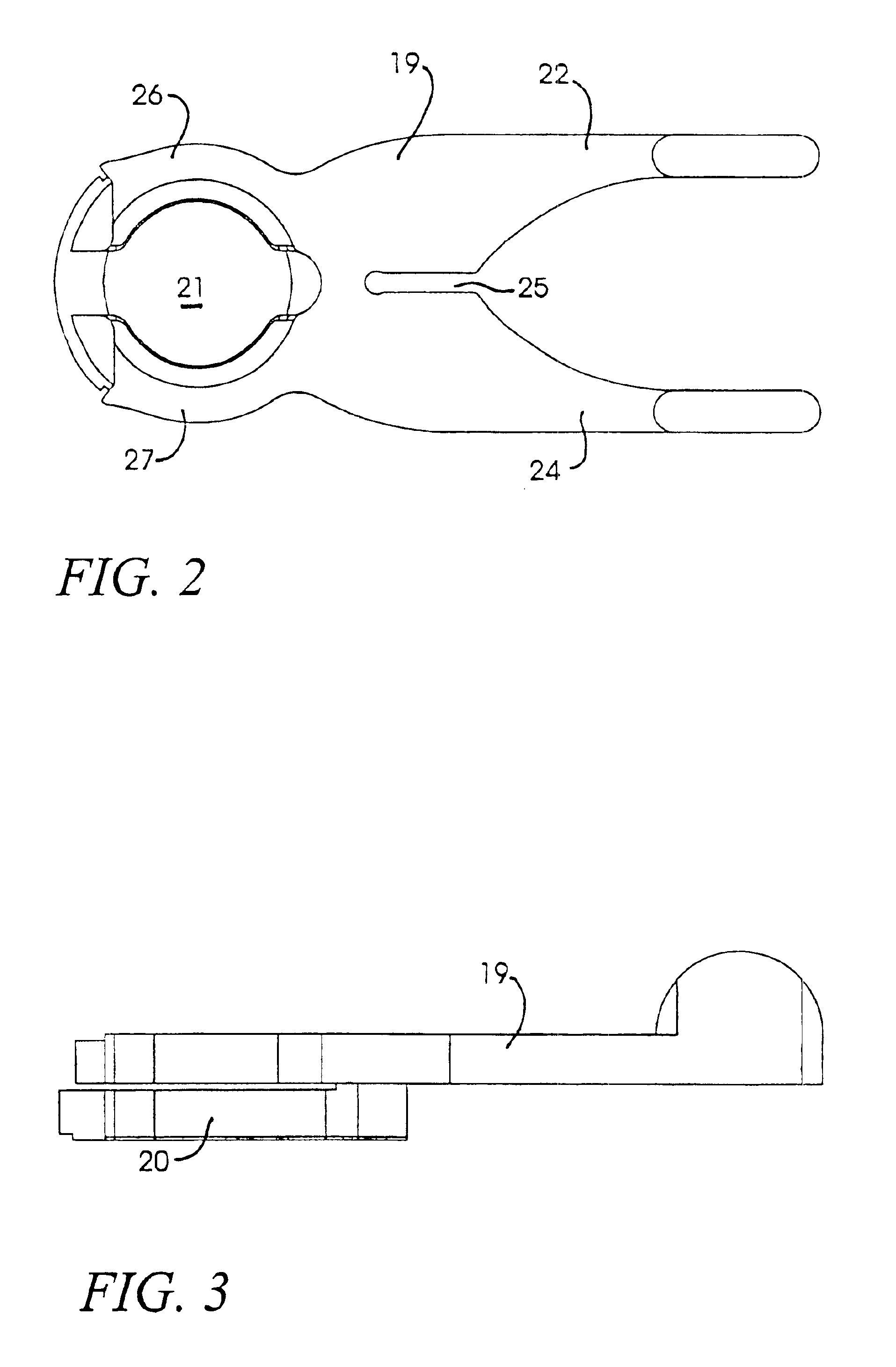
Applanation lens and method for ophthalmic surgical applications
InactiveUS6899707B2Guaranteed stable engagementResist discolorationLaser surgeryDiagnosticsHigh energyTransmittance
An improved applanation lens and method for use in an interface between a patient's eye and a surgical laser system does not discolor or lose light transmittance when subjected to gamma radiation. The improved applanation lens has an applanation surface configured to contact the eye upon application of a pressure. The lens is formed of high purity silicon dioxide (SiO2) with purity great enough to resist discoloration upon prolonged irradiation by high-energy radiation such as UV, x-rays, gamma rays or neutrons, and is preferably a fused silica.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
System and method for bracketing and removing tissue
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
Image-guided medical intervention apparatus and method
ActiveUS7265356B2Image is differentSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansGamma rayNuclear medicine
In some embodiments, an image-guided radiotherapy apparatus and method is provided in which a radiotherapy radiation source and a gamma ray photon imaging device are positioned with respect to a patient area so that a patient can be treated by a beam emitted from the radiotherapy apparatus and can have images taken by the gamma ray photon imaging device. Radiotherapy treatment and imaging can be performed substantially simultaneously and / or can be performed without moving the patient in some embodiments. The gamma ray photon imaging device can be coupled and movable with respect to any part of a building structure, can be located on a portable frame movable to and from the radiotherapy radiation source and patient, or can take other forms. In some embodiments, the gamma ray photon imaging device can be used for imaging in connection with other types of medical interventions.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
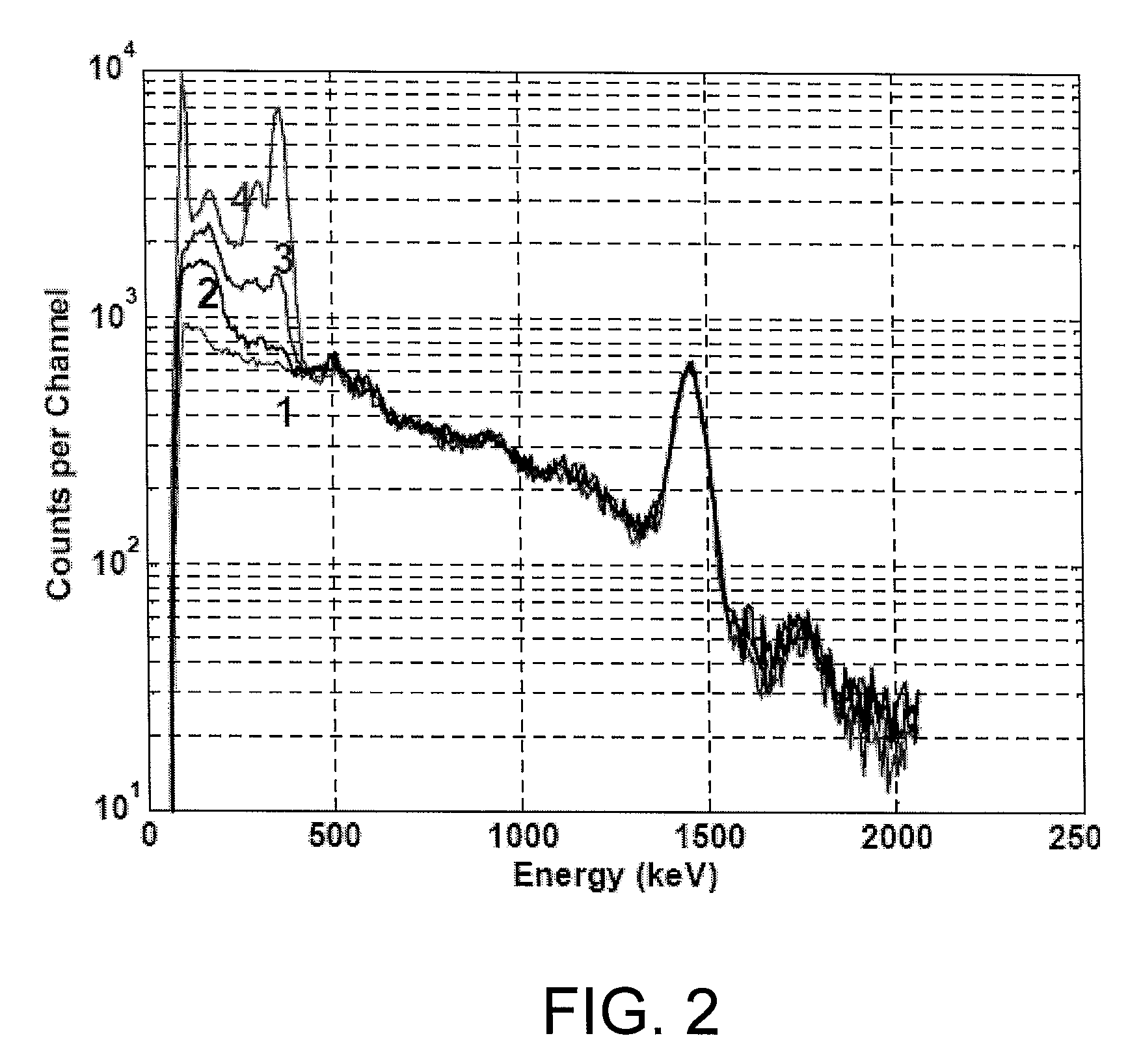
Inverse ratio of gamma-ray and neutron emissions in the detection of radiation shielding of containers
InactiveUS7116235B2Reduce instabilityTrolley cranesX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentNeutron emissionGamma ray
Owner:VERITAINER ASSET HLDG LLC
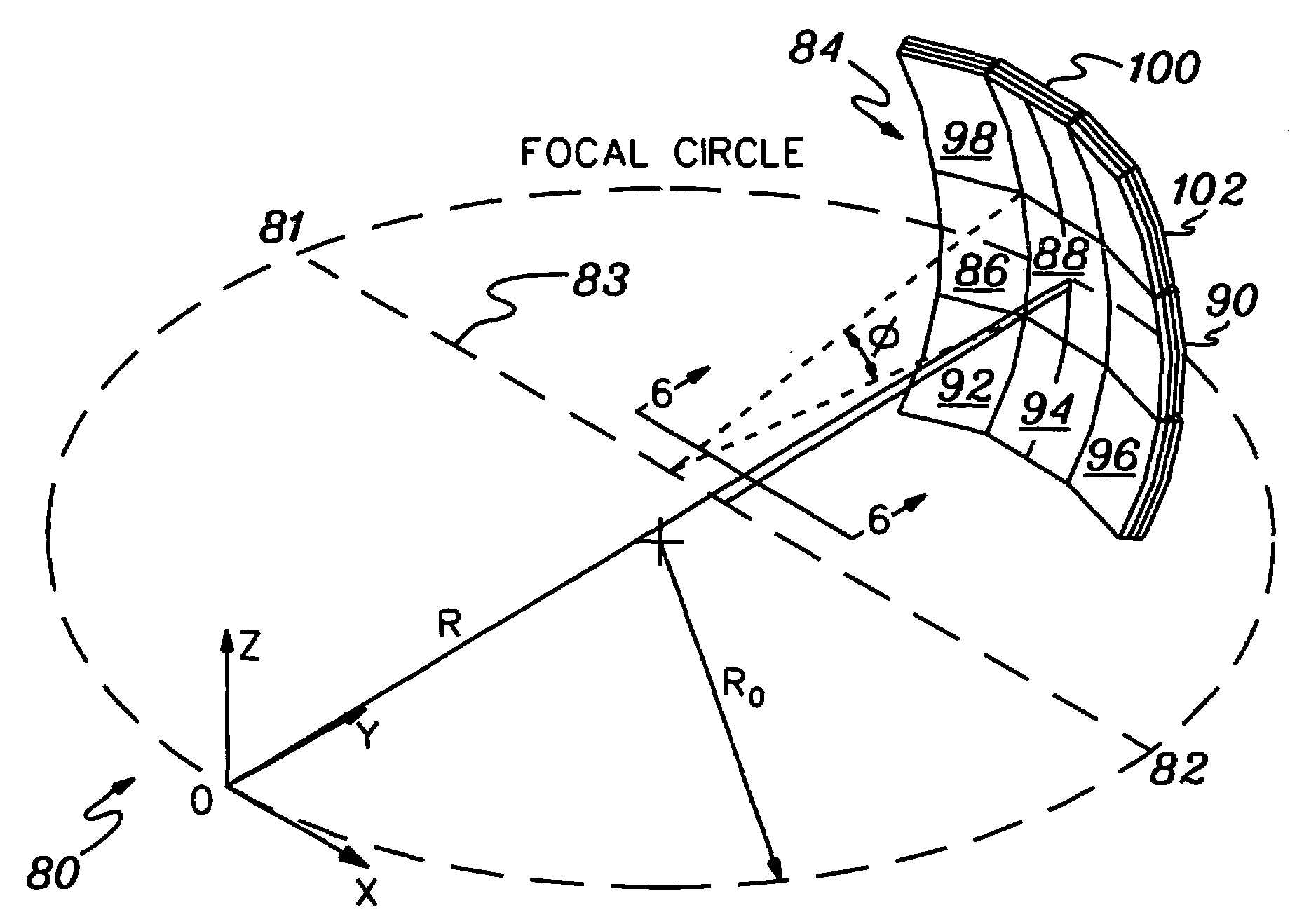
Edge-on SAR scintillator devices and systems for enhanced spect, pet, and compton gamma cameras
InactiveUS20090134334A1Improved SAR resolutionReduce photodetector readout noiseSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansHigh energyX-ray
The invention provides methods and apparatus for detecting radiation including x-ray, gamma ray, and particle radiation for nuclear medicine, radiopaphic imaging, material composition analysis, high energy physics, container inspection, mine detection and astronomy. The invention provides detection systems employing one or more detector modules (102) comprising edge-on scintillator detectors (101) with sub-aperture resolution (SAR) capability employed, e.g., in nuclear medicine, such as radiation therapy portal imaging, nuclear remediation, mine detection, container inspection, and high energy physics and astronomy. The invention also provides edge-on imaging probe detectors for use in nuclear medicine, such as radiation therapy portal imaging, or for use in nuclear remediation, mine detection, container inspection, and high energy physics and astronomy.
Owner:MINNESOTA IMAGING & ENG
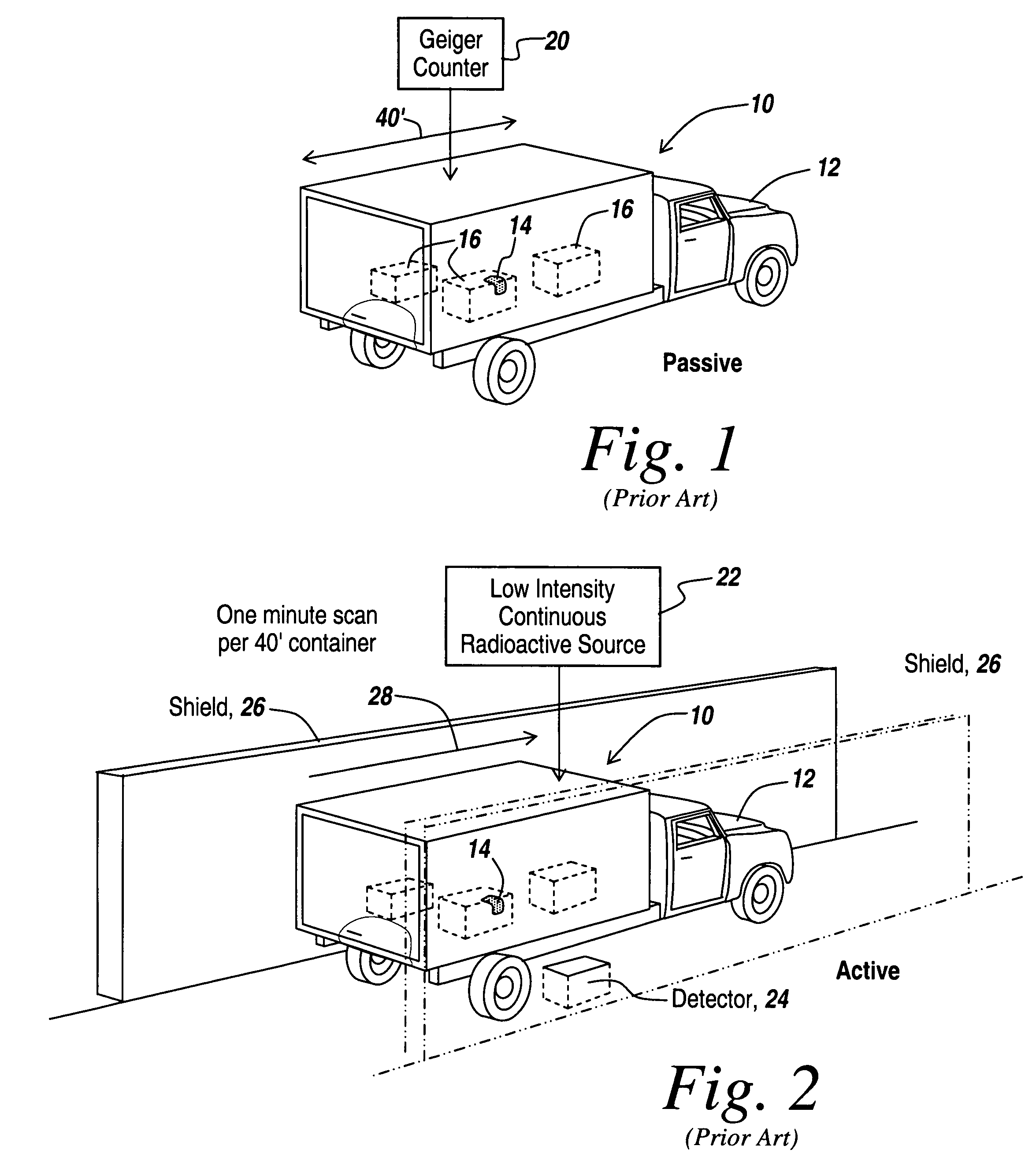
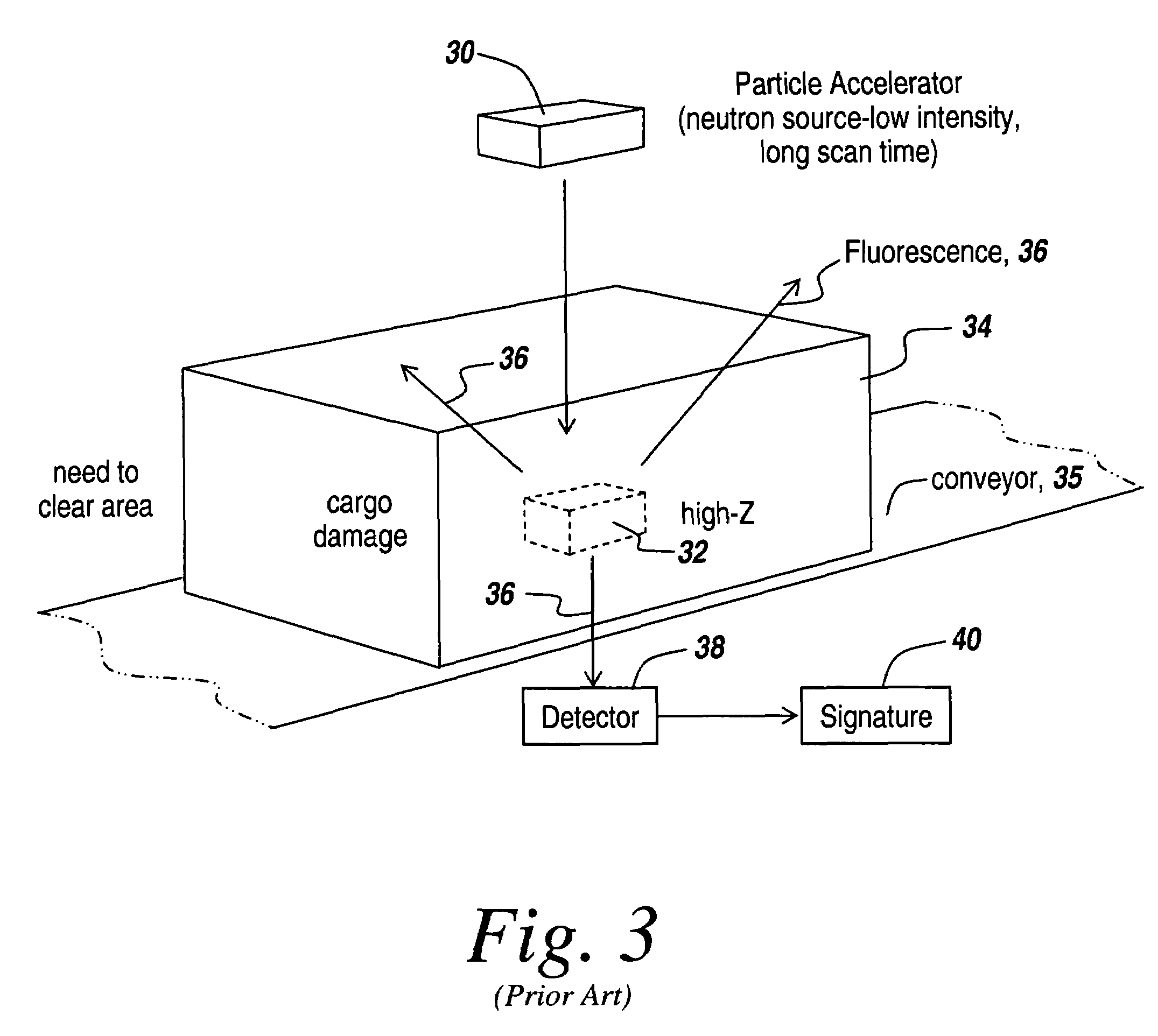
Method and apparatus for the safe and rapid detection of nuclear devices within containers
ActiveUS7379530B2Faster scan timeAccurate detectionX-ray apparatusMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationDisplay deviceHigh intensity
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
A method and apparatus for detection of radioactive materials
InactiveUS20070001123A1Enhanced gamma ray sensitivityReducing background radiation interferenceMeasurement by spectrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansImage resolutionHigh energy
In the present invention there is a provided an array of radiation detectors comprising at least one detector capable of detecting both low and high energy gamma radiation and adapted to provide spectrometric identification of the gamma source; at least one detector capable of detecting and providing spectrometric identification of fast neutrons and low resolution gamma spectra; at least one detector adapted to detect thermal neutrons; and, at least one plastic scintillator to give enhanced gamma ray sensitivity.
Owner:BUBBLE TECH INDS
Inverse ratio of gamma-ray and neutron emissions in the detection of radiation shielding of containers
InactiveUS20050275545A1Reduce instabilityTrolley cranesX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentNeutron emissionGamma ray
The presence of radiation shielding material concealing illegitimate content in a container is detected by obtaining each of measured gamma-ray data and measured neutron data from the container, and comparing the measured gamma-ray and neutron data to expected gamma-ray and neutron data. An anomaly between the measured data and the expected data is an indicum of the presence of such material shielding such illegitimate content.
Owner:VERITAINER ASSET HLDG LLC
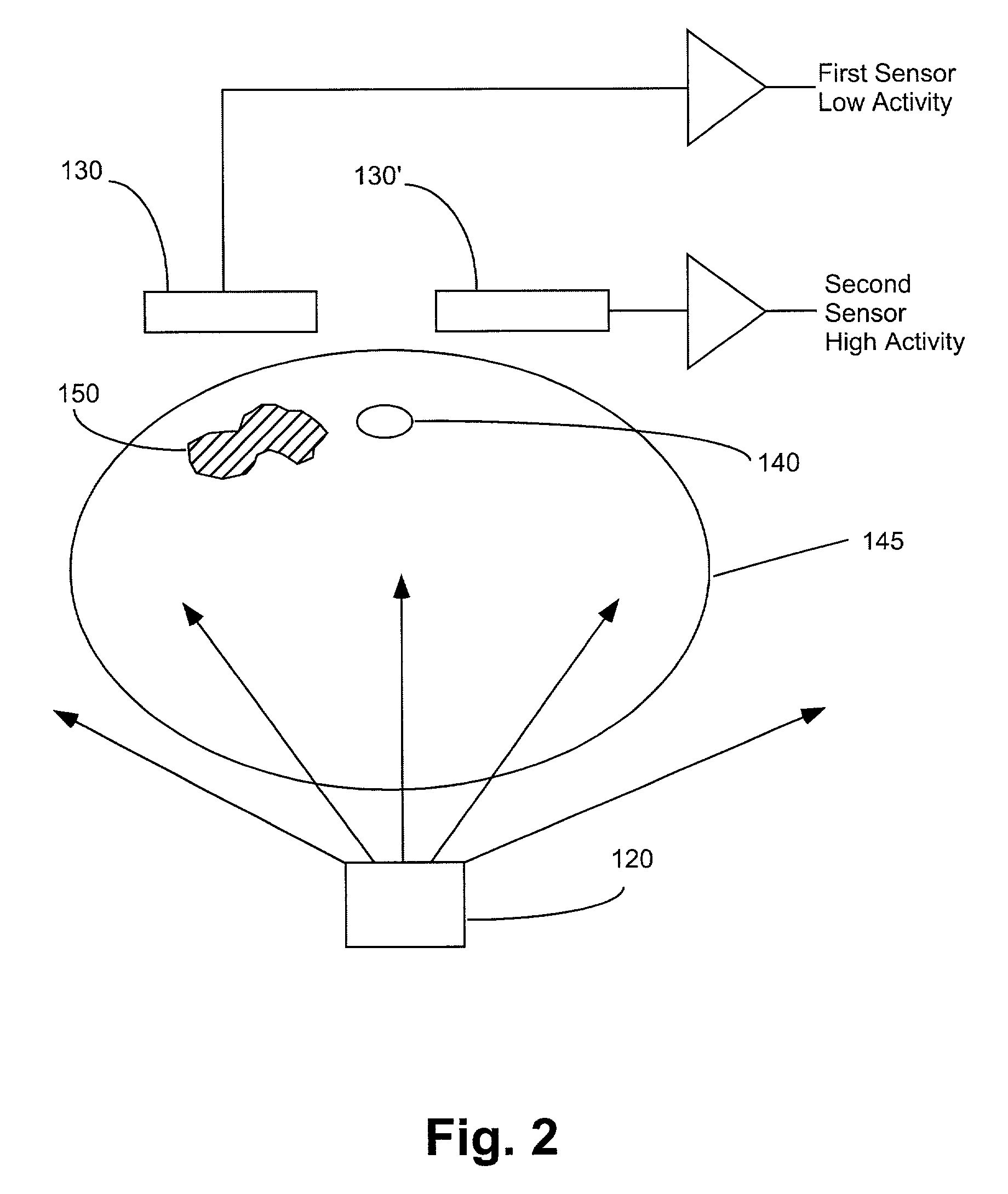
Apparatuses, systems and methods for extravasation detection
InactiveUS7047058B1Enhance the imageSensitive measurementUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis using microwave meansMedicineX-ray
An apparatus for the detection of extravasation in an imaging procedure includes at least a first source of energy to supply imaging energy to tissue in the vicinity of a site and at least a first sensor to measure a signal resulting from the energy supplied to the tissue by the first imaging energy source. In preferred embodiment, the energy may be one of X-ray, gamma ray or ultrasound energy.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
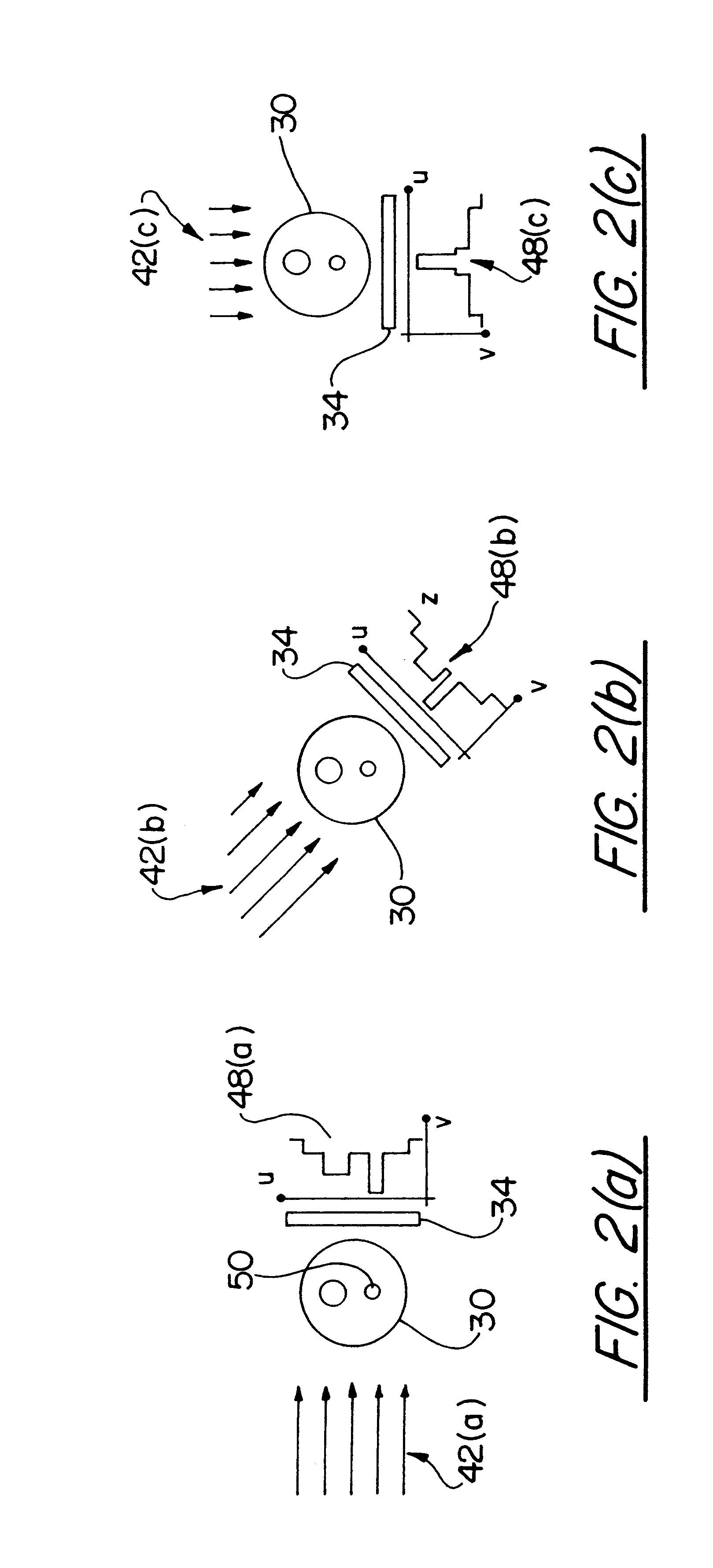
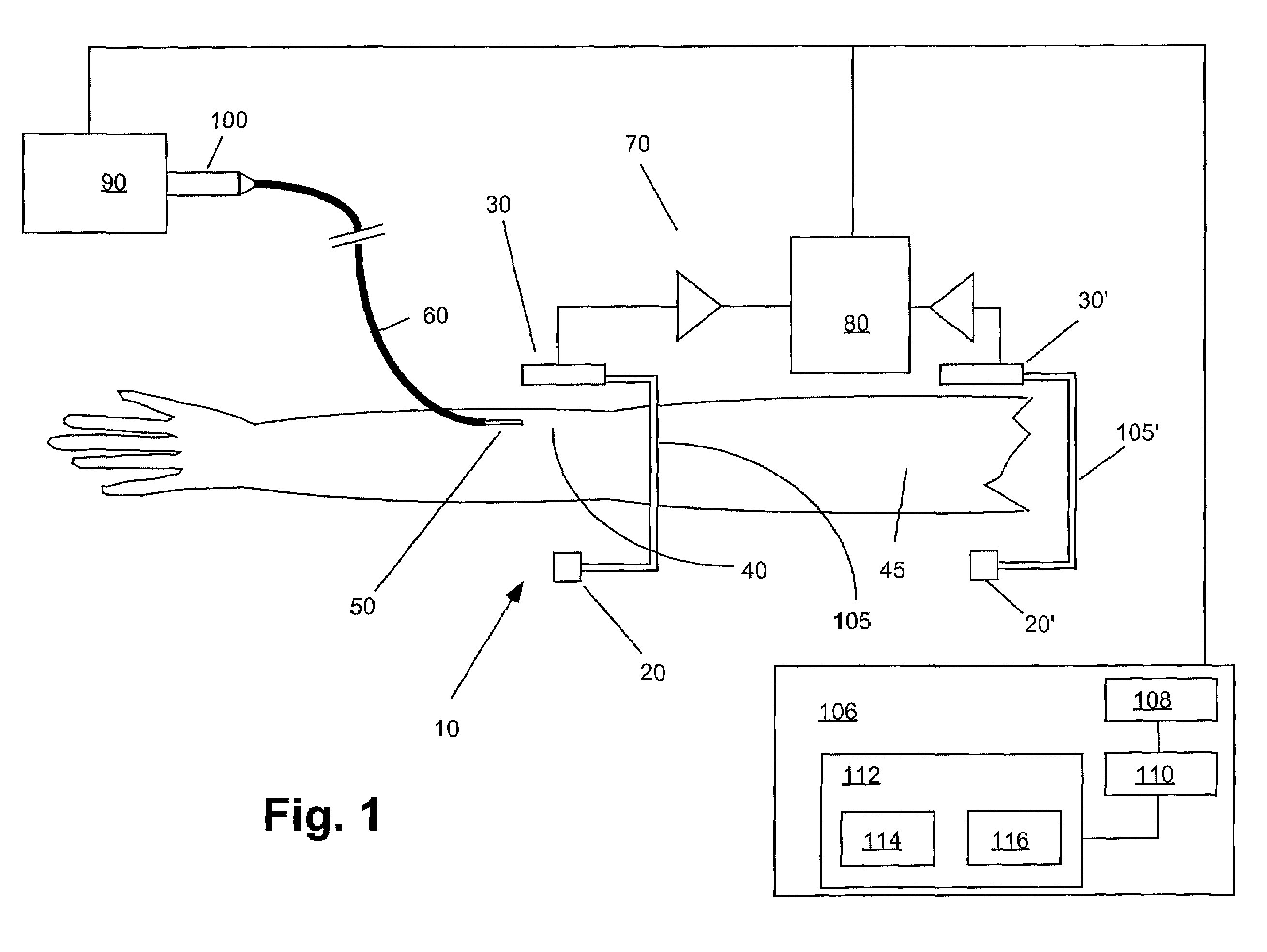
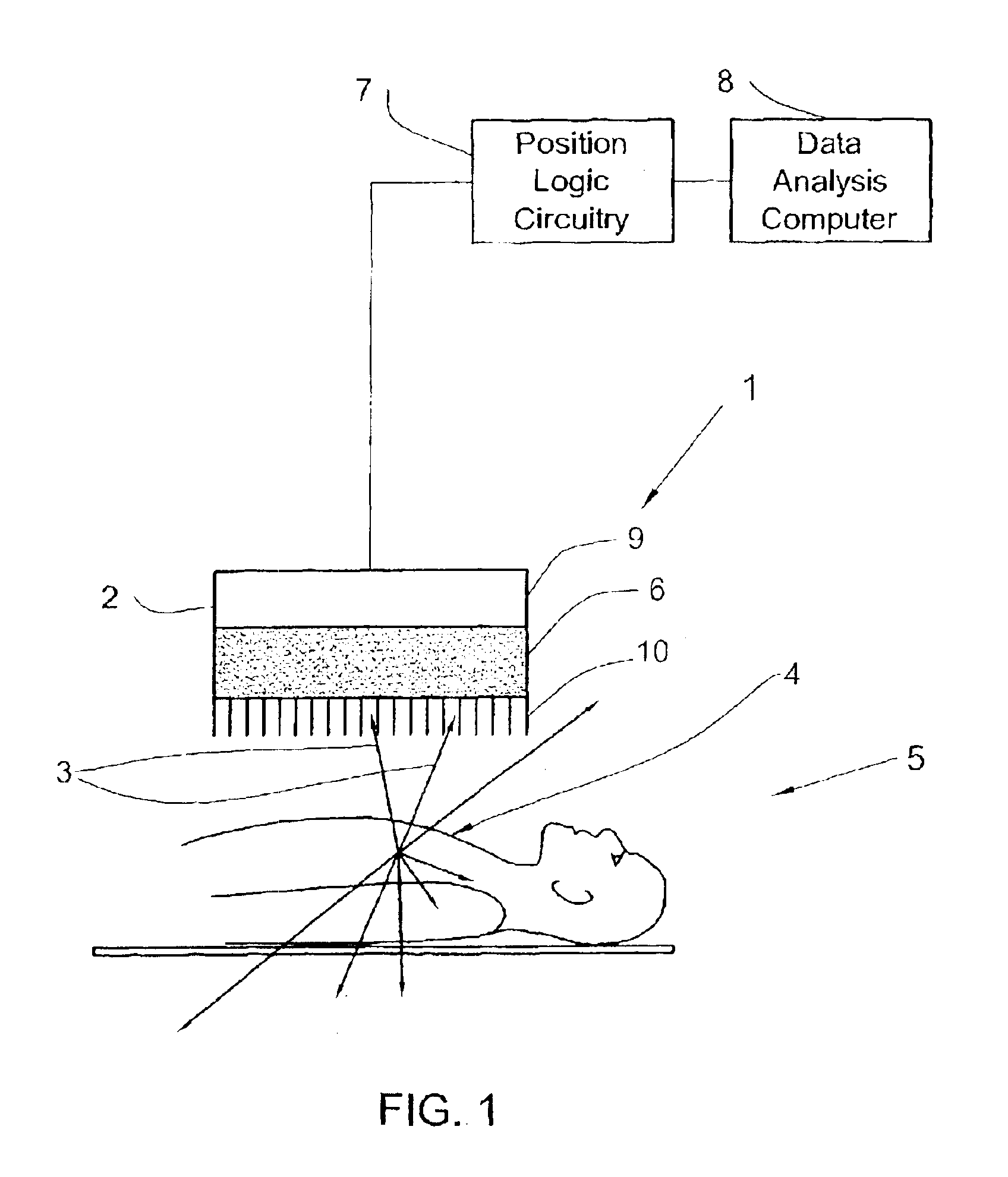
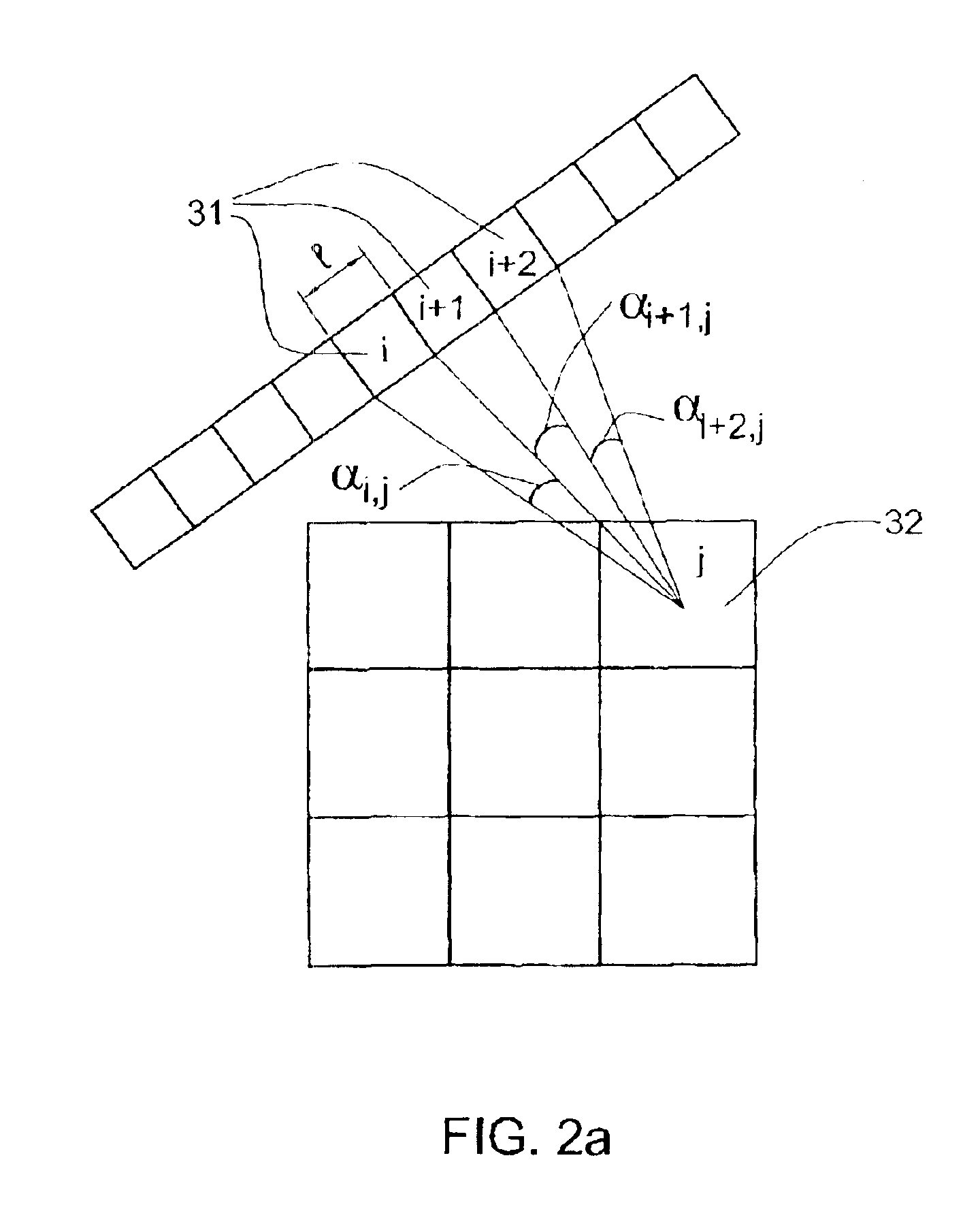
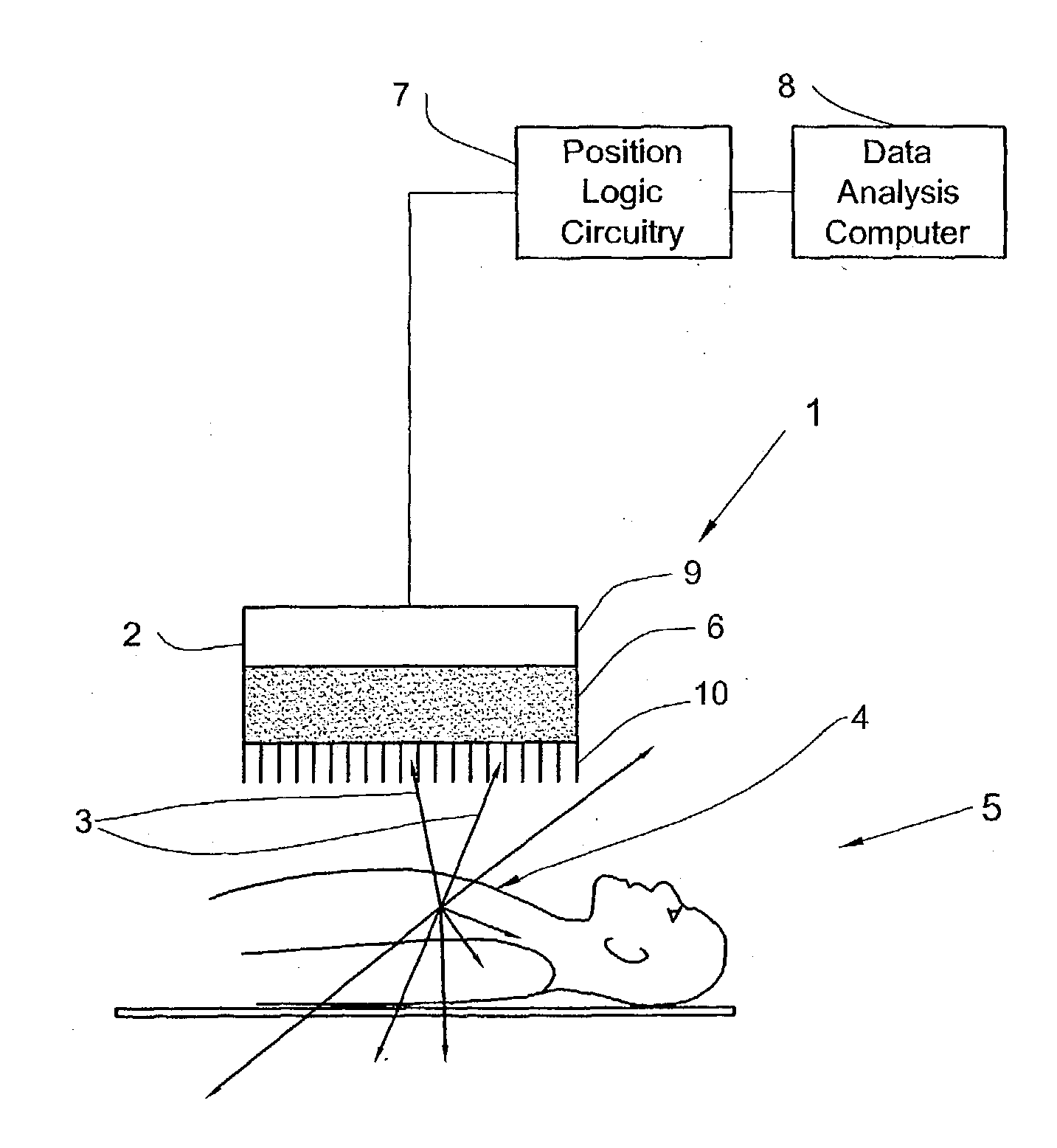
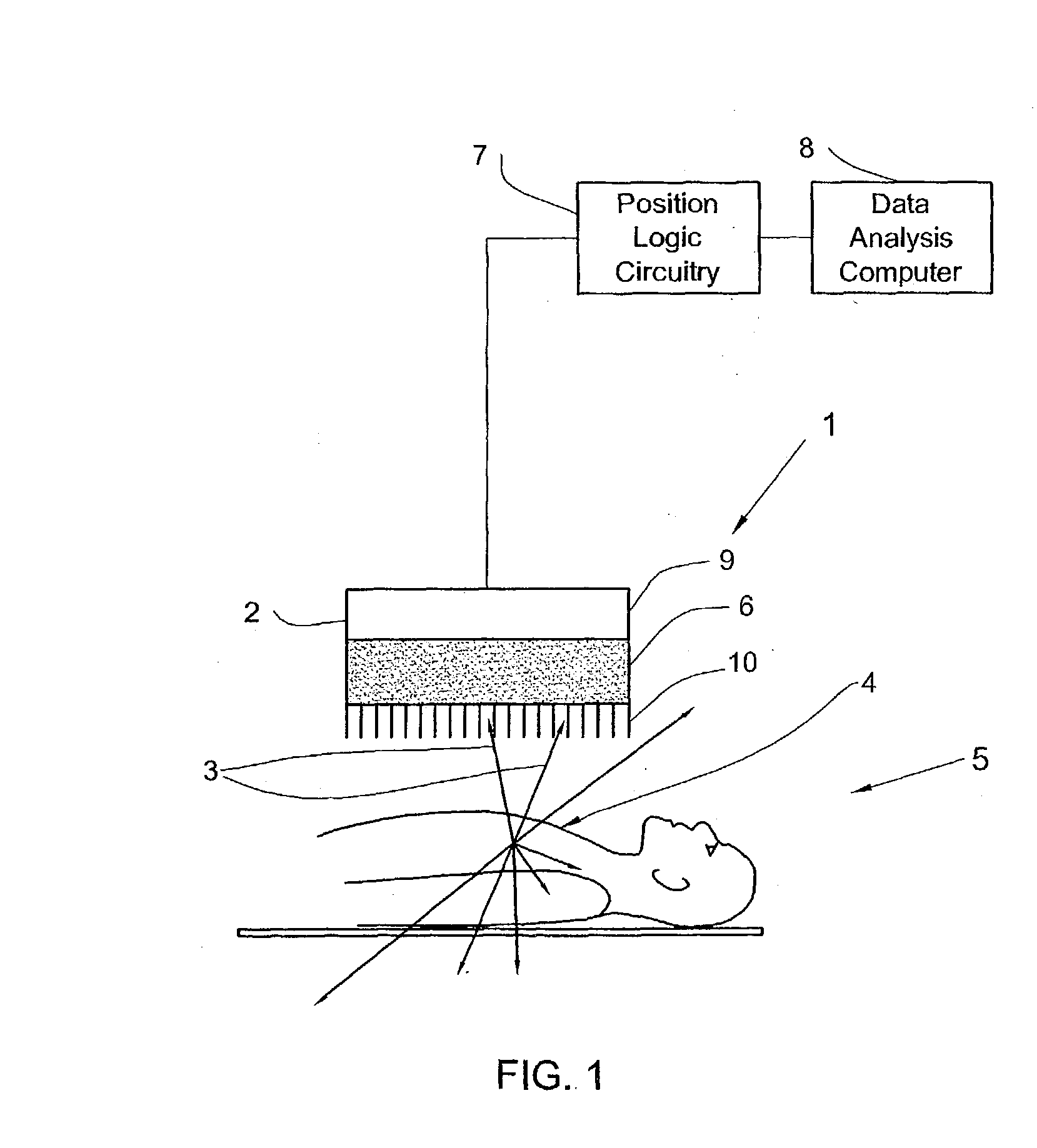
SPECT gamma camera
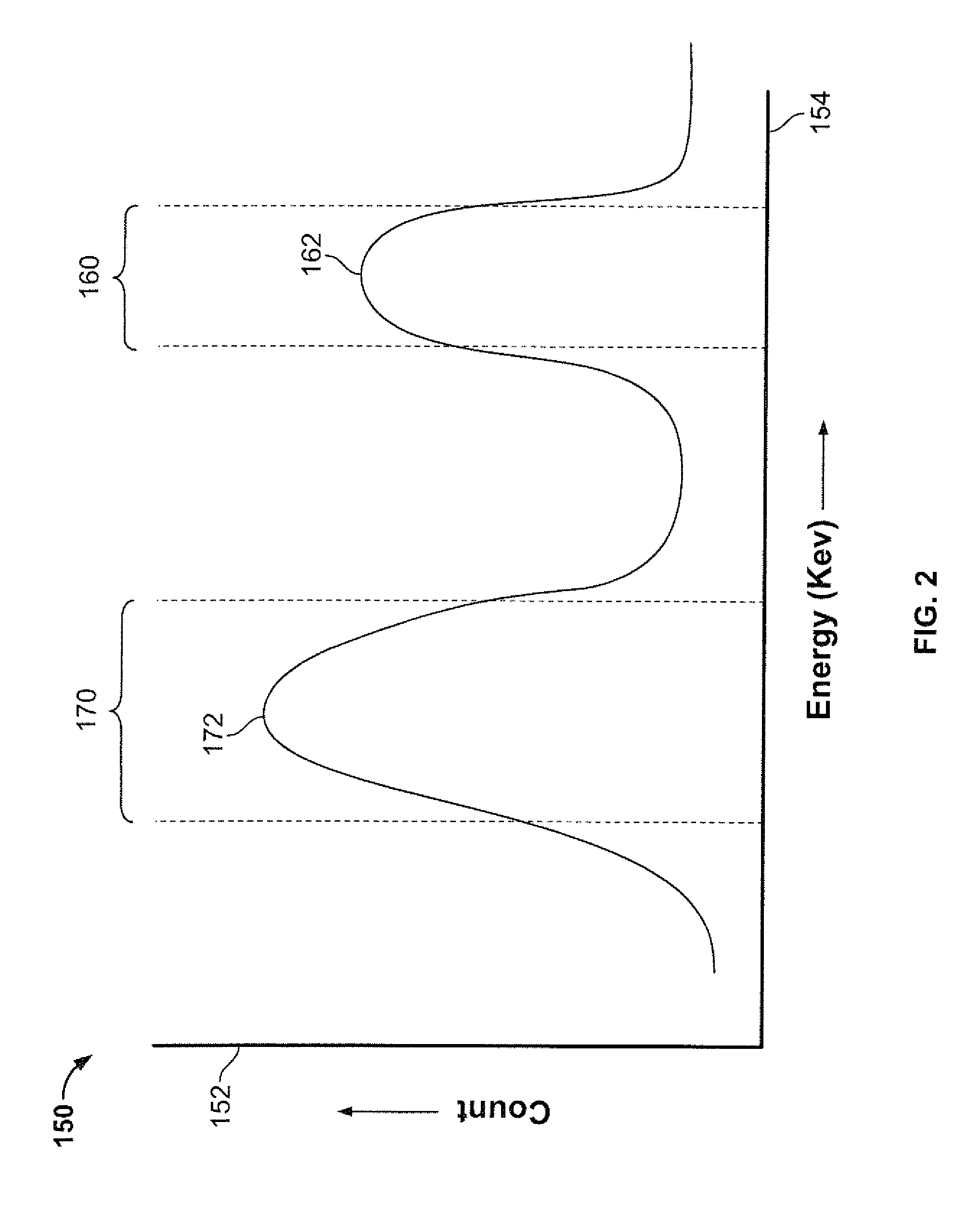
InactiveUS6943355B2Improve imaging resolutionEnhance the imageMaterial analysis by optical meansDiagnostic recording/measuringSingle photon emission computerized tomographyGamma ray
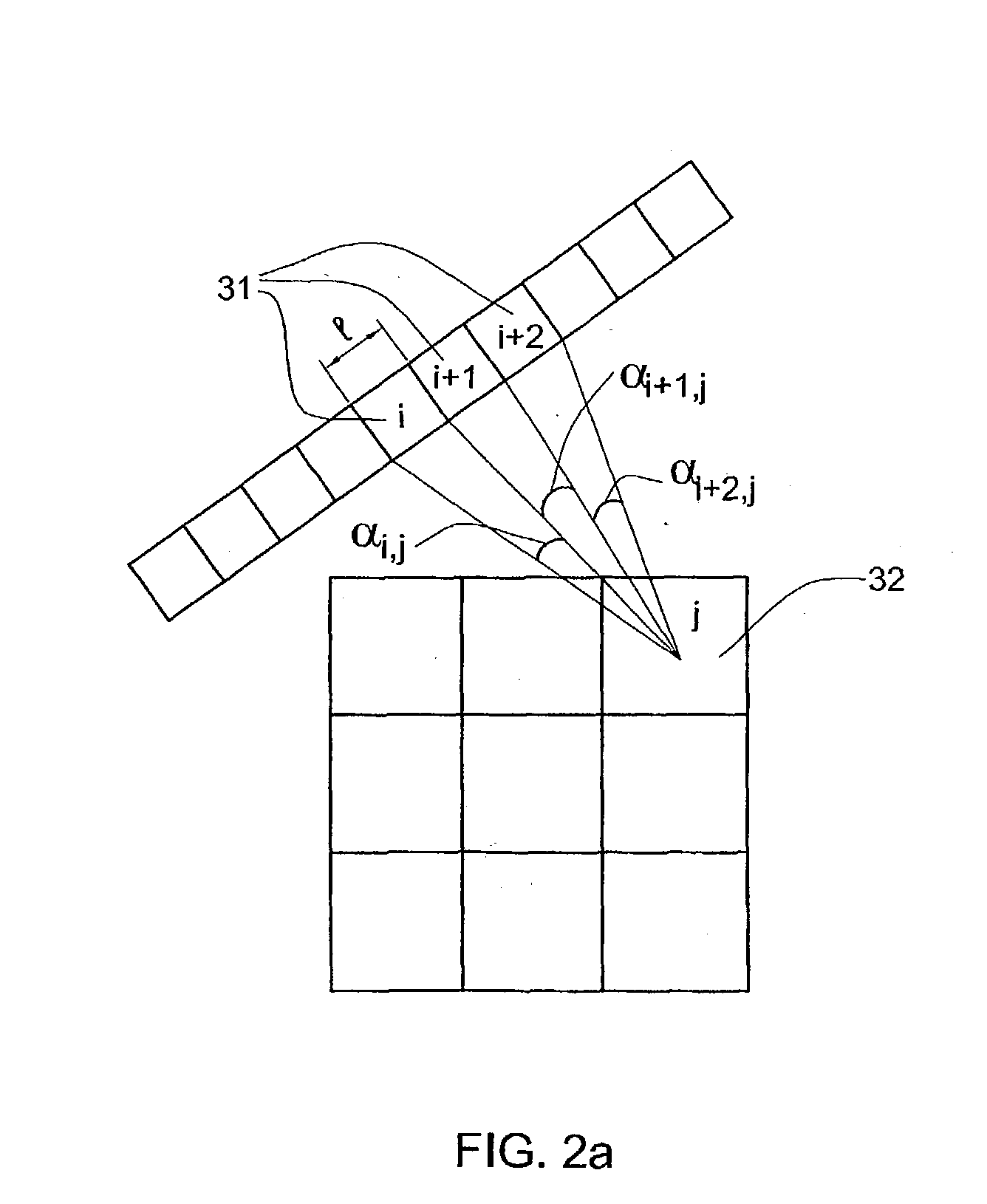
A method and apparatus of obtaining and reconstructing an image of a portion of a body, administered by a radiopharmaceutical substance, by using Single-photon emission computerized tomography (SPECT) for determination of functional information thereon. The method comprises (a) acquiring gamma ray photons emitted from said portion by means of a detector capable of converting the photons into electric signals, the detector having at least one crystal and allowing said gamma rays having incident angles essentially exceeding 5 degrees and, preferably, exceeding 10 degrees to be detected; (b) processing said electric signals by a position logic circuitry and thereby transforming them into data indicative of positions on said photon detector crystal, where the photons have impinged the detector; and (c) reconstructing an image of a spatial distribution of the pharmaceutical substance within the portion of the body by processing said data and taking into consideration weight values which are functions of angles and, possibly, distances between different elements of the portion of the body and corresponding elements of this position's projection on the detector.
Owner:ULTRASPECT
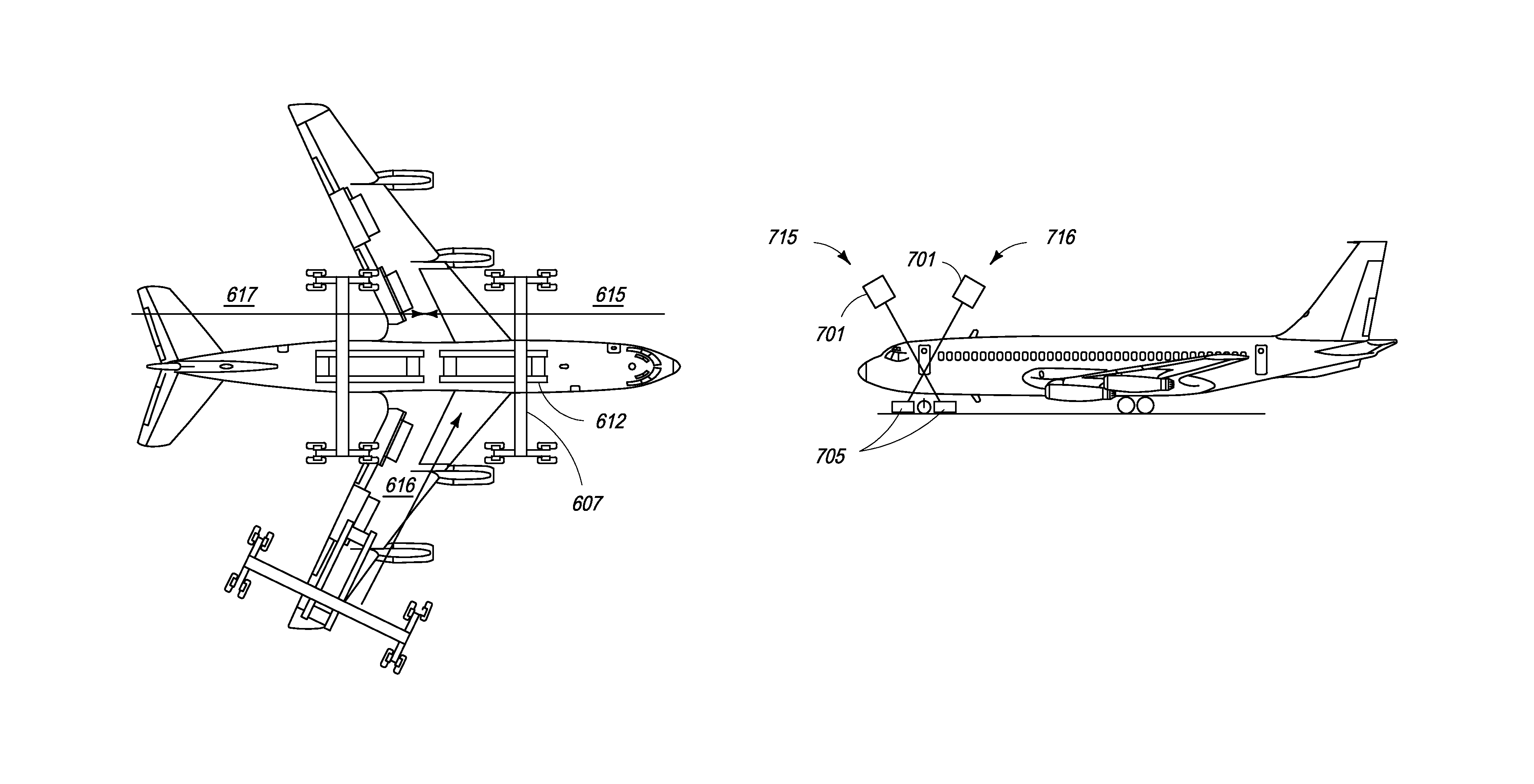
Mobile aircraft inspection system
A system for scanning aircraft for concealed threats is provided. The system comprises a vehicle and a manipulator arm attached with a scanning head that can be maneuvered in multiple directions to completely scan an aircraft from the outside. The system uses transmission based X-ray detection, backscatter based X-ray detection or a combination thereof, in various embodiments. The system also includes gamma-ray and neutron detectors, for detection of nuclear and radioactive materials.
Owner:RAPISCAN SYST INC (US)
Efficient single photon emission imaging
InactiveUS7026623B2Shorten the timeImprove image qualityReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis by optical meansRadioactive drugRadiology
Owner:ULTRASPECT
Logging tool for determination of formation density (embodiments)
InactiveUS20080061225A1Alleviate borehole effectPossible to discriminateNuclear radiation detectionGamma rayIrradiation
An apparatus for investigating underground formations surrounding a borehole, comprises a tool body; a common gamma ray source mounted in the tool body and which, when the apparatus is positioned in a borehole, provides axi-symmetric distribution of gamma rays so as to provide substantially complete circumferential irradiation of the formation surrounding the borehole; and a detector for detecting gamma rays returning from the formation, the detector being responsive to gamma rays from only part of the borehole circumference. A method for investigating underground formations surrounding a borehole with a tool comprising a tool body having a gamma ray source and a detector mounted thereon, comprises irradiating the complete circumference of the borehole wall using a common gamma ray source which provides axi-symmetric distribution of gamma rays; and detecting gamma rays returning from the formation from only part of the borehole circumference.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
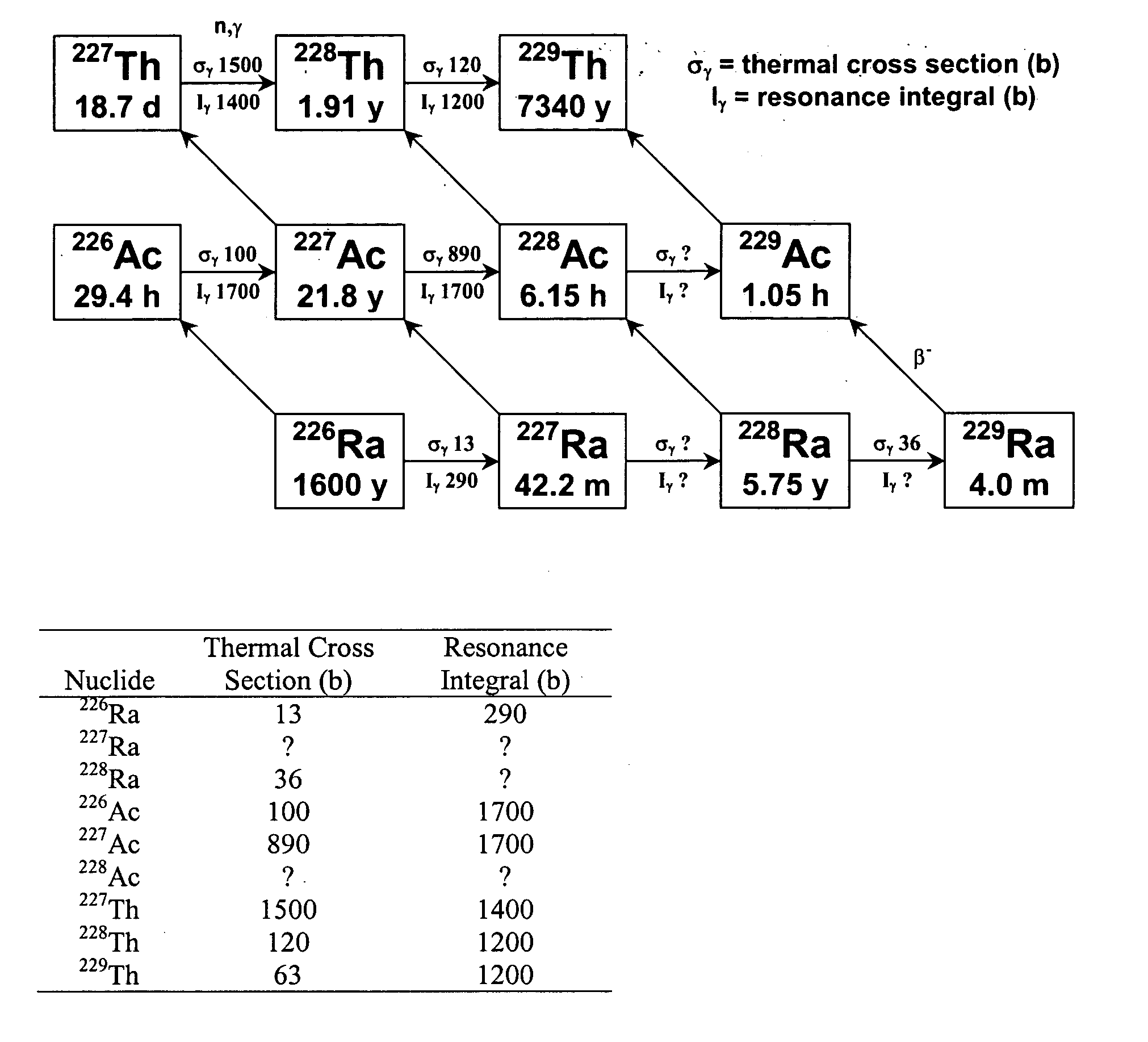
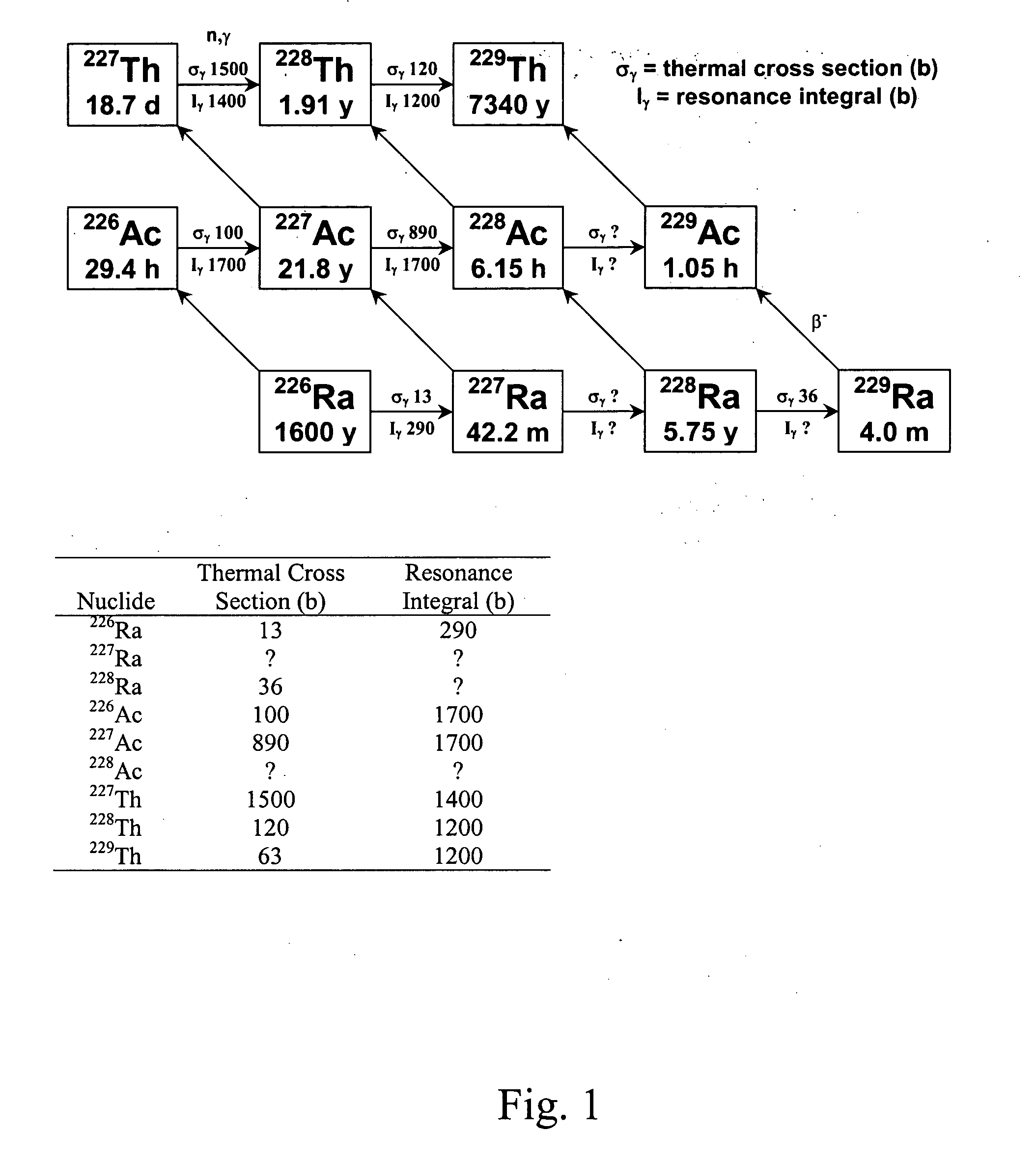
Production of thorium-229
InactiveUS20050105666A1Conversion outside reactor/acceleratorsRadioactive sourcesNeutron captureAlpha particle
A method for producing 229Th includes the steps of providing 226Ra as a target material, and bombarding the target material with alpha particles, helium-3, or neutrons to form 229Th. When neutrons are used, the neutrons preferably include an epithermal neutron flux of at least 1×1013 n s−1·cm−2. 228Ra can also be bombarded with thermal and / or energetic neutrons to result in a neutron capture reaction to form 229Th. Using 230Th as a target material, 229Th can be formed using neutron, gamma ray, proton or deuteron bombardment.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Radiation sources and radiation scanning systems with improved uniformity of radiation intensity
InactiveUS6954515B2Uniform radiation intensityImproved intensity distributionRadiation/particle handlingCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingFluenceX-ray
A radiation source is disclosed comprising a source of charged particles that travel along a path. Target material lies along the path to generate radiation upon impact by the beam. A magnet is provided to deflect the beam prior to impacting the target. The magnet may generate a time-varying magnetic field or a constant magnetic field. A constant magnetic field may be varied spatially across the beam. The magnet may be an electromagnet or a permanent magnet. In one example, deflection of the beam results in impact of the beam on the target along a plurality of axes. In another example, portions of the beam are differentially deflected. The source may thereby irradiate an object to be scanned with more uniform radiation. The charged particles may be electrons or protons and the radiation may be X-ray or gamma ray radiation, or neutrons. Scanning systems incorporating such sources, methods of generating radiation and methods of examining objects are disclosed, as well.
Owner:VAREX IMAGING CORP
Efficient single photon emission imaging
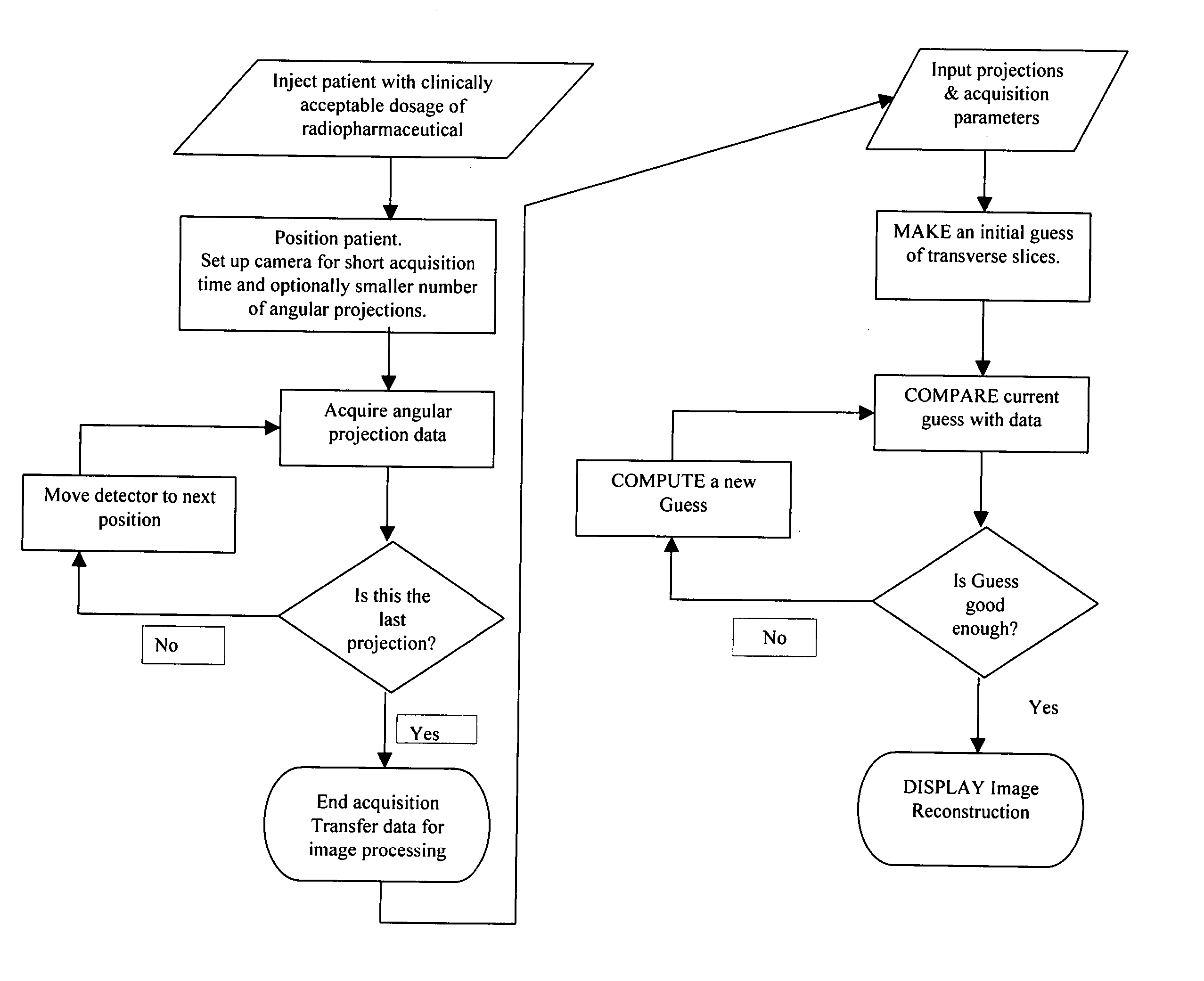
InactiveUS20050145797A1Data acquisition time can be shortenedImprove image qualityReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis by optical meansAcquisition timeGamma ray
A method of diagnostic imaging in a shortened acquisition time for obtaining a reconstructed diagnostic image of a portion of a body of a human patient who was administered with dosage of radiopharmaceutical substance radiating gamma rays, using SPECT. The method comprises acquiring photons emitted from said portion of the body, by means of a detector capable of converting the photons into electric signals, wherein the total time of photon acquiring is substantially shorter than the clinically acceptable acquisition time; processing said electric signals by a position logic circuitry and thereby deriving data indicative of positions on said photon detector crystal, where the photons have impinged the detector; and reconstructing an image of a spatial distribution of the pharmaceutical substance within the portion of the body by iteratively processing said data.
Owner:ULTRASPECT
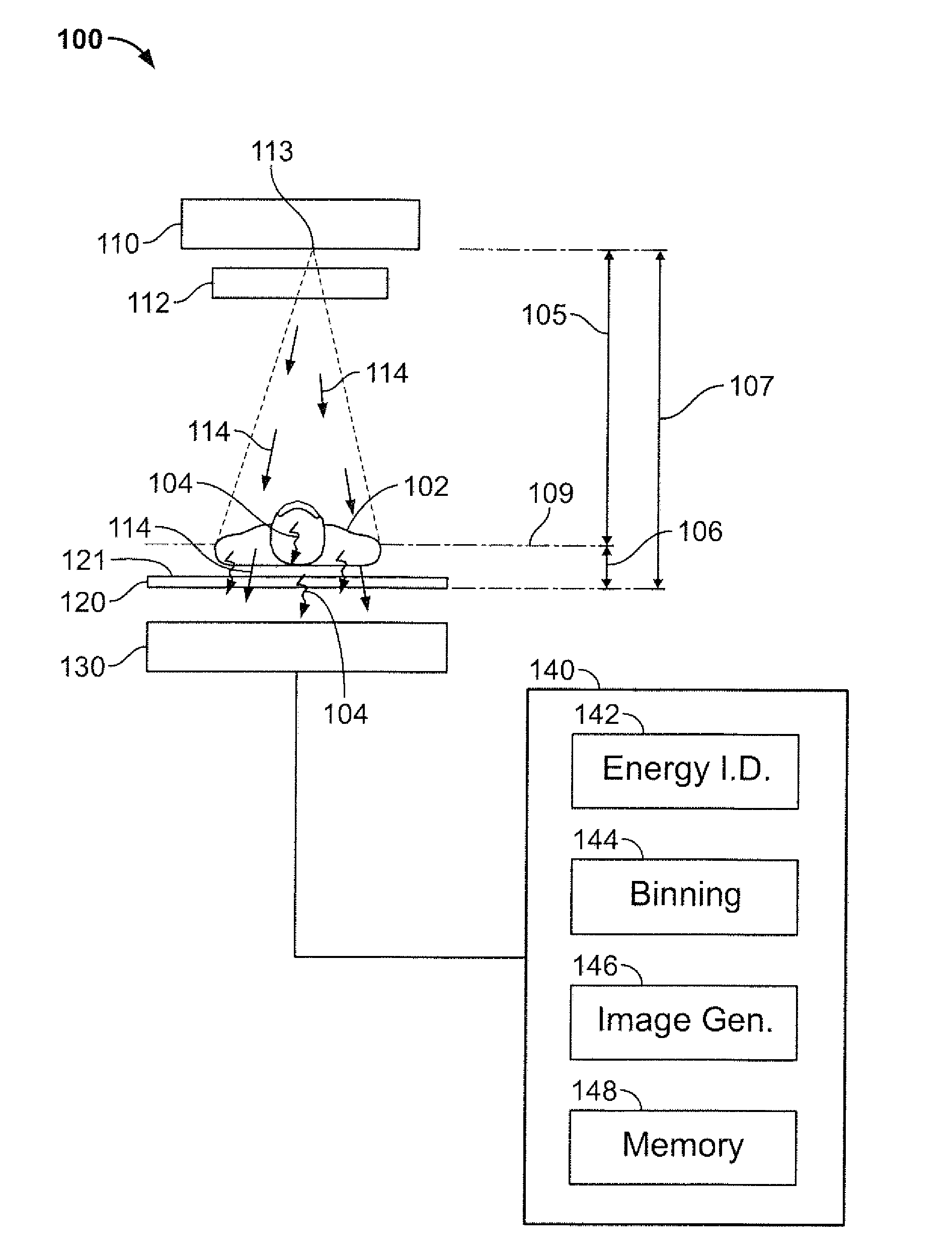
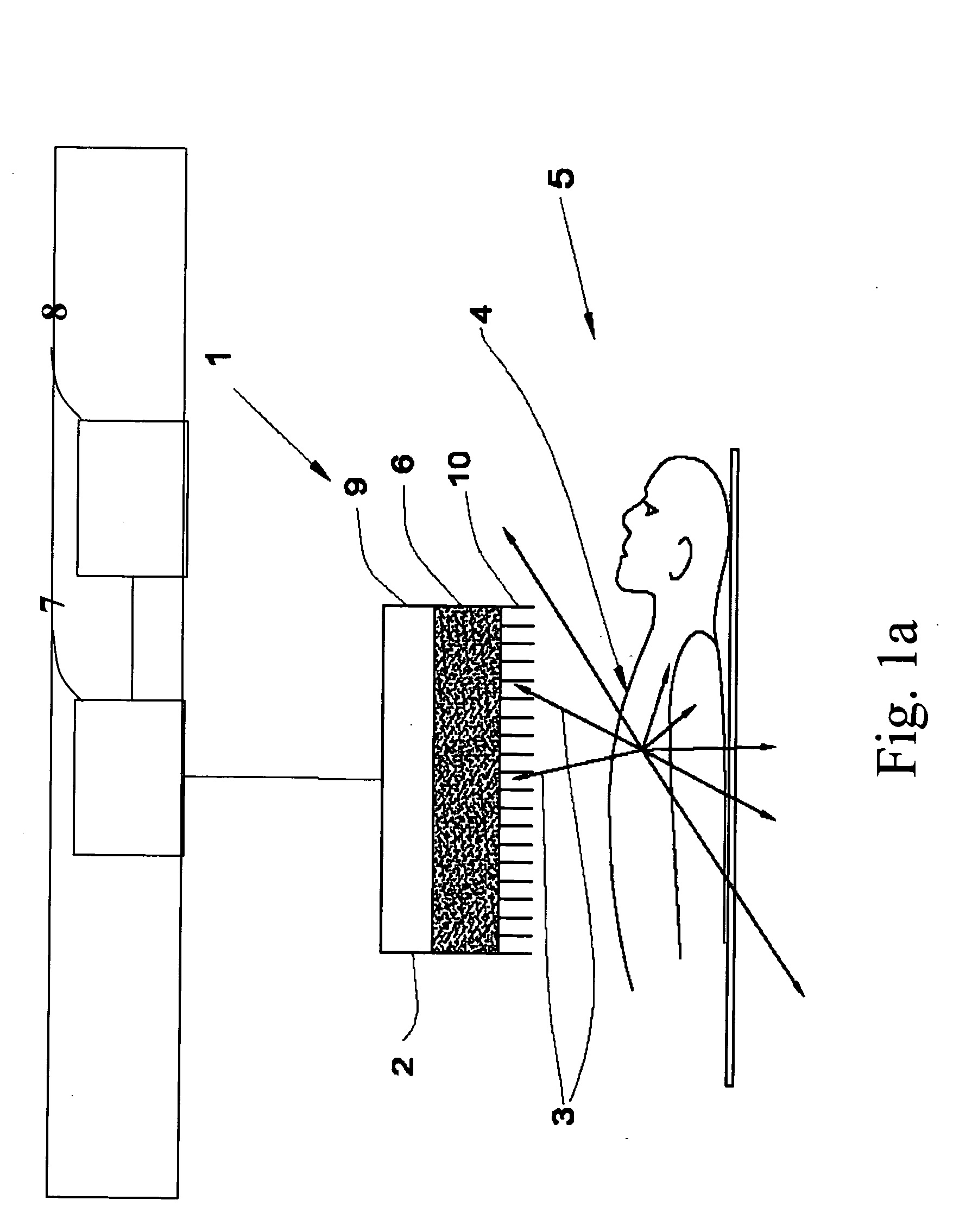
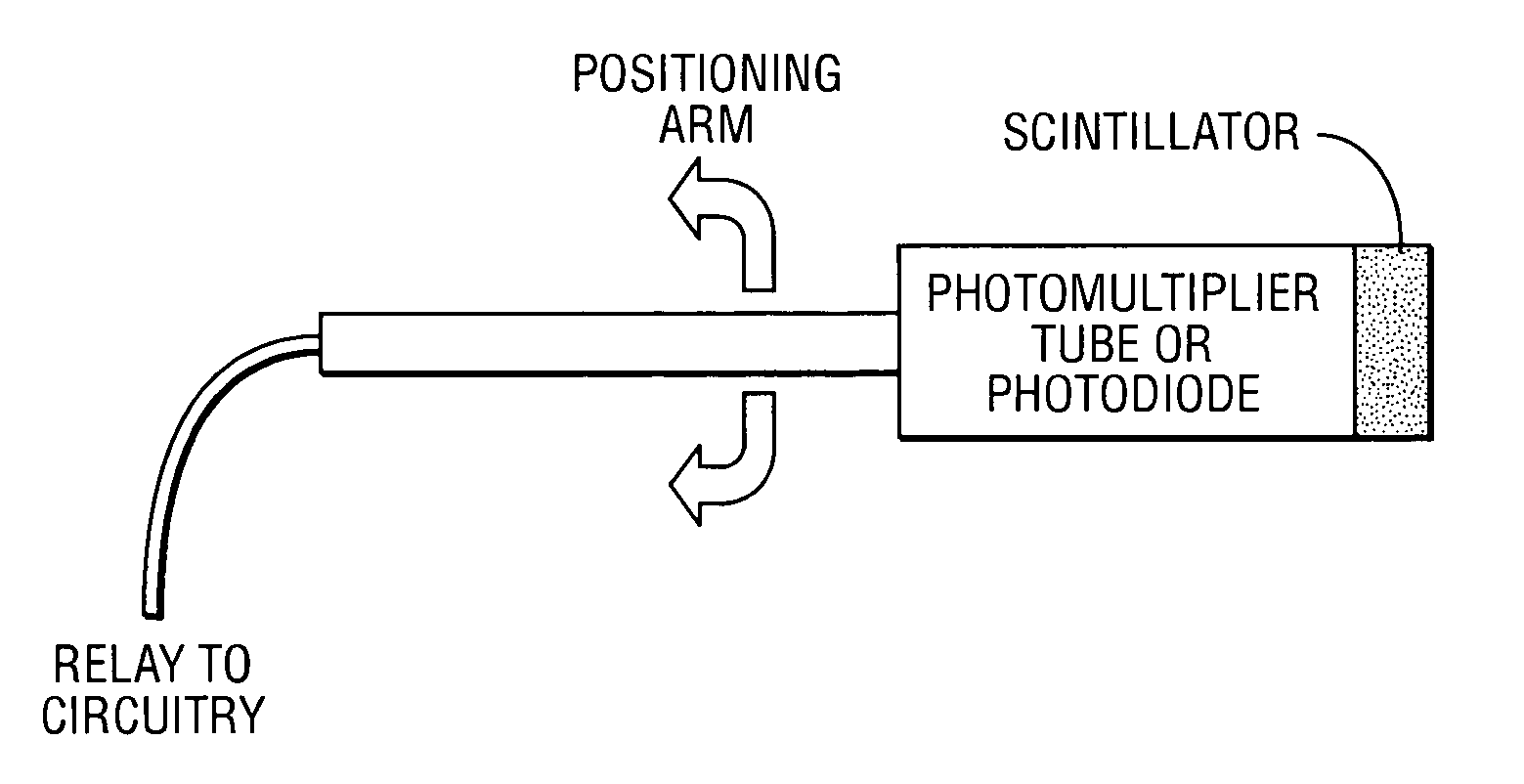
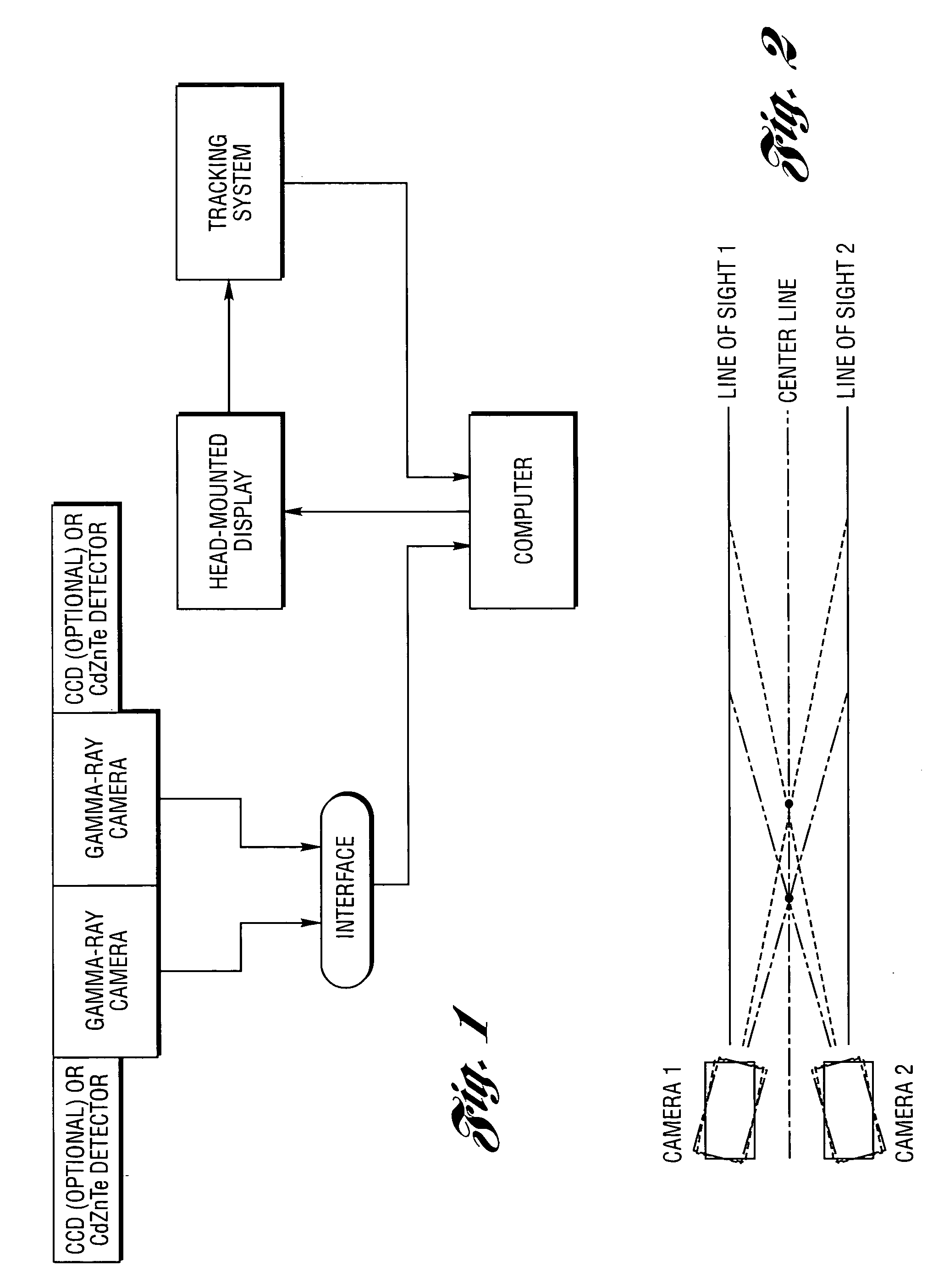
Method and system for high-speed, 3D imaging of optically-invisible radiation and detector and array of such detectors for use therein
InactiveUS20050017181A1Reduce exposureStrong applicationElectric discharge tubesSolid-state devicesHuman exposureSpectroscopy
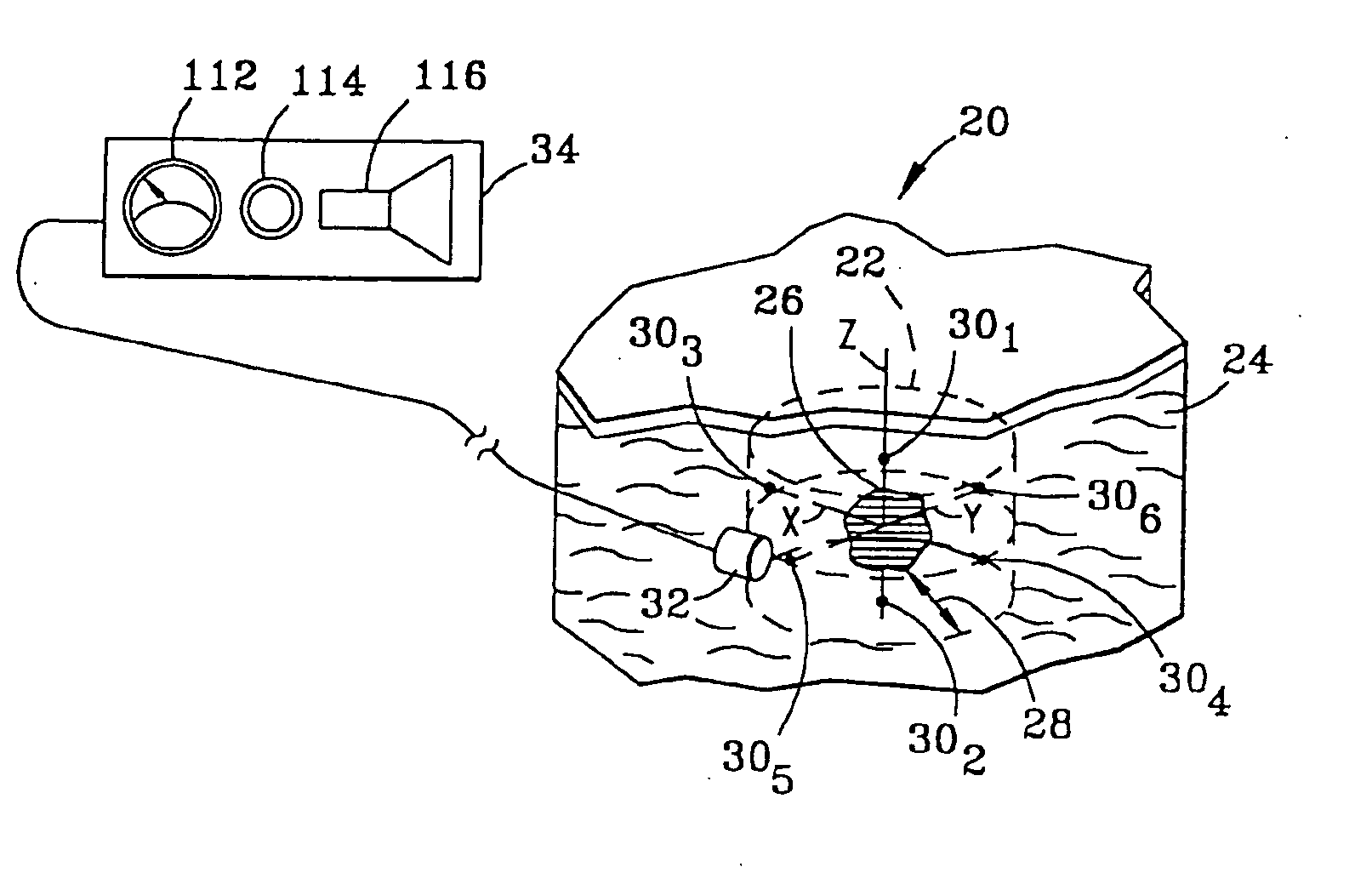
A high-speed, three-dimensional, gamma-ray imaging method and system as well as a detector and array of such detectors for use therein are provided which characterize radioactivity distributions in nuclear and radioactive waste and materials facilities by superimposing radiation images on a view of the environment using see-through display screens or shields to provide a stereoscopic view of the radiation. The method and system provide real-time visual feedback about the locations and relative strengths of radioactive sources. The method and system dynamically provide continuous updates to the displayed image illustrating changes, such as source movement. A pair of spaced gamma-ray cameras of a detector subsystem function like “gamma eyes”. A pair of CCD cameras may be coupled to the detector subsystem to obtain information about the physical architecture of the environment. A motion tracking subsystem is used to generate information on the user's position and head orientation to determine what a user “sees”. The invention exploits the human brain's ability to naturally reconstruct a 3D, stereoscopic image from 2D images generated by two “imagers” separated by a known angle(s) without the need for 3D mathematical image reconstruction. The method and system are not only tools for minimizing human exposure to radiation thus assisting in ALARA (As Low As Reasonably Achievable) planning, but also are helpful for identifying contamination in, for example, laboratory or industrial settings. Other optically-invisible radiation such as infrared radiation caused by smoldering fires may also be imaged. Detectors are manufactured or configured in curvilinear geometries (such as hemispheres, spheres, circles, arcs, or other arrangements) to enable sampling of the ionizing radiation field for determination of positional activity (absolute or relative amounts of ionizing radiation) or spectroscopy (energy distributions of photons). More than one detector system may be used to obtain three-dimensional information. The detector systems are specifically suitable for direct visualization of radiation fields.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Device and system for improved imaging in nuclear medicine and mammography
InactiveUS7147372B2Easy to optimizeEnhance analysis capabilityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingAdaptive imagingDetector array
A method and apparatus for detecting radiation including x-ray, gamma ray, and particle radiation for radiographic imaging, and nuclear medicine and x-ray mammography in particular, and material composition analysis are described. A detection system employs fixed or configurable arrays of one or more detector modules comprising detector arrays which may be electronically manipulated through a computer system. The detection system, by providing the ability for electronic manipulation, permits adaptive imaging. Detector array configurations include familiar geometries, including slit, slot, plane, open box, and ring configurations, and customized configurations, including wearable detector arrays, that are customized to the shape of the patient. Conventional, such as attenuating, rigid geometry, and unconventional collimators, such as x-ray optic, configurable, Compton scatter modules, can be selectively employed with detector modules and radiation sources. The components of the imaging chain can be calibrated or corrected using processes of the invention. X-ray mammography and scintimammography are enhanced by utilizing sectional compression and related imaging techniques.
Owner:MINNESOTA IMAGING & ENG
Semiconductor X-ray photocathodes devices
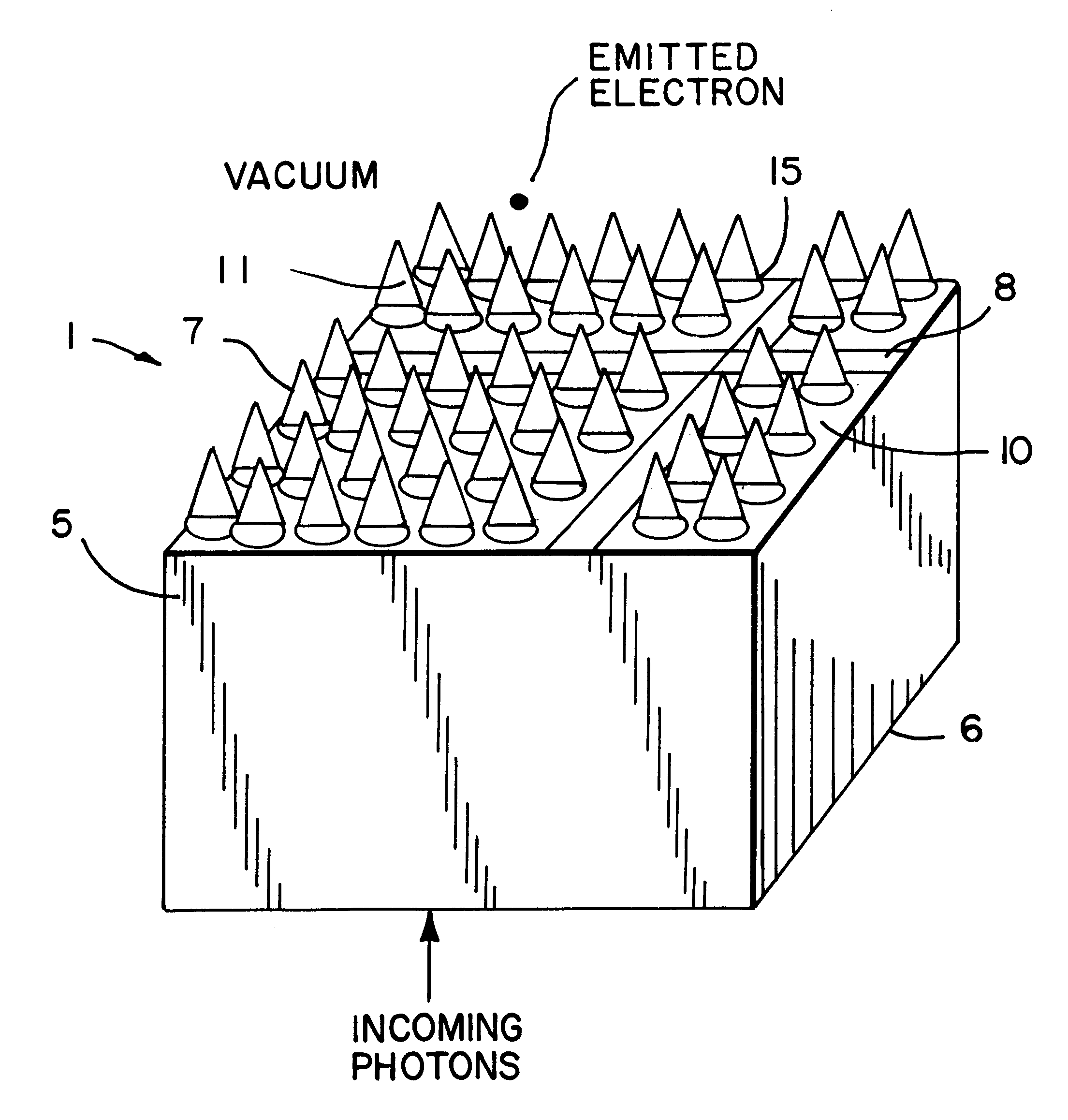
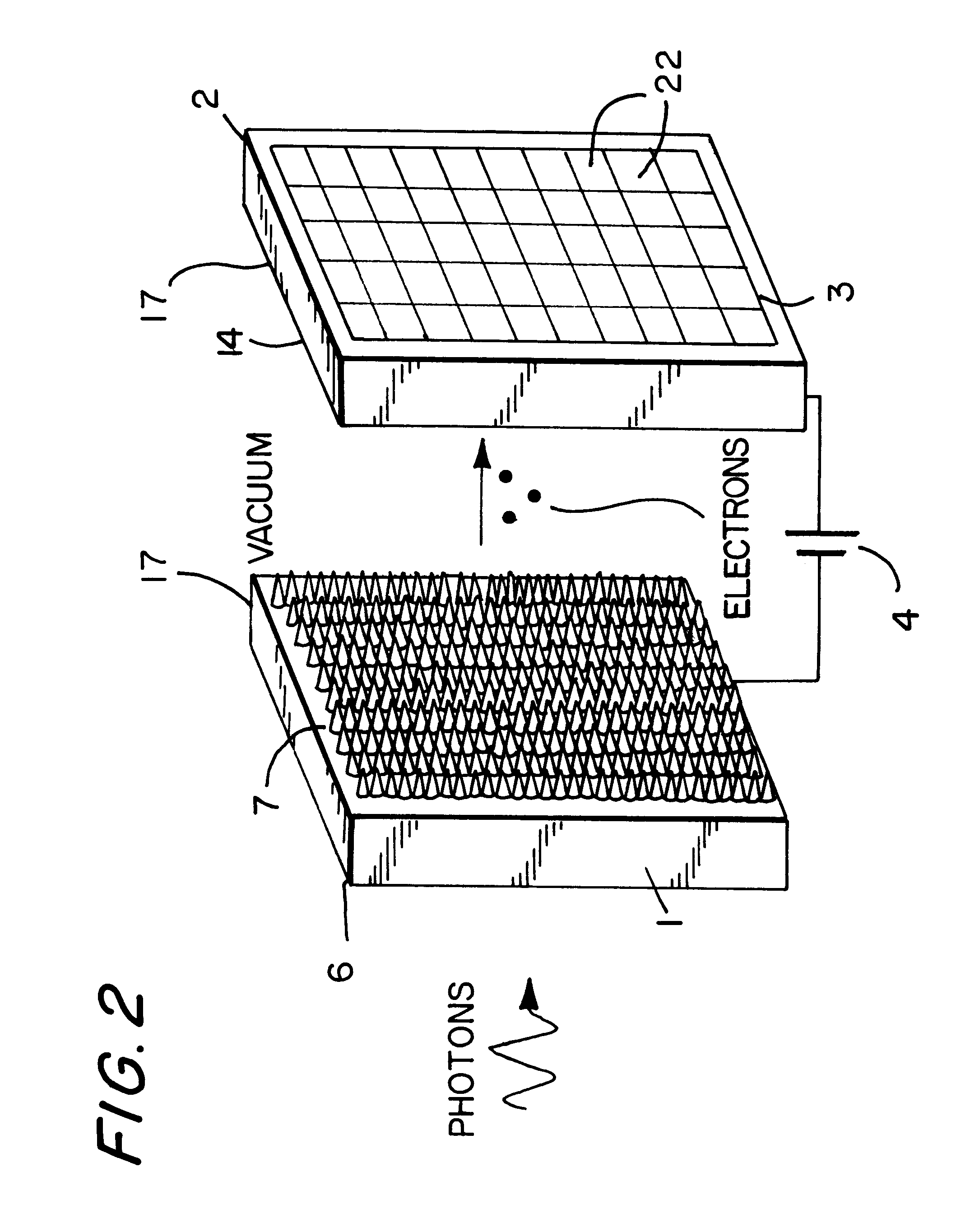
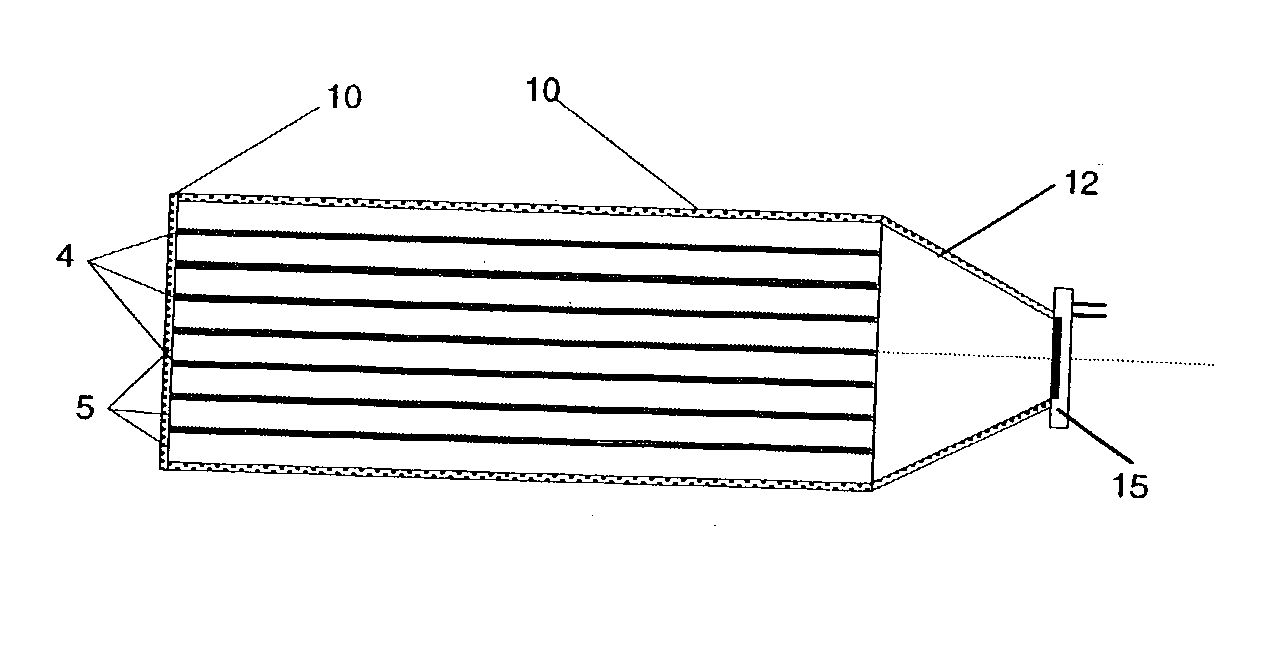
InactiveUS6201257B1Reduce noiseHigh x-ray energy discriminationDischarge tube luminescnet screensCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesPhotocathodePhotonic sensor
An energy dispersive x-ray and gamma-ray photon counter is described. The counter uses a photon sensor which incorporates a unique photocathode called Advanced Semiconductor Emitter Technology for X-rays (ASET-X) as its critical element for converting the detected photons to electrons which are emitted into a vacuum. The electrons are multiplied by accelerations and collisions creating a signal larger than the sensor noise and thus allowing the photon to be energy resolved very accurately, to within ionization statistics. Because the signal is already above the sensor noise it does not have to be noise filtered therefore allowing high-speed counting. The photon sensor can also be used as a device to visualize and image gamma-ray and x-ray sources.
Owner:ADVANCED SCI CONCEPTS
Neutron detector with layered thermal-neutron scintillator and dual function light guide and thermalizing media
ActiveUS20050224719A1Shorten speedKinetic energy is lostMeasurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansHydrogenFluorescence
A broad spectrum neutron detector has a thermal neutron sensitive scintillator film interleaved with a hydrogenous thermalizing media. The neutron detector has negligible sensitivity to gamma rays and produces a strong and unambiguous signal for virtually all neutrons that interact with the hydrogenous volume. The interleaving of the layers of thermal neutron sensitive phosphors helps ensure that all parts of the thermalizing volume are highly sensitive.
Owner:LEIDOS
Scintillation substances (variants)
ActiveUS20060086311A1Reduce manufacturing costHigh light yieldPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltFractographyLutetium
Inventions relate to scintillation substances and they may be utilized in nuclear physics, medicine and oil industry for recording and measurements of X-ray, gamma-ray and alpha-ray, nondestructive testing of solid states structure, three-dimensional positron-emission tomography and X-ray computer tomography and fluorography. Substances based on silicate comprising lutetium and cerium characterised in that compositions of substances are represented by chemical formulae CexLu2+2y−xSi1−yO5+y, CexLiq+pLu2−p+2y−x−zAzSi1−yO5+y−p, CexLiq+pLu9.33−x−p−z□0.67AzSi6O26−p, where A is at least one element selected from group consisting of Gd, Sc, Y, La, Eu, Tb, x is value between 1×10−4 f.units and 0.02 f.units., y is value between 0.024 f.units and 0.09 f.units, z is value does not exceeding 0.05 f.units, q is value does not exceeding 0.2 f.units, p is value does not exceeding 0.05 f.units. Achievable technical result is the scintillating substance having high density, high light yield, low afterglow, and low percentage loss during fabrication of scintillating elements.
Owner:ZECOTEK HLDG INC
Radiation detectors
InactiveUS7304309B2Improve efficiencyEasy accessMaterial analysis by optical meansNanoopticsRecoil electronPhotonic bandgap
The invention consists in structuring scintillation radiation detectors as Photonic Bandgap Crystals or 3D layers of thin filaments, thus enabling extremely high spatial resolutions and achieving virtual voxellation of the radiation detector without physical separating walls. The ability to precisely measure the recoil electron track in a Compton camera enables to assess the directions of the gamma rays hitting the detector and consequently dispensing with collimators that strongly reduce the intensity of radiation detected by gamma cameras. The invention enables great enhancements of the capabilities of gamma cameras, SPECT, PET, CT and DR machines as well as their use in Homeland Security applications. Methods of fabrication of such radiation detectors are described.
Owner:SUHAMI AVRAHAM
Spect gamma camera
InactiveUS20030208117A1Improve imaging resolutionShort acquisition timeDiagnostic recording/measuringTomographySingle photon emission computerized tomographyGamma ray
A method and apparatus of obtaining and reconstructing an image of a portion of a body, administered by a radiopharmaceutical substance, by using Single-photon emission computerized tomography (SPECT) for determination of functional information thereon. The method comprises (a) acquiring gamma ray photons emitted from said portion by means of a detector capable of converting the photons into electric signals, the detector having at least one crystal and allowing said gamma rays having incident angles essentially exceeding 5 degrees and, preferably, exceeding 10 degrees to be detected; (b) processing said electric signals by a position logic circuitry and thereby transforming them into data indicative of positions on said photon detector crystal, where the photons have impinged the detector; and (c) reconstructing an image of a spatial distribution of the pharmaceutical substance within the portion of the body by processing said data and taking into consideration weight values which are functions of angles and, possibly, distances between different elements of the portion of the body and corresponding elements of this position's projection on the detector.
Owner:ULTRASPECT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com