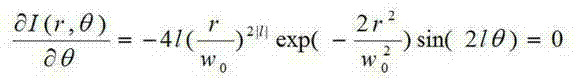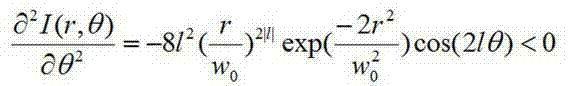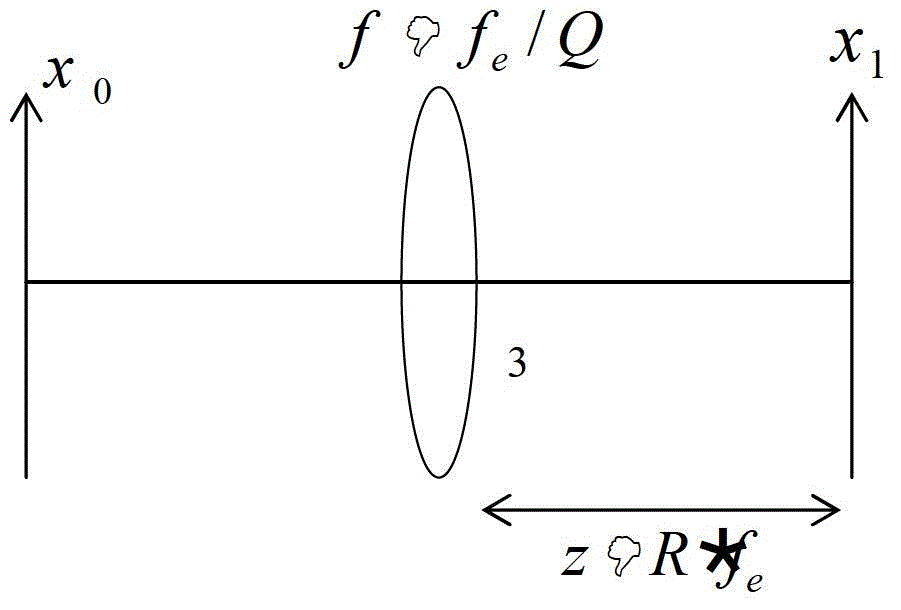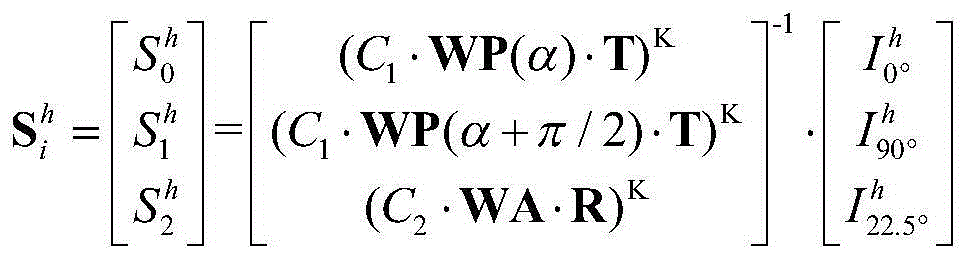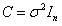Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
803 results about "Grism" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
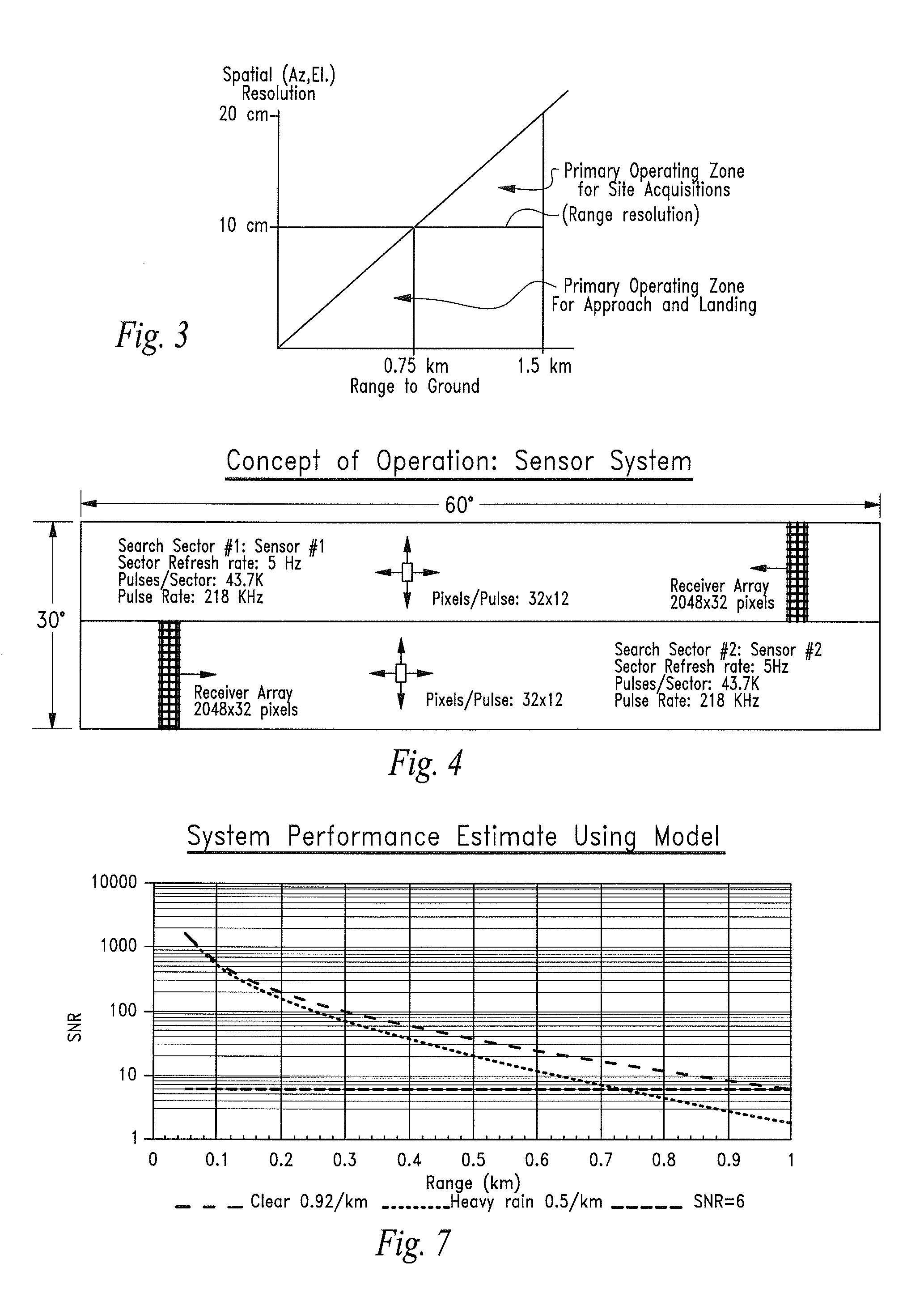
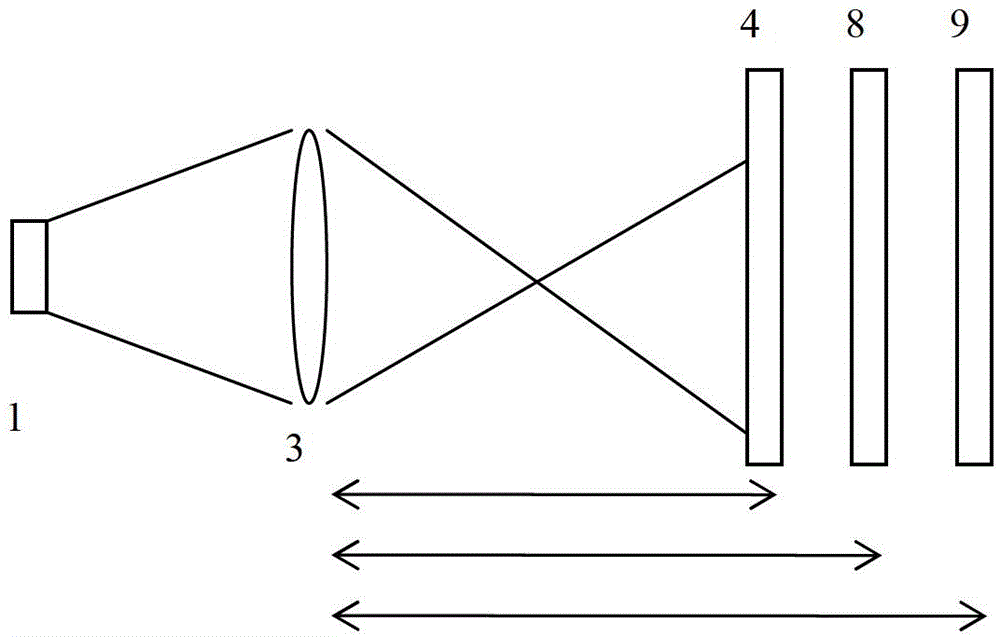
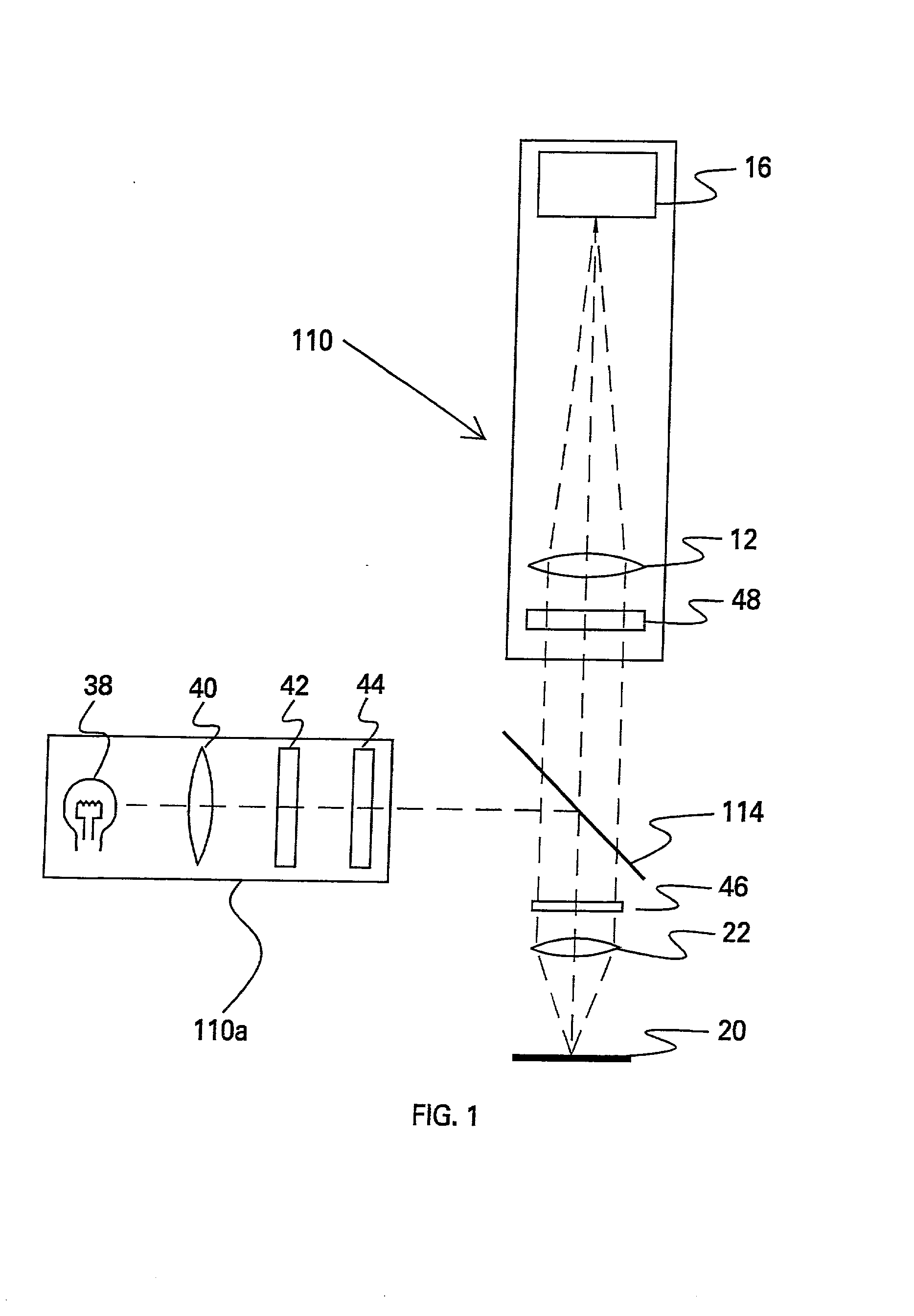
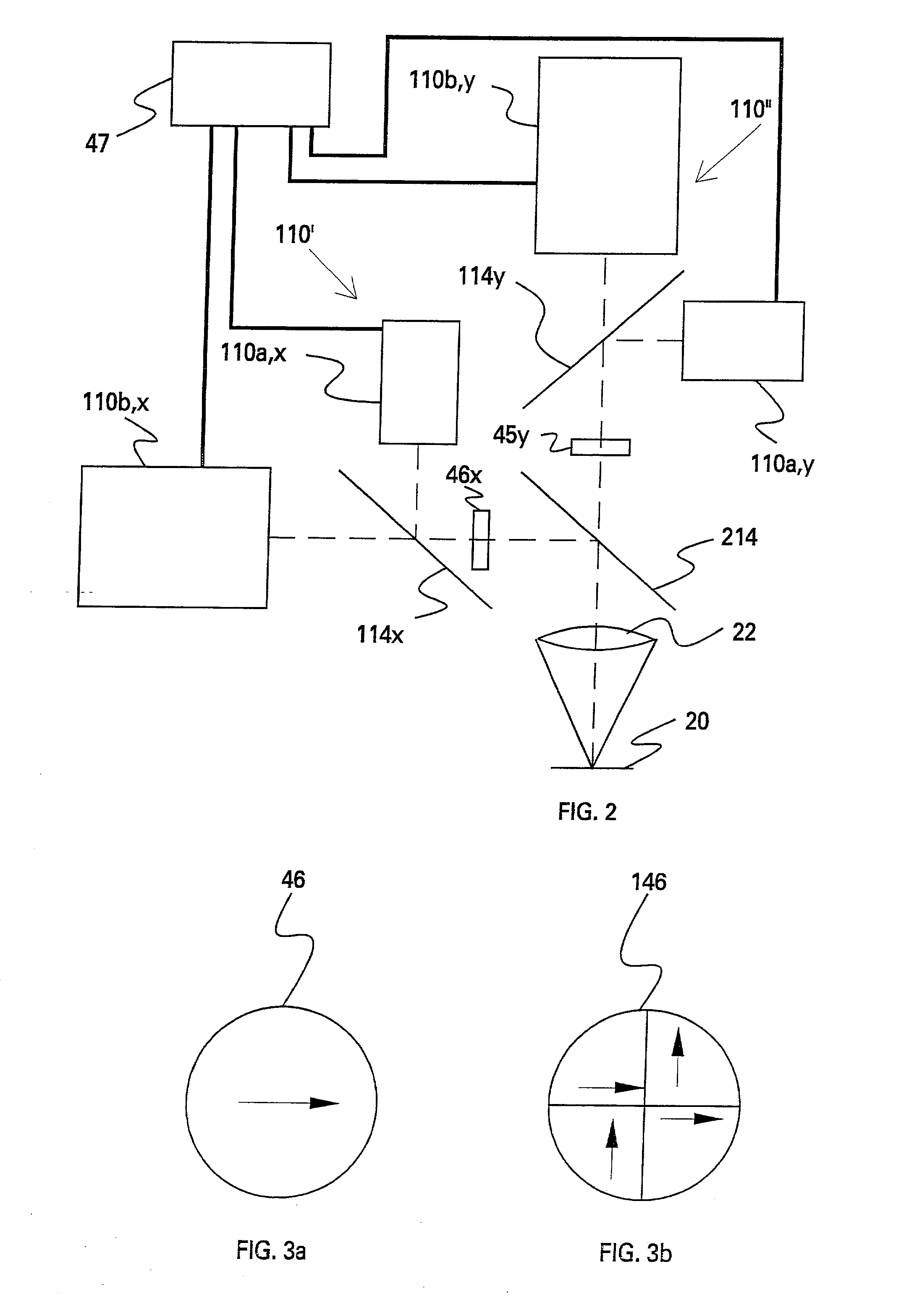
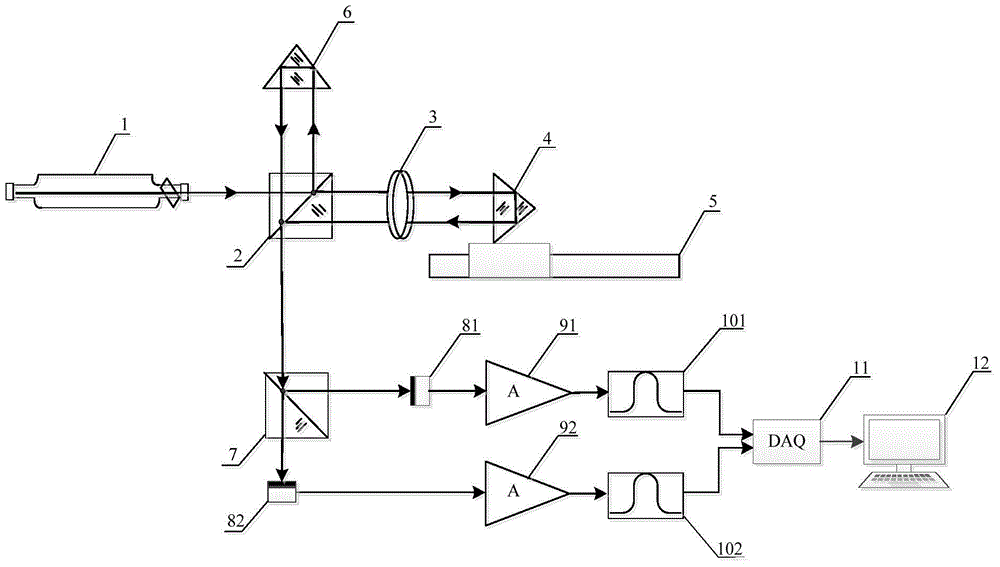
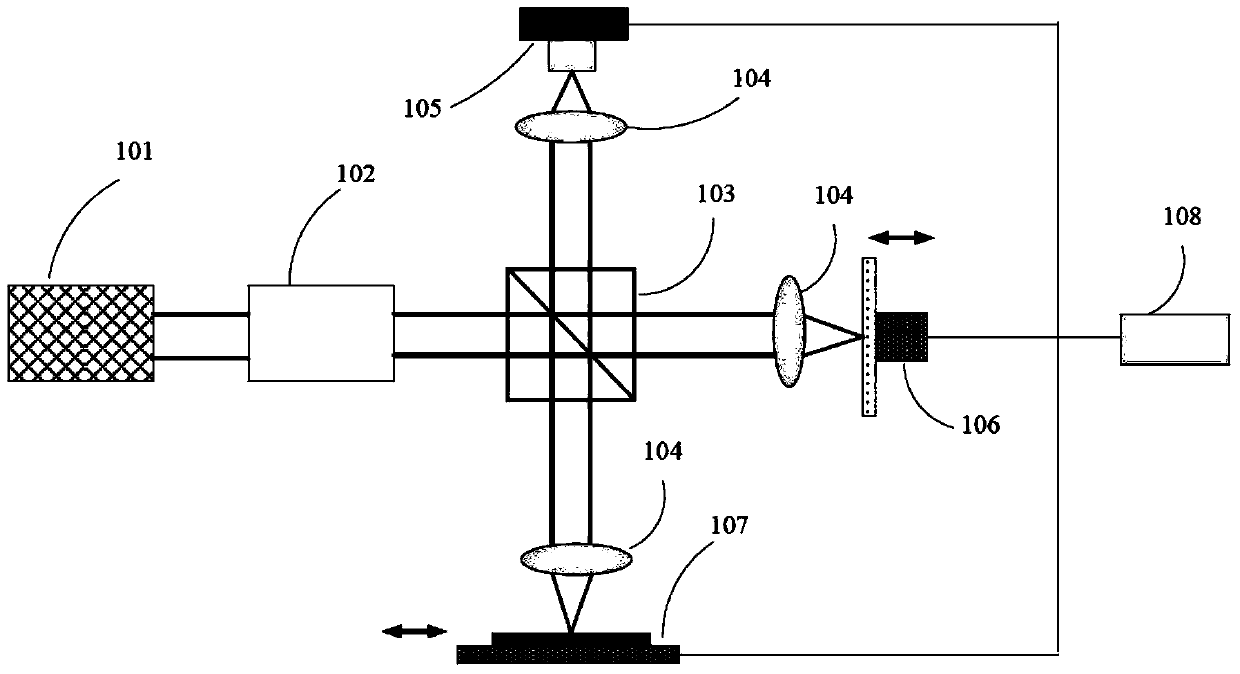
A grism (also called a grating prism) is a combination of a prism and grating arranged so that light at a chosen central wavelength passes straight through. The advantage of this arrangement is that one and the same camera can be used both for imaging (without the grism) and spectroscopy (with the grism) without having to be moved. Grisms are inserted into a camera beam that is already collimated. They then create a dispersed spectrum centered on the object's location in the camera's field of view.
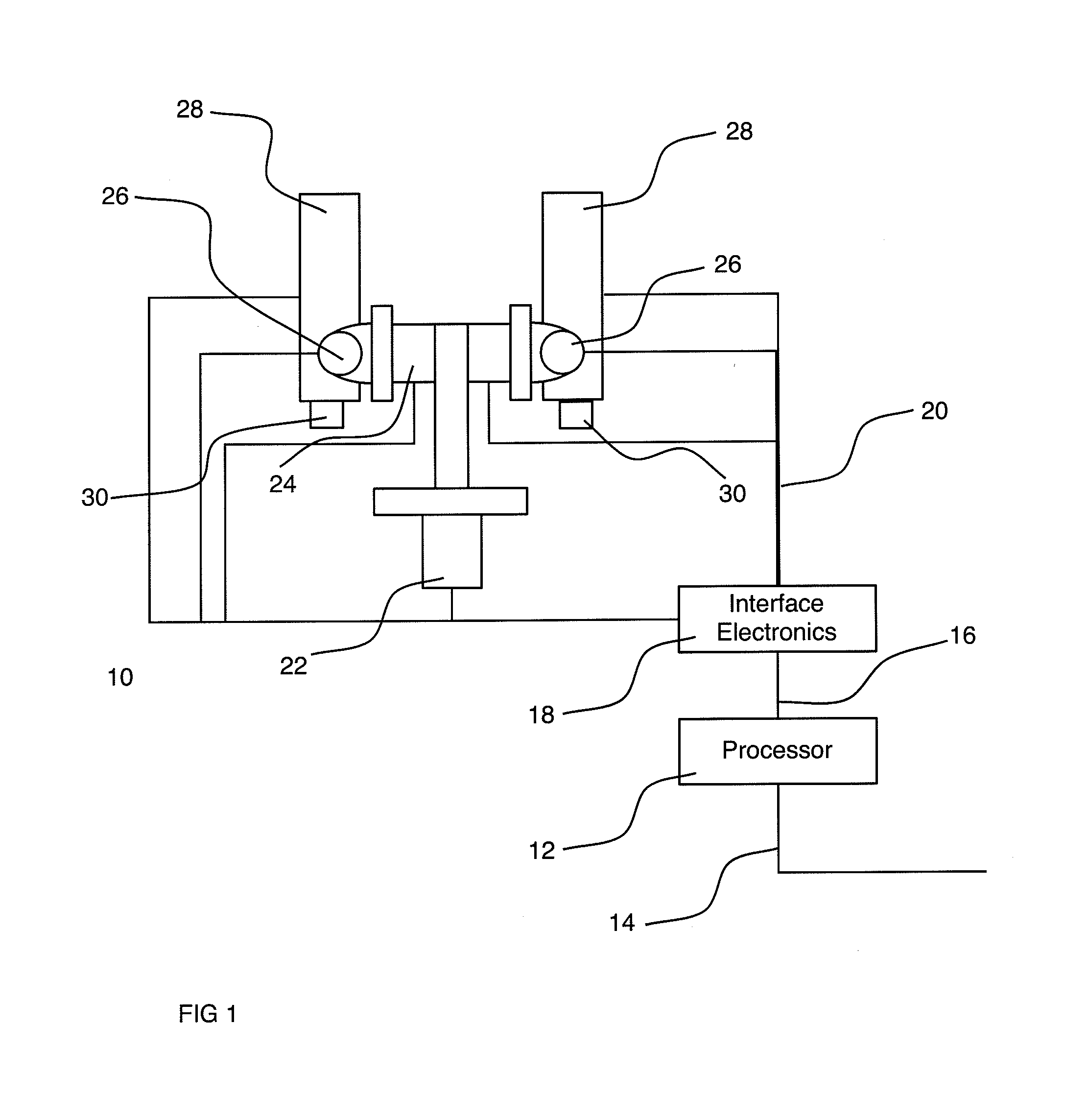
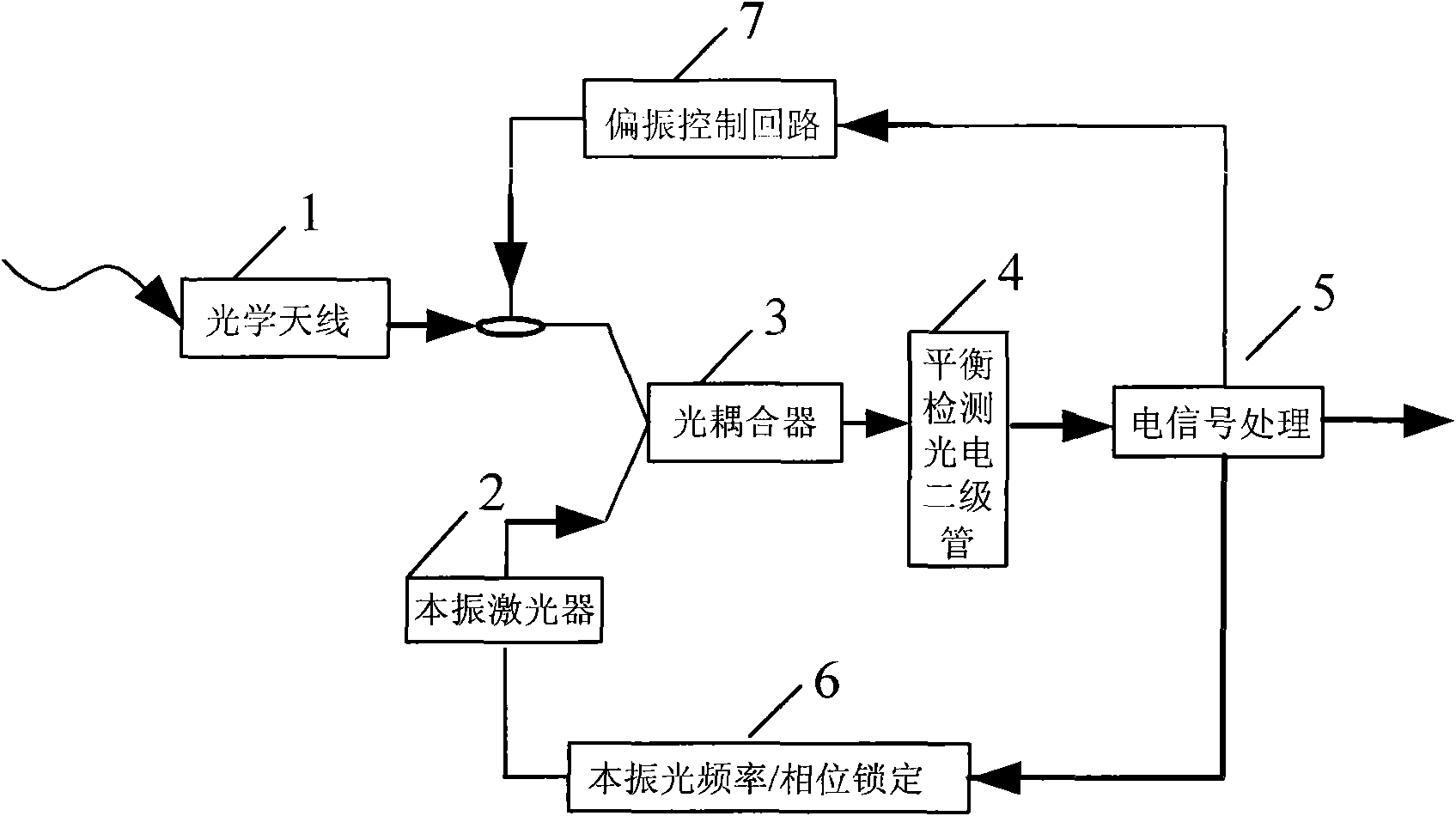
Low power fingerprint capture system, apparatus, and method
ActiveUS20050169506A1Shorter focal distanceImprove aberrationCharacter and pattern recognitionGratingBarcode reader
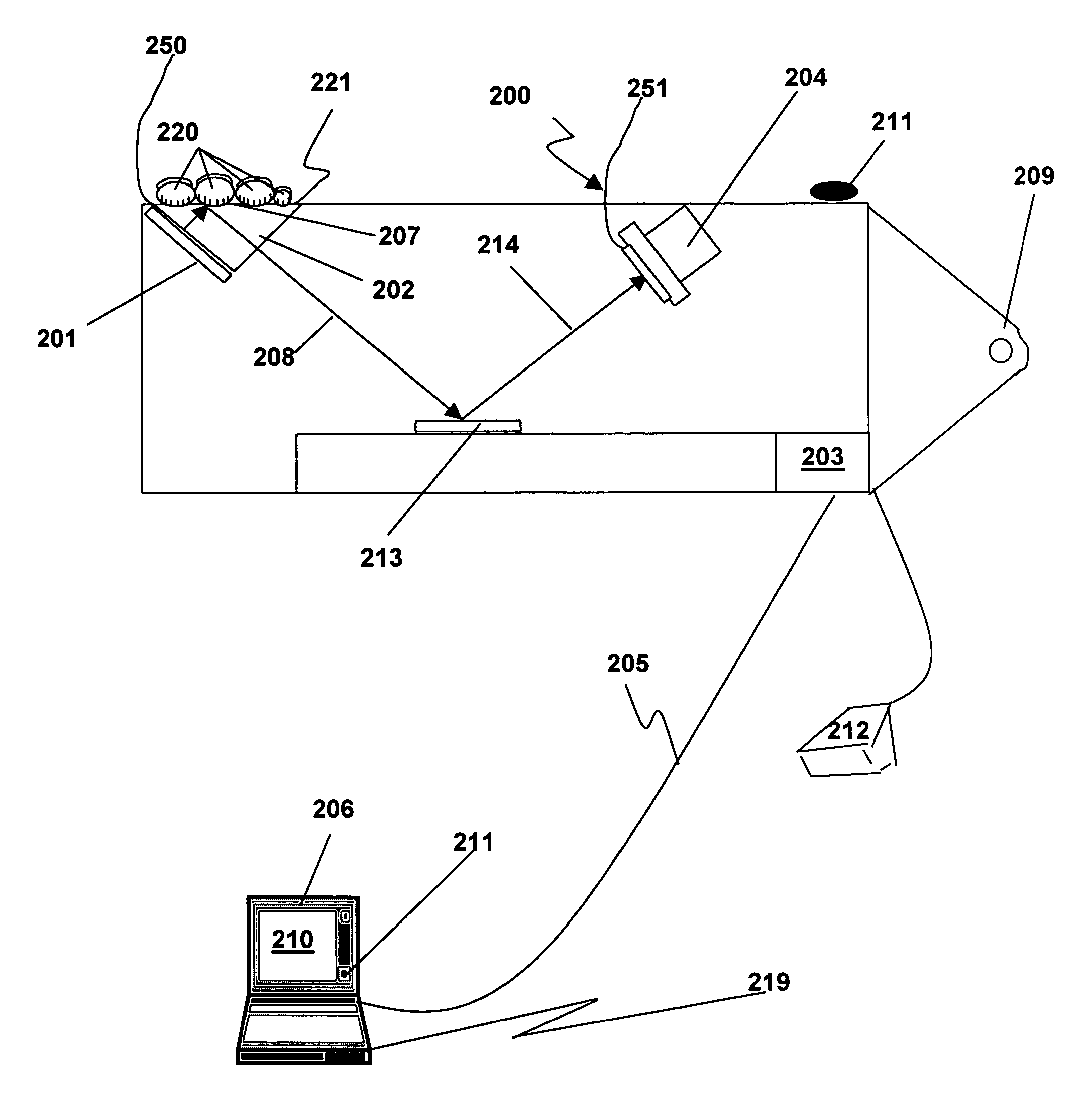
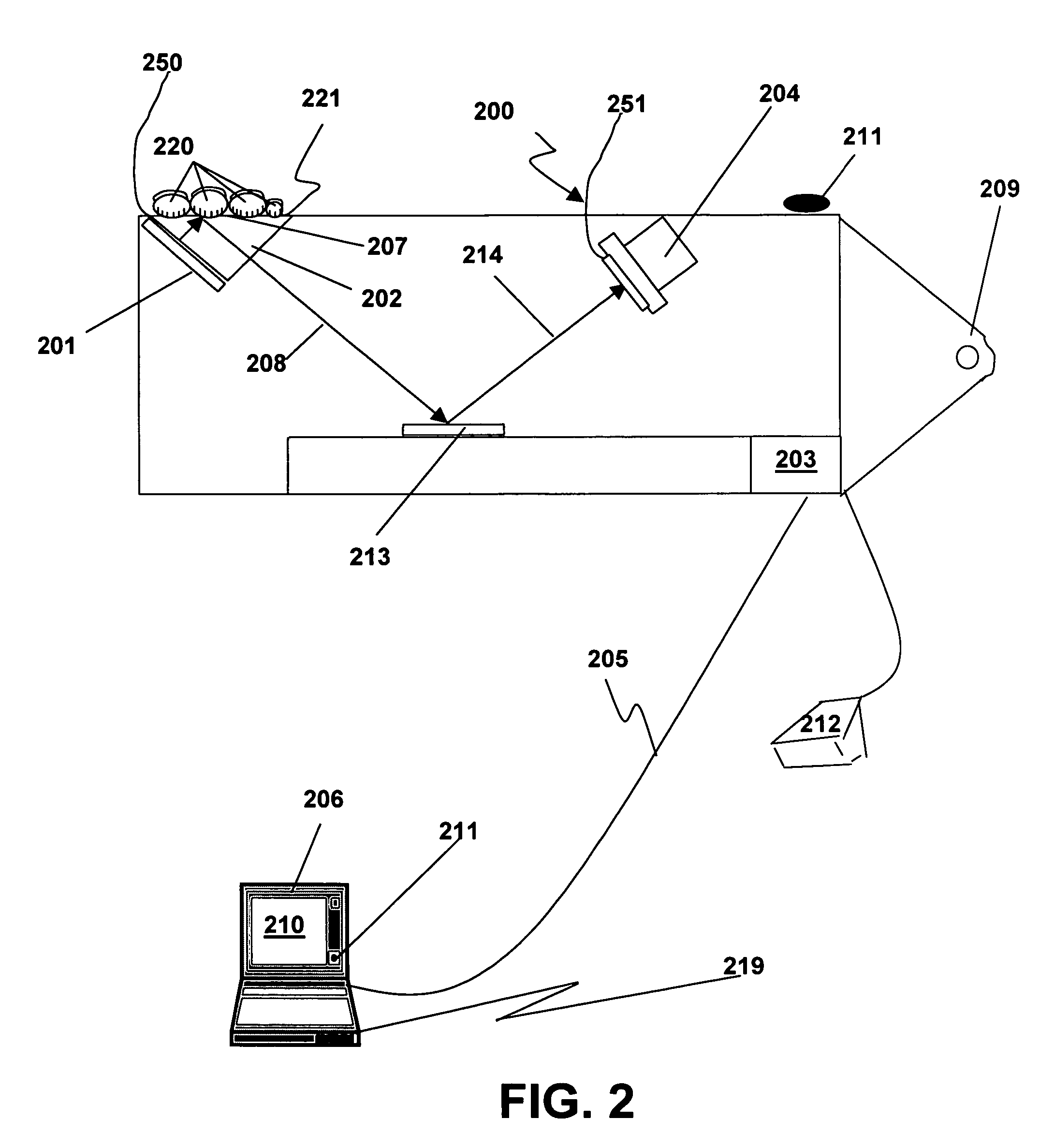
The present invention provides a large format fingerprint capture apparatus, system and method that is low power, compact, and lightweight and has a platen area greater than 3.0 square inches. The present system is typically powered, controlled, and exchanges data over a single data / control / power connection to a host PC, e.g., a desk top computer, PDA, or laptop computer although the system can also be used in a wireless fashion with a power subsystem so no physical connections are required. In a preferred embodiment the large format fingerprint device is directly connected to a completely disconnected portable PC, such as a laptop having only a battery power source. The primary system components of the present invention combine to minimize power, size and weight and, thus, enhance portability and battery life. The system typically includes a light source, a prism, a camera (including the lens), and a case. Optional elements comprise holographic elements such as gratings and holographic optical elements (HOEs), a battery subsystem, magnetic stripe reader, barcode reader, platen heater, platen blower, and mirrors to divert the image beam.
Owner:IDENTIFICATION INT
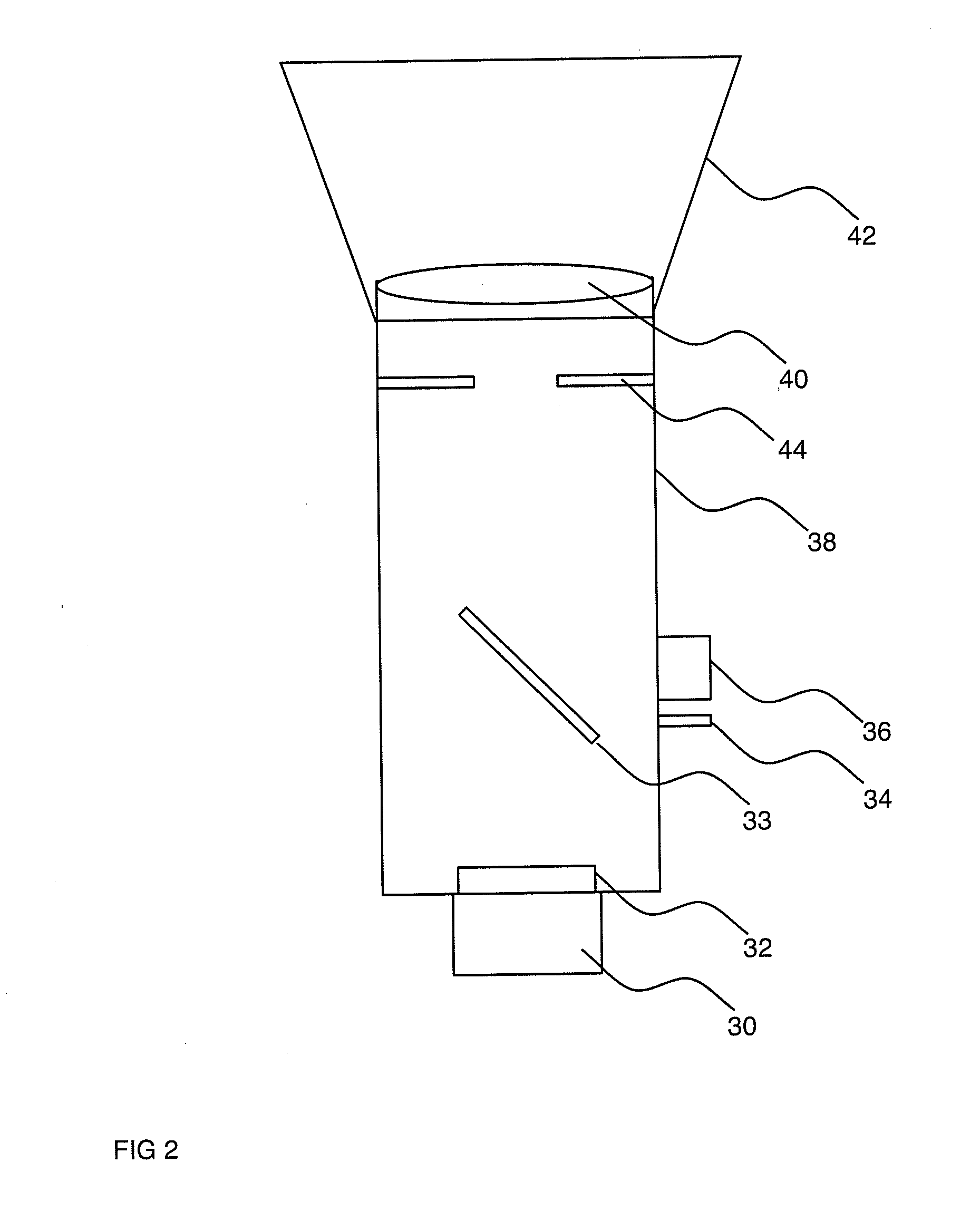
Light scanning probe apparatus using light of low coherence
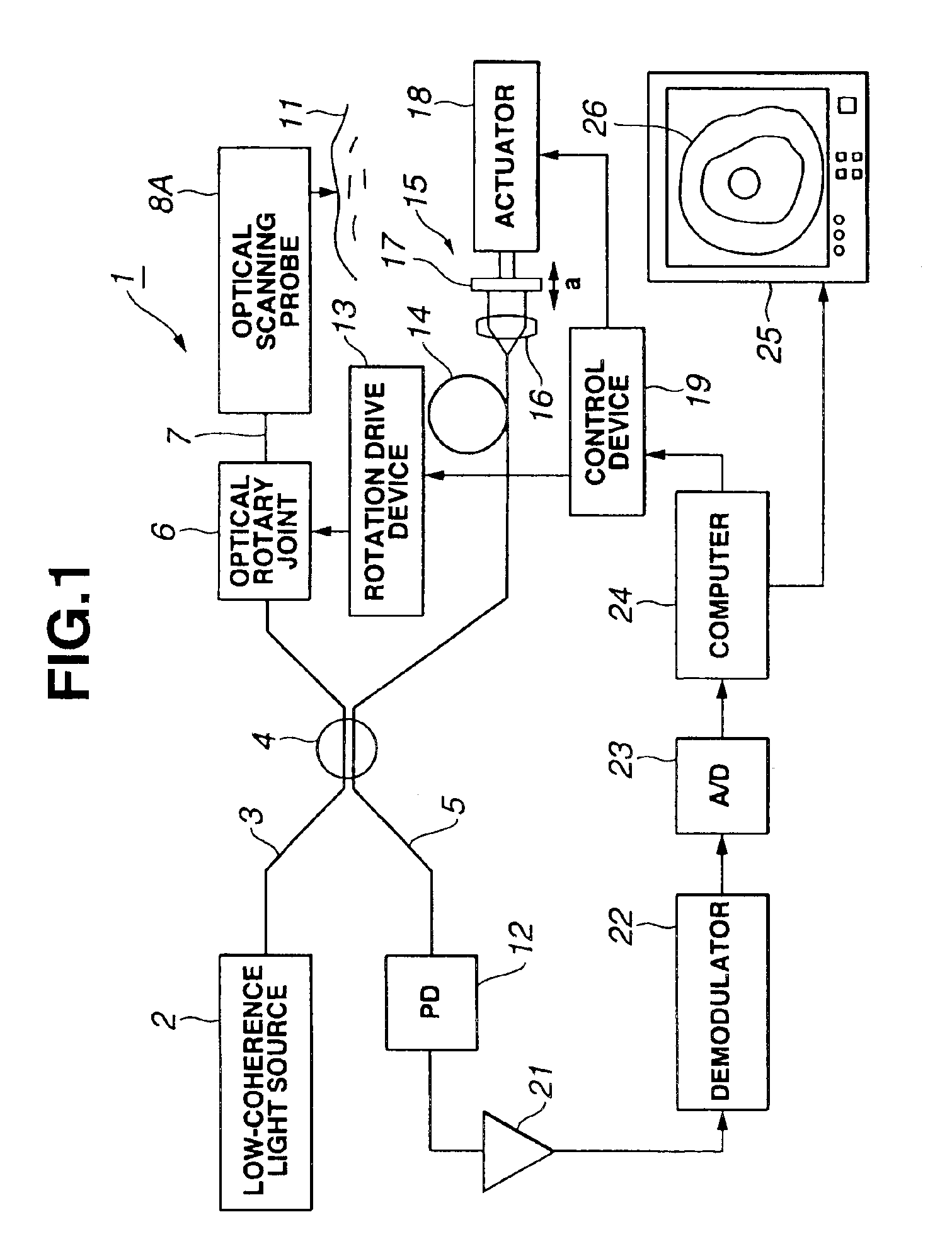
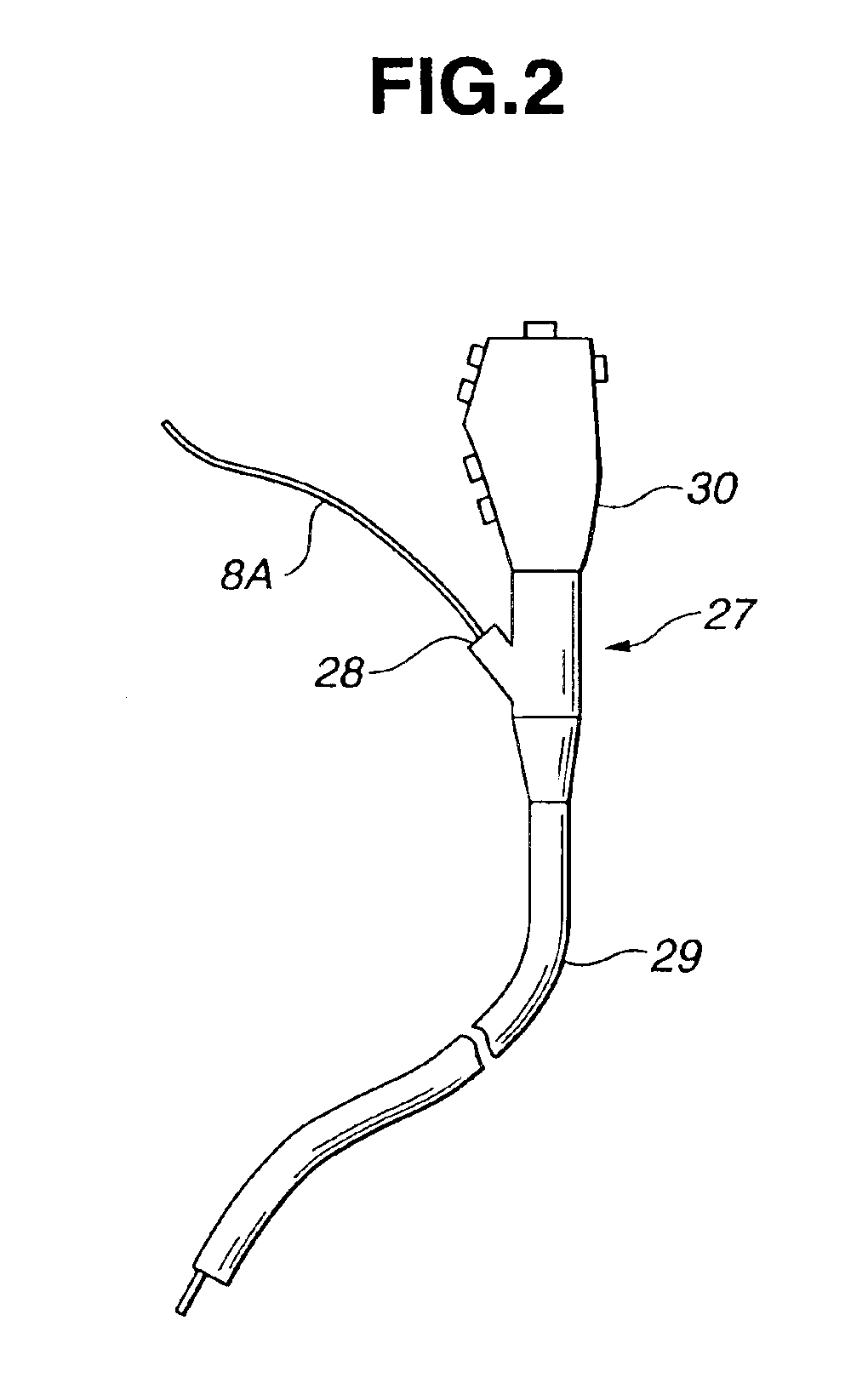
InactiveUS6888119B2Easy to operateHigh light transmittanceSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsBiological bodyGrism
A flexible shaft driven to rotate is inserted through a transparent sheath having pliability. By a fiber inserted through the inside thereof, low-coherence light is guided and is made to exit to a living-body tissue side which is an observation target through a lens and a prism forming an exit and entrance portion at the tip portion. Subsequently, the light reflected on the living-body tissue side is guided in order to produce an image. In that case, a positioning member for keeping the exit and entrance portion and the living-body tissue at a proper distance is formed at the tip portion of the sheath or the tip portion of an endoscope through which an optical probe is inserted and, therefore, a stable tomogram image can be produced.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Sensor Element and System Comprising Wide Field-of-View 3-D Imaging LIDAR
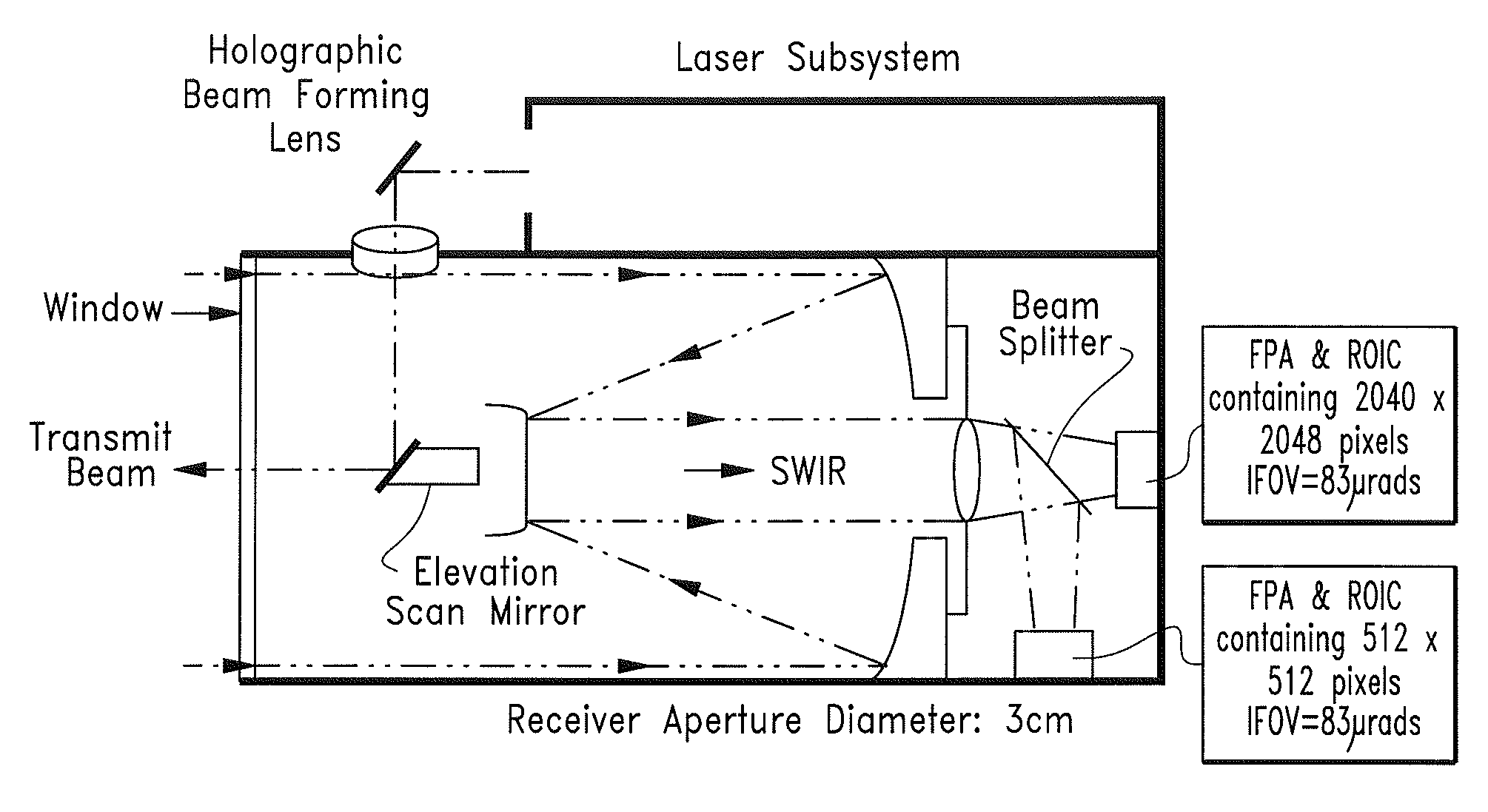
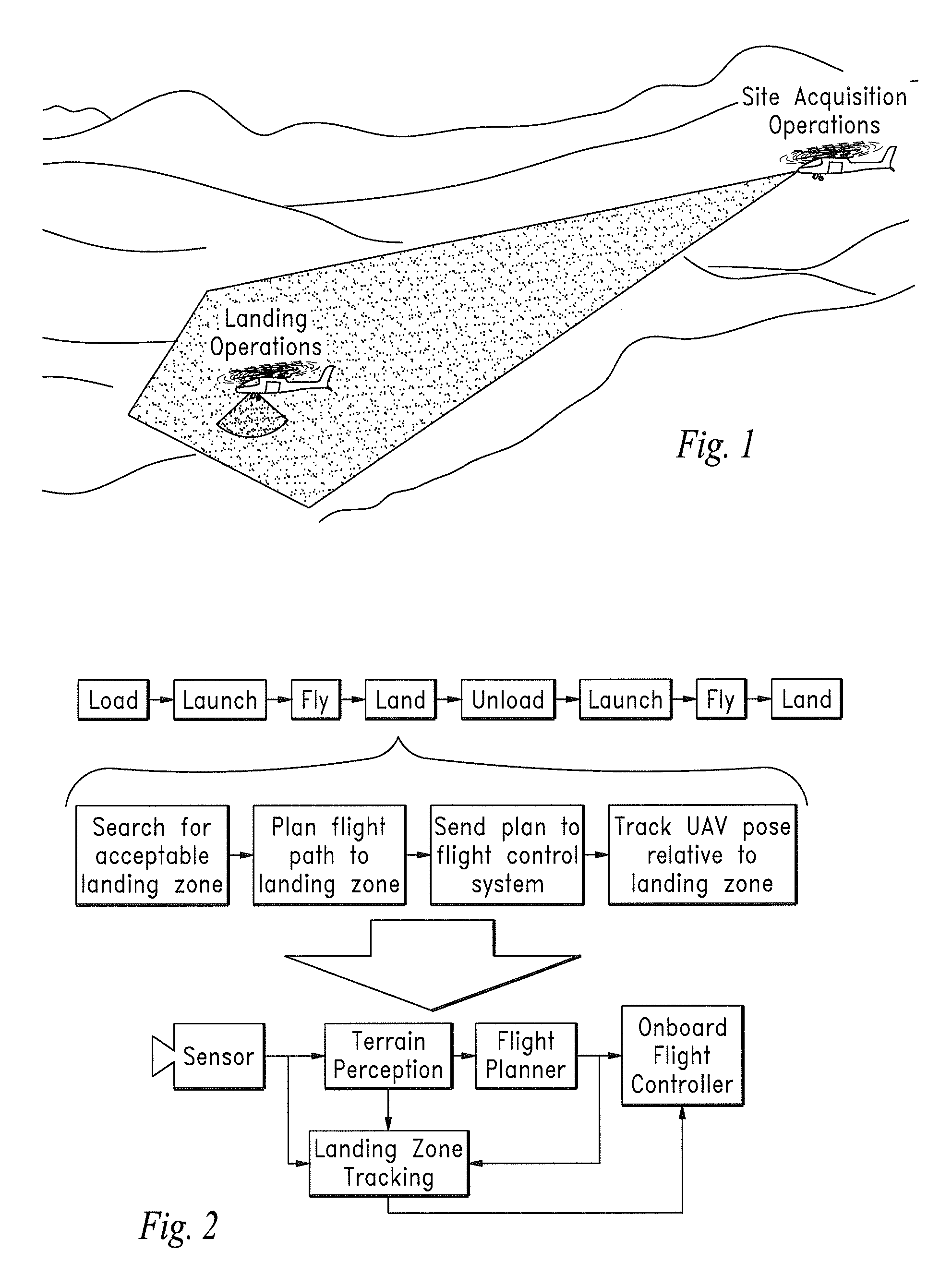
InactiveUS20110285981A1Optical rangefindersVehicle position/course/altitude controlPhotodetectorBeam steering
A LIDAR sensor element and system for wide field-of-view applications such as autonomous UAS landing site selection is disclosed. The sensor element and system have an imaging source such as a SWIR laser for imaging a field of regard or target with a beam having a predefined wavelength. The beam is scanned over the field of regard or target with a beam steering device such as Risley prism. The reflected beam is captured by the system by receiving optics which may comprise a Risley prism for receiving and imaging the reflected beam upon a photodetector array such as a focal plane array. The focal plane array may be bonded to and a part of a three-dimensional stack of integrated circuits, a plurality of which may comprise one or more read out integrated circuits.
Owner:PFG IP +1
Fourier transform spectrometer apparatus using multi-element mems
InactiveUS20050185179A1Low costHigh enough speedRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationGratingPhotovoltaic detectors
A Fourier Transform (FT) spectrometer apparatus uses multi-element MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical-Systems) or D-MEMS (Diffractive Micro-Electro-Mechanical-Systems) devices. A polychromatic light source is first diffracted or refracted by a dispersive component such as a grating or prism. The dispersed beam is intersected by a multi-element MEMS apparatus. The MEMS apparatus encodes each spectral component thereof with different time varying modulation through corresponding MEMS element. The light radiation is then spectrally recombined as a single beam. The beam is further split into to a reference beam and a probe beam. The probe light is directed to a sample and then the transmitted or reflected light is collected. Both the reference beam and probe beam are detected by a photo-detector. The detected time varying signal is analyzed by Fourier transformation to resolve the spectral components of the sample under measurement.
Owner:METROHM SPECTRO INC
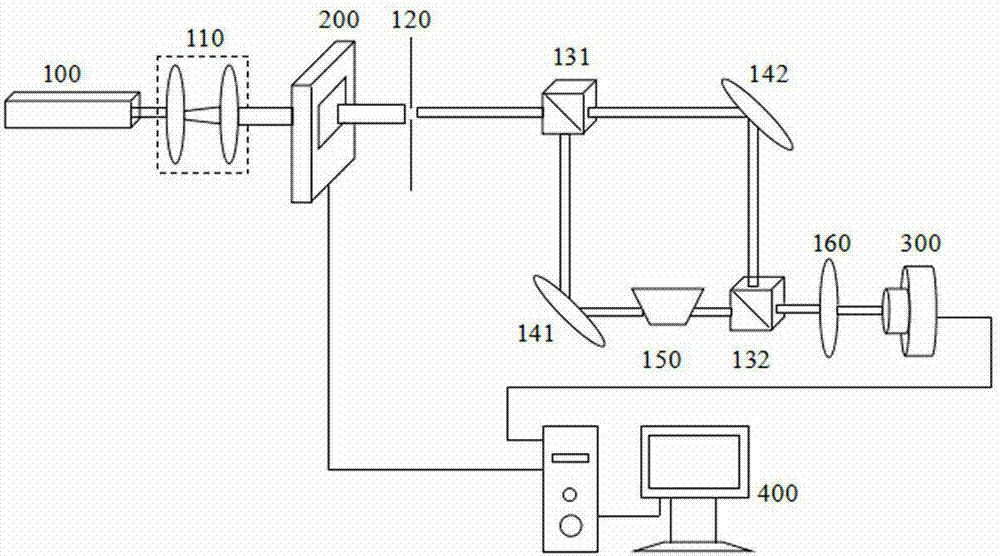
Measuring device for measuring vortex light beam high-order topological charge
A measuring device for measuring vortex light beam high-order topological charge is provide with a He-Ne laser device, wherein collimation and beam expanding devices are sequentially arranged in the light beam advancing direction of the laser device, a spatial light modulator where a forked phase hologram generated by a computer is input generates vortex light beams (shown in the description), and then the vortex light beams pass through a round hole diaphragm and a polarization beam splitter (shown in the description). The vortex light beams (shown in the description) passed through the polarization beam splitter (shown in the description) are divided into transmitting vortex light (shown in the description) and reflecting vortex light (shown in the description), the reflecting vortex light (shown in the description) and the transmitting vortex light (shown in the description) form an included angle of 90 degrees, the reflecting vortex light (shown in the description) advances and then is irradiated onto a reflecting mirror (shown in the description). The reflecting vortex light advances and then passes through a Dove prism to serve as mirror image light beams of the vortex light beams and to be irradiated onto the polarization beam splitter (shown in the description), and the transmitting vortex light (shown in the description) passes through the reflecting mirror (shown in the description) and then serves as the vortex light beams (shown in the description) to be irradiated onto the polarization beam splitter (shown in the description). The vortex light beams (shown in the description) and the mirror image light beams of the vortex light beams pass through the polarization beam splitter (shown in the description) and then are combined to form an interference-superimposed vortex light beam. The interference-superimposed vortex light beam passes through a convergent lens and then enters a CCD camera to be imaged, and then an image is stored in the computer. The device achieves measurement of the vortex light beam high-order topological charge and has the advantages of being simple, quick and accurate.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Large field of view modulating retro reflector (MRR) for free space optical communication
A modulating retro-reflector (MRR) can be configured to provide a large field of view. The MRR can include a solid corner cube reflector (CCR) manufactured of a material having a high index of refraction at the desired operating wavelength. CCRs made from high index materials such as InP or Si, have an index of refraction of approximately 3.48 at an operating wavelength of approximately 1550 nm and can provide a conical Field of View (FOV) of greater than ±60 degrees compared to less than ±30 degrees for CCRs made from BK-7. Each CCR can include one or more elements configured to modulate an optical signal incident on the CCR. A retro-modulating transponder can use fewer large FOV MRRs to support communication over a predetermined incident optical span compared to narrower FOV MRRs resulting in lower cost, smaller size, weight and power requirements.
Owner:CUBIC CORPORATION
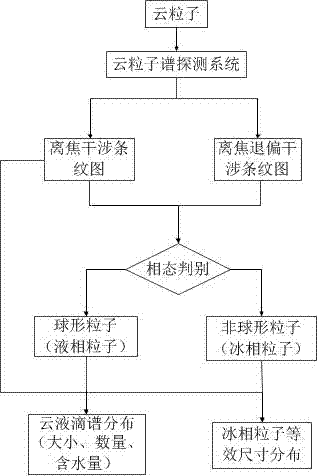
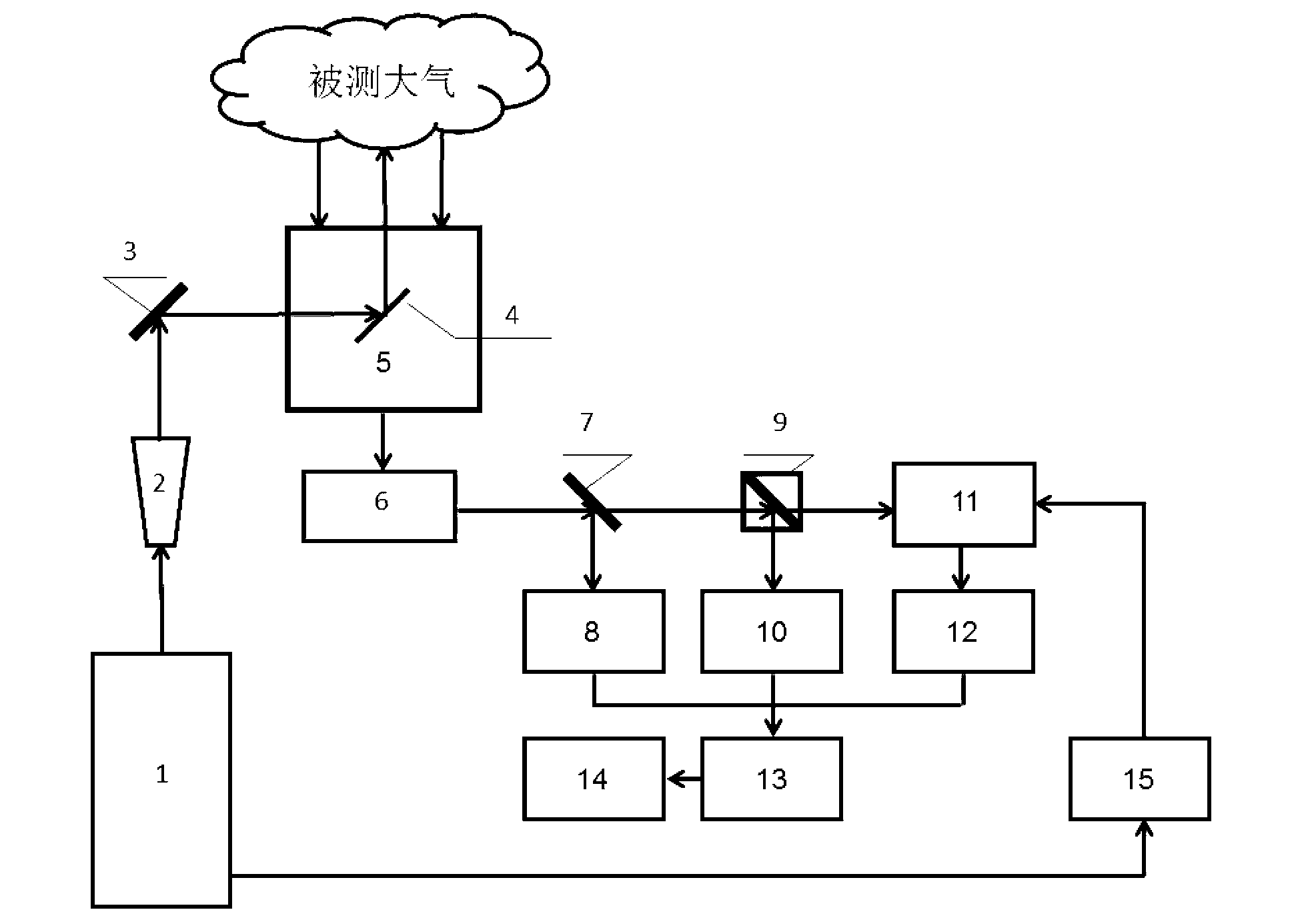
Cloud particle spectrum distribution measuring method and system
ActiveCN103868831ARealize the discrimination of phase stateAchieve inversionScattering properties measurementsParticle size analysisGrismBeam splitter
The invention discloses a cloud particle spectrum distribution measuring method and system. The measuring system comprises a disc-shaped polarization laser beam generating system, a grain scattered light detection system and a computer system. The measuring method provided by the invention comprises the steps of irradiating cloud grains by polarized light, dividing scattered signals into two ways by a beam splitter prism, carrying out detection of an out-of-focus interference pattern on one way of scattered signals directly by a photoelectric image detector while carrying out detection on a depolarization out-of-focus interference pattern on the other way of scattered signals by a depolarizer and a photoelectric image detector, distinguishing a cloud particle phase state by comparing the out-of-focus interference pattern with the depolarization out-of-focus interference pattern, and inverting according to out-of-focus interference fringe pattern information to obtain a liquid phase cloud particle size and an ice phase cloud particle equivalent size. The cloud particle distribution measuring method provided by the invention serves as a new diagnostic method for atmosphere particle detection, can be used for onboard cloud micro physic detection, and is capable of implementing on-line measurement of the phase state, size, distribution and water content of cloud particles so as to provide the powerful basis for meteorology forecast and manual intervention.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Cassegrain optical system for framing aerial reconnaissance camera
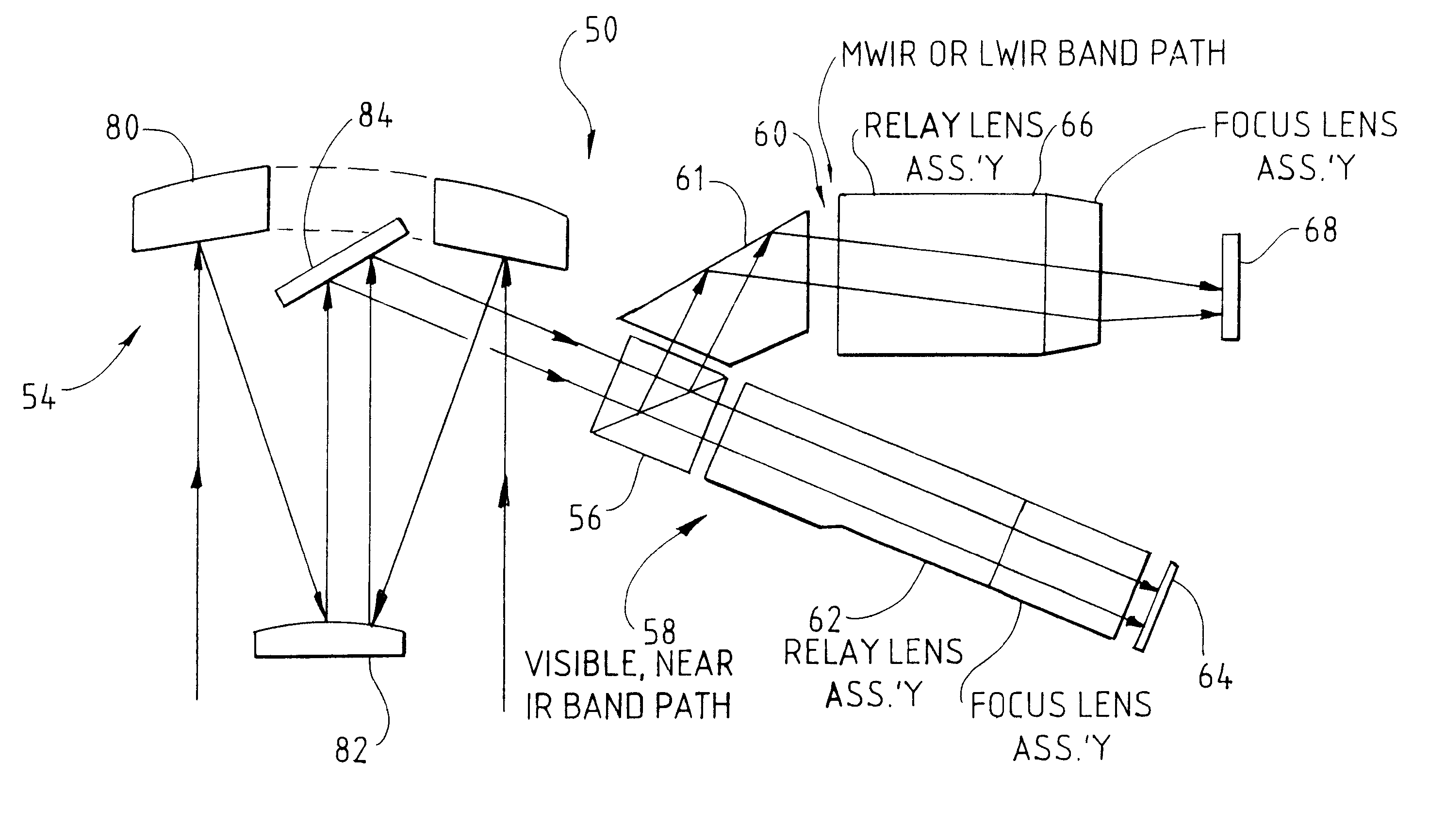
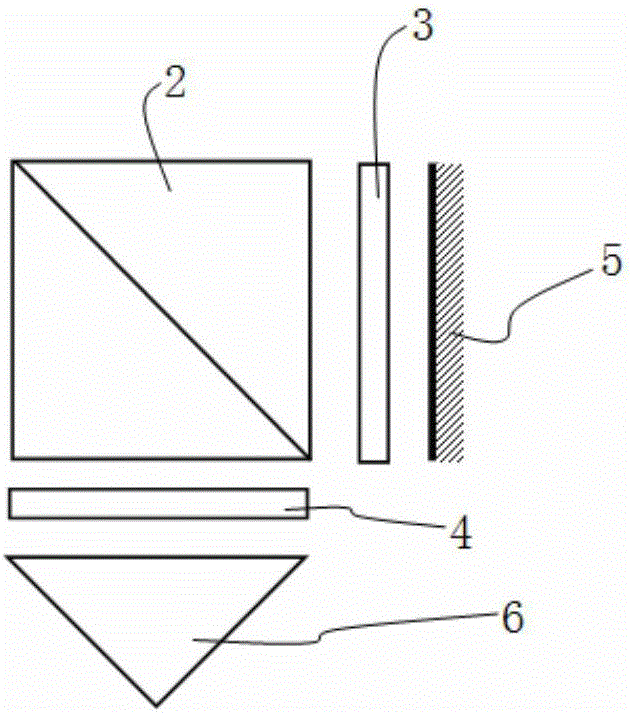
InactiveUS6374047B1High resolutionEliminate needPicture taking arrangementsColor television detailsOptical pathWave band
A dual band optical system for a framing aerial reconnaissance camera is described. The camera including at least two two-dimensional image recording media for generating frames of imagery of a scene external of an aerial reconnaissance vehicle carrying the camera. The camera includes a Cassegrain optical system forming an objective lens for the optical system, including a a primary mirror having a central aperture and a secondary mirror. The primary and secondary mirrors are aligned along an objective optical axis. The optical system also includes an azimuth mirror receiving radiation from the secondary mirror. The azimuth mirror is placed between the primary and secondary mirrors. A spectrum-dividing element in the form of a prism receives radiation from the azimuth mirror. The spectrum-dividing element directs radiation in a first band of the electromagnetic spectrum into a first optical path and radiation in a second band of the electromagnetic spectrum into a second optical path different from the first optical path. A first two-dimensional image recording medium is placed in the first optical path and a second two-dimensional image recording medium is placed in the second optical path. The first and second image recording media generating first and second images in two different portions of the electromagnetic spectrum simultaneously.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
Single-frequency laser interferometer non-linear error compensation device
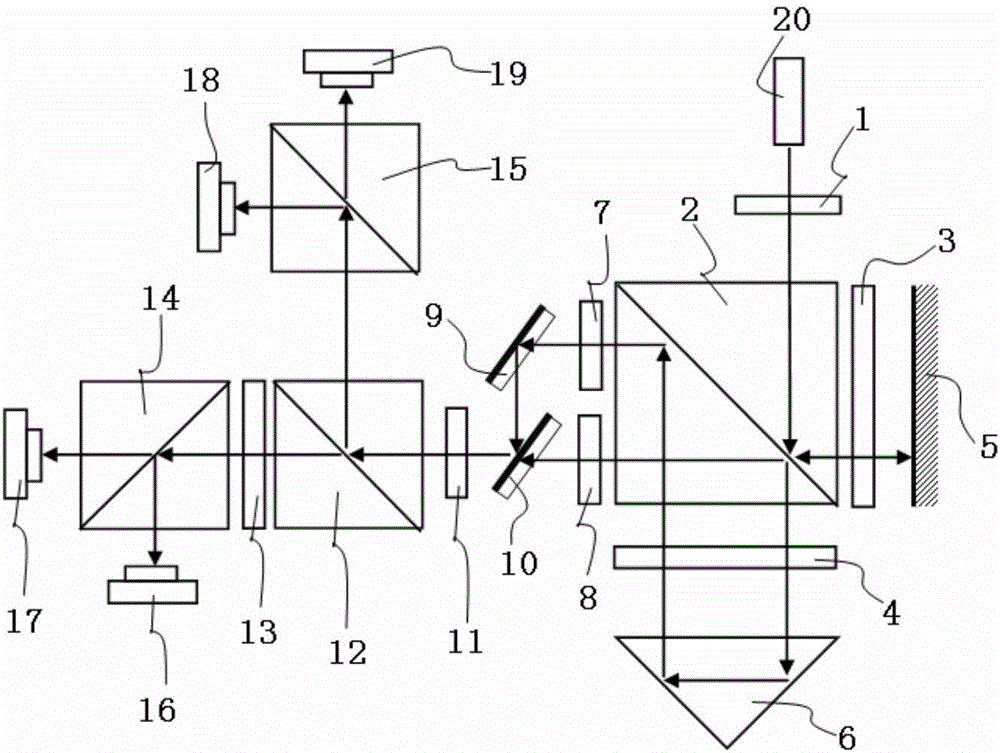
ActiveCN106225667ACompensate for phase non-orthogonality errorCompensate for non-linear errorsUsing optical meansGrismPlane mirror
The present invention discloses a single-frequency laser interferometer non-linear error compensation device. The single-frequency laser interferometer non-linear error compensation device is characterized in that after a light beam emitted by a laser is split by a polarization splitting prism, the transmitted light is projected to a rectangular prism and is returned to the polarization splitting prism to form the reference light S; the reflected light is projected to a plane mirror and is returned to the polarization splitting prism to form the measurement light P; a linear polaroid along an S direction is placed in a reference light path, and a linear polaroid along a P direction is arranged in a measurement light path, thereby realizing the nonorthogonal error compensation; the semi-transparent and semi-reflective mirrors are arranged in the emergent light paths of the linear polaroids, so that the reference light and the measurement light are combined and then are split by a depolarization splitting prism evenly, the transmitted light generates the interference signals I1 and I2 via a quarter-wave plate and the polarization splitting prism, the reflected light generates the interference signals I3 and I4 via the polarization splitting prism, and the mutual phase difference of the signals I1, I2, I3 and I4 is 90 degrees. According to the present invention, a non-linear error of the single-frequency laser interferometer is compensated effectively.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Holographic projection method
ActiveCN102749793ABreak through the limitation of imaging distanceProjectorsGrismSpatial light modulator
The invention discloses a holographic projection method which comprises the following steps of: (10) laying projection devices: successively laying a phase spatial light modulator, a beam splitting prism, a lens and a screen, laying a mono-color laser and a polarizing film on the same side of the beam splitting prism, and connecting the phase spatial light modulator with a computer; (20) measuring the distance of an imaging face; (30) measuring and calculating the relationship between the focal length of the lens and the distance of the imaging face; (40) after determining the order of fractional Fourier transformation in the system, and carrying out iteration by using the fractional Fourier transformation formula and the inverse transformation formula to obtain the phase of a two-dimensional image; and (50) transmitting the phase hologram to the phase spatial light modulator via the computer, and projecting the phase hologram onto the screen in the specific location by using the phase spatial light modulator. With the holographic projection method, the holographic reconstructed two-dimensional image can be projected onto any plane behind the lens, and the focal length of the lens does not need to be changed to control the distance of imaging.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Simultaneous polarization phase-shifting interferometer
InactiveCN102944169AEliminate measurement effectsRealize continuous dynamic measurementUsing optical meansBeam splitterPhase difference
The invention relates to a simultaneous polarization phase-shifting interferometer. The interferometer uses a HeNe laser as a linear polarization coherent light source and comprises reference light and measurement light carrying phase information of a standard lens and a lens to be measured. The reference light and the measurement light are reflected and transmitted by a polarization splitting prism respectively to be combined into one light beam in a same light path respectively, and a 1 / 4 wave plate and a beam splitter prism are arranged successively on the light path respectively; the light beam can be split into two portions with equal amplitudes by a depolarization splitting prism, and polarization splitting prisms are arranged on two split light paths; and image acquisition devices are arranged on the light paths after the light beams pass through the polarization splitting prisms respectively. According to the simultaneous polarization phase-shifting interferometer, the wave plate and polarization prism structures are used, and polarized light interference is used, so that four interference images with a phase difference of pi / 2 successively can be obtained at a same moment, effects of airflows and ambient vibration on measurement can be eliminated, the interferometer can be applied to field inspection of optical systems and optical inspection in complicated and severe environments, and continuous dynamic measurement can be achieved.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Blurring image processing-based dynamic grain measuring device and method
InactiveCN102692364AEasy to handleAvoid synchronizationParticle size analysisUsing optical meansCamera lensBeam splitter
The invention discloses a blurring image processing-based dynamic grain measuring device and a method. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: lighting grains to be measured by adopting a light source or through a visual window, dividing light coming from a camera lens into two paths by a beam splitter prism, imaging by adopting two CCDs (Charge Coupled Device) or CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) image sensors with optical distance unequal to that of two corresponding emergent surfaces of the beam splitter prisms, judging whether the grains are positioned in front or behind a focusing plane according to different optical distances and different obtained grain image blurring extent, and calculating the positions of grains and the distance of the focusing plane according to defocusing amount of grains in one picture, thus determining a three-dimensional position of the grains; and further obtaining the three-dimensional movement speed information of the grains by combining motion blurring parameter of the grains, thus being capable of accurately determining the grain size of the grains. The invention has the benefits of being capable of realizing three-dimensional measurement on dynamic grains only by one camera lens, simplifying a measuring system and the data processing course and lowering the system cost.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Cross-polarization laser feedback grating interferometer of phase modulation type, and measurement method thereof
The invention relates to a cross-polarization laser feedback grating interferometer of a phase modulation type, and a measurement method thereof. The measurement principle is based on the grating diffraction, optical Doppler effect, Lamb semi-classical theory and time-domain orthogonal demodulation principle. The orthogonally polarized light outputted by a birefringent dual-frequency helium-neon laser is perpendicularly incident to a polarization beam splitting prism and is divided into two linearly polarized light beams in different polarization directions. The two polarized light beams respectively pass through two different electrooptical modulators and then are respectively reflected by a reflector at a + / -1-order Littrow incidence angle to a reflection-type diffraction grating. The diffracted light returns to the laser cavity along the respective incident light, and performs self-mixing interference with the light in the cavity. The backward output light of the laser passes through a polarizer and then only the single-mode light is retained and accepted by a photodetector. An output signal of the photodetector is outputted to a data processing module for data processing, and the two-dimensional displacement of a target to be measured is obtained. The grating interferometer has the advantages of simple structure, large measuring range and high measurement resolution.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Optical navigation attitude determination and communications system for space vehicles
The invention is for a sensor for use in spacecraft navigation and communication. The system has two articulated telescopes providing navigation information and orientation information as well providing communications capability. Each telescope contains a laser and compatible sensor for optical communications and ranging, and an imaging chip for imaging the star field and planets. The three optical functions share a common optical path. A frequency selective prism or mirror directs incoming laser light to the communications and ranging sensor. The Doppler shift or time-of-flight of laser light reflected from the target can be measured. The sensor can use the range and range rate measured from the incoming laser along with measurements from the imaging chip to determine the location and velocity of the spacecraft. The laser and laser receiver provide communications capability.
Owner:PRINCETON SATELLITE SYST
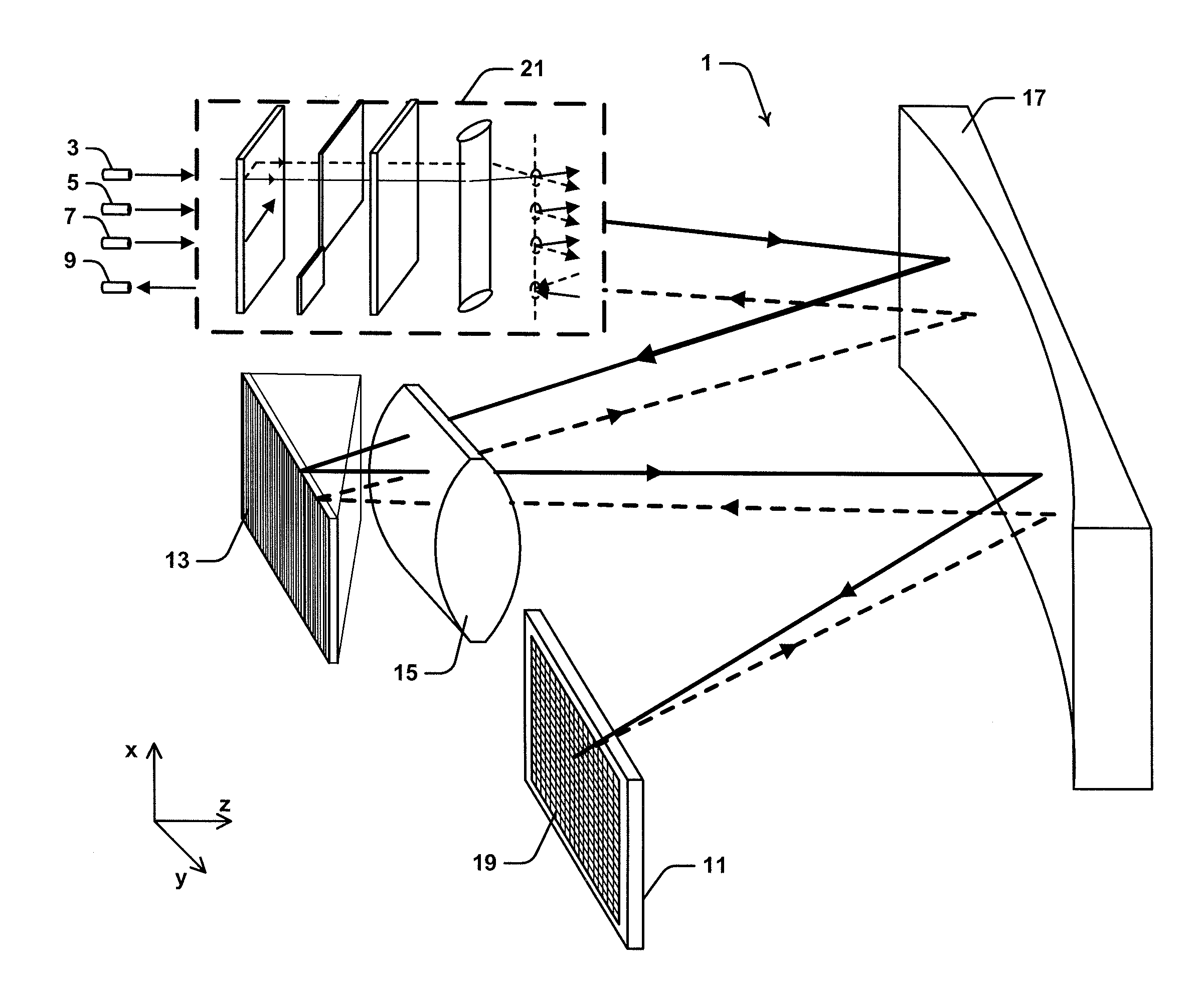
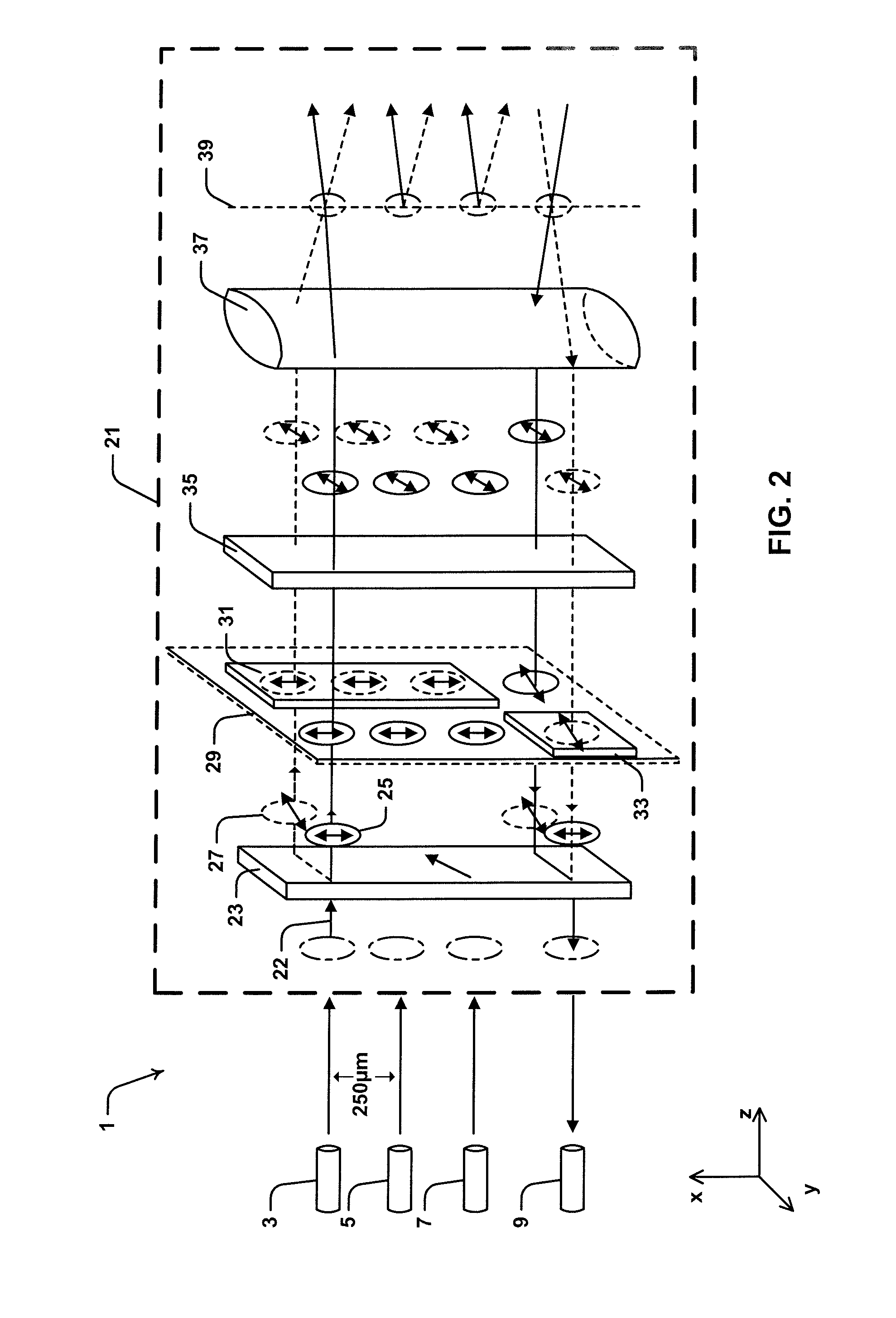
Polarization Diverse Wavelength Selective Switch
ActiveUS20150208143A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsPolarisation multiplex systemsGrismPolarization diversity
Described herein is a wavelength selective switch (WSS) type optical switching device (1) configured for switching input optical beams from input optical fiber ports (3, 5 and 7) to an output optical fiber port (9). Device (1) includes a wavelength dispersive grism element (13) for spatially dispersing the individual wavelength channels from an input optical beam in the direction of a second axis (y-axis). The optical beams propagate from input ports (3, 5 and 7) in a forward direction and are reflected from a liquid crystal on silicon (LCOS) device (11) in a return direction to output port (9). The input optical beams are transmitted through a port selecting module (21), which provides polarization diversity to device (1) and provides capability to restrict optical beams returning from LCOS device (11) from being coupled back into input ports (3, 5 and 7).
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
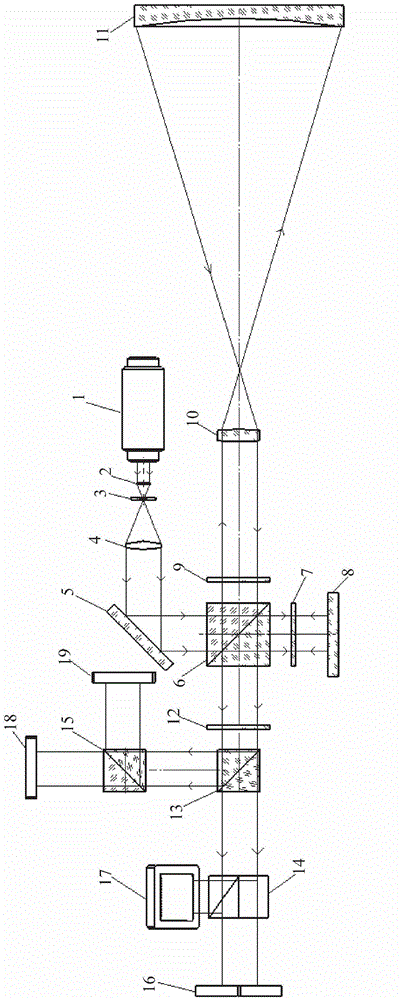
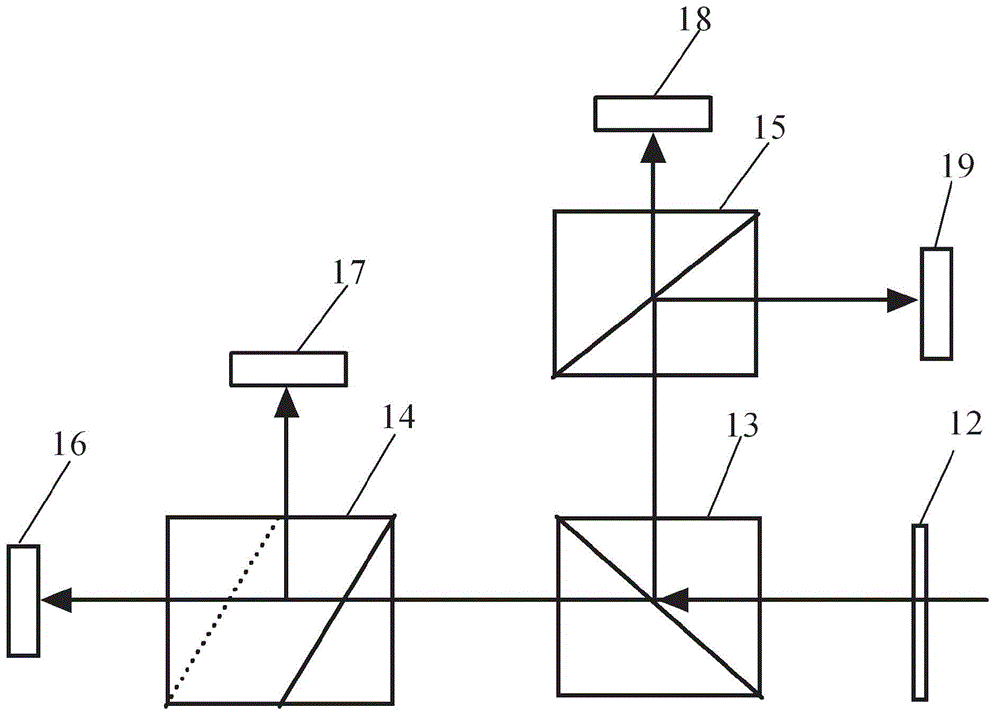
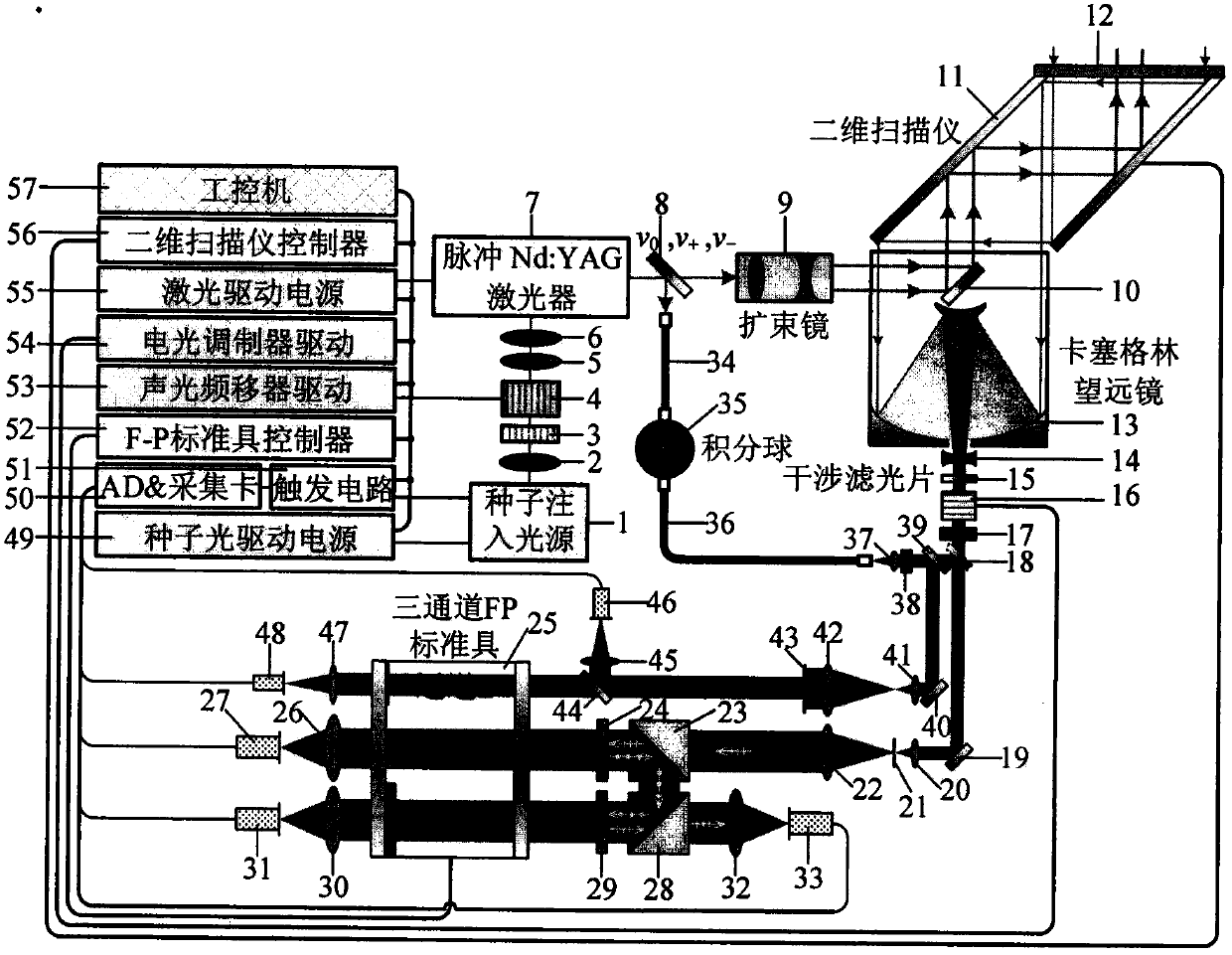
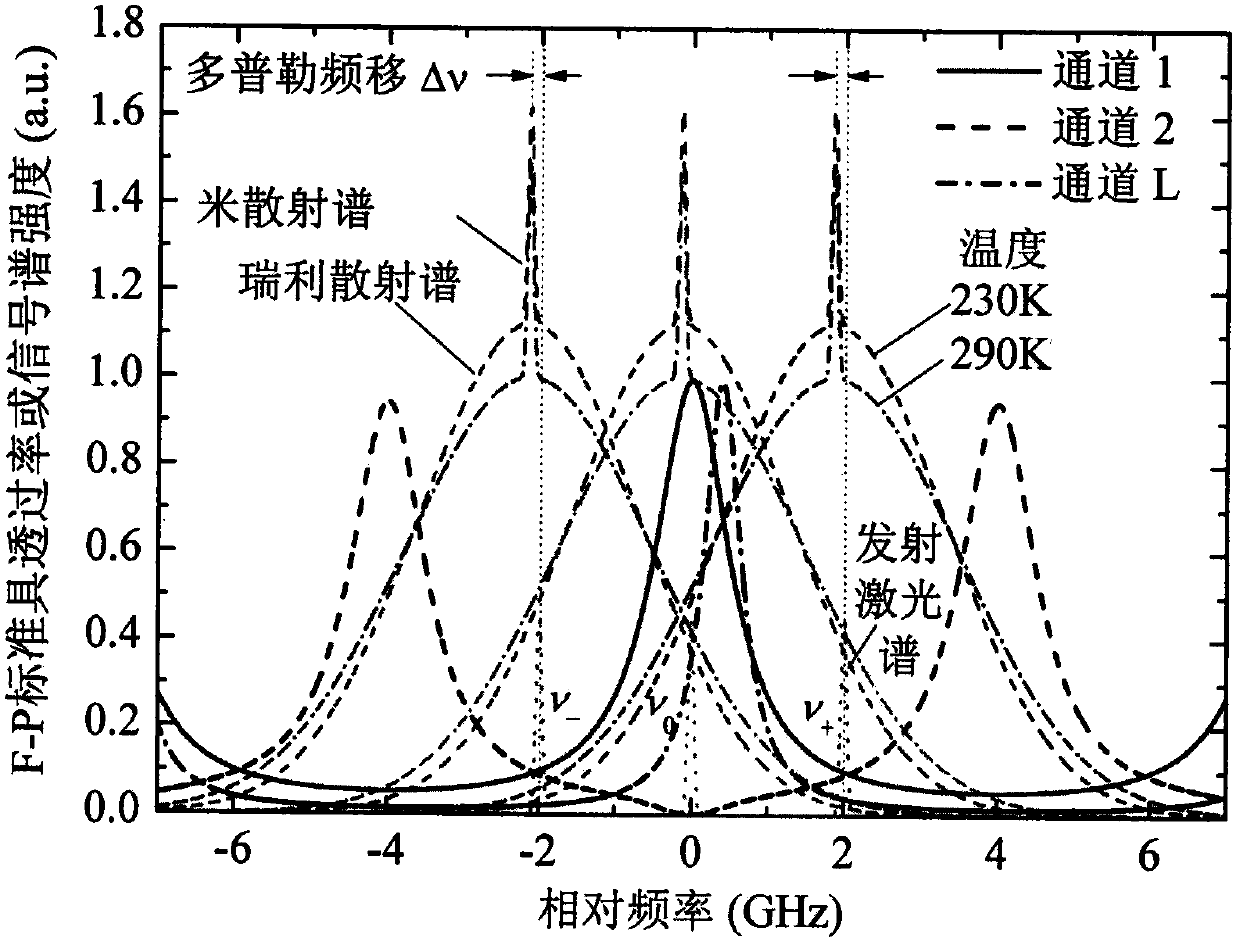
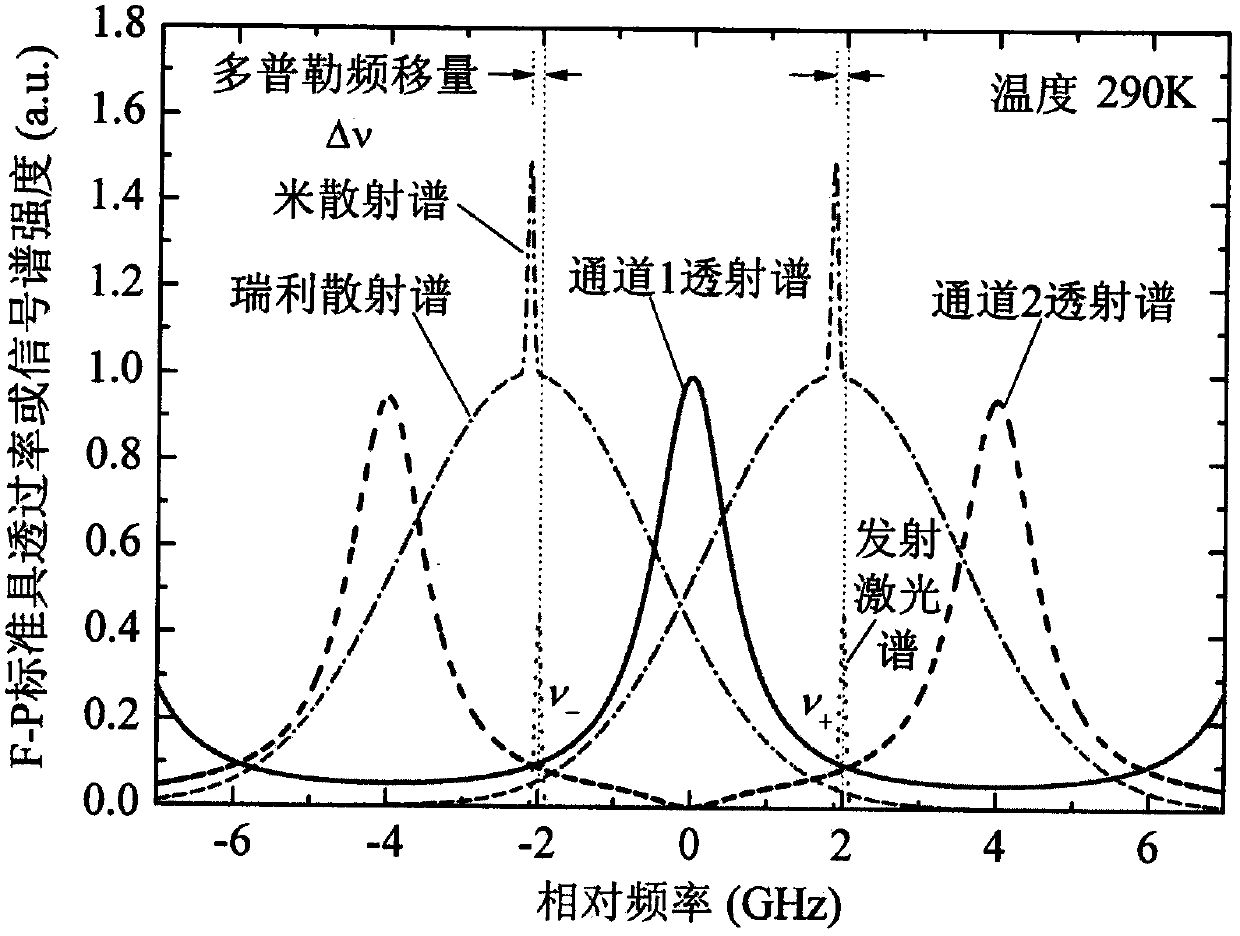
Ultraviolet three-frequency high spectrum resolution laser radar system based on F-P etalon and detection method thereof
ActiveCN107193015AImprove signal-to-noise ratioImprove detection signal-to-noise ratioElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationPhysicsImage resolution
The invention relates to an ultraviolet three-frequency high spectrum resolution laser radar system based on three-channel FP etalon and a detection method thereof, wherein the system and the method can be used to simultaneously detect a 0-35km height wind field, a temperature and an aerosol in a high precision mode. The system is characterized in that an emission laser frequency is alternatively changed among v0, v0-2GHz and v0+2GHz; channels L, 1 and 2 of the etalon are designed into one body, a free spectral spacing is 8GHz, spectral widths are 0.2GHz, 1GHz and 1GHz, 1-L and 1-2 peak to peak intervals are 0.1GHz and 4GHz; the v0 is locked at a peak value of the channel 1; and a quarter wave plate and a polarizing beam splitter prism form a cascading light path. The system and the method have advantages that a single radar can simultaneously measure the 0-35km height wind field, the temperature and the aerosol in the high precision mode; and disadvantages that detection precision of a single parameter detection technology is not high, a detection range can not be covered and three parameters mutually influence each other so that an inversion error is large are overcome.
Owner:YANCHENG TEACHERS UNIV
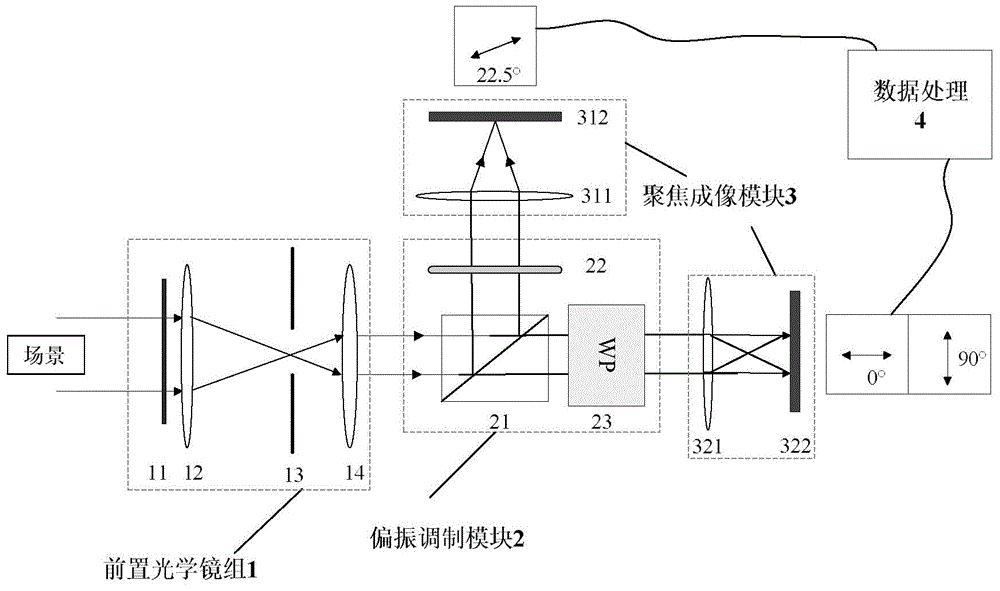
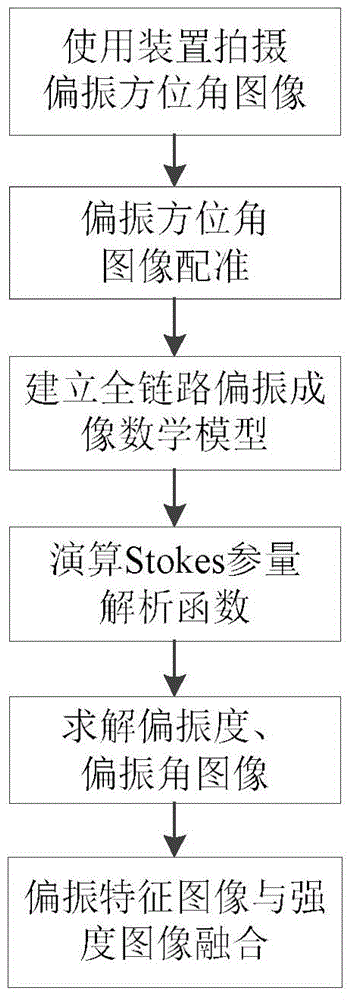
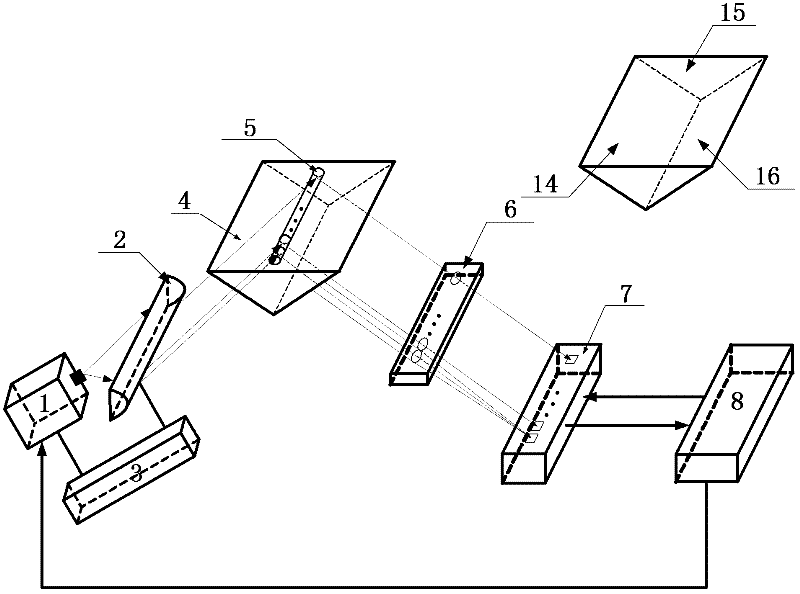
Three-channel and single-Wollaston prism polarization imaging device and polarization information detecting method
The invention discloses a three-channel and single-Wollaston prism polarization imaging device and a polarization information detecting method and aims to solve the problem that the prior art is redundant in structure and low in resolution and cannot detect target polarization information in real time. The polarization imaging device comprises a front optical lens group (1), a polarization modulation module (2), a focusing imaging module (3) and a data processing module (4), wherein the polarization modulation module (2) is a polarization modulation structure composed of a non-polarization beam-splitting prism (21), a linear polarizer (22) and a single Wollaston prism (23), three polarization azimuth angle images of a target can be obtained by one exposure through the polarization modulation structure, and super-resolution reconstruction and registration and polarization state analysis and fusion are sequentially performed on the three polarization azimuth angle images through the data processing module (4) to obtain a target image containing the target polarization information and scene detail information. The three-channel and single-Wollaston prism polarization imaging device is simple in structure, high in space resolution and applicable to target detection and environment monitoring.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Imaging optical microfluid sensing device and method thereof
InactiveCN102519908ARealize space division multiplexingFlexible constructionPhase-affecting property measurementsMountingsResonant cavityPhotovoltaic detectors
Disclosed are an imaging optical microfluid sensing device and a method thereof. The sensing device comprises a tunable laser light source, a collimating lens, an incidence angle adjusting rack, a reflection prism, an optical microfluid resonant cavity array, a microlens array, an array photoelectric detector, and a signal control and processing unit. Lights emitted from the light source pass through the collimating lens and become parallel light beams, which are incident on the reflection prism. The incident lights at the bottom of the reflection prism are coupled through an evanescent fieldso as to excitate resonant mode of the optical microfluid resonant cavity array for sensing. The reflected lights with the wavelength information of the resonant mode are incident on the array photoelectric detector for imaging. When continuously tuning laser light output wavelength, corresponding multiple-frame images are recorded. Serial processing is carried out on each pixel in the array photoelectric detector in the signal processing unit according to record light source wavelength, so as to realize wavelength sensing querying of each optical microfluid resonant cavity. The apparatus caneffectively realize multichannel optical microfluid sensing and can be used for the construction of a high-flux optical microfluid detection system.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Detecting device and detecting method for dark field cofocal subsurface based on coaxial two conical lenses
InactiveCN109470710ASimple designEasy to transformOptically investigating flaws/contaminationBeam splittingOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a detecting device and a detecting method for dark field cofocal subsurface based on two coaxial conical lenses. Light emitted by a point light source passes through a collimating lens to form parallel light; the parallel light sequentially passes through a beam expander, a conical lens I and a conical lens II to form ring light; the ring light is converged to a to-be-tested sample by a beam splitting prism and an objective lens; reflected light and scattered light which are emitted by the to-be-tested sample pass through the objective lens and the beam splitting prismsequentially and enter a detection complementary diaphragm; the reflected light is shielded by the detection complementary aperture; the scattered light passes through the detection complementary diaphragm, a collecting lens and a detection pinhole sequentially and enters a photoelectric detector. The ring light illumination with adjustable duty factor is realized by adopting a beam expander and one group of symmetrically-putted coaxial conical lenses; dark field cofocus is realized by in combination with the detection complementary diaphragm; the problems of low signal-noise ratio, non-adjustable duty ratio of a shield type ring optical generator and great energy loss in the detection of the subsurface by an ordinary cofocal microtechnique are solved; the detecting device and the detecting method are suitable for subsurface nondestructive testing.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for calibrating double orthogonal high-precision accelerometers
InactiveCN101852817AEliminate the effects ofImprove test accuracyTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesCollimatorGrism
The invention discloses a method for calibrating double orthogonal high-precision accelerometers, and relates to the improved method for identifying an error model of the double orthogonal high-precision accelerometers, and aims to solve the problem of inaccurate accelerometer error parameter calibration caused by an angular error. The method comprises the following steps of: sleeving a polyhedral prism onto a main shaft of a grating dividing head, fixing two miniature high-precision accelerometers to be measured onto a mounting fixture in a way that the two accelerometers are vertical to each other, and fixing the mounting fixture onto the main shaft of the grating dividing head; making a light beam passing through a photoelectric auto-collimator irradiate the polyhedral prism, precisely determining zero offset terms in coefficients of the model of the accelerometers with readings at the positions of between 0 and 180 degrees, and for the positions of between 90 and 270 degrees, adopting the same method; and then obtaining each parameter of the error model by an orthogonal double-accelerometer method to finish the calibration. The method has the advantage of improving the testing precision of a gravitational field, and is particularly suitable for occasions of testing the accelerometers with precision higher than 1 mu g.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Wavelength multiplexed quantitative differential interference contrast microscopy
InactiveUS20020089741A1Rapid and robust measurementMaximize useUsing optical meansMicroscopesBeam splitterPupil
A differential interference contrast (DIC) microscope system is provided comprising: (a) an illumination source for illuminating a sample ; (b) a lens system for viewing the illuminated sample, including an objective, defining an optical axis; (c) at least one detector system for receiving a sample image; (d) mechanisms for wavelength multiplexing the shear direction or shear magnitude or both on the sample and demultiplexing the resultant DIC images on the detector; and (e) a mechanism for modulating the phase of the interference image. Various approaches are disclosed to accomplish wavelength multiplexing of shear direction and demultiplexing the two DIC images that result. It is possible for the two, wavelength multiplexed DIC images to differ in either or both shear direction or magnitude. These approaches include (1) two DIC microscopes, each operating at a different wavelength, but which share a single objective through a beam splitter; (2) a segmented DIC prism that is made in four sections where opposite sections are paired and have the same shear direction and amount, and each pair of sections have filters transmitting different wavelengths; (3) a segmented DIC prism that is located in or near an aperture stop or pupil of said DIC microscope to obtain data in two shear directions that is multiplexed by wavelength; (4) a dual field-of-view optical system with two DIC prisms, one in each path to wavelength multiplex shear direction or shear magnitude through said objective; (5) demultiplexing wavelength multiplexed DIC images through the use of a wavelength selective beam splitter and two detectors; (6) demultiplexing wavelength multiplexed DIC images through the use of a wavelength controlled source and a single detector; and (7) demultiplexing wavelength multiplexed DIC images through the use of dual field-of-view optics and a single detector. These various approaches permit rapid, robust measurement of slope in two directions. Further, phase shifting and DIC microscopy are limited to measurements within the depth of focus (DOF) of the objective while WLI microscopy is not.
Owner:KUHN WILLIAM P
Orthogonal homodyne laser interferometer and measurement method thereof
InactiveCN105043243AImprove general performanceImprove performanceUsing optical meansBeam splitterBand-pass filter
The invention discloses an orthogonal homodyne laser interferometer and a measurement method thereof. The interferometer is simple and reliable in structure, and comprises a helium-neon laser, a beam splitter prism, a lambda / 8 wave plate, a cubic pyramid prism, a measuring cubic pyramid prism, a precision guide rail, a photoelectric detector, a small signal amplification module, a band-pass filter module, an analog-to-digital conversion unit and a computer data processing unit. According to the invention, laser light emitting by the laser is split into reference light and measuring light after passing through the beam splitter prism, the measuring light firstly passes through the lambda / 8 wave plate and is then reflected by the measuring cubic pyramid prism so as to acquire a light beam, the light beam passes through the lambda / 8 wave plate again and generates interference with a reference light beam reflected by a reference cubic pyramid prism, and finally, two paths of orthogonal polarized light are acquired after passing through a polarization splitting prism; the photoelectric detector receives light signals and converts the light signals into electric signals, and signal conditioning is carried out by an amplification and filtering module; and the analog-to-digital conversion unit is controlled by a computer unit to acquire the conditioned electric signals, the phase is demodulated, and the real-time displacement of the measuring cubic pyramid prism is acquired and displayed.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
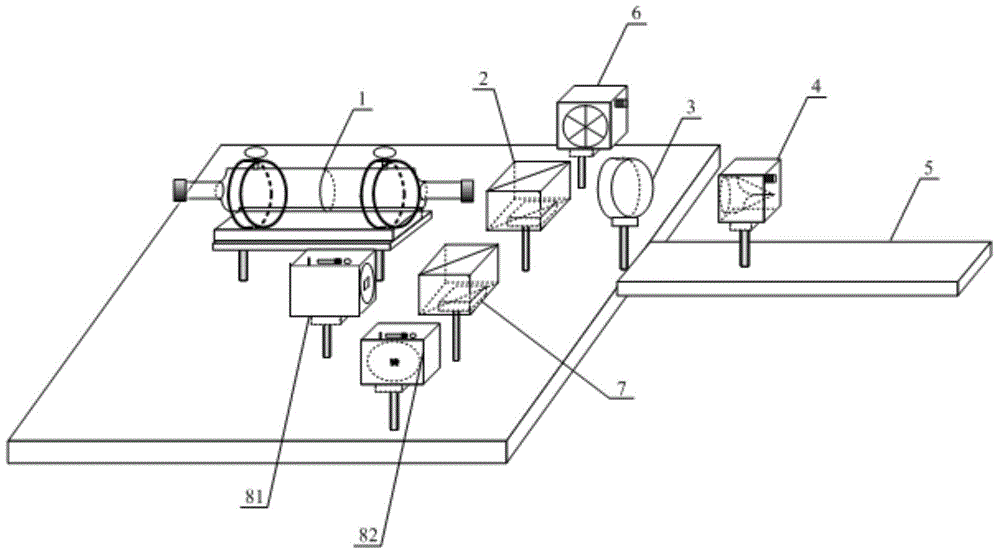
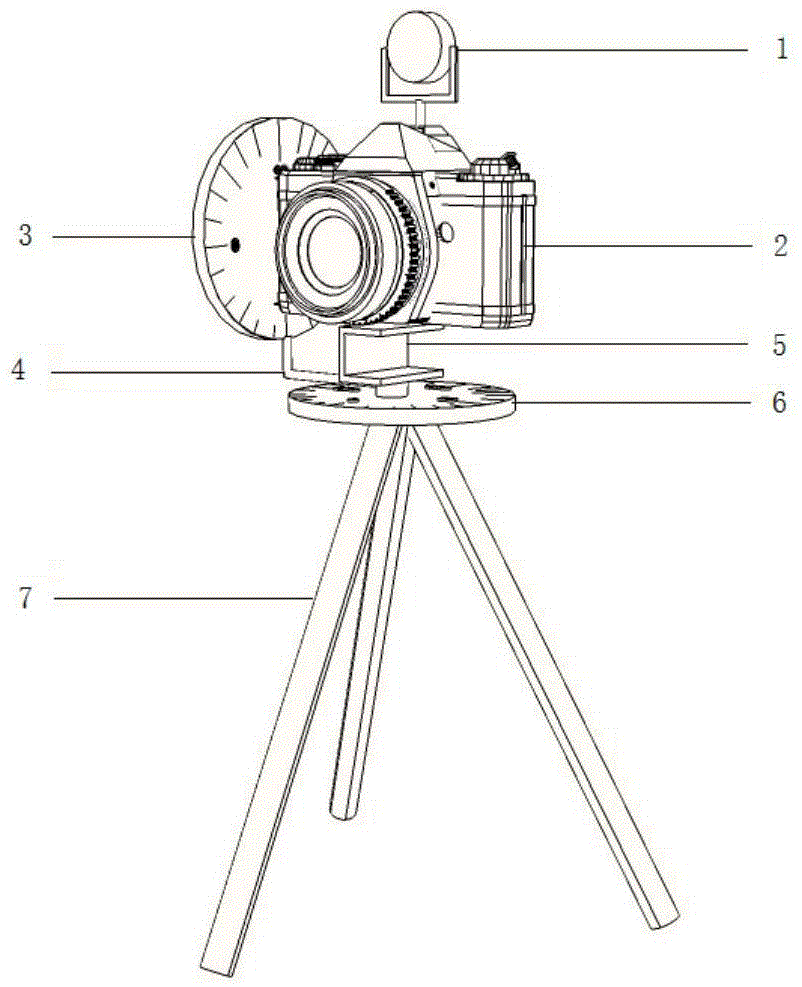
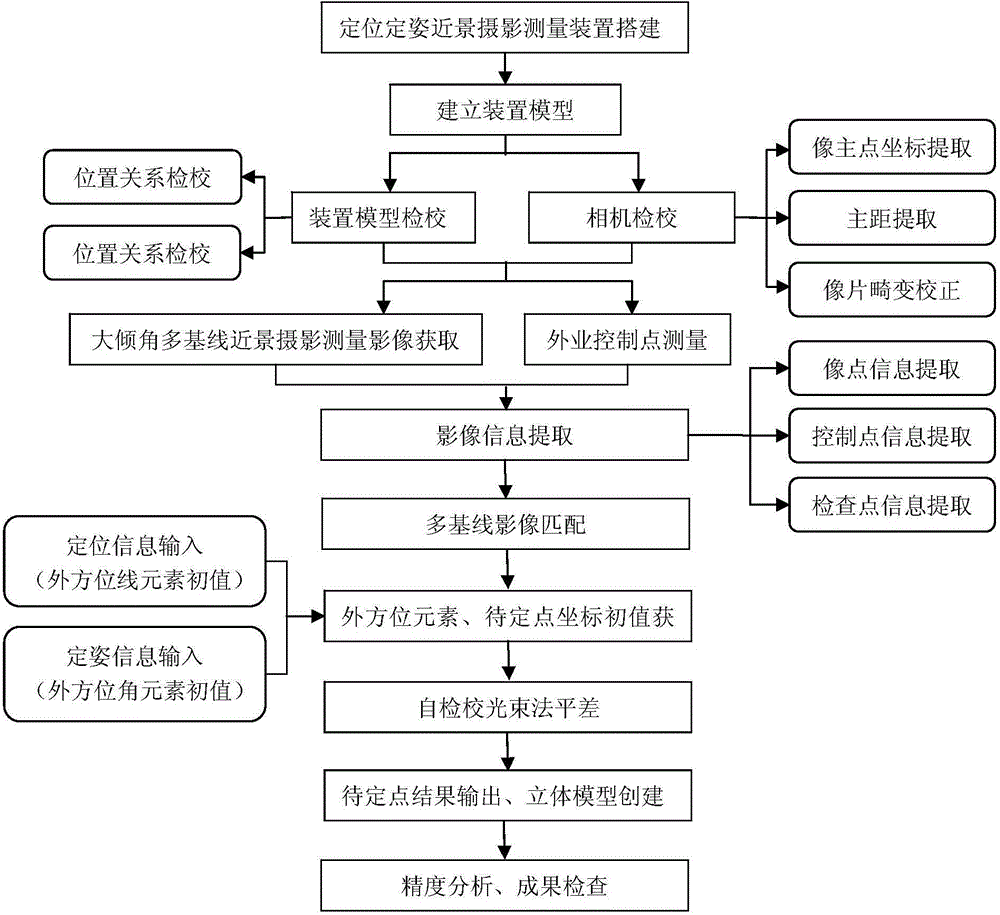
Close-shot photography measurement system capable of realizing positioning and attitude determination and close-shot photography measurement method capable of realizing positioning and attitude determination
ActiveCN104964673ALow costHigh precisionAngle measurementPicture taking arrangementsGrismData translation
The invention discloses a close-shot photography measurement system capable of realizing positioning and attitude determination and a close-shot photography measurement method capable of realizing positioning and attitude determination, belongs to the technical field of science of surveying and mapping, and particularly relates to a photography measurement technology. The system is subjected to real-time tracking and positioning by a prism mounted on a camera and a total station erected within a whole-visible range; a horizontal dial mounted below a holder at the bottom of the camera and a vertical dial mounted on the left side or right side of the camera are used for carrying out real-time attitude determination. By construction of a relation model of the prism, the horizontal dial, the vertical dial and the camera, positioning and attitude determination data are converted to the center of the camera, so that an image can be shot by the photography measurement, and information such as the position and attitude of the camera can be acquired. By use of a large-inclination-angle multi-base-line photography measurement algorithm and combination of line element and angle element initial values of the exterior orientation provided by a positioning and attitude determination system, large-inclination-angle and multi-base-line close-shot photography measurement can be quickly calculated; therefore, the efficiency and accuracy of image matching are improved, and the data processing precision is improved.
Owner:上海市房地产科学研究院 +1
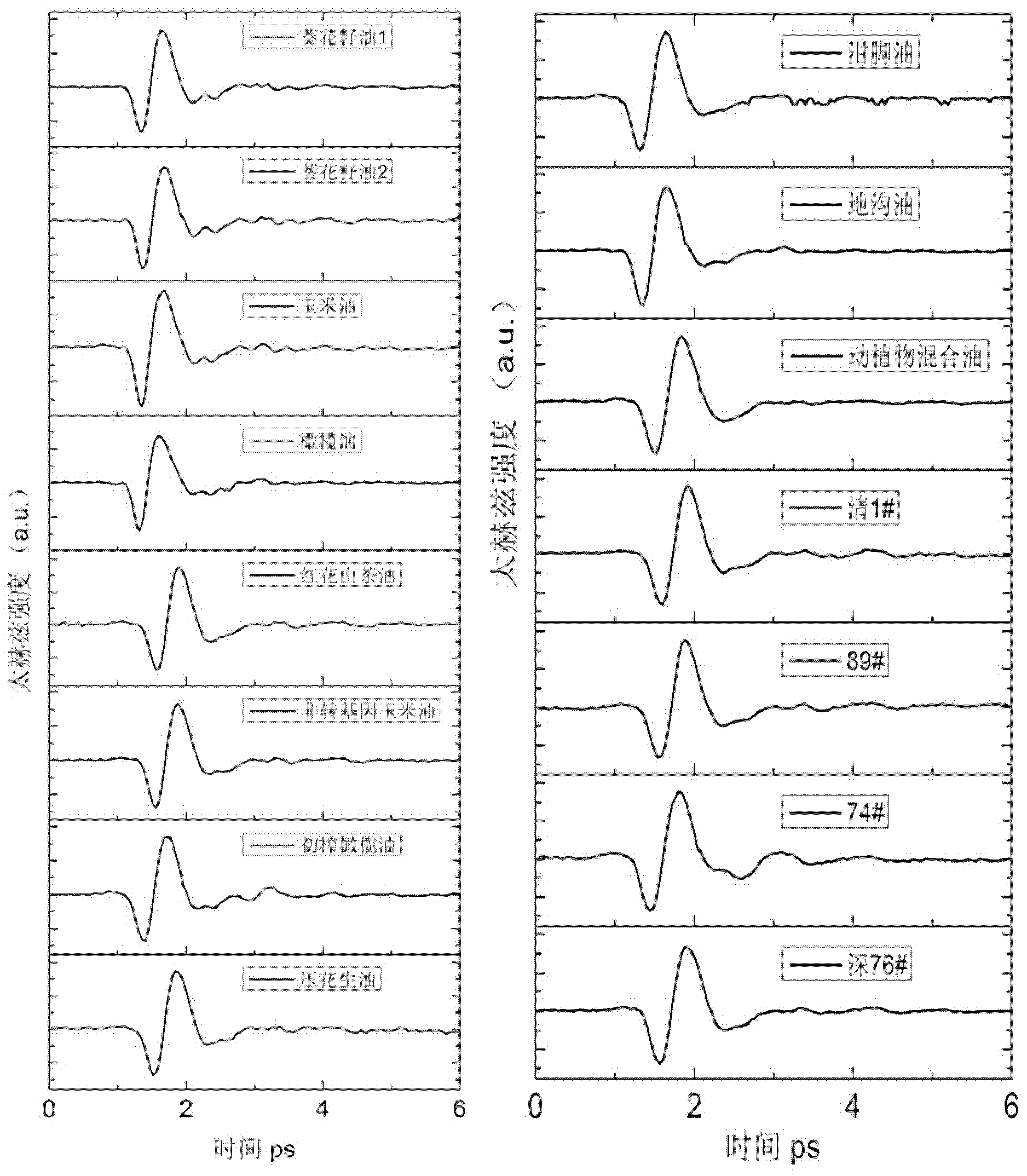
Swill-cooked dirty oil detecting system and detecting method
InactiveCN102564996ASimple processGood for healthColor/spectral properties measurementsBeam splitterHigh resistivity silicon
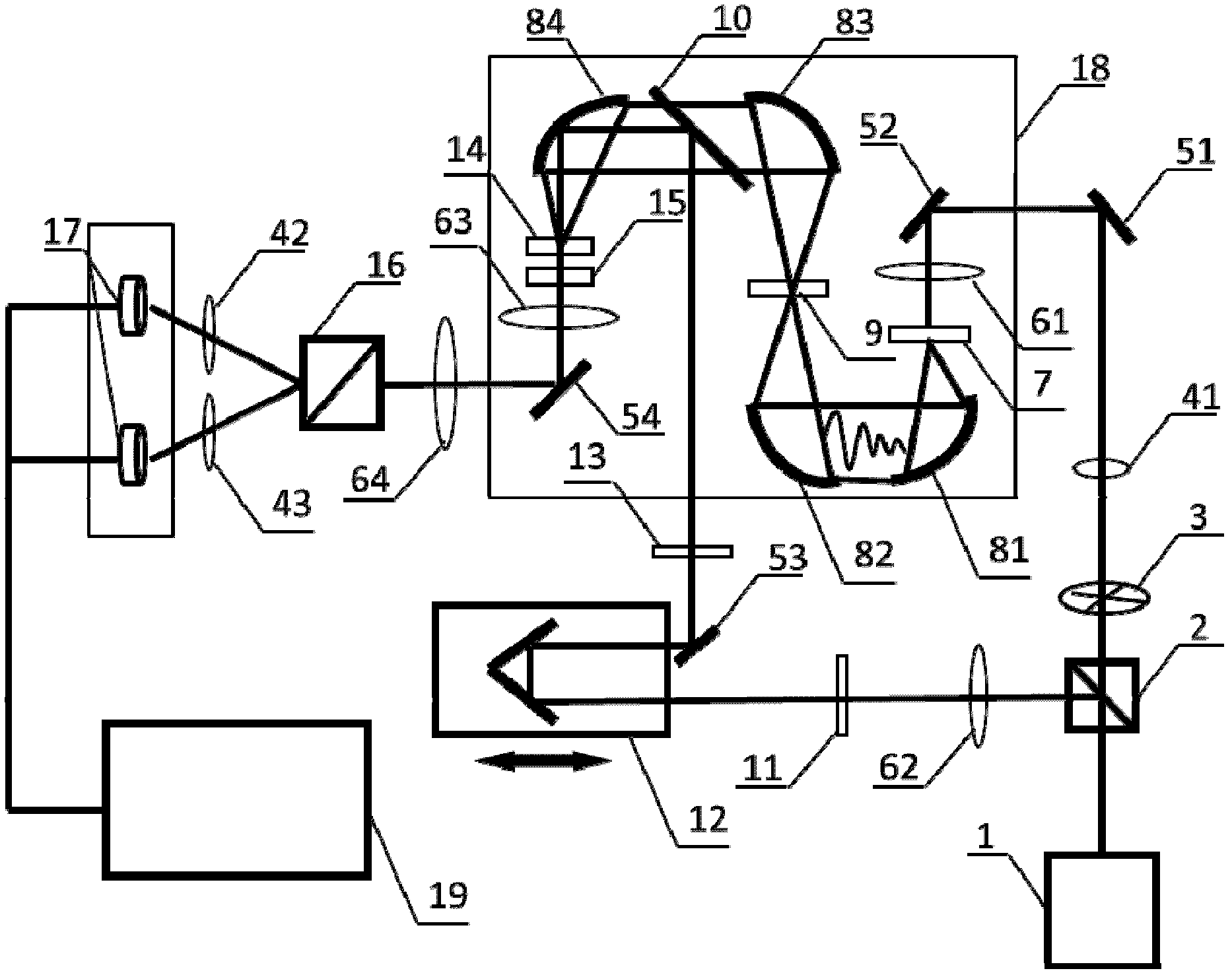
The invention provides a swill-cooked dirty oil detecting system. A semi-reflection and semi-transmission beam splitter is arranged at an emission port of a femtosecond laser; a pulse laser light is split into a pump light path and a detecting light path; the pump light path is connected with a photochopper, a first attenuation sheet, a first reflecting mirror, a second reflecting mirror, a first focusing lens and a gallium arsenide photoconductive antenna in sequence; a sample box is arranged on a confocal point of second and third paraboloidal mirrors; a second collimating lens, a half wave plate, a light path delay device, a third reflecting mirror, a polarizer and a high resistivity silicon reflecting mirror are arranged on the detecting light path in sequence; the femtosecond laser after being sampled by an electrooptic crystal is detected by being directed with a photoelectric detector via a quarter wave plate, a third focusing lens, a fourth reflecting mirror, a fourth focusing lens, a Wollstone prism as well as second and third attenuation sheets; and the variation of voltage magnitude caused by terahertz waves is recorded, so that a time domain terahertz signal including swill-cooked dirty oil information is obtained. The swill-cooked dirty oil detecting system provided by the invention has the advantages of simple detecting process, high efficiency, rapidness and accurate detecting result.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH +2
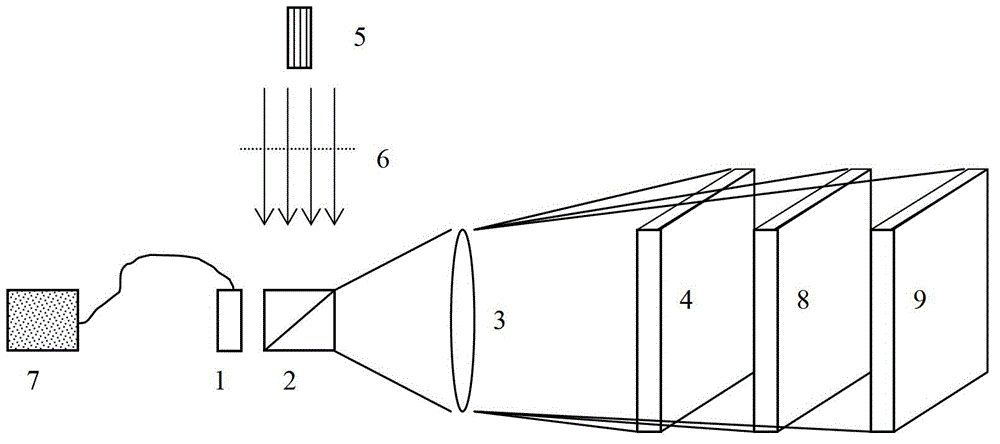
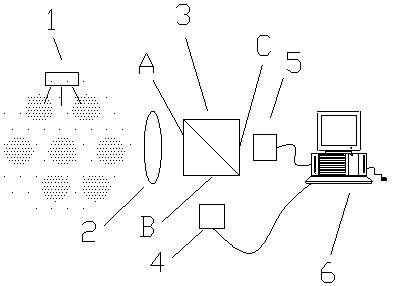
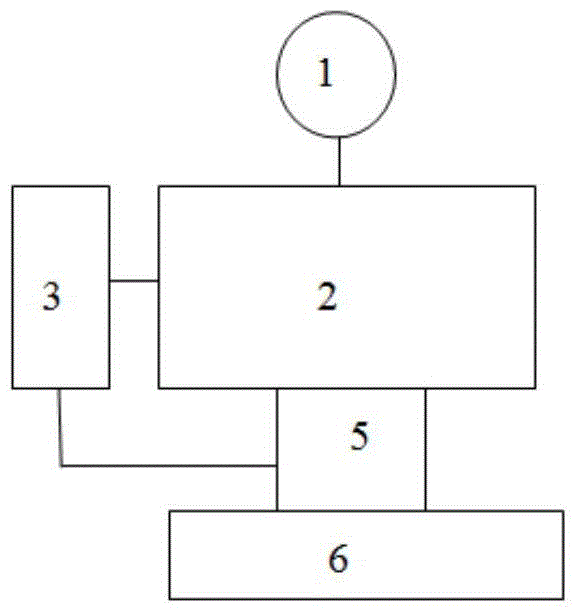
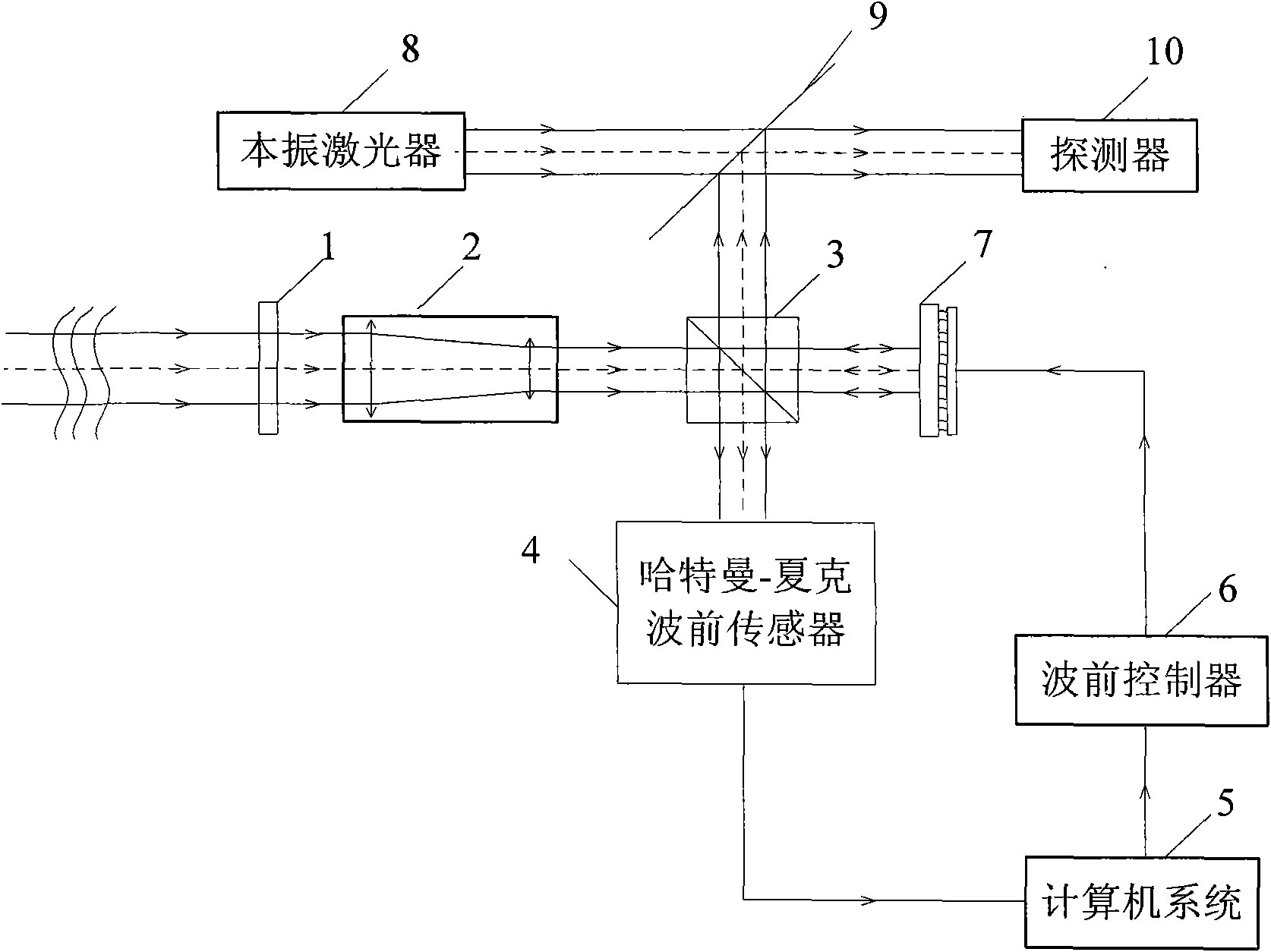
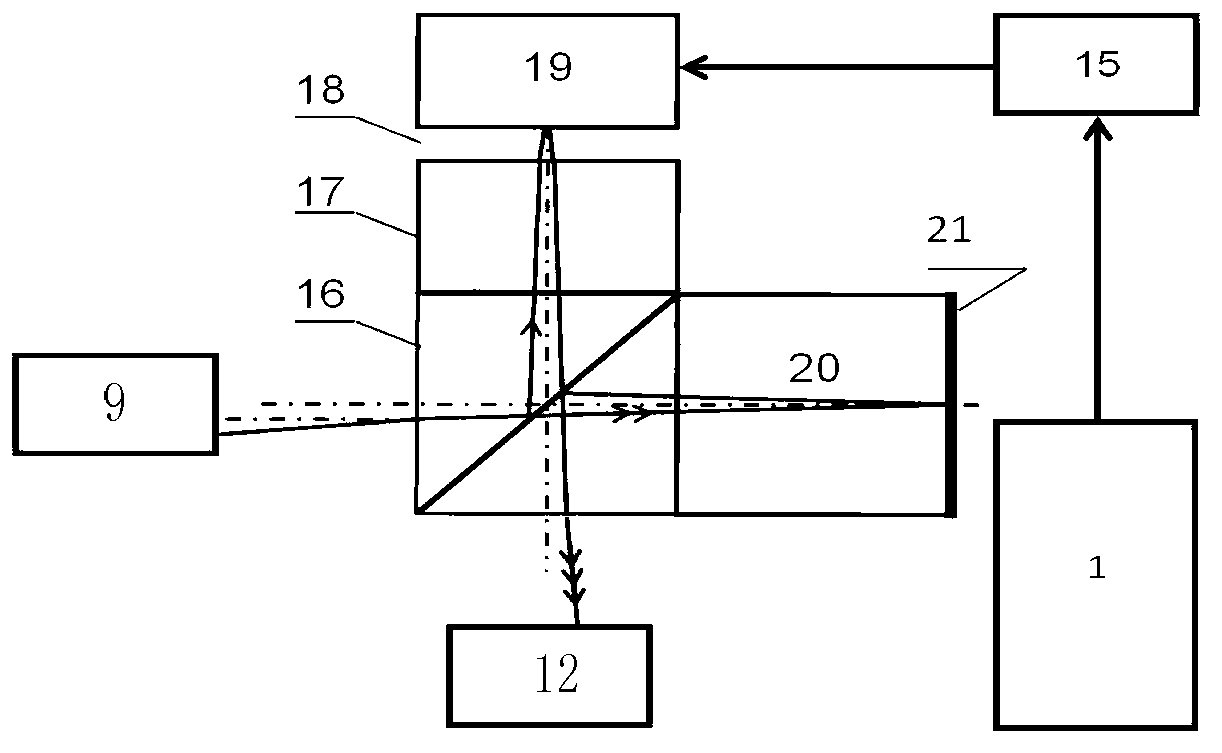
Coherent laser communication system based on wavefront correction
The present invention provides a coherent laser communication system based on wavefront correction. The device is composed of a polarizer (1), a telescope system (2), a beam splitter prism (3), a Hartmann-Shack wavefront sensor (4), a computer system (5), a wavefront controller (6), a spatial light modulator (7), a local oscillator laser (8), an optical coupler (9) and a detector (10). The telescope system (2) receives the laser which passes through the atmosphere. The Hartmann-Shack wavefront sensor (4) detects the deformed wavefrotn signal. The computer system (5) applies the Zernike polynomial for reconstructing the non-deformed wavefront signal. After the correction of spatial light modulator (7), the non-deformed wavefront signal is executed with frequency mixing with the light beam emitted from the local oscillator laser (8) for generating the coherent intermediate frequency signal and transmitting to the detector (10). The whole system corrects the laser which passes through the atmosphere through the above mode for causing that the detector (10) obtains the coherent laser signal after correcting the deformed wavefront signal.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Laser radar set with high spectral resolution
ActiveCN103308926AWidened field of viewBreak through the limitations of fewer applicable wavelengthsElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationBeam splitterEngineering
The invention discloses a laser radar set with high spectral resolution. After a frequency locking system frequency-locks an expanded-field-based Michelson interferometer filter to a single-frequency polarized pulse laser, beams emitted by the single-frequency polarized pulse laser are reflected to detected atmosphere by reflectors a and b after passing a beam expander; after the beams are scattered by atmospheric molecules and aerosol particles, laser radar echo signals are generated; the laser radar echo signals are collected by a telescope; after sky background radiation is filtered by an optical filter, the signals are split by a beam splitter; one signal is reflected into a photoelectric detector a, and the other signal penetrates a polarizing splitter prism b before being divided into two; S-polarized signals are reflected into a photoelectric detector b, and P-polarized signals penetrate a high spectra resolution filer; the P-polarized signals passes the expanded-field-based Michelson interferometer filter to be received by a photoelectric detector c. The laser radar set with high spectral resolution is free of wavelength limitation, has large visual angle and is highly capable of searching laser radar echo signals.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Imaging polarimetry
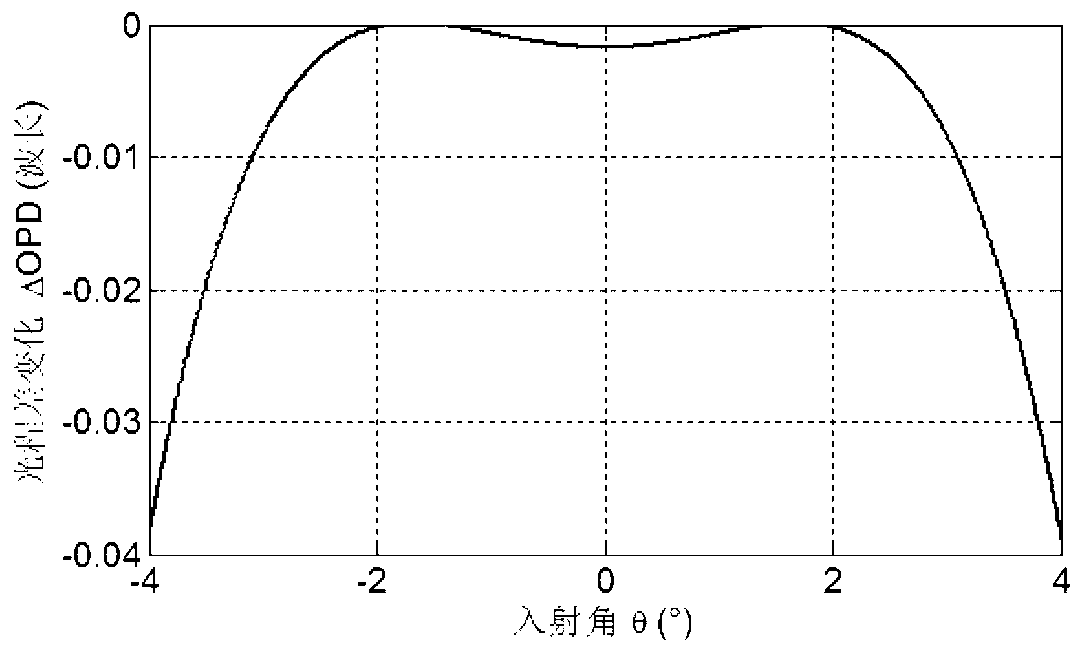
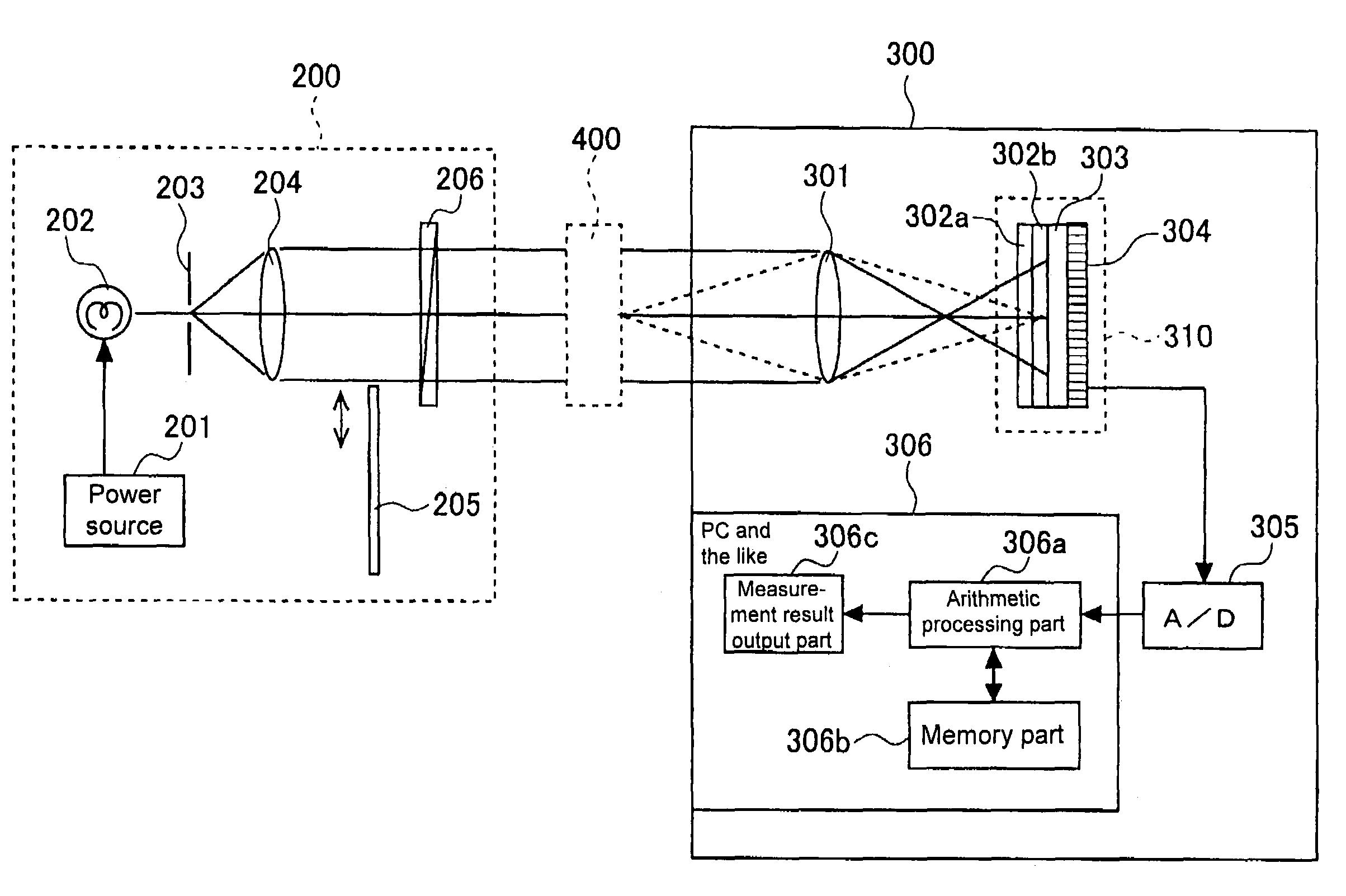
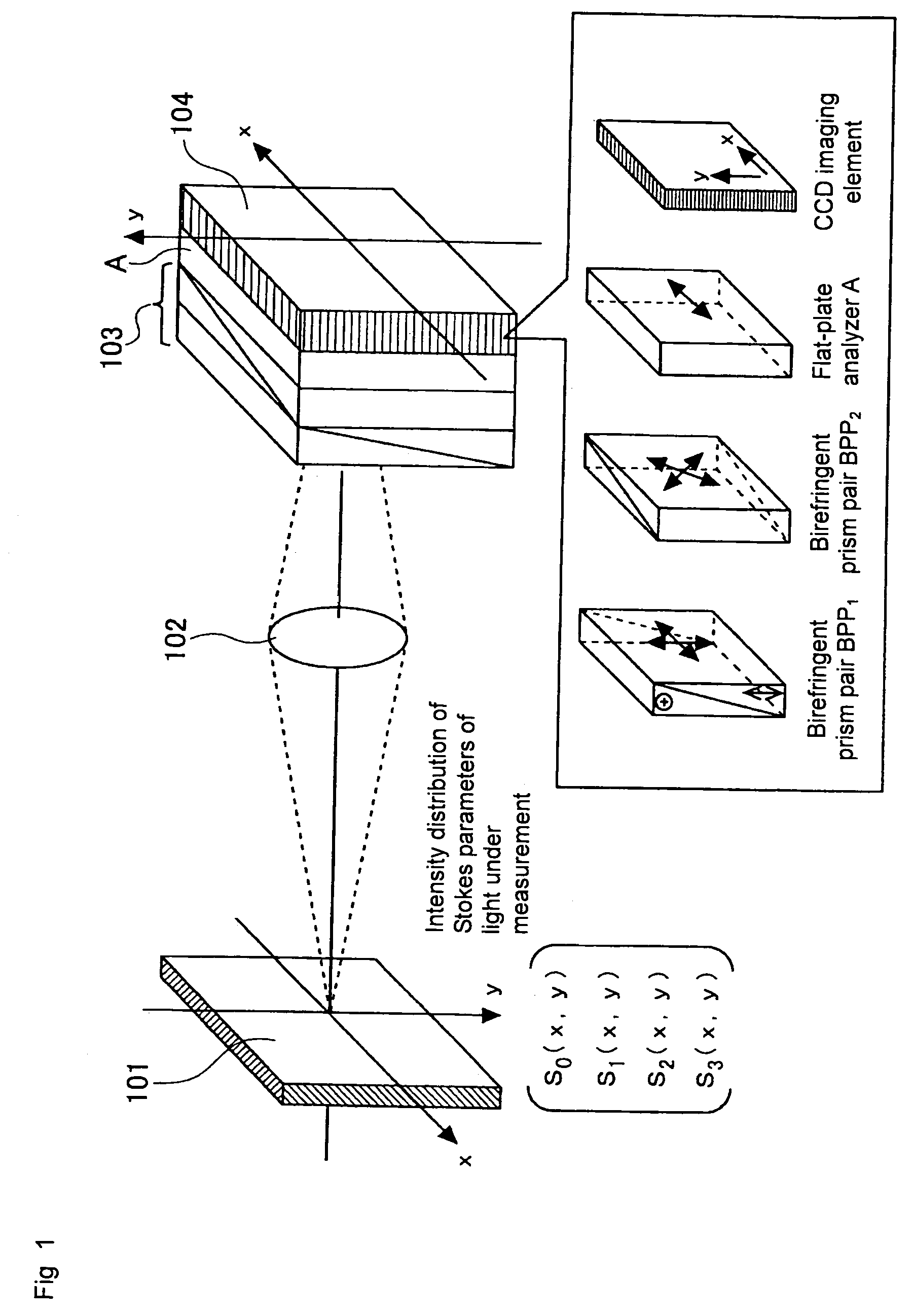
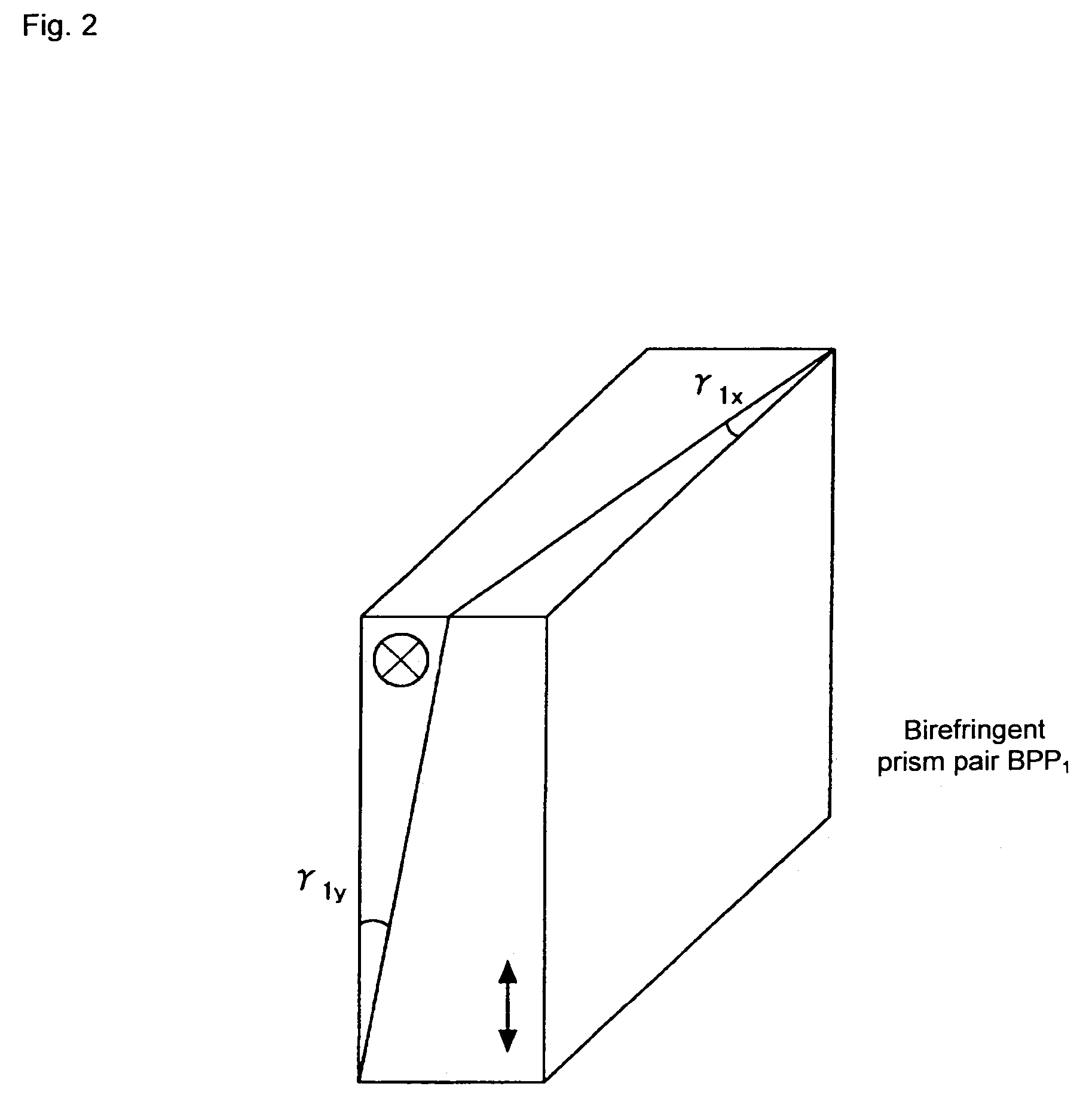
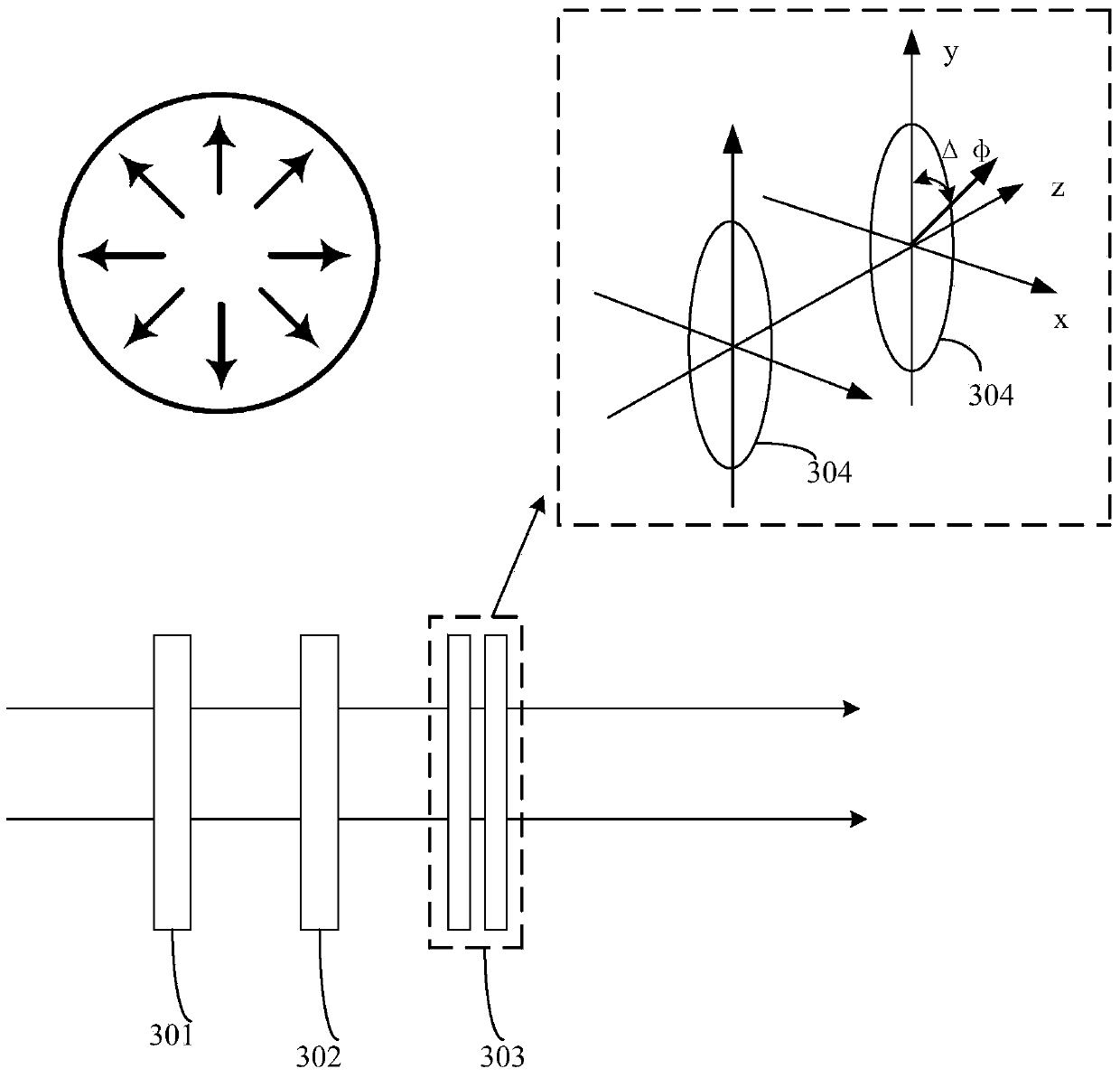
To effectively reduce a measurement error in a parameter indicating two-dimensional spatial distribution of a state of polarization generated by variations in retardation of a birefringent prism pair due to a temperature change or other factors, while holding a variety of properties of an imaging polarimetry using the birefringent prism pair. By noting that reference phase functions φ1(x, y) and φ2(x, y) are obtained by solving an equation from each vibration component contained in an intensity distribution I(x, y), the reference phase functions φ1(x, y) and φ2(x, y) are calibrated concurrently with measurement of two-dimensional spatial distribution S0(x, y), S1(x, y), S2(x, y), and S3(x, y) of Stokes parameters.
Owner:HOKKAIDO UNIVERSITY +1
Optical coherence tomography method and device based on radial-direction polarized beams
ActiveCN103431845AImprove imaging resolutionFix horizontal resolutionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBeam splitterOptoelectronics
The invention provides an optical coherence tomography method and device based on radial-direction polarized beams. The method comprises the following steps that after light beams emitted by a low-coherence light source are processed through a Kohler illumination system, the polarization state of the light beams is adjusted and controlled through a polarization transformation system, the amplitude and phase distribution of the light beams are adjusted and controlled through a pupil filter, and accordingly the radial-direction light beams are formed; the radial-direction polarized beams enter a beam splitter prism in an incident mode, are divided into two paths, and enter a sample arm and a reference arm respectively; the two-path light beams are focused on a sample to be measured and a reference plane mirror through microscope objectives of the two-path light beams respectively; returned light after being reflected by the sample to be measured and the reference plane mirror joins in the position of the beam splitter prism, is focused through a focusing lens, is imaged in a probe and is then transmitted to a computer to be post-processed; the reference plane mirror transversely moves to achieve transverse scanning; the sample to be measured is placed on a three-dimensional horizontal-moving table capable of moving in space to achieve three-dimensional imaging of the sample.
Owner:BEIJING INFORMATION SCI & TECH UNIV
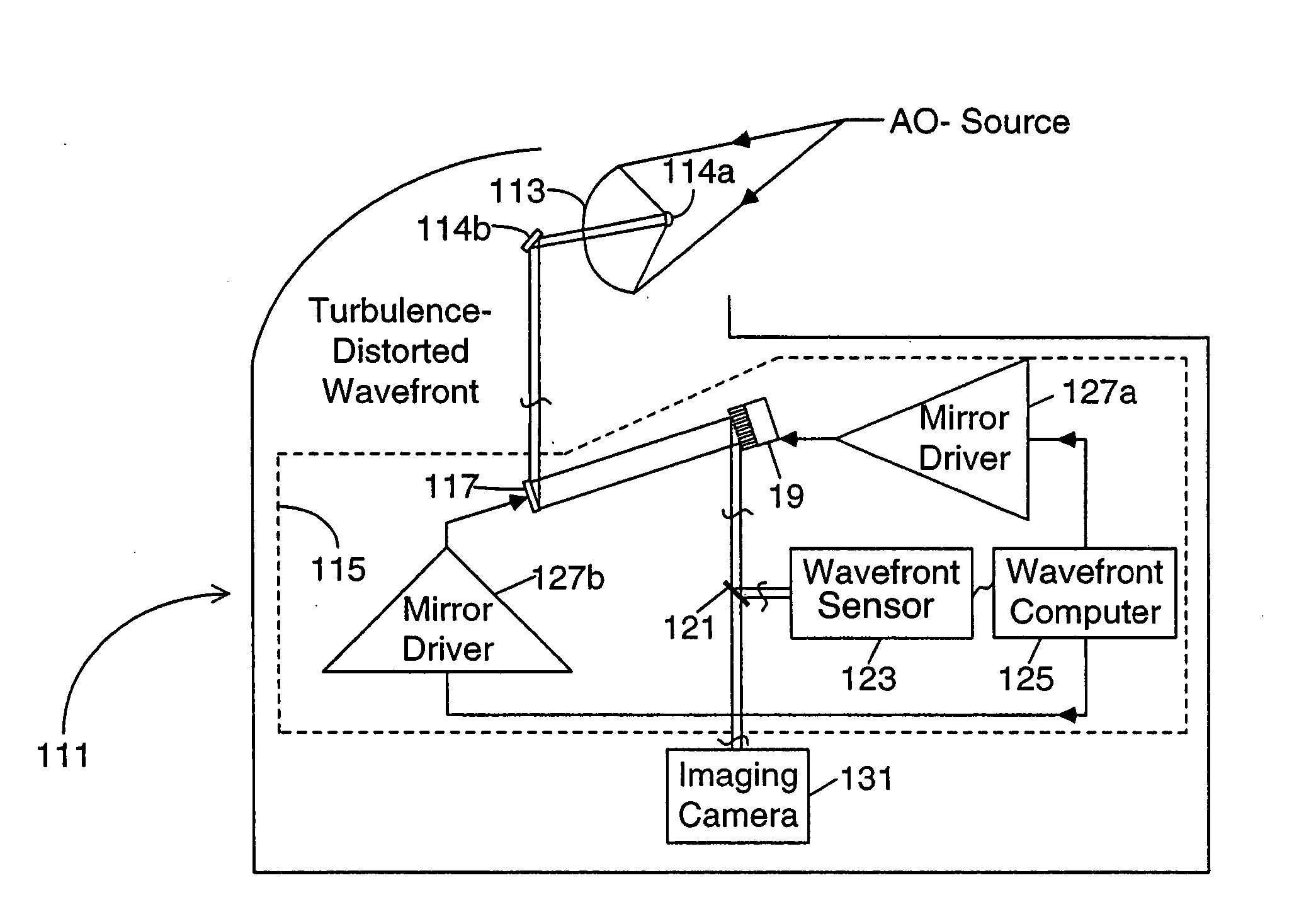
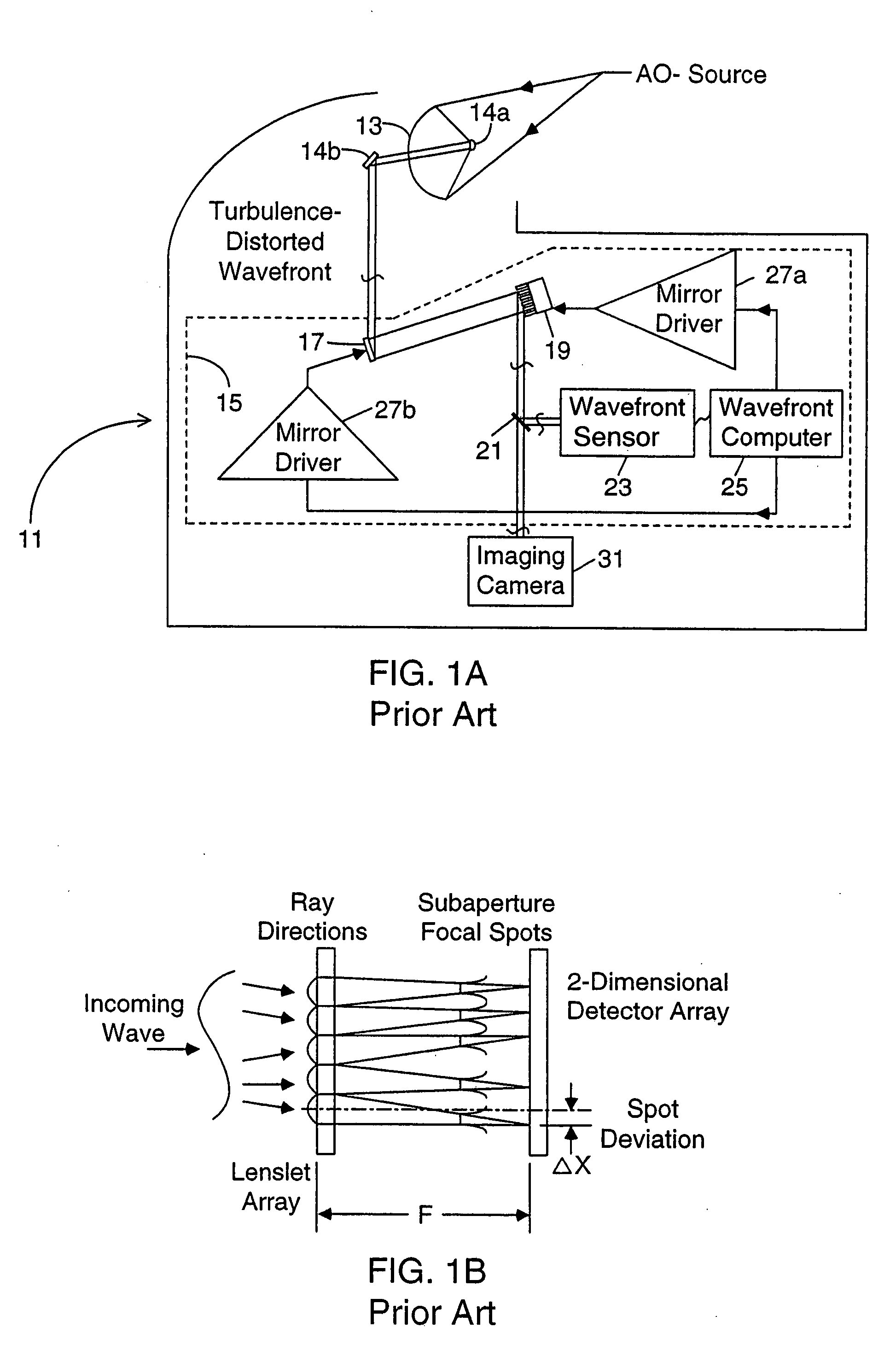
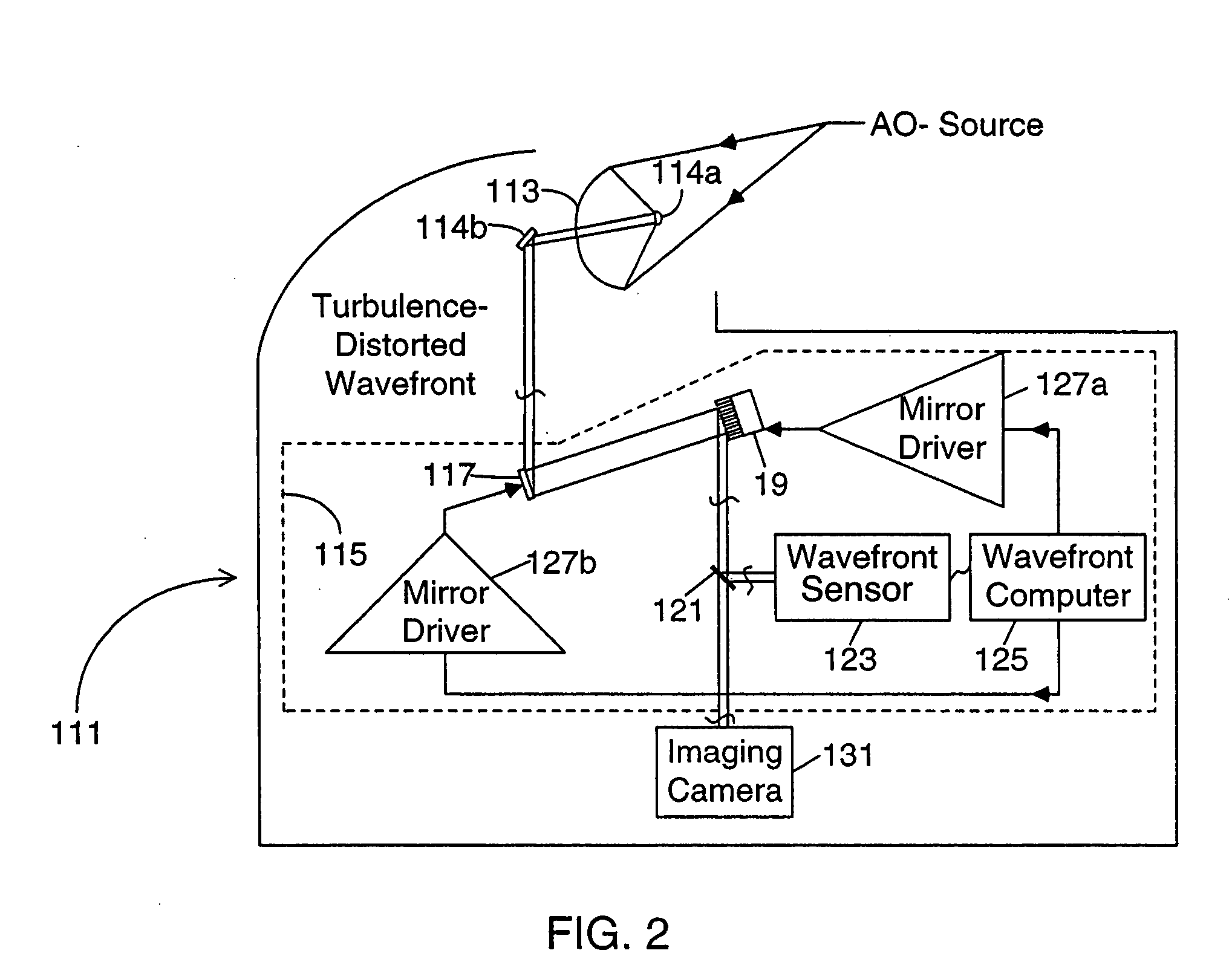
Method and apparatus for wavefront measurement that resolves the 2-pi ambiguity in such measurement and adaptive optics systems utilizing same
InactiveUS20050098707A1Step of become largeImprove tolerancePhotometry using reference valueOptical measurementsWavefront sensorAmbiguity
An improved wavefront sensor for characterizing phase distortions in incident light including optical elements that spatially sample the incident light and form a dispersed spot with a fringe pattern corresponding to samples of the incident light. An imaging device captures an image of the dispersed spot with said fringe pattern formed by said optical elements. And an image processor that analyzes the spectral components of the fringe pattern of a given dispersed spot to derive a measure of the local phase distortion without ambiguity in the corresponding sample of incident light. The optical elements may comprise refractive elements, diffractive elements or a combination thereof (such as a grism). The wavefront sensor may be part of an adaptive optic system (such as a large-aperture space telescope) to enable the measurement and correction of large phase steps across adjacent mirror segments of a deformable mirror.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
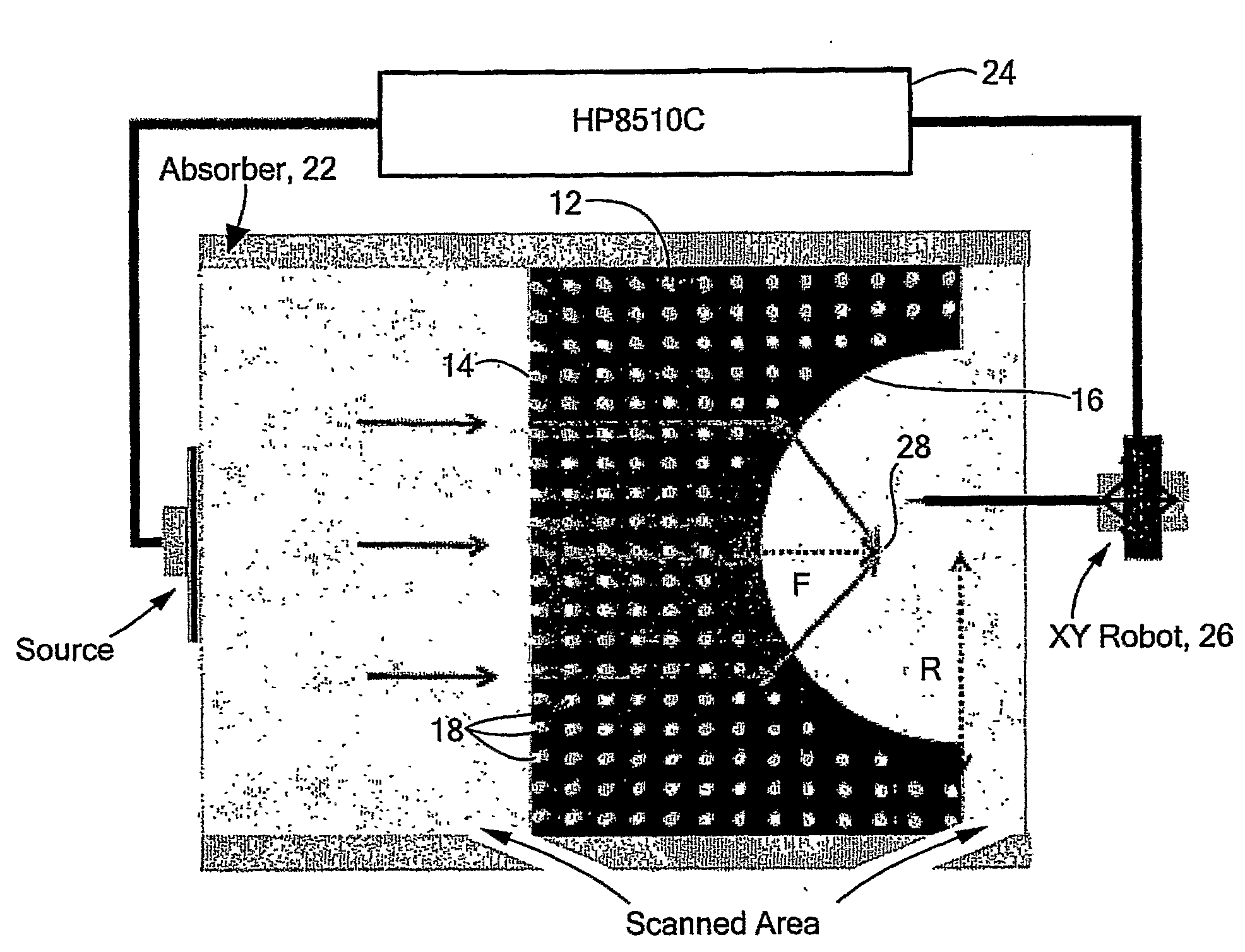
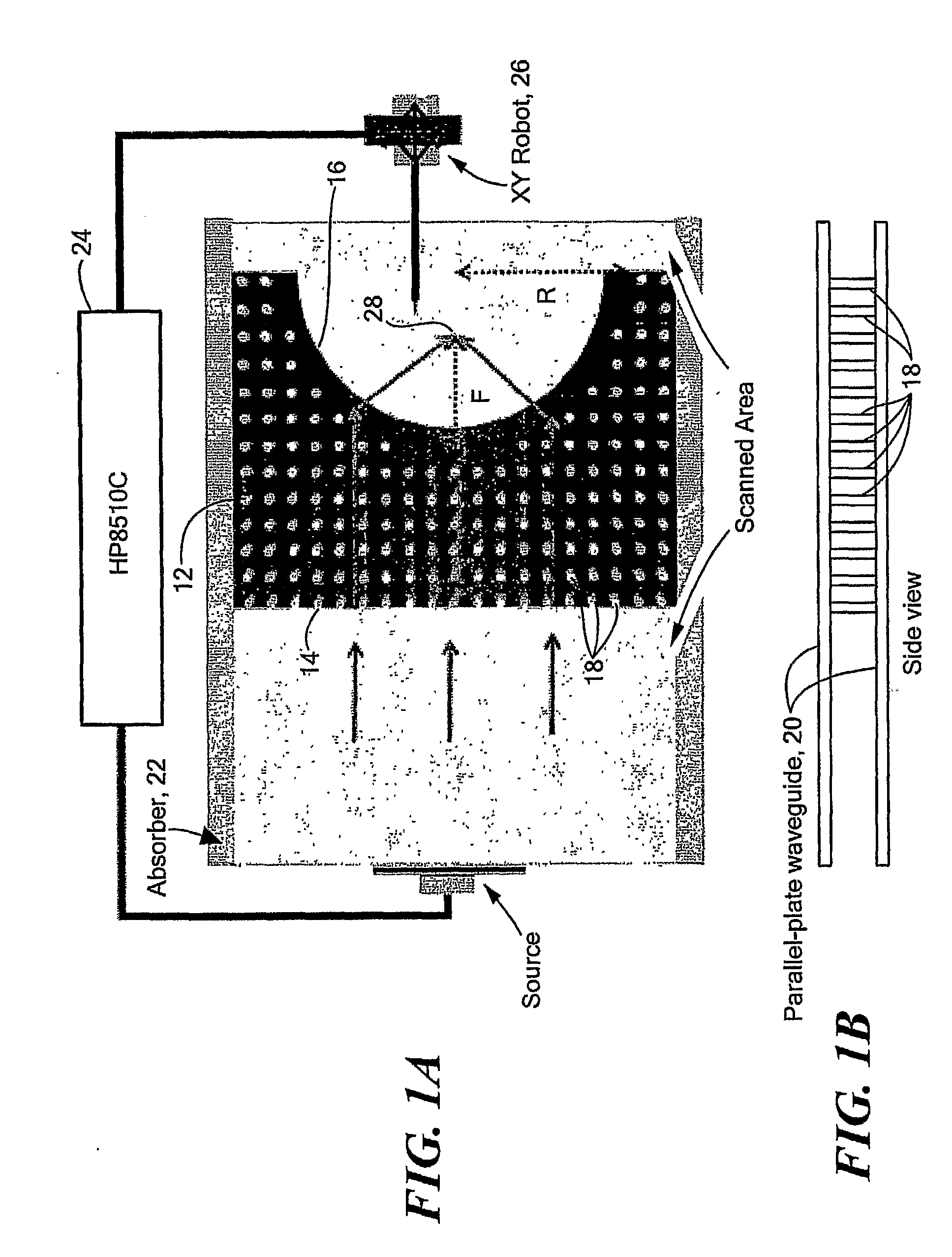
Photonic Crystal Devices Using Negative Refraction
Negative refraction in photonic crystals and diffraction grating is used to design plano-concave lenses to focus plane waves. Microwave experiments are carried out to demonstrate negative refraction and the performance of these lenses. Demonstration of negative refraction of visible light is also performed for the grism. These lenses can be used in optical circuits, astronomical applications, etc.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com