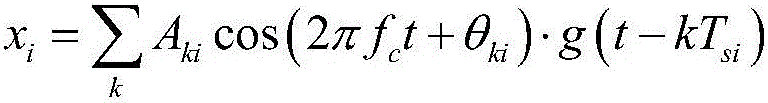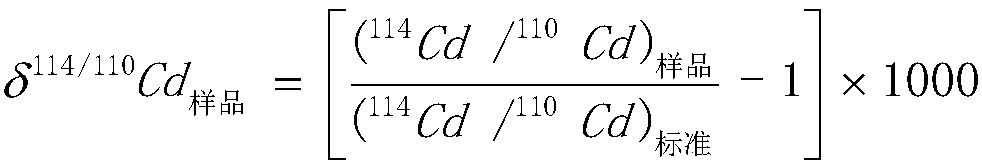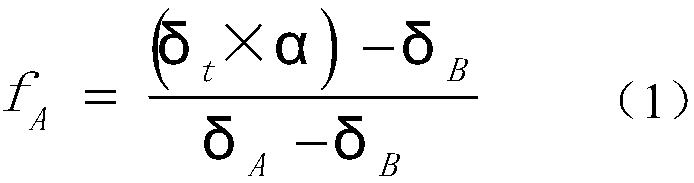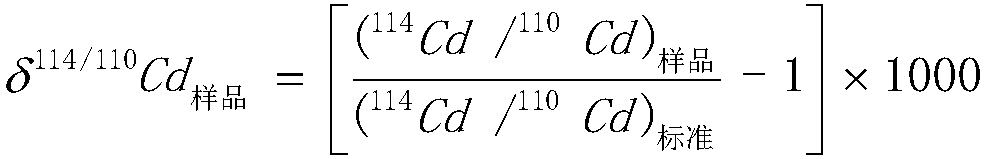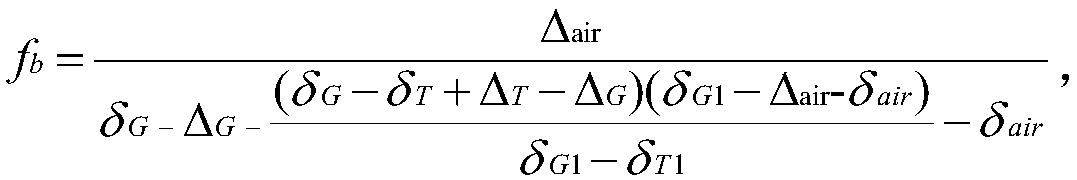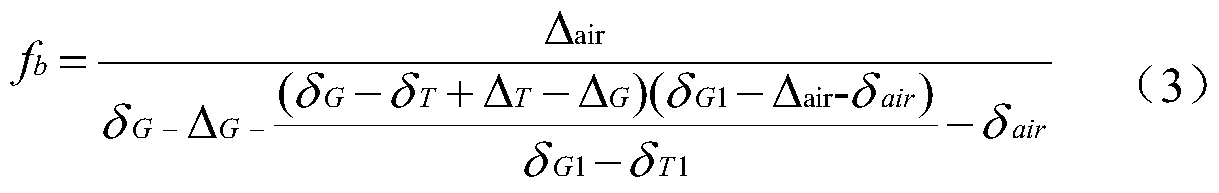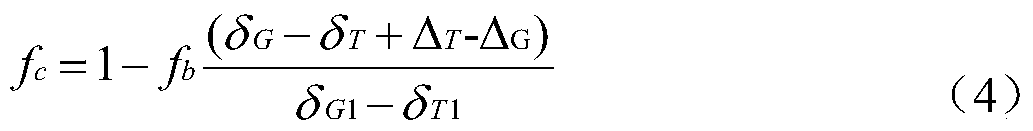Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
57 results about "Isotope fractionation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
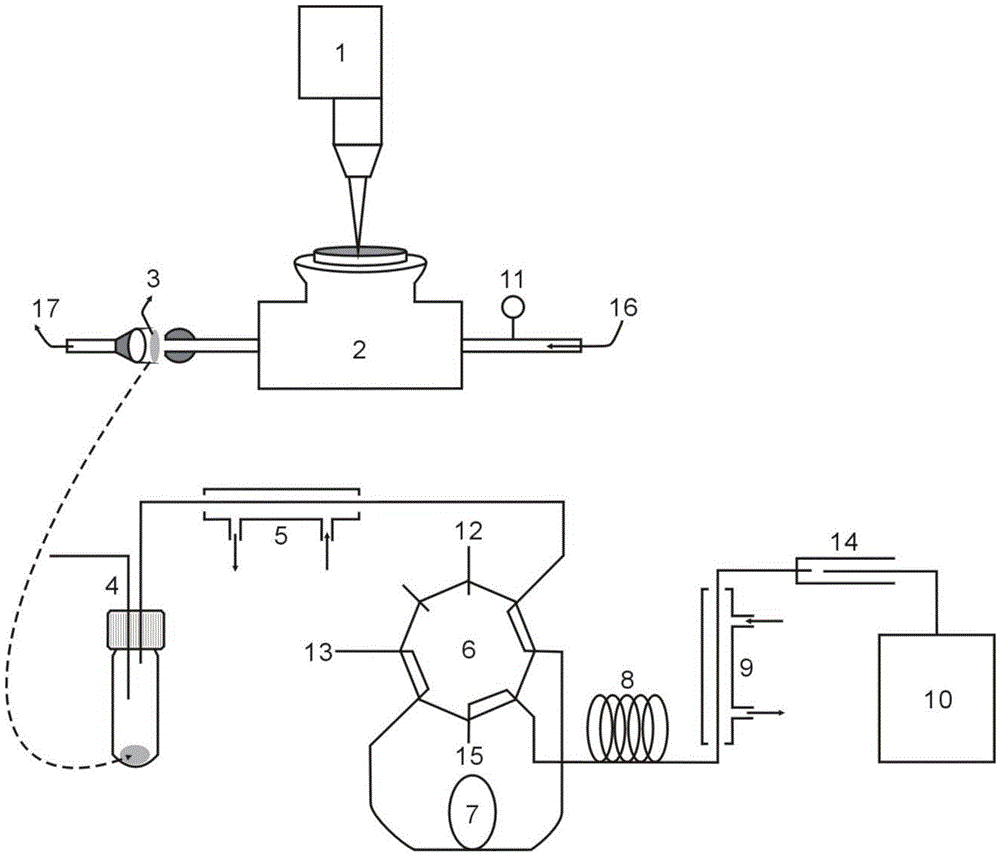
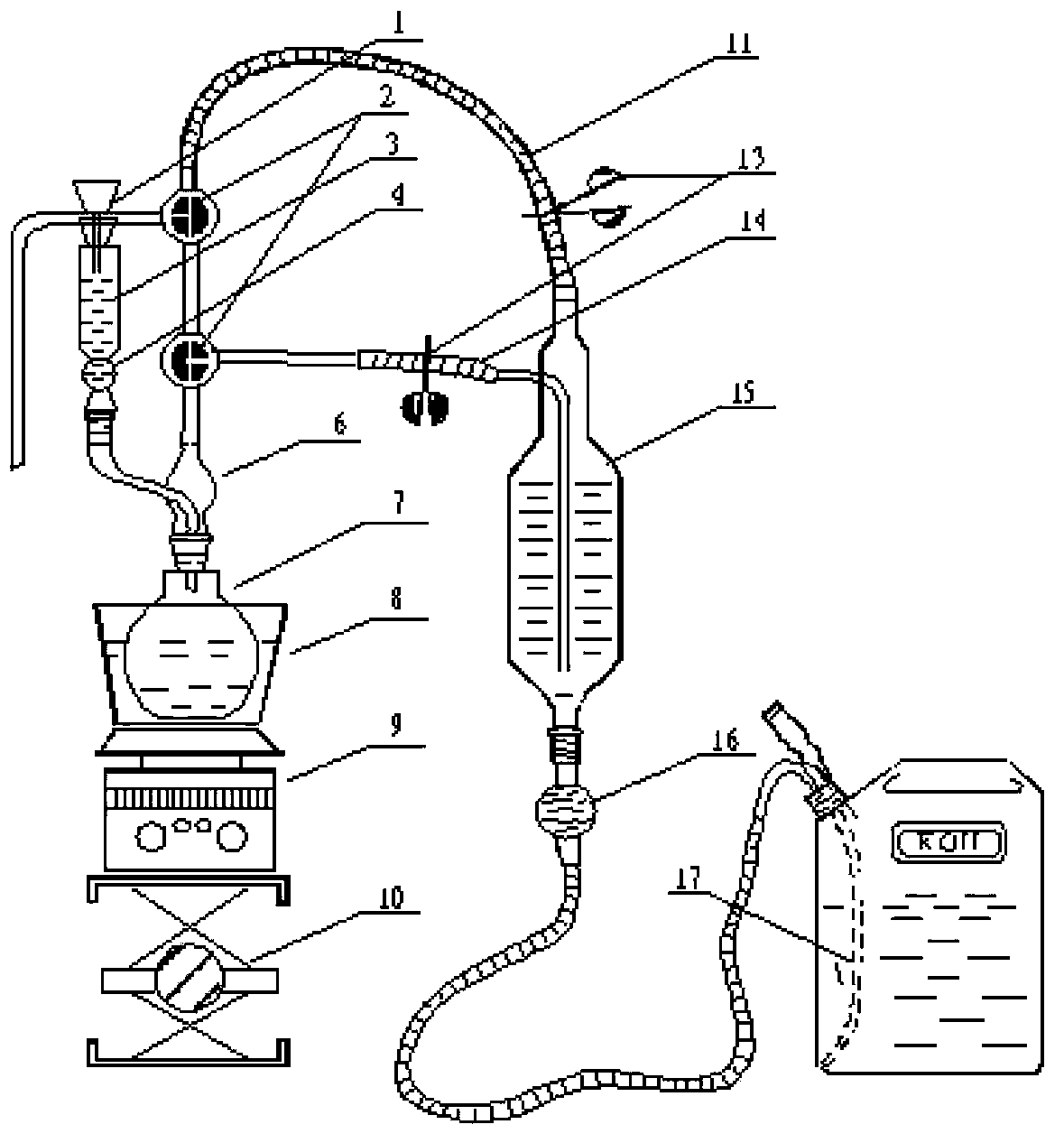
Supercritical-state gas adsorption desorption apparatus and application method thereof
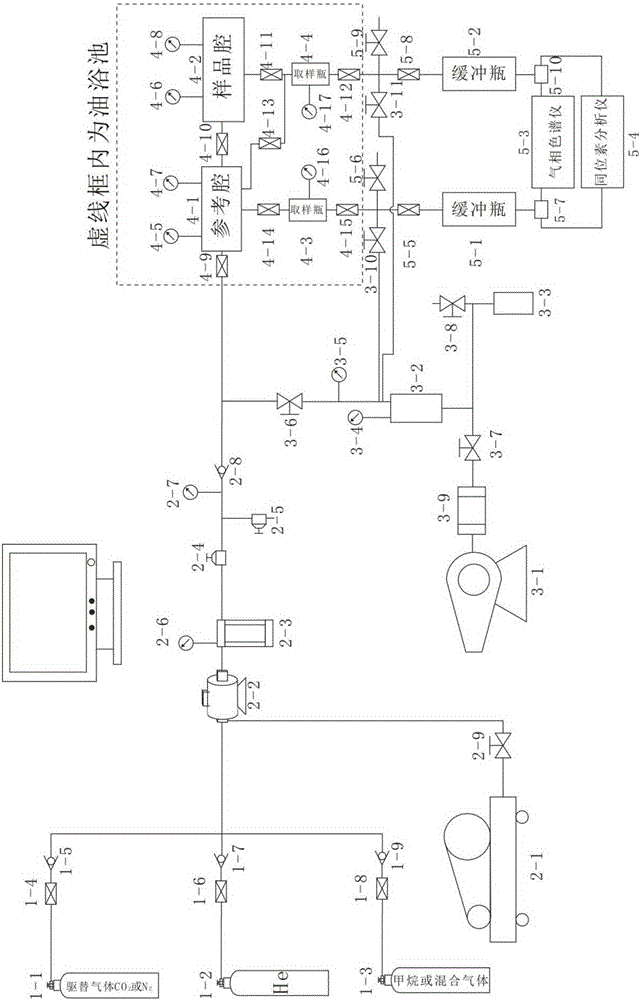
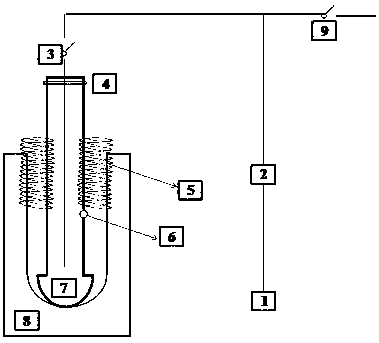
The invention relates to a supercritical-state gas adsorption desorption apparatus and an application method thereof. The apparatus is capable of simulating gas isothermal pressurization absorption, isothermal pressure-reduction desorption and isotope fractionation experiments under stratum conditions. The apparatus comprises a gas feed system, a pressurization system, a vacuumization system, a gas adsorption desorption system, a gas acquisition and analysis system, and a data acquisition and processing system. The apparatus is capable of realizing isothermal pressurization absorption and isothermal pressure-reduction desorption experiments, the sampling point quantity is more and is controllable according to experiment requirements, the adsorption and desorption trends are relatively well reflected, also the temperature in the experiment process is controllable, the oil bath temperature is set according to experiment requirement, relatively similar effect compared with actual stratum conditions is realized, shale gas exploitation is simulated through an isothermal pressure-reduction process, so that the stratum-condition maximum gas desorption amount is calculated. Operation in the experiment process is simple and safe, and error caused by human factors is reduced by acquiring data through the data acquisition and processing system. The apparatus is widely applicable to gas adsorption and desorption experiment processes.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
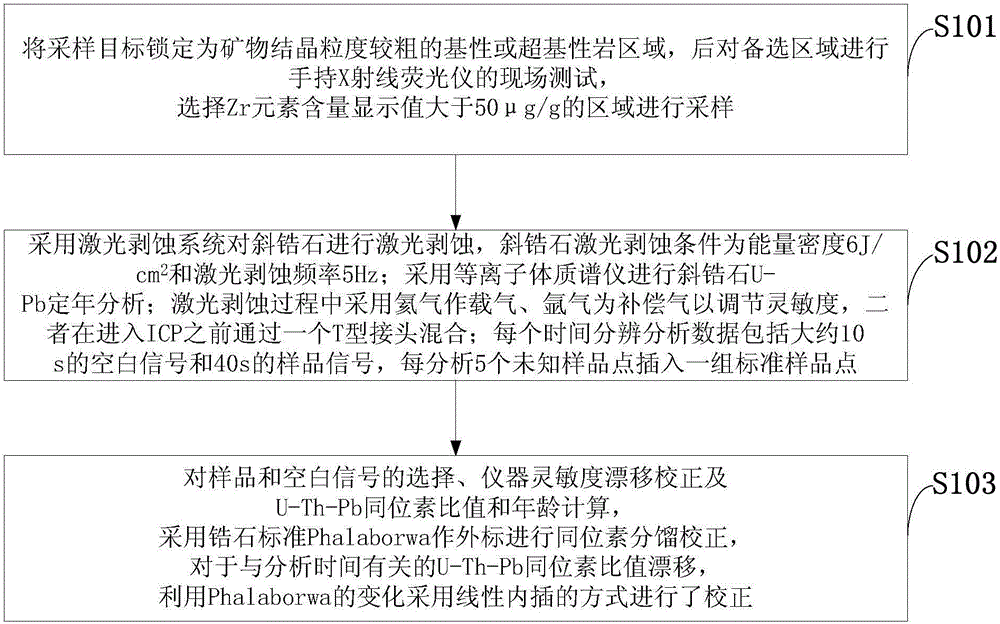
Baddeleyite U-Pd dating method based on LA-ICP-(Q)MS (Laser Ablation-Inductively Coupled Plasma-(Quadrupole) Mass Spectrometer)
InactiveCN106483189AEffective controlEfficient collectionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansInductively coupled plasmaQuadrupole
The invention discloses a baddeleyite U-Pd dating method based on a LA-ICP-(Q)MS (Laser Ablation-Inductively Coupled Plasma-(Quadrupole) Mass Spectrometer). A region of which the displayed value of the content of an element Zr is more than 50 mu g / g is selected to carry out sampling; laser ablation is carried out on baddeleyite by adopting a laser ablation system, and baddeleyite U-Pd dating analysis is carried out by adopting a plasma mass spectrometer; helium is adopted as a carrier gas and argon is adopted as a compensation gas to regulate sensitivity in a laser ablation process; a sample and a blank signal are selected, the sensitivity drift of an instrument is corrected, the U-Th-Pb isotope specific value and age are calculated, the zircon standard Phalaborwa is adopted as an external standard to carry out isotope fractionation correction, and the correction is carried out by utilizing the change of the Phalaborwa and by adopting a linear interpolation way. By using the baddeleyite U-Pd dating method based on the LA-ICP-(Q)MS, the effective collection on a baddeleyite sample and the effective control and the accurate correction on an elemental fractionation effect are realized.
Owner:XIAN CENT OF GEOLOGICAL SURVEY CGS
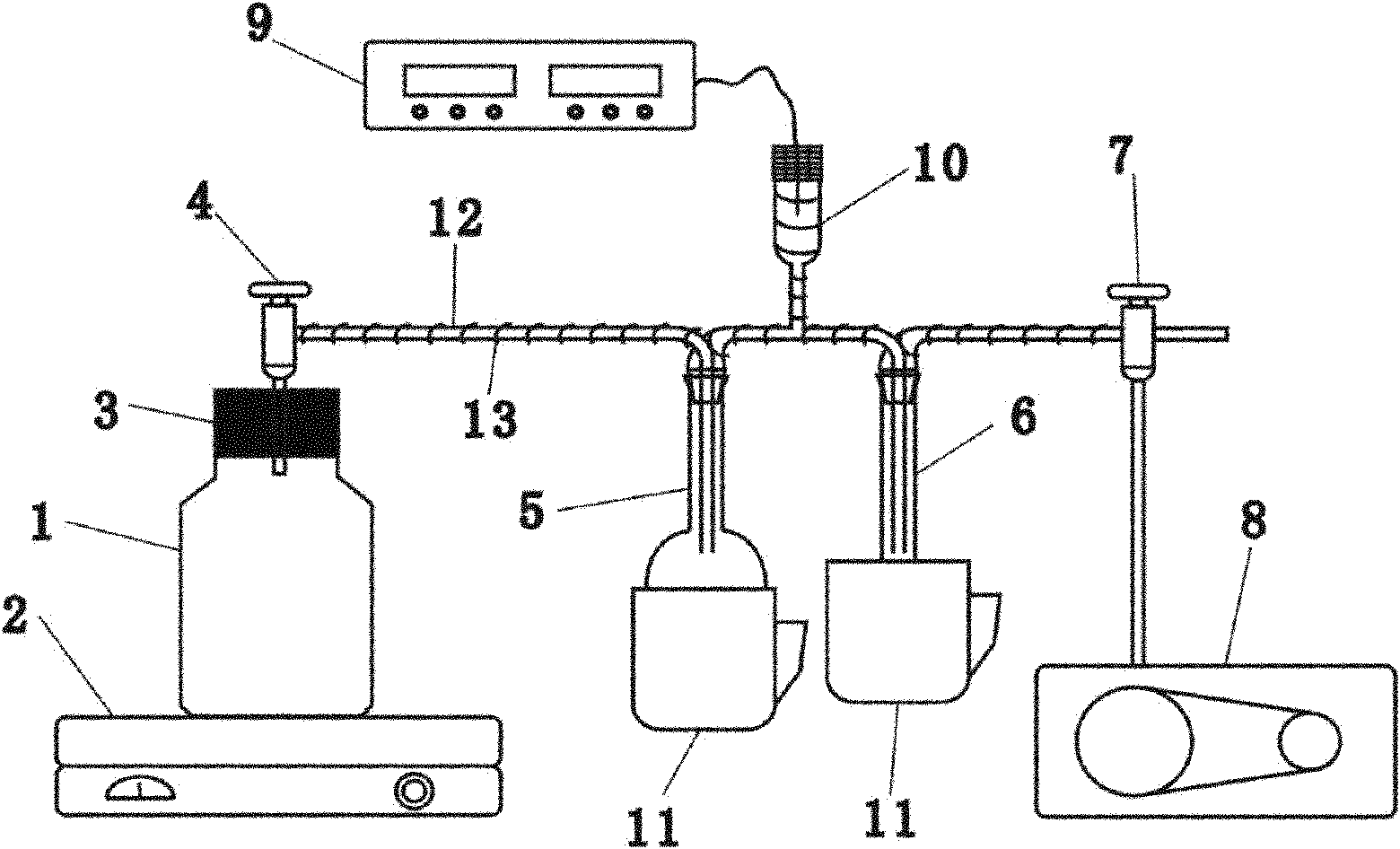
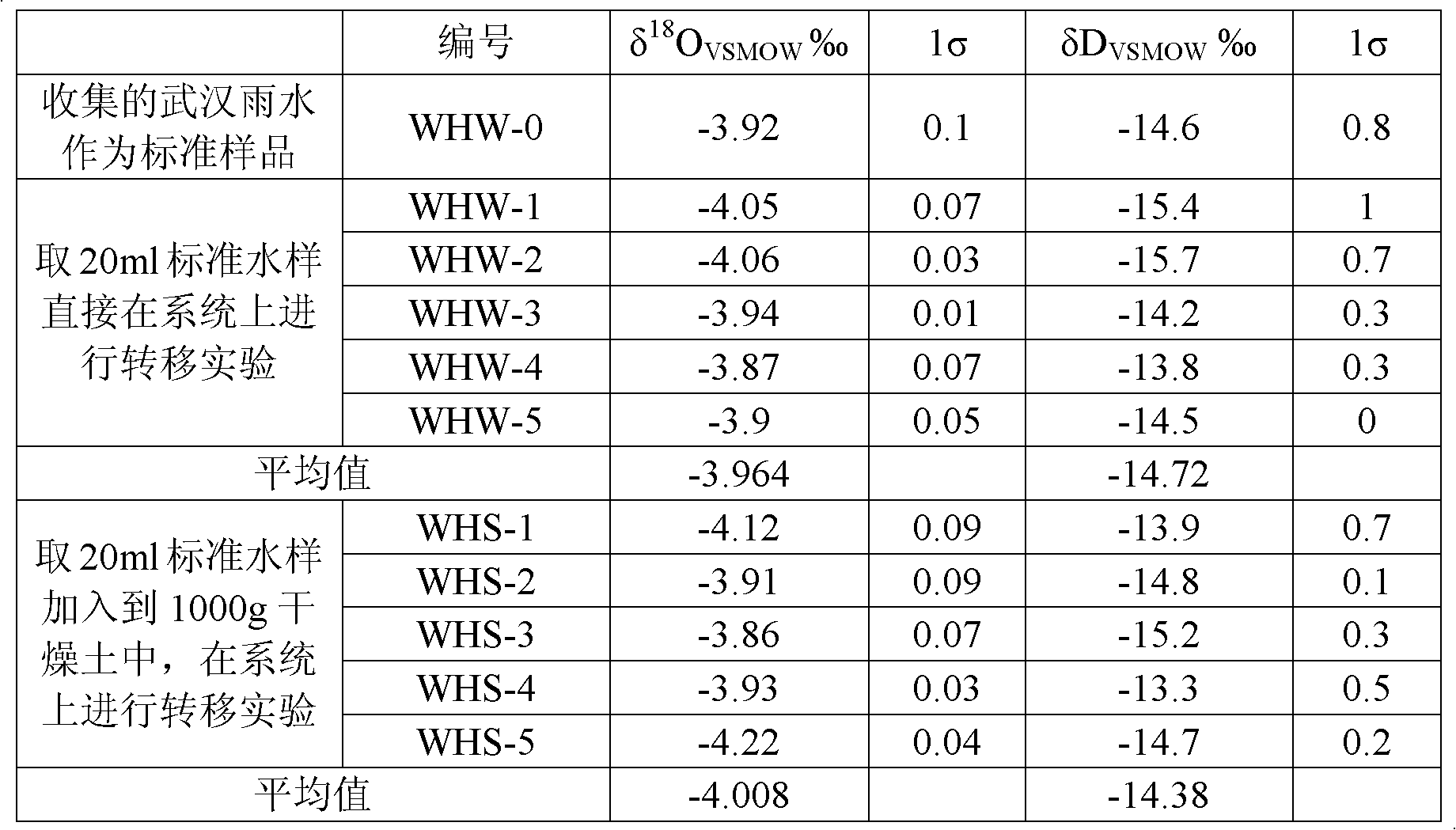
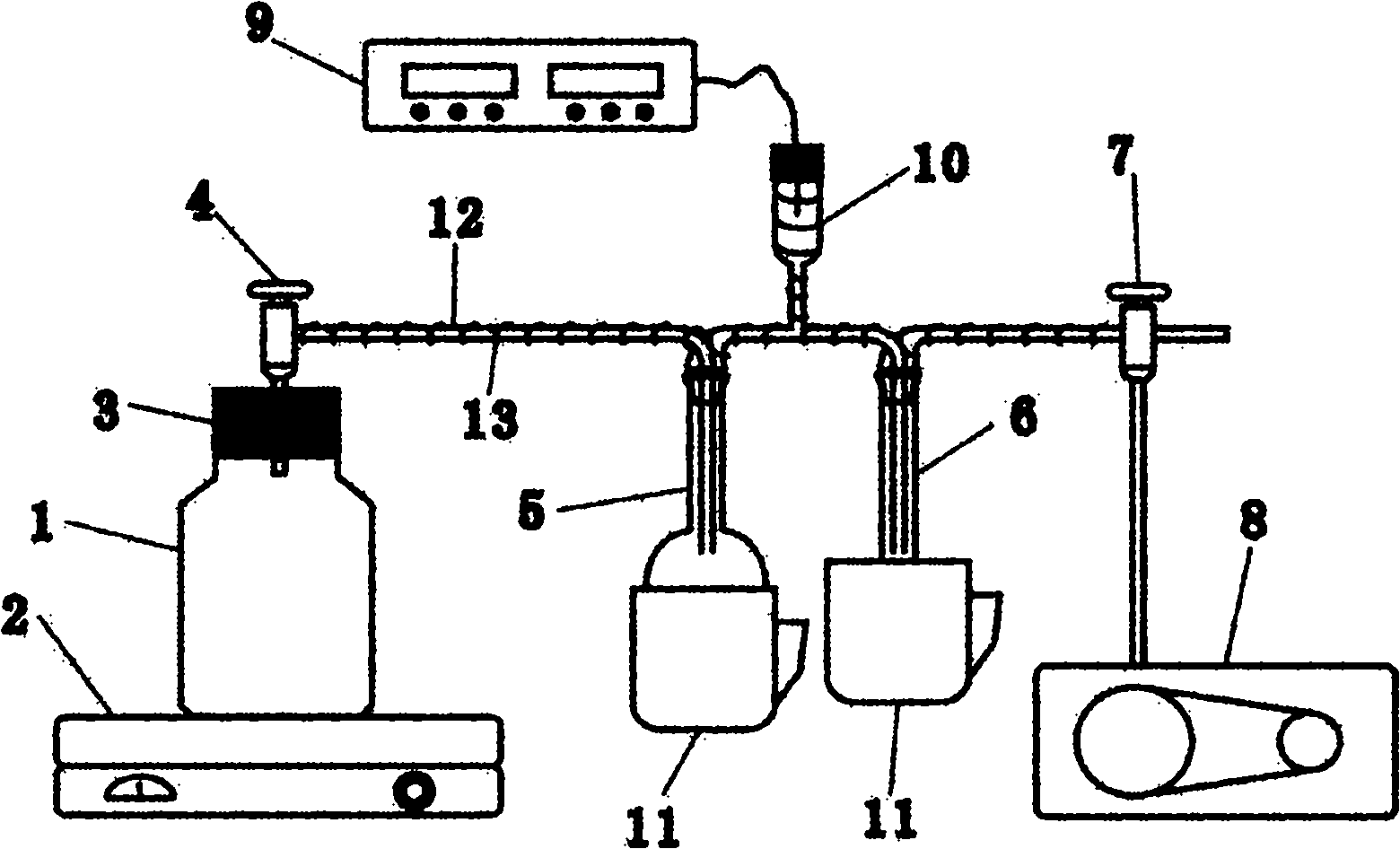
Isotopic water-sample extraction and purification device
InactiveCN102012327AAchieve transferAvoid getting lostWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationBiological bodyEngineering
The invention discloses an isotopic water-sample extraction and purification device which at least comprises a sample bottle, a heating device, a water-sample collector, a cold trap and a vacuum pump, wherein the air inlet end and air outlet end of the water-sample collector are respectively communicated with the air inlet ends of the sample bottle and the cold trap, and the air outlet end of the cold trap is communicated with the vacuum pump; and pistons are respectively arranged between the sample bottle and the water-sample collector and between the cold trap and the vacuum pump, a vacuum gauge connected with a vacuometer is arranged between the water-sample collector and the vacuum pump, and the water-sample collector and the cold trap are respectively sleeved with a cryogenic beaker. By using the device provided by the invention, sufficient water samples without isotope fractionation can be obtained from objects which are difficult to dehydrated, such as low-permeability geotechnical layers, organisms and the like, and the isotope fractionation is not be caused in the process of desalinating high-salinity water samples, therefore, the device provided by the invention can widely be applied to the scientific researches and productions in universities, research institutes, industrial and mining enterprises and the like.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Measuring device and method for carbon and oxygen isotopes of carbonate rocks
The invention discloses a measuring device and method for carbon and oxygen isotopes of carbonate rocks. The device comprises an ultraviolet laser ablation device and a carbon and oxygen isotope measurer. The ultraviolet laser ablation device comprises an ultraviolet laser and a carbonate sample cell. The ultraviolet laser is arranged above the carbonate sample cell. The carbonate sample cell is provided with a helium inlet and a helium outlet. A helium outlet pipe is provided with a spherical grinding connector, and a quartz filtering film is arranged in the middle of the spherical grinding connector. The oxygen isotope measurer comprises an automatic sample injector, a water removing trap A, an eight-way valve, a chromatographic column, a water removing trap B, an opening shunt and a mass spectrometer, all of which are connected in sequence. The method comprises the steps that a carbonate sample ablated through the ultraviolet laser device is conveyed to the carbon and oxygen isotope measurer, and the carbon and oxygen isotopes are measured through the phosphoric acid hydrolysis method. The problem that in an infrared laser probe carbonate microcell normal-position carbon and oxygen isotope analyzing method, the isotope fractionation cannot be accurately corrected is solved, and the precision and accuracy of an analysis result are greatly improved.
Owner:INST OF MINERAL RESOURCES CHINESE ACAD OF GEOLOGICAL SCI
Separation method of boron in gypsum mineral and/or hard gypsum mineral and measurement method of boron isotope
ActiveCN107991378ASatisfied with precise determinationGood repeatability ratioPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBoron containingMaceral
The invention relates to the technical field of ore element separation and measurement, in particular to a separation method of boron in a gypsum mineral and / or a hard gypsum mineral and a measurementmethod of boron isotope. The separation method comprises the following steps: reaction: taking a sample(s) of a gypsum mineral and / or a hard gypsum mineral, adding ammonium hydrogen carbonate and boron-removed ionized water, reacting to obtain first supernate and a sediment, and adding hydrochloric acid into the sediment for reacting, thus obtaining second supernate after the sediment is wholly decomposed; separation: performing boron enrichment on the first supernate through a boron special resin exchange column, regulating pH of the second supernate to be alkaline, and then performing boronenrichment through the boron special resin exchange column; leaching the boron special resin exchange column with enriched boron, thus obtaining boron-containing leacheate; enabling the boron-containing leacheate with boron content not smaller than 1mu g / g to pass through an anion-cation mixed resin exchange column, thus obtaining a neutral boron containing solution. By adopting the separation method, boron in indissolvable minerals can be extracted, and boron isotope fractionation hardly occurs.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
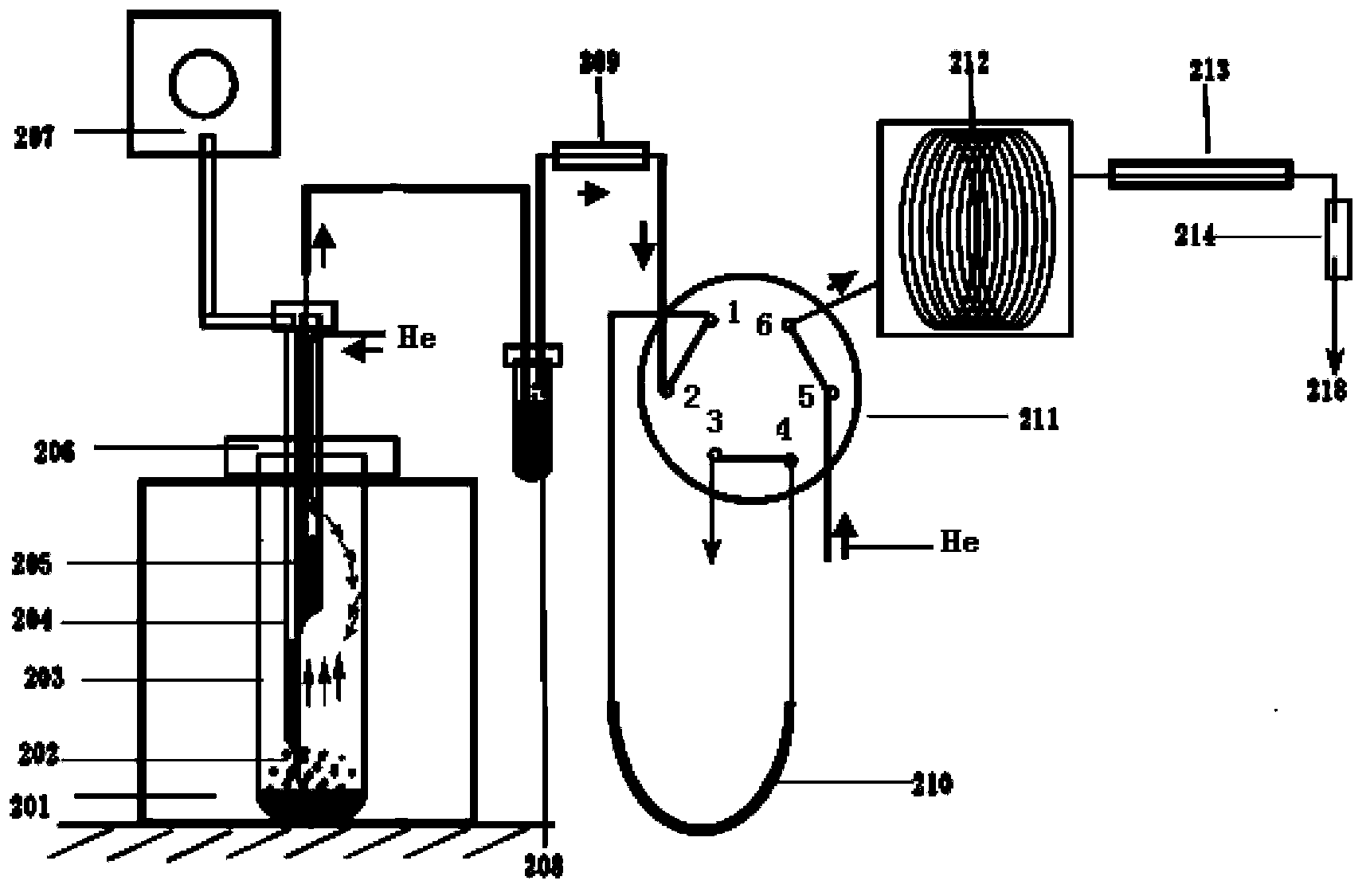
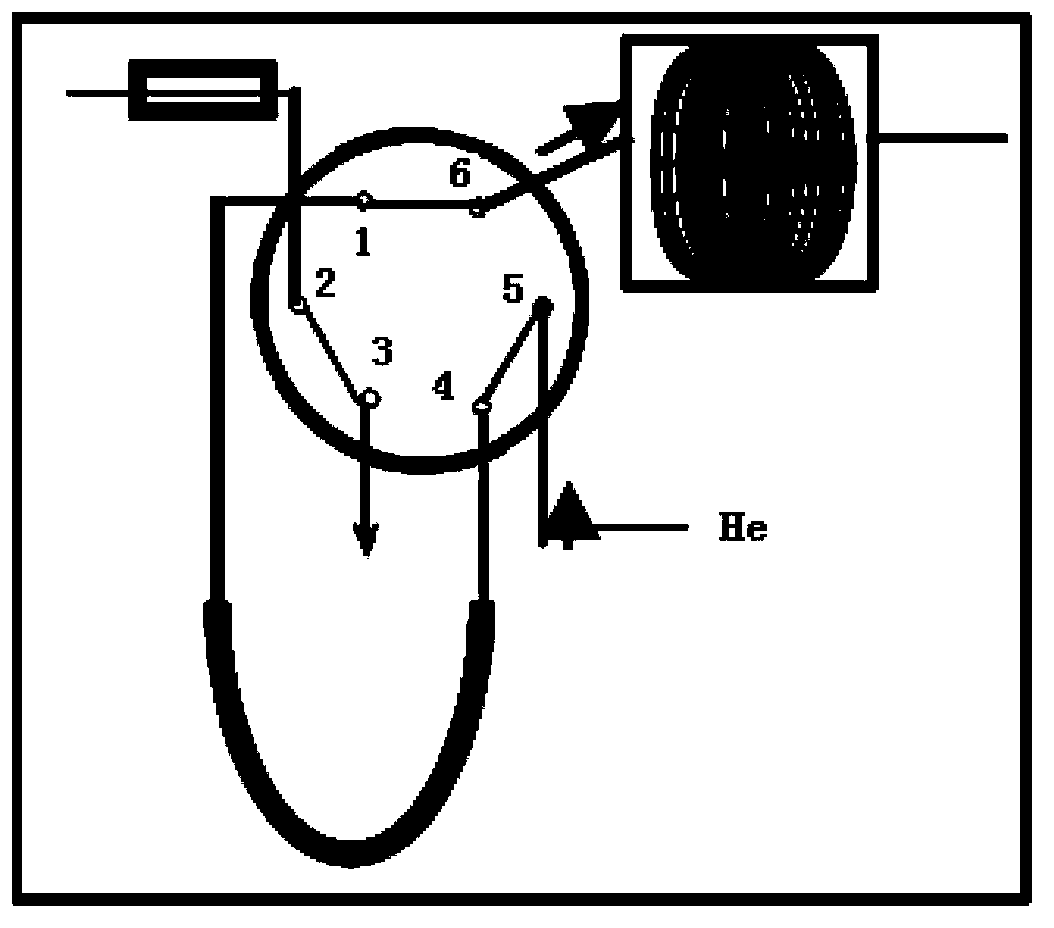
On-line degassing system for isotopc analysis of gaseous hydrocarbon acidolysis gas in rock
The invention discloses an on-line degassing system for isotopc analysis of gaseous hydrocarbon acidolysis gas in rock. The system comprises an acidolysis gas degasser, an adsorption enrichment apparatus, a six-way valve and a separator; the acidolysis gas degasser comprises a sample disk, a sample bottle, an acid needle, a sample introduction needle; a cover is arranged on the sample disc, the sample bottle passes through the cover and is placed in the sample disc, the acid needle and the sample introduction needle respectively pass through a sample bottle plug and are inserted into the sample bottle; the adsorption enrichment apparatus comprises an alkali lye bottle, a de-watering trap and a cold trap made by a special material; one end of the sample introduction needle is inserted into the alkali lye bottle, the de-watering trap inlet tube is inserted into the alkali lye bottle, the de-watering trap outlet pipe is connected to the six-way valve, the separator comprises a chromatographic column, an oxidation furnace and an opening shunt tube; two ends of the cold trap are respectively connected to the six-way valve; a port 5 of the six-way valve is connected to a helium introduction pipe, and a port 6 of the six-way valve is connected to the chromatographic column. The on-line degassing system realizes the on-line analysis of acidolysis hydrocarbon isotope and avoids the isotope fractionation effect, and the test result is accurate.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
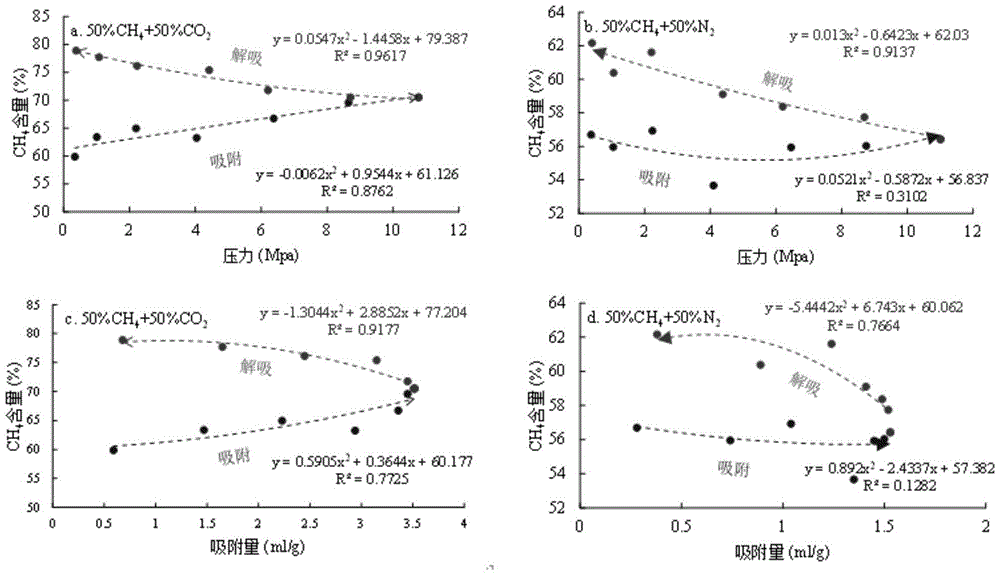
Method for representing component and isotope fractionation effect in natural gas adsorption and desorption process of shale
InactiveCN105717202ARealize fine descriptionComponent separationMathematical simulationHigh pressure
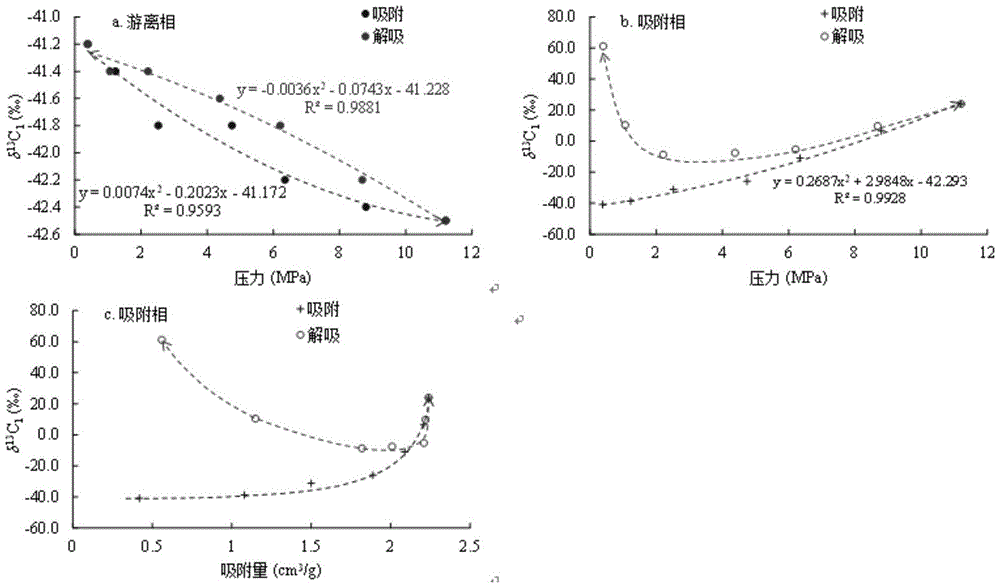
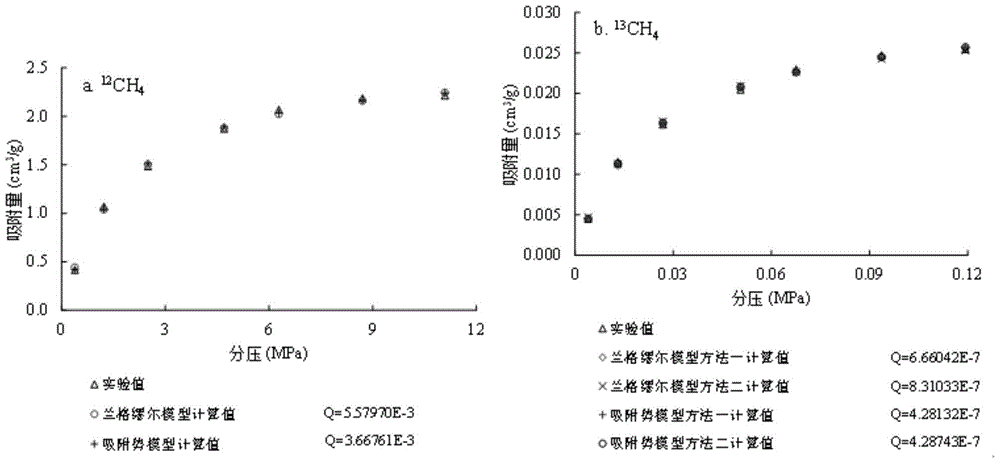
The invention relates to a method for representing the component and isotope fractionation effect in the natural gas adsorption and desorption process of shale and belongs to the technical field of instruments used for analyzing materials by aid of measuring physical properties of the materials. The problem that in the prior art, due to the fact that a large amount of gas is lost in the drilling and sampling process, the experiment result cannot completely reflect the desorption process of shale gas is solved. According to the method, a competitive adsorption experiment is carried out in the shale gas adsorption and desorption process under high temperature and high pressure conditions, qualitative analysis is conducted on component fractionation in the process, qualitative analysis is conducted on isotope fractionation, and meanwhile a Langmuir model and an adsorption model are adopted for conducting numerical simulation on the adsorption quantity and the isotope value. Thus, elaborate description of the competitive adsorption effect in the shale gas adsorption and desorption process is realized, and it is beneficial for guiding gas-driven exploitation of the shale gas. The method can be widely applied to mathematical simulation research, gas-driven exploitation of the shale gas and other occasions.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Boron And Lithium Isotopic Method For Tracing Hydrocarbons And Their By-Products
ActiveUS20150198577A1Enhanced overall recoveryEasy to explainEarth material testingIsotope separationGroundwater contaminationRock sample
The invention relates to methods for determining the source of hydrocarbons presented in the pores of a host rock or found in contaminated groundwater. The method includes the steps of (a) determining a first isotopic composition of boron and / or lithium in one or more components within a potential source rock sample, such as kerogen, clay, or water; (b) determining a second isotopic composition of boron and / or lithium in the hydrocarbons found within the pores of a host rock sample or in contaminated groundwater; and (c) comparing the first and second isotopic compositions to determine whether the potential source rock is the source of the hydrocarbons within the pores of the host rock or in contaminated groundwater. The comparison is facilitated by using the isotope fractionation between the kerogen, clay, or water components and the bitumen component of the potential source rock, which allows one to predict the isotope composition of any hydrocarbons originating in the bitumen component of the source rock, based on the isotope composition of one of the other three phases. The method can be used to select host rock for extracting oil and other hydrocarbons, as well as in remediating groundwater contamination.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
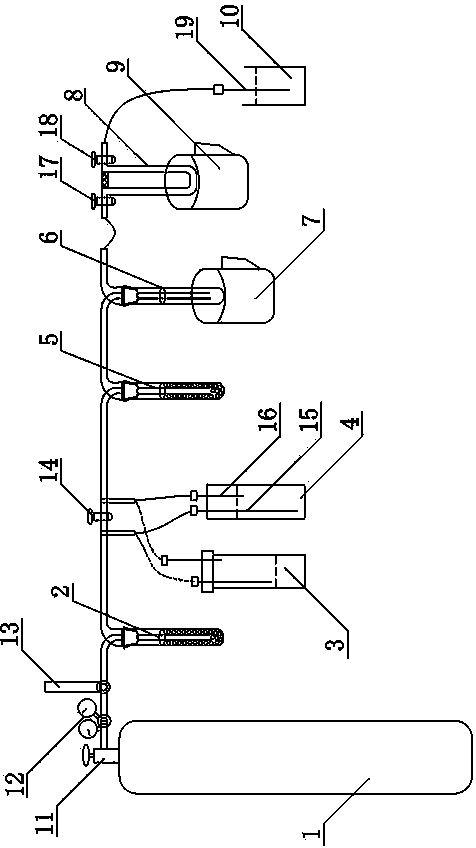
Nitrogen extracting and purifying device of nitrogen isotope sample in water
InactiveCN103776674ANo cumbersome chemical treatment processAvoid fractionationPreparing sample for investigationChemical treatmentNitrite
The invention relates to a nitrogen extracting and purifying device of a nitrogen isotope sample in water. The nitrogen extracting and purifying device comprises a nitrogen bottle (1), a carbon dioxide absorption cold trap A (2), a carbon dioxide absorption cold trap B (5), a water-vapor absorption cold trap (6) and a U-shaped gas sample collector (8), which are successively connected end to end, wherein the gas outlet end of the U-shaped gas sample collector (8) is communicated with a long needle B (19) through a rubber tube, and the long needle B (19) enters below the liquid level in a gas monitoring cup B (10). The device has the advantages that a tedious chemical treatment process is avoided, and the device is time-saving and labor-saving and simple and efficient; the nitrate, nitrite and solubleness nitrogen in the water are completely converted into pure nitrous oxide gas or pure nitrogen which can be completely collected, so that the isotope fractionation is avoided; the CO2 and water-vapor can be removed, and the interference in testing is avoided; the device can be widely applied to the scientific search and production of colleges, scientific research institutions, industrial and mining enterprises, and the like.
Owner:XIHUA UNIV
System and method for analyzing oxygen isotope composition in water of oxygen-free mineral inclusion
PendingCN107422024AIncrease vacuumGuaranteed vacuumPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCooking & bakingMass spectrometry measurement
The invention belongs to the field of measurement of isotope composition in water of mineral inclusions and particularly discloses a system and a method for analyzing oxygen isotope composition in water of an oxygen-free mineral inclusion. One end of an inclusion burst extraction / purification separation / extract conversion system of the system is connected with a product collection and measurement system, and the other end of the inclusion burst extraction / purification separation / extract conversion system is connected with a waste treatment system. The method comprises steps as follows: sampling of a mineral sample; baking and vacuum degassing; bursting, extraction and purification of the mineral inclusion; conversion of the water in the mineral inclusion; collection and mass spectrometric measurement of a converted product; waste treatment of a reaction product. The problems that water extraction of the mineral inclusion is not thorough, impurity ingredient separation is not complete, oxygen isotope fractionation is easily caused in the conversion process and the like are solved, and the analysis and test accuracy and the analysis and test efficiency are improved.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF URANIUM GEOLOGY
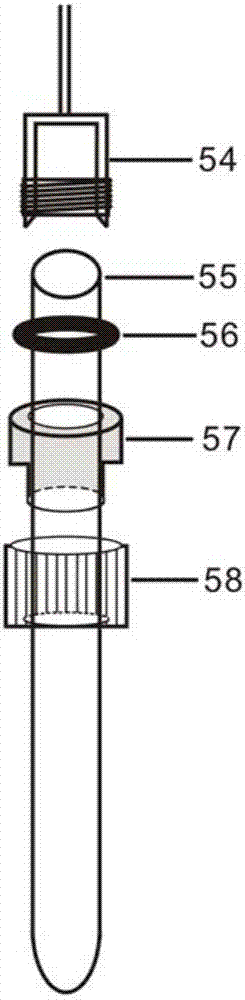
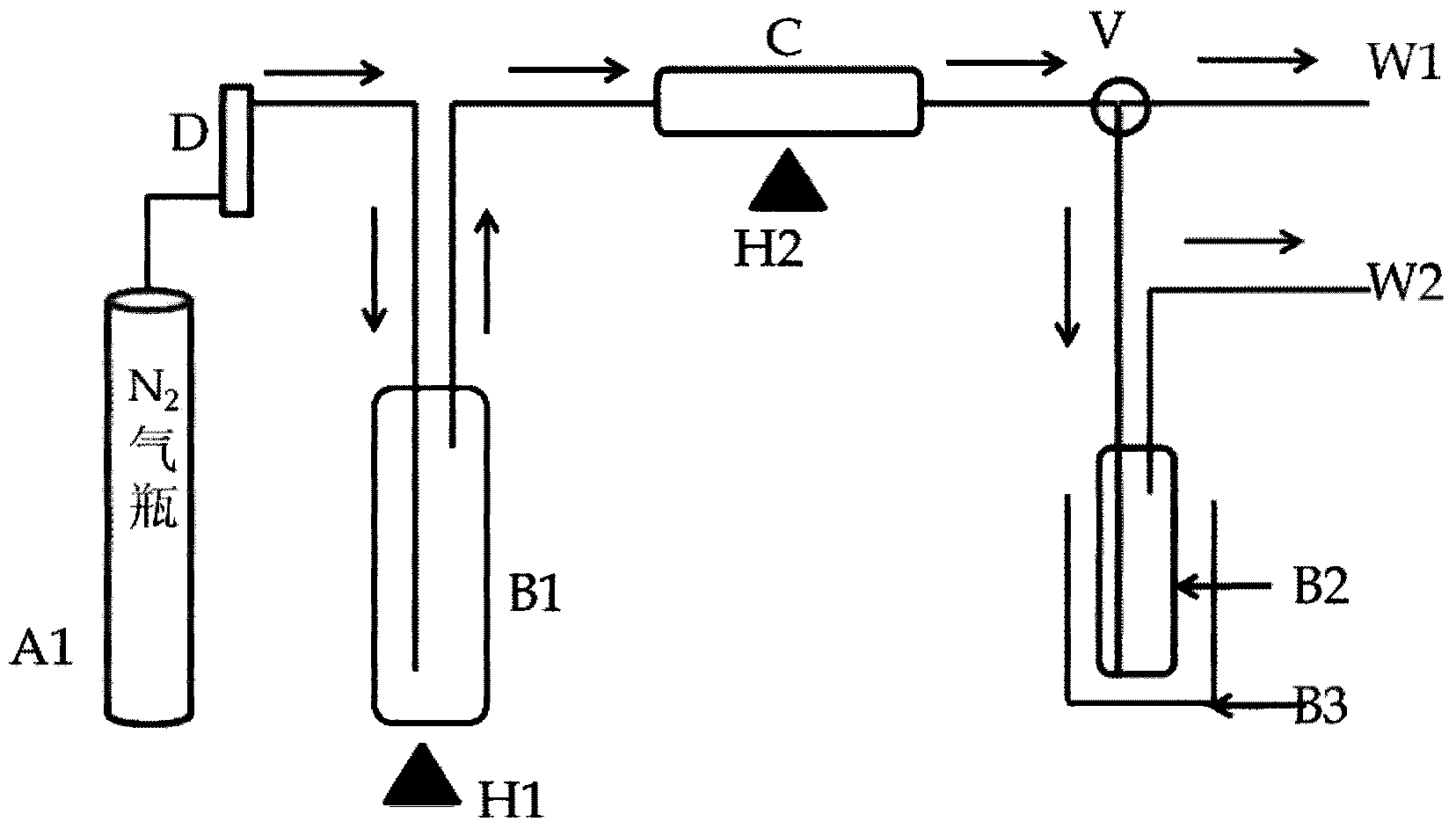
Method for separating water in alcoholic beverage for assaying isotope of H and O
The invention discloses a method for separating water in an alcoholic beverage for assaying an isotope of H and O. An assaying device is built through an N2 gas bottle, a bubble bottle, an absorption pipe, a condensation bottle, a three-way valve and a liquid nitrogen tank, the water in the alcoholic beverage is effectively separated by using an evaporation-capturing-liquid nitrogen condensation technology, and the isotope ratio of the H and the O is assayed through an elemental analysis-stable isotope mass spectrometer. According to the method, the water in various alcoholic beverages can be extracted, and the isotopes of the H and the O of the water are assayed; a sample is completely evaporated and separated, so that isotope fractionation cannot be generated in the process; a drying agent is made of a material which specifically absorbs the water and does not absorb alcohol, and impurity interference cannot be caused after separation. A low-price glass or stainless steel assembly is adopted in the process and can be recycled, so that the cost is saved. The high-accuracy testing capacity can be provided by offline separation assaying.
Owner:SHENZHEN ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE +2
Device and method for releasing and extracting hydrocarbon gases in inclusion body
ActiveCN108956836ATest accurateAchieve releaseComponent separationPreparing sample for investigationMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryProduct gas
The invention discloses a device for releasing and extracting hydrocarbon gases in an inclusion body, the device comprises an inclusion grinding system and a vacuum system; the inclusion grinding system comprises a sample cell and a vacuum blasting hammer; and the vacuum system comprises a vacuum tube and a mechanical pump. The invention also discloses a method for releasing and extracting the hydrocarbon gases in the inclusion body: (1) vacuum detection; (2) sample treatment; (3) gas release, to be more specific, knocking and grinding a sample with the vacuum blasting hammer for 60 min; (4) gas extraction, to be more specific, injecting saturated saline into the sample cell, and removing the gases released by the inclusion body through a gas-tight needle. The device and the method realizethe extraction of gaseous hydrocarbons in the inclusion body, and isotope analysis of the gaseous hydrocarbons in the inclusion body is realized for the first time by subsequent chromatographic-isotope mass spectrometry technique. The sample is ground under vacuum condition, and the sample in the inclusion body can be released at normal temperature, isotope fractionation effect can be prevented,and the accuracy of sample testing can be ensured.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Determining method of tissue cultured seedling sucrose
ActiveCN105684899ACalculation of sucrose utilization rateReduce manufacturing costPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsSucroseSaccharum
The invention discloses a determining method of tissue cultured seedling sucrose. The method comprises the following steps of respectively adopting beet sucrose and sugarcane sucrose as organic carbon sources to prepare a beet sucrose culture medium and a sugarcane sucrose culture medium; culturing tissue cultured seedlings with consistent growth vigors until the fresh weight is increased by over 20 times, and finishing the culturing; determining delta<13>C values of the beet sucrose, the sugarcane sucrose and newly-growing leaves; according to the tissue cultured seedlings of plants to be determined, utilizing the sugarcane sucrose and the beet sucrose to produce carbon isotope fractionation values, and utilizing a fractionation value of carbon dioxide in air, the weight increment of the tissue cultured seedlings and sugarcane consumption to calculate the sugarcane utilization rate of the tissue cultured seedlings. The method provided by the invention not only can be used for quantitatively determining the autotrophy portion, the heterotrophy portion and the like of the tissue cultured seedlings in one growth period, but also can be used for calculating the sugarcane utilization rate of the tissue cultured seedlings in the same period, has an important guide value on regulation of tissue cultured environment factors, and provides technical parameters for domestication and transplantation of later tissue cultured seedlings.
Owner:INST OF GEOCHEM CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Measurement method of inorganic nitrogen isotope fractionation value of ammonium salt assimilated by plant
ActiveCN107153091AEfficient managementAvoid wastingMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansNitrateInorganic nitrogen
The invention discloses a measurement method of an inorganic nitrogen isotope fractionation value of an ammonium salt assimilated by a plant. Clonal tissue culture seedlings are cultured in culture media, in which two kinds of nitrate with different stable nitrogen isotope values serve as sole nitrogen sources, respectively; after the tissue culture seedlings are cultured for 5 weeks, the stable nitrogen isotope values of leaves of the tissue culture seedlings cultured under the two kinds of nitrate are measured; similarly, clonal tissue culture seedlings are additionally taken, and are cultured in culture media with mixed nitrogen sources formed by the ammonium salt and the two kinds of nitrate whose stable nitrogen isotope values are different respectively; the stable nitrogen isotope values of the leaves of the tissue culture seedlings cultured under the two mixed nitrogen sources are measured; shares, which are utilized by the tissue culture seedlings, of the nitrate are calculated, and accordingly, afterwards, the stable nitrogen isotope values after the ammonium salts assimilated by the tissue culture seedlings cultured under the mixed nitrogen sources generate nitrogen isotope fractionation are calculated; finally, the stable nitrogen isotope fractionation values generated by the ammonium salts assimilated by the tissue culture seedlings, namely, to-be-measured stable nitrogen isotope fractionation values generated by the ammonium salts assimilated by the plants, are obtained. The measurement method can measure the inorganic nitrogen isotope fractionation value of the ammonium salt assimilated by a plant which cannot grow due to monoammonium or a plant which grows under the mixed nitrogen source; as a culture experiment is developed by utilizing the clonal tissue culture seedlings of the same genotype, the measurement result is more reliable.
Owner:INST OF GEOCHEM CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for comprehensively determining water absorption and utilization by plants
ActiveCN109856332AEasy to operateMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGrowth plantRelational model
The invention, which belongs to the field of the detection method for plant water absorption and utilization, discloses a method for comprehensively determining the water absorption and utilization byplants. The method comprises the following steps: drying plant leaves and grinding the dried leaves; measuring carbon and oxygen isotope fractionation coefficients respectively; calculating carbon and oxygen stable isotope ratios of the leaves; establishing a leaf carbon and oxygen stable isotope ratio relationship model: delta<18>O=mdelta<13>C+n; and carrying out comparison based on a formula WUE=Ca[b-(detla<13>Ca-delta<13>Cp) / (1+delta<13>Cp / 1000)] / [1.6(b-a)] to determine a plane water absorption and utilization situation. According to the invention, the water absorption and water utilization situations of plants within the certain period of time can be determined rapidly and accurately during the plant growth process and the plants are protected from being damaged. The disclosed methodis a comprehensive method for characterizing the water absorption and utilization of plants.
Owner:GUIZHOU SERICULTURE RES INST GUIZHOU PEPPER RES INST +1
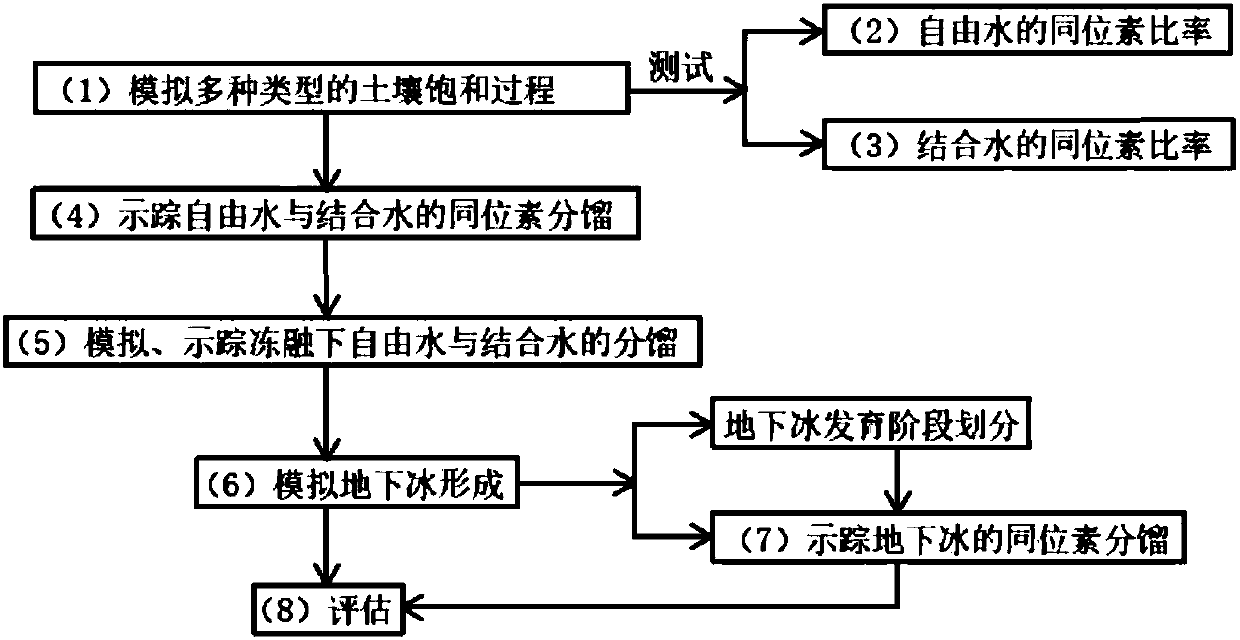
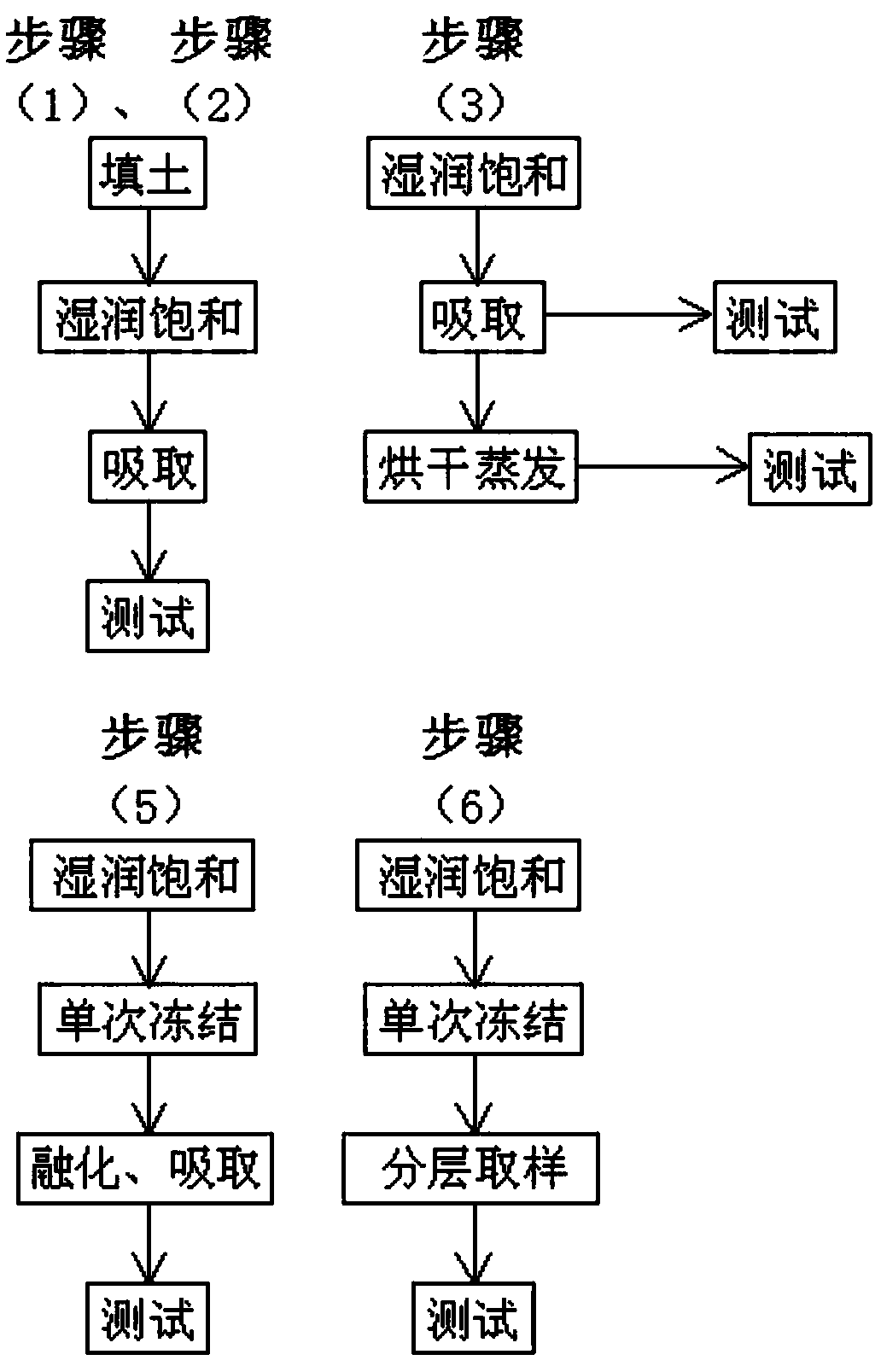
Indoor simulating and monitoring method of underground ice isotope fractionation process
InactiveCN107621531AImprove operational efficiencyImprove portabilityEarth material testingBound waterSoil science
The invention provides an indoor simulating and monitoring method of an underground ice isotope fractionation process. The indoor simulating and monitoring method of the underground ice isotope fractionation process comprises the following steps: simulating many types of soil saturation processes; testing isotope ratios of free water in the soil saturation processes; testing isotope ratios of bound water in the soil saturation processes; tracing isotopic fractionation of the free water and the bound water in the soil saturation processes; simulating the freezing and thawing process of saturated soil; tracing the isotopic fractionation of the free water and the bound water in the freezing and thawing process; simulating the forming process of underground ice in the saturated soil, and dividing the development stage of the underground ice; tracing isotope fractionation of the underground ice according to the development stage of the underground ice; assessing isotope fractionation of thefree water and the bound water in the process of participating in formation of the underground ice. By the indoor simulating and monitoring method, the operating efficiency is high, the portability is strong, a moisture and soil coupling action as well as the isotope fractionation process in the free water and bound water migrating and converting process and other key processes are scientificallyanalyzed, and obtained research results are reliable.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Method for analyzing cadmium element pollution in rice seeds
ActiveCN107817289AAccurate quantitative analysisAchieve traceabilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBiologyCadmium pollution
The invention discloses a method for analyzing cadmium element pollution in rice seeds. The method comprises the following steps: I, testing Cd isotope ratios deltaA, deltaB and deltat of a pollutionsource A and a pollution source B in soil and rice seeds respectively; II, calculating a contribution rate fA of the pollution source A to the cadmium element in the rice seeds according to a source analysis equation (1) as shown in the specification, wherein in the equation, deltat is a cadmium element isotope ratio in rice seeds to be analyzed; alpha is a cadmium element isotope fractionation coefficient in soil to rice seeds; deltaA is the cadmium element isotope ratio in the pollution source A; deltaB is the cadmium element isotope ratio of the pollution source B; and the rice seeds to beanalyzed are harvested from the soil. By adopting the method, isotope ratios in different pollution sources and rice seeds are introduced into equations, and together with correction of the fractionation coefficient alpha, quantitative analysis on the source of cadmium pollution in the rice seeds can be precisely implemented, and the contribution rates of different pollution sources to cadmium inrice seeds can be confirmed.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method for efficiently separating clastic thorium in near-shore coral bones
InactiveCN110006728AEfficient separationHigh precisionPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPrillKnowledge Field
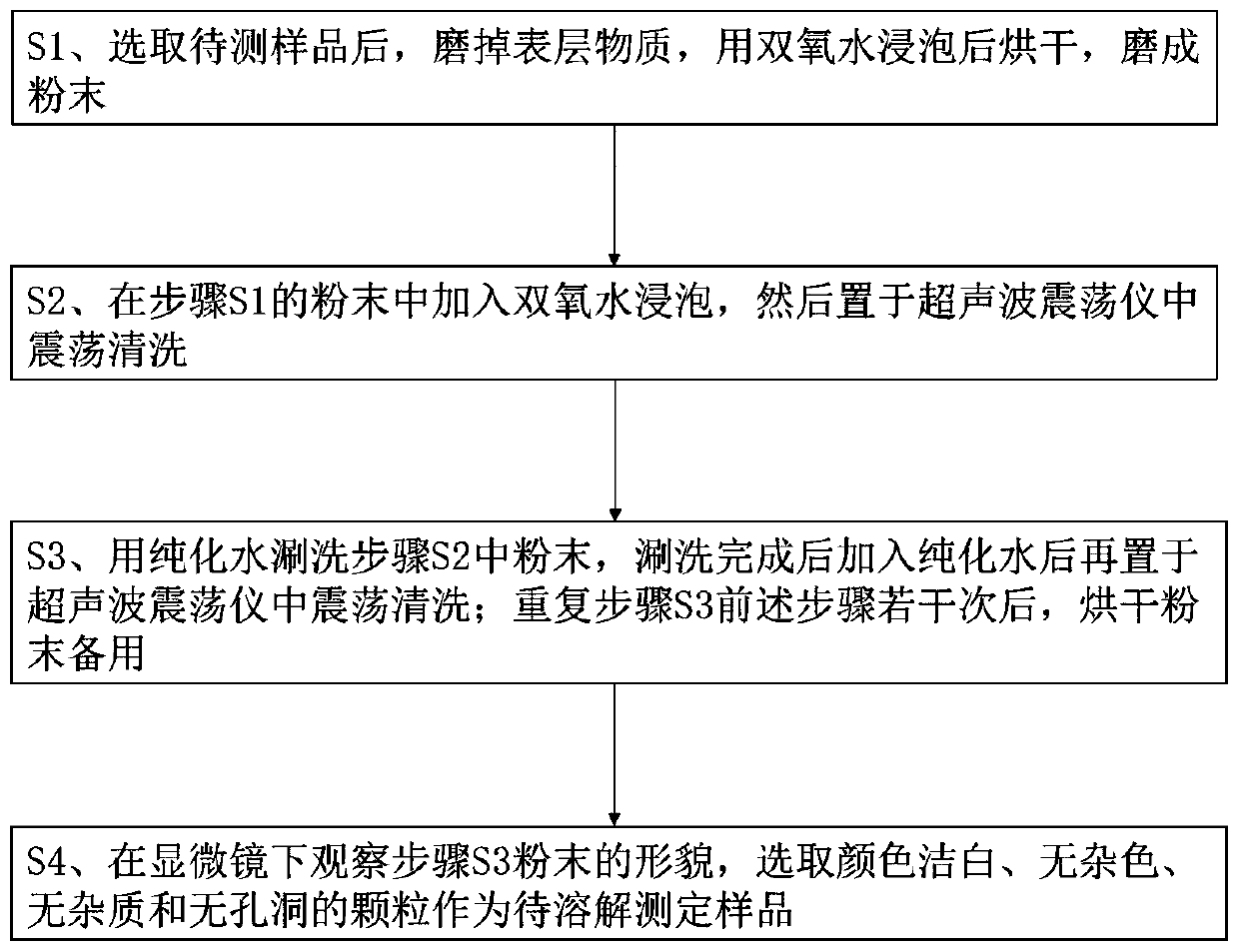
The invention discloses a method for efficiently separating clastic thorium in near-shore coral bones, and belongs to the field of coral chronology. The method comprises the following steps of S1, grinding a surface layer substance after a sample to be tested is selected, soaking with hydrogen peroxide, drying, and grinding into powder; S2, soaking the powder in the step S1 into the hydrogen peroxide and then vibrating and cleaning in an ultrasonic oscillator; S3, rinsing the powder in the step S2 by using purified water, adding the purified water after rinsing, and vibrating and cleaning in the ultrasonic oscillator; repeating the step S3 for several times, and drying the powder for future use; and S4, observing the morphology of the powder in the step S3 under a microscope, and selectingthe particles with white color, no mixed color, no impurity and no hole as a to-be-dissolved test sample. The method disclosed by the invention is simple in experimental equipment, convenient to operate and free of isotope fractionation, more than 95% of clastic thorium in the sample can be effectively removed, and the determination of the age precision of the near-shore coral can be remarkably improved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
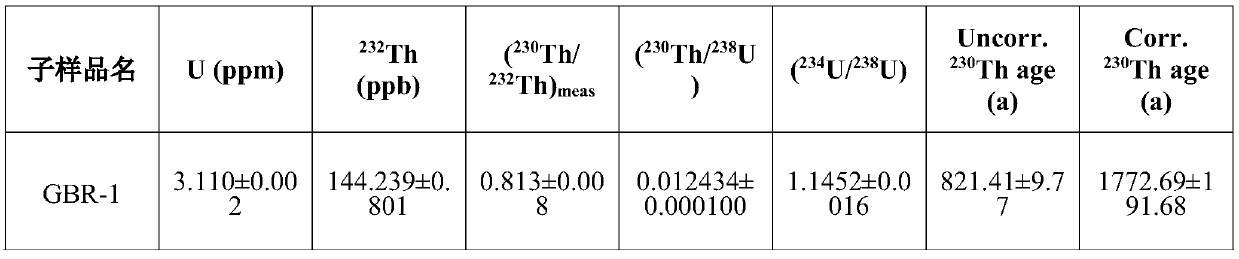
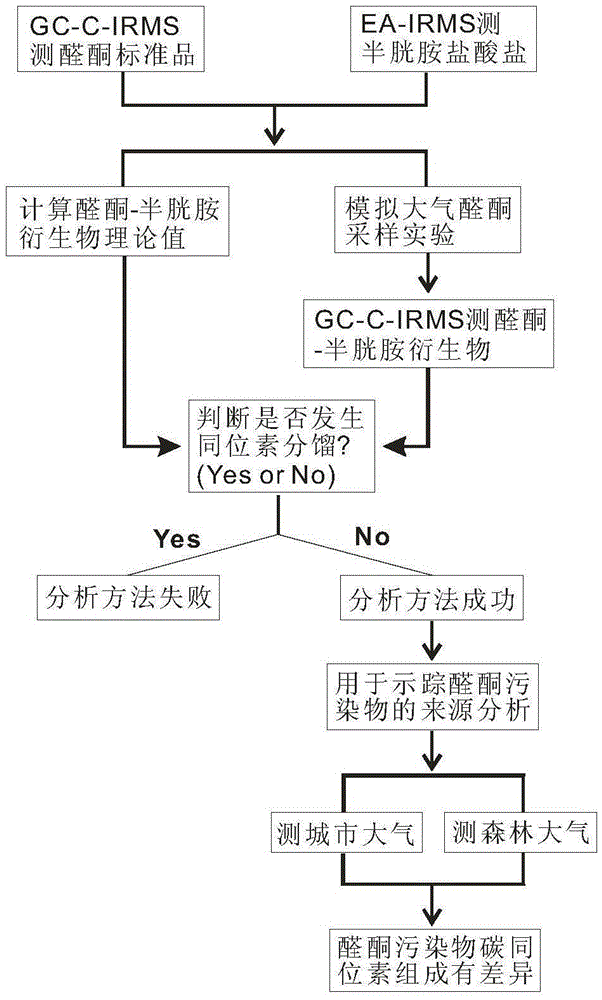
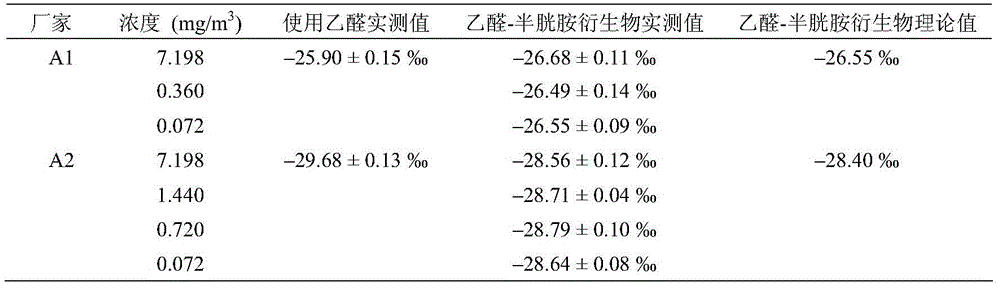
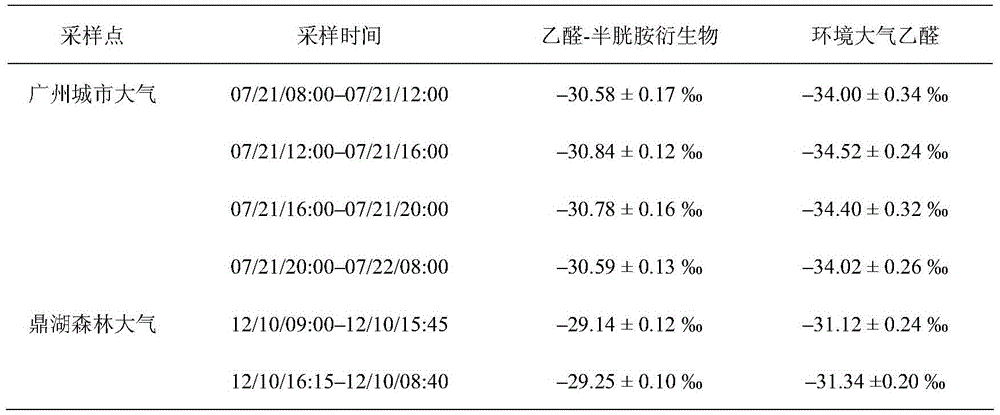
Carbon isotope method for tracing aldehyde ketone pollutants
The invention discloses a carbon isotope method for tracing aldehyde ketone pollutants. The method is characterized in that sources of aldehyde ketone pollutants in atmosphere environment are judged according to occurrence of isotope fractionation or not and the difference of the carbon isotope ratio (delta<13>C value). An experiment result shows that the method has the advantages of good recurrence and high precision of a determination result, and effective overcoming of the defects of traditional concentration measurement methods (EPA TO-11A), can be used to determine the carbon isotope composition (delta<13>C value) of atmosphere aldehyde ketone pollutants in order to realize direct and accurate judgment of the sources of the atmosphere aldehyde ketone pollutants, can be used to trace the sources of the atmosphere aldehyde ketone pollutants as an effective way, is helpful for researching the formation mechanism of atmosphere organic pollution, and provides scientific bases for researches of the atmosphere organic environment pollution.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
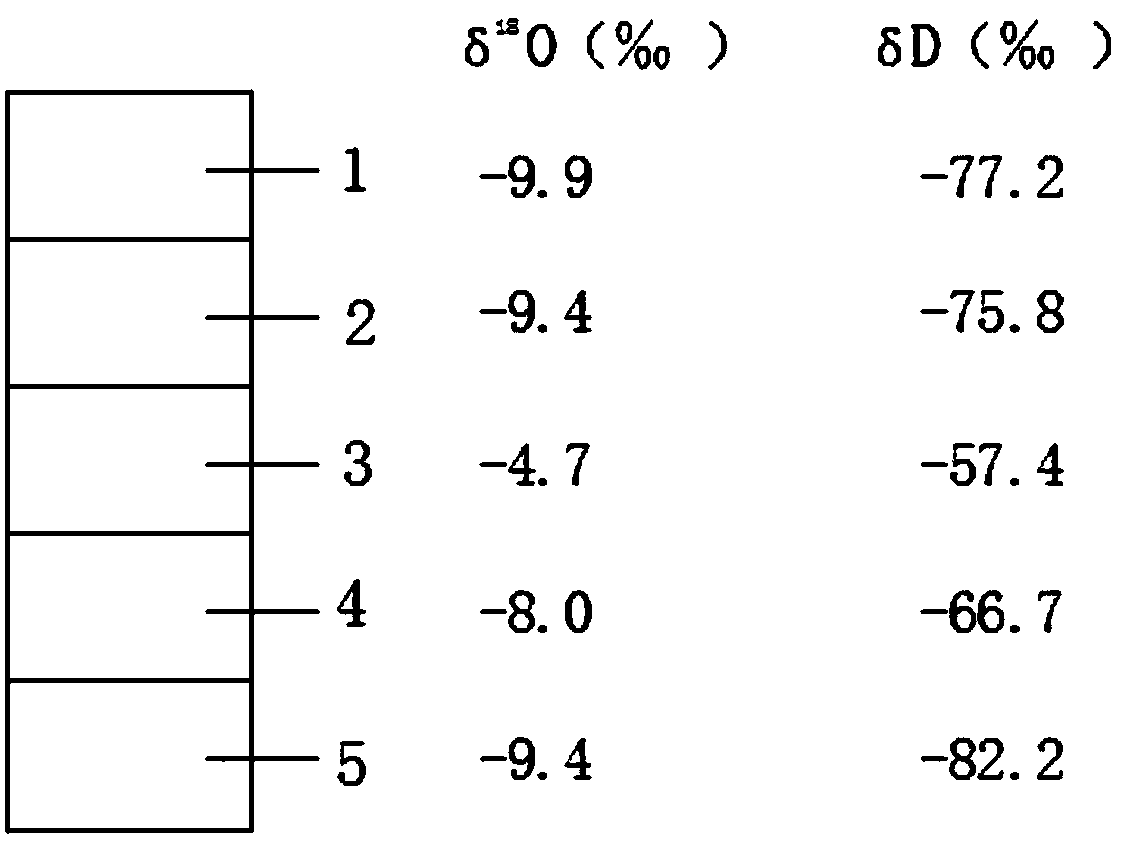
Lake replenishment water source tracing method utilizing hydrogen and oxygen isotopes
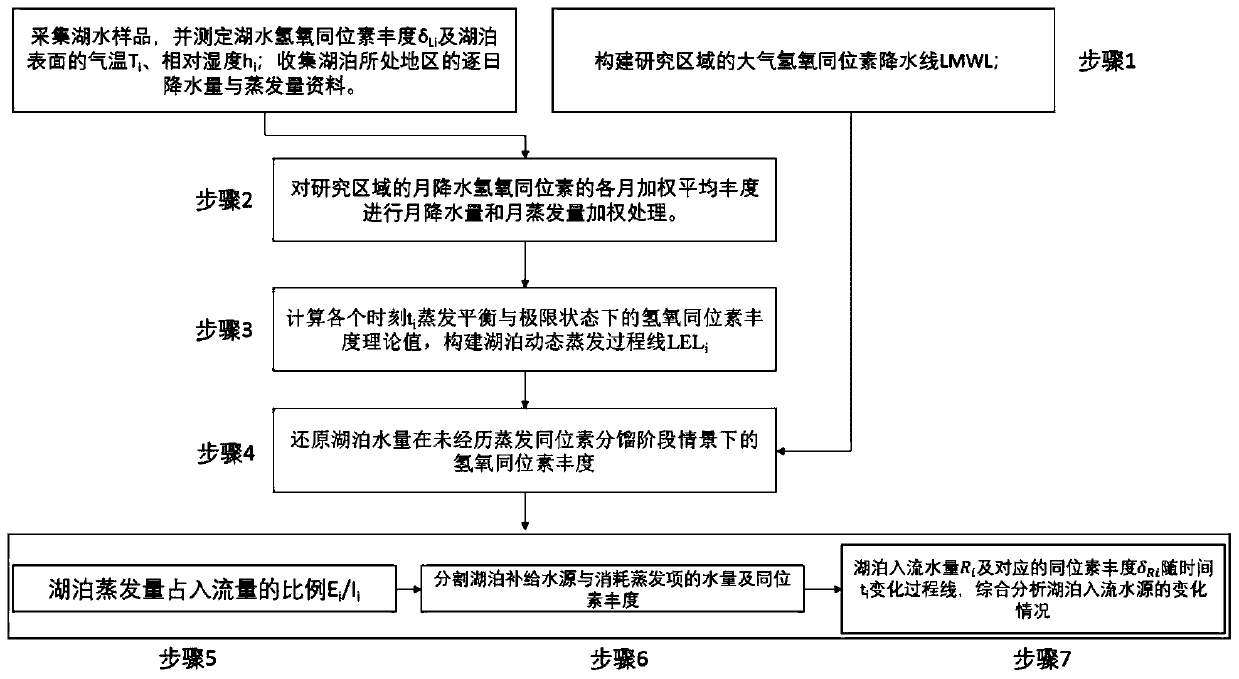
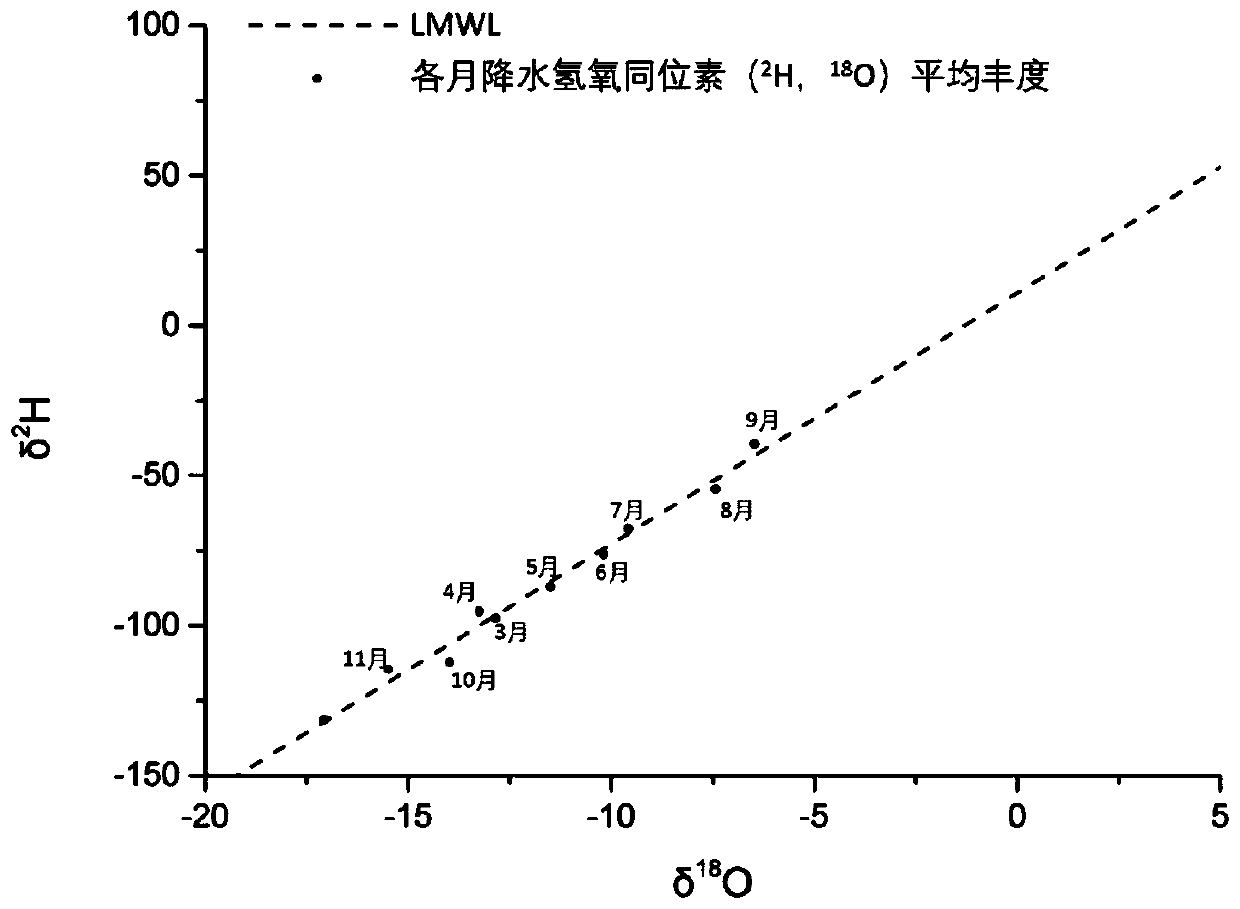
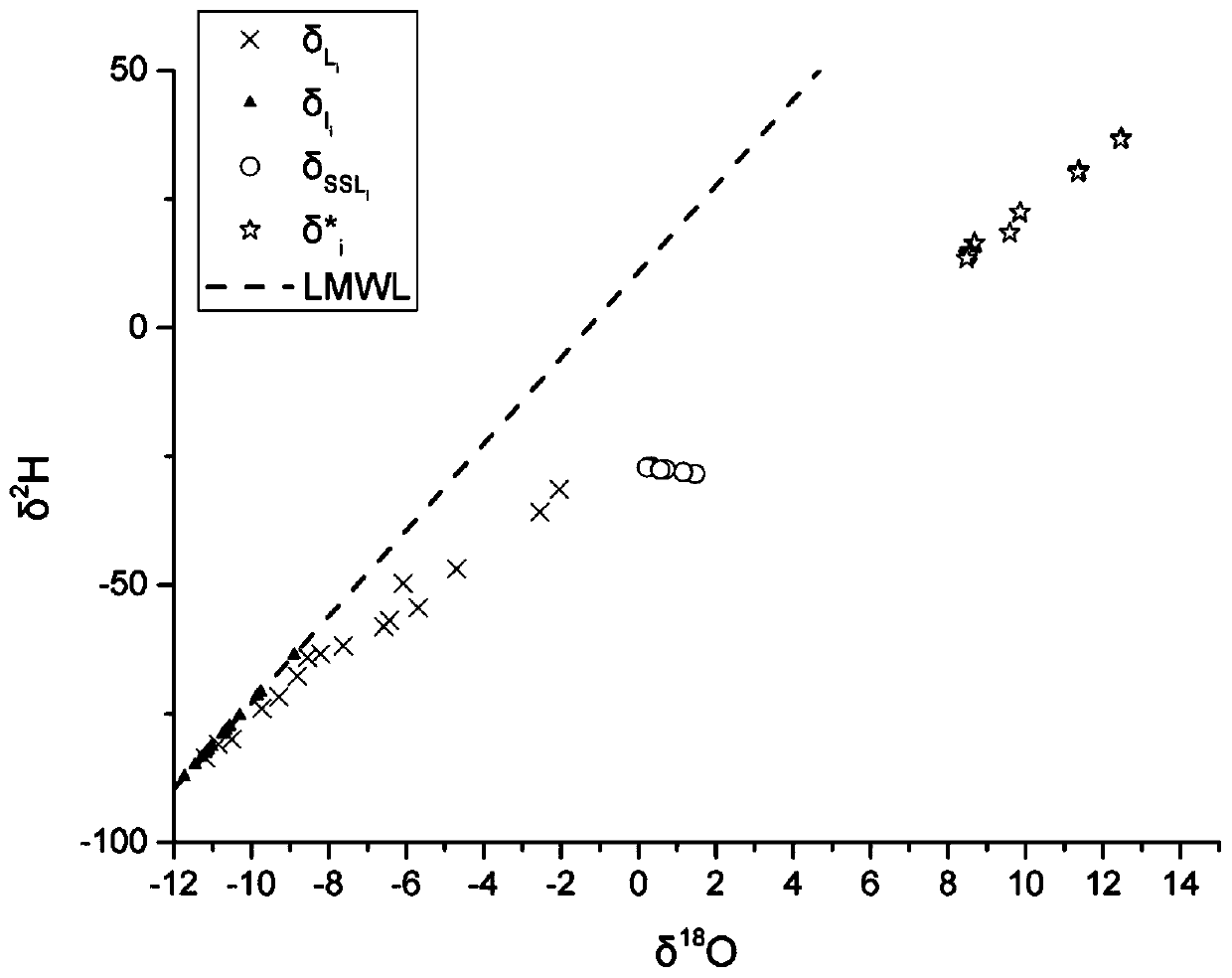
InactiveCN111504277ASolid physical foundationHigh precisionOpen water surveyComplex mathematical operationsWater sourcePrecipitationshed
The invention discloses a lake replenishment water source tracing method using hydrogen and oxygen isotopes. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: collecting a lake water sample; measuring the abundance of the hydrogen and oxygen isotopes (2H, 18O) of the lake water; obtaining the air temperature, relative humidity, daily precipitation and evaporation data of a region where a lake islocated; constructing the atmospheric precipitation line of the research region; calculating the theoretical value of the abundance of the hydrogen and oxygen isotope under an evaporation balance andlimit state at each moment; constructing a lake dynamic evaporation process line; reducing the abundance of the hydrogen and oxygen isotopes of the water quantity of the lake under the condition thatthe water quantity of the lake is not subjected to an evaporation isotope fractionation stage; calculating the proportion of the lake evaporation capacity in inflow in each time period; using a lakewater quantity and isotope mass conservation equation to finely segment the water quantity and isotope abundance of a lake replenishment water source and consumption evaporation items in each time period so as to obtain a lake inflow water quantity Ri and a corresponding isotope abundance change-along-with-time process line; and comprehensively analyzing the change condition of the lake inflow water source.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV +3
Hf isotope analysis method and system for rich Hf mineral or rock
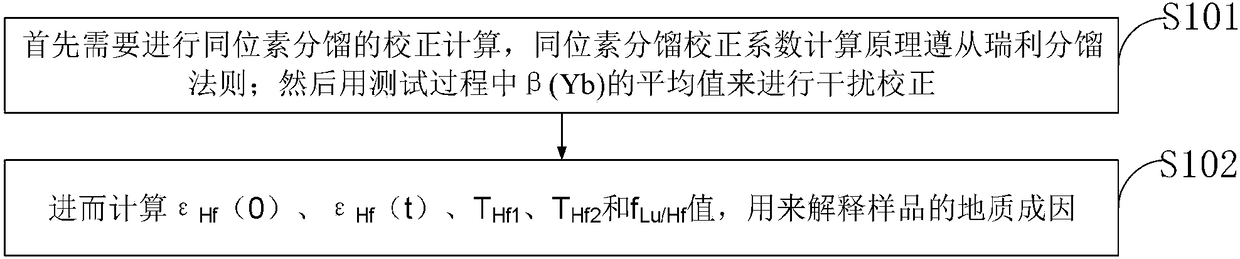
ActiveCN108399149ALess heavy workImprove work efficiencyComplex mathematical operationsGreek letter epsilonAnalysis method
The present invention belongs to the technical field of geological isotope detection, and discloses a method and a system for Hf isotope analysis of an Hf-rich mineral or rock. The method comprises: performing isotope fractionation correction calculation, wherein a isotope fractionation correction coefficient calculation principle follows the Rayleigh fractionation rule; using the average value of[beta](Yb) in the test process for interference correction; and calculating values of [epsilon]Hf(0), [epsilon]Hf(t), THf1, THf2 and fLu / Hf to explain the geological origin of the sample. According to the technical scheme of the present invention, the heavy work of manual calculation in the geological work is eliminated, and the technical scheme can provide a better service for the geological work.
Owner:XIAN CENT OF GEOLOGICAL SURVEY CGS
Method for determining stable carbon isotope of volatile compounds in wine based on SPME-GC-IRMS
The invention relates to a method for determining stable carbon isotope of volatile compounds in a wine based on SPME-GC-IRMS. The method is characterized in that volatile compounds in the wine are extracted through a solid phase microextraction technology, and the compounds are separated by a gas chromatography column; and isotope mass spectrometry is used to determine the delta 13C value in CO2produced by the combustion of the volatile compounds. According to the invention, the solid phase microextraction technology is used to extract the volatile compounds in a wine sample, and GC-IRMS isused to determine the delta 13C value of individual compounds; compared with a method of using EA-IRMS to determine the delta 13C value of ethanol in the wine, the method provided by the invention does not require pretreatment, has the advantage of simple and convenient operation, and is free of an organic solvent; the delta 13C value of volatile materials is accurately and precisely determined; isotope fractionation is prevented; and a useful new method is provided for wine authenticity identification.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for obtaining total assimilative capacity of plant inorganic carbon under outdoor ecological environment
ActiveCN108508156ARapid determinationAccurate measurementTesting plants/treesEcological environmentBiology
The invention discloses a method for obtaining the total assimilative capacity of plant inorganic carbon under an outdoor ecological environment, and belongs to the fields of a crop information detecting technology, a plant physiological information detecting technology and ecological environment management. The method is characterized by calculating the share of actually assimilated carbon dioxide of plant leaves according to a stable carbon isotope fractionation value of completely assimilated carbon dioxide of the plant leaves and the stable carbon isotope fractionation value of the actually assimilated carbon dioxide of the plant leaves; converting the total assimilative capacity of the plant inorganic carbon according to actual carbon dioxide assimilative capacity measured through a portable photosynthesis system. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the carbon dioxide utilization shares of plants in different seedling ages and different growth periods under the outdoor ecological environment can be quickly, conveniently and accurately obtained in real time, and meanwhile, the bicarbonate utilization capacity of the plants under the outdoor ecological environment can also be obtained.
Owner:INST OF GEOCHEM CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Boron and lithium isotopic method for tracing hydrocarbons and their by-products
ActiveUS9429554B2Easy to explainEnhanced overall recoveryIon sources/gunsEarth material testingHydrocotyle bowlesioidesGroundwater contamination
The invention relates to methods for determining the source of hydrocarbons presented in the pores of a host rock or found in contaminated groundwater. The method includes the steps of (a) determining a first isotopic composition of boron and / or lithium in one or more components within a potential source rock sample, such as kerogen, clay, or water; (b) determining a second isotopic composition of boron and / or lithium in the hydrocarbons found within the pores of a host rock sample or in contaminated groundwater; and (c) comparing the first and second isotopic compositions to determine whether the potential source rock is the source of the hydrocarbons within the pores of the host rock or in contaminated groundwater. The comparison is facilitated by using the isotope fractionation between the kerogen, clay, or water components and the bitumen component of the potential source rock, which allows one to predict the isotope composition of any hydrocarbons originating in the bitumen component of the source rock, based on the isotope composition of one of the other three phases. The method can be used to select host rock for extracting oil and other hydrocarbons, as well as in remediating groundwater contamination.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
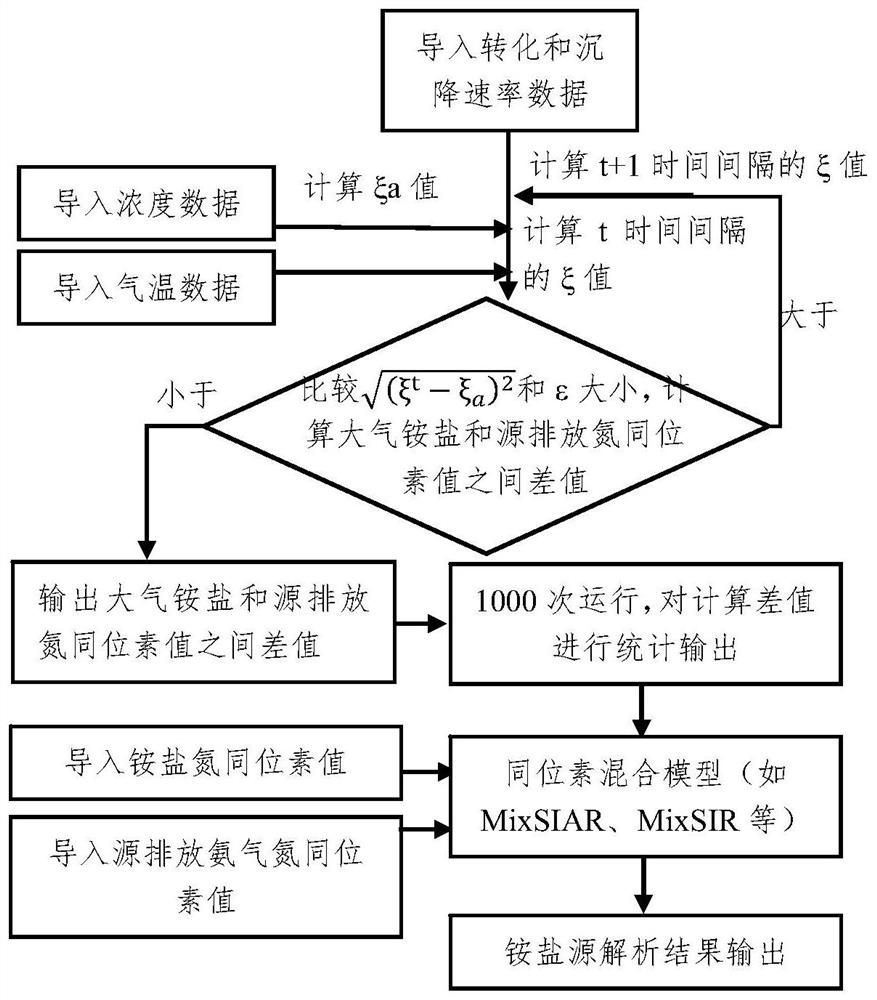
Optimization method for analyzing ammonium salt source in atmospheric particulates based on nitrogen isotopes
ActiveCN112379044AAccurate Source Resolution ResultsHigh temporal frequencyAnalysing gaseous mixturesComplex mathematical operationsParticulatesAtmospheric sciences
The invention relates to an optimization method for analyzing an ammonium salt source in atmospheric particulates based on nitrogen isotopes. According to the method, the nitrogen isotope change of ammonium salt in atmospheric particulates caused by nitrogen isotope fractionation of ammonia gas-ammonium salt conversion in the atmospheric environment and atmospheric settlement of ammonia gas and ammonium salt is considered at the same time, and the difference value between the nitrogen isotope value of ammonium salt in atmospheric particulates and the nitrogen isotope value of source emission ammonia gas is calculated; and the difference value is inputted into an isotope mixing model (such as MixSIAR, MixSIR and the like), and contribution ratios of various emission sources to ammonium salts in atmospheric particulates are analyzed. The method has the advantages that the contribution ratio of various emission sources to the ammonium salt in the atmospheric particulates is more objectively reflected, the calculation efficiency is high, and the operation is simple.
Owner:YANTAI INST OF COASTAL ZONE RES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
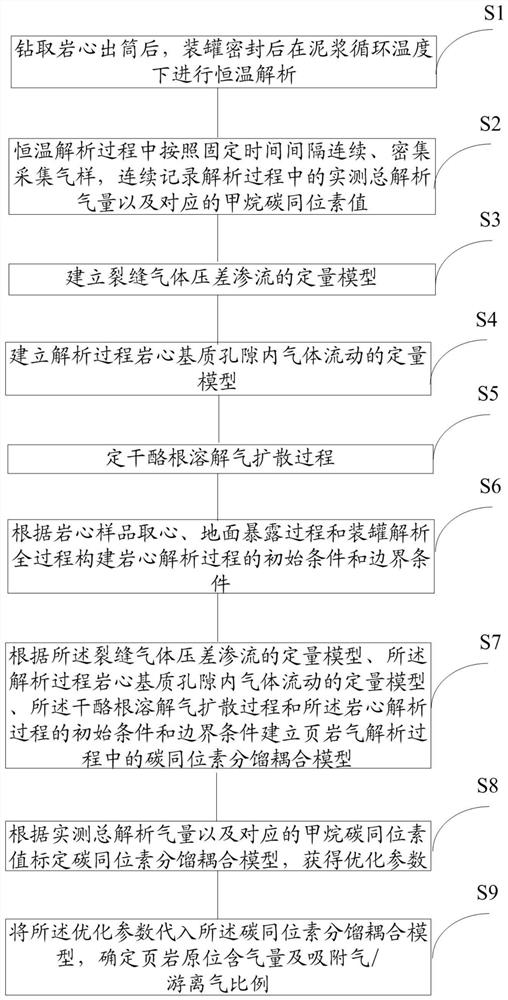
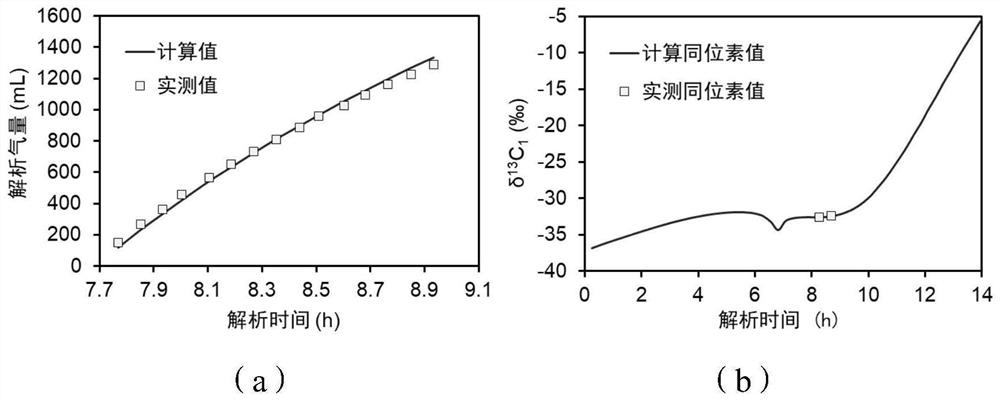
Shale in-situ gas-bearing parameter determination method and system based on carbon isotope fractionation
ActiveCN112151124AImprove accuracyEasy to operateMolecular entity identificationDesign optimisation/simulationKerogenPhysical chemistry
The invention provides a shale in-situ gas-bearing parameter determination method and system based on carbon isotope fractionation. A carbon isotope fractionation coupling model in the shale gas analysis process is established according to the quantitative model of crack gas differential pressure seepage, the quantitative model of gas flow in core matrix pores in the analysis process, and the initial conditions and boundary conditions of the kerogen dissolved gas diffusion process and the core analysis process; the shale in-situ gas content and the adsorbed gas / free gas ratio are determined based on the carbon isotope fractionation coupling model, the accuracy, operability and practicability of shale gas resource prediction are improved, and geological application and popularization are facilitated.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Method for judging anaerobic digestion process by using carbon stable isotope fractionation ratio
InactiveCN109613136ARespond quicklyGreat application potentialComponent separationWaste based fuelMicroorganismMethanogenesis
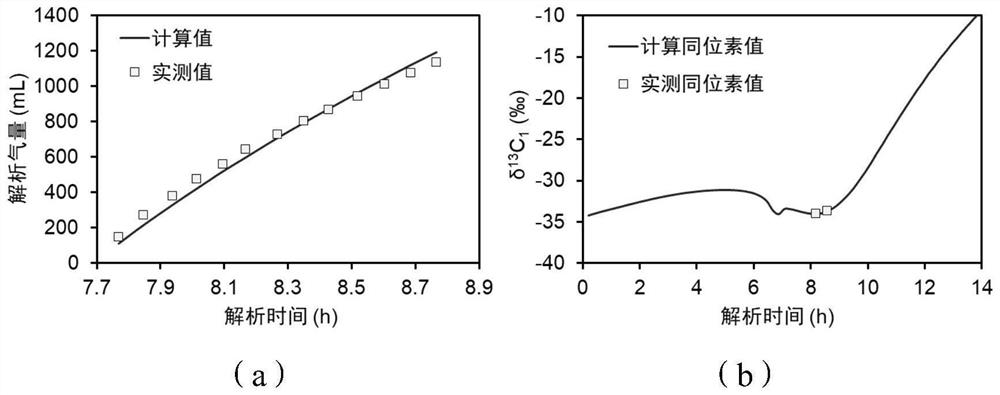
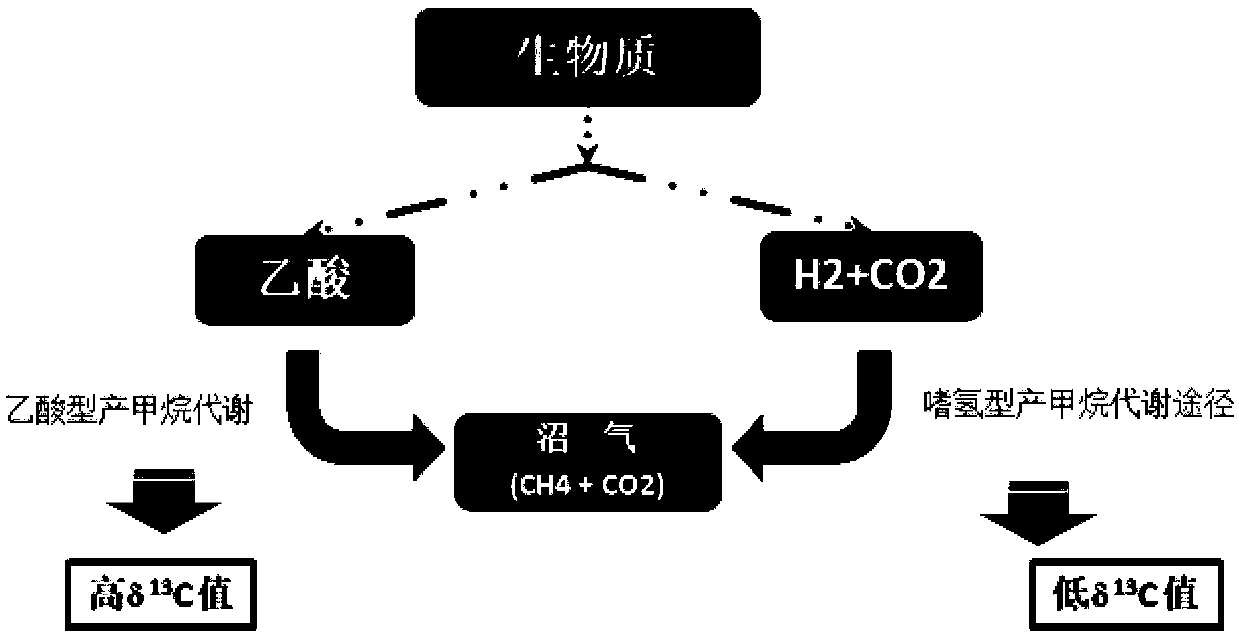
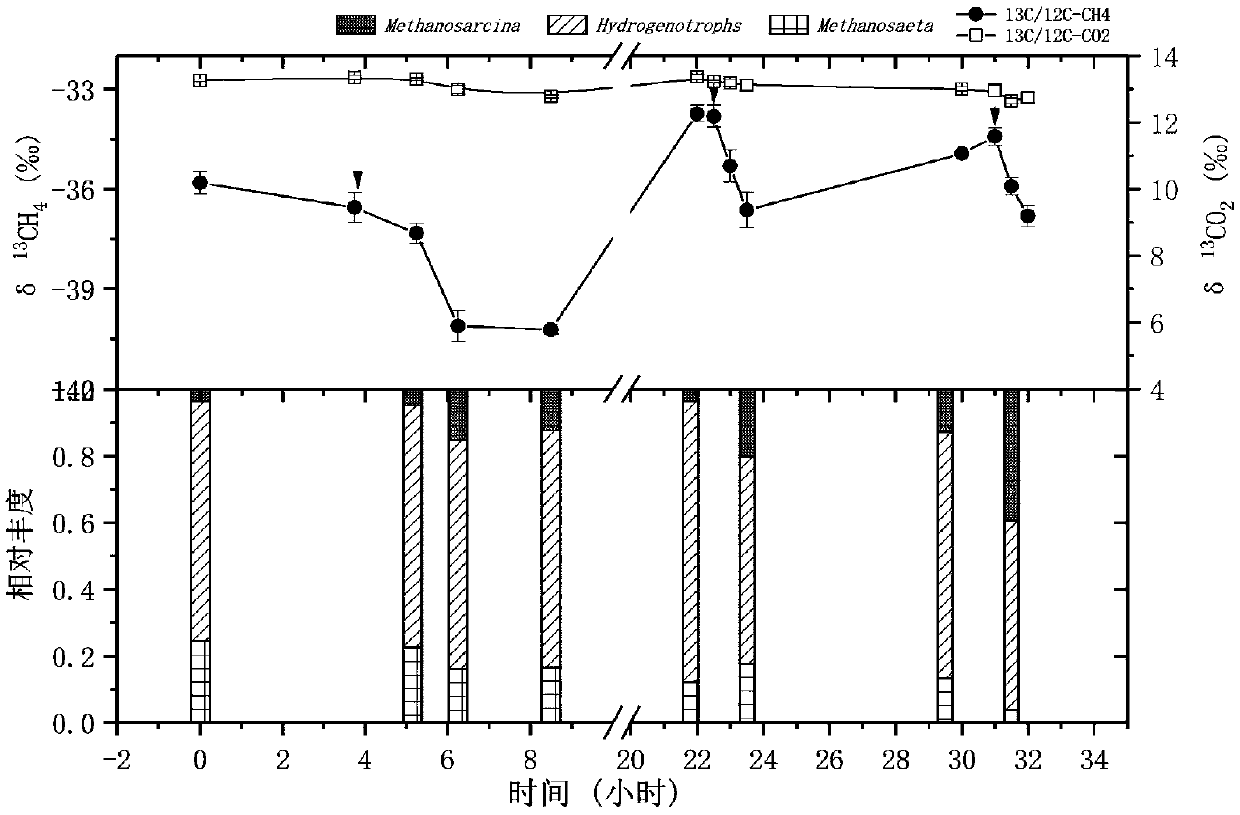
The invention relates to a method for judging an anaerobic digestion process by using a carbon stable isotope fractionation ratio in methane. The method for judging the anaerobic digestion process byusing the carbon stable isotope fractionation ratio in the methane includes the following steps of firstly, collection of a biogas; secondly, measurement of delta13 / 12CH4 and delta 13 / 12CO2; thirdly,calculation of delta 13 value (permillage); and fourthly, calculation of a ratio alpha value of the delta 13 / 12CH4 and the delta 13 / 12CO2. Aiming at the difficult problem that monitoring a methanogenesis process in the anaerobic digestion process is difficult, and combining the support of a large number of molecular biological data at the early stage, the method for judging the anaerobic digestionprocess by using the carbon stable isotope fractionation ratio in the methane finds out a statistical relationship of composition changes of microbial communities and especially the statistical relationship between a fluctuation of methanogenesis archaea community and a delta value and an alpha value, and a method of rapidly reflecting metabolism of the methanogenesis archaea by using the delta value and the alpha value is obtained; and the method of rapidly reflecting the metabolism of the methanogenesis archaea by using the delta value and the alpha value breaks through the technical barriers of traditional molecular biotechnology of time-consumption, labor-consumption, high cost, poor application potentiality and the like, and achieves the rapid reflection of a methanogenesis metabolicpathway in the anaerobic digestion process.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
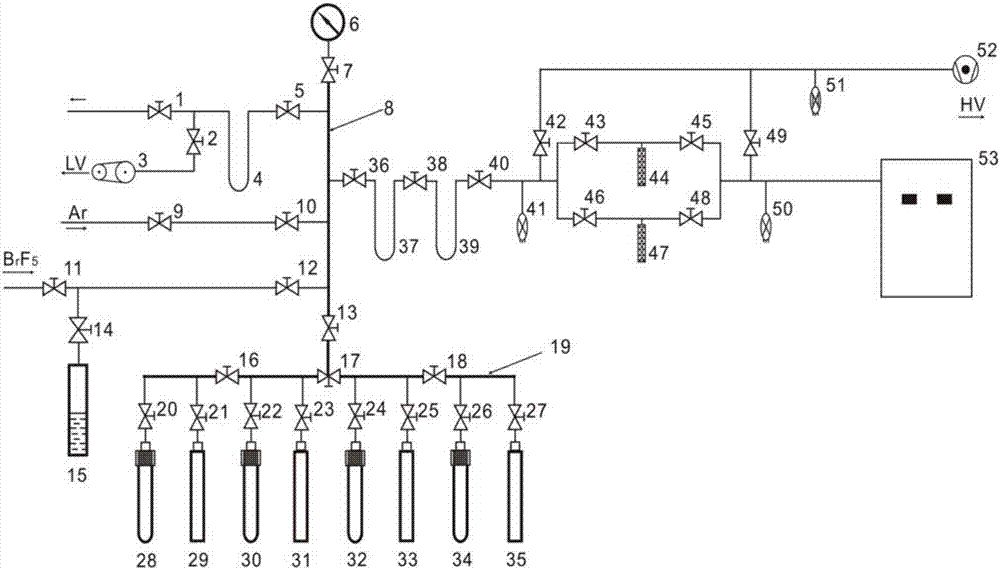
Analyzing and extracting device and method of oxygen isotope composition in rocks and minerals
PendingCN110031536AImprove analysis efficiencyClean up thoroughlyMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPentafluorideCollection system
The invention belongs to the technical field of isotope composition determination of rocks and minerals, and particularly relates to an analyzing and extracting device and method of oxygen isotope composition in the rocks and the minerals. The analyzing and extracting device comprises a waste treatment system, a first 1 / 2 inch stainless steel vertical main pipeline and twelve sets of identical oxygen isotope sample extraction, separation, purification and collection systems; the analyzing and extracting method comprises the following steps that 1, sample introducing is conducted; 2, a whole system is baked to be vacuum-degassed; 3, pentafluoride bromine reagent is transferred, and fluorination reaction is conducted; 4, oxygen is separated, purified and collected; and 5, the waste is treated. According to the analyzing and extracting device and method of oxygen isotope composition in the rocks and the minerals, the problem that oxygen isotope fractionation is prone to being caused in the process of isotope sample preparation can be solved, and the accuracy of analysis and test and the efficiency of analysis and test are improved.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF URANIUM GEOLOGY
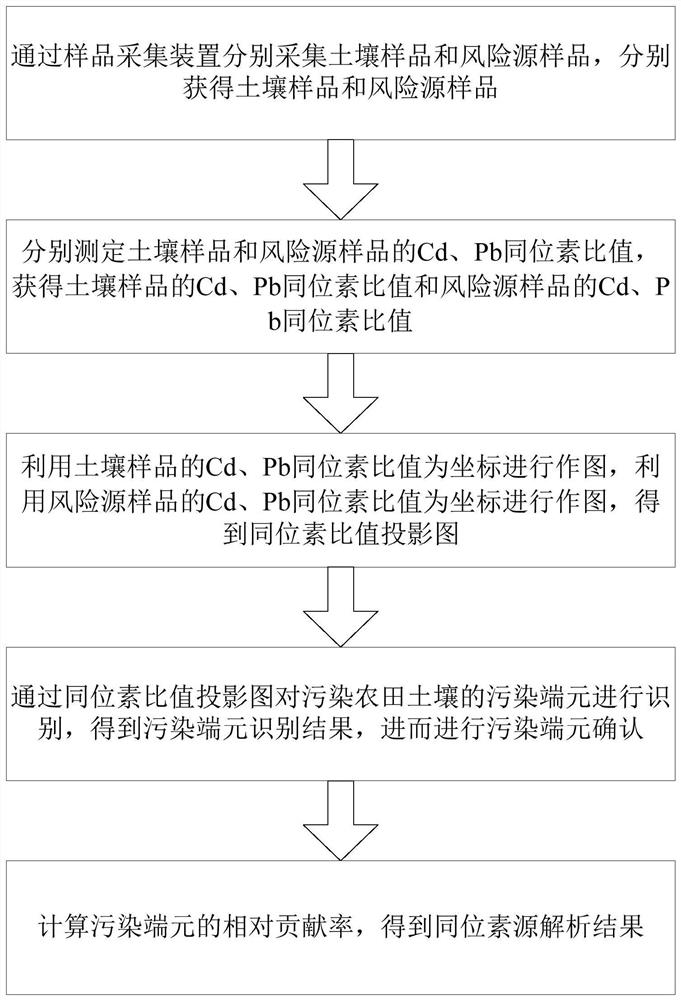
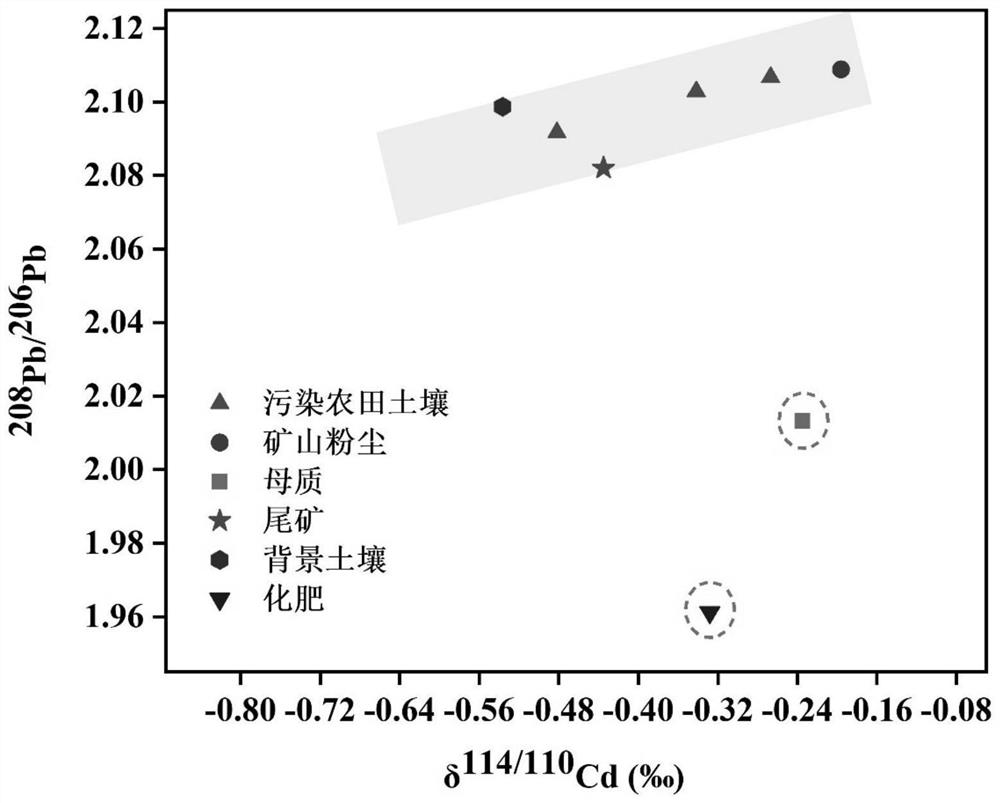
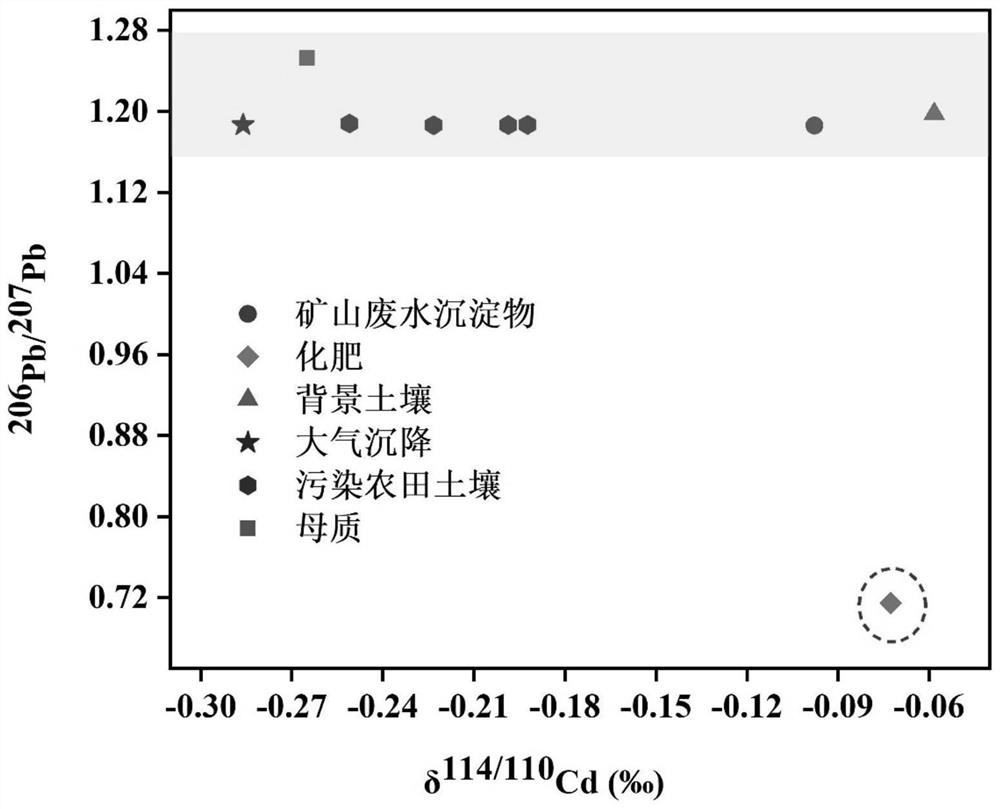
Soil Cd/Pb combined pollution bimetallic isotope source analysis method and system
ActiveCN114062476AAccurate quantitative analysisDetermine Quantitative Contribution RateMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGeneral water supply conservationSoil scienceEdaphic
The invention discloses a farmland soil Cd / Pb combined pollution bimetallic isotope source analysis method. The method comprises the following steps of respectively collecting a soil sample and a risk source sample through a sample collection device; respectively measuring Cd and Pb isotope ratios of the soil sample and the risk source sample; drawing by using the Cd and Pb isotope ratios of the soil sample and the risk source sample as coordinates to obtain an isotope ratio projection drawing; identifying a polluted end member of the polluted farmland soil through the isotope ratio projection drawing to obtain a polluted end member identification result, and further confirming the polluted end member; and calculating the relative contribution rate of the polluted end member to obtain an isotope source analysis result. The method is advantaged in that by utilizing mutual restriction and mutual verification of Cd-Pb metal isotopes, a problem of poor analysis accuracy caused by similar or overlapped sample isotope values and isotope fractionation is solved, and accurate identification and quantitative analysis of the Cd / Pb heavy metal pollution source of the farmland soil are realized.
Owner:INST OF GEOCHEM CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Determination method of sucrose utilization rate in tissue culture seedlings
ActiveCN105684899BCalculation of sucrose utilization rateReduce manufacturing costHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureSaccharumSucrose
The invention discloses a determining method of tissue cultured seedling sucrose. The method comprises the following steps of respectively adopting beet sucrose and sugarcane sucrose as organic carbon sources to prepare a beet sucrose culture medium and a sugarcane sucrose culture medium; culturing tissue cultured seedlings with consistent growth vigors until the fresh weight is increased by over 20 times, and finishing the culturing; determining delta<13>C values of the beet sucrose, the sugarcane sucrose and newly-growing leaves; according to the tissue cultured seedlings of plants to be determined, utilizing the sugarcane sucrose and the beet sucrose to produce carbon isotope fractionation values, and utilizing a fractionation value of carbon dioxide in air, the weight increment of the tissue cultured seedlings and sugarcane consumption to calculate the sugarcane utilization rate of the tissue cultured seedlings. The method provided by the invention not only can be used for quantitatively determining the autotrophy portion, the heterotrophy portion and the like of the tissue cultured seedlings in one growth period, but also can be used for calculating the sugarcane utilization rate of the tissue cultured seedlings in the same period, has an important guide value on regulation of tissue cultured environment factors, and provides technical parameters for domestication and transplantation of later tissue cultured seedlings.
Owner:INST OF GEOCHEM CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com