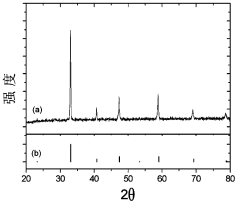
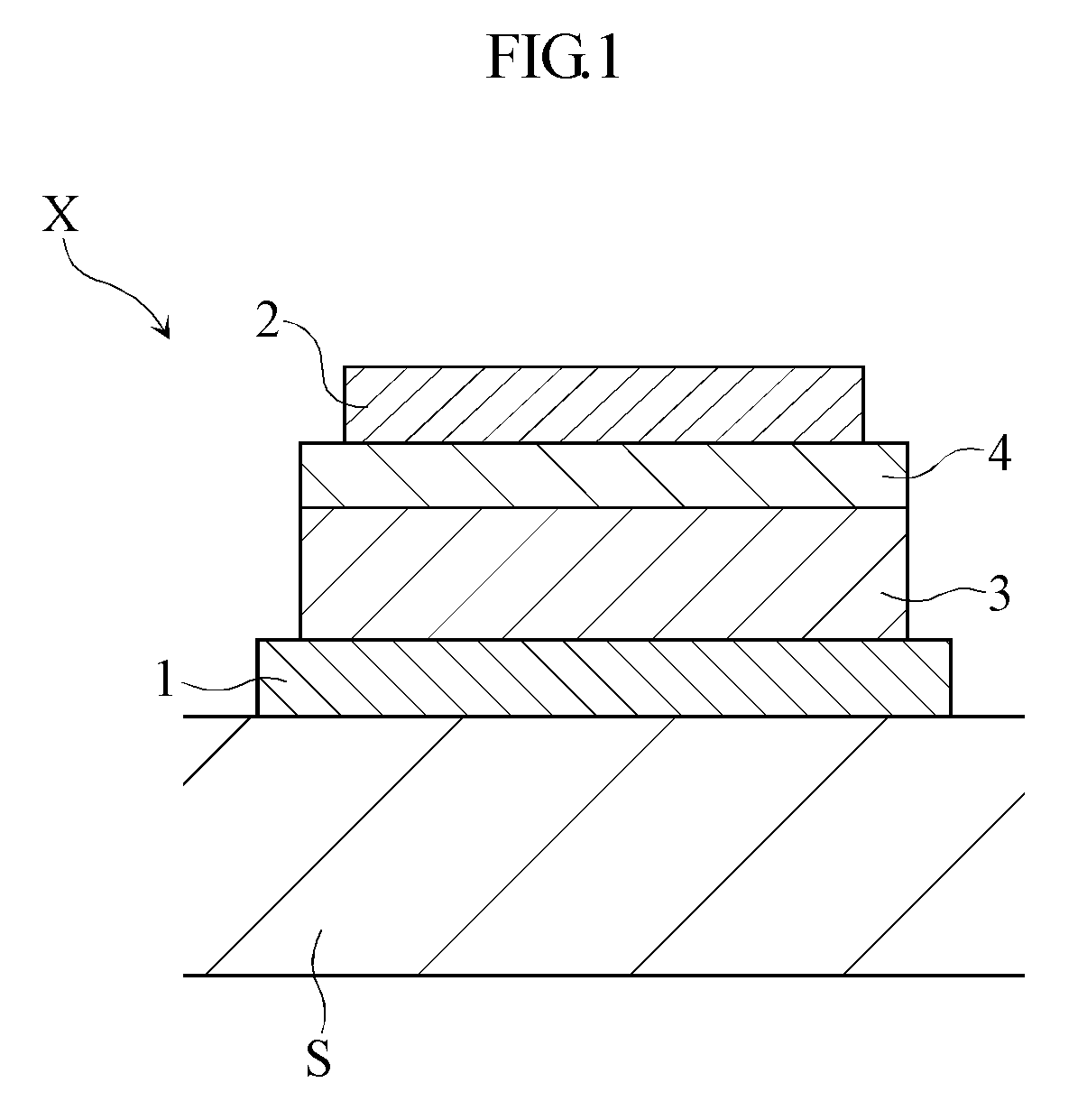
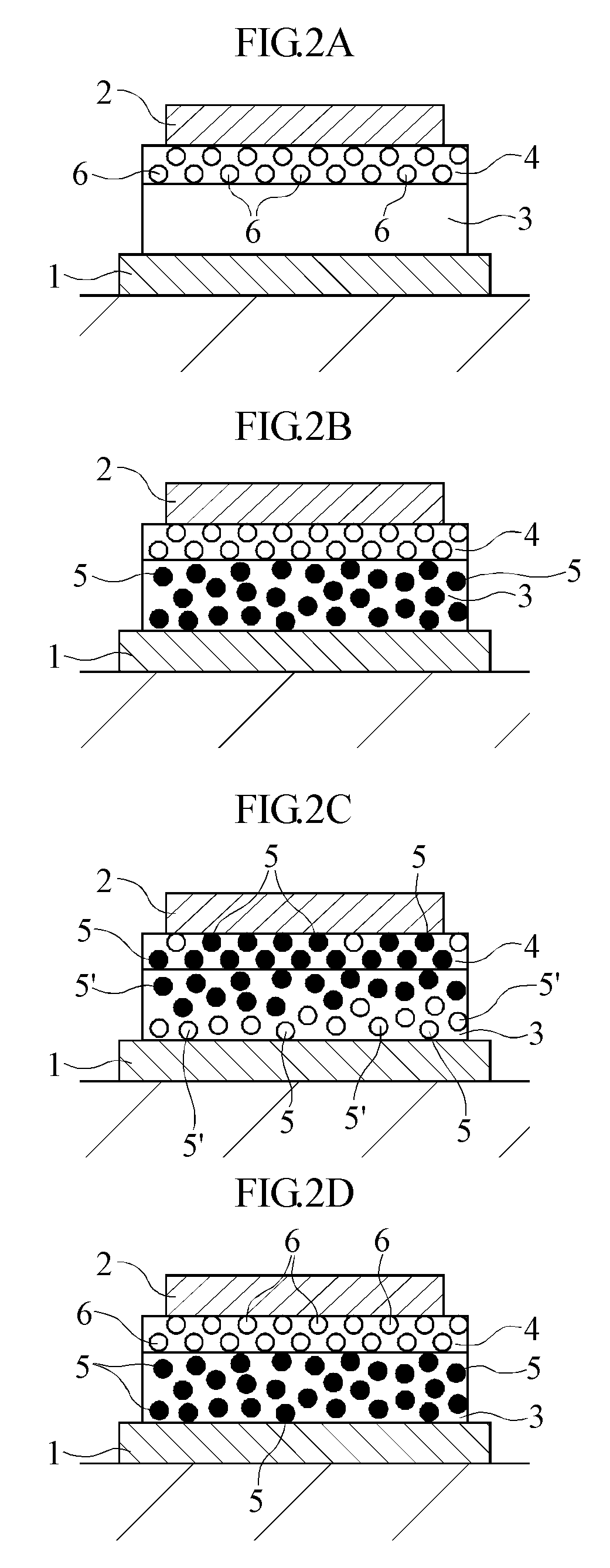
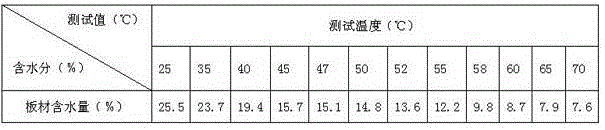
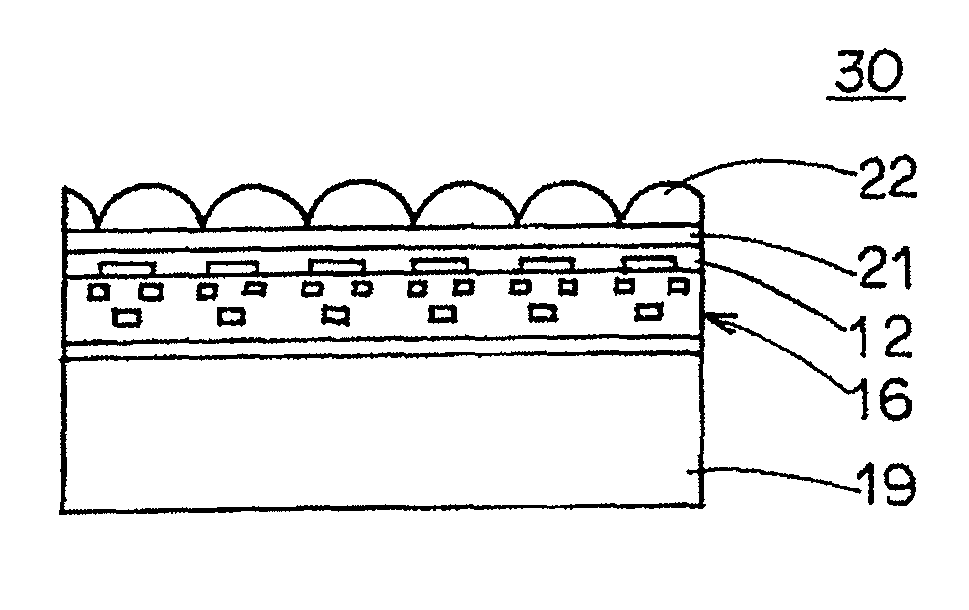
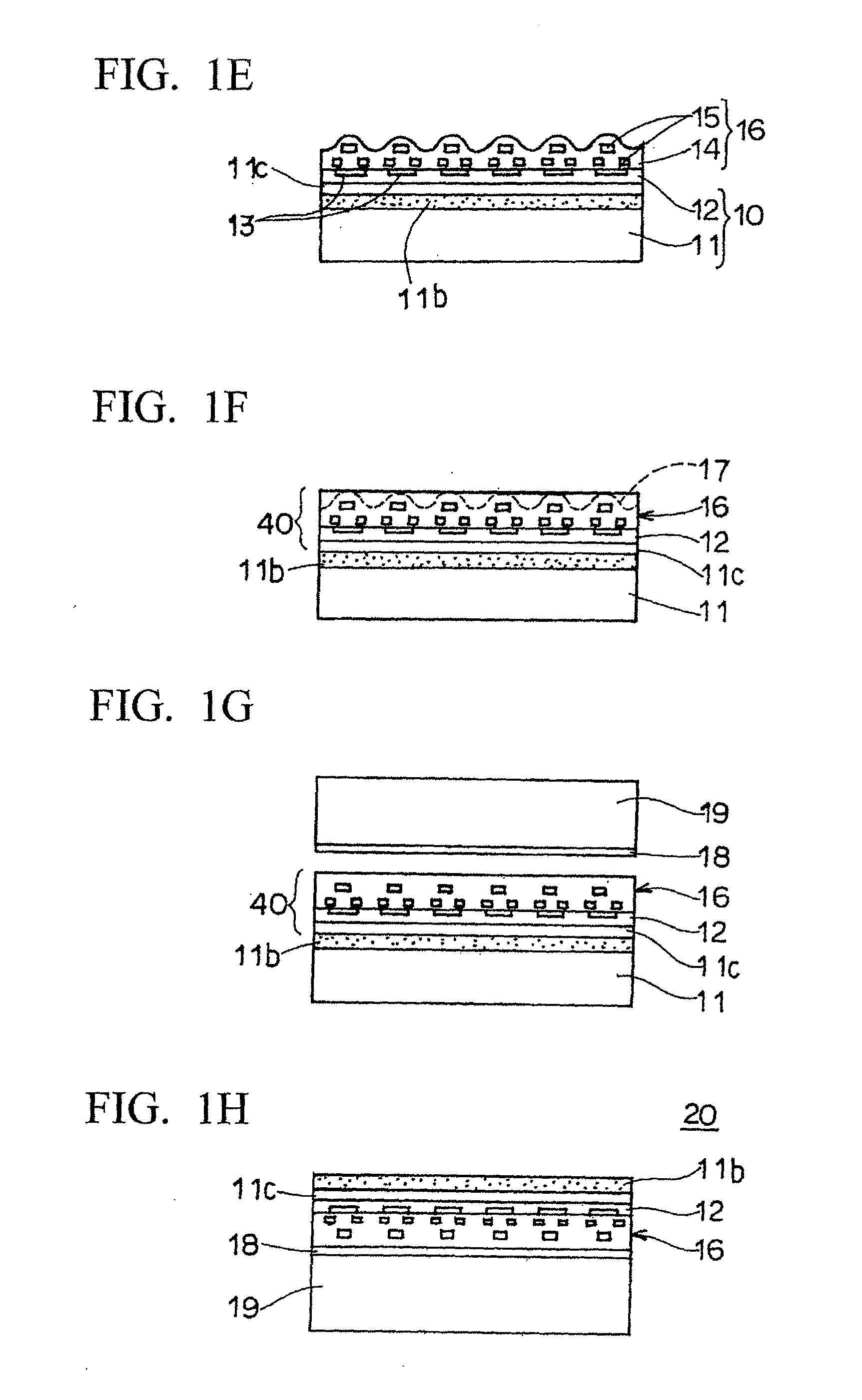
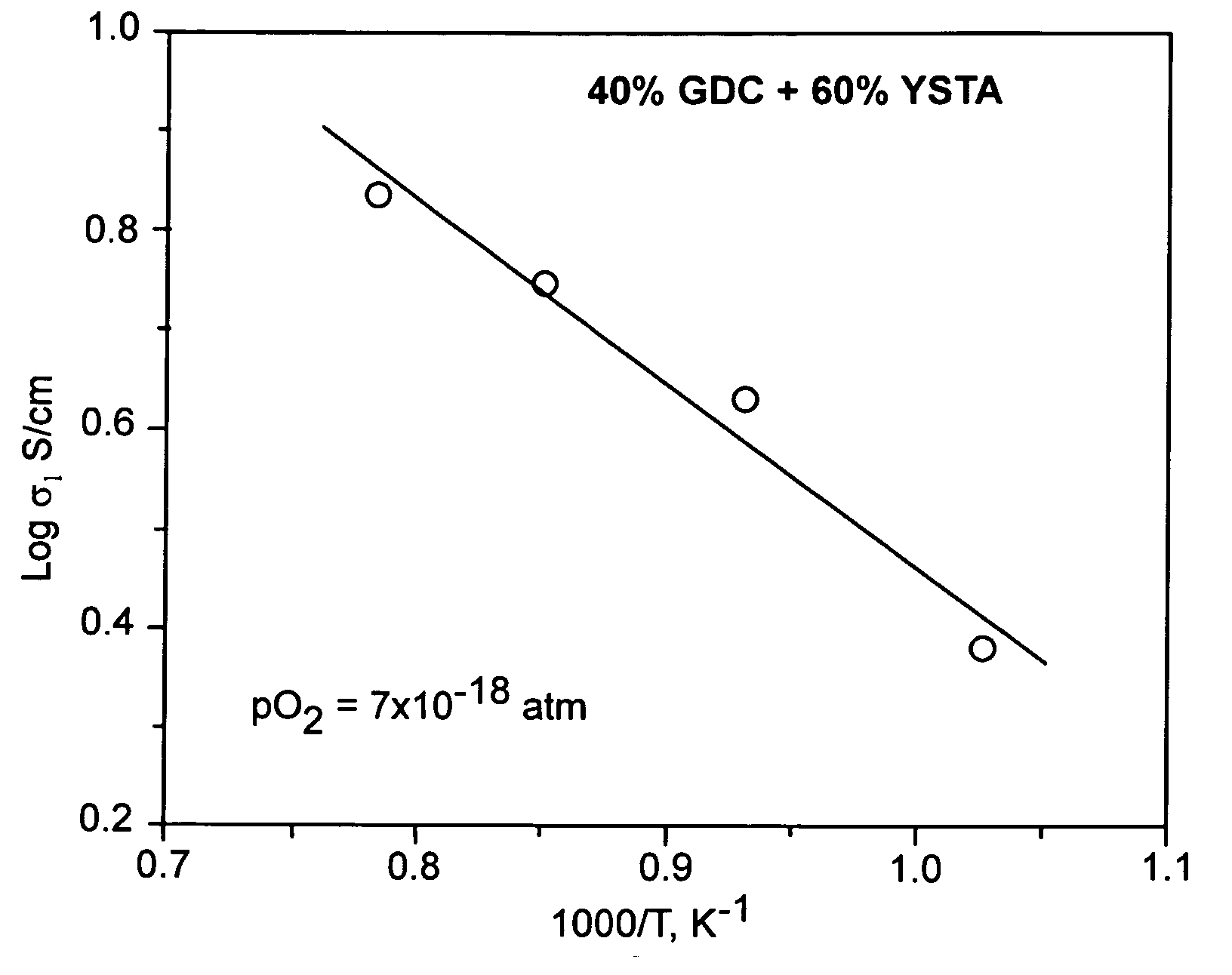
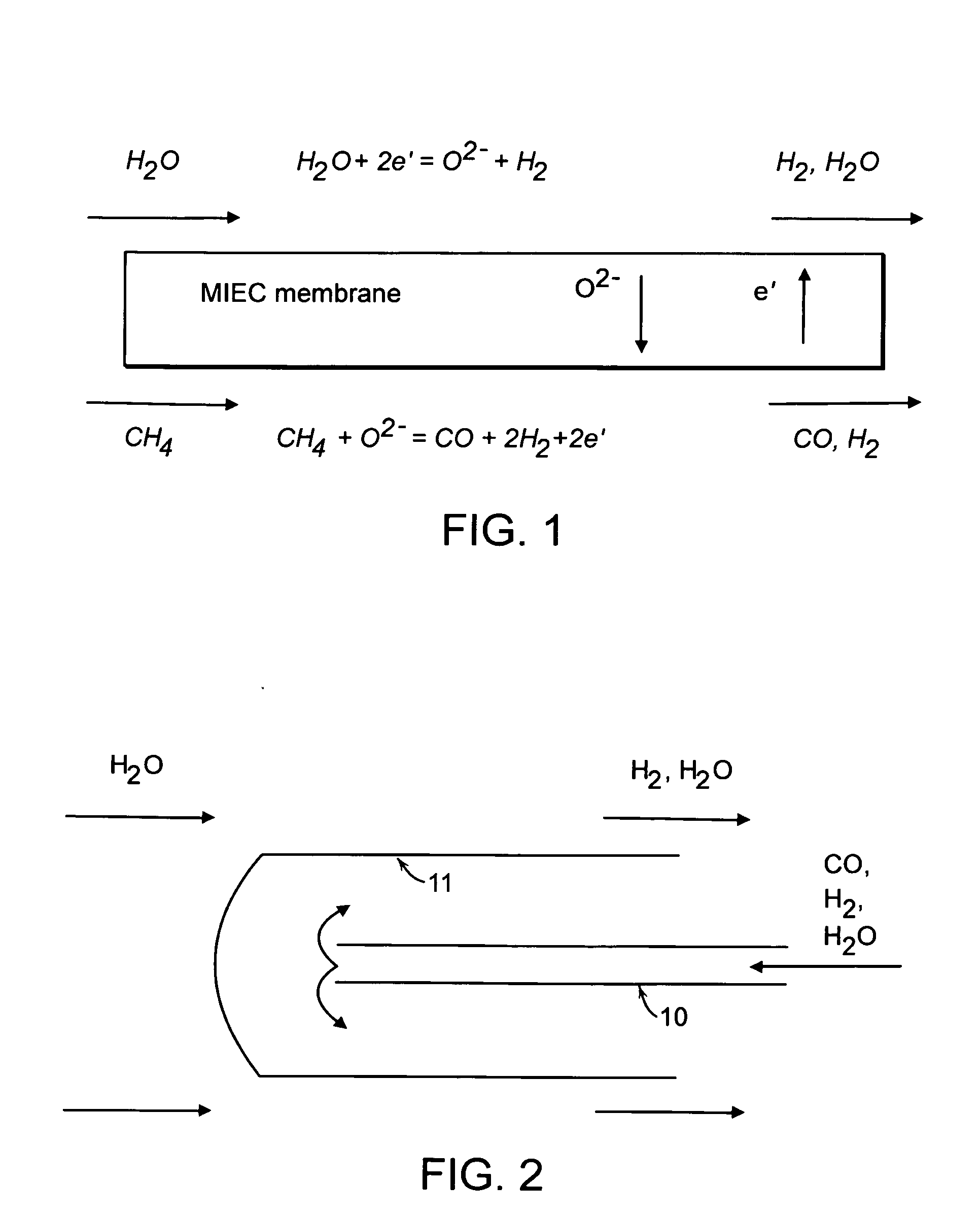
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3459 results about "Oxygen ions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Oxygen ions have a charge of -2. Oxygen atoms have 8 protons and 8 electrons. Two electrons are located in the first energy level, and 6 electrons are located in the second energy level. By adding two electrons to the second energy level, a more stable noble gas is achieved by the oxygen.
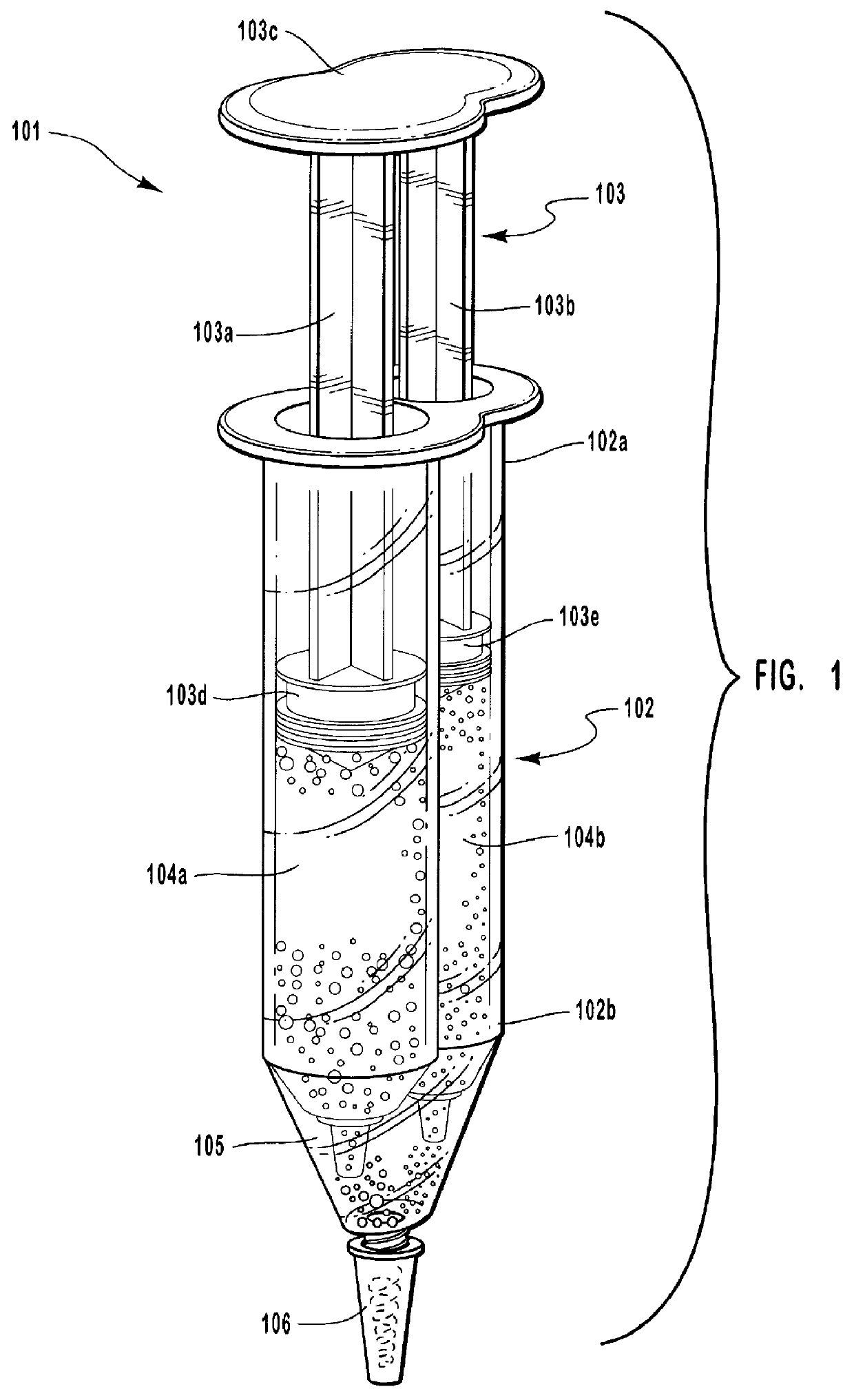
Binary energizer and peroxide delivery system for dental bleaching
A dental bleach storage, mixing and delivery device and related method are disclosed. The device includes a barrel with at least two chambers. The chambers store components that when mixed can form a dental bleach or whitener. A plunger is provided that can be reciprocated within the barrel to force such components from their chambers. A mixing tip is provided for the end of the barrel. The components may be forced through the mixing tip which thoroughly mixes them together. The resulting bleach or whitener is applied to a patient's teeth where oxygen ions released from the bleach or whitener and will whiten the patient's teeth.
Owner:CAO GROUP
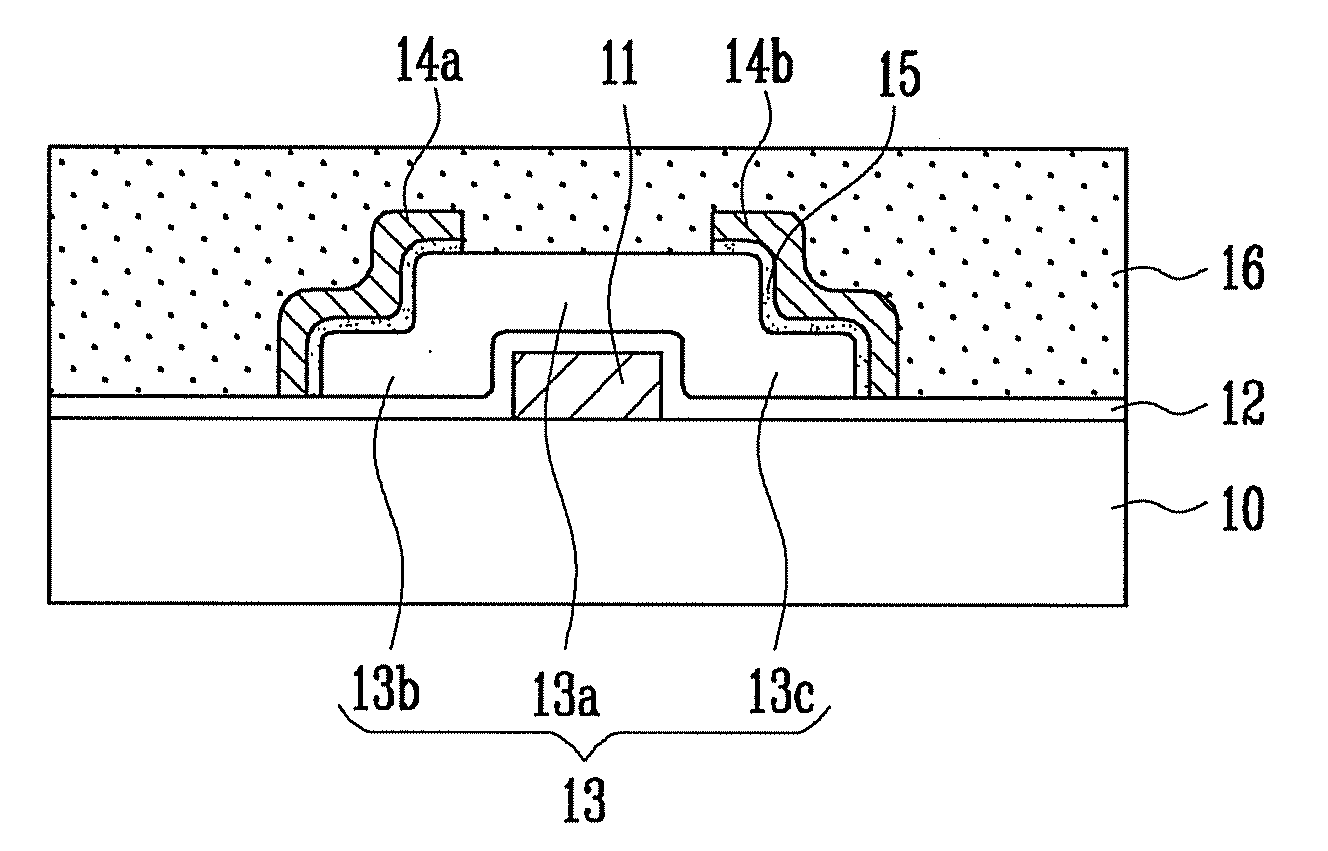
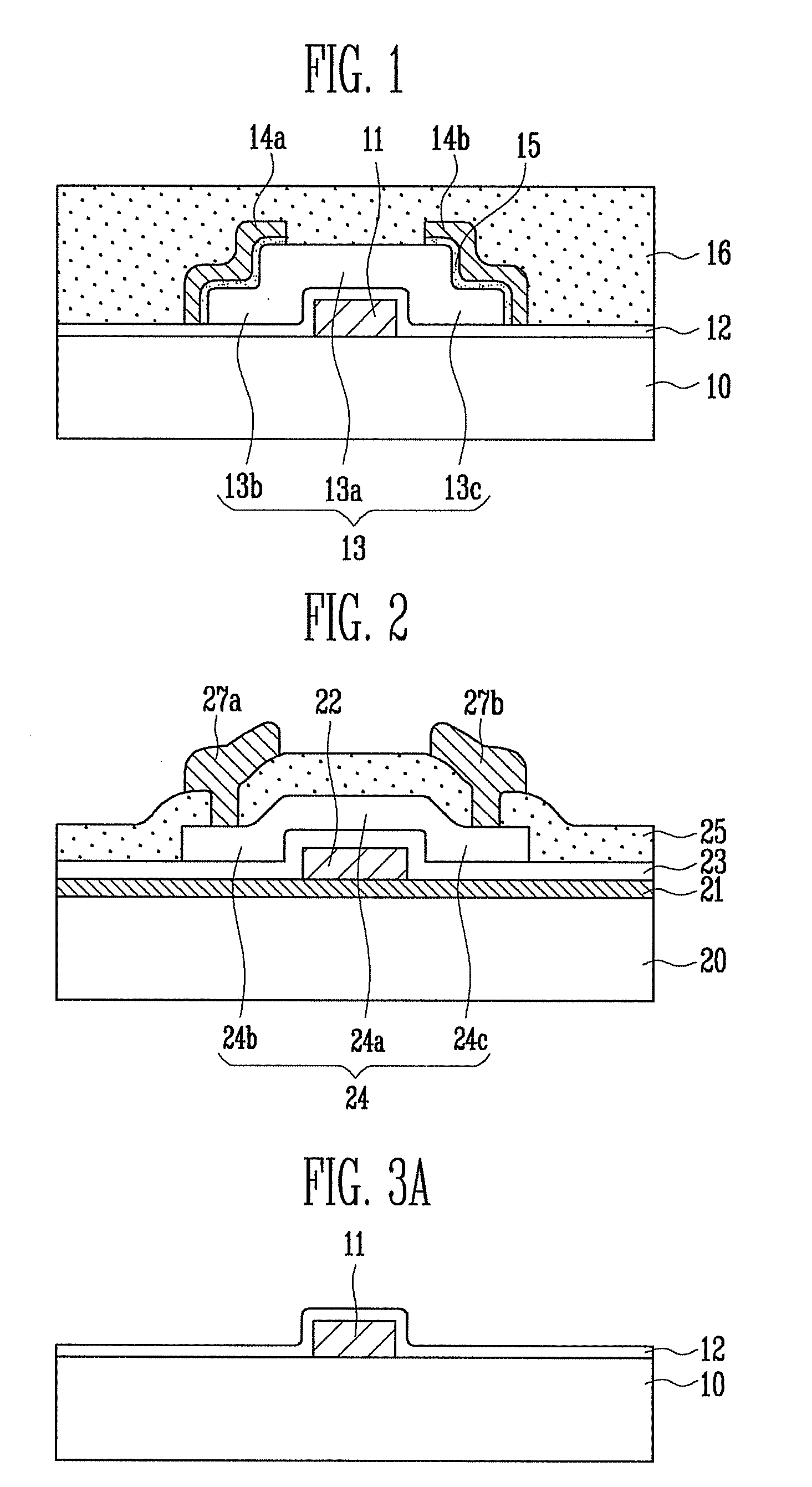
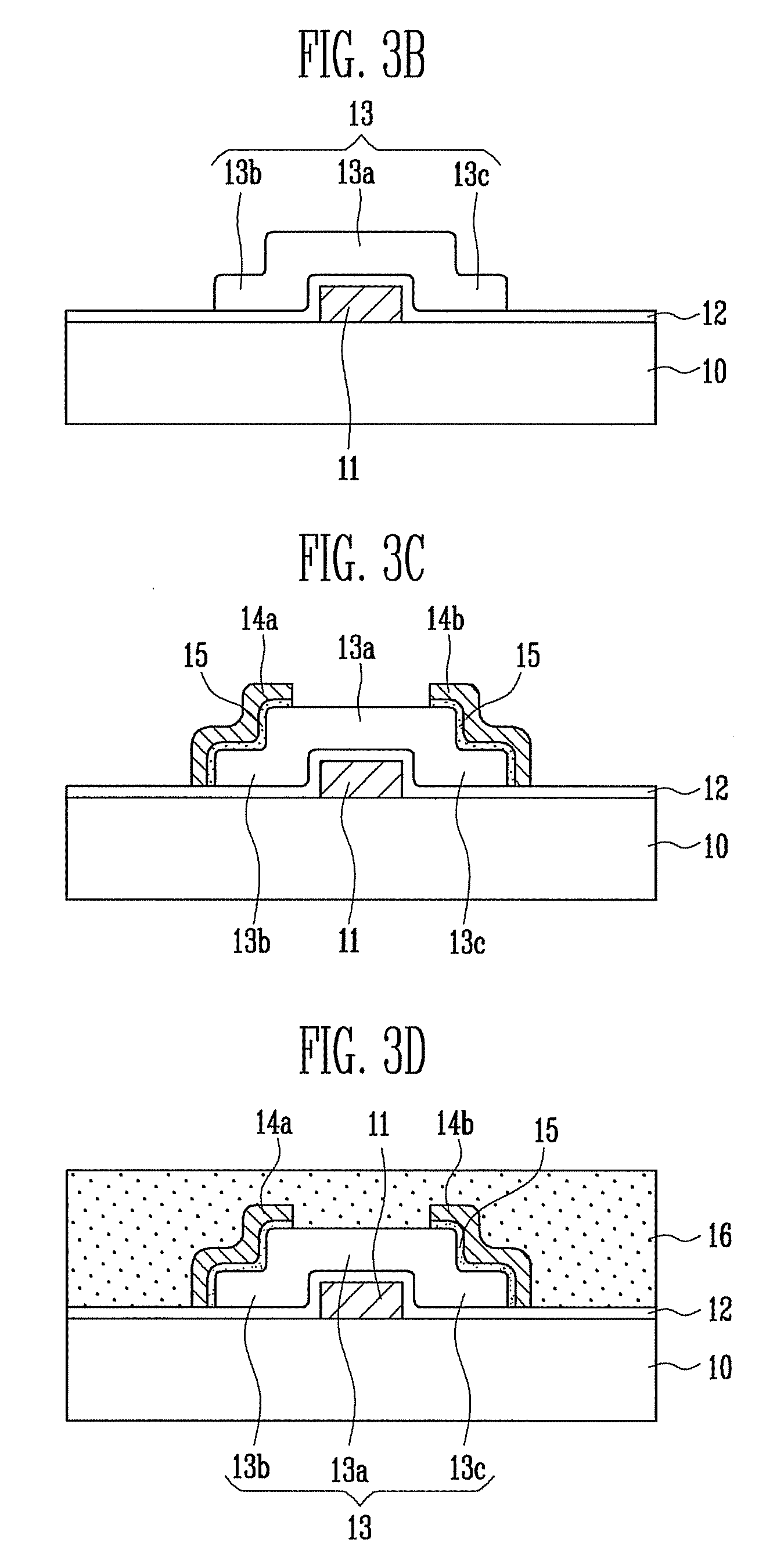
Method of manufacturing thin film transistor and method of manufacturing organic light emitting display having thin film transistor
ActiveUS20090155940A1Preventing and reducing property changeReliability and electrical property is raisedTransistorSolid-state devicesCharge-carrier densityOxygen ions
A method of manufacturing a thin film transistor having a compound semiconductor with oxygen as a semiconductor layer and a method of manufacturing an organic light emitting display having the thin film transistor include: forming a gate electrode on an insulating substrate; forming a gate insulating layer on the gate electrode; forming a semiconductor layer including oxygen ions on the gate insulating layer, and including a channel region, a source region, and a drain region; forming a source electrode and a drain electrode to contact the semiconductor layer in the source region and the drain region, respectively; and forming a passivation layer on the semiconductor layer by coating an organic material, wherein a carrier density of the semiconductor layer is maintained in the range of 1E+17 to 1E+18 / cm3 to have stable electrical property.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
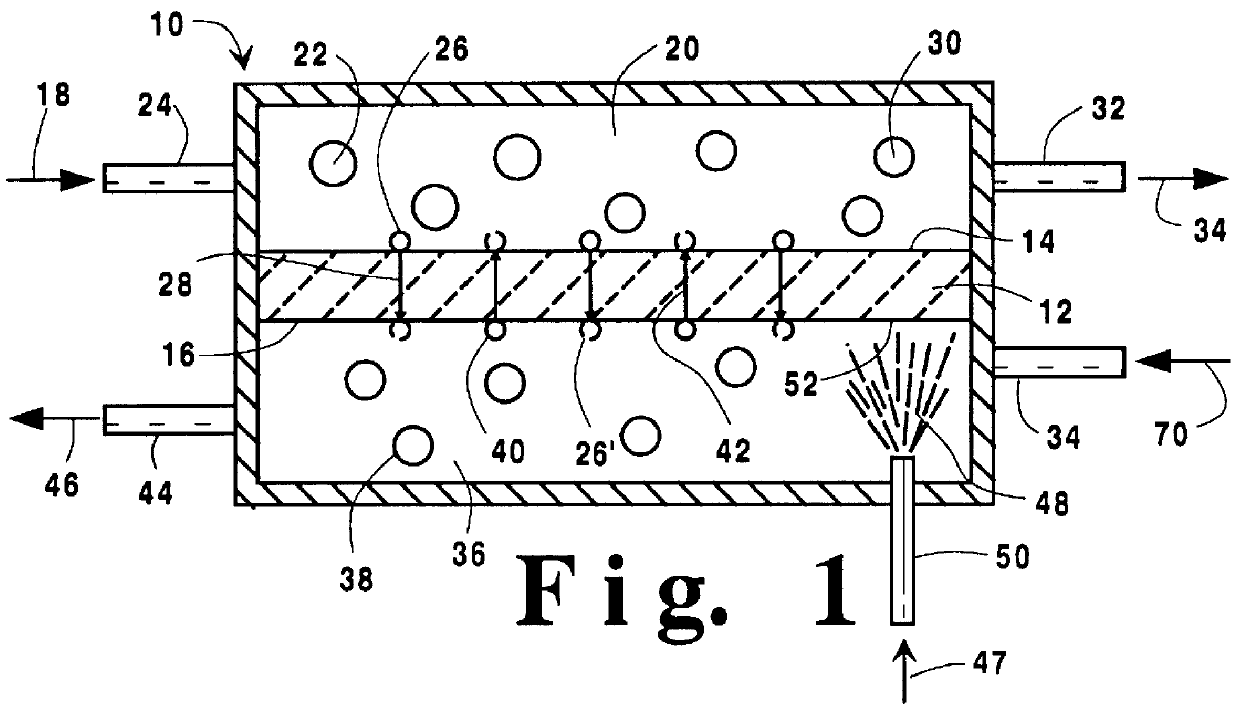
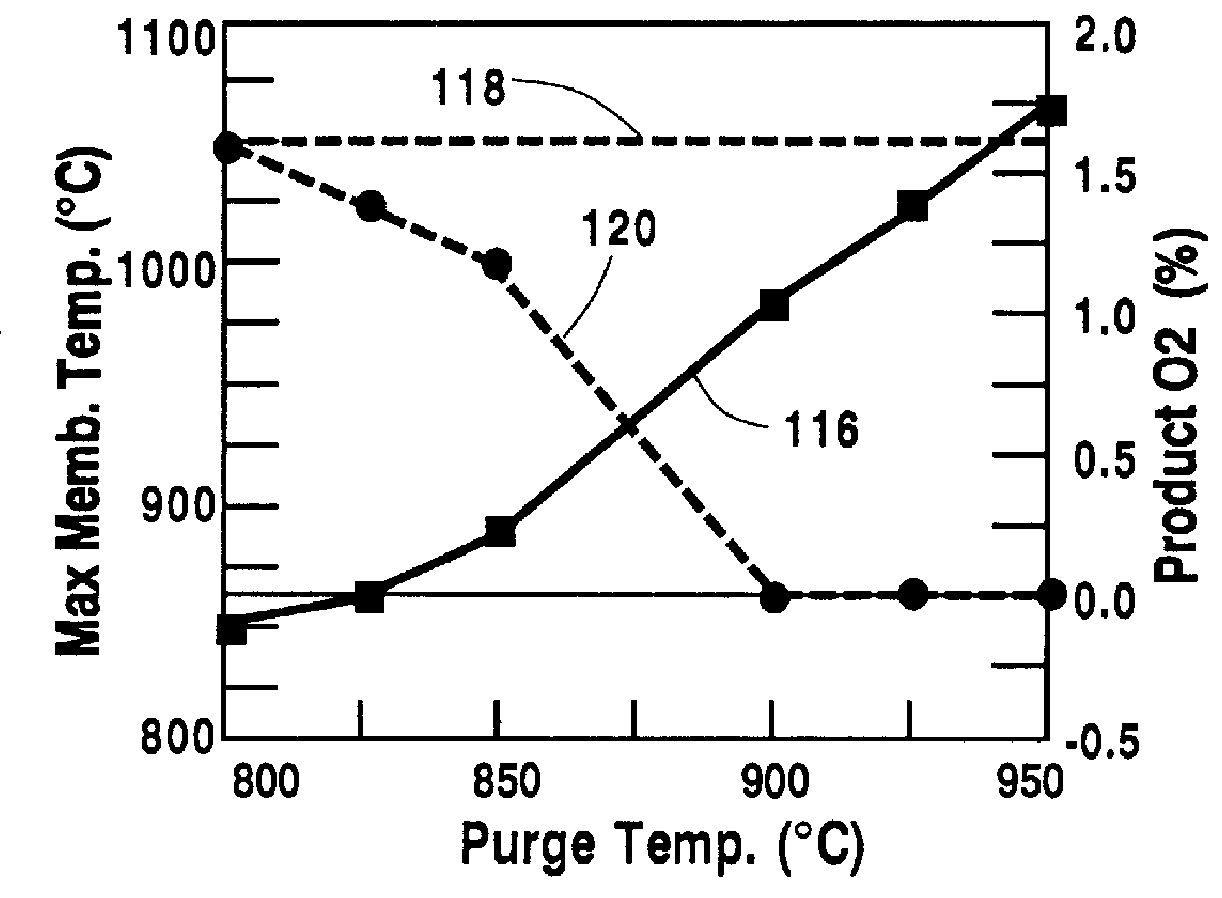
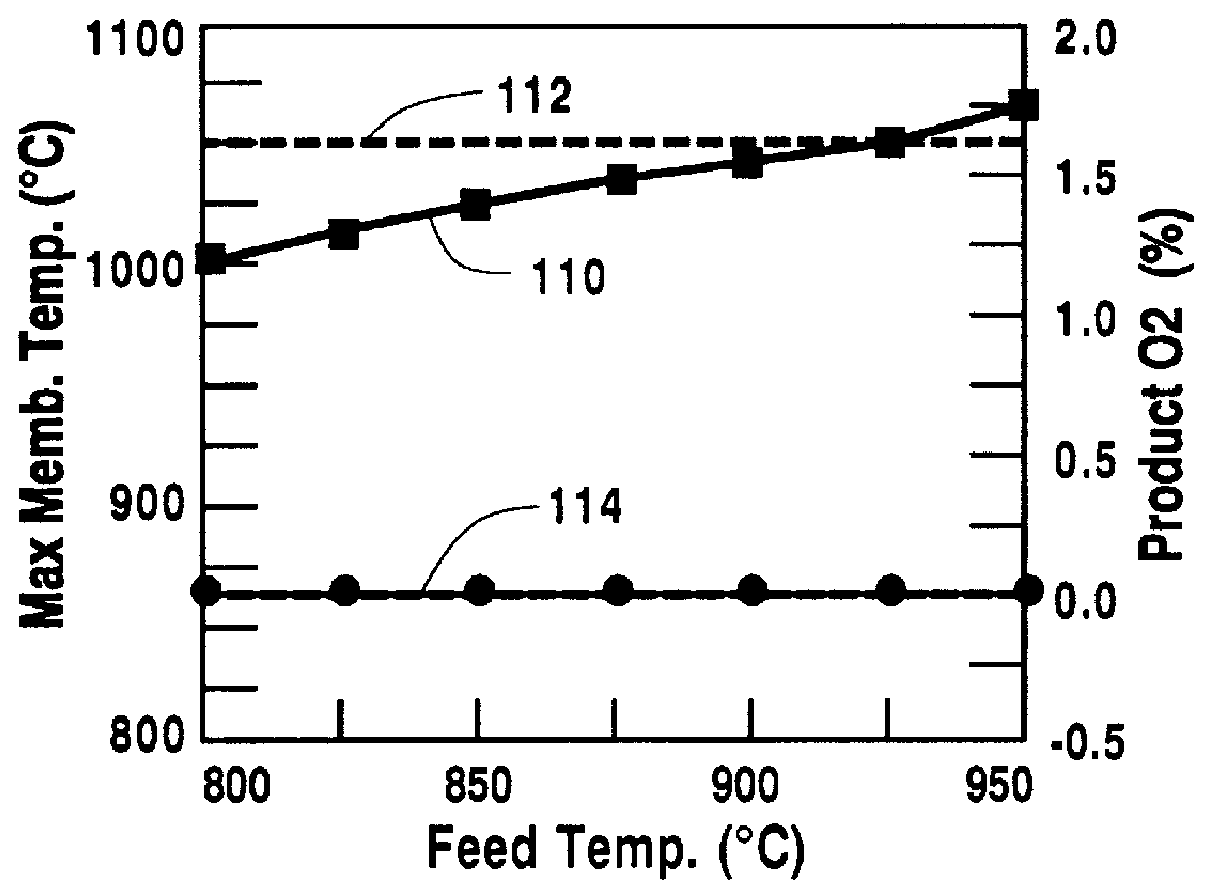
Temperature control in a ceramic membrane reactor
InactiveUS6010614AEnhance exchangeFine surfaceHydrogenLiquid separation by electricityTemperature controlOxygen ions
A method for maintaining the temperature of an oxygen-selective ion transport membrane within a desired temperature range includes providing an ion transport reactor with the oxygen-selective ion transport membrane. An oxygen-donating feed gas is delivered to a cathode side at a first temperature, at a first rate, and at a first oxygen partial pressure and a reactant gas is supplied to an anode side at a second temperature and a second rate. A physical condition is then established within the ion transport reactor that favors the transport of elemental oxygen through the oxygen selective ion transport membrane as oxygen ions. One or more process variables are then regulated to maintain the temperature of the oxygen selective ion transport membrane within the desired range.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
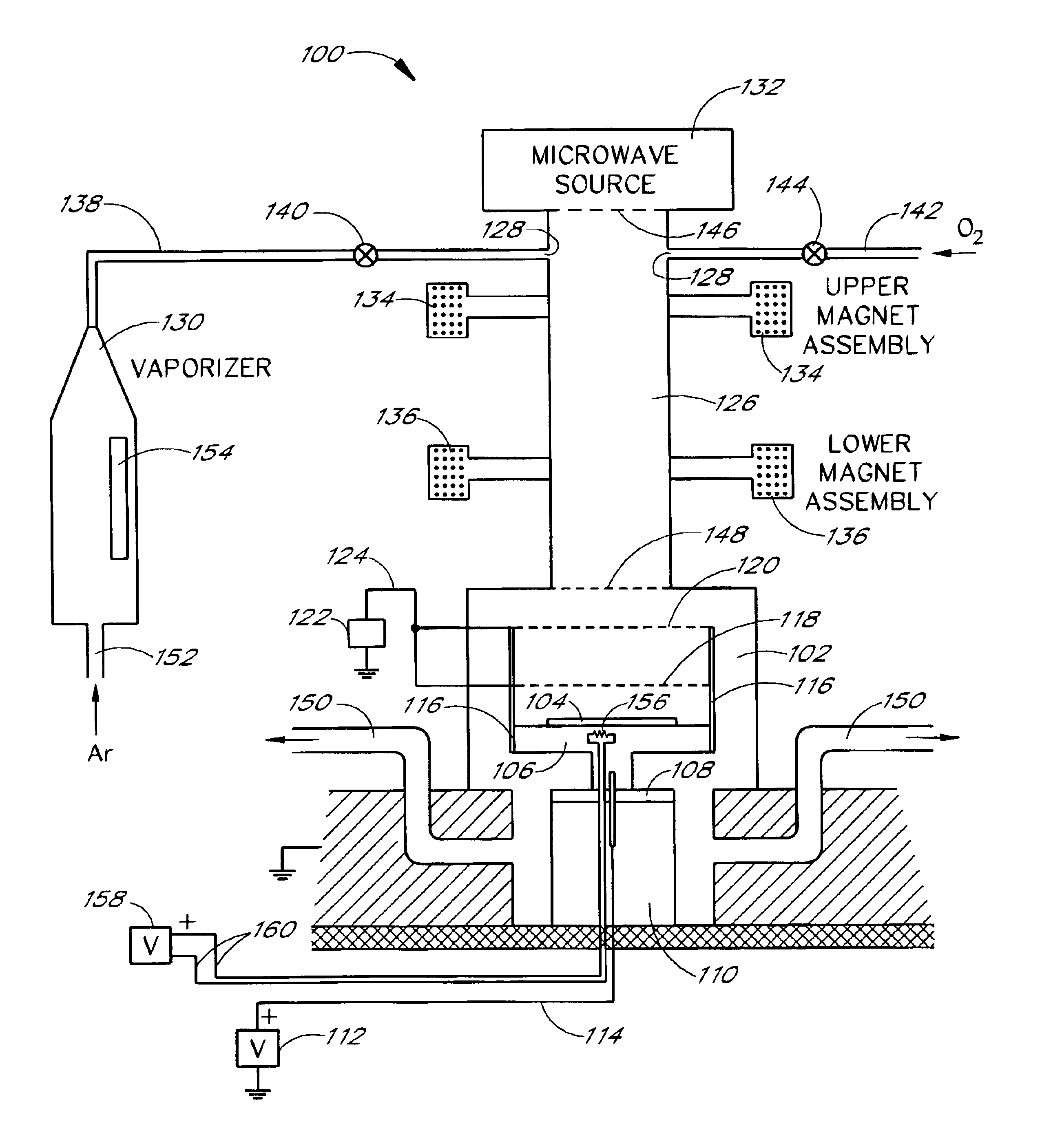
Method and apparatus for the fabrication of ferroelectric films
InactiveUS6858120B2Improve economyEasy to customizeCellsElectric discharge tubesFerroelectric thin filmsOxygen ions
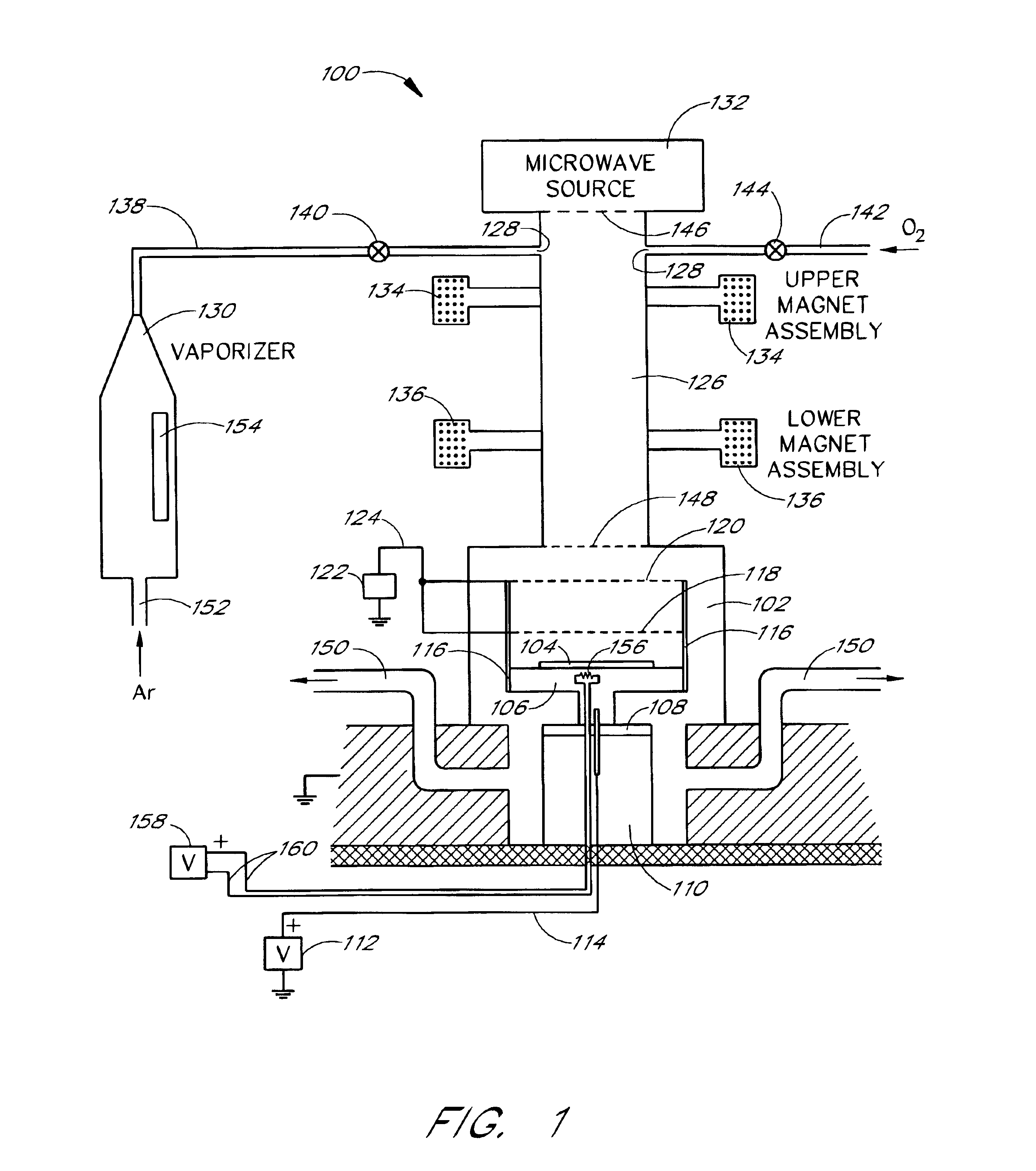
The present invention is related to methods and apparatus for processing weak ferroelectric films on semiconductor substrates, including relatively large substrates, e.g., with 300 millimeter diameter. A ferroelectric film of zinc oxide (ZnO) doped with lithium (Li) and / or magnesium (Mg) is deposited on a substrate in a plasma assisted chemical vapor deposition process such as an electron cyclotron resonance chemical vapor deposition (ECR CVD) process. Zinc is introduced to a chamber through a zinc precursor in a vaporizer. Microwave energy ionizes zinc and oxygen in the chamber to a plasma, which is directed to the substrate with a relatively strong field. Electrically biased control grids control a rate of deposition of the plasma. The control grids also provide Li and / or Mg dopants for the ZnO to create the ferroelectric film. A desired ferroelectric property of the ferroelectric film can be tailored by selecting an appropriate composition of the control grids.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
Diatom internal wall coating with humidity-regulating and air purifying functions and preparation process thereof
The invention relates to an indoor decorative material, in particular to a diatom internal wall coating with humidity-regulating and air-purifying functions and a preparation process thereof, and aims at overcoming the defects existing in the prior art and providing the diatom internal wall coating and the preparation process thereof, wherein the diatom internal wall coating has an excellent indoor air humidity-regulating function, can eliminate peculiar smell, preserve heat, reduce noise, remove harmful gases including formaldehyde, toluene and the like in the air, can continuously release negative oxygen ions, has a lasting environmental-protection function, a humidity-regulating function and the air-purifying function, and is rich in colors, strong in texture and environment-friendly. The diatom internal wall coating with the humidity-regulating and air-purifying functions and the preparation process of the diatom internal wall coating have the advantages that ingredients can be used after screened, weighed, evenly mixed in a grading mode, checked out and packaged. When the diatom internal wall coating is used, water is added into the coating to prepare a pasty or milky coating, and texture shape construction can be performed in a batch-coating, blade-coating or wipe-coating mode or in a roll-coating, spraying or brush-coating mode. An appropriate construction process can be selected according to the decorative requirements.
Owner:长春市兰亭序吉硅藻新材料有限公司
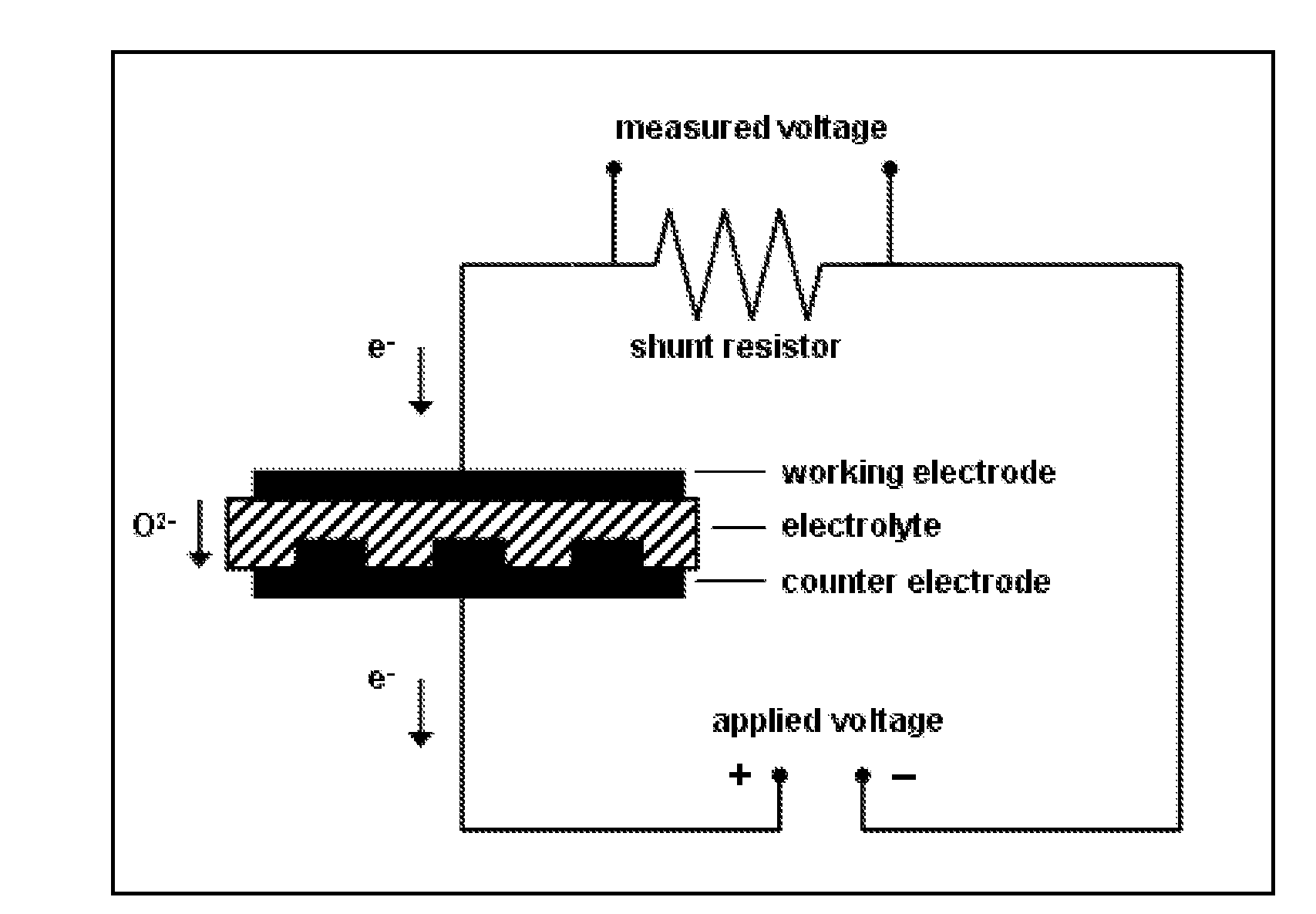
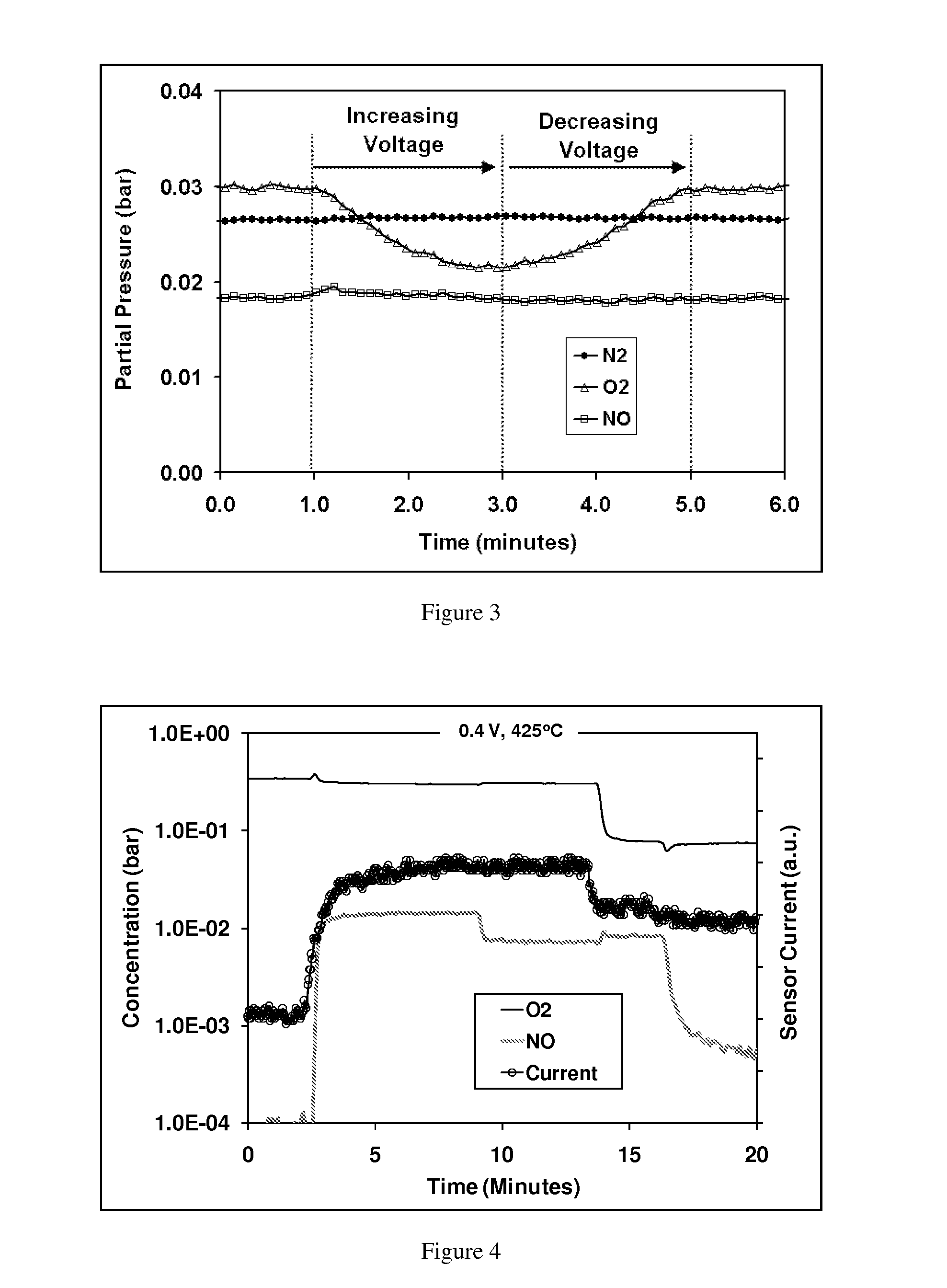
Methods and apparatus for measuring NOx gas concentration, for detecting exhaust gas concentration and for calibrating and controlling gas sensor
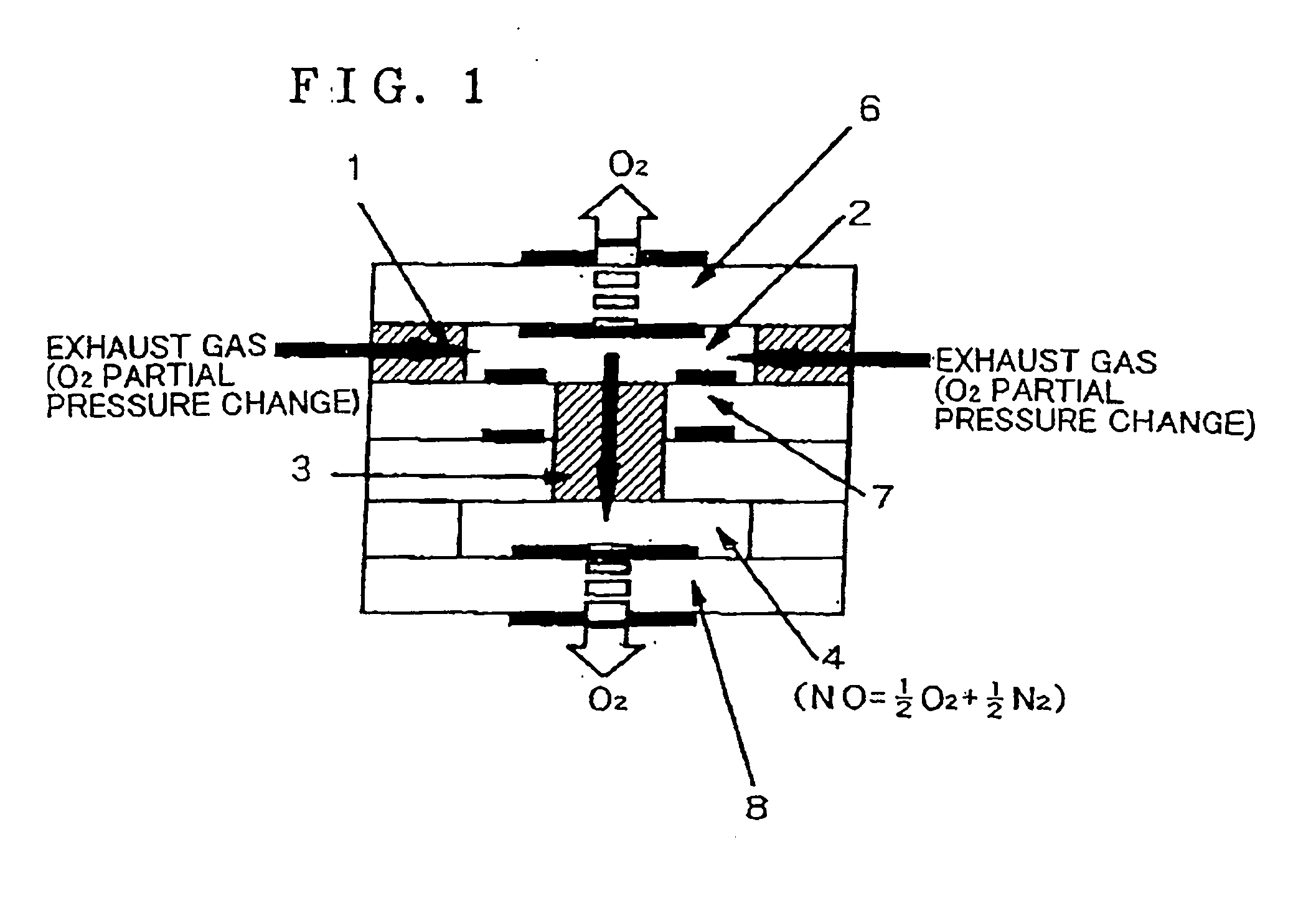
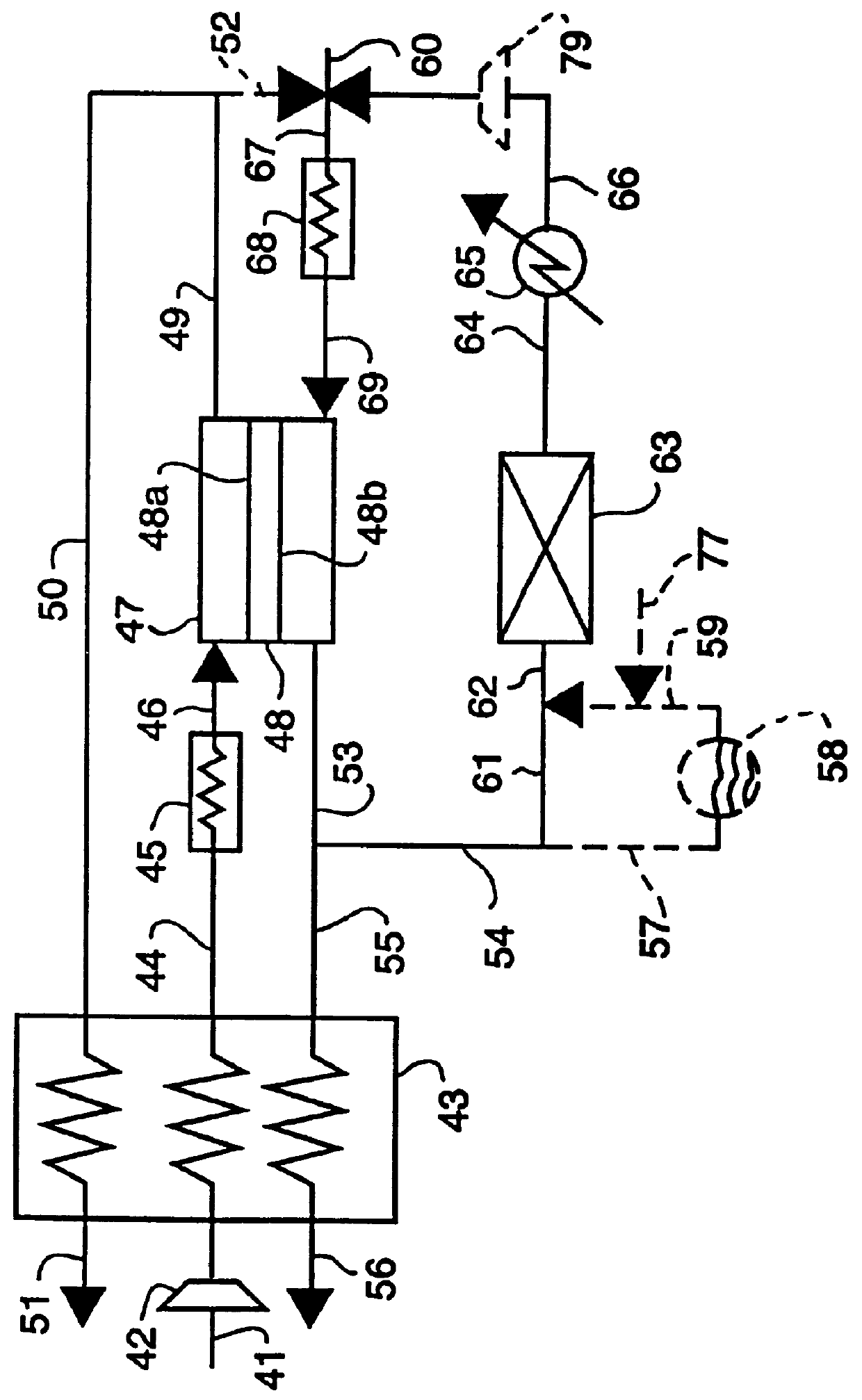
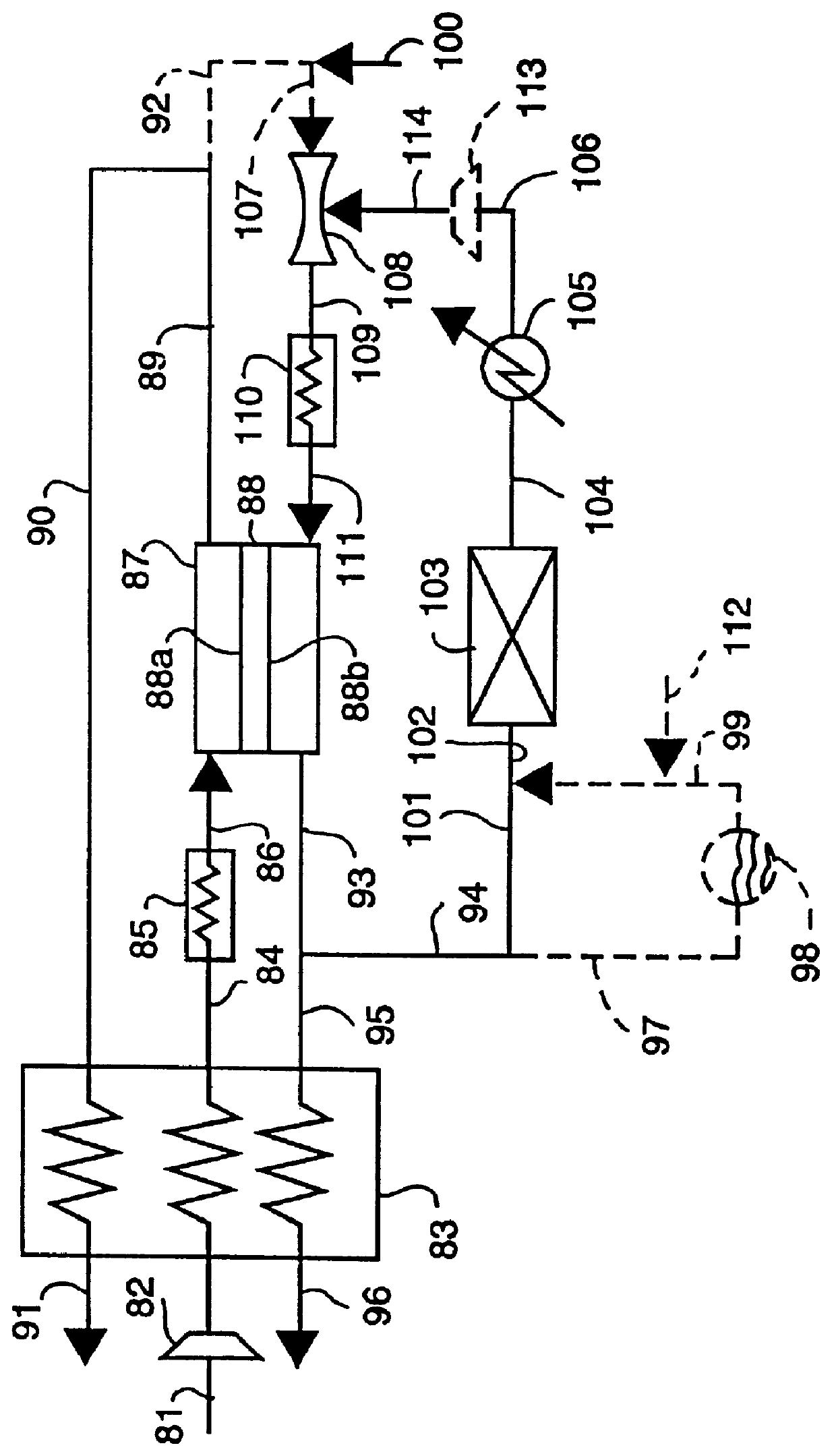
InactiveUS6375828B2Accurate measurementElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesElectrical resistance and conductanceDiffusion resistance
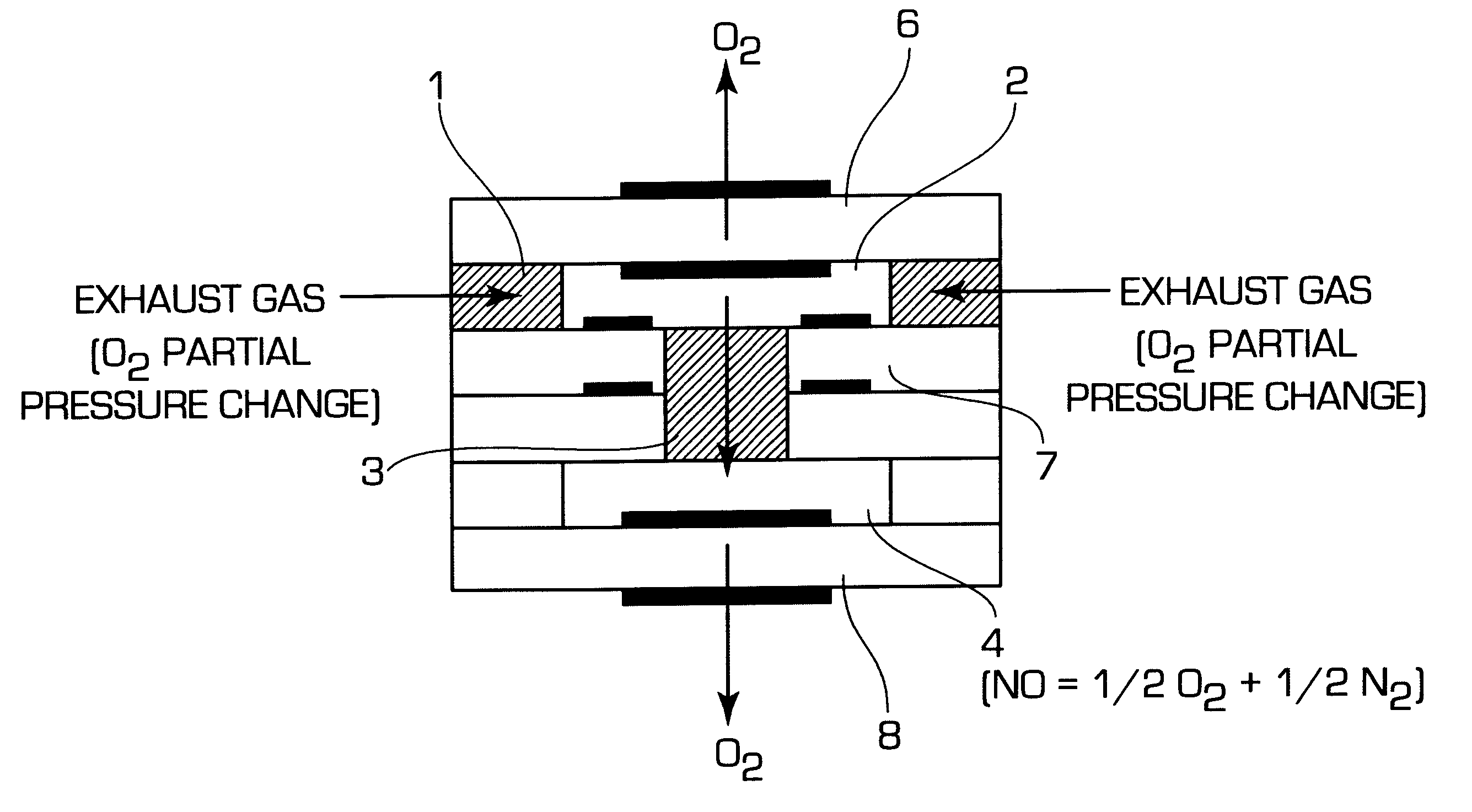
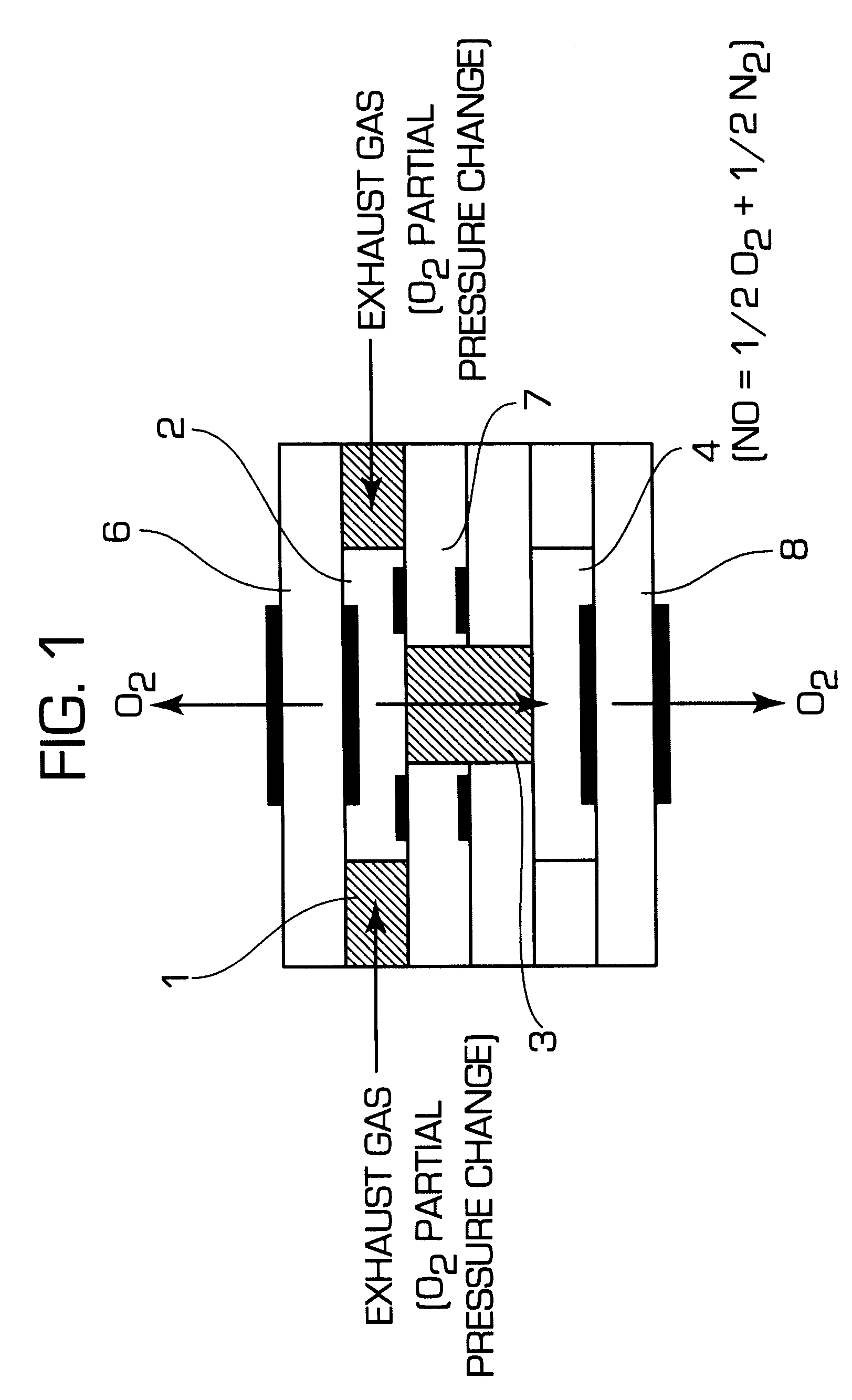
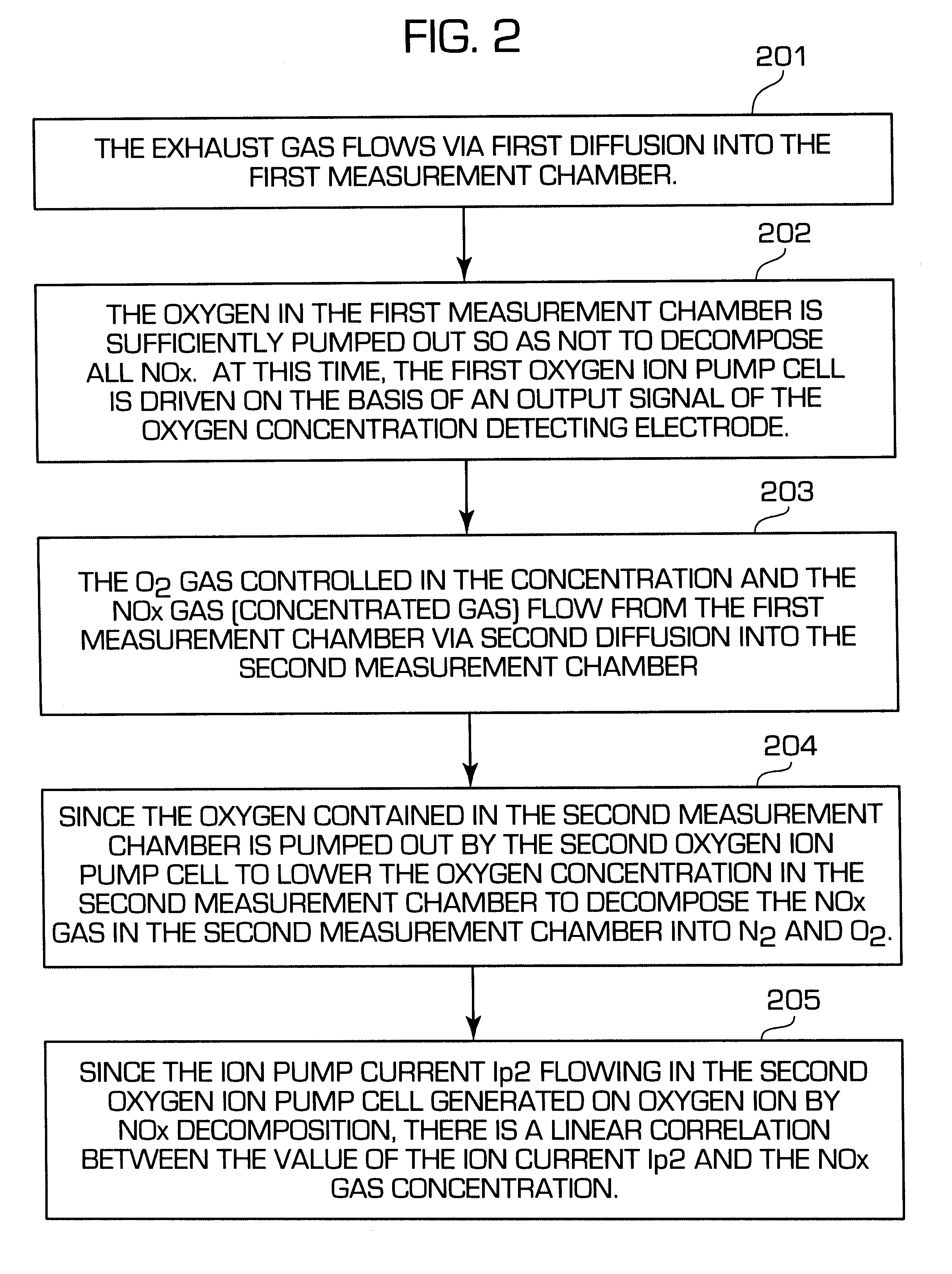
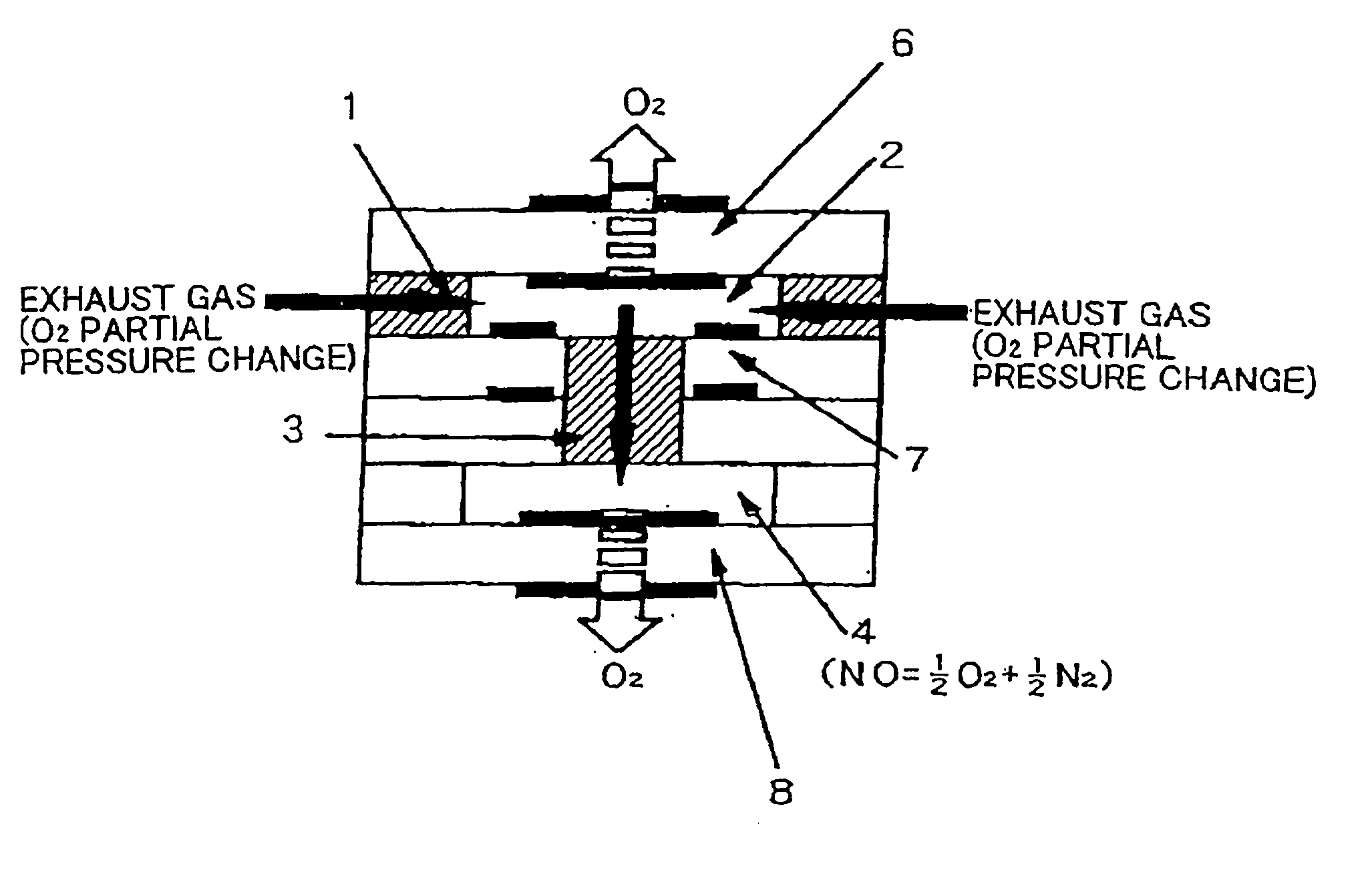
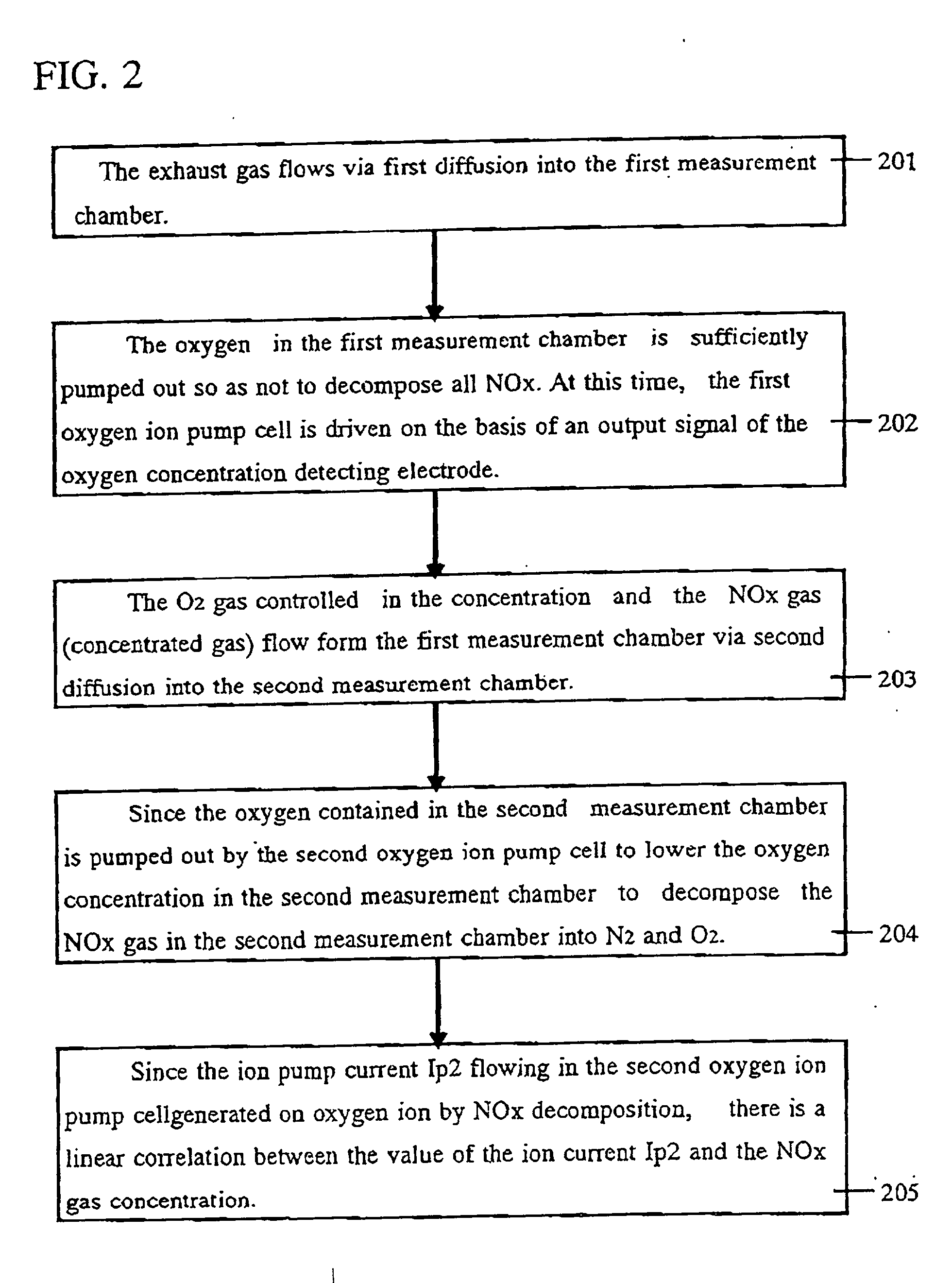
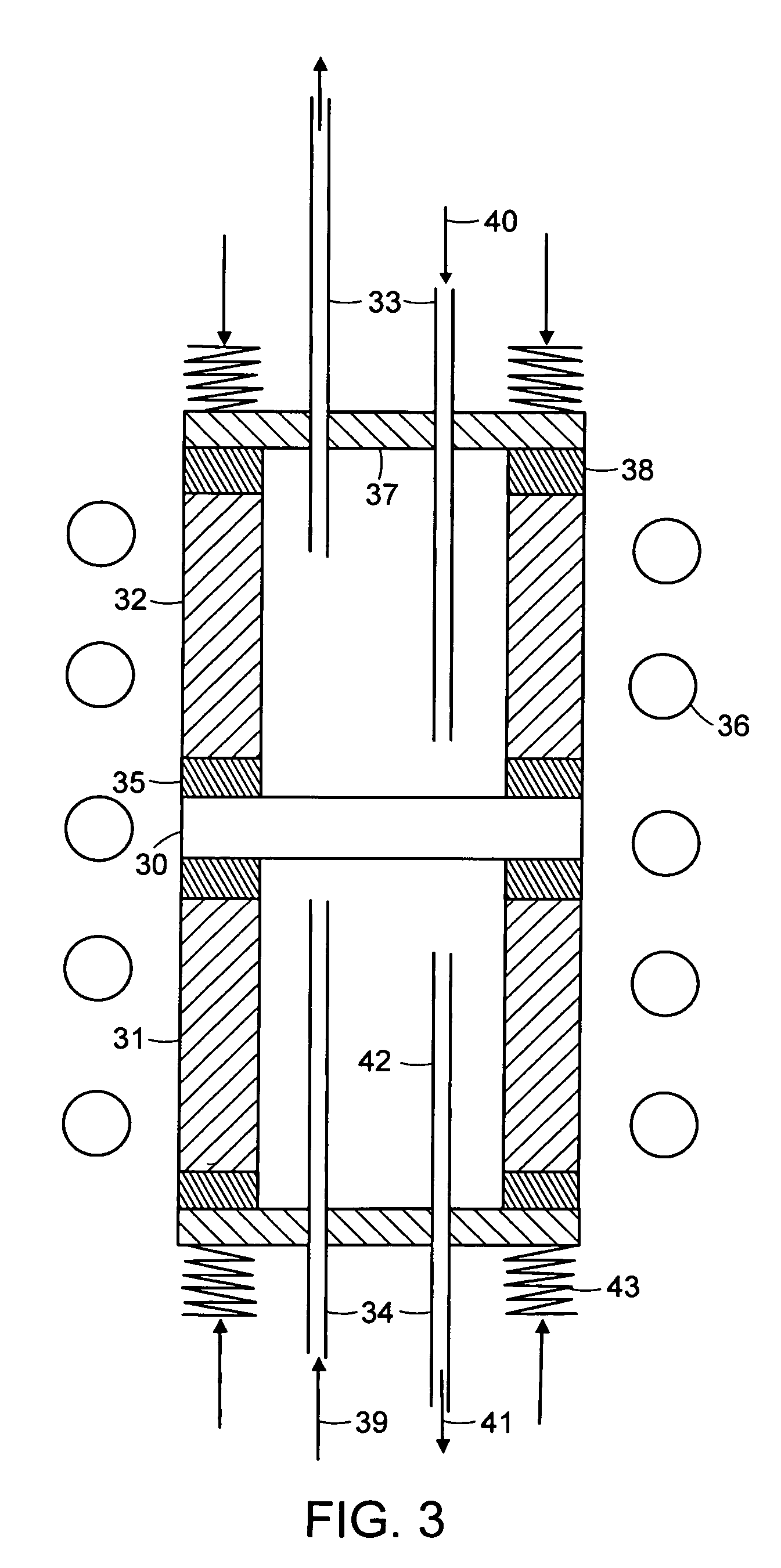
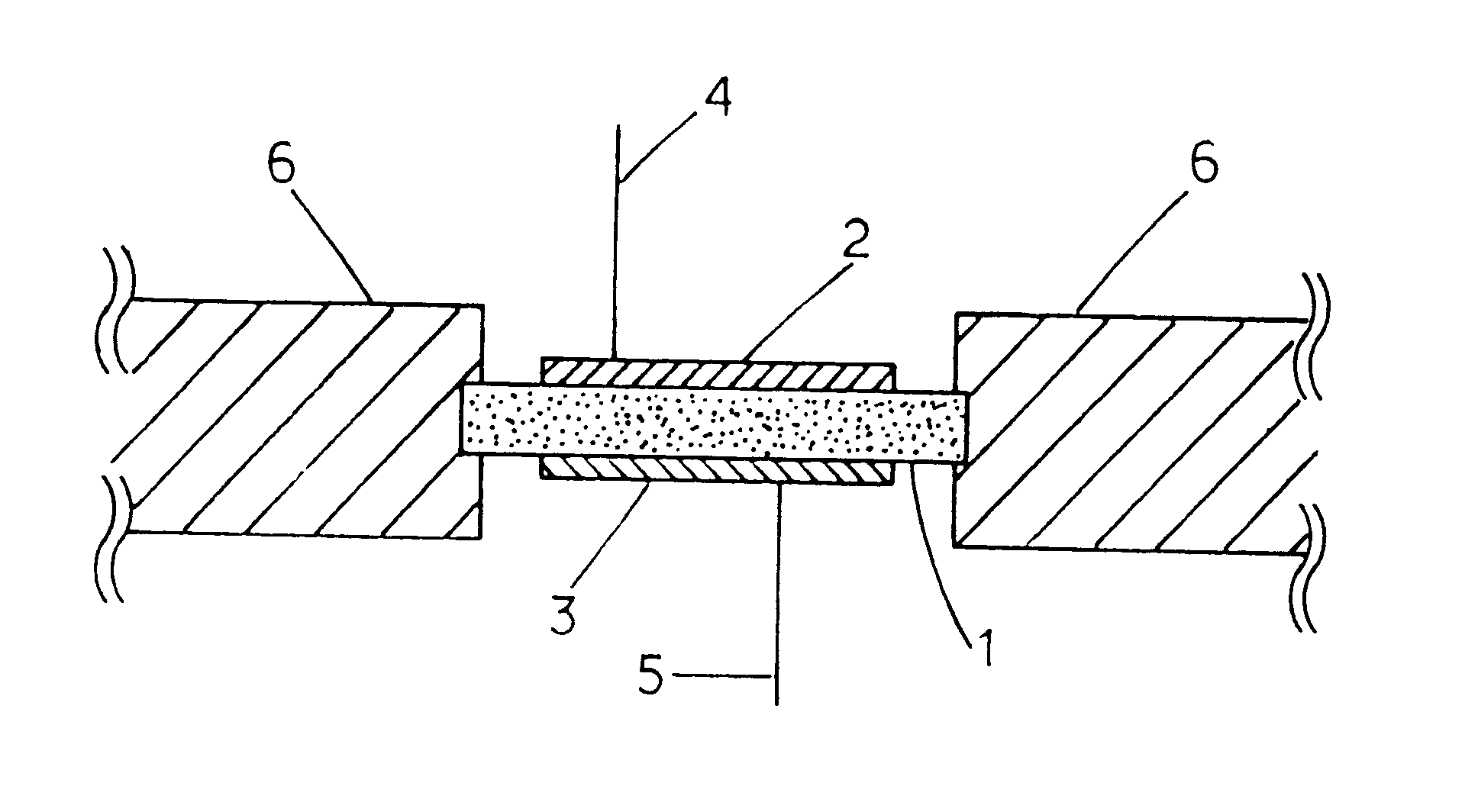
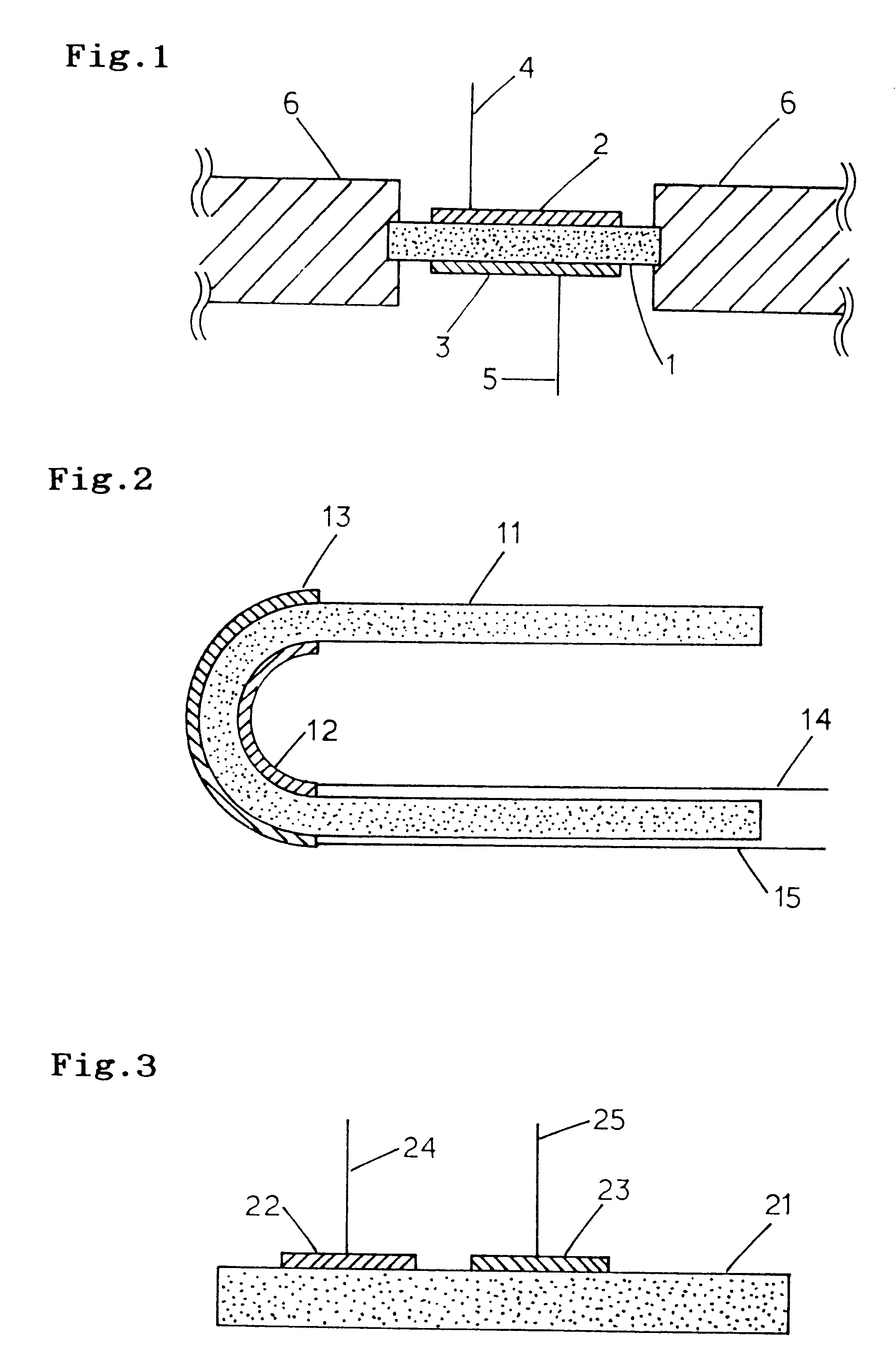
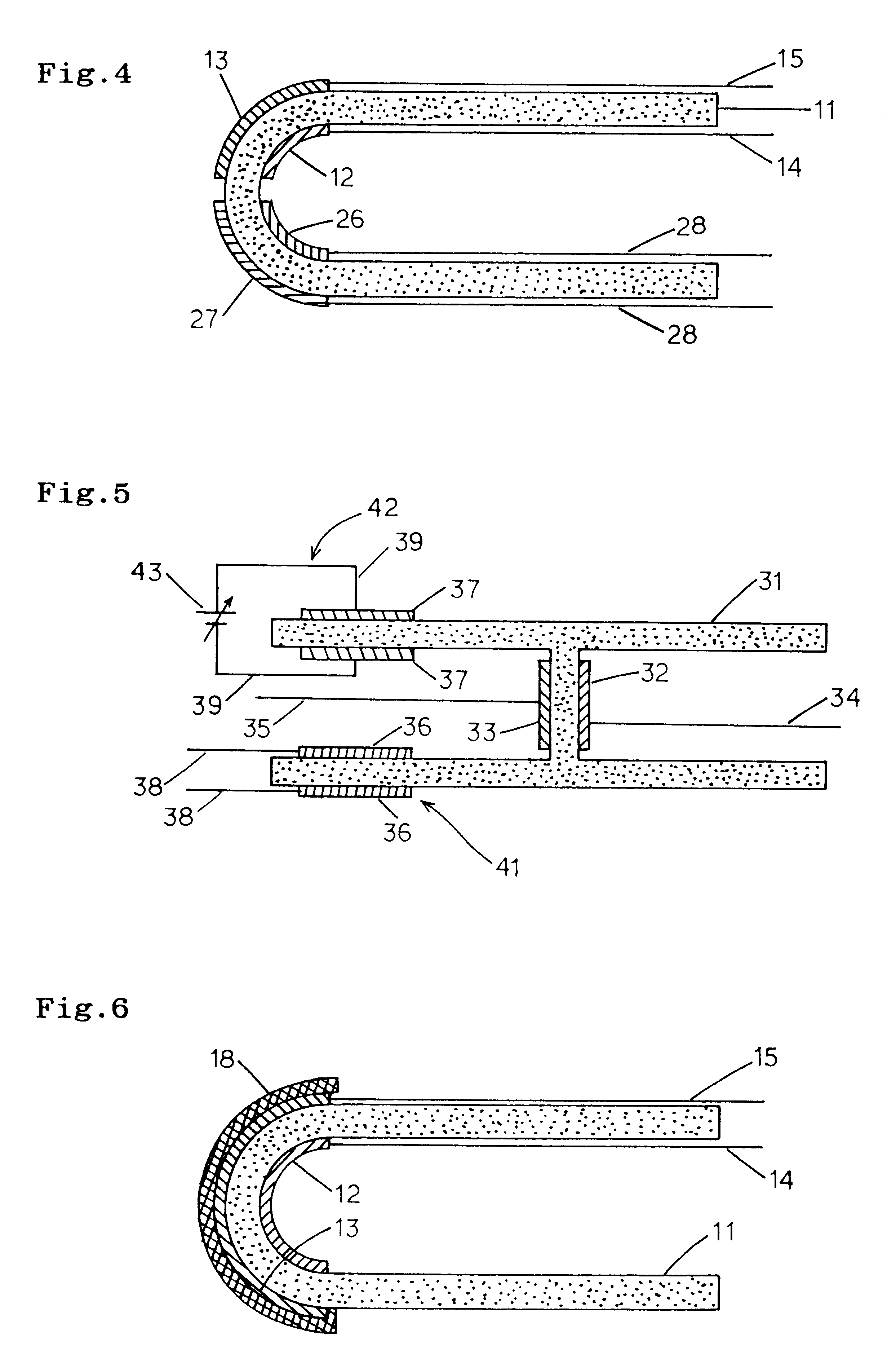
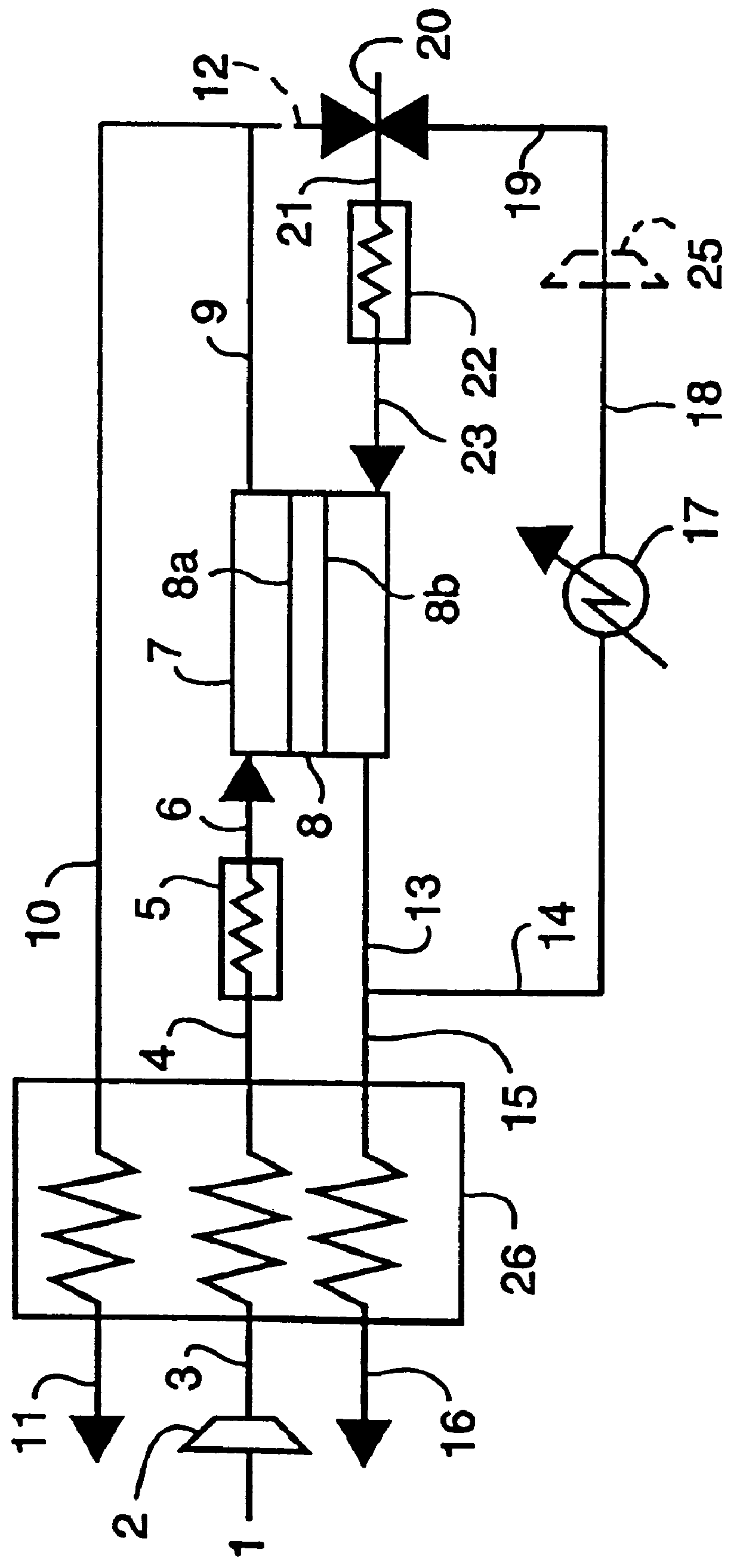
A nitrogen oxide concentration detector has a first measurement chamber 2 into which is introduced a measurement gas via a first diffusion resistance 1; an oxygen concentration detection electrode 7a for measuring the oxygen concentration in the measurement gas in said first measurement chamber 1; a first oxygen ion pump cell 6 for pumping out oxygen in the measurement gas from said first measurement chamber 2 based on the potential of said oxygen concentration detection electrode 7a; a second measurement chamber 8 into which the gas is introduced from said first measurement chamber 2 via a second diffusion resistance 3; and a second oxygen ion pump cell 8 having a pair of electrodes 8a,8b across which a voltage is applied to decompose NOx in the second measurement chamber 4 to pump out dissociated oxygen to cause a circuit Ip2 corresponding to the NOx concentration to flow in the second oxygen ion pump cell 8. Variation of NOx concentration is a function of variation of Ip2. The concentration obtained based on the Ip2 is corrected responsive to the oxygen concentration in the measurement gas. Particularly, a coefficient of the variation of the Ip2, gain, in said function is corrected responsive to the oxygen concentration in the measurement gas.
Owner:BERKLEY INC +1
Oxygen ion conductors for electrochemical cells
InactiveUS20070054170A1Stable oxygen concentrationImprove electrode stabilityCell electrodesFinal product manufactureElectrical conductorAlkaline earth metal
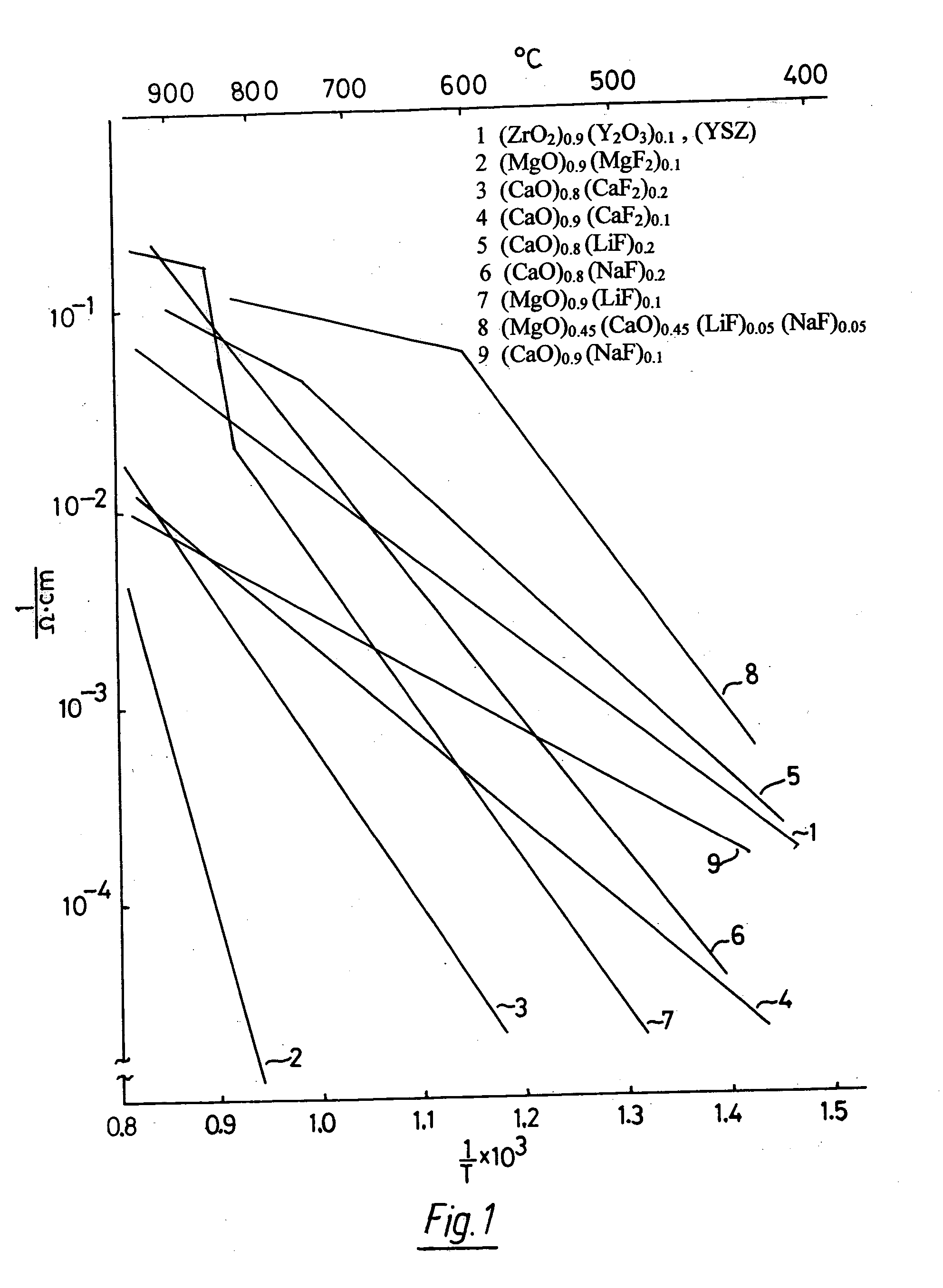
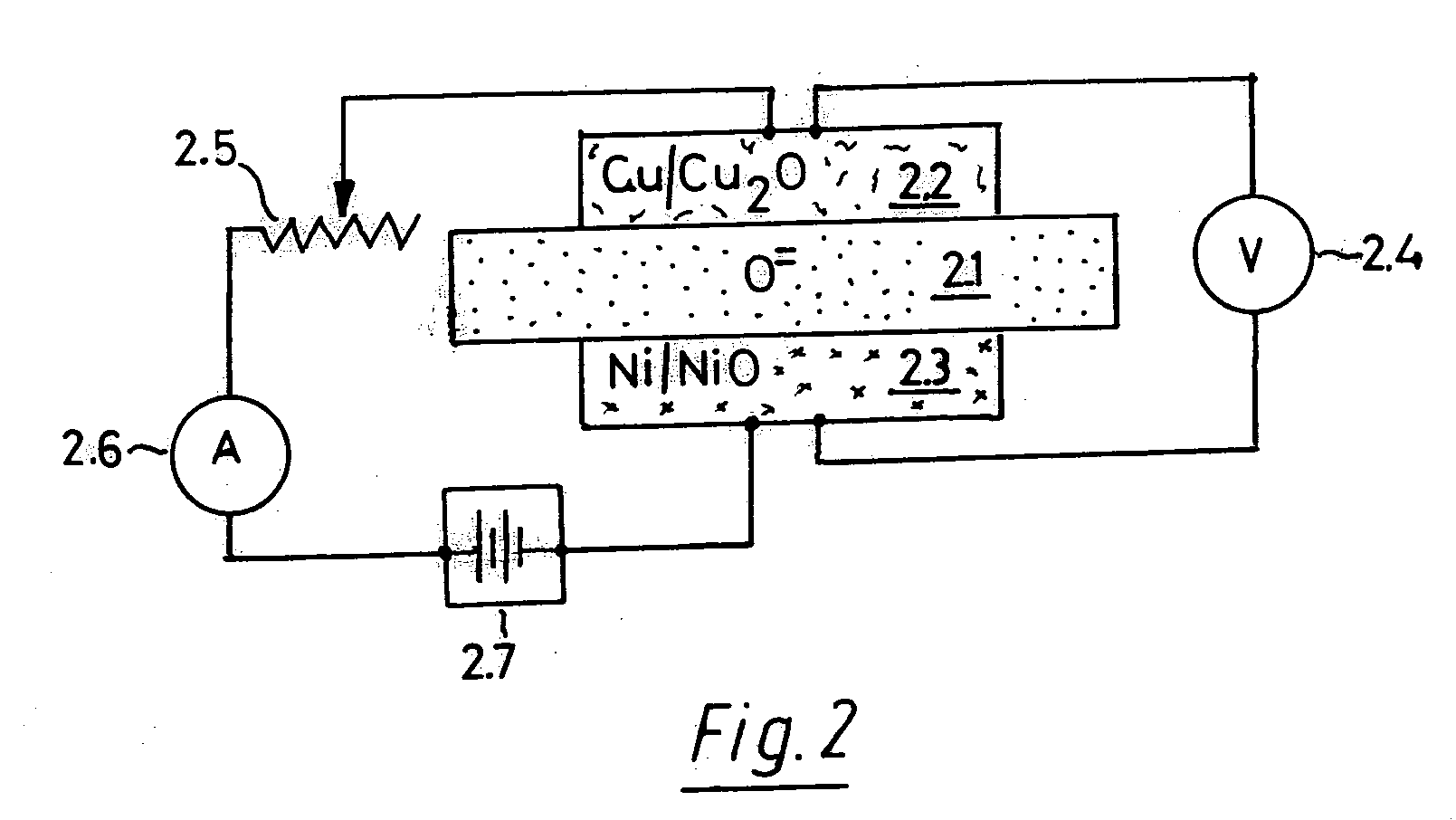
In solid oxygen ion conducting electrolytes for electrochemical cells based on magnesium oxide and calcium oxide, obtained by the addition of metal fluorides selected from elements in the groups of alkali metals and earth alkali metals to the host oxides of magnesium and calcium, conductivity values are obtained, which are comparable with those of stabilized zirconia, but the magnesium oxide and calcium oxide based oxygen ion conducting electrolytes have a superior thermodynamic stability and, therefore, can operate at much lower oxygen concentrations in comparison with other oxygen ion conducting electrolytes and without becoming noticeably electronically conductive.
Owner:ISENBERG ARNOLD O
Hydrogen Producing Method and Apparatus
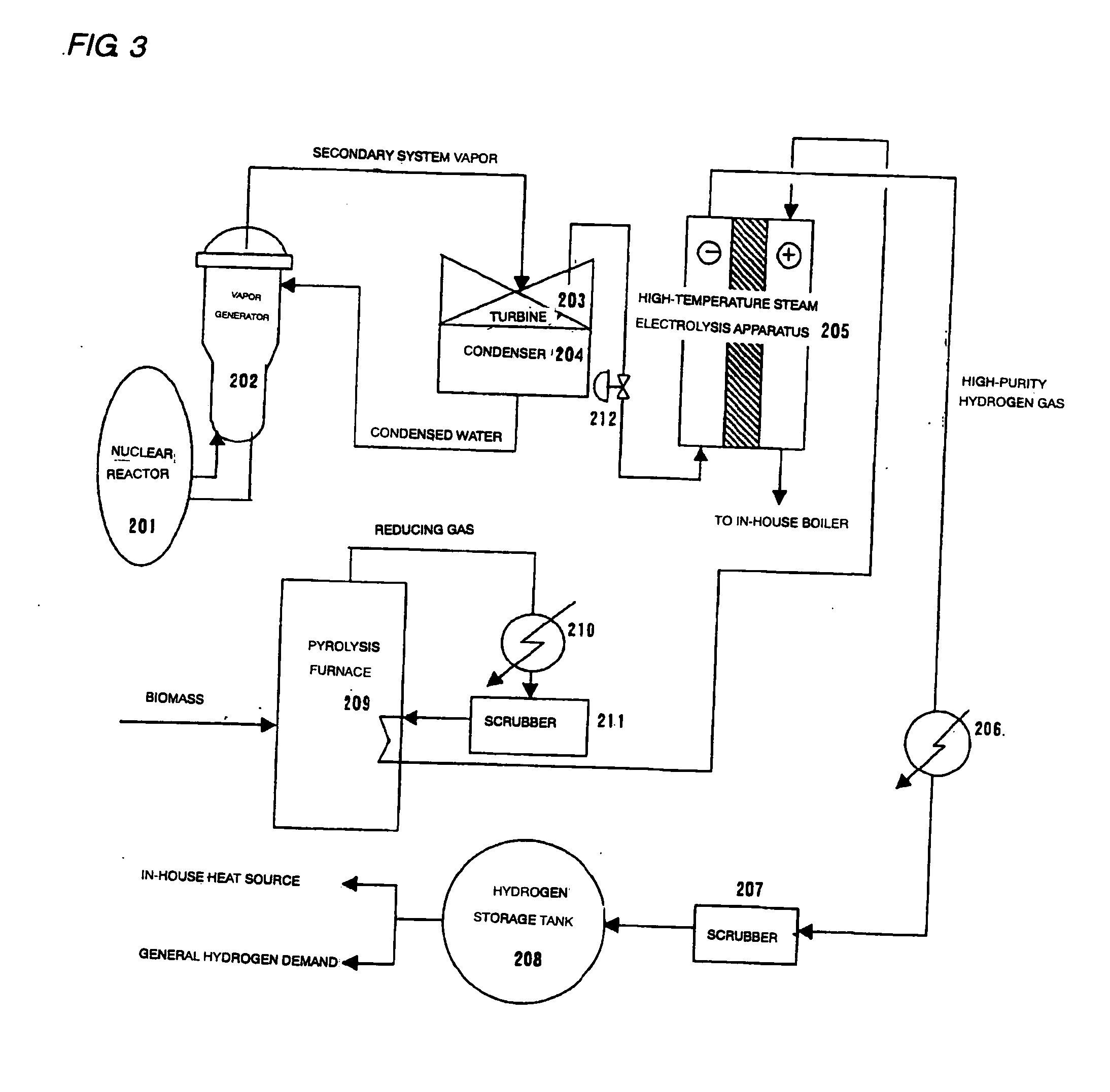
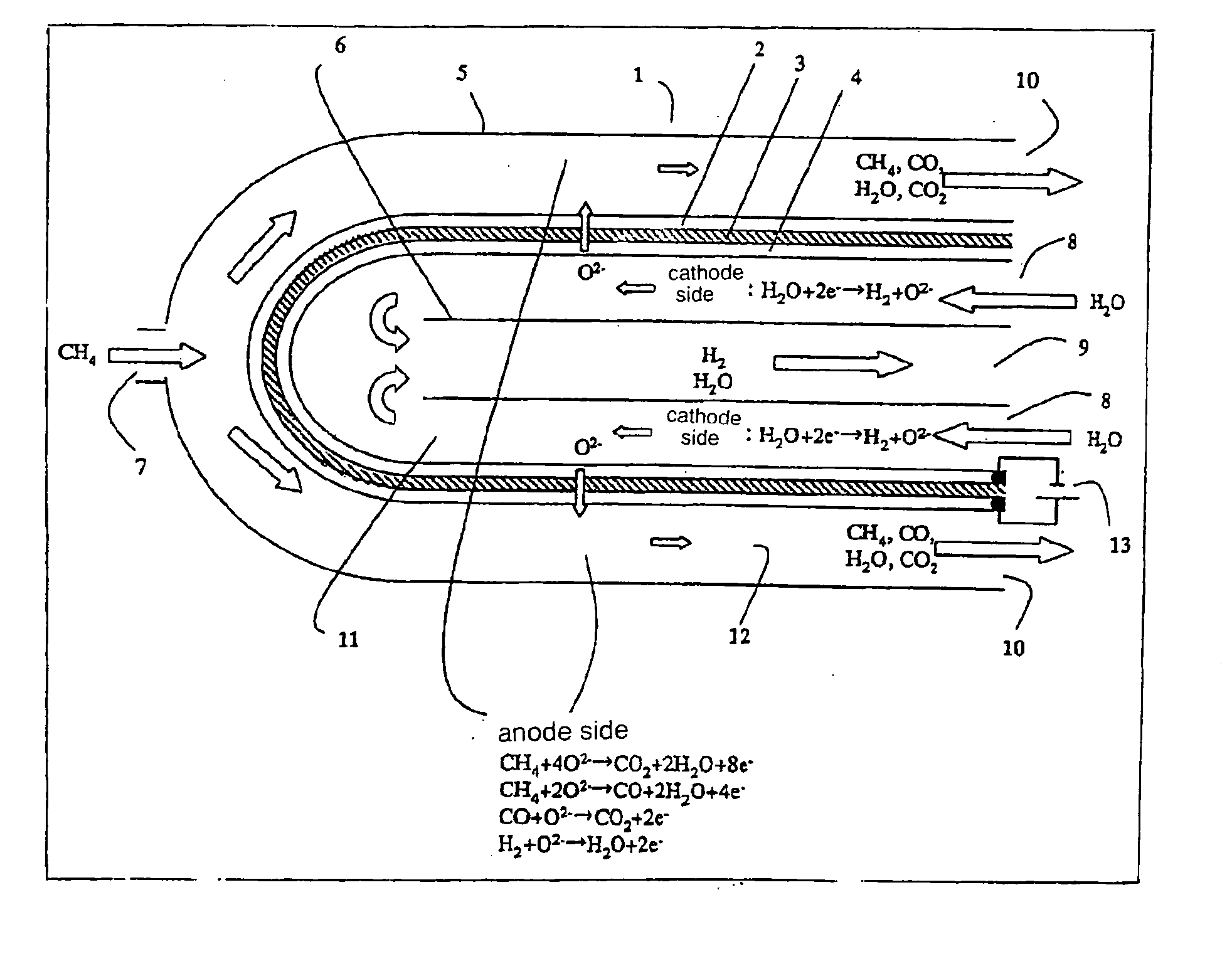
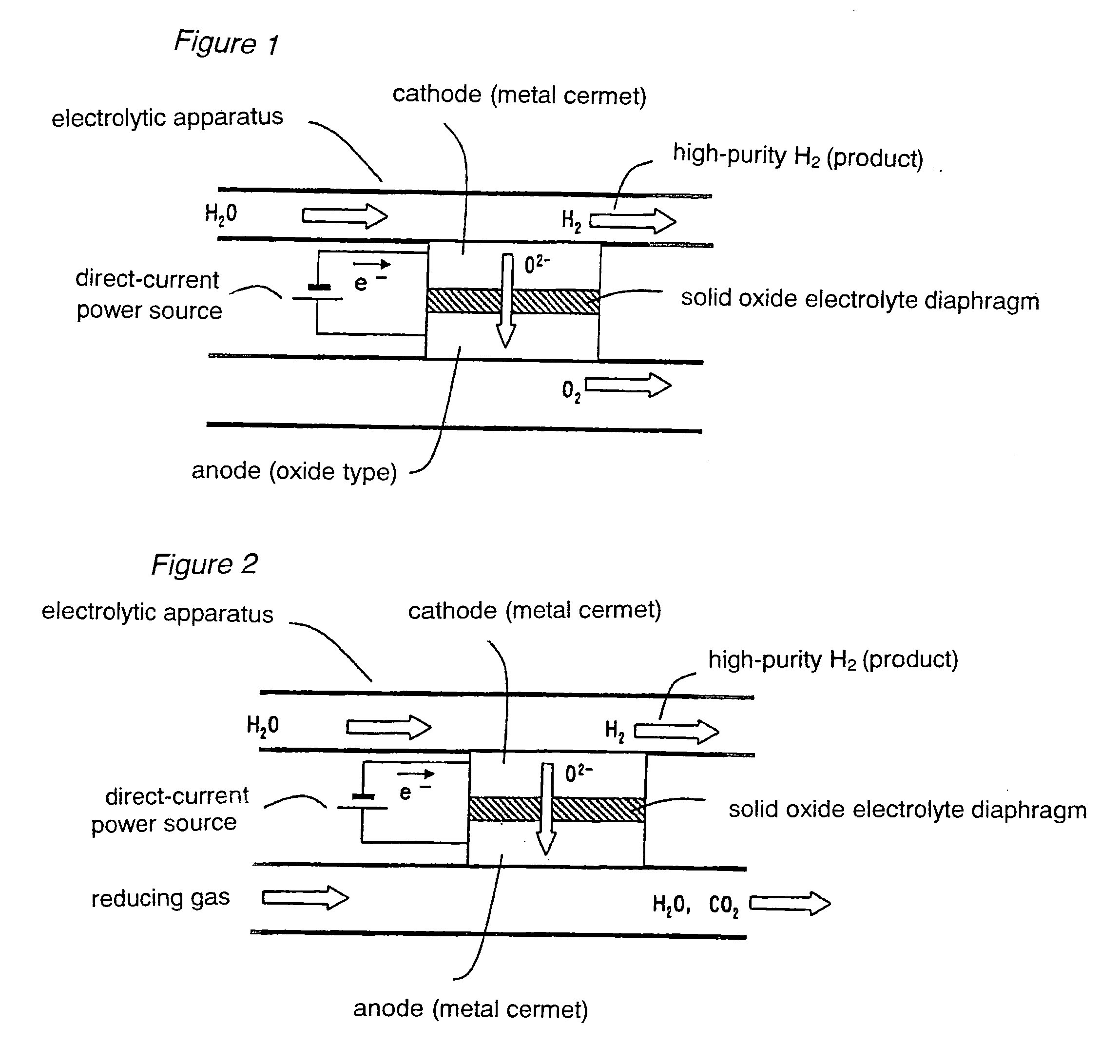
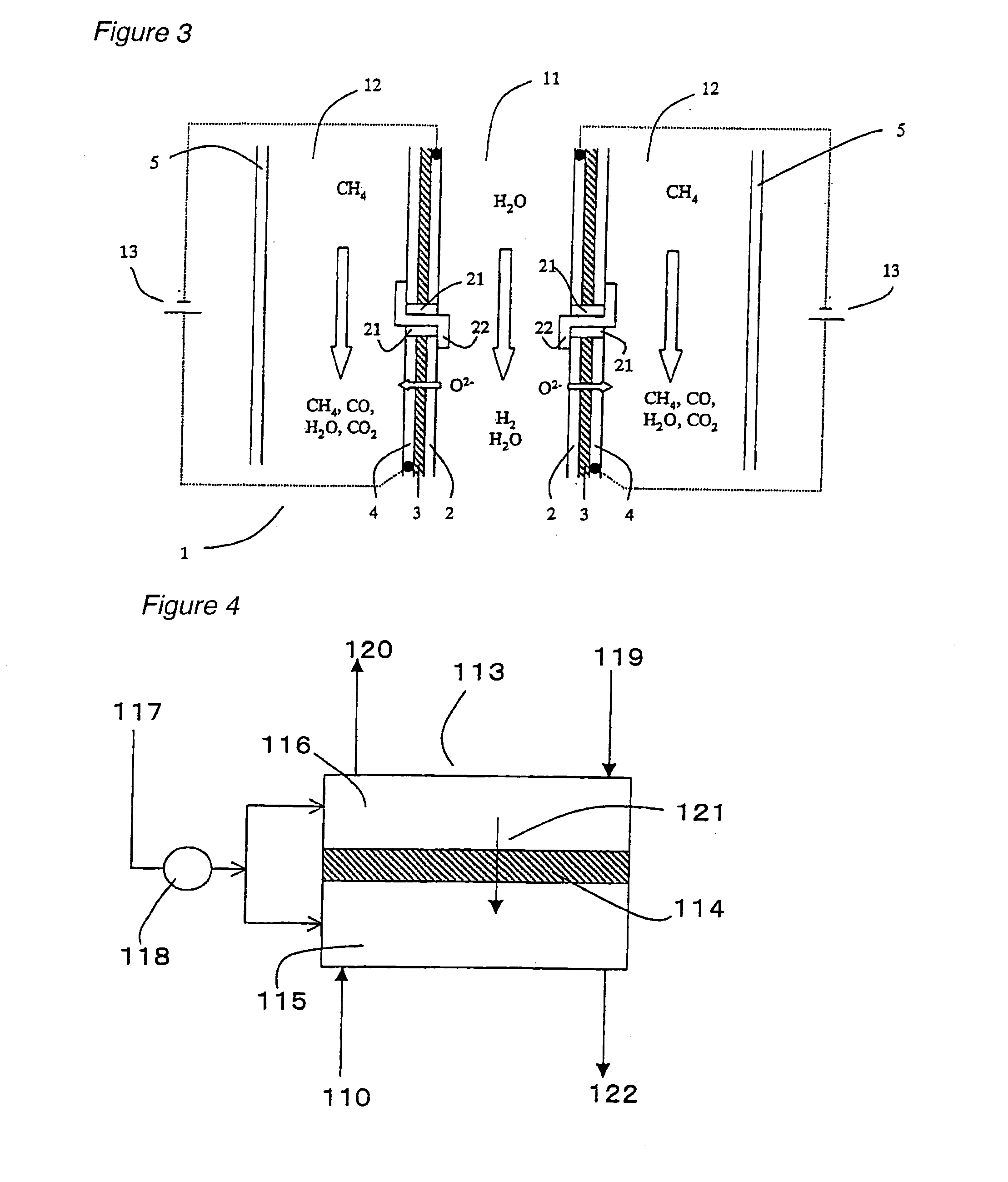
A method for producing hydrogen wherein use is made of a high temperature steam electrolysis apparatus having an electrolysis vessel being partitioned into the anode side and the cathode side by the use of a solid oxide electrolyte film as a diaphragm, steam is fed to the above cathode side and a reducing gas is fed to the anode side, and steam electrolysis is carried out at a high temperature, characterized in that the reducing gas and the steam fed to the electrolysis vessel has a temperature of 200 to 500° C. The above temperature range for the reducing gas and the steam fed to the electrolysis vessel has been found to be an optimum temperature range, as a result of taking the heat balance within the vessel into consideration, in a high temperature steam electrolysis apparatus wherein a solid oxide electrolyte film is used, a reducing gas is fed to the anode side and steam is fed to the cathode side, an oxygen ion is allowed to react with said reducing gas on the cathode side, to thereby generate a concentration gradient for an oxygen ion and thus reduce an electrolysis voltage.
Owner:EBARA CORP
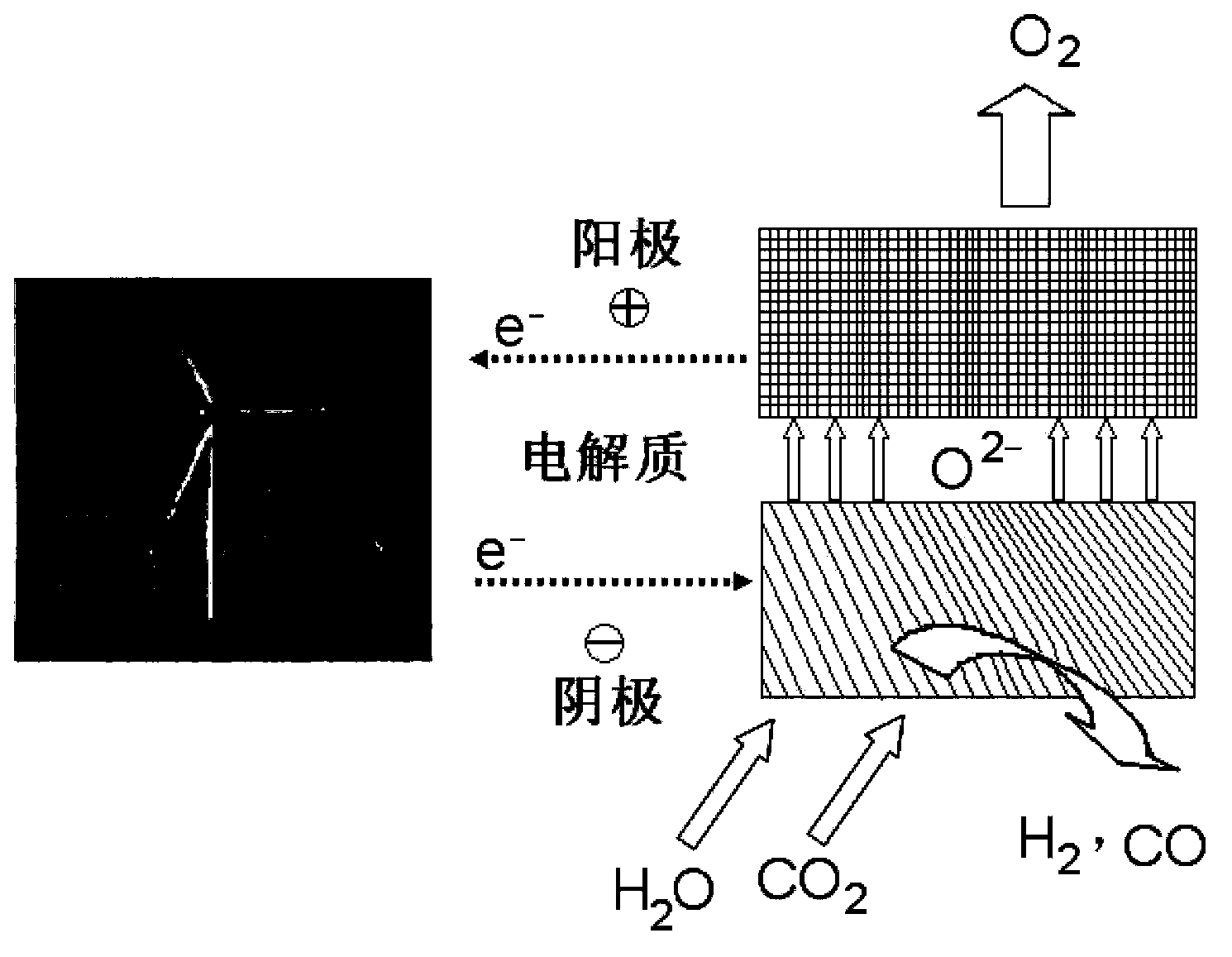
Efficient Reversible Electrodes For Solid Oxide Electrolyzer Cells
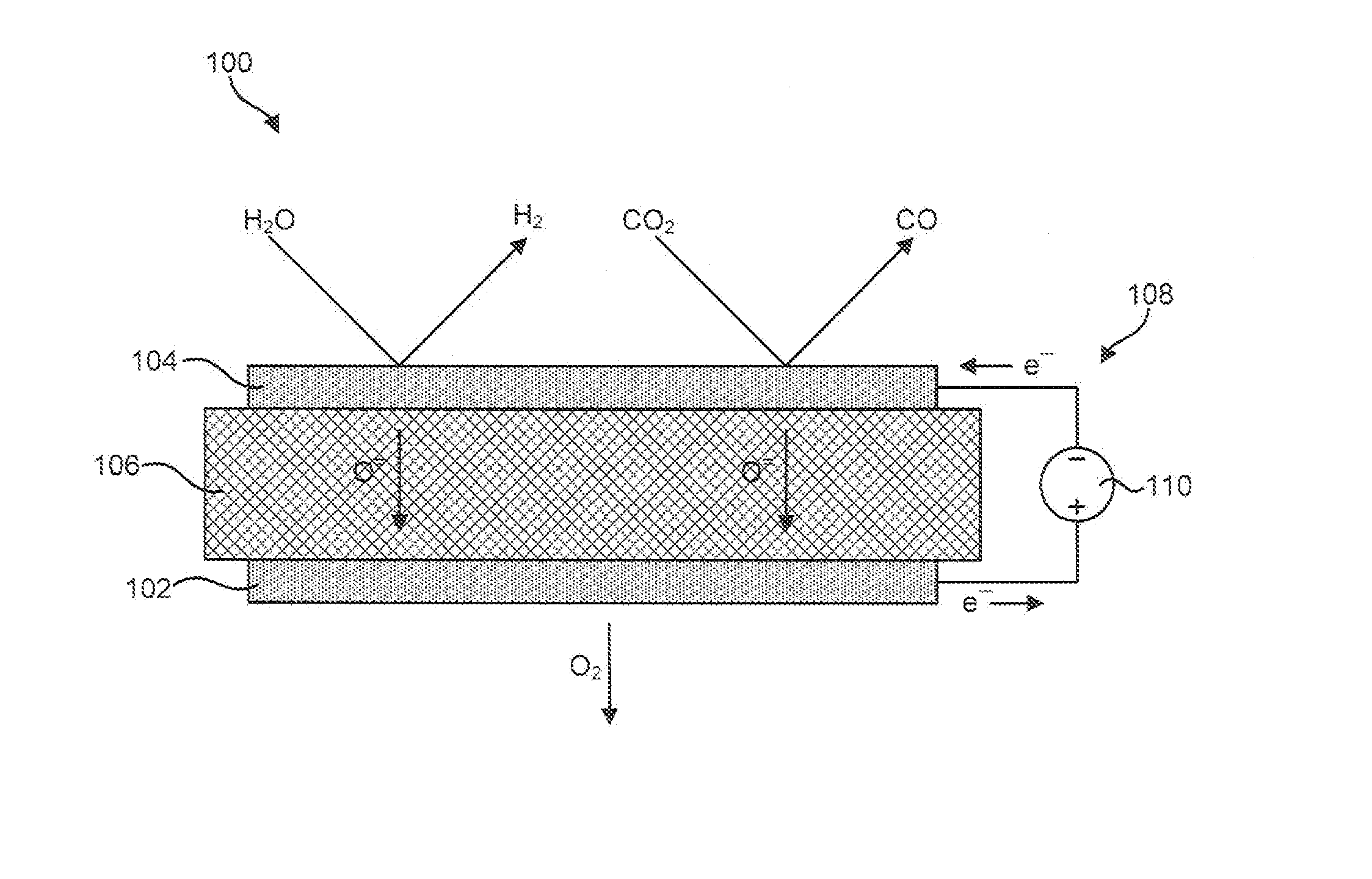
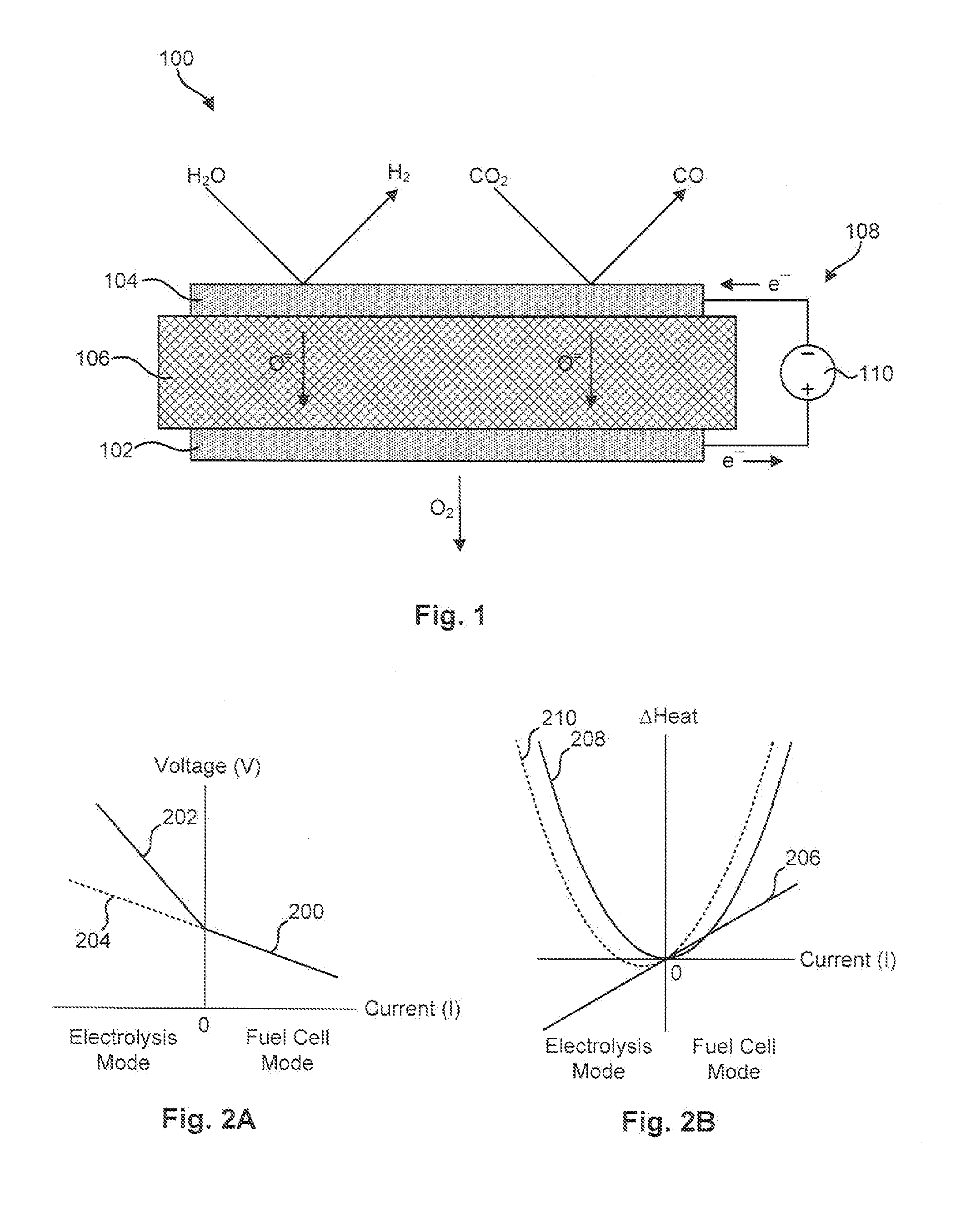
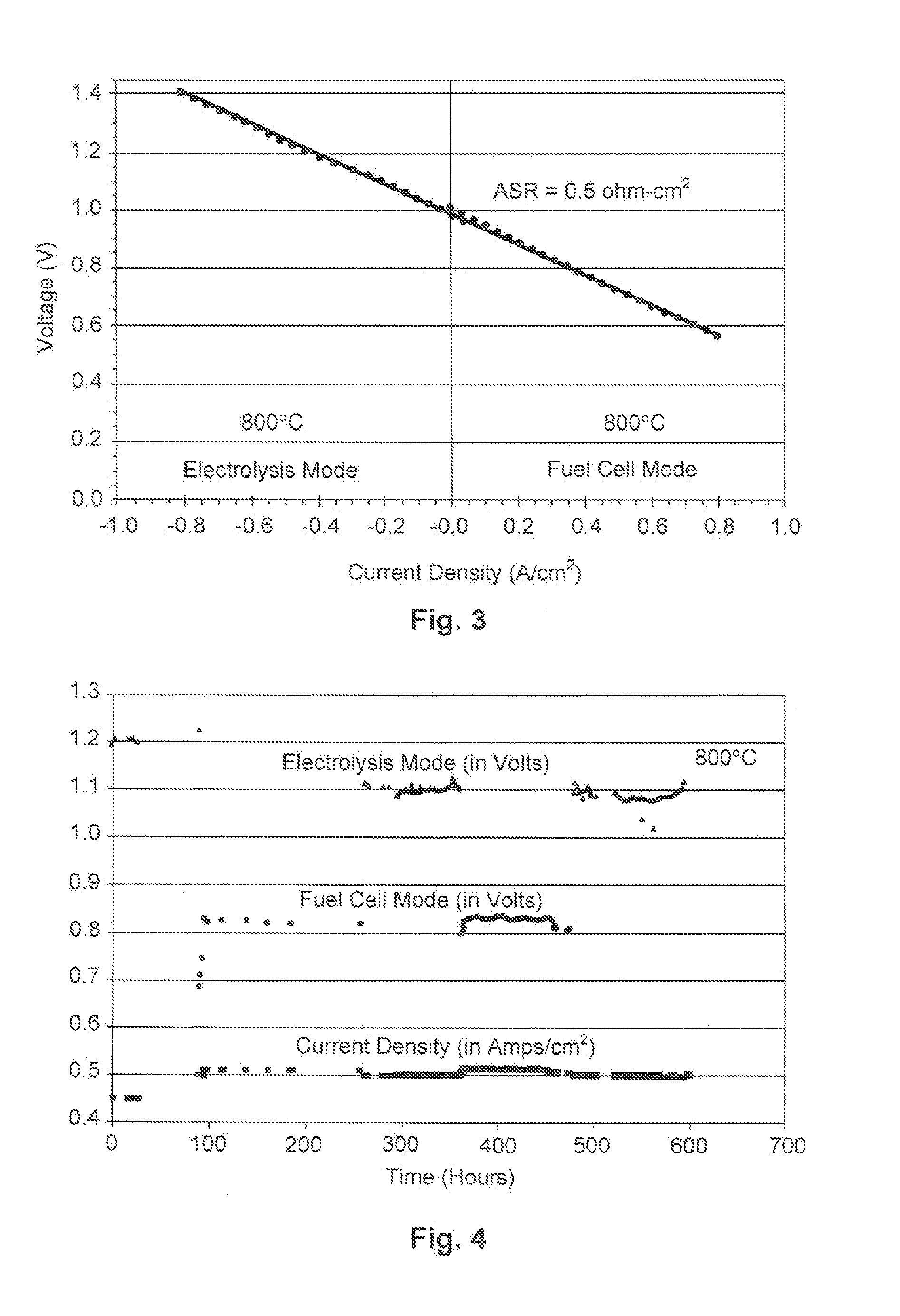
An electrolyzer cell is disclosed which includes a cathode to reduce an oxygen-containing molecule, such as H2O, CO2, or a combination thereof, to produce an oxygen ion and a fuel molecule, such as H2, CO, or a combination thereof. An electrolyte is coupled to the cathode to transport the oxygen ion to an anode. The anode is coupled to the electrolyte to receive the oxygen ion and produce oxygen gas therewith. In one embodiment, the anode may be fabricated to include an electron-conducting phase having a perovskite crystalline structure or structure similar thereto. This perovskite may have a chemical formula of substantially (Pr(1-x)Lax)(z-y)A′yBO(3-∂), wherein 0≦x≦0.5, 0≦y≦0.5, and 0.8≦z≦1.1. In another embodiment, the cathode includes an electron-conducting phase that contains nickel oxide intermixed with magnesium oxide.
Owner:COORSTEK INC
Ion-catching, broad-spectrum, highly effective, dynamic and quick air sterilization purifier
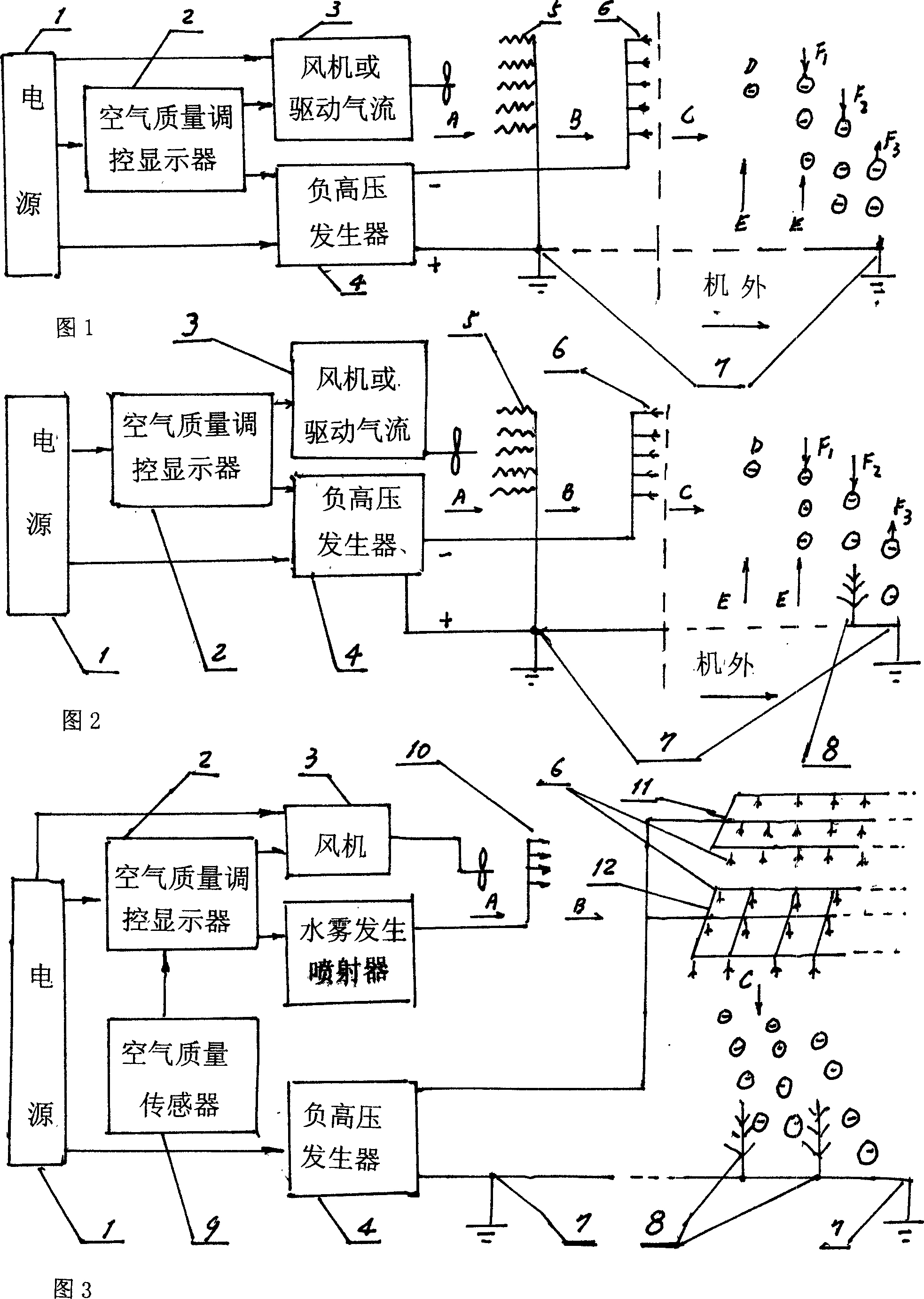
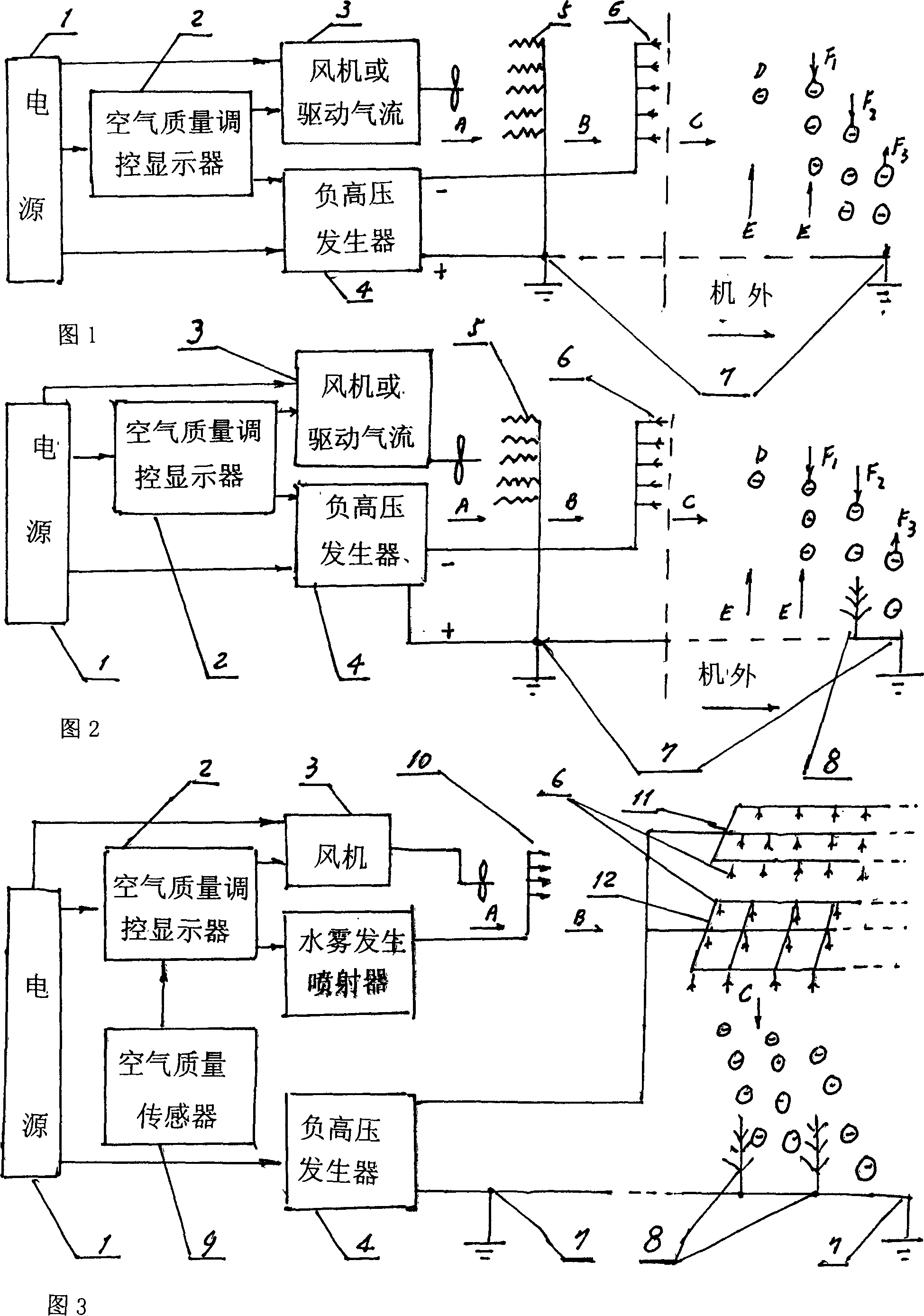
A ionic catching broad-spectrum highly effective dynamic rapid air sterilizing and cleaning machine, belonging to field of application research of air ionizing technique in the artificial environmental science, electrical climatology and iatrophysics; comprising power supply, air quality regulating display, fan or drive air flow, negative high pressure generator, electrical dust collector connected with earth inside and outside of the machine, and negative oxygen ion emission electrode; the negative end of the negative high pressure generator is connected with negative oxygen ion emission electrode to emit negative oxygen ion of high concentration to space, the positive end of it is connected with earth and electrical dust collector; the air quality regulating display can be equipped with water spray in outside, the water spray together with the fine particle in air acts as carrier adsorbing various pollutant in room air, and becomes negative larger dust particle gradually by using negative oxygen ion as kernel, and when its gravity together with the electric field force is larger than floating force, it will quickly fall to positive earth and dust collector, through which realizes purpose of broad-spectrum highly effective dynamic rapid air sterilizing and cleaning, and thus effectively controls the disease spread.
Owner:仇剑梅
Gas-detecting element and gas-detecting device comprising same
InactiveUS20030205078A1Improve Interface StabilityHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPotential differenceOxygen ions
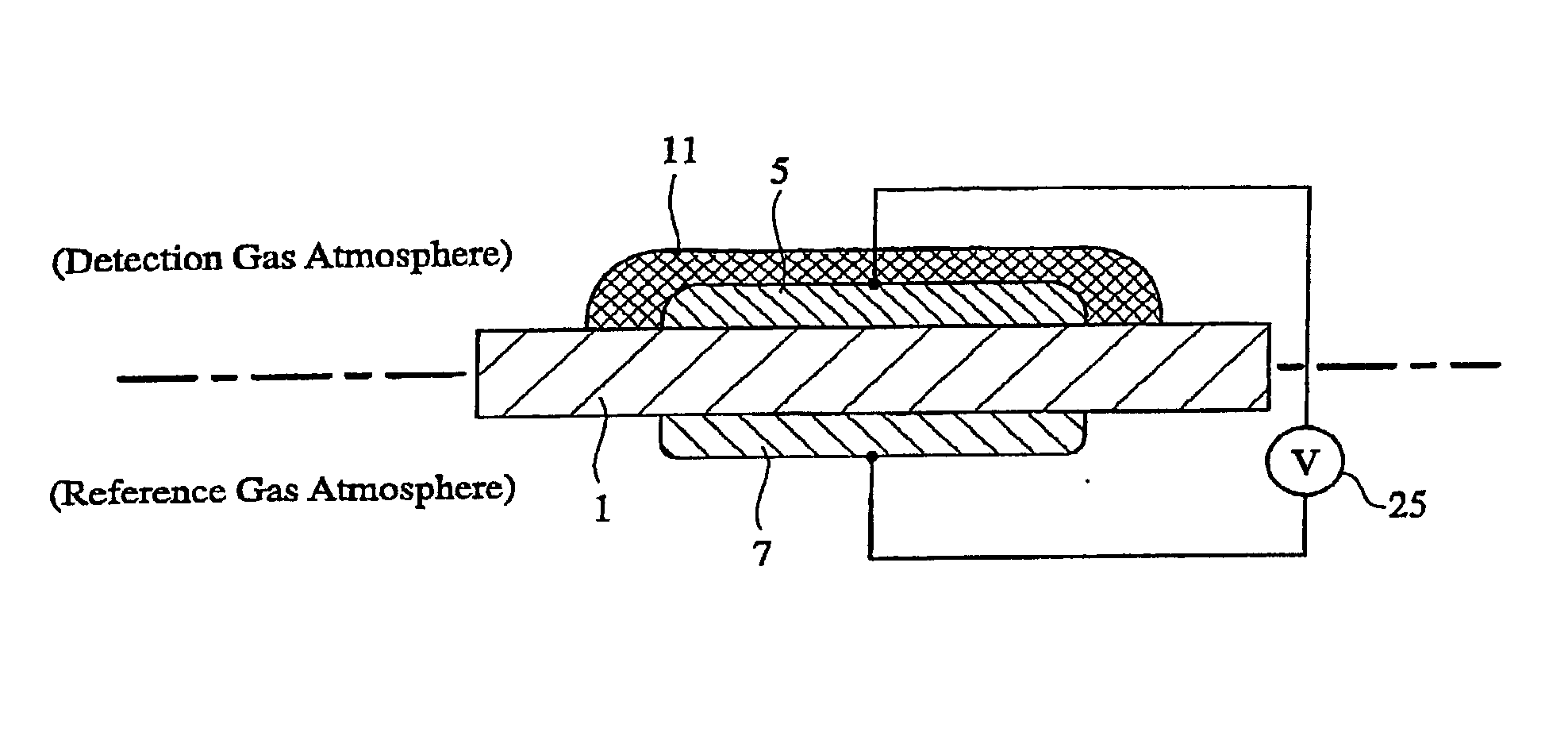
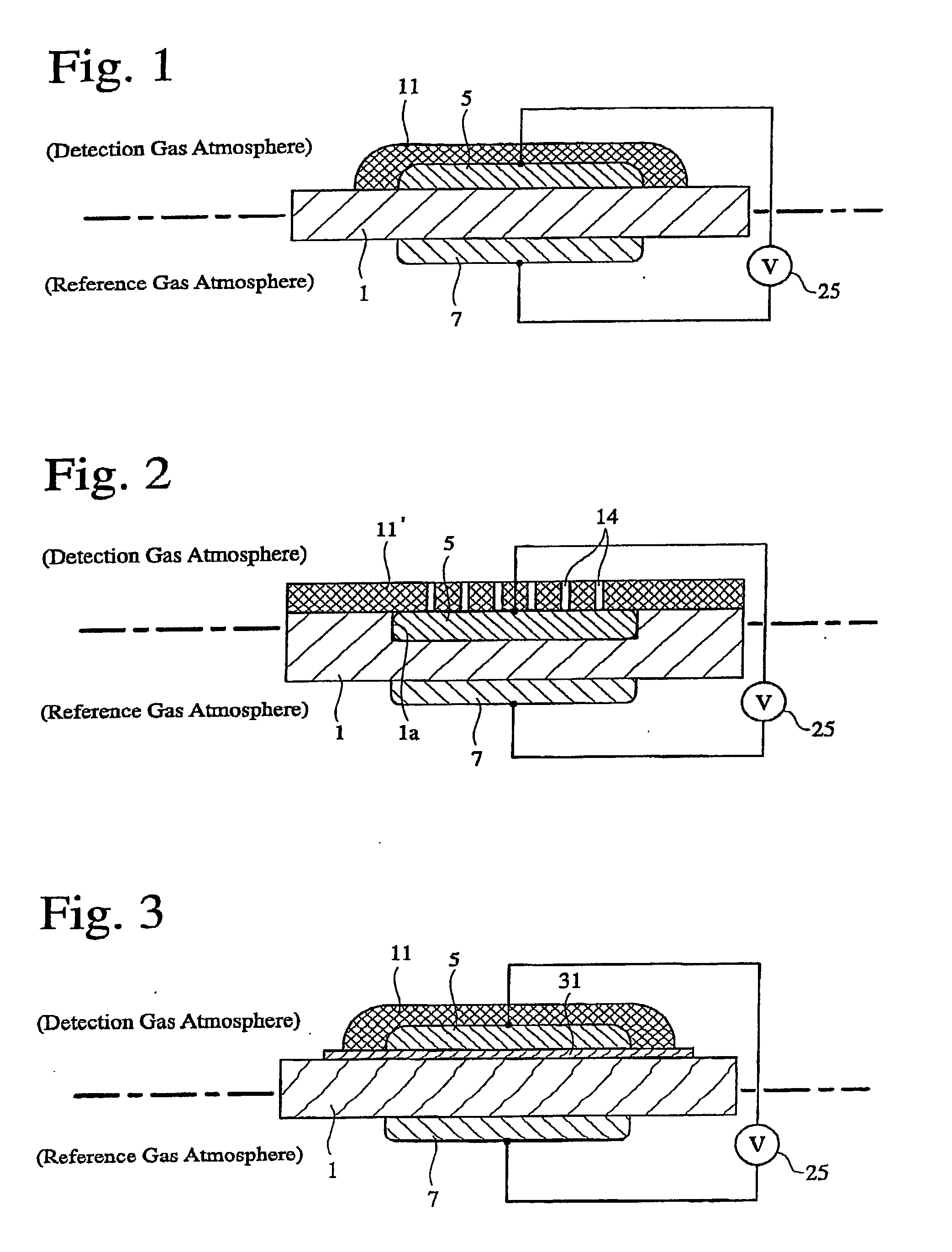
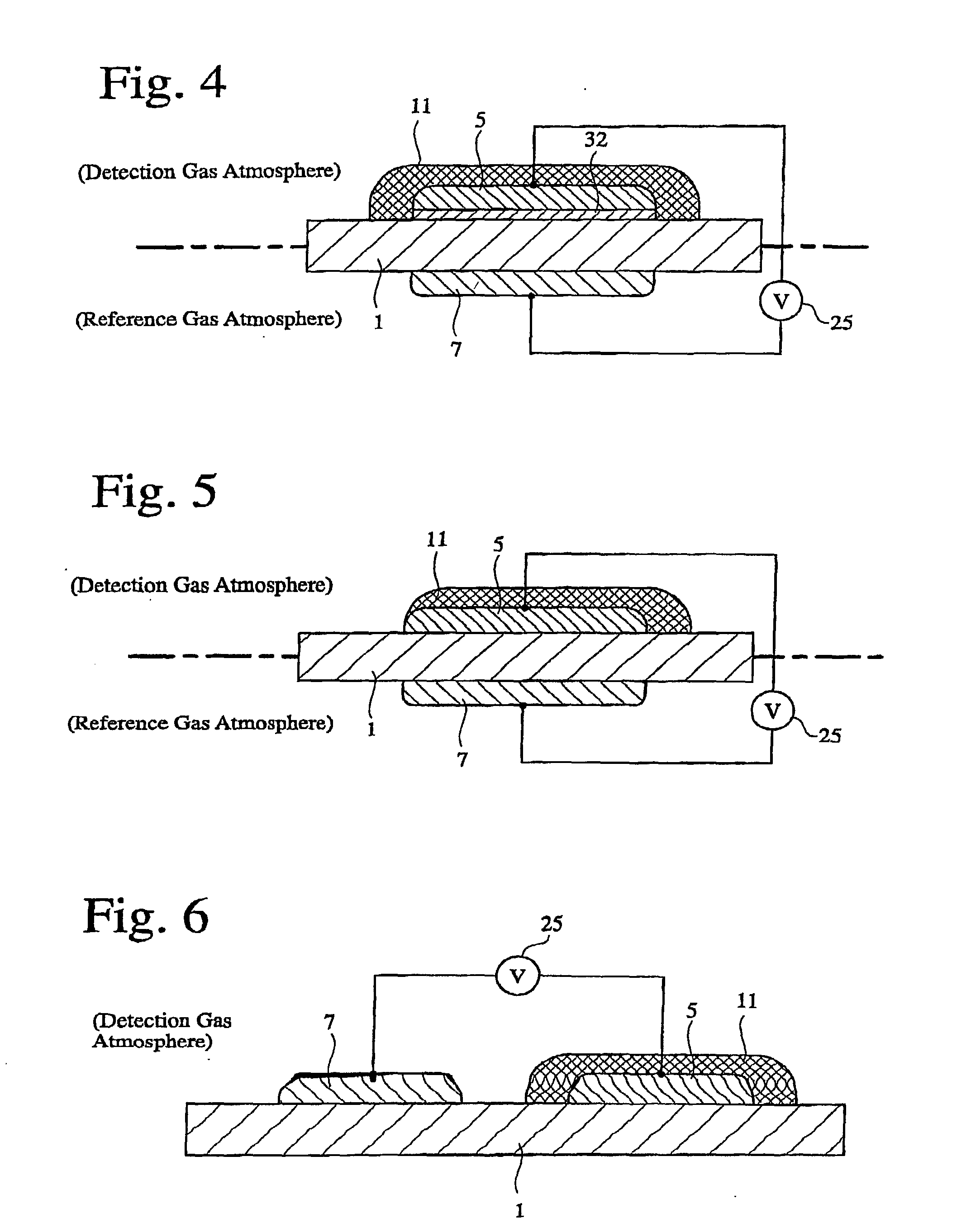
A gas-detecting element comprising an oxygen-ion-conductive solid electrolyte substrate, a sensing electrode fixed onto said solid electrolyte substrate and active with a detection object gas and oxygen, and a reference electrode fixed onto said solid electrolyte substrate and active with at least oxygen, for detecting potential difference between the sensing electrode and the reference electrode to determine the concentration of the detection object gas, the sensing electrode and / or the reference electrode being covered by an electrode-coating layer made of an oxygen-ion-conductive solid electrolyte, and the electrode-coating layer having a portion bonded to the solid electrolyte substrate directly or via an electrode underlayer made of an oxygen-ion-conductive solid electrolyte.
Owner:RIKEN CO LTD
Method and apparatus for producing hydrogen
An electrolyzer structure is provided that is suitable for use in a method that produces hydrogen by steam electrolysis by feeding reducing gas to an anode side and feeding steam to a cathode side of an electrolyzer that is partitioned into the anode side and the cathode side by a diaphragm of solid oxide electrolyte, and feeding power to the anode and cathode of the electrolyzer. One embodiment of the present invention relates to an apparatus that produces hydrogen by high temperature steam electrolysis and that comprises an electrolyzer partitioned into an anode side and a cathode side by a solid oxide electrolyte diaphragm, a conduit that feeds reducing gas to the anode side of the electrolyzer, and a conduit that feeds steam to the cathode of the electrolyzer, in which a metal cermet stable in a reducing atmosphere is used as the material of the anode and the cathode. Another embodiment of the present invention relates to a method of producing hydrogen by high temperature steam electrolysis for reducing electrolysis voltage by feeding steam to a cathode side and feeding hydrocarbon-containing gas to an anode side for reaction with oxygen ion, the cathode side and the anode side being provided in a high temperature steam electrolytic apparatus in which an electrolyzer is partitioned into the anode side and the cathode side using a solid oxide electrolyte as the diaphragm, wherein offgas discharged from the anode side of the electrolytic apparatus is admixed into the hydrocarbon-containing gas that is fed to the anode side of the electrolytic apparatus.
Owner:EBARA CORP +1
Methods and apparatus for measuring NOX gas concentration, for detecting exhaust gas concentration and for calibrating and controlling gas sensor
InactiveUS20020017467A1Accurate measurementElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesElectrical resistance and conductanceNitrogen oxides
A nitrogen oxide concentration detector has a first measurement chamber 2 into which is introduced a measurement gas via a first diffusion resistance 1; an oxygen concentration detection electrode 7a for measuring the oxygen concentration in the measurement gas in said first measurement chamber 1; a first oxygen ion pump cell 6 for pumping out oxygen in the measurement gas from said first measurement chamber 2 based on the potential of said oxygen concentration detection electrode 7a; a second measurement chamber 8 into which the gas is introduced from said first measurement chamber 2 via a second diffusion resistance 3; and a second oxygen ion pump cell 8 having a pair of electrodes 8a,8b across which a voltage is applied to decompose NOx in the second measurement chamber 4 to pump out dissociated oxygen to cause a current Ip2 corresponding to the NOx concentration to flow in the second oxygen ion pump cell 8. Variation of NOx concentration is a function of variation of Ip2. The concentration obtained based on the Ip2 is corrected responsive to the oxygen concentration in the measurement gas. Particularly, a coefficient of the variation of the Ip2, gain, in said function is corrected responsive to the oxygen concentration in the measurement gas.
Owner:BERKLEY INC +1
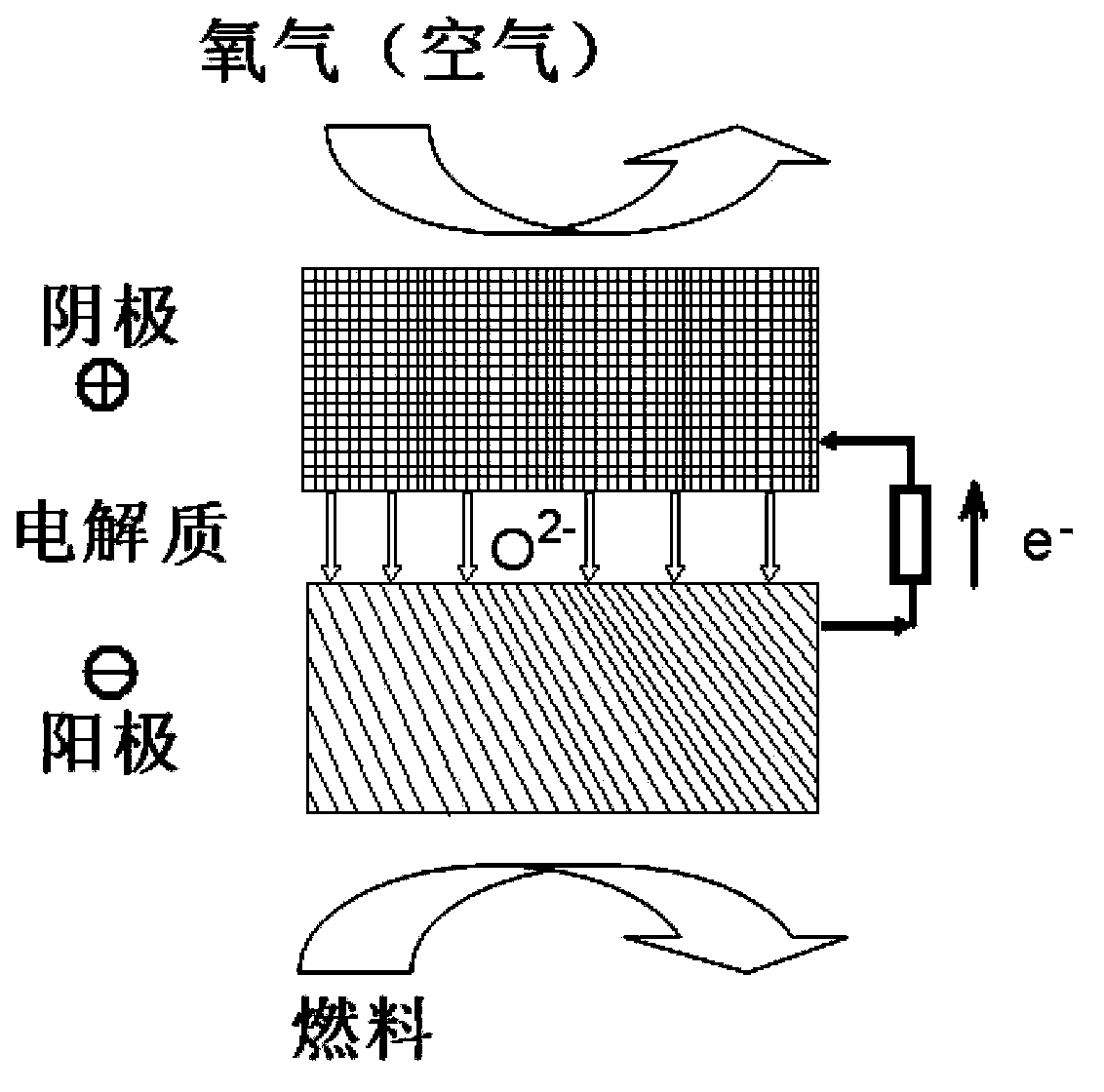
Mestastable ceramic fuel cell and method of making same
InactiveUS20050244693A1Little attentionSpeed up coolingFinal product manufactureCell electrodesSolubilityOxide ceramic
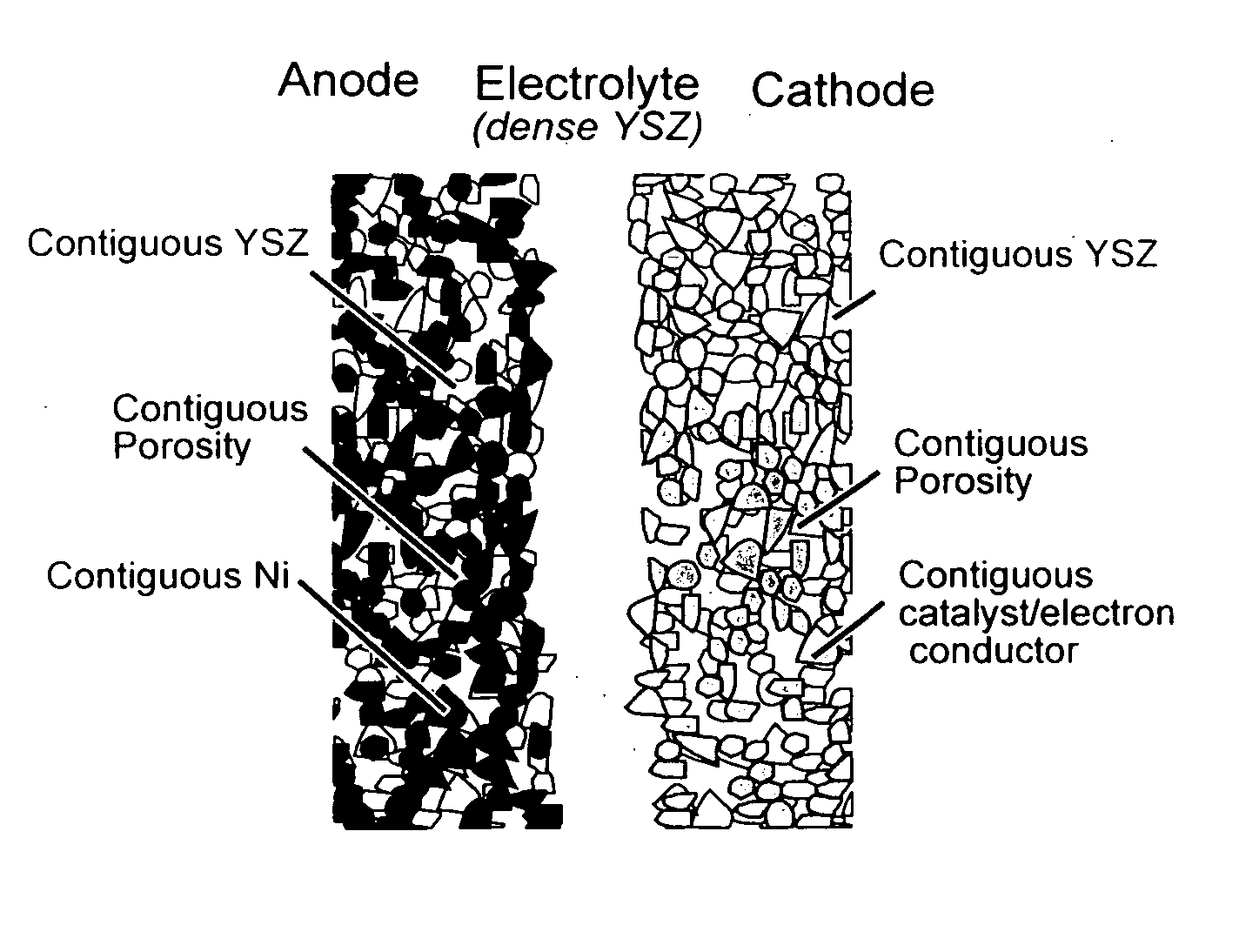
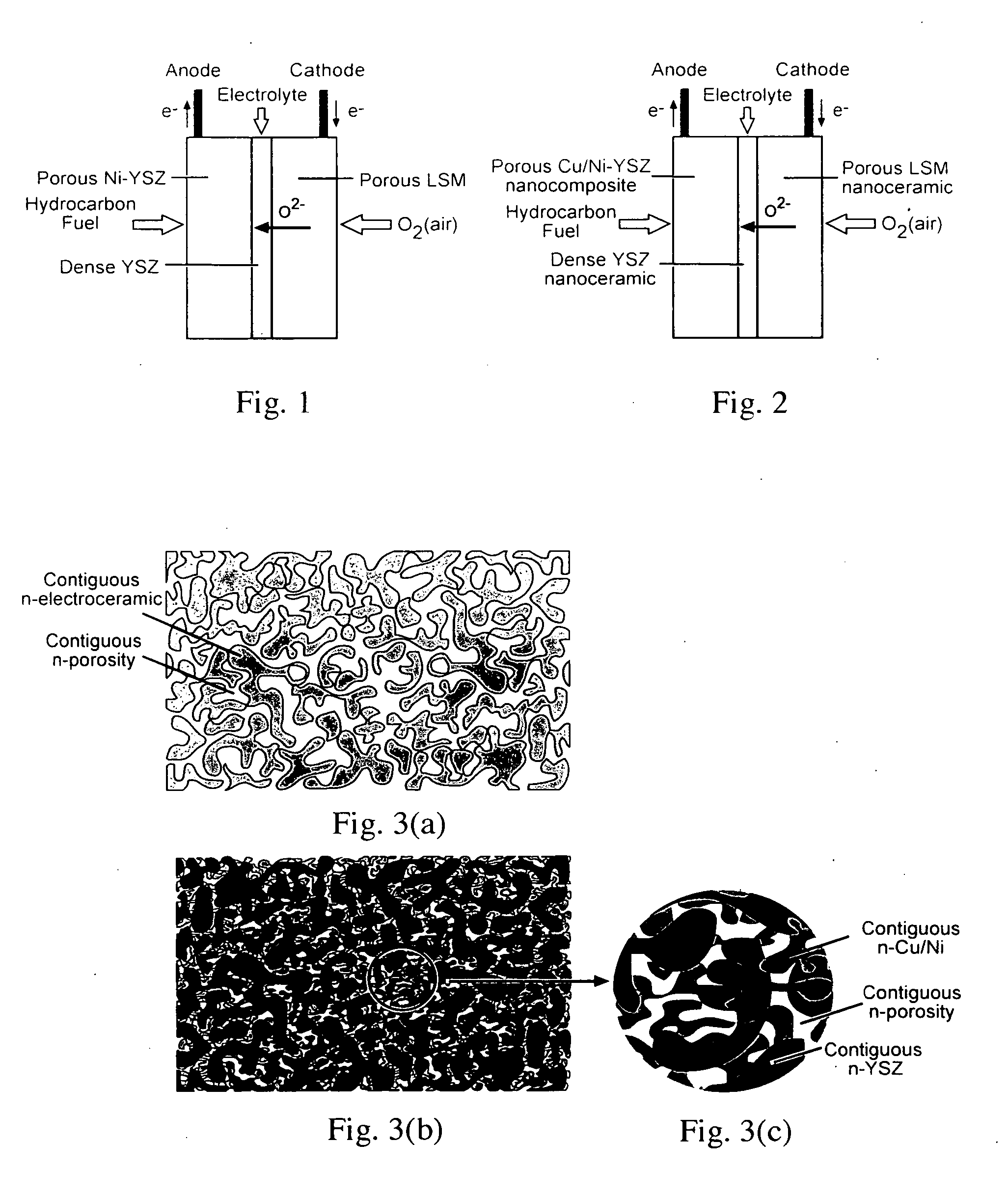
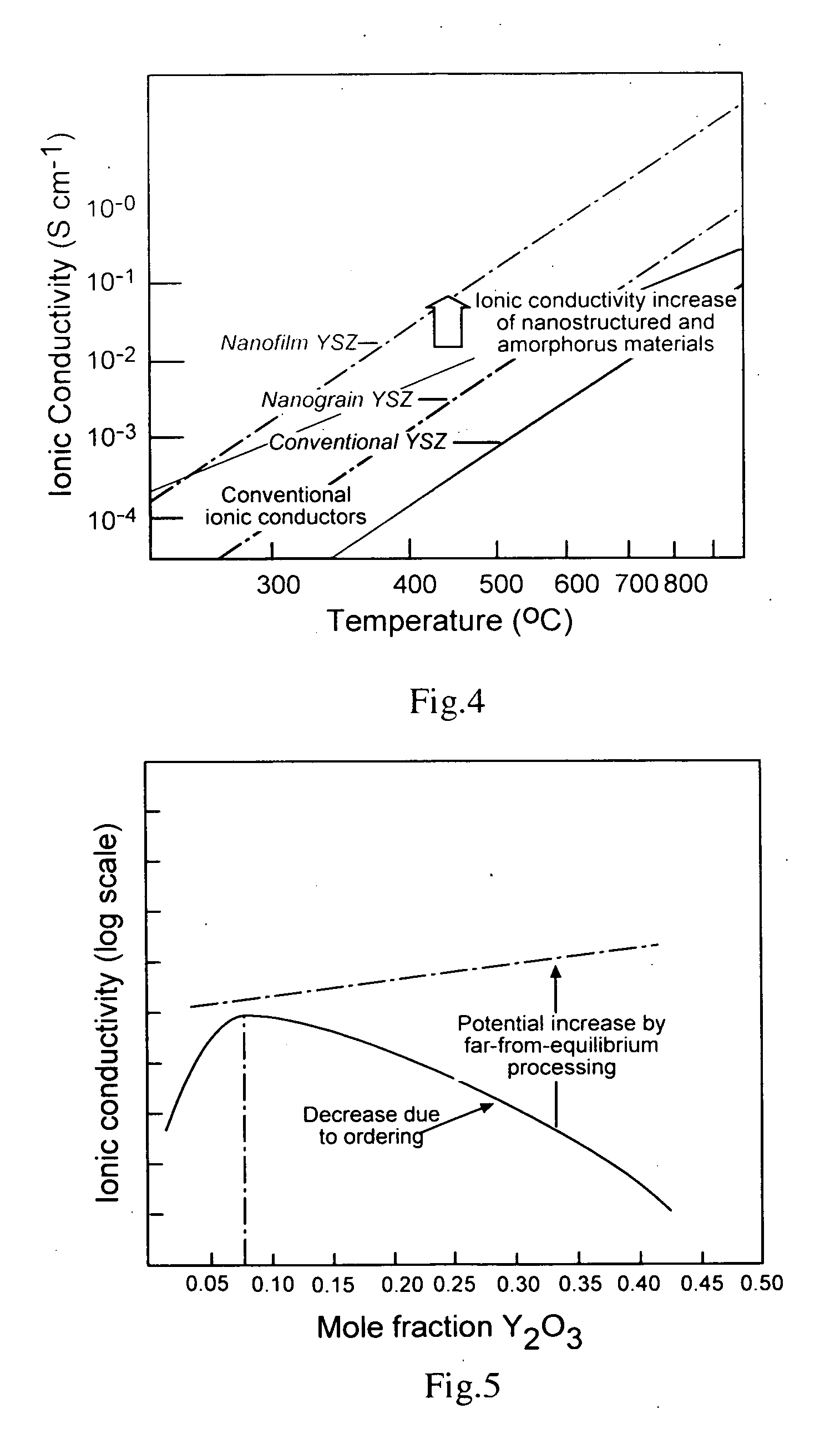
A solid oxide fuel cell has anode, cathode and electrolyte layers each formed essentially of a multi-oxide ceramic material and having a far-from-equilibrium, metastable structure selected from the group consisting of nanocrystalline, nanocomposite and amorphous. The electrolyte layer has a matrix of the ceramic material, and is impervious and serves as a fast oxygen ion conductor. The electrolyte layer has a matrix of the ceramic material and a dopant dispersed therein in an amount substantially greater than its equilibrium solubility in the ceramic matrix. The anode layer includes a continuous surface area metallic phase in which electron conduction is provided by the metallic phase and the multi-oxide ceramic matrix provides ionic conduction.
Owner:NANOCELL SYST
Composite antibacterial anion air cleanser and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103190442APromote decompositionImprove efficiencyBiocidePhysical/chemical process catalystsSide effectOxygen ions
The invention discloses a composite antibacterial anion air cleanser and a preparation method thereof. The air cleanser comprises the following raw materials by weight percent: 0.5-30 % of colorless and transparent anion crystal / powder, 0.5-2 % of photocatalyst powder, 1-10 % of a transparent nano silver solution, 1-15 % of food-grade ethanol, 0.1-5 % of natural plant essential oil and 20-50 % of deionized water. The air cleanser provided by the invention can rapidly decompose formaldehyde, benzene, ammonia and other harmful gases in spaces in a few minutes, with a cleansing rate of more than 98 %, and is rapidly and durably antibacterial and antivirus; furthermore, the air cleanser does not contain toxic chemical compositions, and is free of any side effects on the body and secondary pollution. According to the invention, the air cleanser decomposes odor molecules through anion and photocatalytic decomposition factors to remove odors, and can durably release a lot of negative oxygen ions, wherein the negative oxygen ions are known as "air vitamin" and are beneficial for human's physical and mental health, so that the air cleanser provided by the invention has relatively good health care function.
Owner:DONGGUAN JIN JI ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION CO LTD
Process integrating a solid oxide fuel cell and an ion transport reactor
InactiveUS6017646AImprove efficiencyMaximize efficiencyHydrogenFuel cell heat exchangeNuclear engineeringOxygen ions
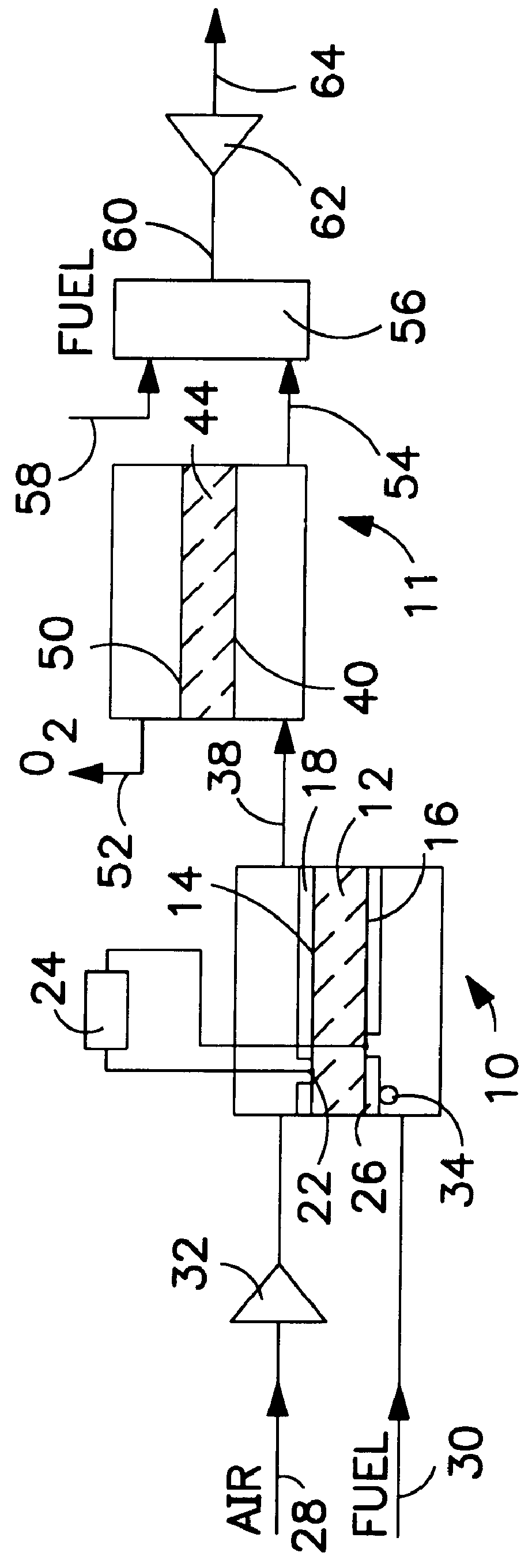
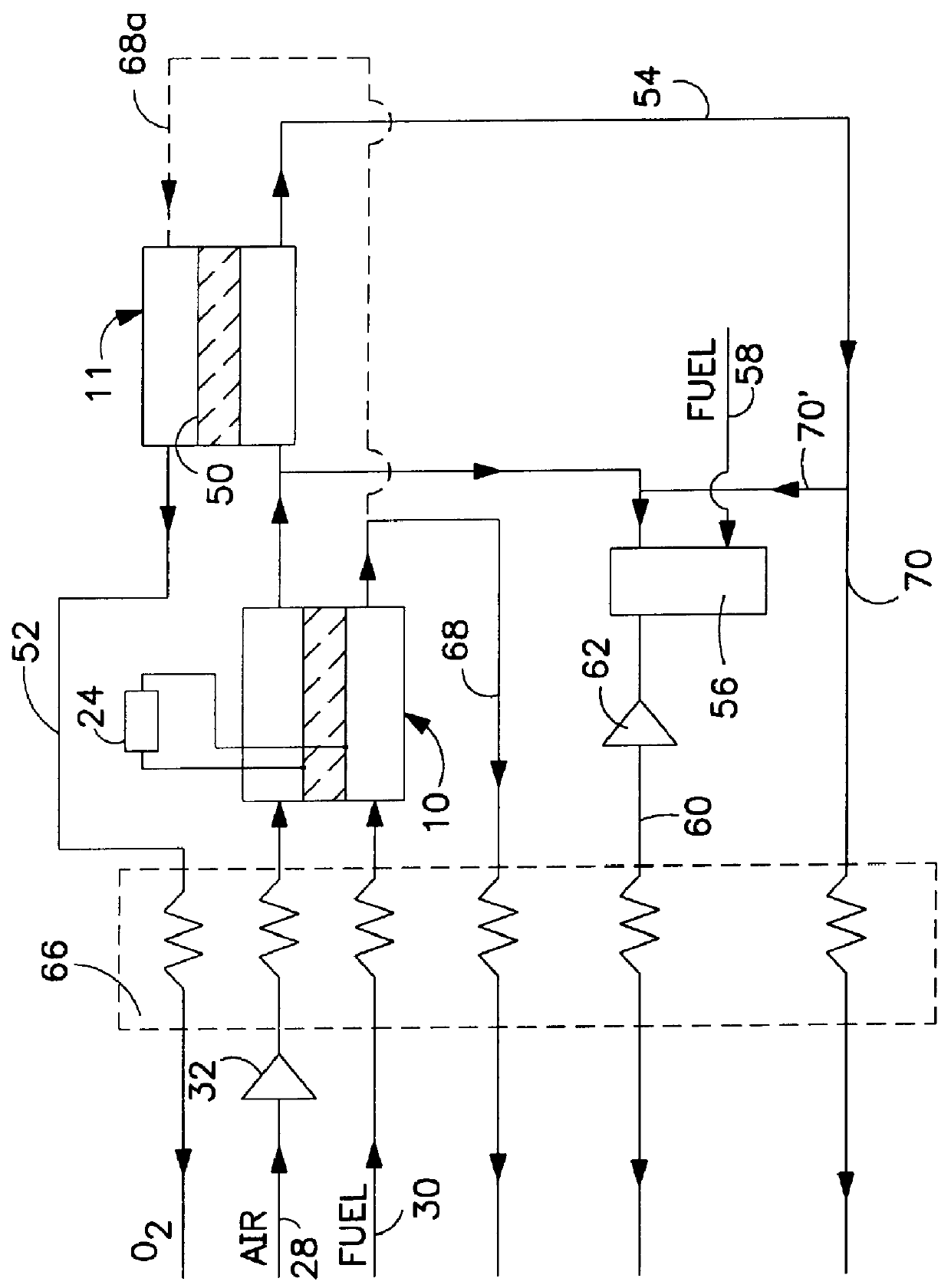
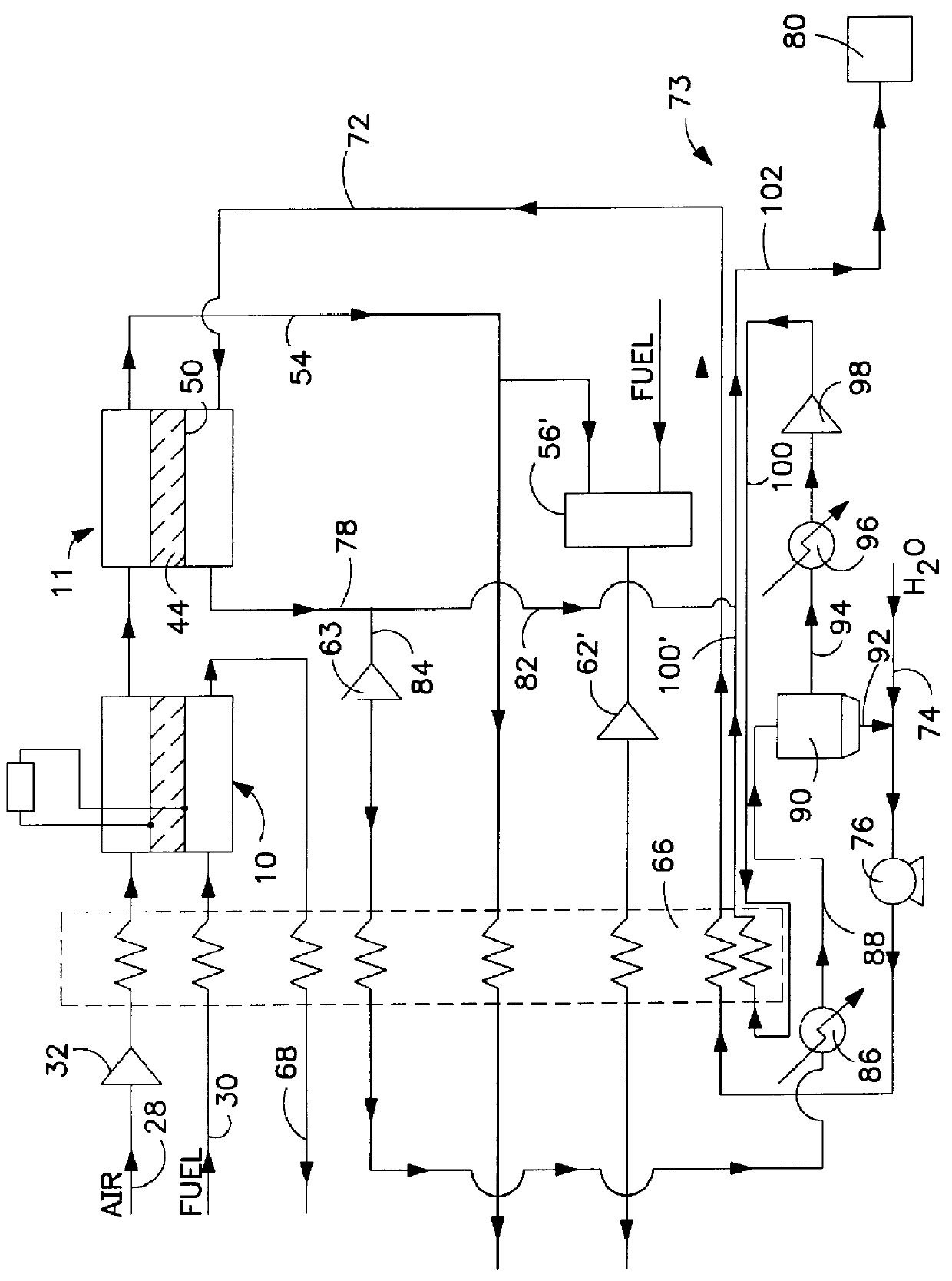
An integrated system utilizing a solid oxide fuel cell and at least one ion transport reactor to generate electric power and a product gas by delivering an oxygen-containing gas, typically air, to a first cathode side of the solid oxide fuel cell and delivering a gaseous fuel to a first anode side. Oxygen ions are transported through a membrane in the fuel cell to the first anode side and exothermally react with the gaseous fuel to generate electric power and heat. The heat and oxygen transport produces a higher-temperature, reduced-oxygen-content gaseous retentate stream exiting the cathode side of the solid oxide fuel cell which is delivered to a first ion transport reactor where a substantial portion of the residual oxygen is transported through an oxygen selective ion transport membrane. A product gas stream is then recovered.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
Multi-layer non-carbon metal-based anodes for aluminum production cells and method
InactiveUS6077415AImprove electrochemical activitySolution to short lifeMachining electrodesIsotope separationElectrical batteryOxygen ions
A composite, high-temperature resistant, non-carbon metal-based anode of a cell for the electrowinning of aluminium comprises a metal-based core structure of low electrical resistance, for connecting the anode to a positive current supply, coated with a series of superimposed, adherent, electrically conductive layers. These layers consist of at least one layer on the core structure constituting a barrier substantially impervious to monoatomic oxygen and molecular oxygen; one or more intermediate, protective layers on the oxygen barrier layer which remain inactive in the reactions for the evolution of oxygen gas; and an electrochemically active layer for the oxidation reaction of oxygen ions present at the anode / electrolyte interface into nascent monoatomic oxygen, as well as for subsequent reaction for the formation of gaseous biatomic oxygen. The active layer on the outermost intermediate layer is slowly consumable during electrolysis and protects the intermediate protective layer by inhibiting its dissolution into the electrolyte.
Owner:MOLTECH INVENT
Amperometric Electrochemical Cells and Sensors
InactiveUS20090218220A1High sensitivityReduce dependenceMaterial electrochemical variablesAir quality improvementOxygen ionsNitrogen oxide
Amperometric ceramic electrochemical cells comprise, in one embodiment, an electrolyte layer, a sensing electrode layer, and a counter electrode layer, wherein the cell is operable in an oxidizing atmosphere and under an applied bias to exhibit enhanced reduction of oxygen molecules at the sensing electrode in the presence of one or more target gases such as nitrogen oxides (NOX) or NH3 and a resulting increase in oxygen ion flux through the cell. In another embodiment, amperometric ceramic electrochemical cells comprise an electrolyte layer comprising a continuous network of a first material which is ionically conducting at an operating temperature of about 200 to 550° C.; a counter electrode layer comprising a continuous network of a second material which is electrically conductive at an operating temperature of about 200 to 550° C.; and a sensing electrode layer comprising a continuous network of a third material which is electrically conductive at an operating temperature of about 200 to 550° C., which sensing electrode is operable to exhibit increased charge transfer in the presence of one or more target gas species. These electrochemical cells and additional electrochemical cell embodiments are suitable for use in gas sensors and methods of sensing or detecting one or more target gases.
Owner:NEXTECH MATERIALS
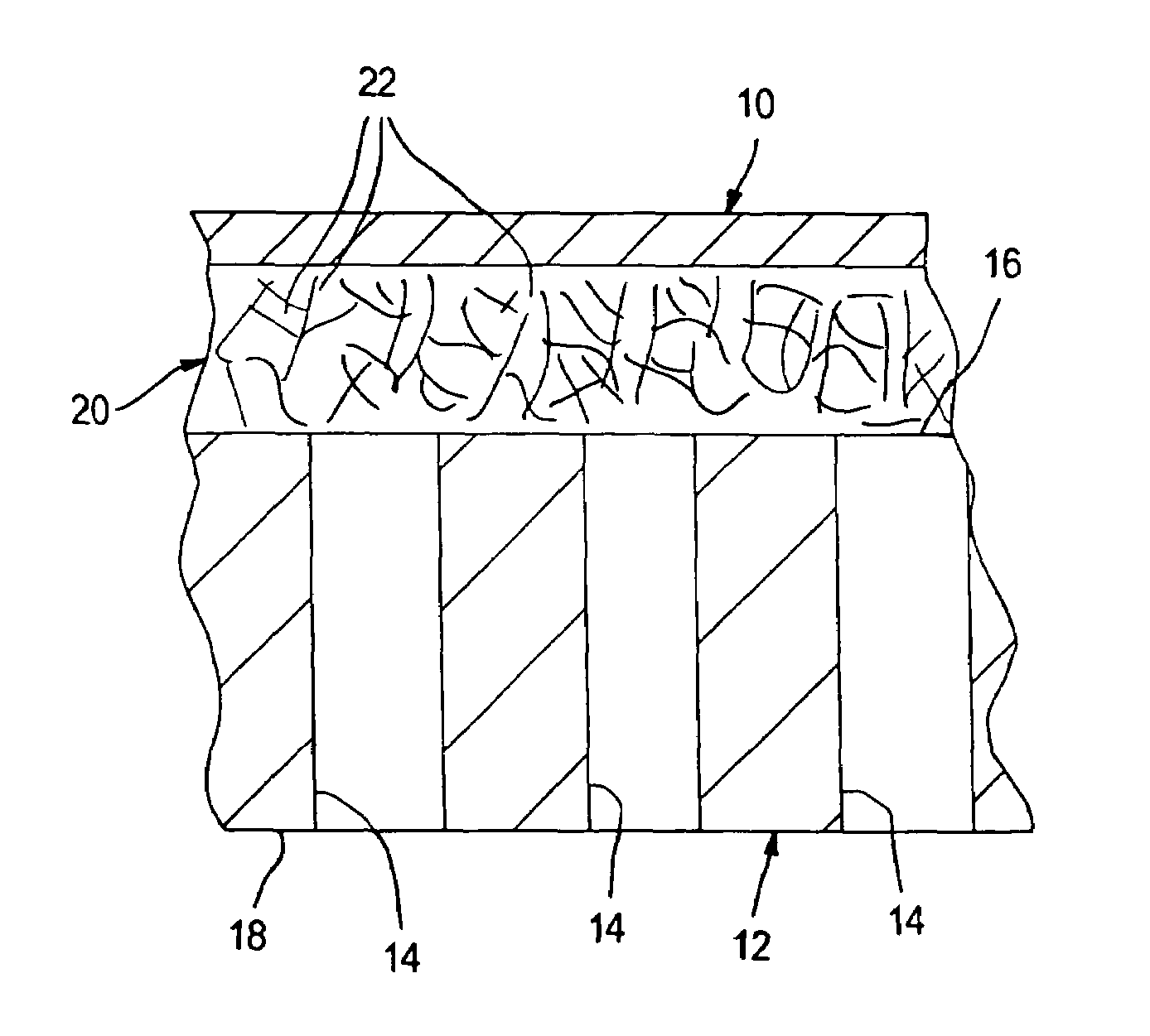
Composite oxygen ion transport element
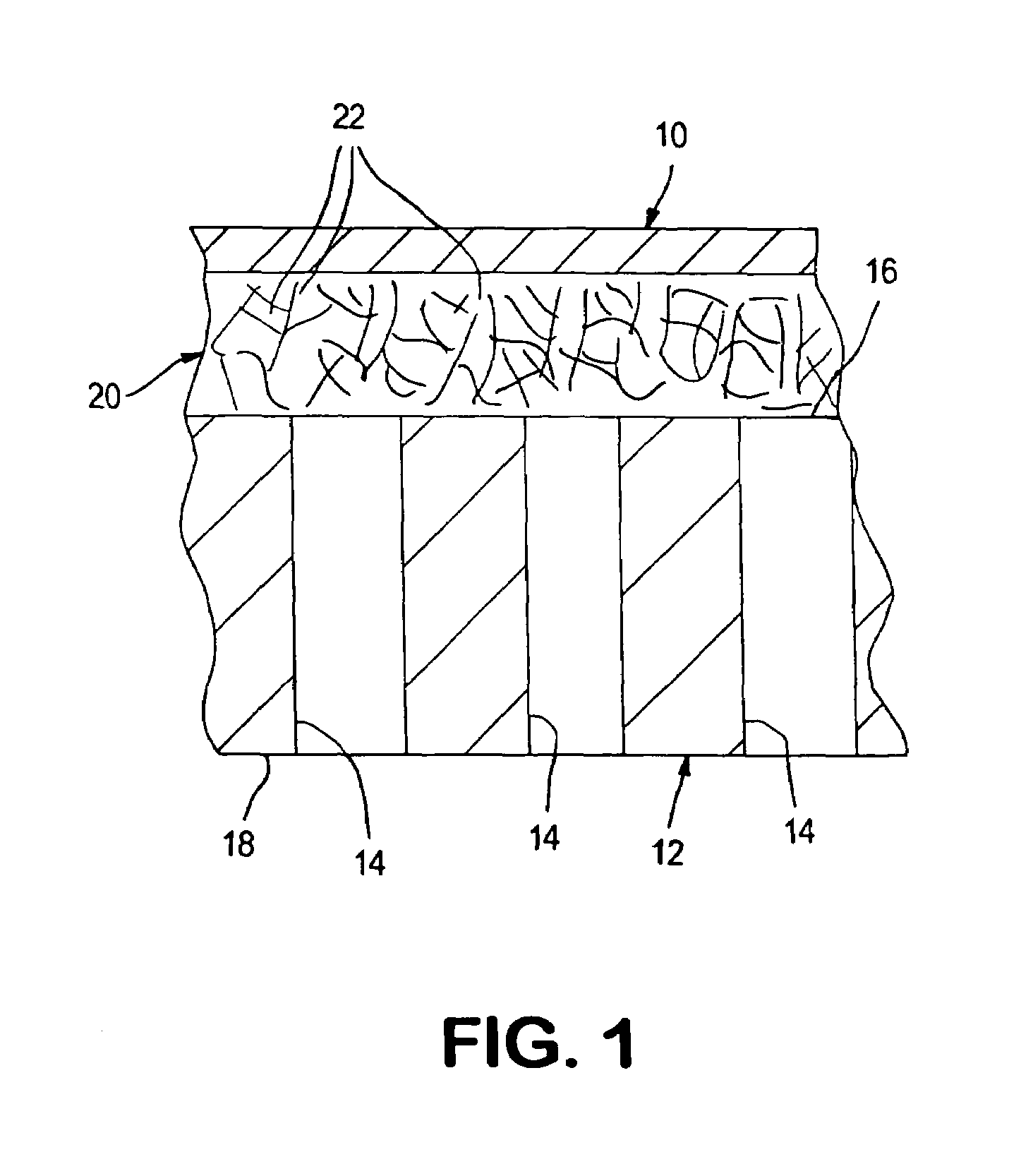
ActiveUS7229537B2Improve flux performanceImprove toughnessLayered productsIsotope separationElectrical conductorDiffusion resistance
A composite oxygen ion transport element that has a layered structure formed by a dense layer to transport oxygen ions and electrons and a porous support layer to provide mechanical support. The dense layer can be formed of a mixture of a mixed conductor, an ionic conductor, and a metal. The porous support layer can be fabricated from an oxide dispersion strengthened metal, a metal-reinforced intermetallic alloy, a boron-doped Mo5Si3-based intermetallic alloy or combinations thereof. The support layer can be provided with a network of non-interconnected pores and each of said pores communicates between opposite surfaces of said support layer. Such a support layer can be advantageously employed to reduce diffusion resistance in any type of element, including those using a different material makeup than that outlined above.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC +1
Composite material containing perovskite structure oxide, preparation method and application thereof
The invention provides a composite material containing a perovskite structure oxide, a preparation method and application thereof. The composite material contains, by weight, 20%-99.99% of the perovskite structure oxide and 0.01%-80% of an oxygen ion conductor oxide. According to the invention, a sol-gel method can be employed to prepare the perovskite structure oxide, a combustion method can be employed to prepare the oxygen ion conductor oxide, and then the perovskite structure oxide and the oxygen ion conductor oxide can be mixed uniformly by means of ball milling or mechanical grinding, thus obtaining the composite material. The invention also relates to application of the composite material in solid oxide fuel cells and solid oxide electrolysis cells.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Resistance variable element
InactiveUS20090218565A1High degree of oxidationPrevent movementSolid-state devicesDigital storageHigh resistanceOxygen ions
A resistance variable element is provided, which is capable of performing bipolar operation by a specified mechanism and usable as a memory. The resistance variable element has a laminated structure including an electrode, an electrode, an oxide layer between the electrodes, and an oxide layer in contact with the oxide layer between the oxide layer and the electrode. The oxide layer is switchable from the low-resistance state to the high-resistance state by donating oxygen ions to the oxide layer, and from the high-resistance state to the low-resistance state by accepting oxygen ions from the oxide layer. The oxide layer is switchable from the low-resistance state to the high-resistance state by accepting oxygen ions from the oxide layer, and from the high-resistance state to the low-resistance state by donating oxygen ions to the oxide layer.
Owner:NAGOYA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY +1
Healthcare plate material capable of generating anions and far infrared rays and composite healthcare plate
The invention discloses a healthcare plate material capable of generating anions and far infrared rays. The plate material comprises the following raw material components in percentage by weight: 70-80 percent of saw dust, 3-5 percent of eaglewood, 5-9 percent of tourmaline powder, 5-9 percent of anion powder, 1-3 percent of preservative, 2-4 percent of adhesive and 1-3 percent of antibacterial agent. The invention further discloses a composite healthcare plate material with the healthcare plate material capable of generating the anions and the far infrared rays. According to the healthcare plate material, healthcare materials beneficial to a human body such as the eaglewood, the anion powder and the tourmaline are adopted, and healthcare plate materials which are pressed under different pressures according to different using functions and are different in hardness and thickness can have different purposes. The healthcare plate material can release negative oxygen ions, the far infrared rays and a magnetic field, and the fitness and the immunity of a human body are unconsciously improved in the life and work of people by virtue of the fragrance of the eaglewood. Meanwhile, the practicality of the healthcare plate material is improved, so that the using function of the healthcare plate material is diversified, and the healthcare plate material is convenient to commonly use and popularize.
Owner:王文娟
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
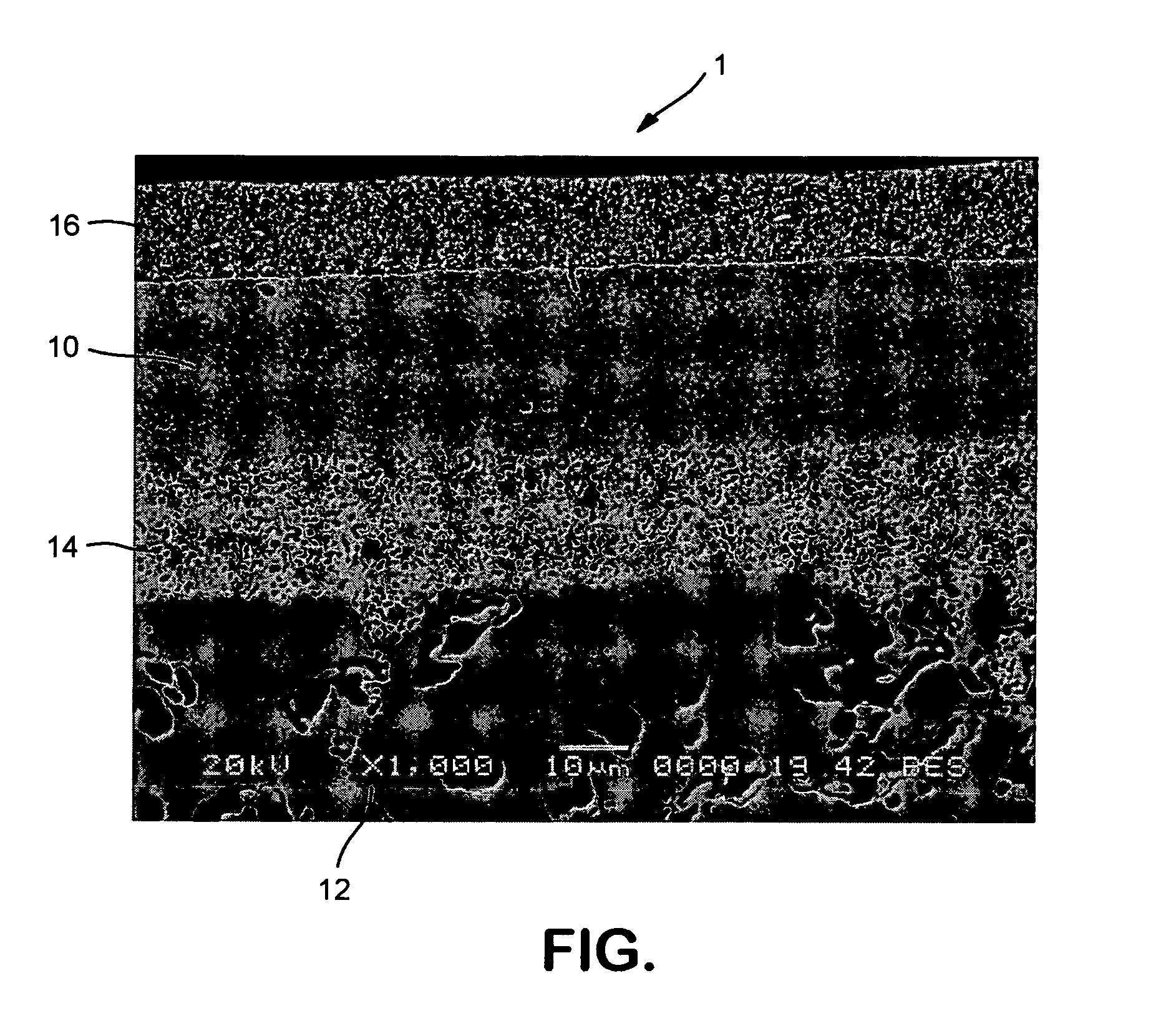
InactiveUS20110089524A1Reduce thickness variationImprove accuracySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface layerOxygen ions
A semiconductor device and a method of manufacturing the same capable of reducing variations in the thickness of a semiconductor device are provided. The amount of oxygen implanted ions is less than the amount of implanted oxygen ions in the conventional epitaxial SIMOX wafers. Oxygen is ion-implanted into the surface layer of a silicon wafer from the surface of the wafer. Then, by heat treating the wafer, a thinning stop layer, which is an imperfect buried oxide film, is formed along the entire plane of the wafer. As a result, variation of the thickness of the semiconductor device formed in an active layer can be reduced, since the, the reliability of the accuracy of the end point of silicon wafer thinning is higher than that of a thinning using the conventional deep trench structure as an end point detector.
Owner:SUMCO CORP
Composite mixed oxide ionic and electronic conductors for hydrogen separation
InactiveUS20060191408A1Efficient separationHigh hydrogen fluxesSemi-permeable membranesMembranesCeramic compositeHydrogen
A mixed ionic and electronic conducting membrane includes a two-phase solid state ceramic composite, wherein the first phase comprises an oxygen ion conductor and the second phase comprises an n-type electronically conductive oxide, wherein the electronically conductive oxide is stable at an oxygen partial pressure as low as 10−20 atm and has an electronic conductivity of at least 1 S / cm. A hydrogen separation system and related methods using the mixed ionic and electronic conducting membrane are described.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Porous non-carbon metal-based anodes for aluminium production cells
InactiveUS6113758AEliminate carbon-generated pollutionReduces high cell operating costMachining electrodesElectrical-based machining electrodesFiberCuprate
A non-carbon, metal-based anode (10) of a cell for the electrowinning of aluminium, comprising an electrically conductive, high temperature resistant and oxidation resistant metal structure (11) in the form of a wire mesh or net, a foraminate sheet, a fibrous network, a reticulated skeletal structure, or a porous structure having voids, recesses and / or pores which are filled or partly filled with an electrochemically active filling (12), such as oxides, oxyfluorides, phosphides, carbides, cobaltites and cuprates making the surface of the anode (10) conductive and electrochemically active for the oxidation of oxygen ions present at the anode surface / electrolyte (5) interface.
Owner:MOLTECH INVENT
Composite oxygen ion transport membrane
ActiveUS7556676B2Closely matchedLow linear expansionSemi-permeable membranesMembranesCeriumOxygen ions
A composite oxygen ion transport membrane having a dense layer, a porous support layer, an optional intermediate porous layer located between the porous support layer and the dense layer and an optional surface exchange layer, overlying the dense layer. The dense layer has electronic and ionic phases. The ionic phase is composed of scandia doped, yttrium or cerium stabilized zirconia. The electronic phase is composed of a metallic oxide containing lanthanum, strontium, chromium, manganese and vanadium and optionally cerium. The porous support layer is composed of zirconia partially stabilized with yttrium, scandium, aluminum or cerium or mixtures thereof. The intermediate porous layer, if used, contains the same ionic and electronic phases as the dense layer. The surface exchange layer is formed of an electronic phase of a metallic oxide of lanthanum and strontium that also contains either manganese or iron and an ionic phase of scandia doped zirconia stabilized with yttrium or cerium.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
Ion-catching, broad-spectrum, highly effective, dynamic and quick air sterilization purifier
A ionic catching broad-spectrum highly effective dynamic rapid air sterilizing and cleaning machine, belonging to field of application research of air ionizing technique in the artificial environmental science, electrical climatology and iatrophysics; comprising power supply, air quality regulating display, fan or drive air flow, negative high pressure generator, electrical dust collector connected with earth inside and outside of the machine, and negative oxygen ion emission electrode; the negative end of the negative high pressure generator is connected with negative oxygen ion emission electrode to emit negative oxygen ion of high concentration to space, the positive end of it is connected with earth and electrical dust collector; the air quality regulating display can be equipped with water spray in outside, the water spray together with the fine particle in air acts as carrier adsorbing various pollutant in room air, and becomes negative larger dust particle gradually by using negative oxygen ion as kernel, and when its gravity together with the electric field force is larger than floating force, it will quickly fall to positive earth and dust collector, through which realizes purpose of broad-spectrum highly effective dynamic rapid air sterilizing and cleaning, and thus effectively controls the disease spread.
Owner:仇剑梅
Composite multifunctional air-activating dust-cleaning sterilization device
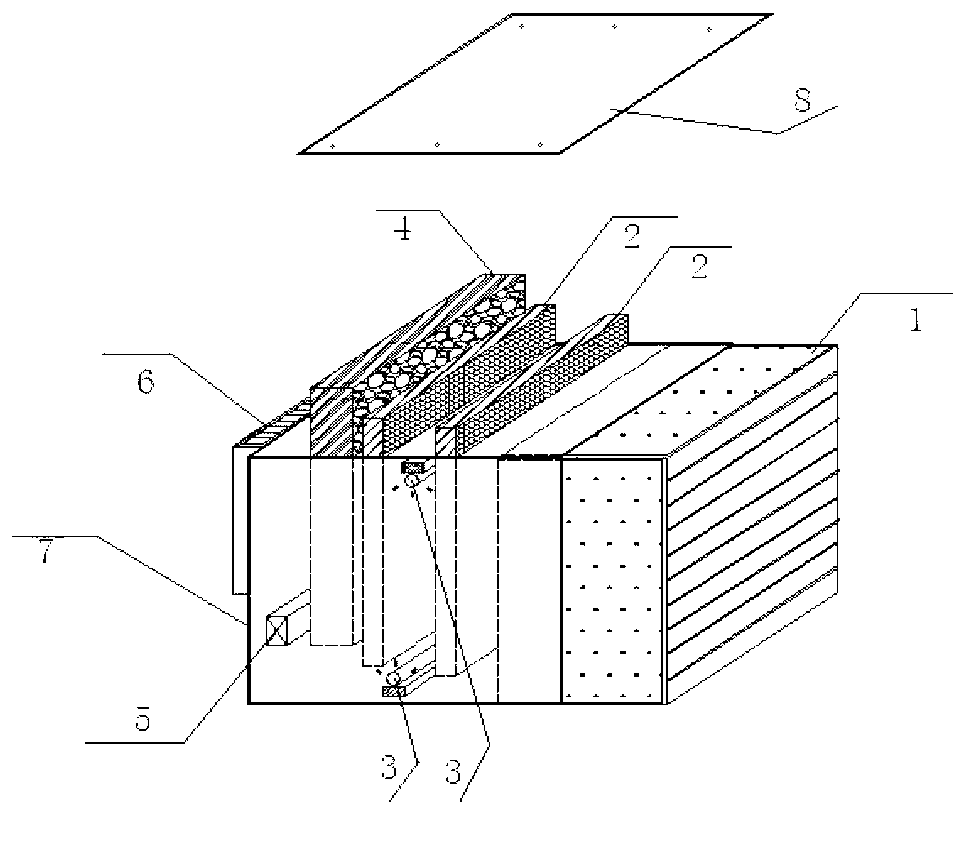
InactiveCN103292386AHigh effect of sterilization and dust removalHumanized remote control operationCombination devicesLighting and heating apparatusOxygen ionsCell membrane
The invention provides a composite multifunctional air-activating dust-cleaning sterilization device comprising a shell, a sterilization dust cleaner and a base. The sterilization dust cleaner is mounted inside the shell, and comprises a mounting shell, a coarse filtrating screen, a two-point potential difference electrostatic sterilization dust-removing unit, photocatalyst filtrating screens, ultraviolet lamps, coconut shell crystal porous adsorption activated carbon, a negative oxygen ion generator and a mute blower. By the device, just entered air can be ionized effectively in an inlet stage so as to kill bacteria and germs momentarily, various organic compounds and part of inorganic substances are decomposed oxidatively by the aid of the photocatalysis nanoscale titanium dioxide photocatalyst filtrating screens, bacterial cell membranes and protein of curing viruses are destroyed, and multi-functional air cleaning effects of sterilization, deodorization, mildew proofing, pollution prevention and self cleaning are achieved by the aid of activated adsorption and negative oxygen ion activation technologies.
Owner:DONGGUAN JINCAI IND
Carbon monoxide gas sensor and measuring device using the same sensor
InactiveUS6254749B1High selectivityHigh sensitivityWeather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementElectricityMeasurement device
In a CO gas sensor composed of a CO gas sensing electrode 3 being made of Au or an Au alloy and a reference electrode 2 electrically connected to at least part of a surface of a solid electrolyte having an oxygen ion transfer property, which is superior in CO gas selectivity, in particular, reducing the affect of the co-existing oxygen to CO, and which works with a high precision at a high temperature, and in a CO gas measuring device using the gas sensor, the gas sensor being capable of determining a CO gas concentration by measuring a electromotive force change due to adsorption / oxidization of the carbon monoxide gas in the sensing electrode 3 when a constant current is caused to flow between the reference electrode 2 and the sensing electrode 3 or a current value caused by the oxidizing reaction of the carbon monoxide gas in the sensing electrode when a voltage is kept constant between the reference electrode 2 and the sensing electrode 3.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Process for reducing carbon production in solid electrolyte ionic conductor systems
InactiveUS6106591AEfficient processingReduce needHydrogenSemi-permeable membranesElectrical conductorReactive gas
A process for inhibiting the formation of carbon and / or coke from a carbon-containing reactive gas stream on the permeate side of an oxygen ion transport membrane, or for increasing the oxygen partial pressure thereon, by separating a feed gas stream to form an oxygen-depleted gas stream on the retentate side and a gas stream containing oxygen reaction products on the permeate side. The permeate side is purged with the carbon-containing reactive gas stream, and at least a portion of the exhaust gas stream formed from the reaction of the reactive gas stream with the separated oxygen is recirculated to purge the permeate side.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com