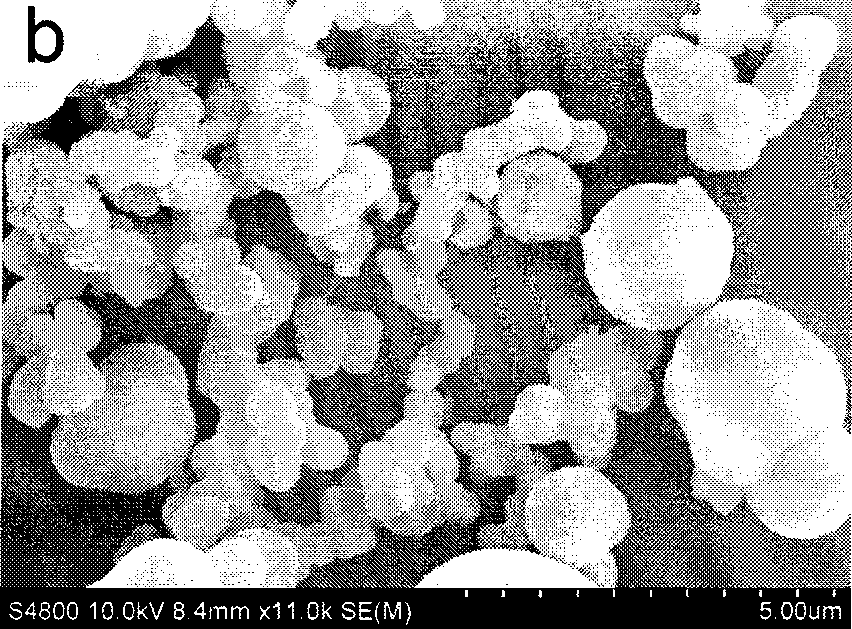Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
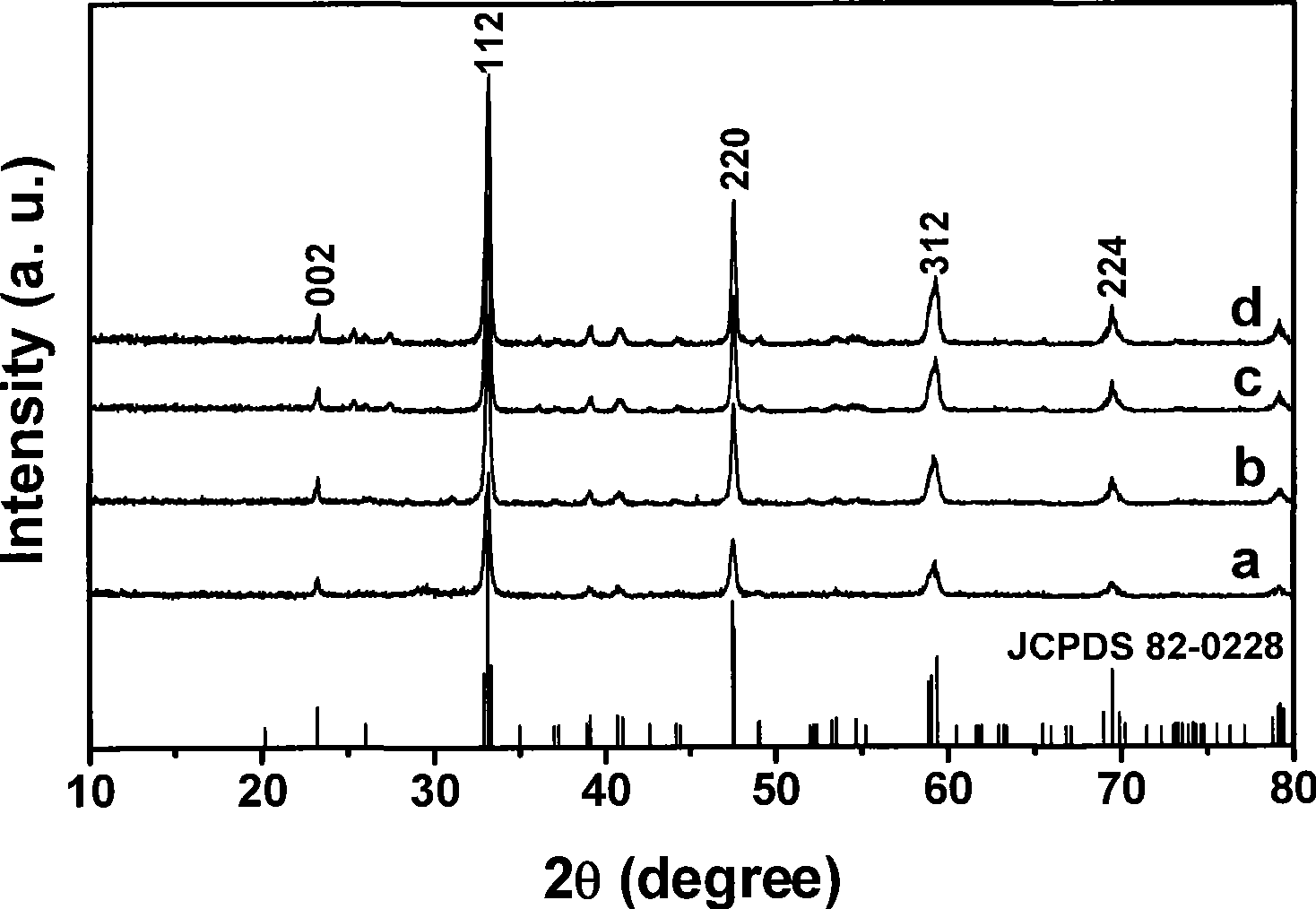
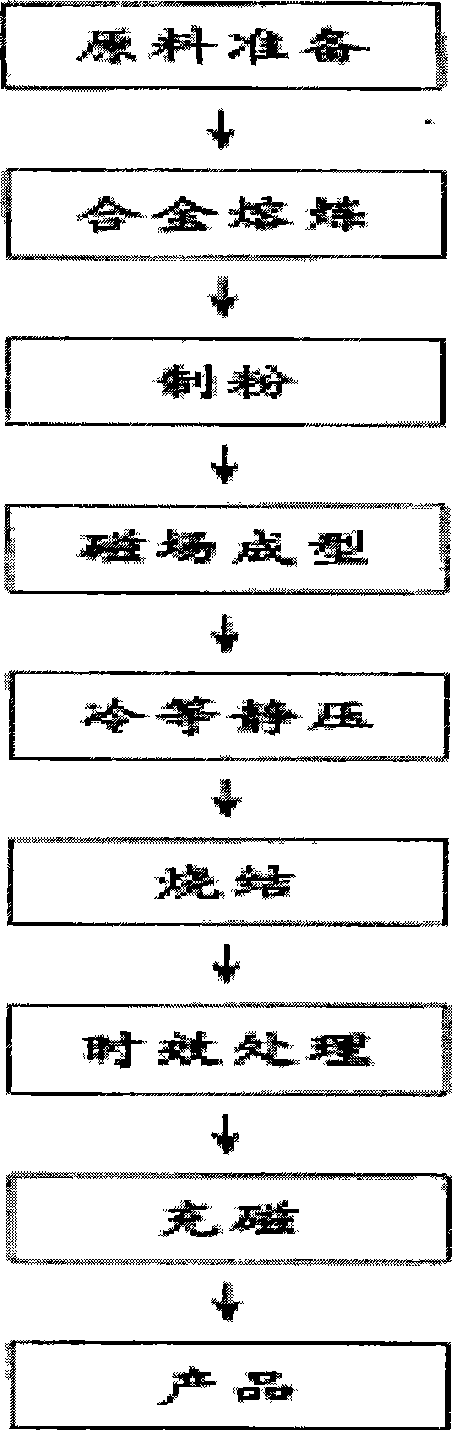
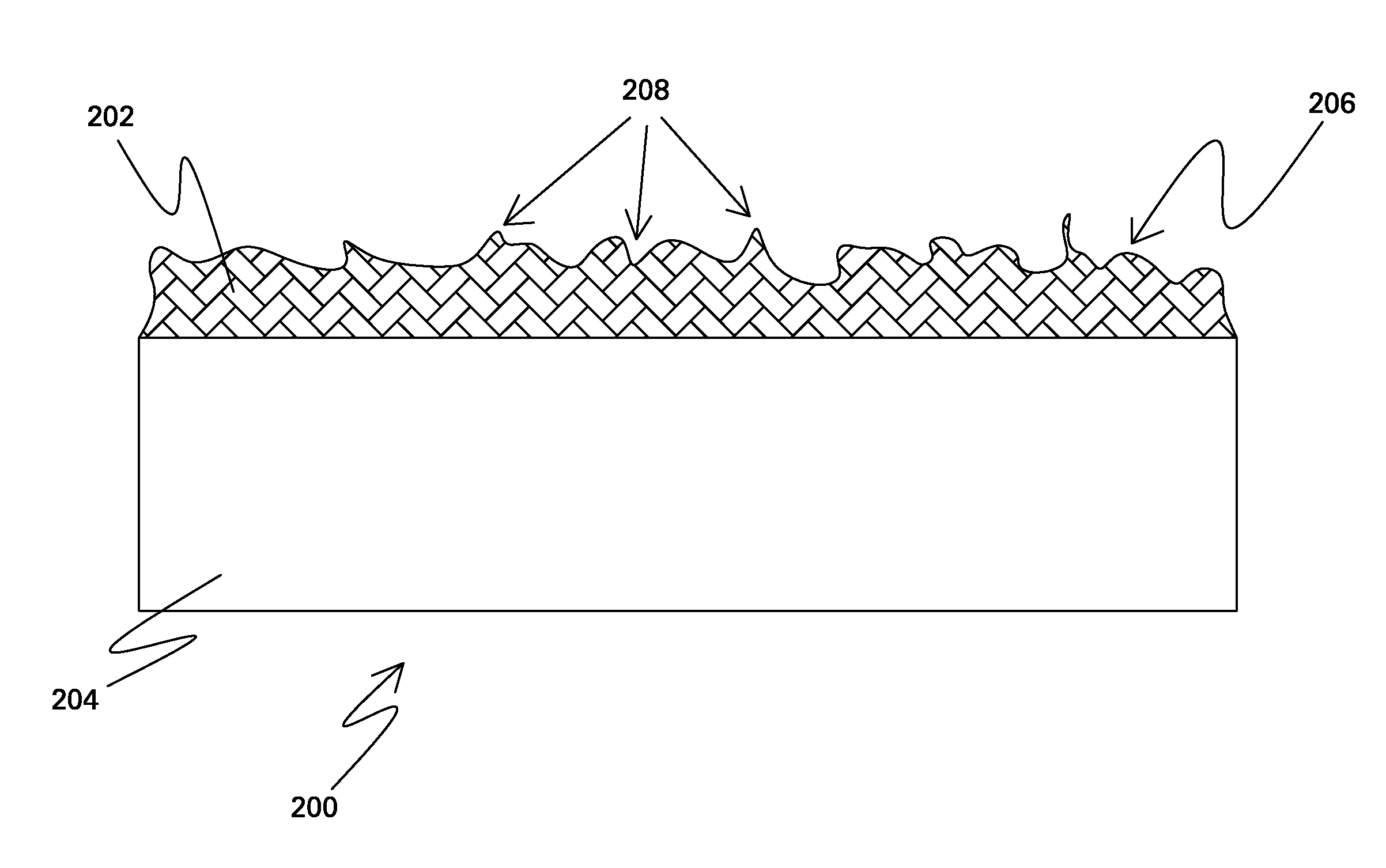
2323 results about "Praseodymium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Praseodymium is a chemical element with the symbol Pr and atomic number 59. It is the third member of the lanthanide series and is traditionally considered to be one of the rare-earth metals. Praseodymium is a soft, silvery, malleable and ductile metal, valued for its magnetic, electrical, chemical, and optical properties. It is too reactive to be found in native form, and pure praseodymium metal slowly develops a green oxide coating when exposed to air.
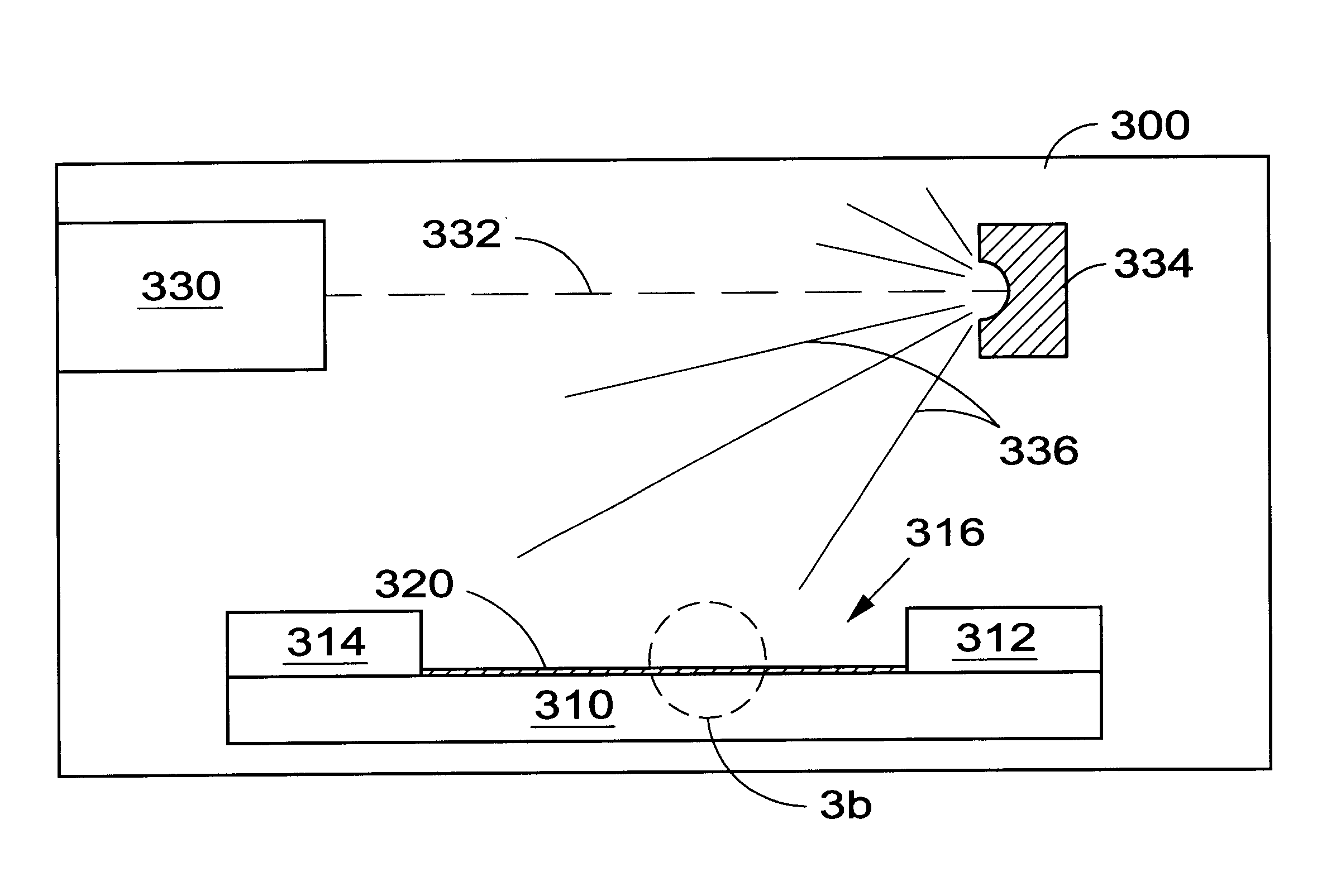
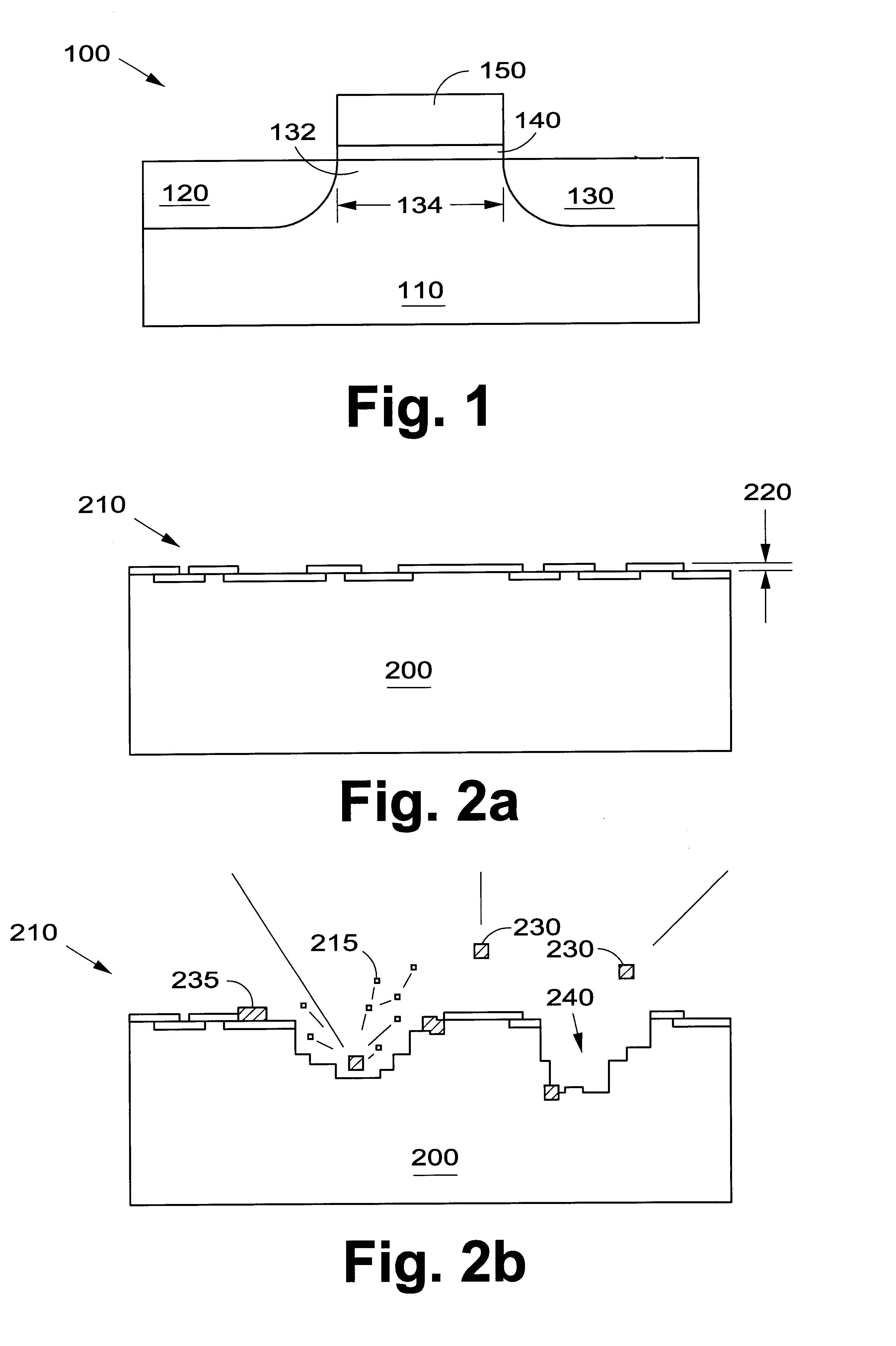
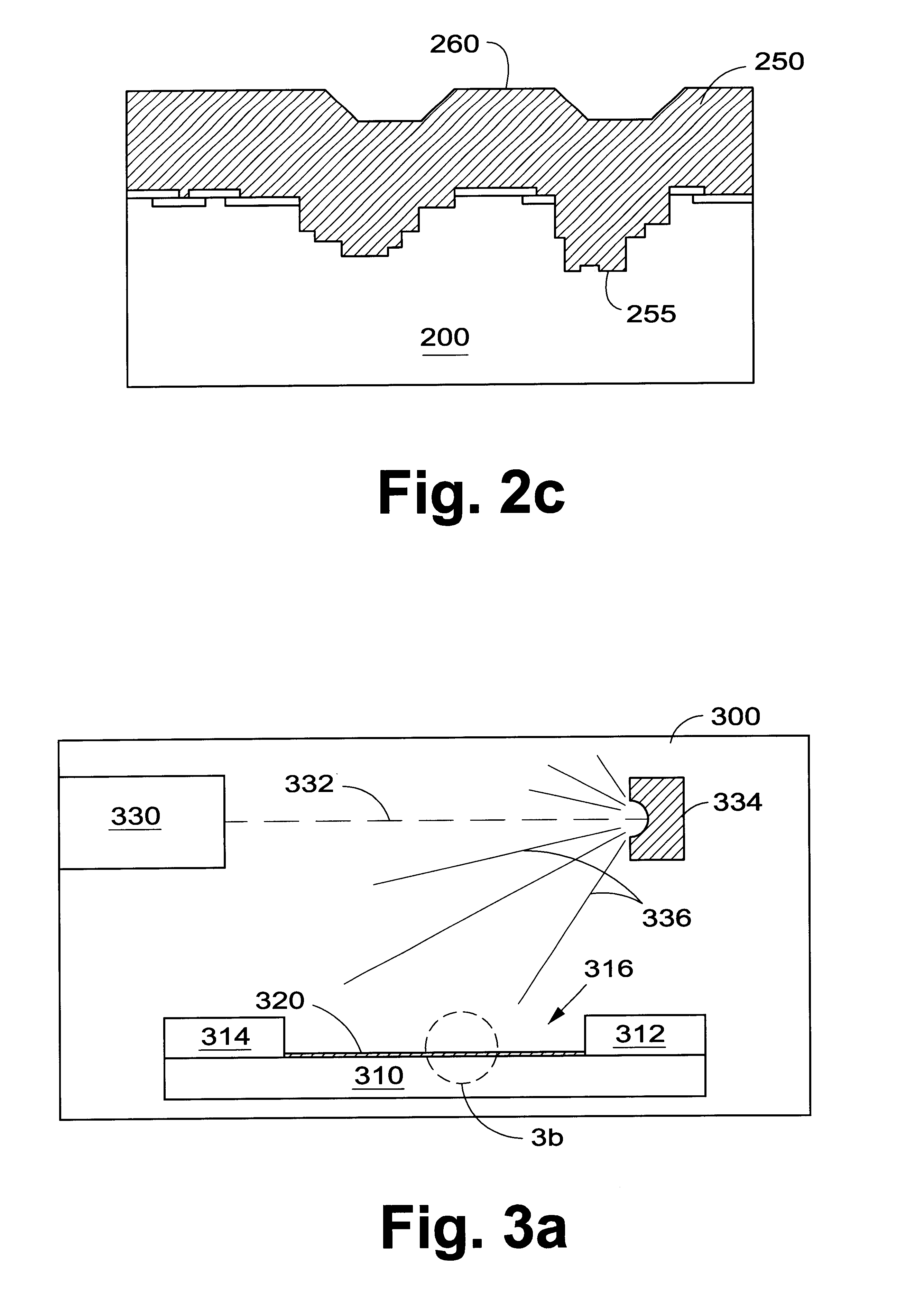
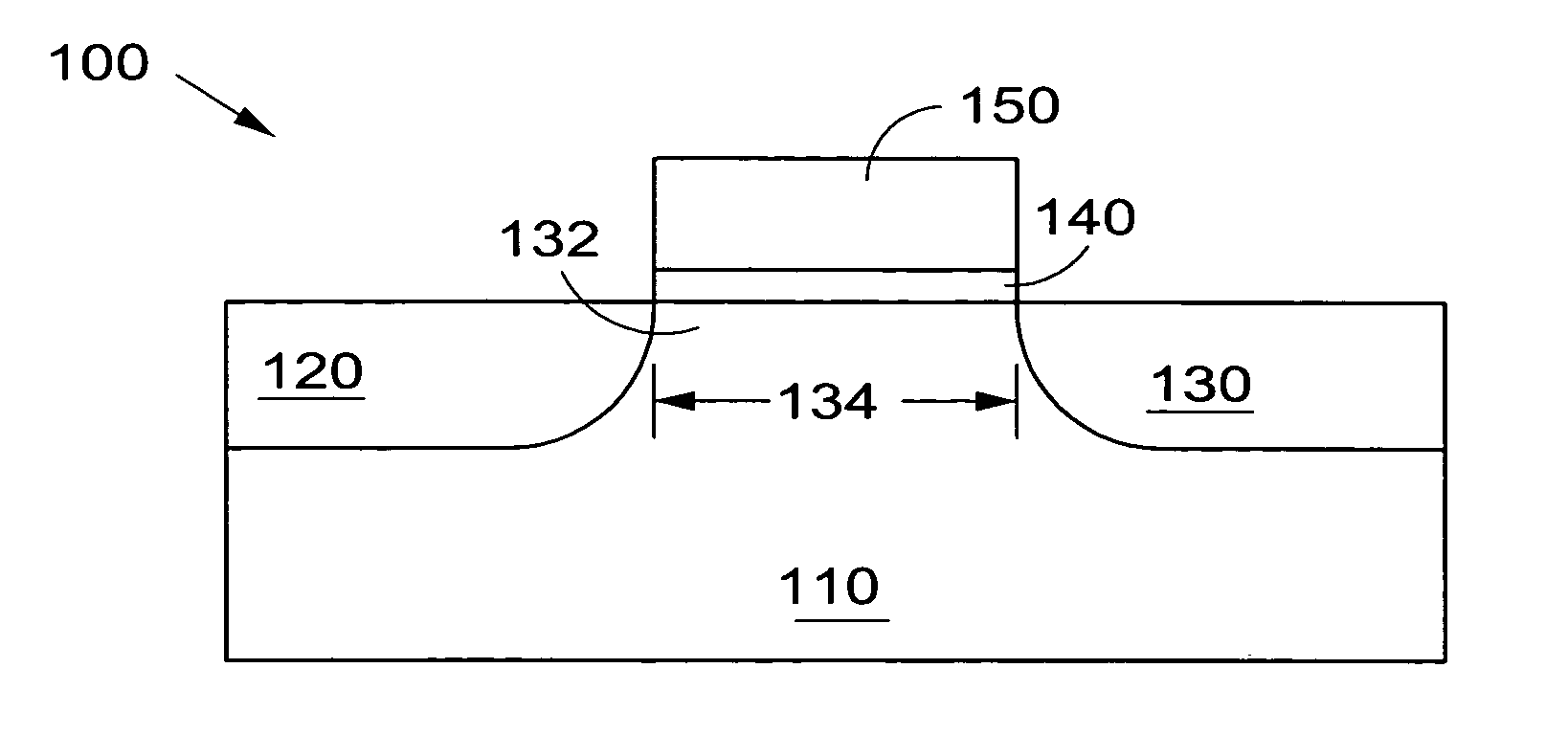
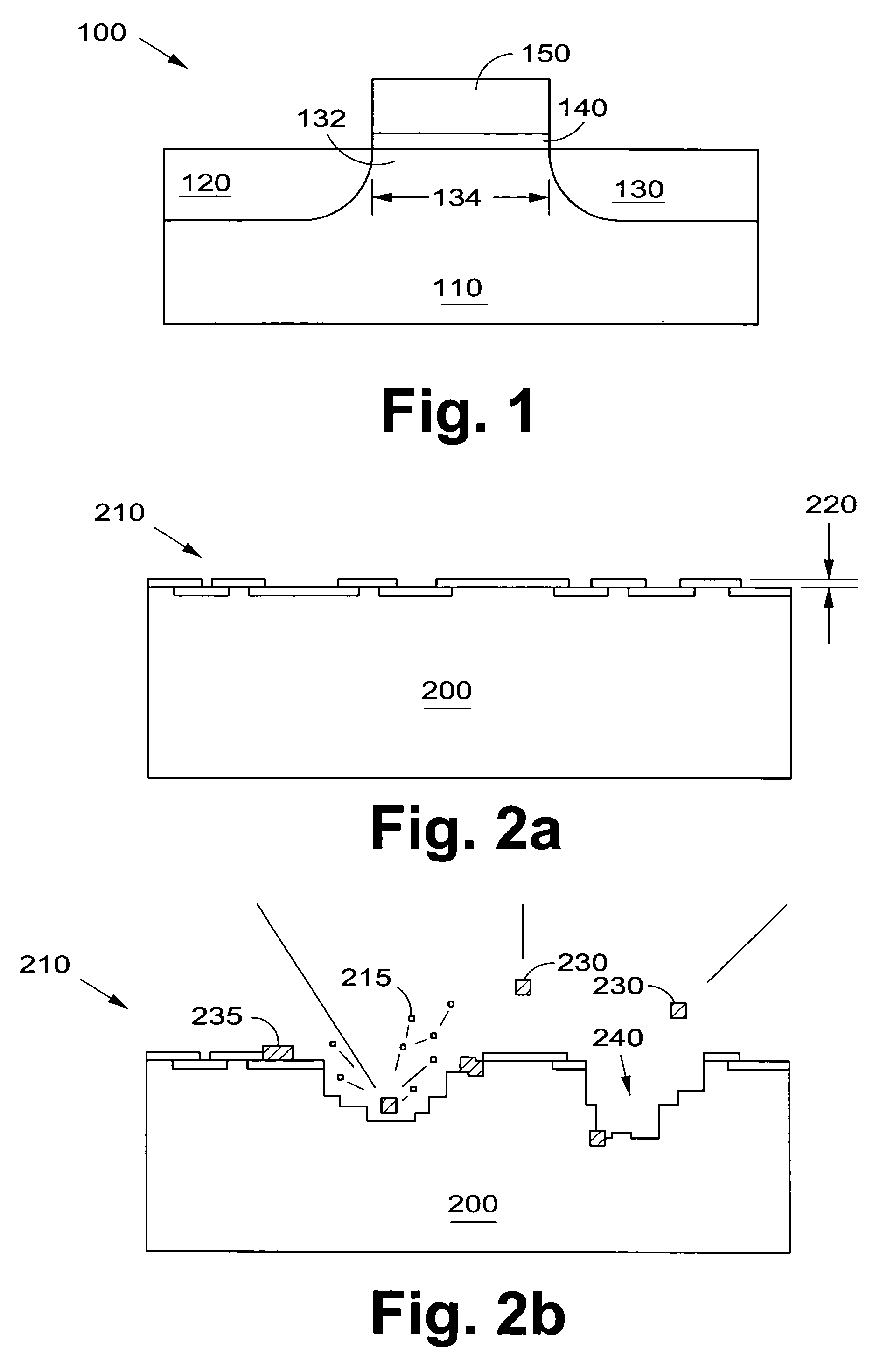
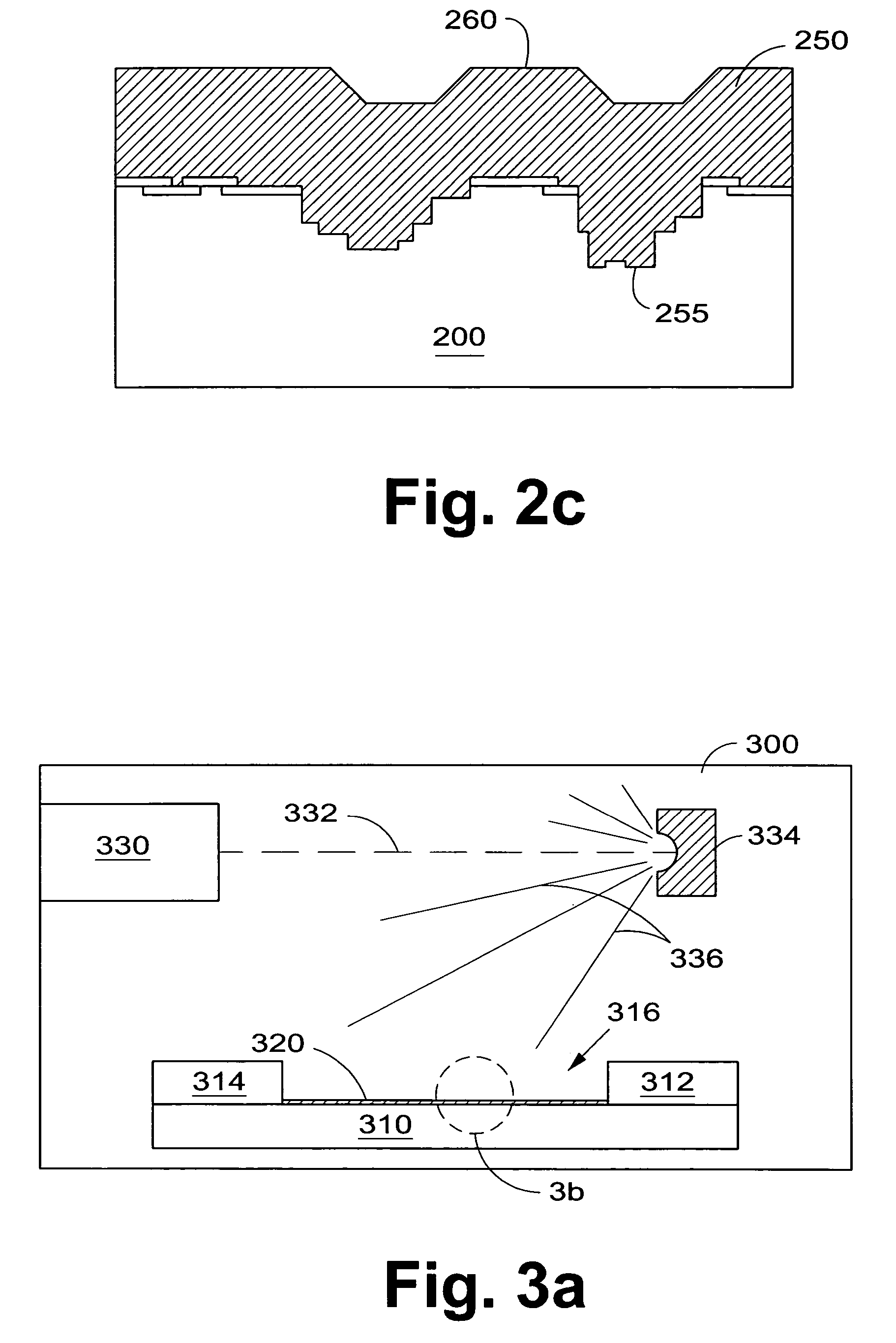
Low-temperature grown high-quality ultra-thin praseodymium gate dielectrics
InactiveUS6900122B2Inhibition formationSave budgetVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingEquivalent oxide thicknessGate dielectric
A praseodymium (Pr) gate oxide and method of fabricating same that produces a high-quality and ultra-thin equivalent oxide thickness as compared to conventional SiO2 gate oxides are provided. The Pr gate oxide is thermodynamically stable so that the oxide reacts minimally with a silicon substrate or other structures during any later high temperature processing stages. The process shown is performed at lower temperatures than the prior art, which further inhibits reactions with the silicon substrate or other structures. Using a thermal evaporation technique to deposit a Pr layer to be oxidized, the underlying substrate surface smoothness is preserved, thus providing improved and more consistent electrical properties in the resulting gate oxide.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
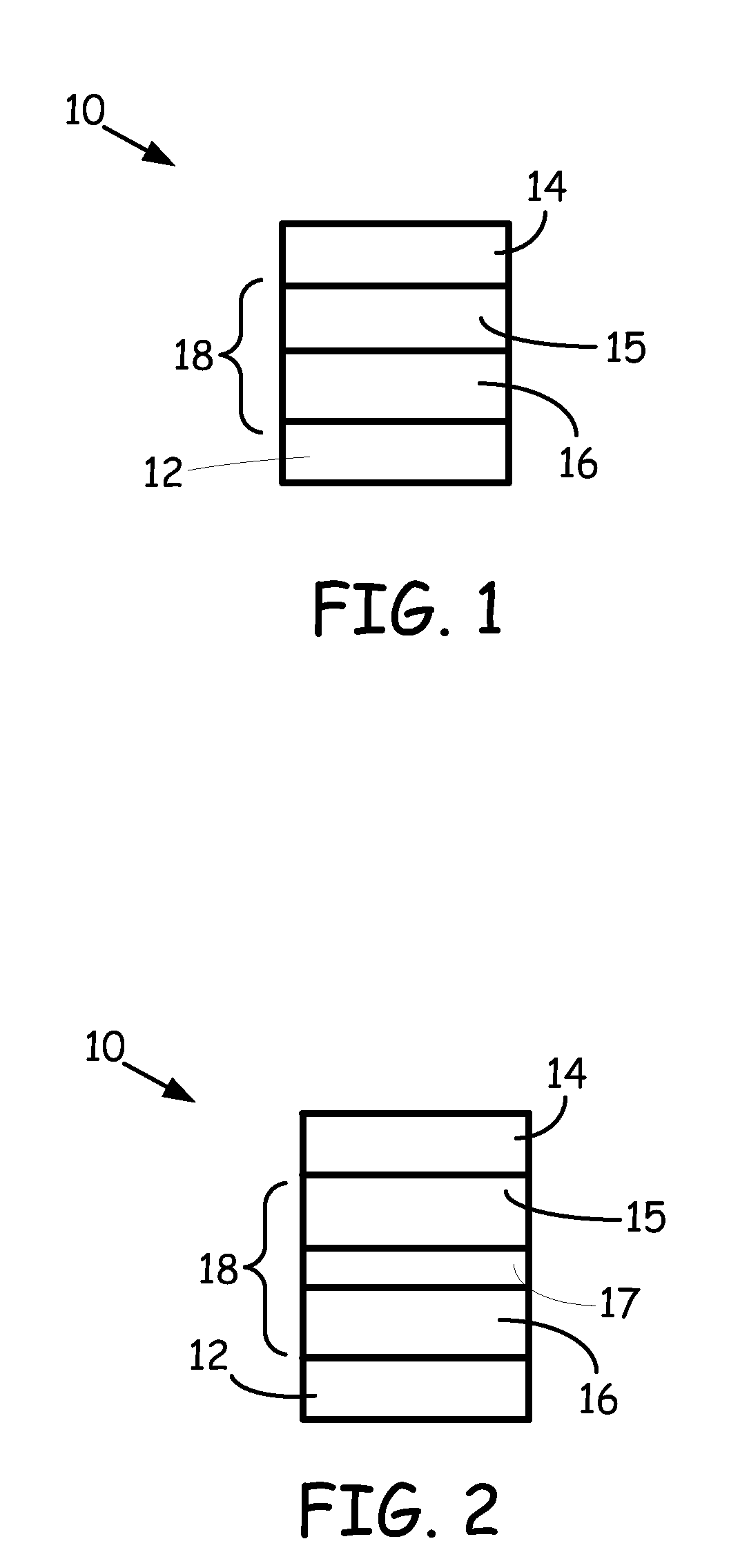
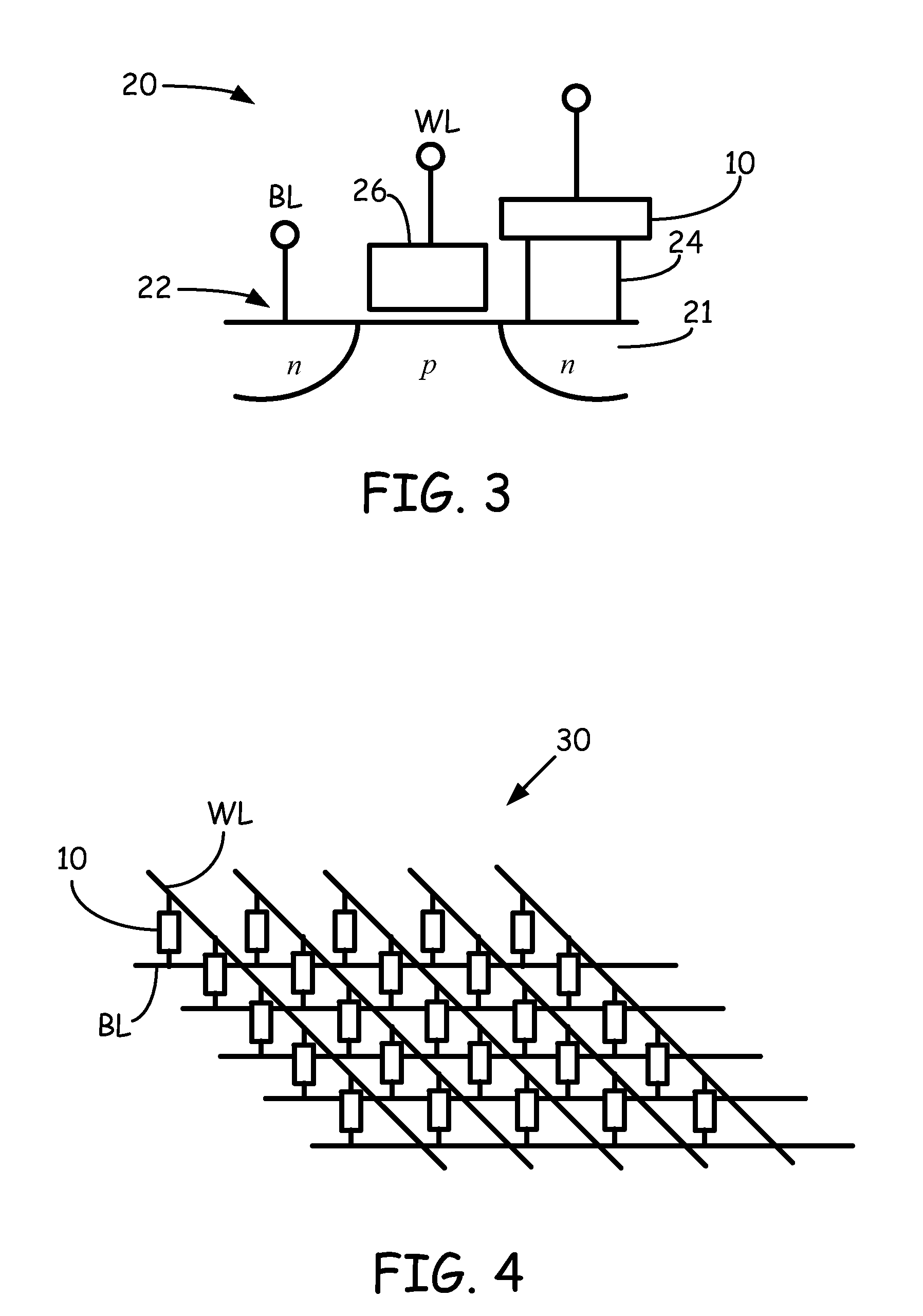
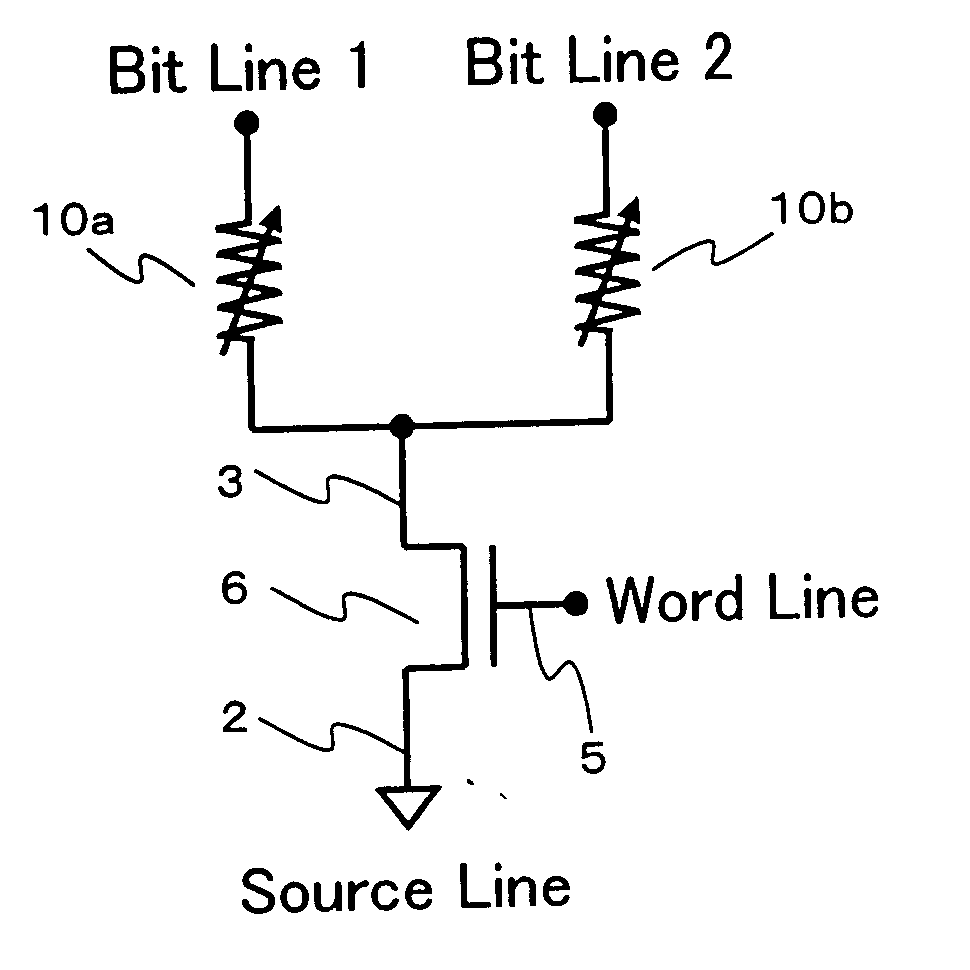
Non-volatile resistive sense memory
ActiveUS20110006275A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsManganese oxide
A resistive sense memory cell includes a layer of crystalline praseodymium calcium manganese oxide and a layer of amorphous praseodymium calcium manganese oxide disposed on the layer of crystalline praseodymium calcium manganese oxide forming a resistive sense memory stack. A first and second electrode are separated by the resistive sense memory stack. The resistive sense memory cell can further include an oxygen diffusion barrier layer separating the layer of crystalline praseodymium calcium manganese oxide from the layer of amorphous praseodymium calcium manganese oxide a layer. Methods include depositing an amorphous praseodymium calcium manganese oxide disposed on the layer of crystalline praseodymium calcium manganese oxide forming a resistive sense memory stack.
Owner:EVERSPIN TECHNOLOGIES
Polymer nanocomposite implants with enhanced transparency and mechanical properties for administration within humans or animals
Polymer nanocomposite implants with nanofillers and additives are described. The nanofillers described can be any composition with the preferred composition being those composing barium, bismuth, cerium, dysprosium, europium, gadolinium, hafnium, indium, lanthanum, neodymium, niobium, praseodymium, strontium, tantalum, tin, tungsten, ytterbium, yttrium, zinc, and zirconium. The additives can be of any composition with the preferred form being inorganic nanopowders comprising aluminum, calcium, gallium, iron, lithium, magnesium, silicon, sodium, strontium, titanium. Such nanocomposites are particularly useful as materials for biological use in applications such as drug delivery, biomed devices, bone or dental implants.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
High-quality praseodymium gate dielectrics
InactiveUS6979855B2Inhibition formationSave budgetTransistorVacuum evaporation coatingEquivalent oxide thicknessGate dielectric
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Layered thermal barrier coatings containing lanthanide series oxides for improved resistance to CMAS degradation
InactiveUS20070160859A1Avoid damageElimination of expensiveBlade accessoriesEfficient propulsion technologiesReaction layerCerium
A coating applied as a two layer system. The outer layer is an oxide of a group IV metal selected from the group consisting of zirconium oxide, hafnium oxide and combinations thereof, which are doped with an effective amount of a lanthanum series oxide. These metal oxides doped with a lanthanum series addition comprises a high weight percentage of the outer coating. As used herein, lanthanum series means an element selected from the group consisting of lanthanum (La), cerium (Ce), praseodymium (Pr), neodymium (Nd), promethium (Pm), samarium (Sm), europium (Eu), gadolinium (Gd), terbium (Tb), dysprosium (Dy), holmium (Ho), erbium (Er), thulium (Tm), ytterbium (Yb), lutetium (Lu) and combinations thereof, and lanthanum series oxides are oxides of these elements. When the zirconium oxide is doped with an effective amount of a lanthanum series oxide, a dense reaction layer is formed at the interface of the outer layer of TBC and the CMAS. This dense reaction layer prevents CMAS infiltration below it. The second layer, or inner layer underlying the outer layer, comprises a layer of partially stabilized zirconium oxide.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
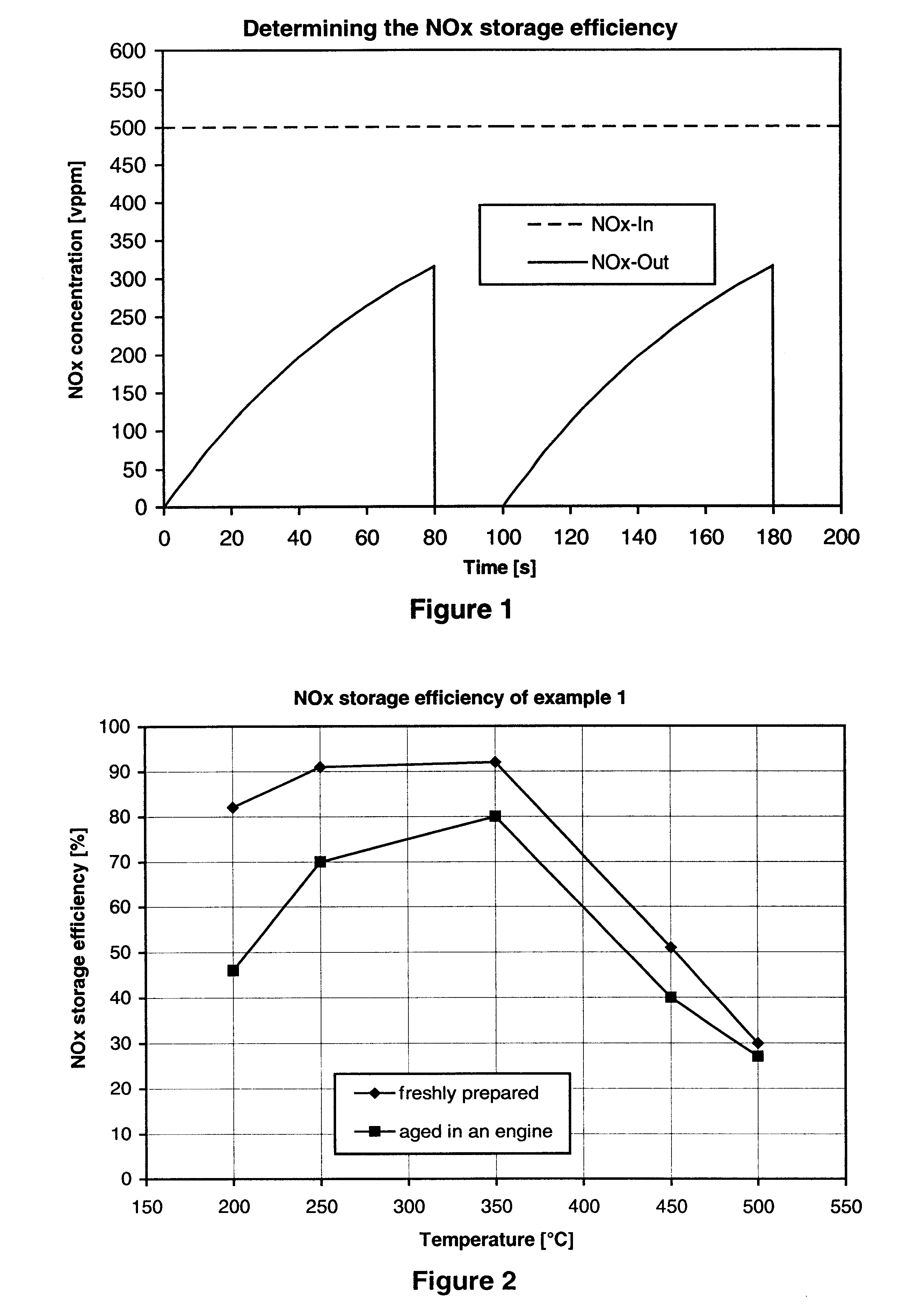
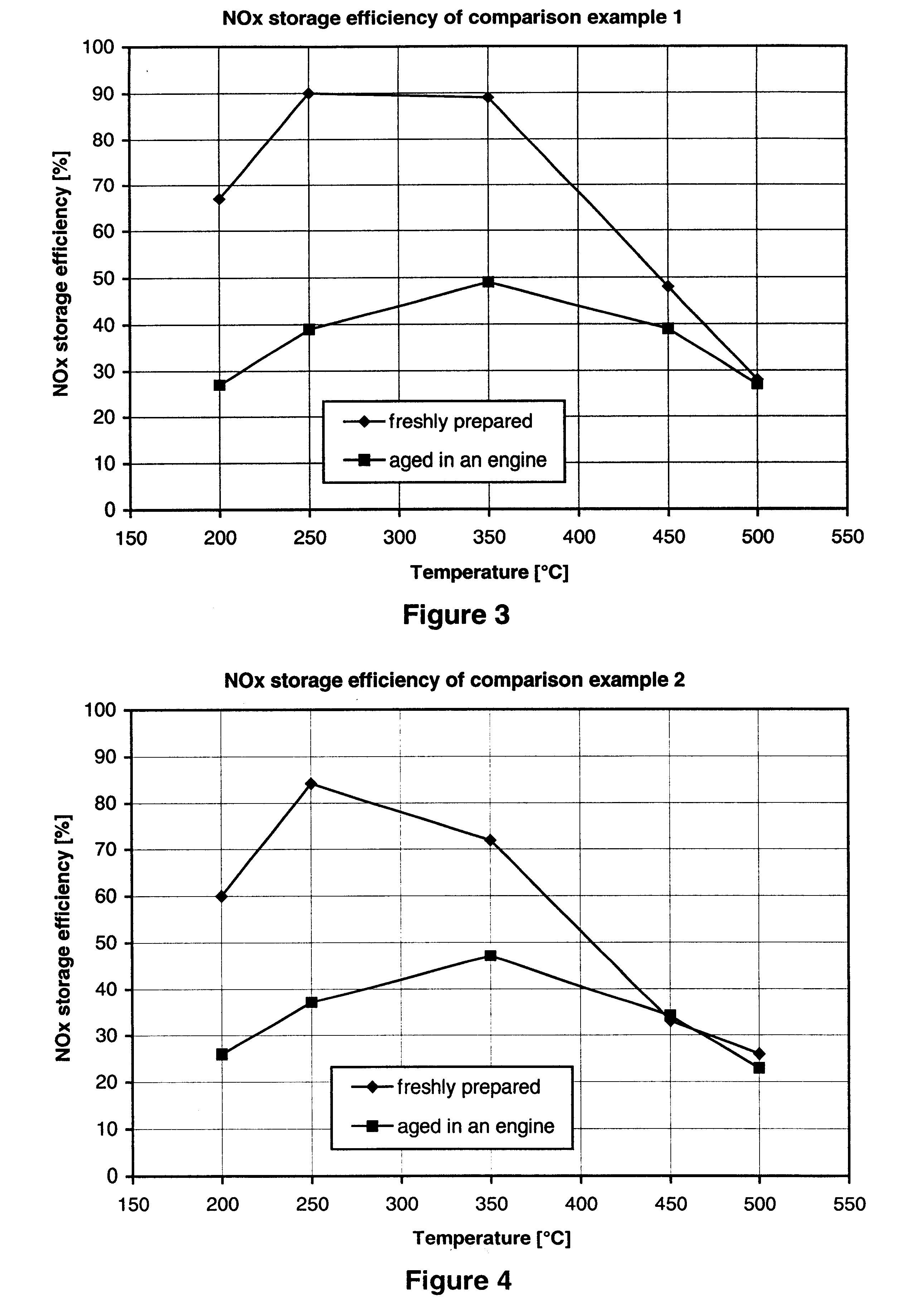
Nitrogen oxide storage material and nitrogen oxide storing catalyst prepared therefrom
InactiveUS6350421B1Determine efficiencyNitrogen compoundsExhaust apparatusAlkaline earth metalCuprate
A nitrogen oxide storage material is disclosed which contains at least one storage component for nitrogen oxides in the form of an oxide, mixed oxide, carbonate or hydroxide of the alkaline earth metals magnesium, calcium, strontium and barium and the alkali metals potassium and caesium on a high surface area support material. The support material can be doped cerium oxide, cerium / zirconium mixed oxide, calcium titanate, strontium titanate, barium titanate, barium stannate, barium zirconate, magnesium oxide, lanthanum oxide, praseodymium oxide, samarium oxide, neodymium oxide, yttrium oxide, zirconium silicate, yttrium barium cuprate, lead titanate, tin titanate, bismuth titanate, lanthanum cobaltate, lanthanum manganate and barium cuprate or mixtures thereof.
Owner:DMC2 DEGUSSA METALS +1
High performance lithium ion battery anode material lithium manganate and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a high performance lithium ion battery anode material lithium manganate and a preparation method of the material. The lithium manganate is a doped lithium manganate LiMn2-yXy04 which is doped with one kind or a plurality of other metal elements X, wherein X element is at least one kind selected form the group of aluminium, lithium, fluorine, silver, copper, chromium, zinc, titanium, bismuth, germanium, gallium, zirconium, stannum, silicon, cobalt, nickel, vanadium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium and rare earth elements lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, promethium, samarium, europium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, thulium, ytterbium and lutetium, and y is larger than 0 but less than or equal to 0.11. The lithium ion battery anode material lithium manganate provided in the invention has extraordinary charge and discharge cycle performance both in the environments of normal temperature and high temperature. According to the invention, the preparation method of the material is a solid phase method, the operation is simple and controllable and the cost is low so that it is easy to realize large-scale productions.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
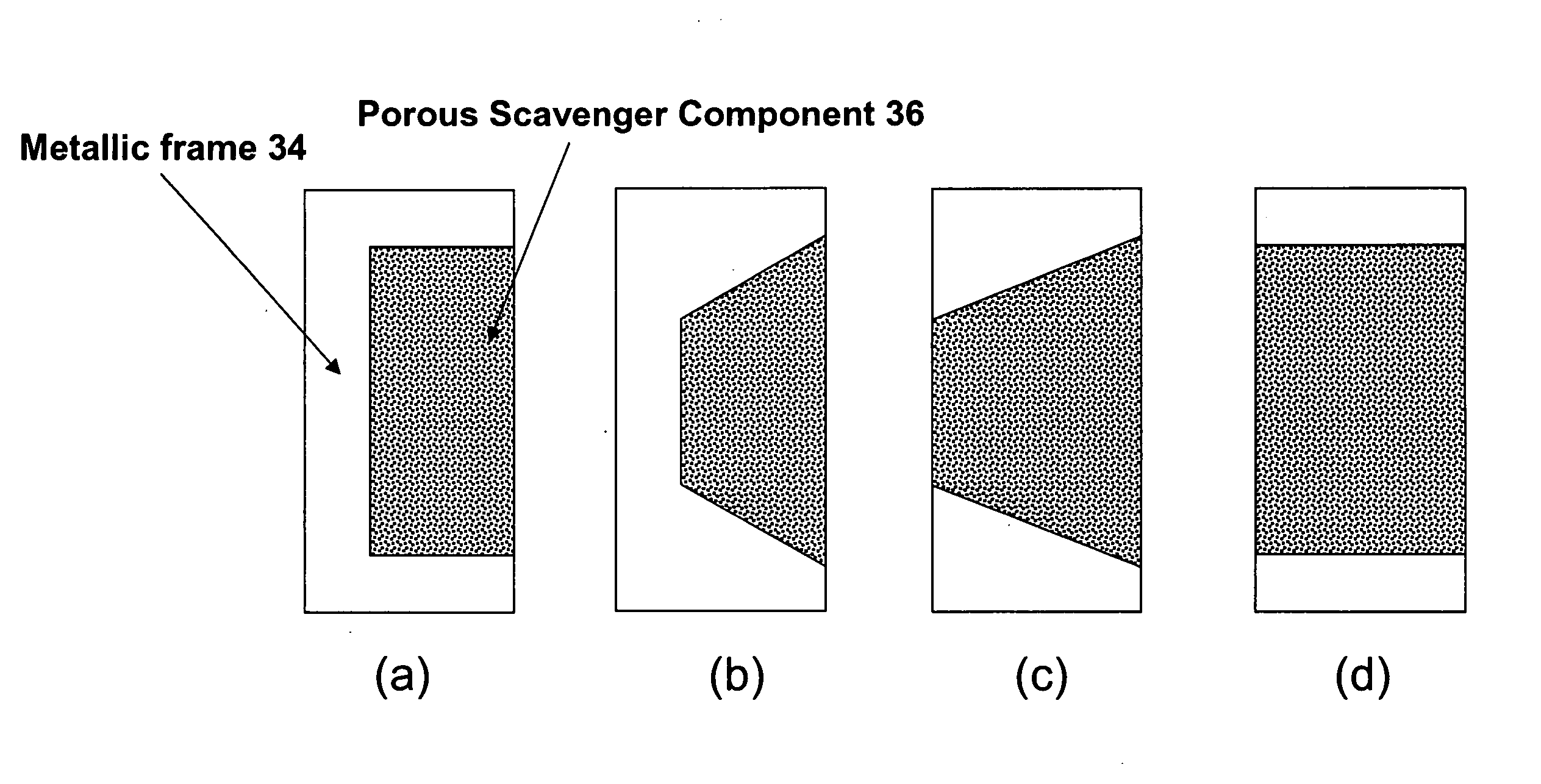
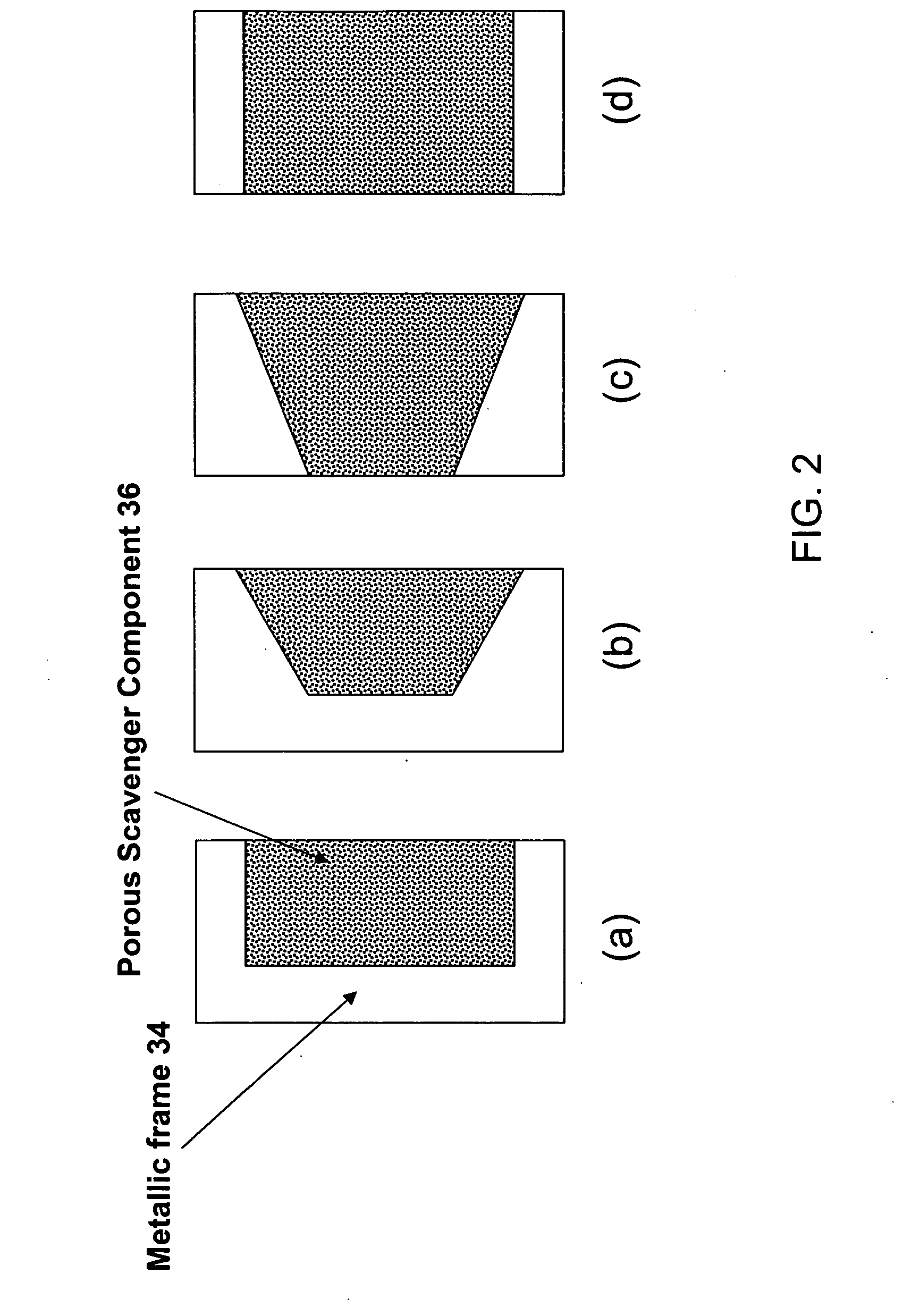
Photomask assembly incorporating a metal/scavenger pellicle frame
A photomask assembly is disclosed having a photomask substrate and a composite pellicle frame that includes both a metallic frame component and a scavenger component. The metallic frame component has a cross-sectional thickness of at least 100 micrometers in all directions, and the volume percentage of the scavenger component relative to the overall volume of the composite frame is in the range of 0.1 to 95%. The scavenger component has a gas permeability to oxygen or nitrogen greater than about 10 ml·mm / cm2·min·MPa, an average pore size between 0.001 and 10 micrometers, and a pore surface area greater than 10 m2 / g. This configuration enables the pellicle frame to have sufficient strength to withstand stresses encountered during normal use, yet also to have the capability of scavenging impurity molecules from the space adjacent to the photomask substrate. In a separate and independent feature of the invention, the scavenger component comprises at least one metal oxide selected from the group consisting of oxides of aluminum, boron, cerium, cobalt, copper, erbium, hafnium, lanthanum, neodymium, praseodymium, scandium, silicon, titanium, yttrium, zirconium, and mixtures thereof. Preferably, the metal oxide is an oxide of zirconium, yttrium, or mixtures thereof.
Owner:YAZAKI CORP
CO oxidation promoters for use in FCC processes
InactiveUS7045056B2Improved CO oxidation promotion activityCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsLanthanideCopper
A composition for controlling CO and NOx emissions during FCC processes comprises (i) acidic oxide support, (ii) cerium oxide, (iii) lanthanide oxide other than ceria such as praseodymium oxide (iv), optionally, oxide of a metal from Groups Ib and IIb such as copper, silver and zinc and (v) precious metal such as Pt and Pd.
Owner:ENGELHARD CORP
Rare-earth doping modified lithium ion battery ternary positive electrode material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103855384AEase of industrial productionImprove charge and discharge efficiencyCell electrodesSecondary cellsCarbon compositesNickel salt
The invention relates to a rare-earth doping modified lithium ion battery ternary positive electrode material and a preparation method of the rare-earth doping modified lithium ion battery ternary positive electrode material. The chemical general formula of the material is as follows: LiNiaCo<1-a-b>MnbRxO2 / M, wherein a is more than 0 and less than 1, b is more than 0 and less than 1, (1-a-b) is more than 0 and less than 1, x is more than 0.005 and less than 0.1, R is one or more of rare-earth lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium and samarium, and M is a composite cladding layer of oxide of aluminum, titanium or magnesium and carbon. The soluble metal nickel salt, cobalt salt, manganese salt and rare-earth compound are mixed to prepare a mixed salt solution, the mixed salt solution is reacted with a mixed alkaline solution prepared by mixing NaOH and ammonium hydroxide, after the reaction solution is filtered, washed and dried, the obtained product is uniformly mixed with lithium salt powder to be ball milled, then the mixture is calcined at the high temperature and coated with the composite cladding layer of the aluminum, titanium or magnesium oxide and carbon, and finally the calcined mixture is calcined at a constant temperature to obtain the rare-earth doping modified lithium ion battery ternary positive electrode material. After doping the rare earth, the metal oxide and carbon composite cladding layer, which are cheap and easy to obtain, are adopted, so that the cycling performance and the rate performance can be improved, and the charging-discharging efficiency of the material also can be improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MEIDARUI NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
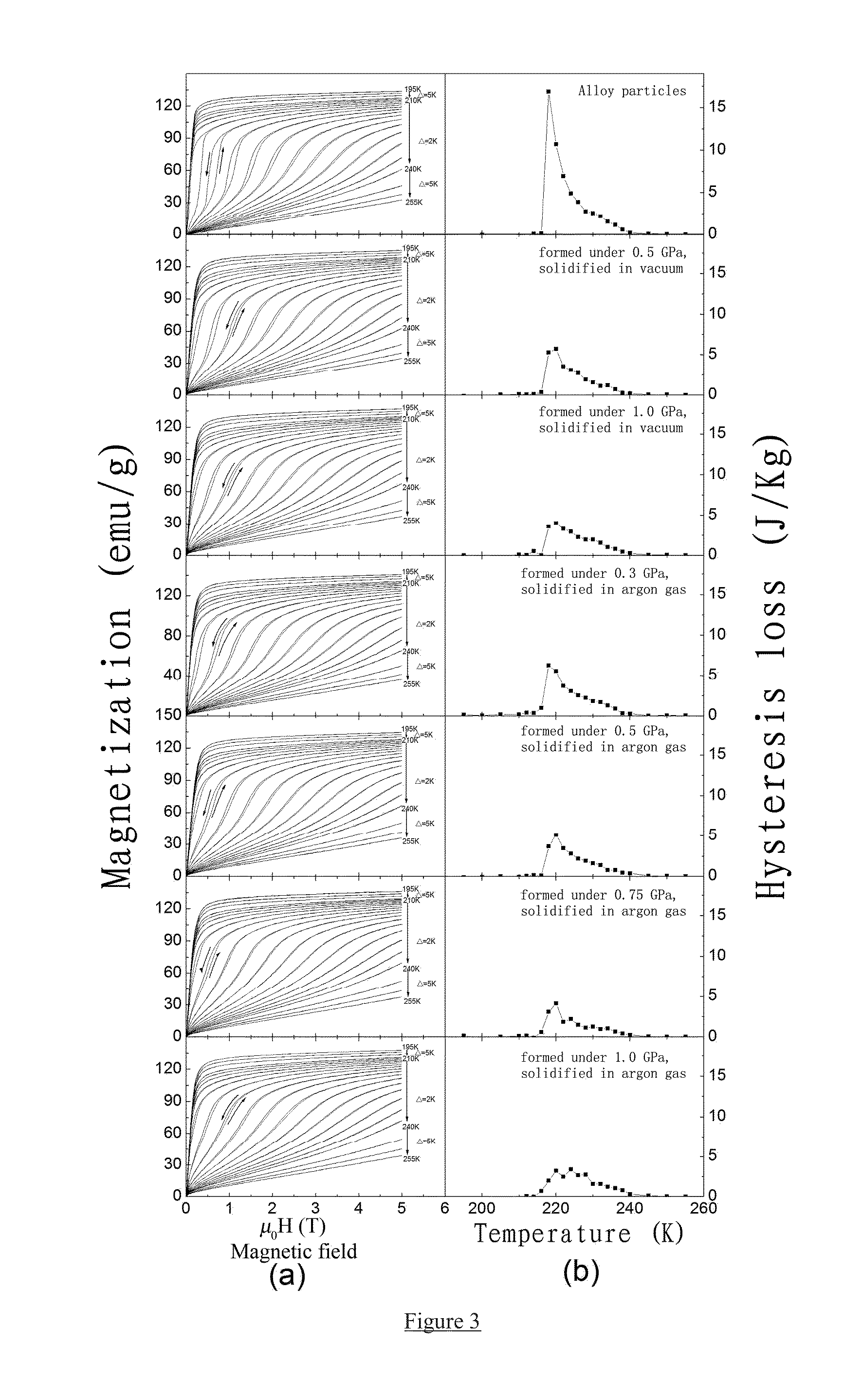
BONDED La(Fe,Si)13-BASED MAGNETOCALORIC MATERIAL AND PREPARATION AND USE THEREOF
InactiveUS20150047371A1Low priceEasy to operateInorganic material magnetismMachines using electric/magnetic effectsCeriumCobalt
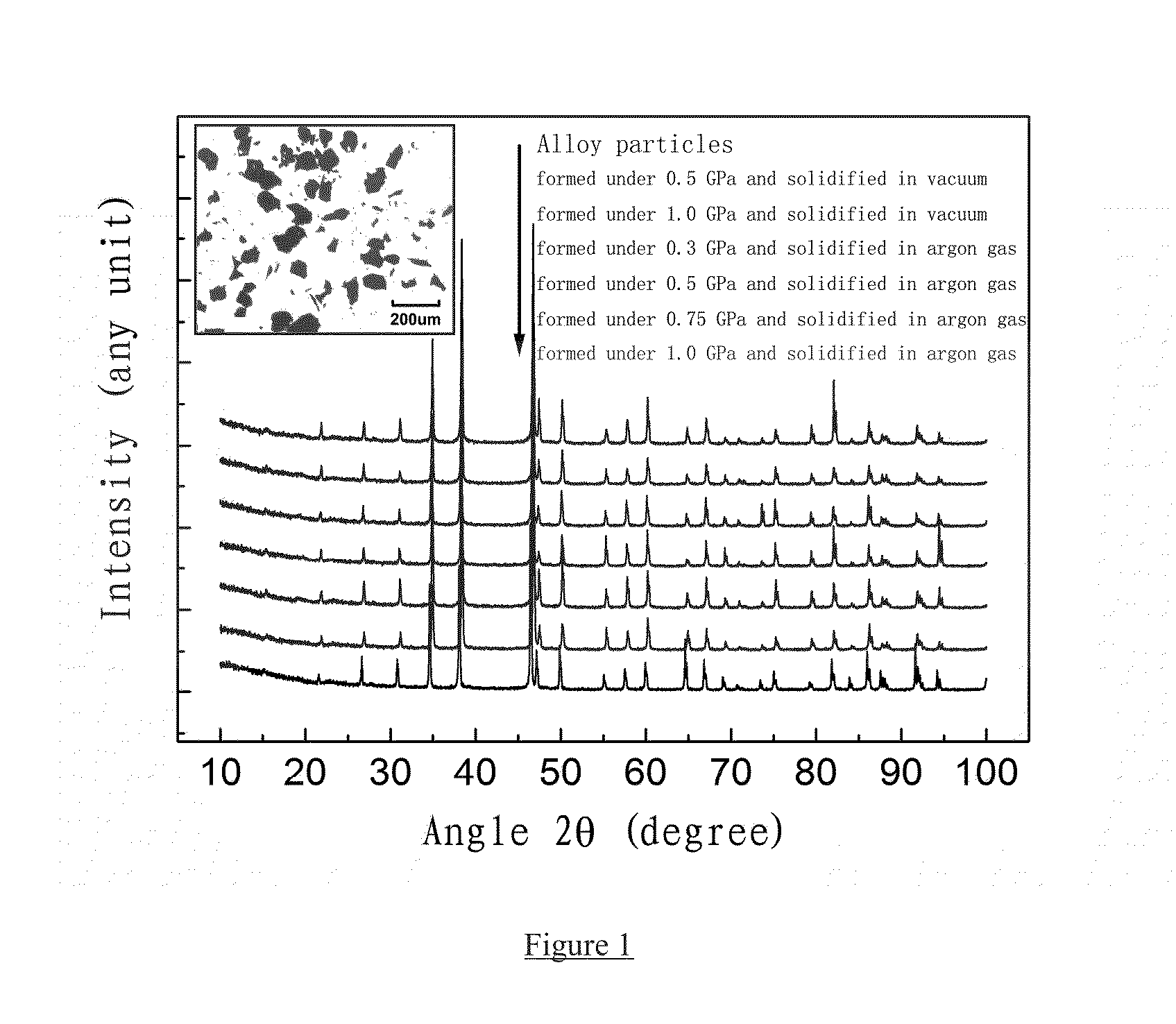
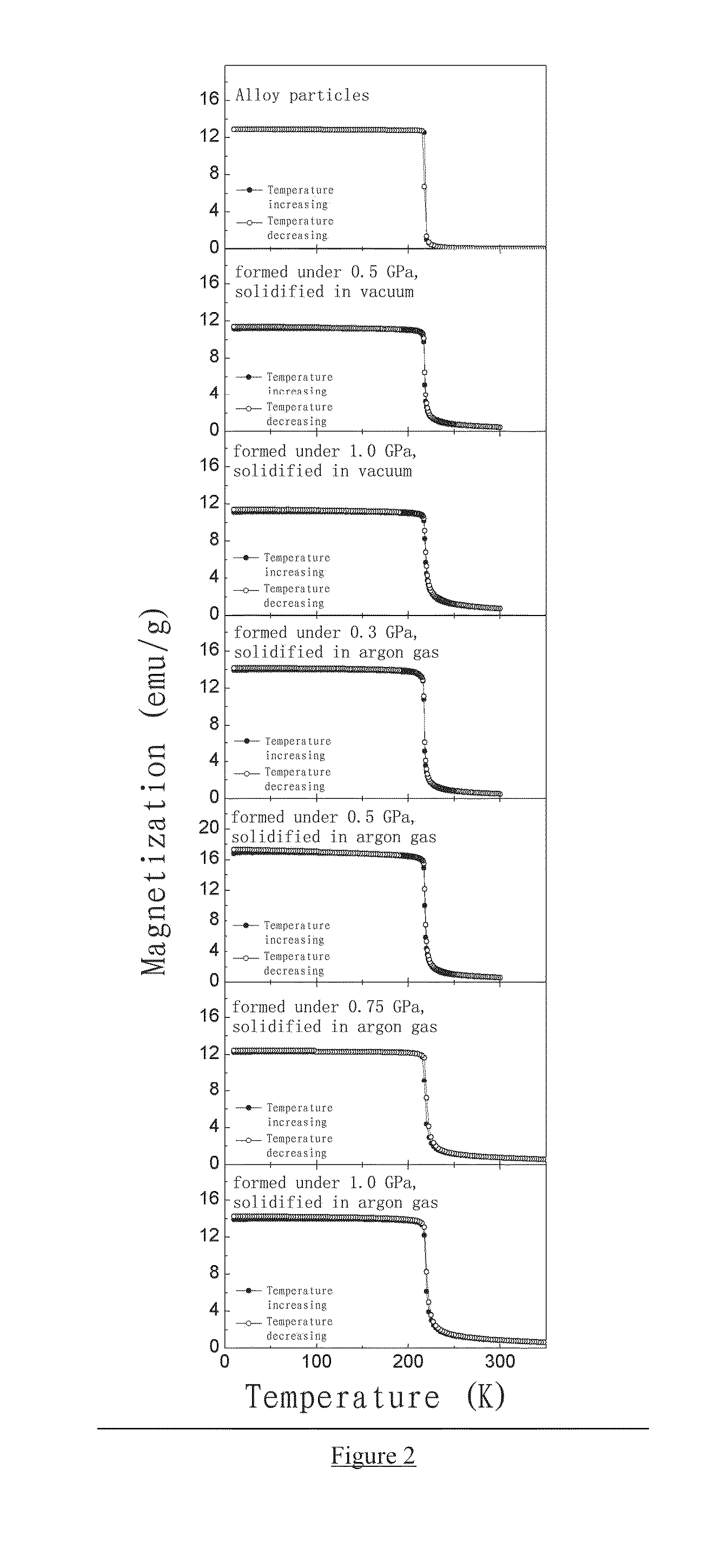
Provided is a high-strength, bonded La(Fe, Si)13-based magnetocaloric material, as well as a preparation method and use thereof. The magnetocaloric material comprises magnetocaloric alloy particles and an adhesive agent, wherein the particle size of the magnetocaloric alloy particles is less than or equal to 800 μm and are bonded into a massive material by the adhesive agent; the magnetocaloric alloy particle has a NaZn13-type structure and is represented by a chemical formula of La1-xRx(Fe1-p-qCopMnq)13-ySiyAα, wherein R is one or more selected from elements cerium (Ce), praseodymium (Pr) and neodymium (Nd), A is one or more selected from elements C, H and B, x is in the range of 0≦x≦0.5, y is in the range of 0.8≦y≦2, p is in the range of 0≦p≦0.2, q is in the range of 0≦q≦0.2, α is in the range of 0≦α≦3.0. Using a bonding and thermosetting method, and by means of adjusting the forming pressure, thermosetting temperature, and thermosetting atmosphere, etc., a high-strength, bonded La(Fe, Si)13-based magnetocaloric material can be obtained, which overcomes the frangibility, the intrinsic property, of the magnetocaloric material. At the same time, the magnetic entropy change remains substantially the same, as compared with that before the bonding. The magnetic hysteresis loss declines as the forming pressure increases. And the effective refrigerating capacity, after the maximum loss being deducted, remains unchanged or increases.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
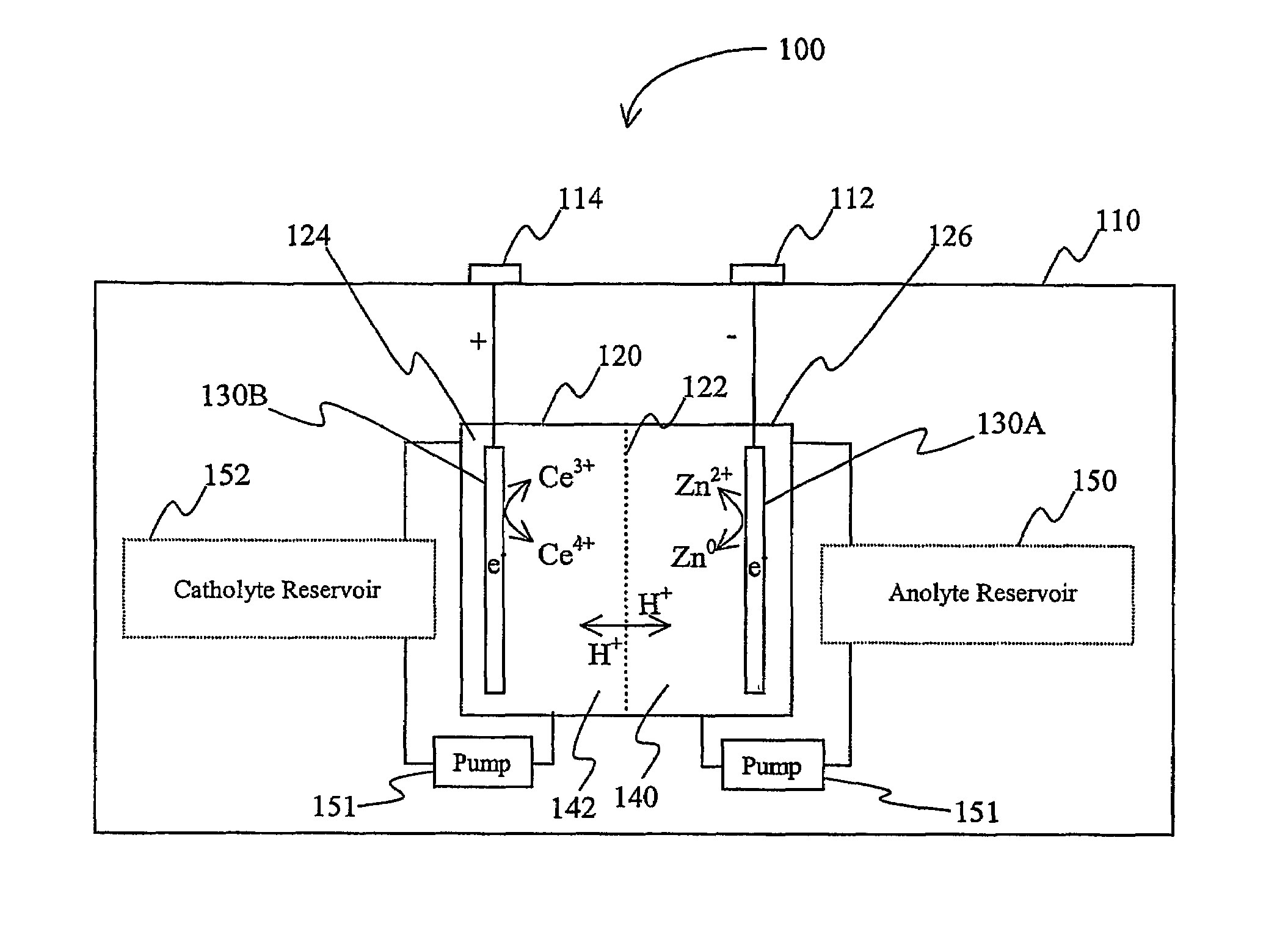
Lanthanide batteries
InactiveUS7252905B2Wide capacity rangeLarge capacityAlkaline accumulatorsSolid electrolyte cellsLanthanideCerium
A battery (100) comprises an electrolyte in which a lanthanide and zinc form a redox pair. Preferred electrolytes are acid electrolytes, and most preferably comprise methane sulfonic acid, and it is further contemplated that suitable electrolytes may include at least two lanthanides. Contemplated lanthanides include cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, terbium, and dysprosium, and further contemplate lanthanides are samarium, europium, thulium and ytterbium.
Owner:PLURION LTD
Ceramic bonding composition, method of making, and article of manufacture incorporating the same
A ceramic bonding composition comprises a first oxide and at least a second oxide having a formula of Me2O3; wherein the first oxide is selected from the group consisting of aluminum oxide, scandium oxide, and combinations thereof; Me is selected from the group consisting of yttrium, lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, samarium, europium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, thulium, ytterbium, lutetium, and combinations thereof. The ceramic bonding composition can further comprise silica. An article of manufacture comprising at least two members attached together with the ceramic bonding composition.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Rare earth permanent magnet produced by applying abundant rare earth cerium (Ce) and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103123839AReduce production and sales balancePromote the balance of production and salesInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsRare-earth elementCost Controls
The invention discloses a rare earth permanent magnet produced by applying abundant rare earth cerium (Ce) and a preparation method of the rare earth permanent magnet produced by applying abundant rare earth Ce. Based on a double-alloy process, main phase alloy formula uses Ce to partly replace neodymium (Nd), an optimized composition design enables a main alloy to form Ce2Fe14B phase and Nd2Fe14B phase to a greatest extent, and therefore high intrinsic magnetic property is guaranteed. A brand new crystal boundary phase is prepared by a crystal boundary reconstitution technology, and high integral magnetic property and corrosion resistant property are guaranteed, and meanwhile a nanometer powder crystal modification method is supplemented, a micro organization structure of a magnet is optimized, crystal boundary distribution is improved, and the magnetic property and the corrosion resistant property are further improved. By applying abundant rare earth cerium, cost is effectively reduced, and meanwhile balance between production and marketing is promoted. Praseodymium (Pr), Nd, and the like are chosen to form a hard magnetic shell layer of a main phase boundary in a composition design of crystal phase auxiliary alloy at the same time, compared high price heavy rare earth elements of dysprosium (Dy) and terbium (Tb) with the elements, and cost control can be further achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Transformation liquid for preparation of corrosion-resistant oxidation film on aluminium alloy surface and method of use thereof
InactiveCN101139708AImprove corrosion resistanceGood adhesionMetallic material coating processesHigh resistancePersulfate
The invention discloses a transforming solution for preparing anti-corrosion compound oxidation film on an aluminum alloy surface and a using method for the oxidation film. The invention is characterized in that, the transforming solution is a film-forming promoter containing rare-earth salt (nitrate or sulfate and compound salt of cerium, praseodymium, and neodymium), such compound oxidant as radical of permanganate, nitrate and perchlorate, etc., film-forming promoter of vanadium salt and strontium salt, etc.; the transforming solution contains no sexavalent chromium, is environmental friendly; the reaction speed is improved by the compound oxidant and the film-forming promoter, no heating is needed for the chemical transforming, the treating time is 1-5 min. The invention can rapidly prepare under room temperature compound oxidation film comprising compound rare-earth oxide, alumina and manganese oxide with good resistance to corrosion on aluminum alloy surface. The treating solution from the invention is of rapid film-forming speed, simple process, even film layer, high resistance to corrosion, and low environmental pollution, etc.
Owner:陈东初 +2
Rare earth aluminum alloy, and method and device for preparing same
The invention discloses a rare earth aluminum alloy, and a method and a device for preparing the same. The alloy contains at least one rare earth metal of lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, thulium, lutetium, scandium and yttrium, the content of raw earth is 5 to 98 weight percent, and the balance is aluminum and inevitable impurities. The device for preparing the rare earth aluminum alloy is characterized in that: a) graphite serves as an electrolysis bath, a graphite plate is an anode, a tungsten bar is a cathode and a molybdenum crucible serves as a rare earth aluminum alloy receiver; b) the diameter of the tungsten bar is 30 to 55 mm; and c) the anode of the graphite consists of a plurality of graphite plates. The rare earth aluminum alloy, and the method and the device for preparing the same have the advantages that: the alloy has uniform components, little segregation and low impurity content; technology for preparing the rare earth aluminum alloy through fusion electrolysis can maximally replace a process for preparing single medium-heavy metal through metallothermic reduction, greatly reduce energy consumption and the emission of fluorine-containing tail gas and solid waste residue, improve current efficiency and metal yield and reduce the consumption of auxiliary materials and the energy consumption; and the rare earth aluminum alloys with different rare earth contents can be obtained by controlling different electrolytic temperatures and different cathode current densities.
Owner:GRIREM ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
NOx reduction composition for use in FCC processes
A composition for controlling NOx emissions during FCC processes comprises (i) an acidic oxide support, (ii) cerium oxide, (iii) a lanthanide oxide other than ceria such as praseodymium oxide, and (iv), optionally, an oxide of a metal from Groups Ib and IIb such as copper, silver and zinc.
Owner:ENGELHARD CORP
Apparatus and process for treating an aqueous solution containing chemical contaminants
Apparatus, process and article for treating an aqueous solution containing a chemical contaminant. The process includes contacting an aqueous solution containing a chemical contaminant with an aggregate composition comprising an insoluble rare earth-containing compound to form a solution depleted of chemical contaminants. The insoluble rare earth-containing compound can include one or more of cerium, lanthanum, or praseodymium. A suitable insoluble cerium-containing compound can be derived from a cerium carbonate, cerium oxalate and / or a cerium salt. The aggregate composition can include more than 10.01% by weight of the insoluble rare earth-containing compound, and in a particular embodiment consists essentially of one or more cerium oxides, and optionally a binder and / or flow aid. Although intended for a variety of fluid treatment applications, such applications specifically include removing or detoxifying chemical contaminants in water.
Owner:MOLYCORP MINERALS
Methods for making barrier coatings comprising taggants and components having the same
Methods for making barrier coatings including a taggant involving providing a barrier coating, and adding from about 0.01 mol % to about 30 mol % of a taggant to the barrier coating wherein the taggant comprises a rare earth element selected from lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, promethium, samarium, europium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, ytterbium, and lutetium, salts thereof, silicates thereof, oxides thereof, zirconates thereof, hafnates thereof, titanates thereof, tantalates thereof, cerates thereof, aluminates thereof, aluminosilicates thereof, phophates thereof, niobates thereof, borates thereof, and combinations thereof.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Composition and process for making the composition
Owner:SECURE NATURAL RESOURCES LLC
Method, sintering aid and materials for preparation of low-temperature cofired medium ceramic and application
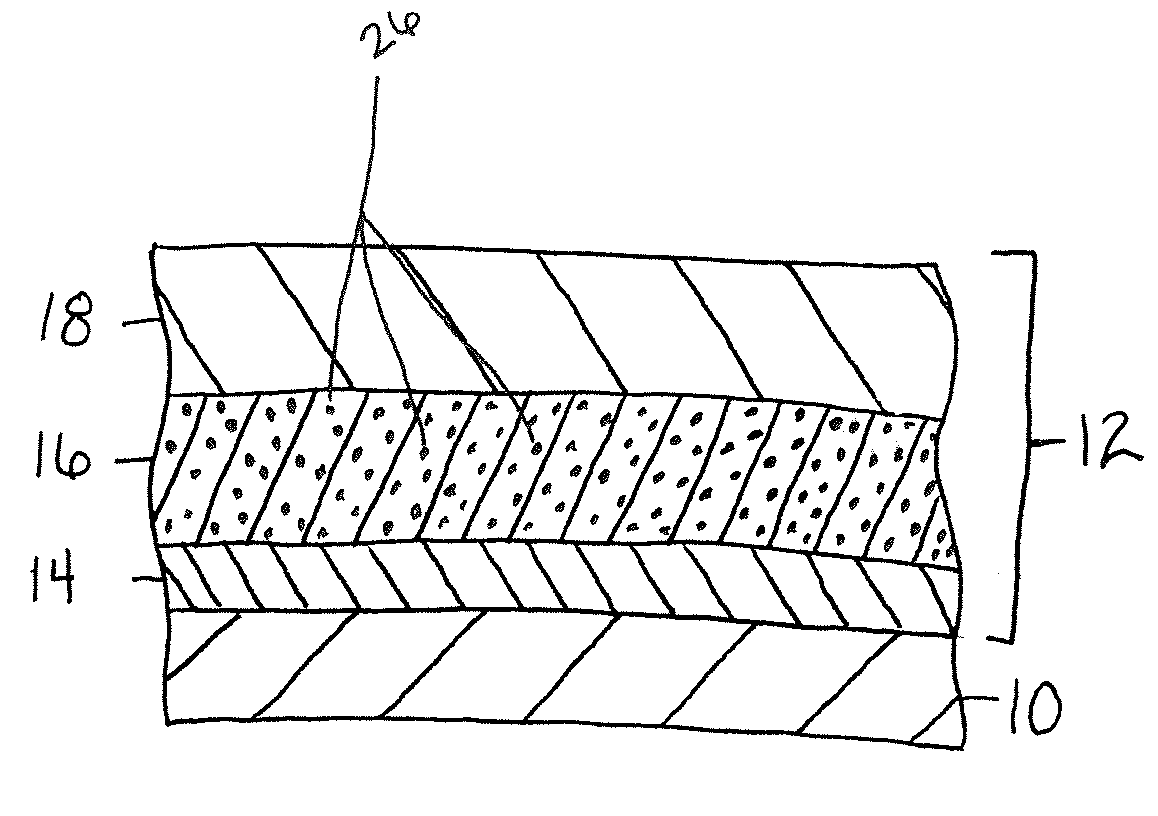
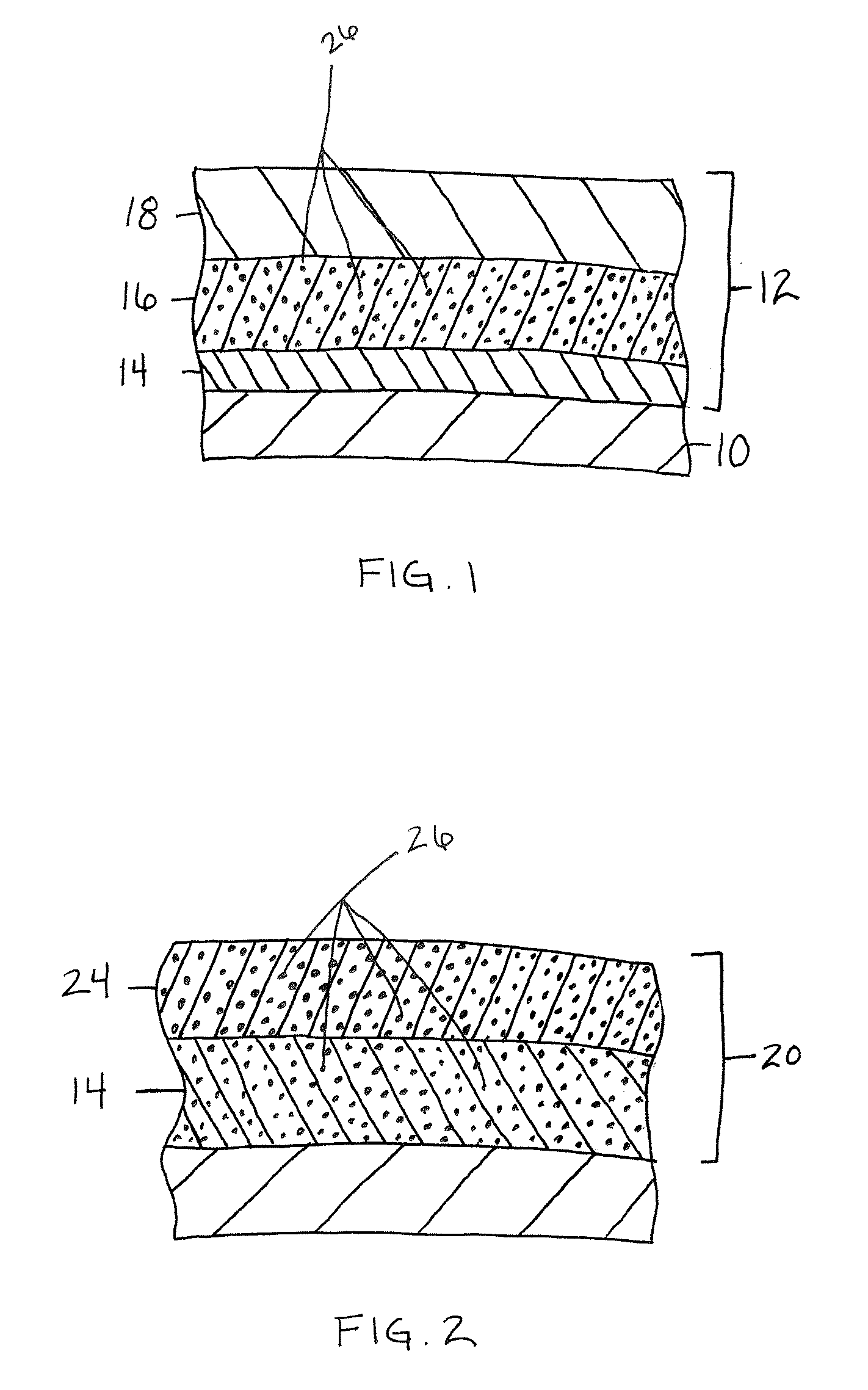
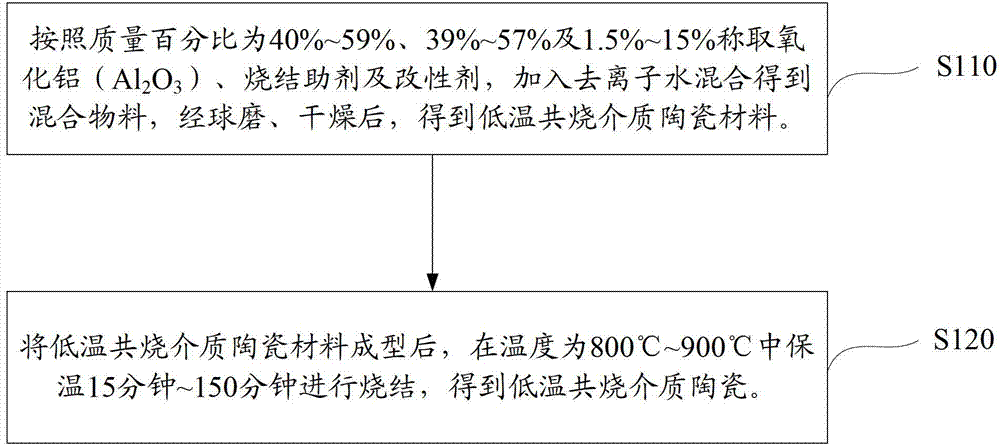
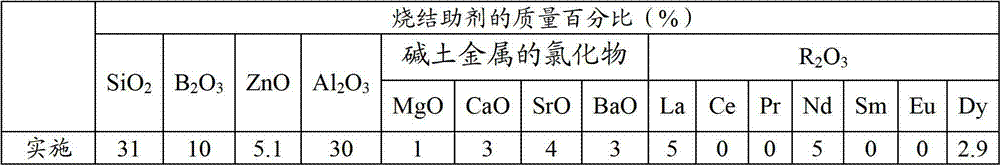
A sintering aid for a low-temperature cofired medium ceramic material is composed of, by weight, 31%-45% of silicon dioxide, 1%-10% of boron oxide, 5.1%-10% of zinc oxide, 18%-30% of aluminum oxide, 11%-24% of alkaline earth metallic oxide and 5%-15% of oxide with the general formula of R2O3, wherein R refers to at least one of lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, samarium, europium and dysprosium, and the alkaline earth metallic oxide refers to one of magnesium oxide, calcium oxide, barium oxide and strontium oxide. Adding the sintering aid into the low-temperature cofired medium ceramic material enables the prepared low-temperature cofired medium ceramic to have excellent thermal mechanical performance and dielectric performance. In addition, the invention provides the low-temperature cofired medium ceramic material and application thereof and a method for preparing the low-temperature cofired medium ceramic.
Owner:GUANGDONG FENGHUA ADVANCED TECH HLDG
CMAS resistant thermal barrier coating
ActiveUS20070172703A1Reduce componentsReduces sand related distressMolten spray coatingBlade accessoriesIndiumCerium
A turbine engine component is provided which has a substrate and a thermal barrier coating applied over the substrate. The thermal barrier coating comprises alternating layers of yttria-stabilized zirconia and a molten silicate resistant material. The molten silicate resistant outer layer may be formed from at least one oxide of a material selected from the group consisting of lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, promethium, samarium, europium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, thulium, ytterbium, lutetium, scandium, indium, zirconium, hafnium, and titanium or may be formed from a gadolinia-stabilized zirconia. If desired, a metallic bond coat may be present between the substrate and the thermal barrier coating system. A method for forming the thermal barrier coating system of the present invention is described.
Owner:RTX CORP
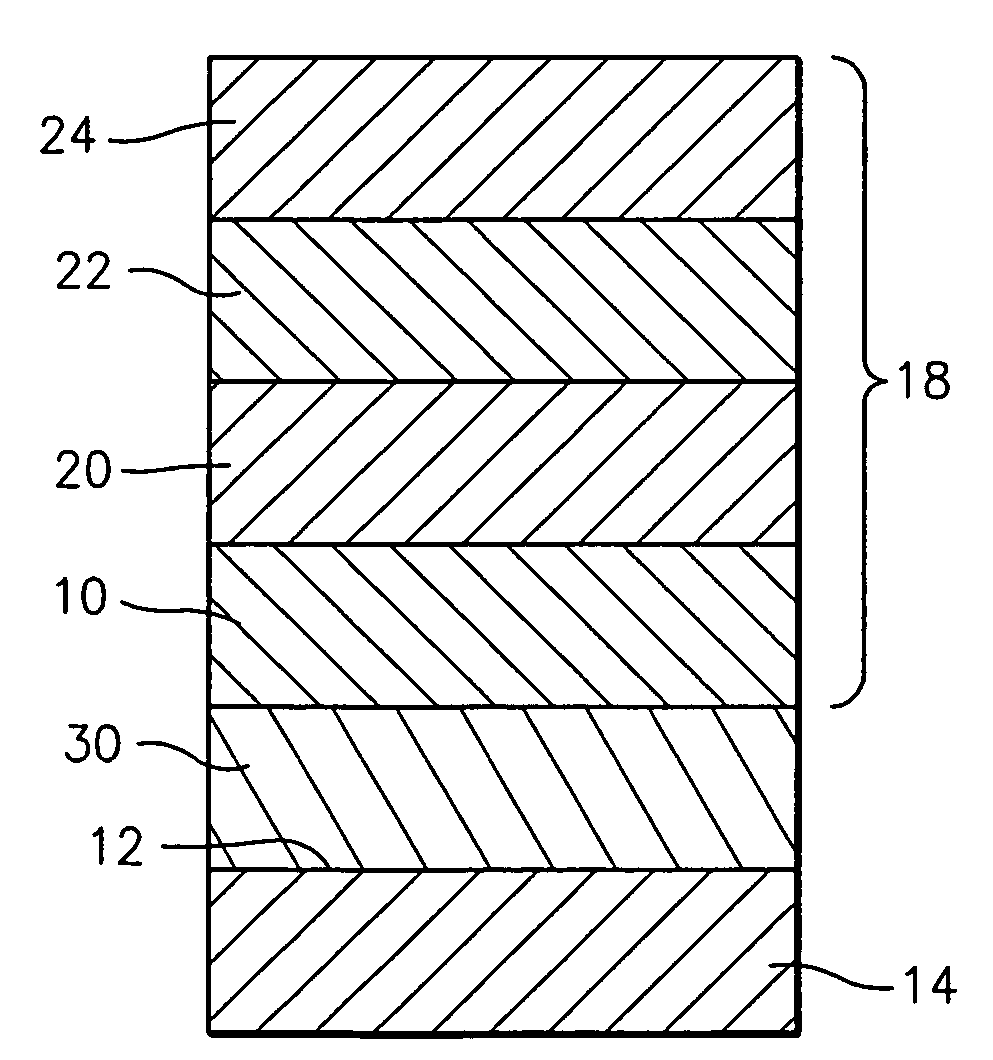
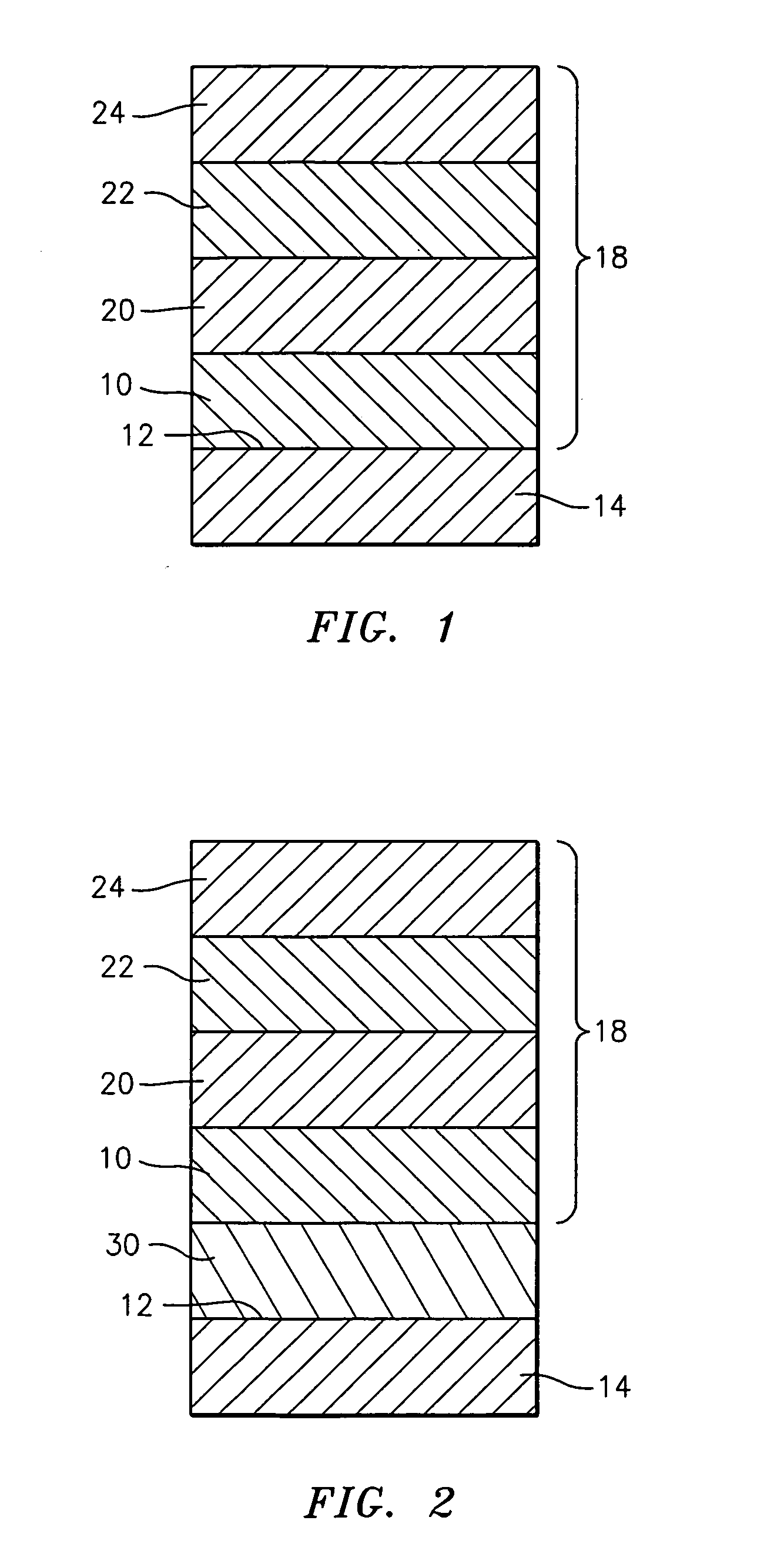
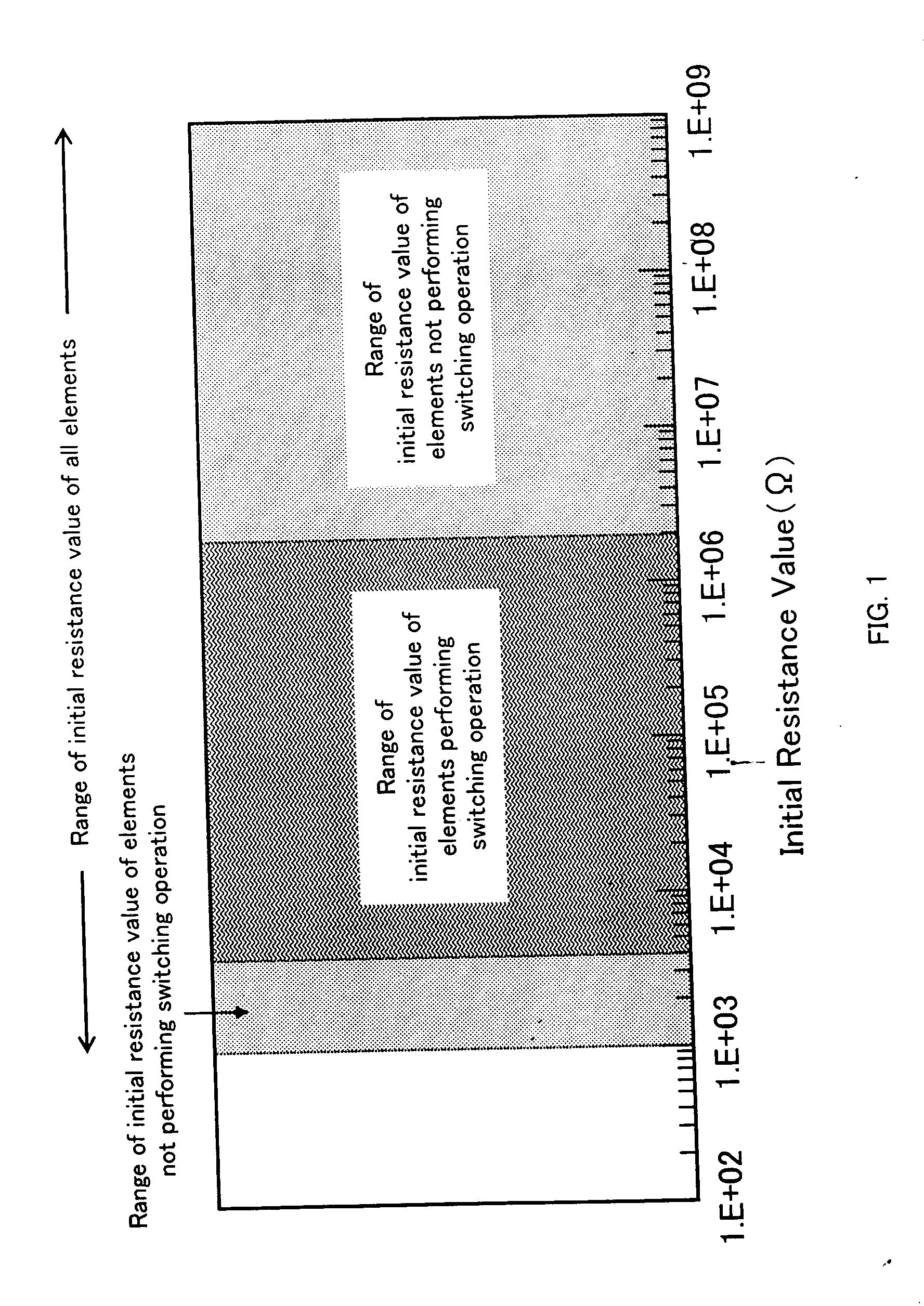
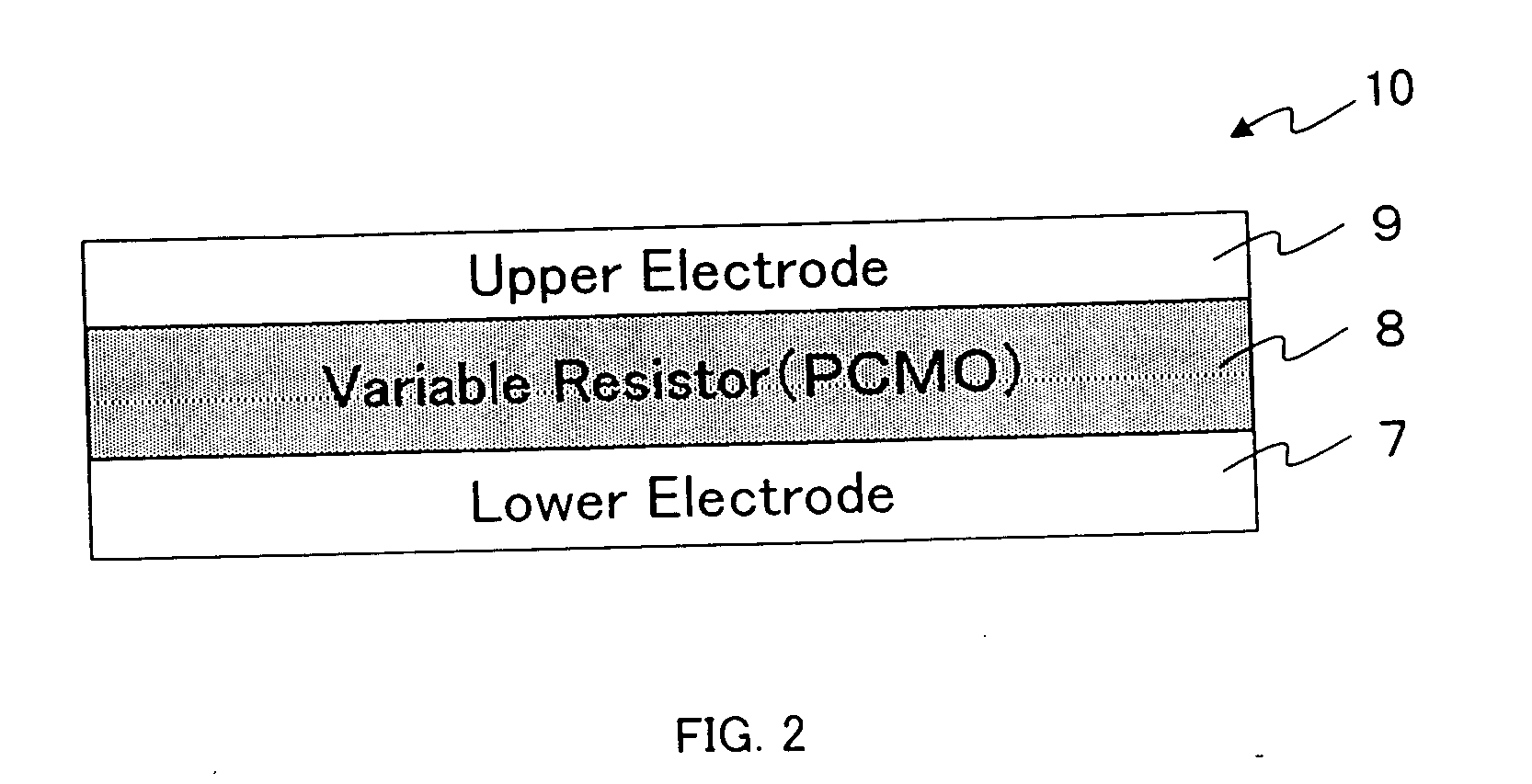
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device
A nonvolatile memory element is formed by layering a lower electrode, a variable resistor and an upper electrode in sequence. The variable resistor is formed in which crystallinity and amorphism are mixed. Thus, the nonvolatile memory element is formed. More preferably, the variable resistor is a praseodymium-calcium-manganese oxide represented by a general formula, Pr1-xCaxMnO3, that has been formed at a film forming temperature from 350° C. to 500° C. Alternatively, the variable resistor is formed as a film at a film forming temperature that allows the variable resistor to become of an amorphous state or a state where crystallinity and amorphism are mixed and, then, is subjected to an annealing process at a temperature higher than the film forming temperature, in a temperature range where the variable resistor can maintain the state where crystallinity and amorphism are mixed.
Owner:XENOGENIC DEV LLC
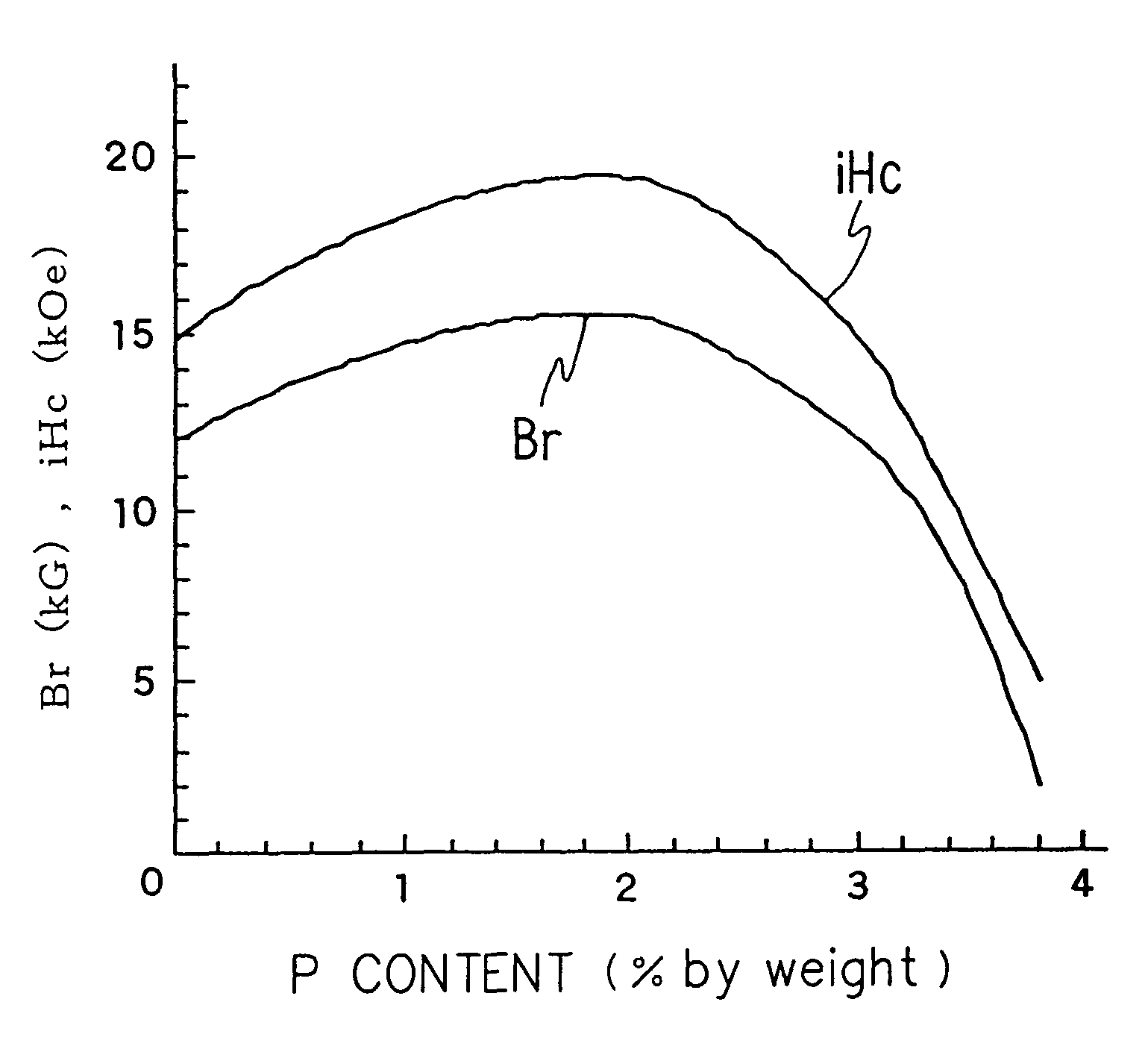
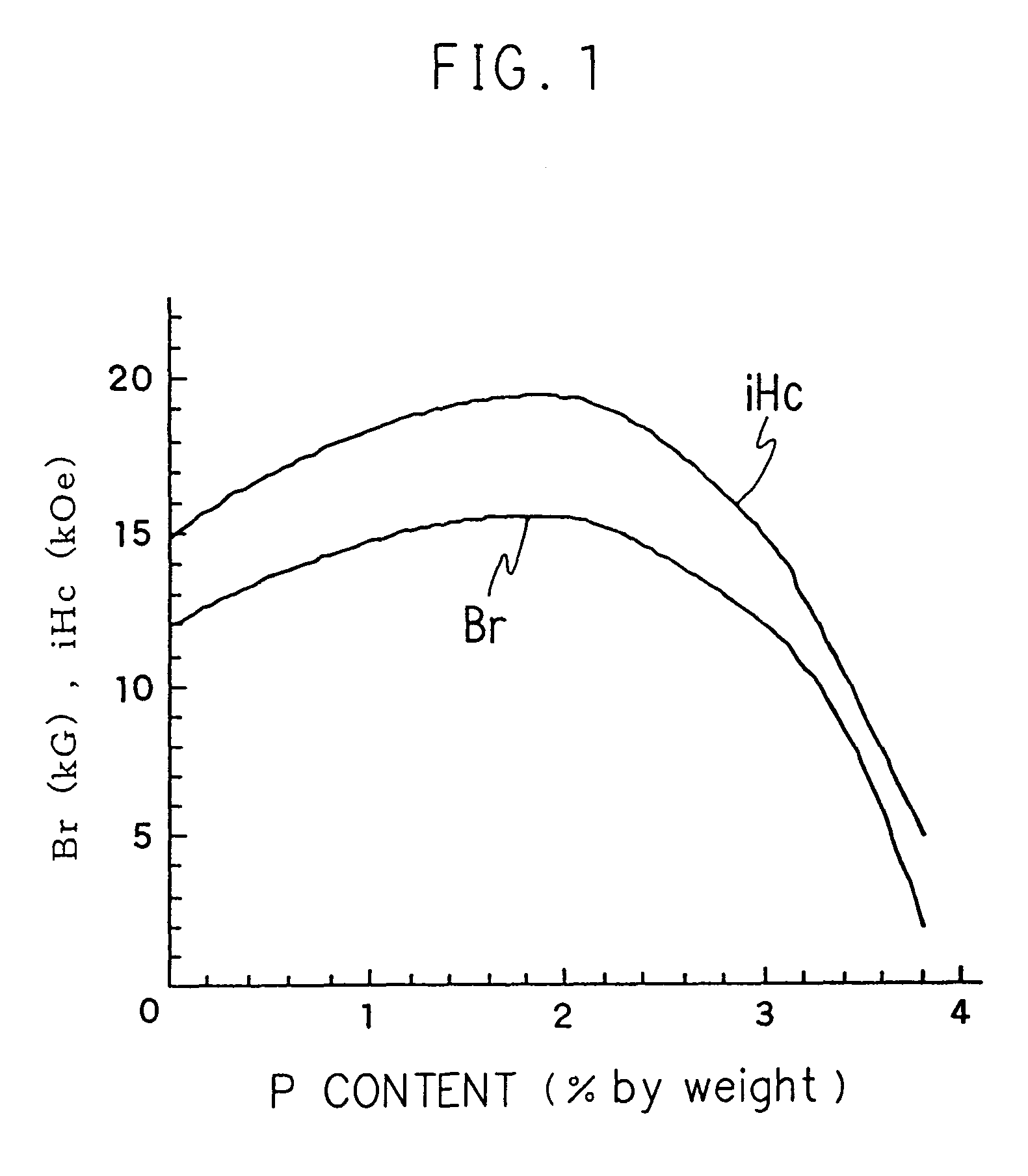
Rare earth element permanent magnet material
A material for a rare earth permanent magnet having a high magnetic coercive force and a high residual magnetic flux density. 28 to 35% by weight of at least one rare earth element selected from the group consisting of neodymium, praseodymium, dysprosium, terbium, and holmium, 0.9 to 1.3% by weight of boron, 0.25 to 3% by weight of phosphorus, iron, and inevitable impurities. It can further comprise 0.1 to 3.6% by weight of cobalt and 0.02 to 0.25% by weight of copper.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Praseodymium-doped calcium titanate luminescent powder and preparation method thereof
The invention provides praseodymium-doped calcium titanate luminescent powder and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: at room temperature, weighing a certain amount of CaCO3 and Pr6O11 solid according to a molar ratio of Pr<3+> / Ca<2+> of 0.005 / 1, dissolving the solid in dilute nitric acid, heating and stirring the solution to remove excessive acid, and heating the solution to a melting state after the pH value of the solution reaches 2 to 3; after the solution is cooled to room temperature, adding 20 milliliters of tetrabutyl titanate and 20 milliliters of water-ethanol solution into the solution according to a stoichiometric proportion, then adding a certain amount of citric acid as complexing agent into the solution, adding polyethylene glycol into the solution, and stirring the solution for 2 hours to obtain an even transparent sol precursor; spraying and drying the obtained precursor solution to obtain precursor powder; and putting the precursor powder into a programmed temperature rising furnace, heating the precursor powder to between 600 and 1,000 DEG C, and then keeping the precursor powder for 3 hours at a constant temperature to obtain CaTiO3:Pr<3+> luminescent powder. The praseodymium-doped calcium titanate luminescent powder prepared by the method has good crystallization degree and high purity, and is a CaTiO3 pure phase of a perovskite structure.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Permanent magnetic RE material and preparation thereof
ActiveCN101364465ASmall temperature coefficientLow coercivityInorganic material magnetismCrystalline oxideSamarium–cobalt magnet
The invention relates to a rare earth permanent magnetic material and a preparation method thereof. The rare earth permanent magnetic material comprises a (Pr, Nd)-Fe-R-Co-Al-Cu-B-M system, and the rare earth as a main phase component has a phase volume ratio of 90%-98%; wherein R is at least two elements selected from Nb, Tb, Dy and Ho; M is at least two nanometer crystalline oxides with particle size of 10-100 nm selected from ZrO2, MgO and ZnO; and the weight of the nanometer crystalline oxides is 0.1%-3% of the total weight. The rare earth permanent magnetic material is a compound nanometer oxidizer enhanced and sintered praseodymium (Pr)-neodymium (Nd)-based permanent magnet with high coercitive force. The inventive product has magnetic features of low temperature coefficient, high coercitive force, low cost and 220 DEG C working temperature, and can overcome the shortcomings of lower coercitive force, high temperature coefficient and high cost of the prior sintered Nd-Fe-B permanent magnet and the sintered samarium-cobalt magnet in application of large motor products. The preparation method provides a powerful guarantee for realizing the positive effects.
Owner:浙江西子富沃德电机有限公司
Preparation method for uniform gradient-colour zirconium oxide porcelain blocks
ActiveCN104909745AContinuous uniform changeEasy to processImpression capsDentistry preparationsPolyethylene glycolMaterials science
The invention relates to zirconium oxide porcelain blocks for dental prosthesis, and aims at providing a preparation method for uniform gradient-colour zirconium oxide porcelain blocks. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) weighing the raw materials of CeO2, Fe2O3, ZrO2, Y2O3, Pr6O11 and Er2O3; (2) adding a polymer binder in the dried mixed powder, and granulating; (3) shaping the granulated material by a die by means of dry pressing to obtain porcelain block blanks; (4) carrying out isostatic cool pressing on the shaped porcelain block blanks; (5) pre-sintering the porcelain block blanks after the isostatic cool pressing; (6) flatly placing the pre-sintered porcelain block blanks in a dyeing container and dyeing, wherein the depth of soaking solution in the dyeing container is 0.1-5mm, the dyeing time is 1-3min, and the used dyeing solution comprises 1-5wt% of polyethylene glycol, 0.1-3wt% of erbium oxide, 0.5-10wt% of praseodymium oxide and the balance of ultrapure water; and (7) sintering the dyed porcelain blocks to obtain the uniform gradient-colour zirconium oxide porcelain blocks for dentistry. The porcelain blocks disclosed by the invention are stable and uniform in colouring, and continuous and uniform in colour changes.
Owner:CHENGDU BESMILE BIOTECH
Wetting resistant materials and articles made therewith
Ceramic materials with relatively high resistance to wetting by various liquids, such as water, are presented, along with articles made with these materials, methods for making these articles and materials, and methods for protecting articles using coatings made from these materials. One particular embodiment is an article that comprises a coating having a surface connected porosity content of up to about 5 percent by volume. The coating comprises a material that comprises a primary oxide and a secondary oxide, wherein (i) the primary oxide comprises a cation selected from the group consisting of cerium, praseodymium, terbium, and hafnium, and (ii) the secondary oxide comprises a cation selected from the group consisting of the rare earth elements, yttrium, and scandium.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Fuel compositions exhibiting improved fuel stability
InactiveUS6652608B1Enhanced combustion structureImprove stabilityNon-fuel substance addition to fuelCombustion enginesIndiumCobalt
A fuel composition of the present invention exhibits minimized hydrolysis and increased fuel stability, even after extended storage at 65° F. for 6-9 months. The composition, which is preferably not strongly alkaline (3.0 to 10.5), is more preferably weakly alkaline to mildly acidic (4.5 to 8.5) and most preferably slightly acidic (6.3 to 6.8), includes a lower dialkyl carbonate, a combustion improving amount of at least one high heating combustible compound containing at least one element selected from the group consisting of aluminum, boron, bromine, bismuth, beryllium, calcium, cesium, chromium, cobalt, copper, francium, gallium, germanium, iodine, iron, indium, lithium, magnesium, manganese, molybdenum, nickel, niobium, nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, palladium, rubidium, sodium, tin, zinc, praseodymium, rhenium, silicon, vanadium, or mixture, and a hydrocarbon base fuel.
Owner:OCTANE INT
Neodymium iron boron permanent magnet for motor and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN101409121AReduce manufacturing costLow costInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsNiobiumMaterials science
The invention discloses an NdFeB permanent magnet used for NdFe motors and a manufacture method thereof. The magnet comprises the following components by weight: 24-28 percent of PrNd, 0.5-7 percent of Gd, 1-5 percent of Ho, 0-6 percent of Dy, 0.9-1.1 percent of B, 0.1-0.15 percent of Cu, 0.2-1.2 percent of Al, 62.35-66.5 percent of Fe, 0.2-1.5 percent of Co and 0.2-0.8 percent of Nb. The magnet is manufactured through the procedures of mixing, melting, milling, forming, sintering and grinding processing. Through the use of cheap gadolinium and holmium instead of expensive praseodymium, neodymium, dysprosium and terbium for the production of high-performance NdFeB permanent magnet, the invention can greatly reduce production cost and the product has high magnetic property and strong market competitiveness.
Owner:SINOSTEEL ANHUI TIANYUAN TECH
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com