Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
585 results about "Primary channel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
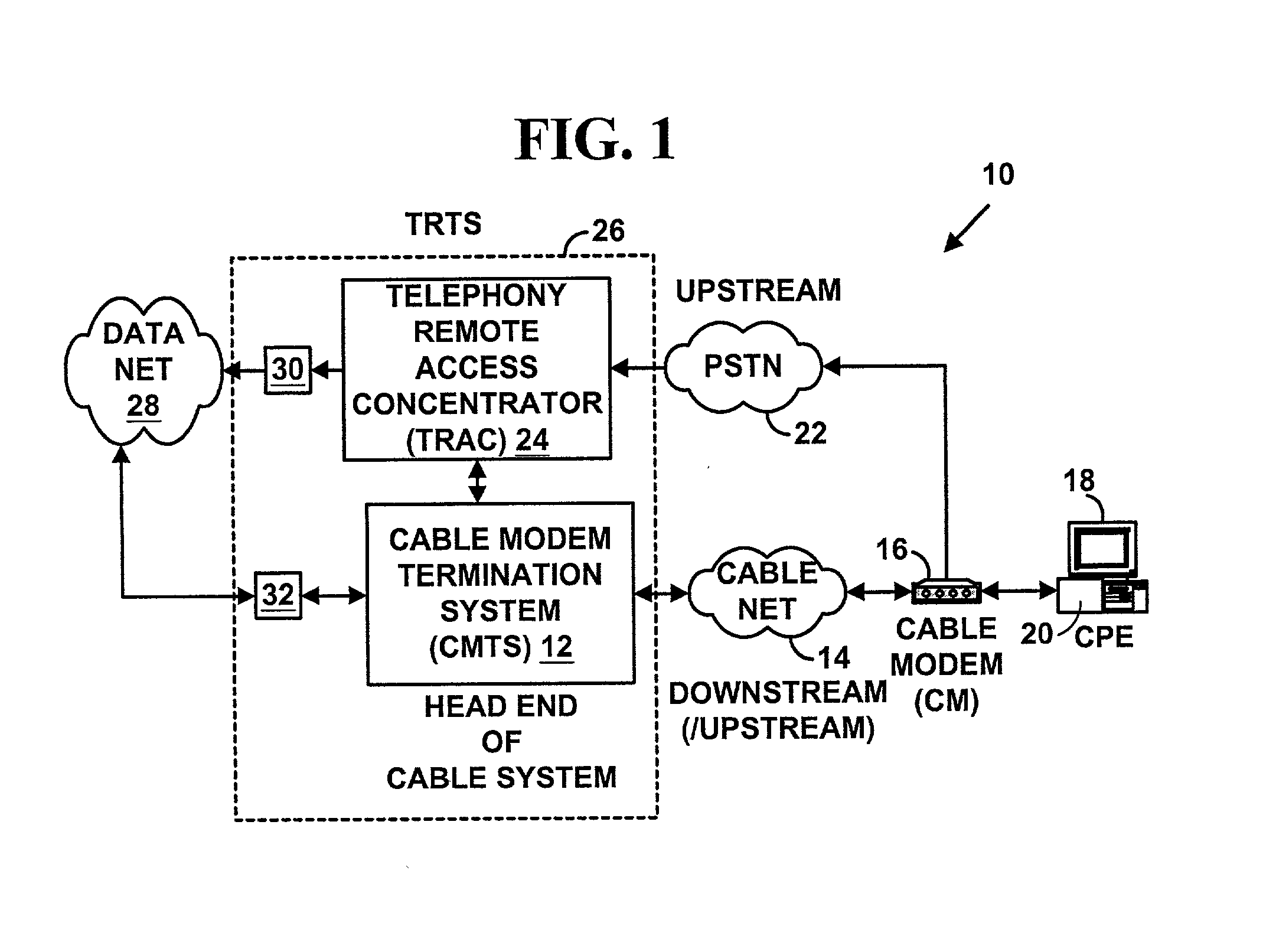
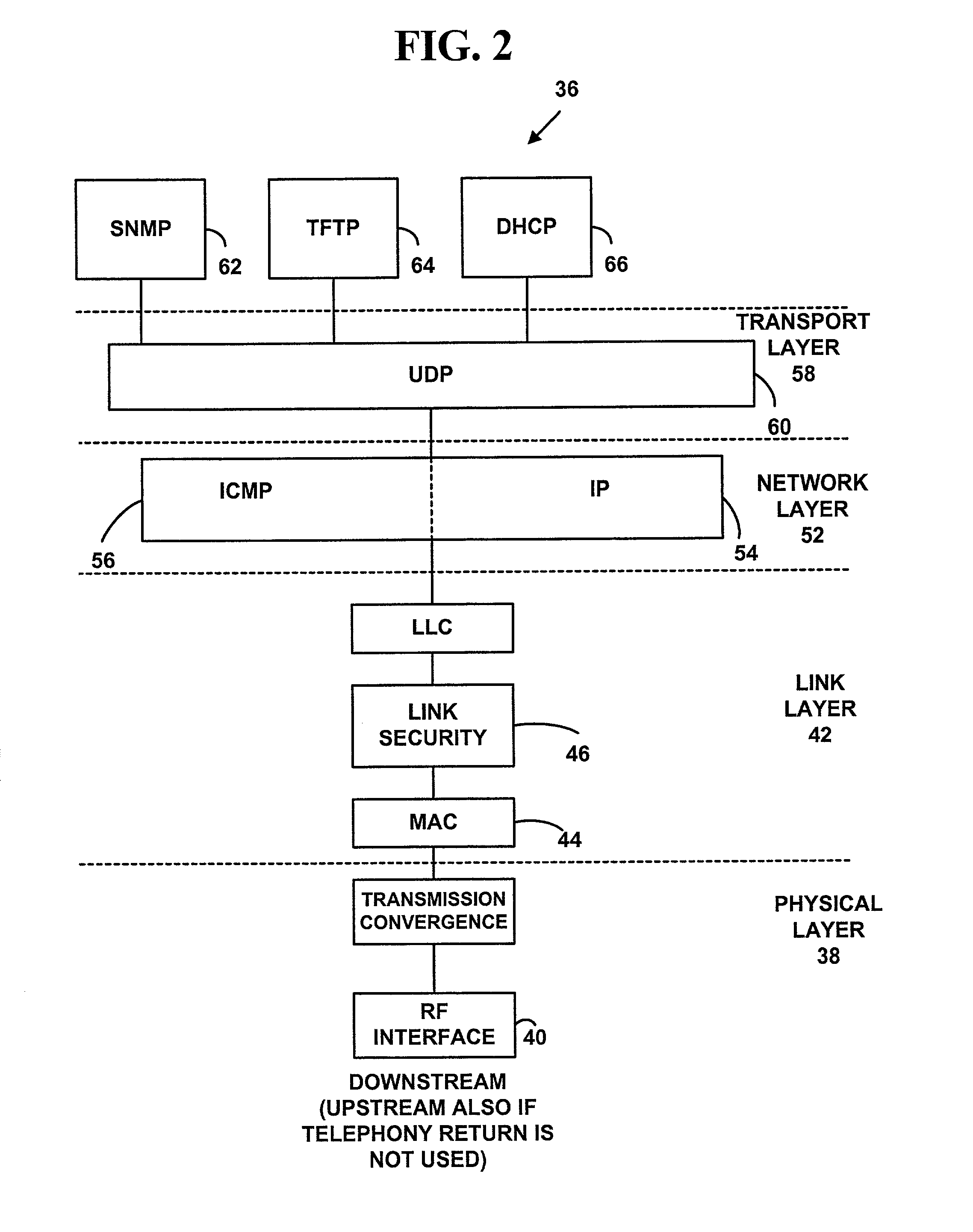
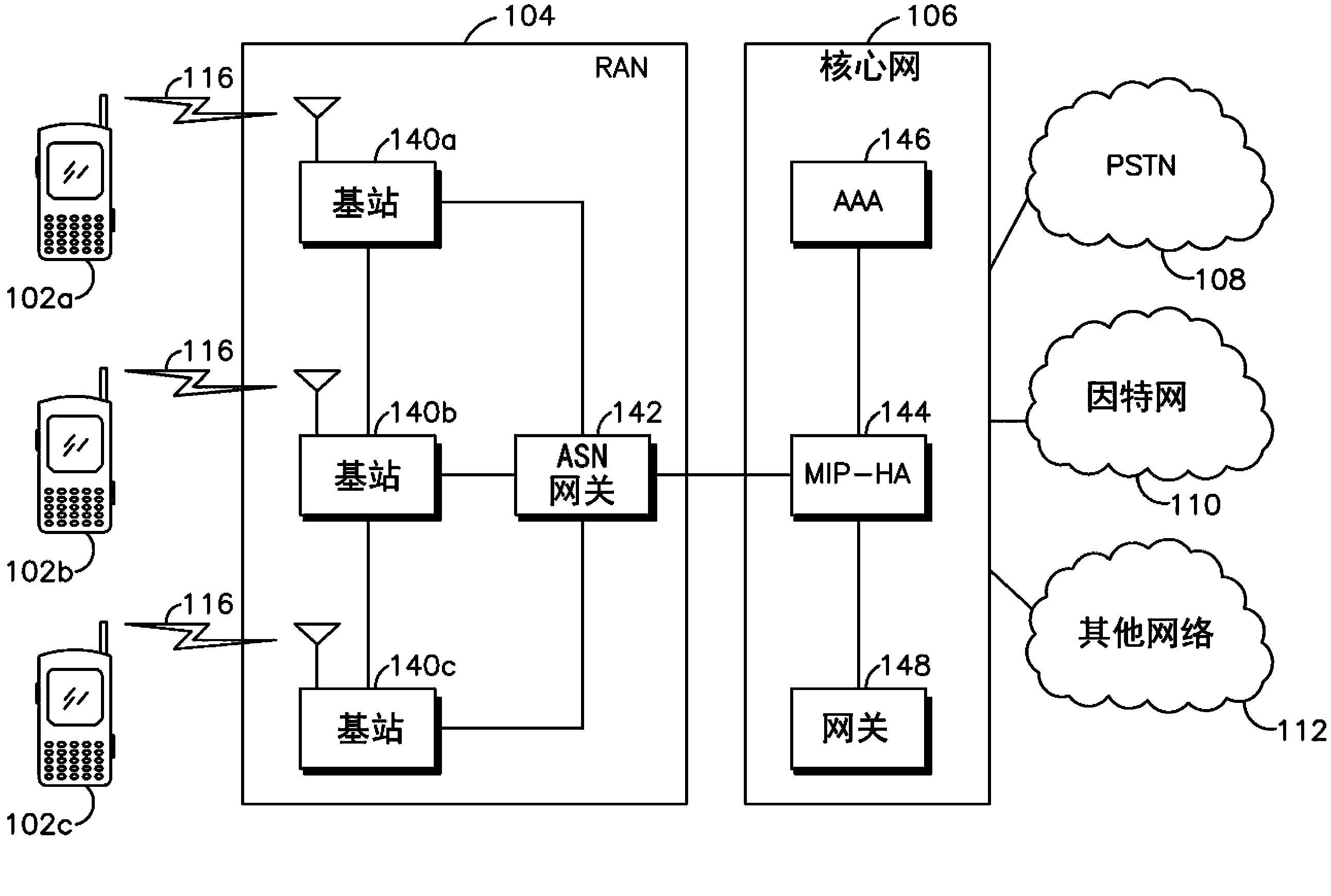
In telecommunication, the term primary channel has the following meanings: The channel that is designated as a prime transmission channel and is used as the first choice in restoring priority circuits. In a communications network, the channel that has the highest data rate of all the channels sharing a common interface. A primary channel may support the transfer of information in one direction only, either direction alternately, or both directions simultaneously.
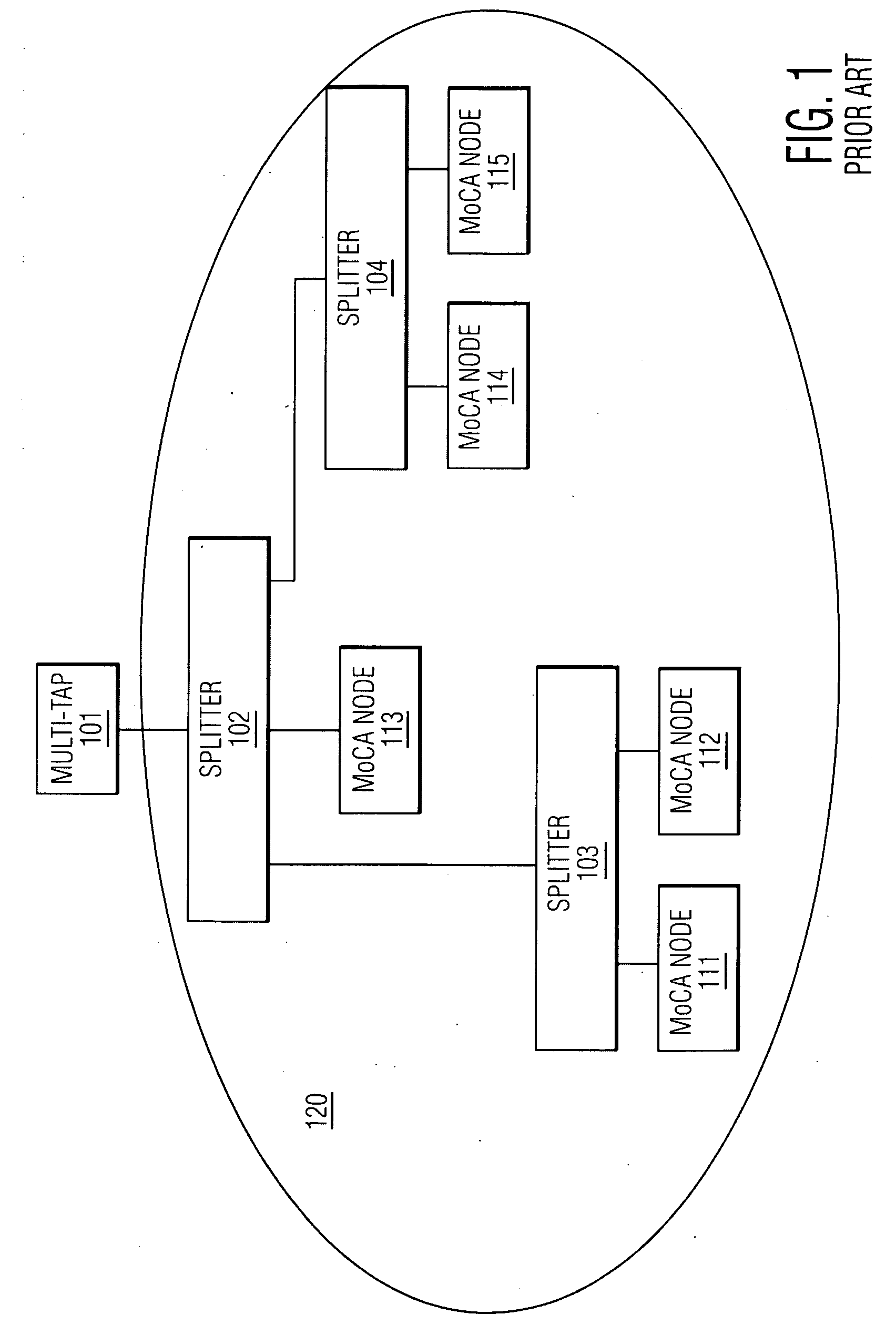
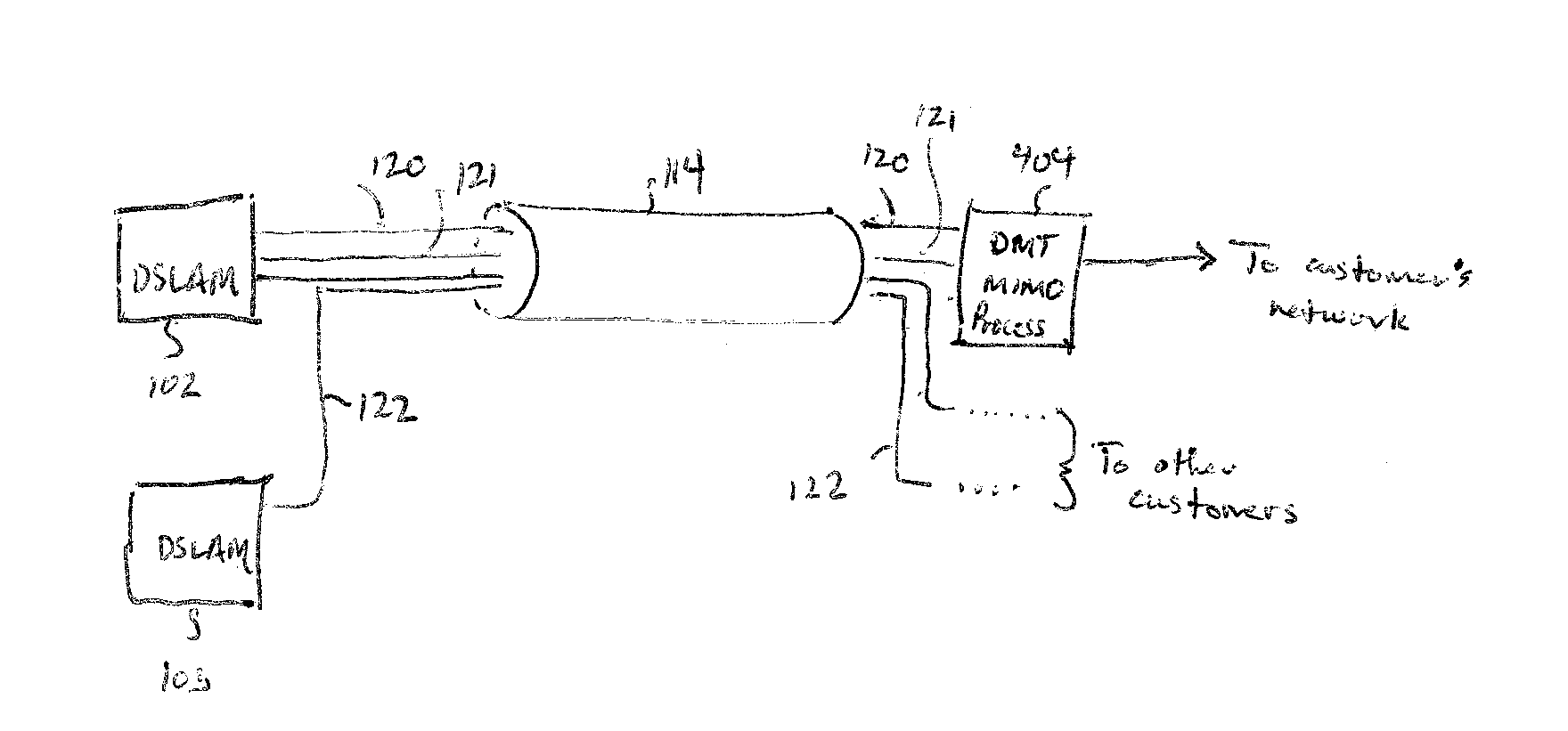
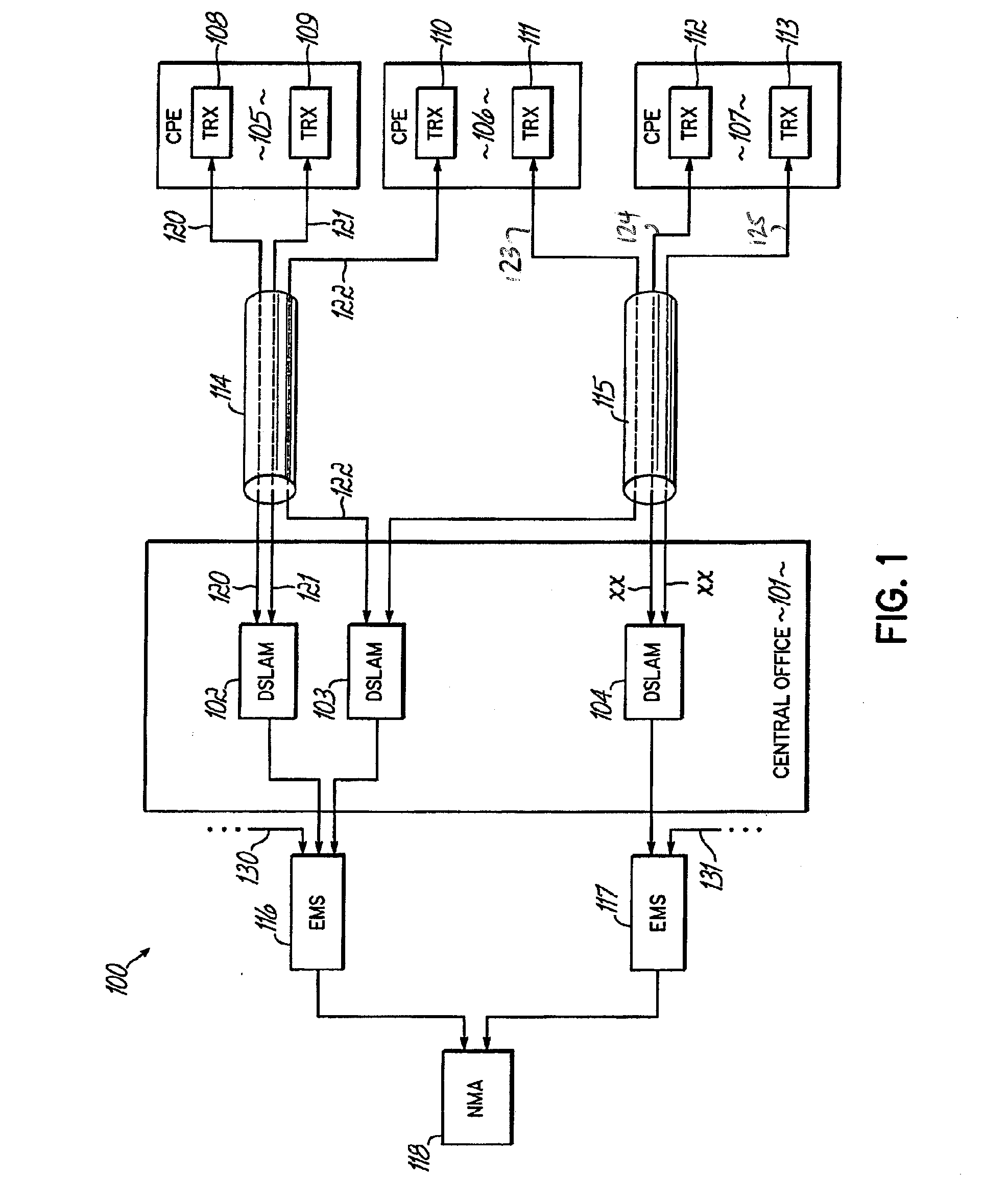
Method, system, and apparatus for extended rate/range communication over a communication network
ActiveUS20090092154A1High data rateImprove reliabilityFrequency-division multiplexRadio transmissionCoaxial cableMedia access control
A technique for communicating multimedia data between nodes over coaxial cable, wherein the nodes are connected via a coaxial cable network, is disclosed. In an embodiment, the technique involves establishing a primary channel for communicating between first and second nodes of the coaxial cable network, establishing a secondary channel for communicating between the first and second nodes of the coaxial cable network, wherein the primary and secondary channels are in different frequency bands and wherein the primary channel is used for communicating media access control frames, and communicating a time series of data frames between the first and second nodes using both the primary channel and the secondary channel.
Owner:ENTROPIC COMM INC
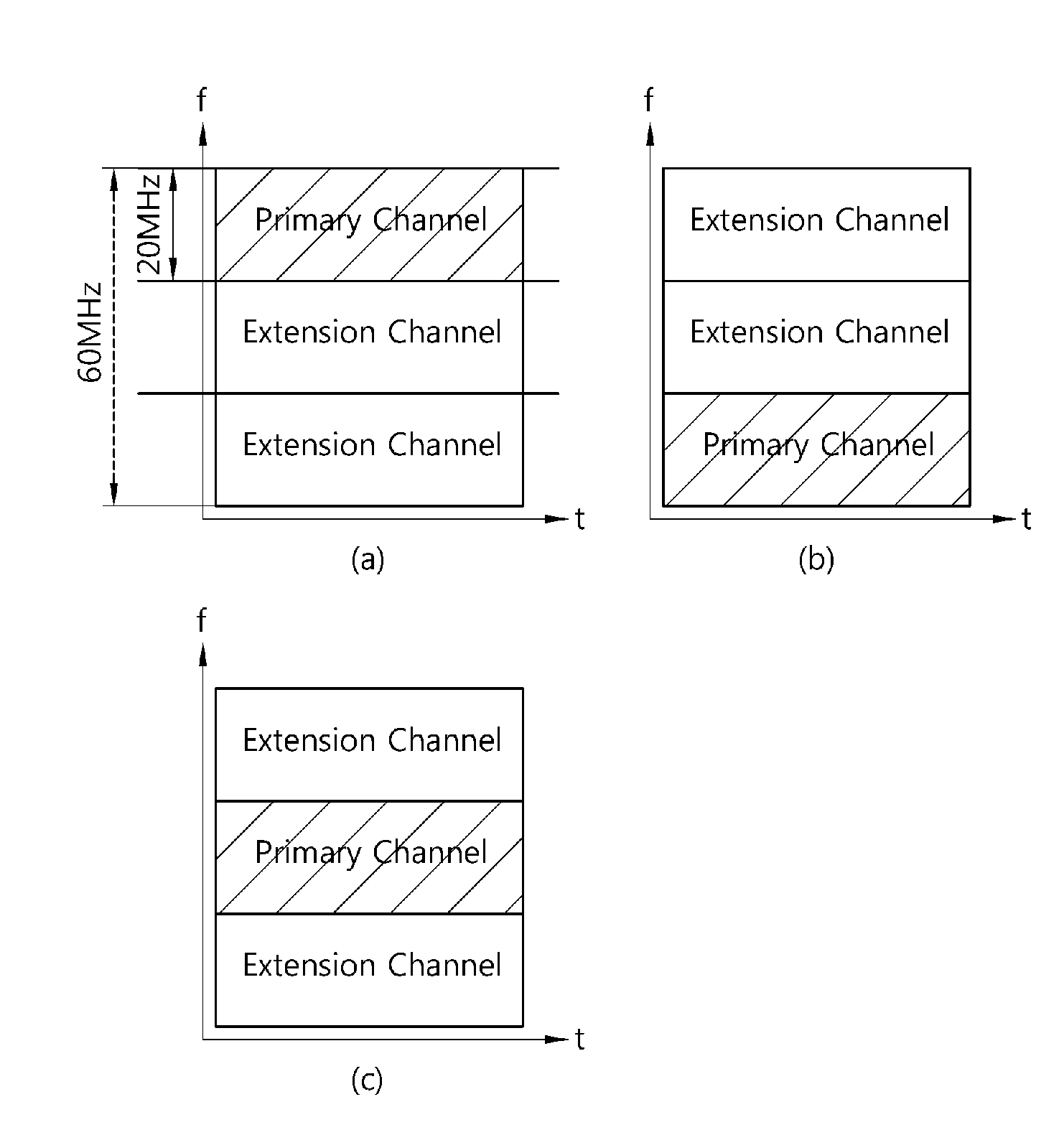
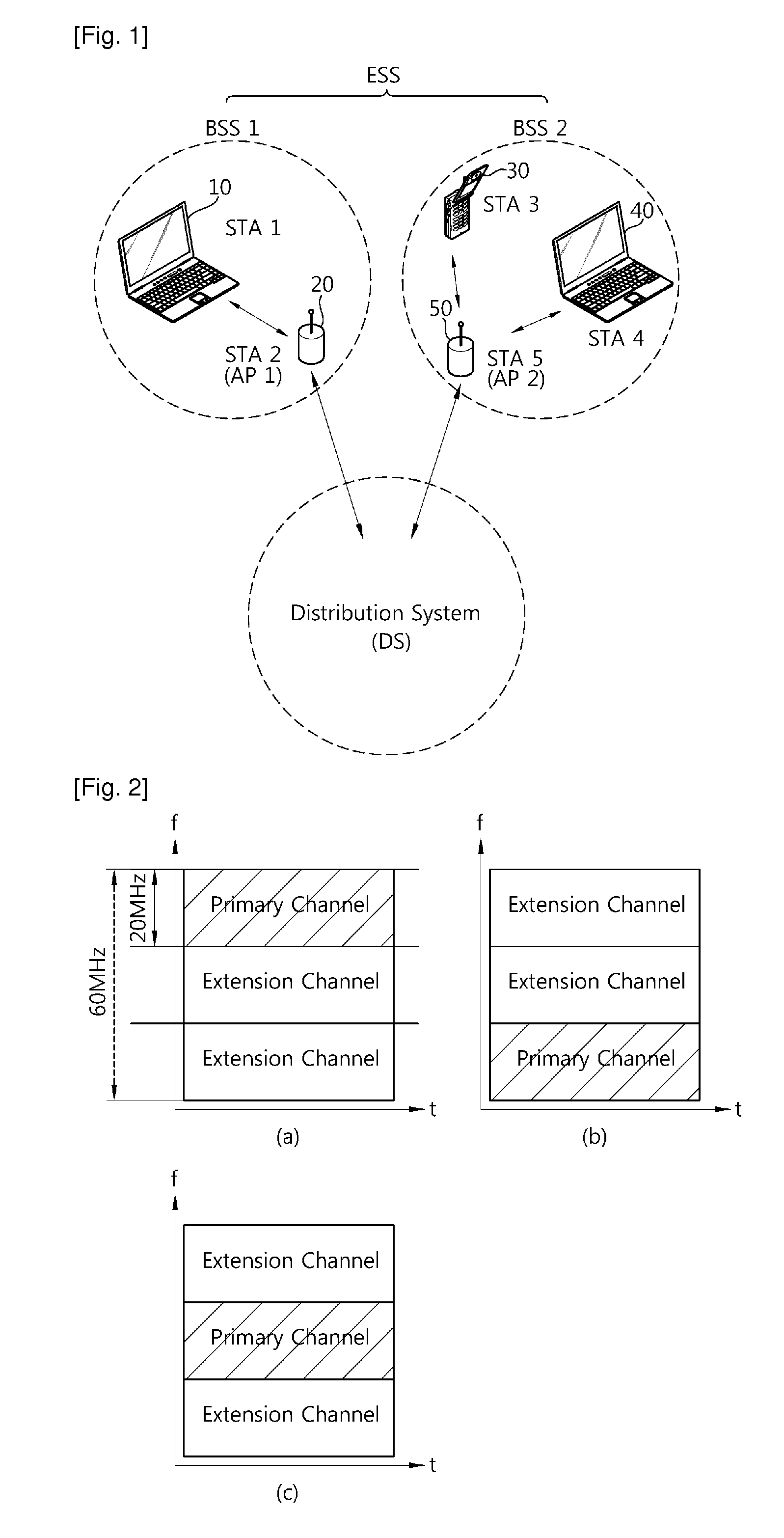
Method and apparatus of accessing channel in wireless communication system
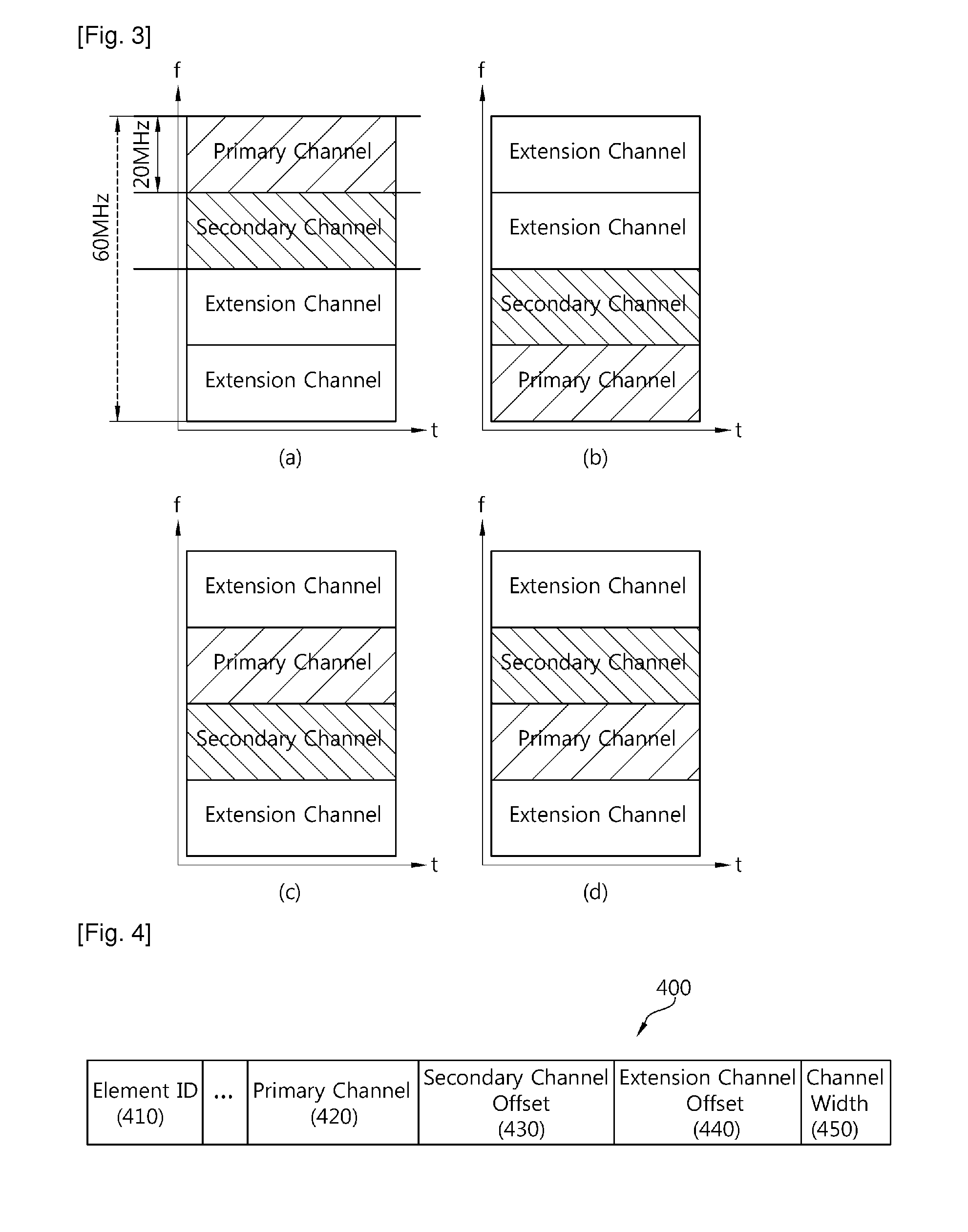
ActiveUS20110096747A1Efficiency of radio can be improvedImprove throughputAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesCommunications systemPrimary channel
A method and apparatus of accessing a channel in a wireless communication system is provided. The method includes receiving a first frame including configuration information on a channel allocated from a bandwidth including a primary channel, a secondary channel and an extension channel from an access point (AP), and transmitting a second frame to the AP by using the allocated channel. The configuration information includes an extension channel off-set element field that sets the extension channel as the offset of the primary channel.
Owner:AEGIS 11 SA
Methods and apparatus that facilitate channel switching during commercial breaks and/or other program segments
ActiveUS20150040176A1Easy to watchEasy to switchTwo-way working systemsSelective content distributionProgram segmentDisplay device
Methods and apparatus that facilitate watching of programming content on a secondary channel during a program segment, e.g., commercial break or program portion which is not of interest to a user, on a primary channel are described. In various embodiments when a user switches to a secondary channel during a program segment, the switch is detected and the program on the primary channel continues to be received and buffered while the content from the secondary channel is output to the display. The program segment on the primary channel may be a commercial break including one or more commercials or a portion of a program identified as a segment in information communicated with the program or via out of band signaling. The end of the segment on the primary channel is detected and the user is notified or automatically switched back to the primary channel at the end of the segment.
Owner:TIME WARNER CABLE ENTERPRISES LLC
Method of content substitution
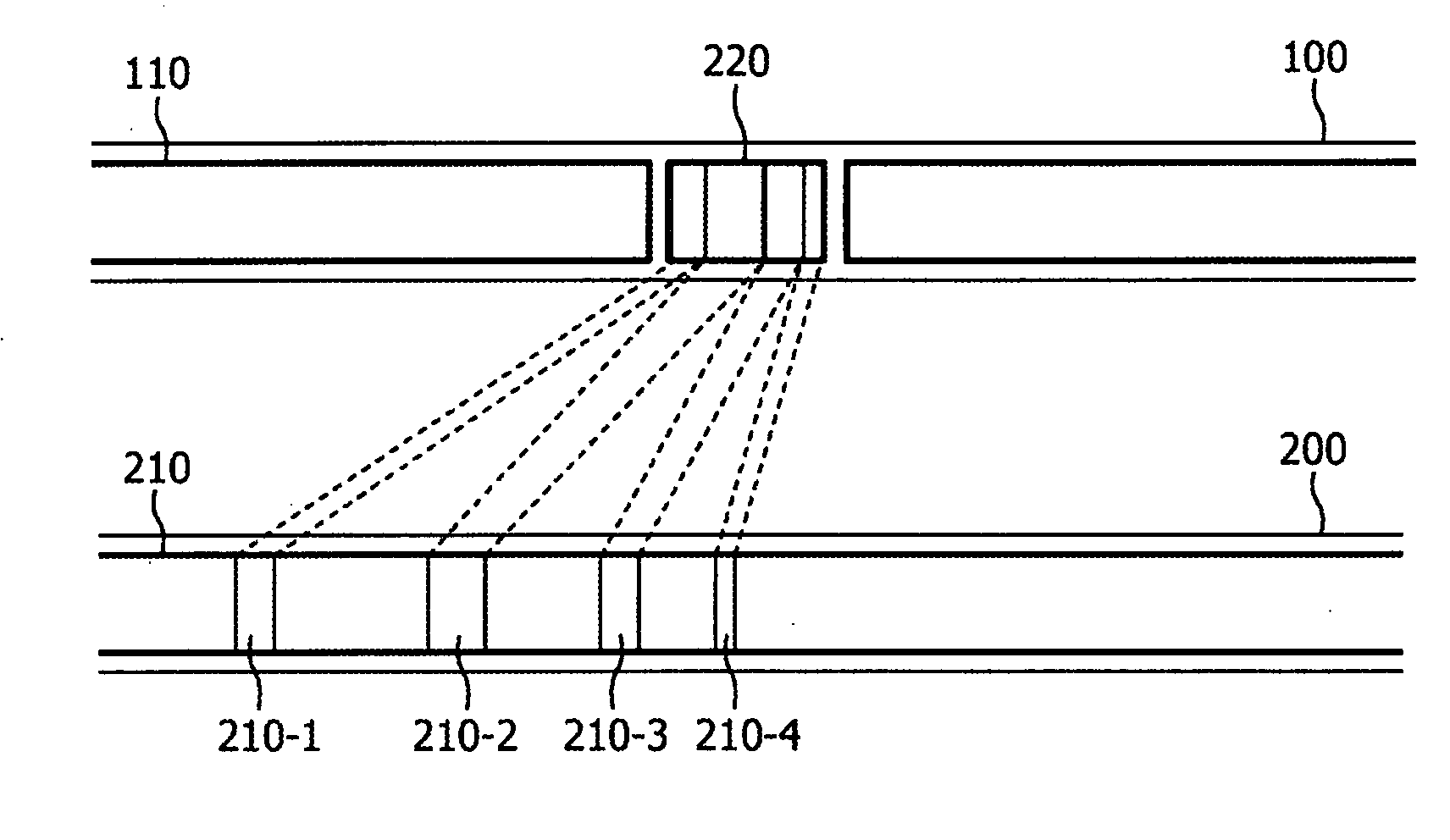
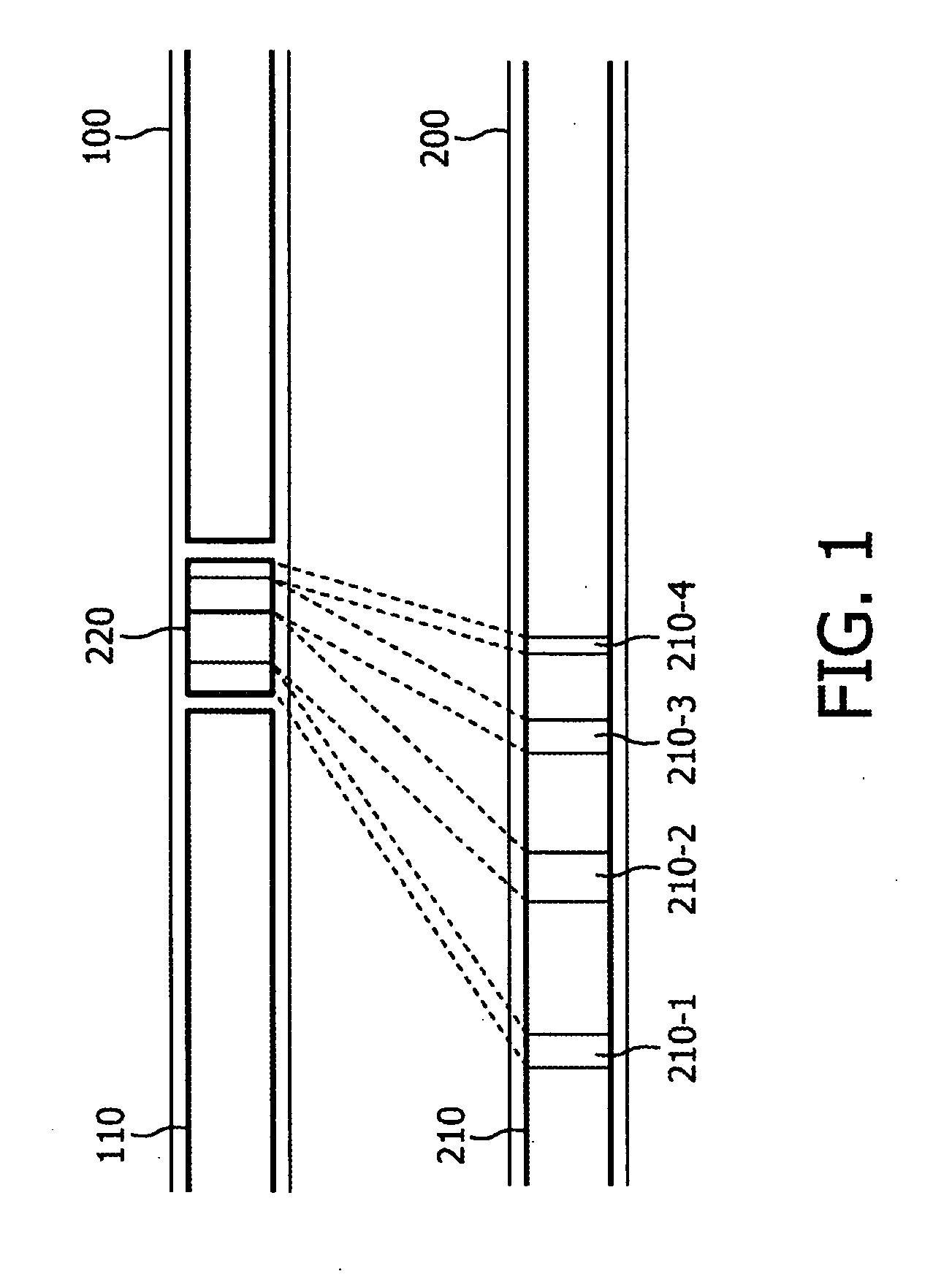
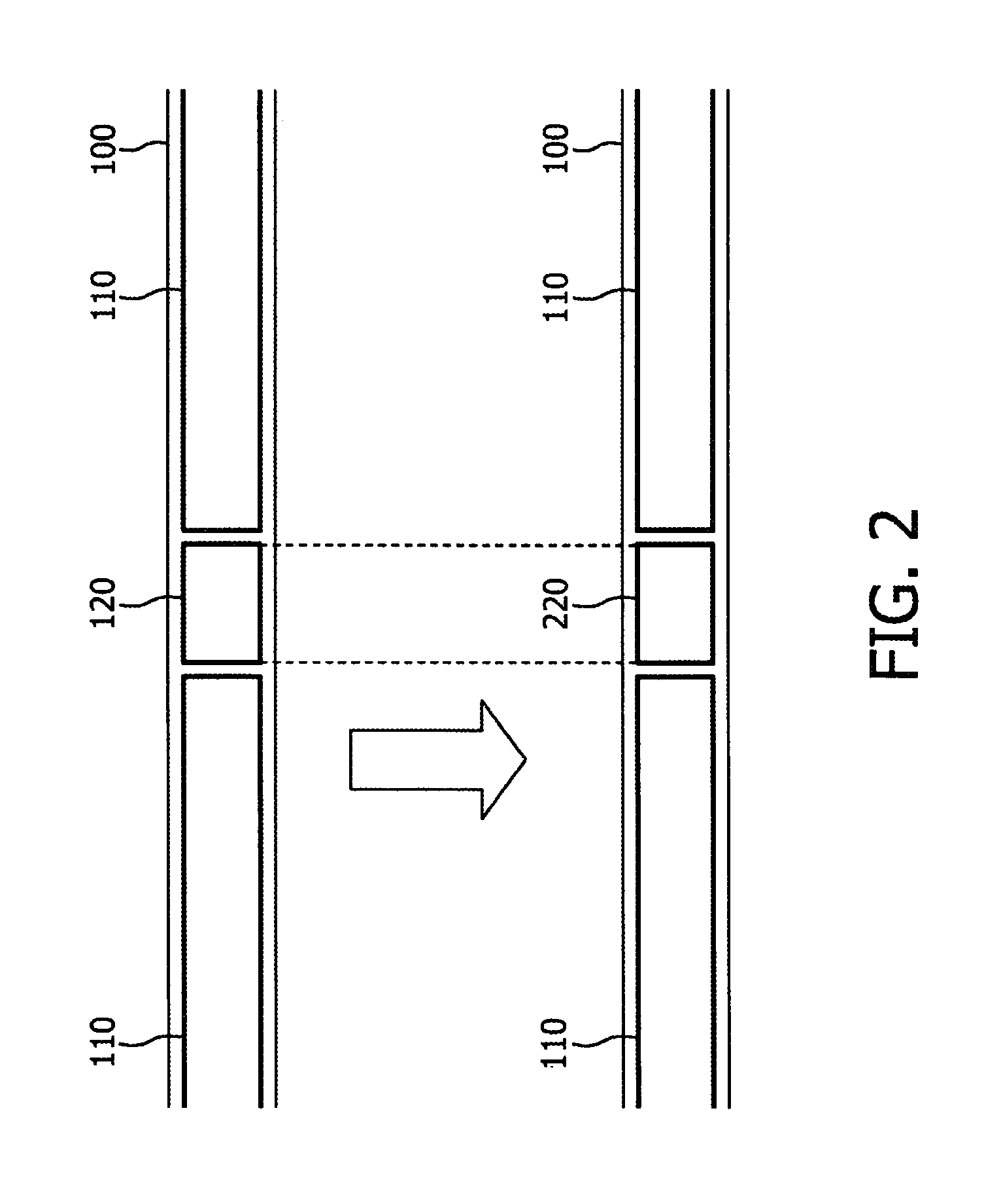
InactiveUS20090235308A1Reduce situationReceiver side switchingPulse modulation television signal transmissionTime shiftingPrimary channel
A method of substituting a primary content (110) being transmitted on a primary channel (100) with a secondary content (220), characterized by said secondary content being a summary of a program (210) being currently transmitted on a secondary channel (200). Preferably the method comprises substitution of the secondary content (220) in response to a commercial break (120) being transmitted on the primary channel (100). Preferably the method comprises transmission of the primary content (110) following the substituted secondary content (220) that is time-shifted to allow the secondary content to be presented to its end. Preferably the method comprises subsequent to presenting the secondary content (220), the program being currently transmitted on the secondary channel (210) that is presented instead of the primary content (110). Preferably the method comprises transmission of the secondary content (220) that is prior to changing of the channel currently watched from the primary channel (100) to the secondary channel (200).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and apparatus for enhancing transfer rate using DLP and multi channels in wireless LAN using PCF and DCF
InactiveUS20050053015A1Reduce contentionData switching by path configurationWireless communicationWireless lanPrimary channel
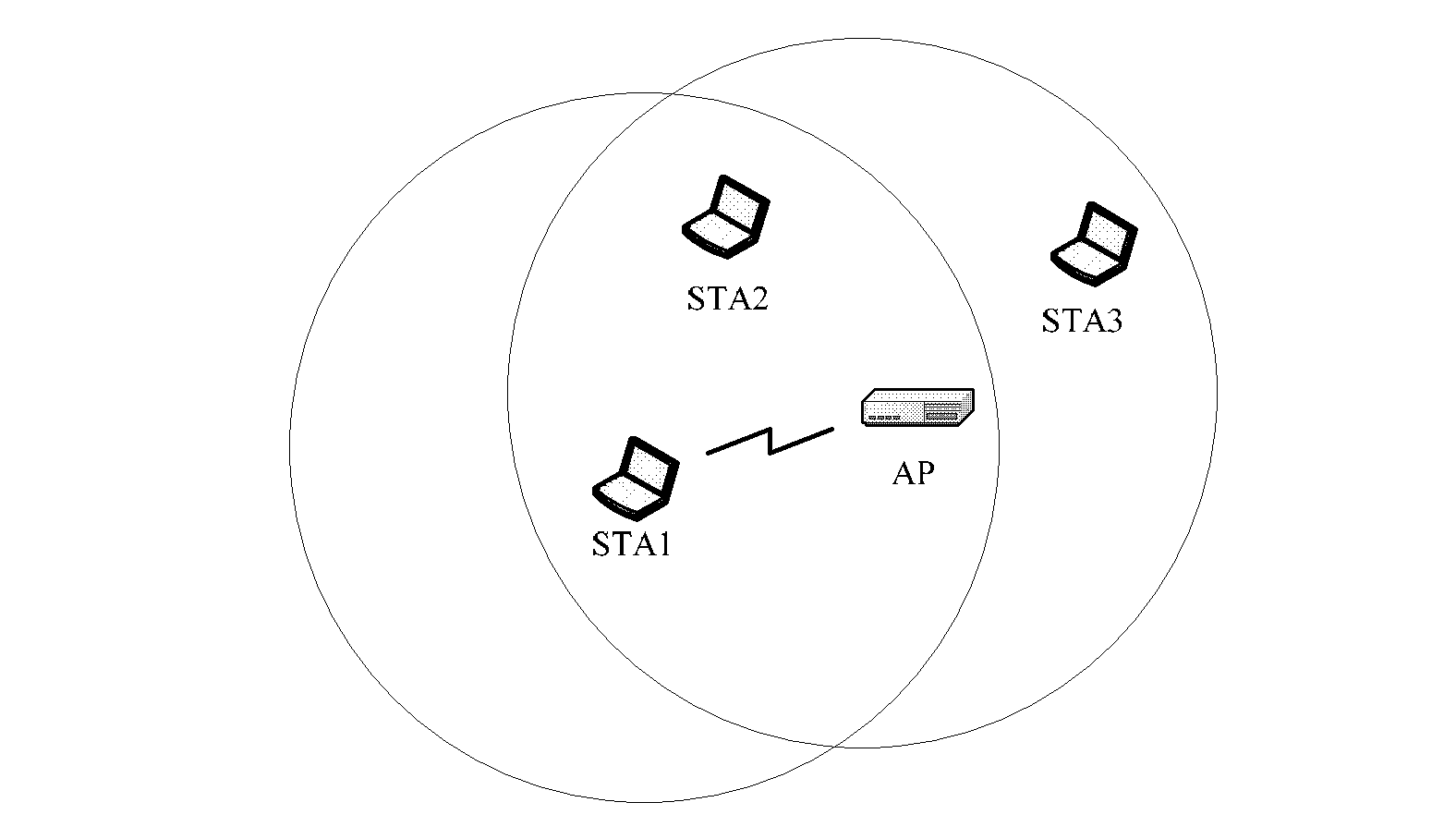
A wireless network communication method and apparatus for enhancing a data transfer rate by using a direct link protocol (DLP) and multi channels during a point coordination function (PCF) period in wireless network communications in which an access point is employed in an infrastructure mode using both a contention-free period and a contention period. The wireless network communication method of the present invention including transmitting / receiving data among stations supporting a direct link, during a given duration, through the direct link using an independent channel; transmitting / receiving data among stations other than the stations supporting the direct link, during the duration, in a specific mode corresponding to the contention-free or contention period; switching the DLP stations to a primary channel after the given duration; and transmitting / receiving data among all stations including the DLP stations, during the remaining duration, in a specific mode corresponding to the contention-free or contention period.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus of accessing channel in wireless communication system
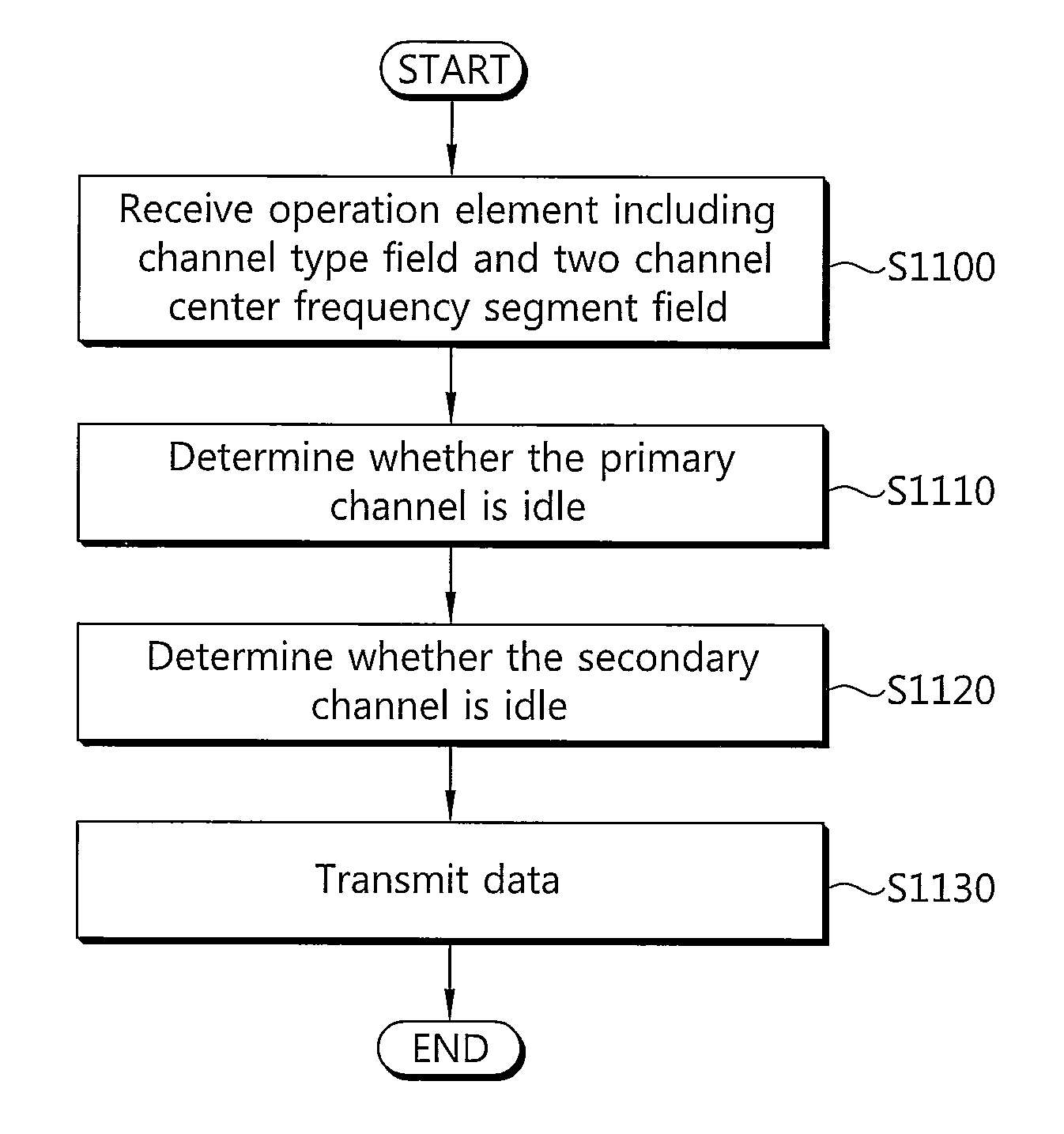
A method and apparatus of accessing a channel in a wireless local area network is provided. The method includes receiving, by a device, an operation element for setting up or switching at least one channel from an access point (AP), the operation element including a channel type field indicating whether the at least one channel is either a single channel or multiple channels, and the operation element including two channel center frequency segment fields indicating channel center frequency of a primary channel and a secondary channel respectively if the channel type field indicates that the at least one channel is multiple channels, determining whether the primary channel is idle during a first interval, determining whether the secondary channel is idle during a second interval if the primary channel is idle, and transmitting data by using the primary channel and the secondary channel to the AP or at least one station in a basic service set (BSS) if the primary channel and the secondary channel are idle.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
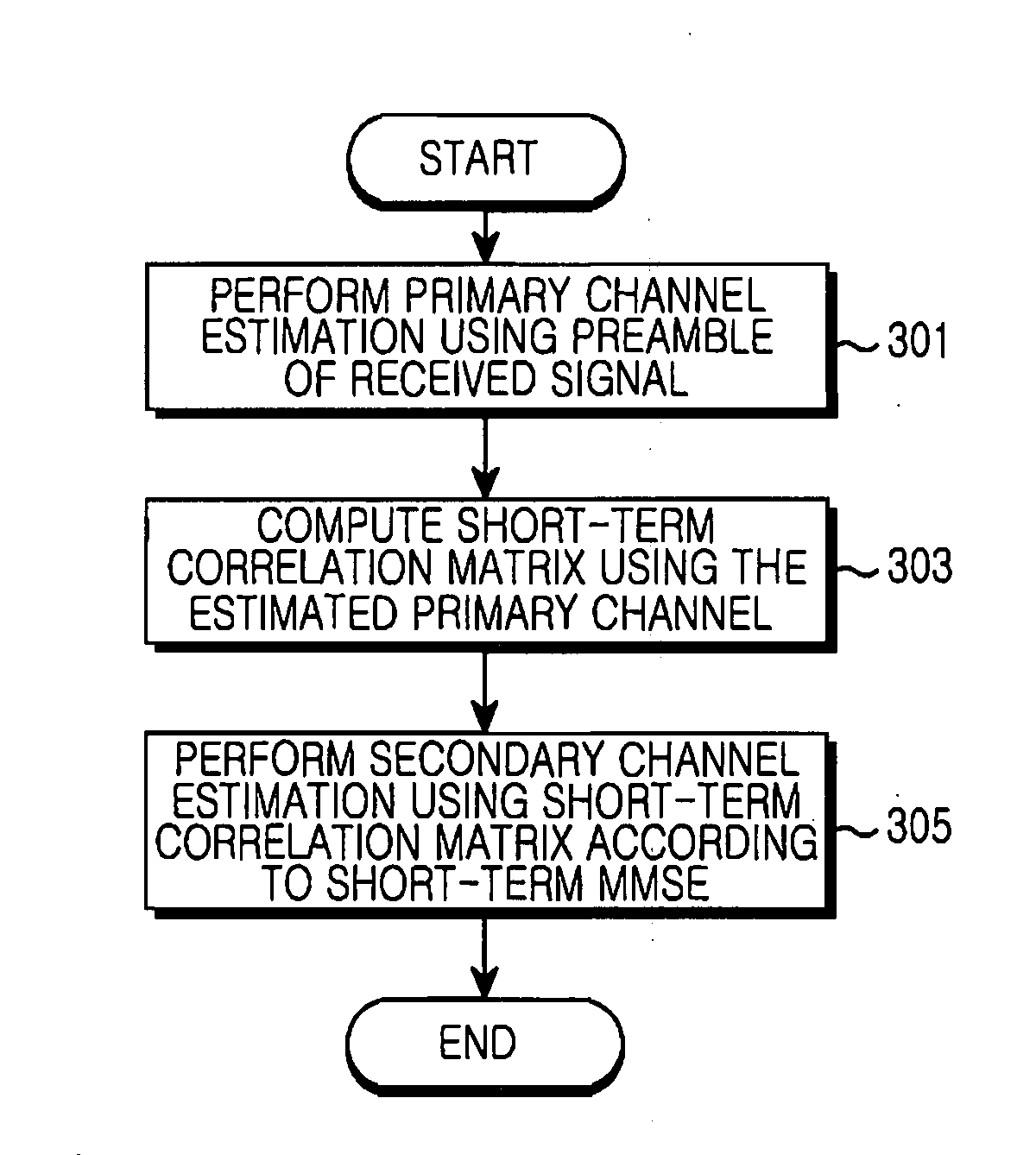
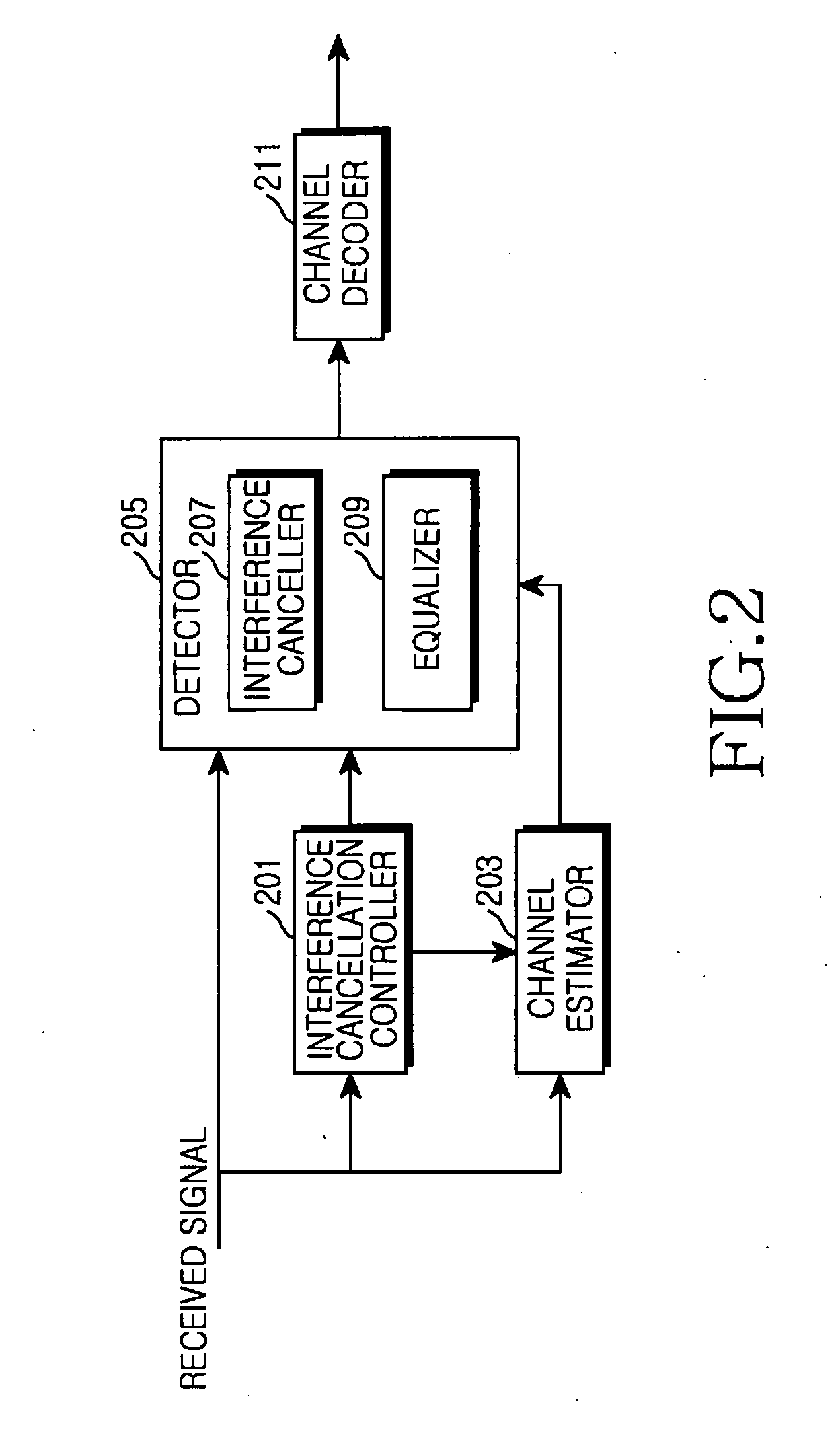
Channel estimation apparatus and method for interference cancellation in mobile communication system
InactiveUS20070242782A1Pipe supportsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsEstimation methodsMobile communication systems
Channel estimation apparatus and method for interference cancellation in a mobile communication system are provided. The channel estimation method includes detecting a preamble from a received signal and estimating a primary channel using the detected preamble; calculating a short-term correlation matrix using the primary channel; and estimating a secondary channel using the calculated short-term correlation matrix according to a certain channel estimation scheme.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
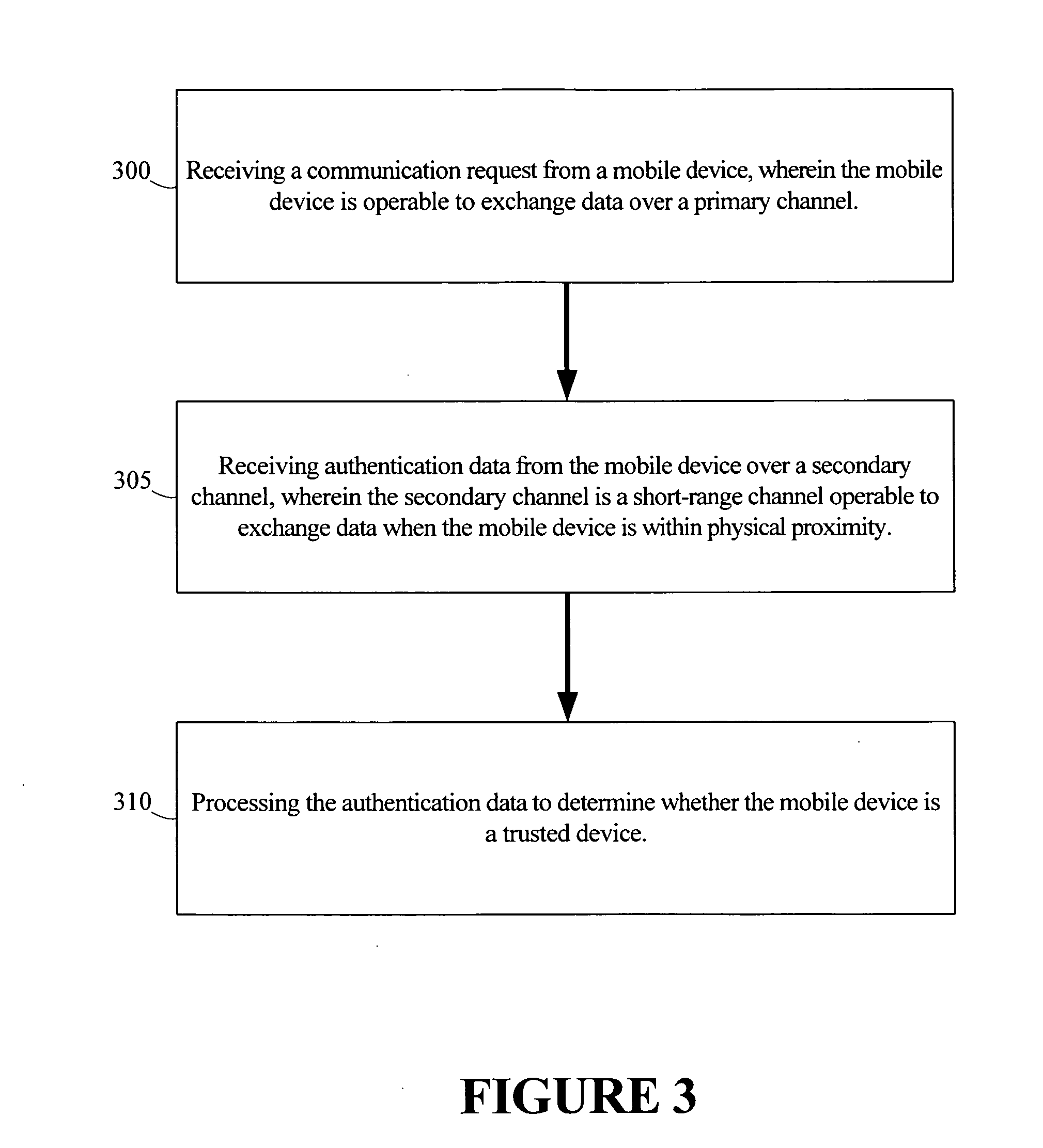
Method for secure authentication of mobile devices
ActiveUS20070178882A1Well formedUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsComputer hardwareData treatment
A method for authenticating a mobile device is provided. The method includes receiving a communication request from the mobile device. The mobile device is operable to exchange data over a primary channel. Authentication data is received from the mobile device over a second channel. The secondary channel is a short-range channel operable for exchanging data when the mobile device is within physical proximity. The authentication data is processed to determine whether the mobile device is a trusted device.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
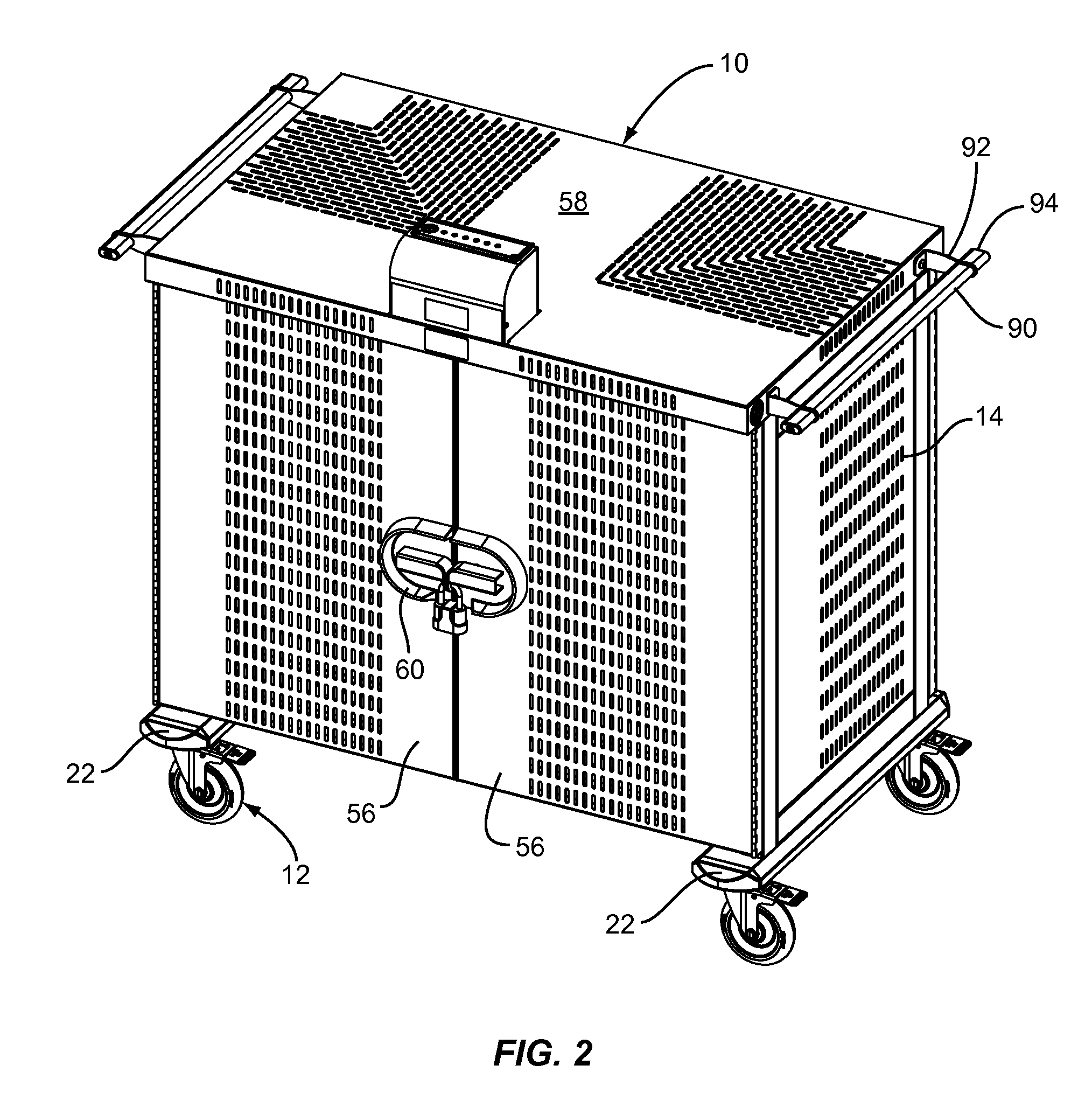
Electrical System for a Computer Cart
ActiveUS20110267782A1Optimizing power usagePower network operation systems integrationCasings/cabinets/drawers detailsElectricityPower flow
An electrical system for a computer cart enables power to be diverted between electrical channels within the cart using an intelligent round robin charging scheme. All power may be diverted to individual channels one at a time for short charging intervals. When a selected primary channel does not require all available power within the cart, excess power is provided to a secondary channel. All three channels may likewise share power if excess is available. Relays are used to allow power to be controlled to the individual channels. Current sensors on each channel sense an amount of current used by the channel. The output of the current sensor is digitized and integrated to determine how much current is being used by the channel. The current is used by the control to detect uncharged laptops and to selectively divert power between channels to optimize use of power within the computer cart.
Owner:BRETFORD MFG
Method and apparatus for communication in a wireless LAN system
ActiveUS20120213204A1Valid choiceImprove throughputAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesWireless lanBasic service
A communication method in a wireless local area network (WLAN) system is provided. The communication method includes: configuring, by a first access point (AP), a first basic service set (BSS) which uses a first primary channel (P-CH) and a first secondary channel (S-CH); and configuring, by a second AP, a second BSS which uses a second P-CH, a second S-CH, a second tertiary channel (T-CH), and a second quaternary channel (Q-CH), wherein a band of the first P-CH overlaps with a band of the second P-CH, and the second P-CH is a common channel which is used in an operation of a member station of the second BSS.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
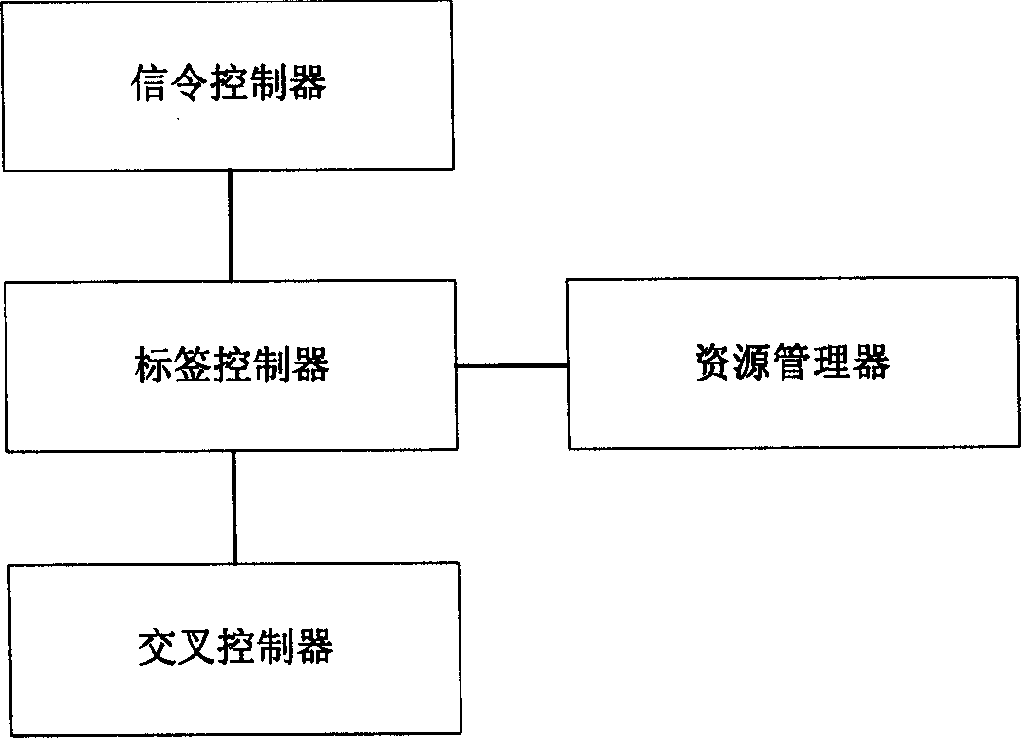
Reactor with primary and secondary channels
Owner:TRIBUTE CREATIONS LLC
Apparatus and Method for Establishing and Utilizing Backup Communication Channels
An apparatus, method, and machine-readable medium are described for establishing, maintaining and utilizing backup channels in a peer-to-peer (“P2P”) network. For example, in one embodiment, each mobile device can establish a primary P2P communication channel with one or more other mobile devices. Once the primary channel is established, each mobile device can use the primary channel to exchange secondary channel connection data and can subsequently open one or more secondary P2P communication channels with the other mobile devices. Upon detecting that the primary P2P communication channel has failed or has degraded below a specified threshold (e.g., a bandwidth or bitrate threshold), one of the secondary P2P communication channels can be automatically promoted to a primary P2P communication channel.
Owner:APPLE INC
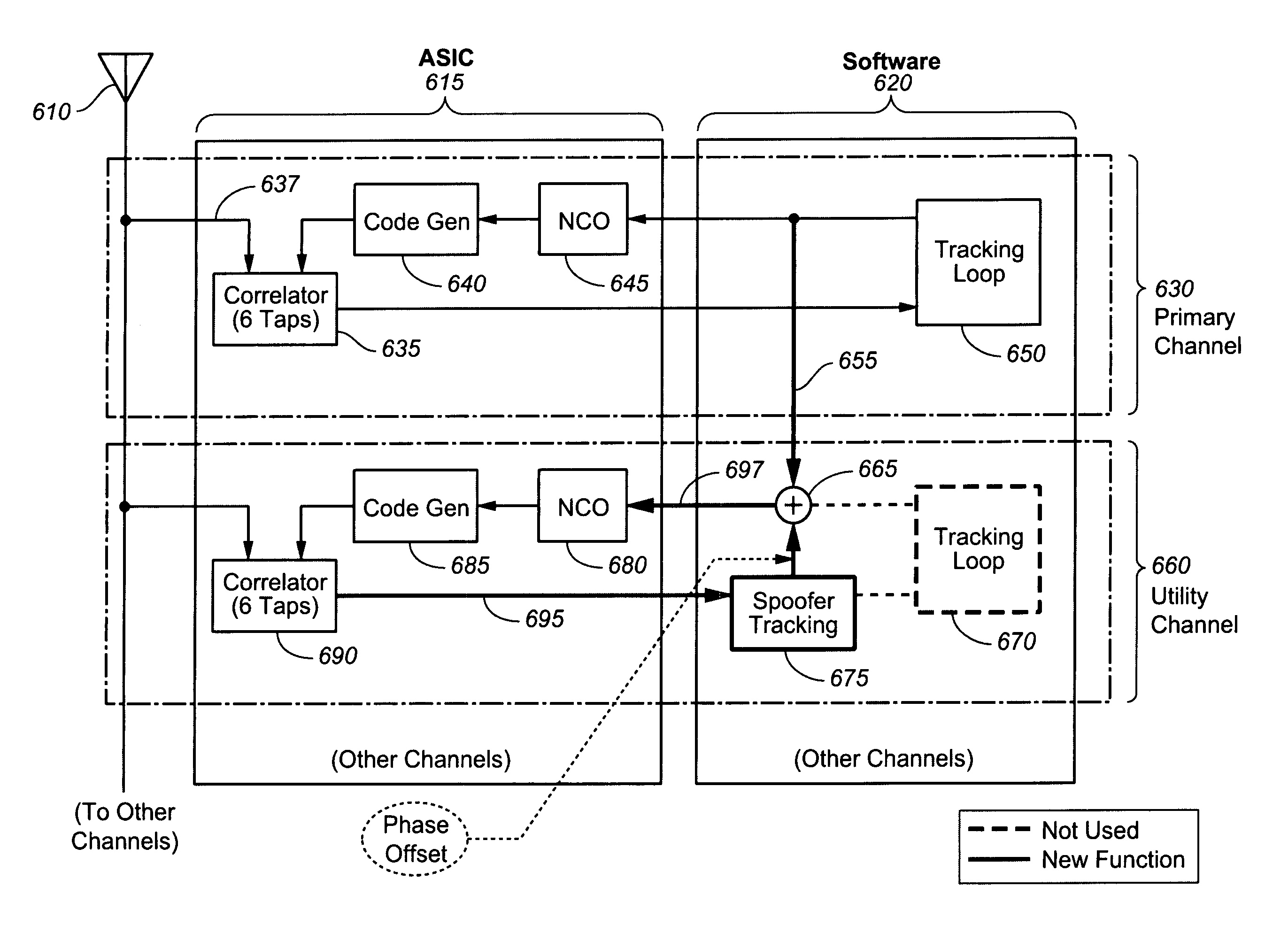
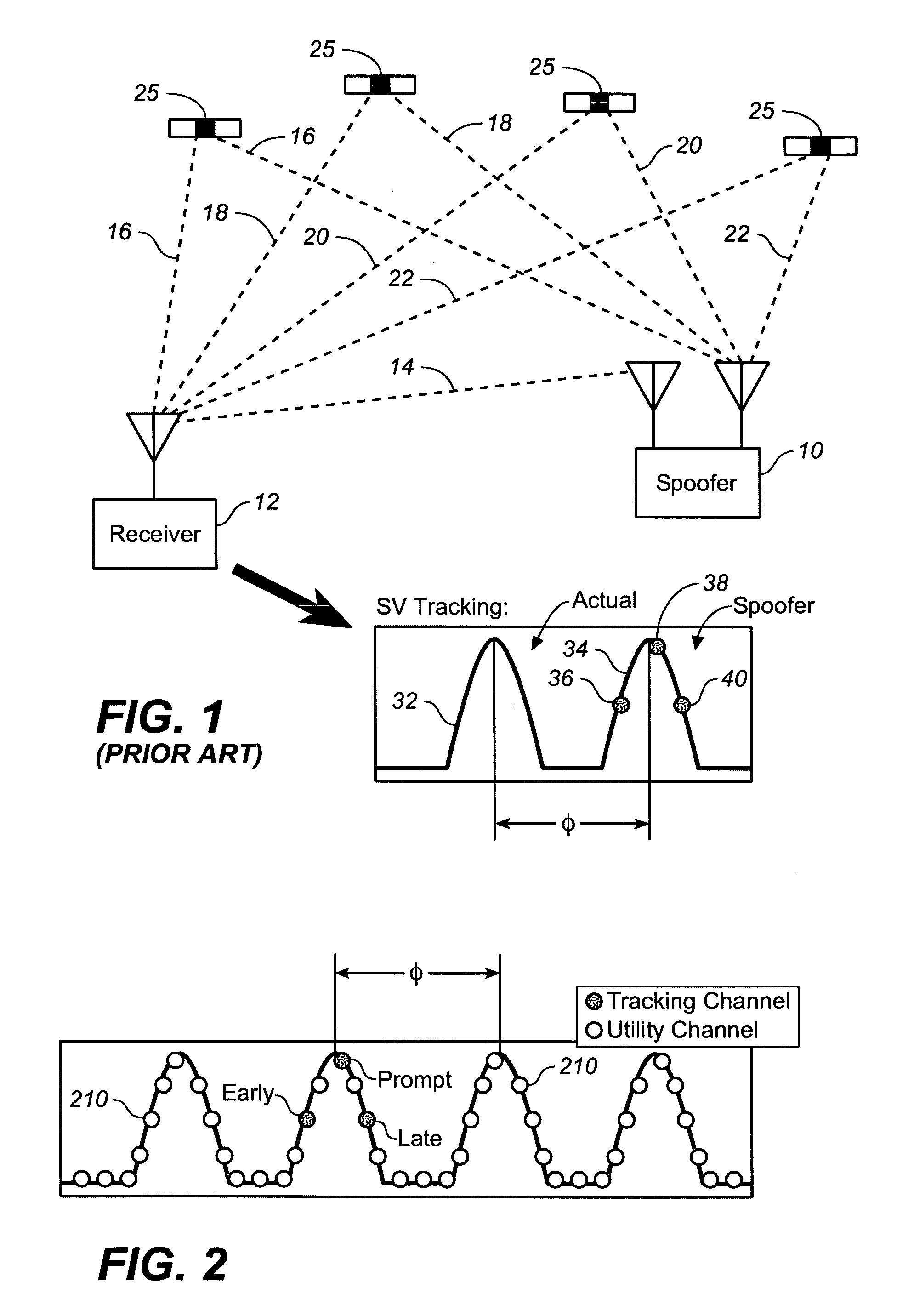
Advanced spoofer mitigation and geolocation through spoofer tracking
ActiveUS7764224B1Mitigating spoofingRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsPosition fixationGps receiverNuller
A GPS receiver employing advanced spoofer mitigation, geolocation and tracking capabilities through the use of a utility channel coupled in parallel to a tracking channel. The tracking channel tracks the direct signal while the utility channel tracks one or more spoofer signals. A signal from the primary channel is used by the utility channel to locate spoofer signals, with the primary channel operating independently of the utility channel. Three complementary spoofer mitigation methods are disclosed for identifying advanced repeaters and security-compromised spoofers, which may also be used for geolocation of such spoofers: (1) the consistency routine; (2) the nuller routine; and (3) the multiple antennas routine. An improved architecture is disclosed to allow easy upgrading and retrofitting of an existing GPS receiver.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
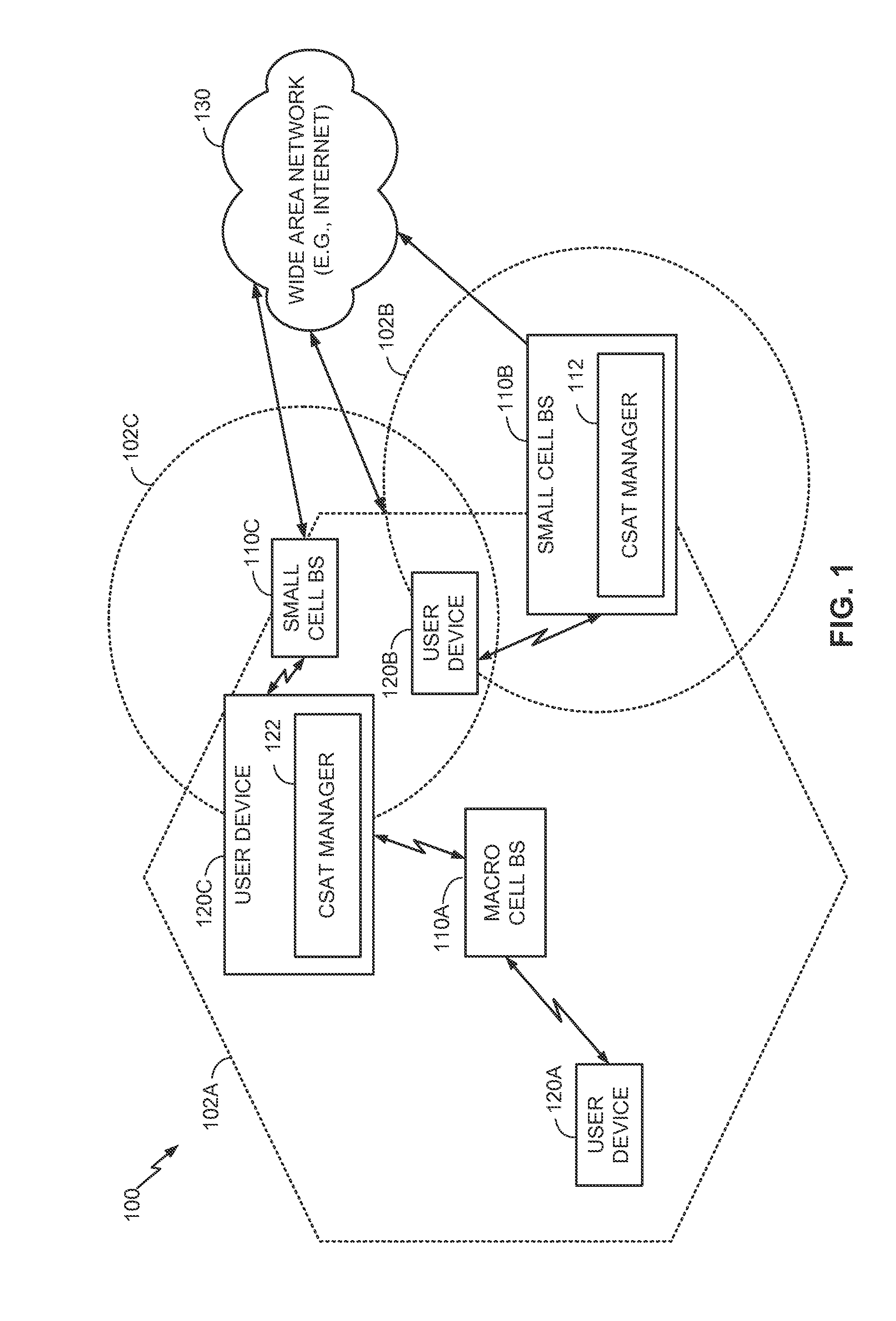
Carrier sense adaptive transmission (CSAT) in unlicensed spectrum
ActiveUS20150085841A1Reduce distractionsExpand coverageSignal allocationTime-division multiplexTransceiverFrequency spectrum
Systems and methods for Carrier Sense Adaptive Transmission (CSAT) and related operations in unlicensed spectrum are disclosed to reduce interference between co-existing Radio Access Technologies (RATs). The parameters for a given CSAT communication scheme may be adapted dynamically based on received signals from a transceiver for a native RAT to be protected and an identification of how that RAT is utilizing a shared resource such as an unlicensed band. Other operations such as Discontinuous Reception (DRX) may be aligned with a CSAT Time Division Multiplexed (TDM) communication pattern by way of a DRX broadcast / multicast message. Different TDM communication patterns may be staggered in time across different frequencies. Channel selection for a co-existing RAT may also be configured to afford further protection to native RATs by preferring operation on secondary channels as opposed to primary channels.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
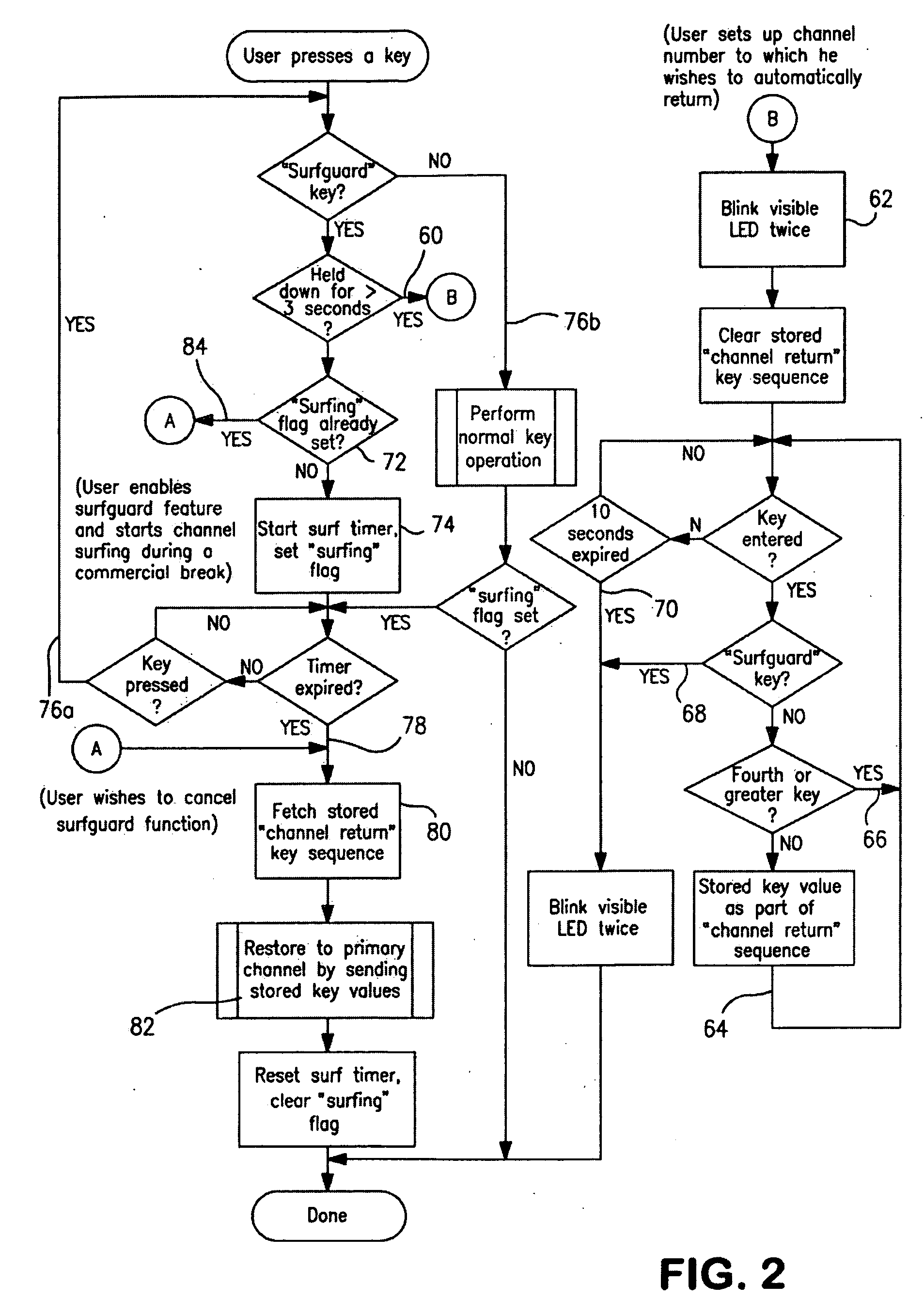
Media return system
InactiveUS20090102984A1Television system detailsColor television detailsRemote controlControl memory
A remote control provides a return to channel feature for use with a media device adapted to play media but not itself equipped with a return to channel feature. The remote control stores a primary channel in memory and is programmed such that, in direct response to a first input being manually provided to a remote control, a timer in the remote control is caused to commence a timing of a predetermined interval such that, in response to expiration of the predetermined interval timed by the timer, the remote control is caused to transmit a command signal corresponding to the primary channel stored in memory to the media device.
Owner:UNIVERSAL ELECTRONICS INC
Carrier sense method and system
InactiveCN102595569AReduce power consumptionPower managementEnergy efficient ICTClear to sendMain channel
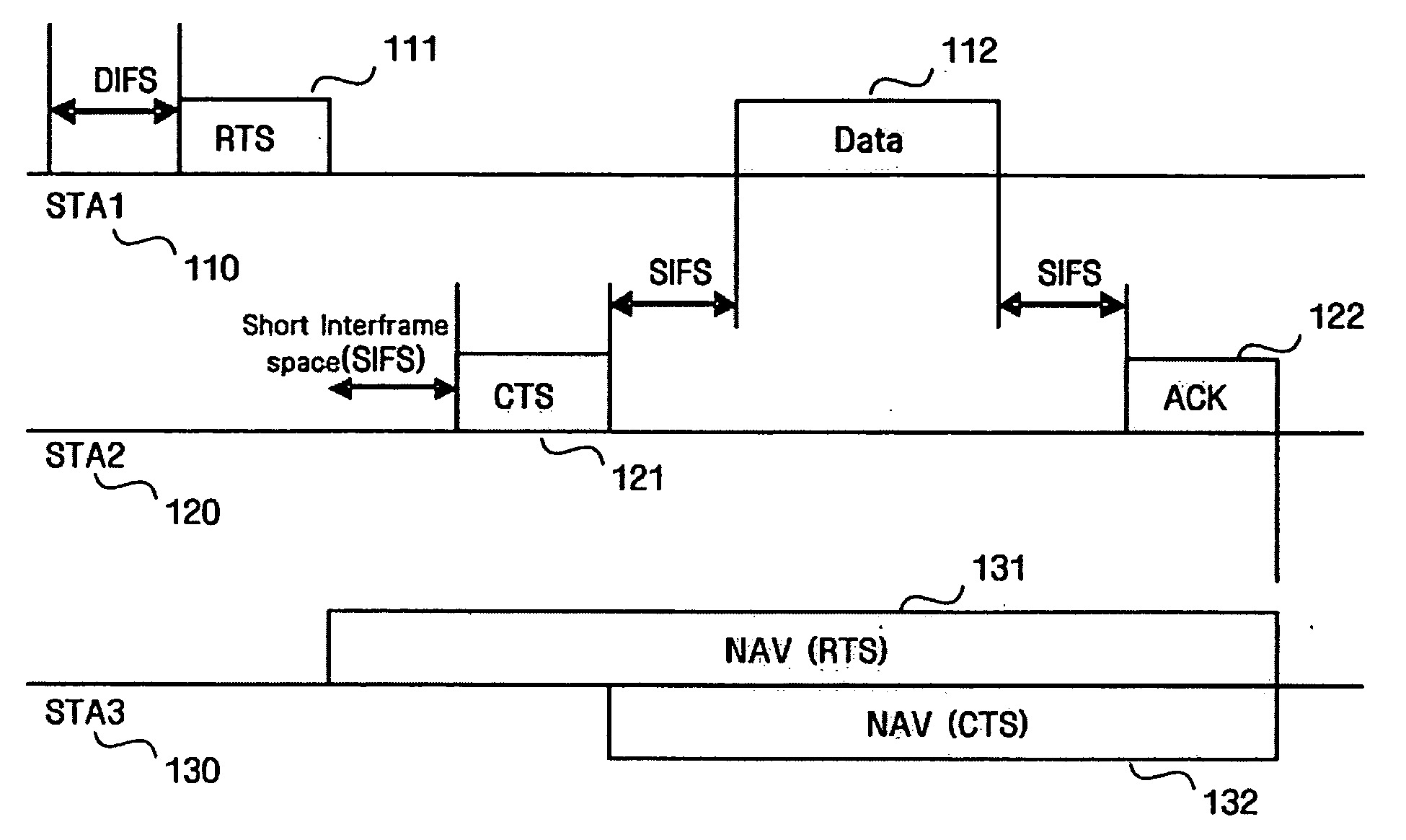
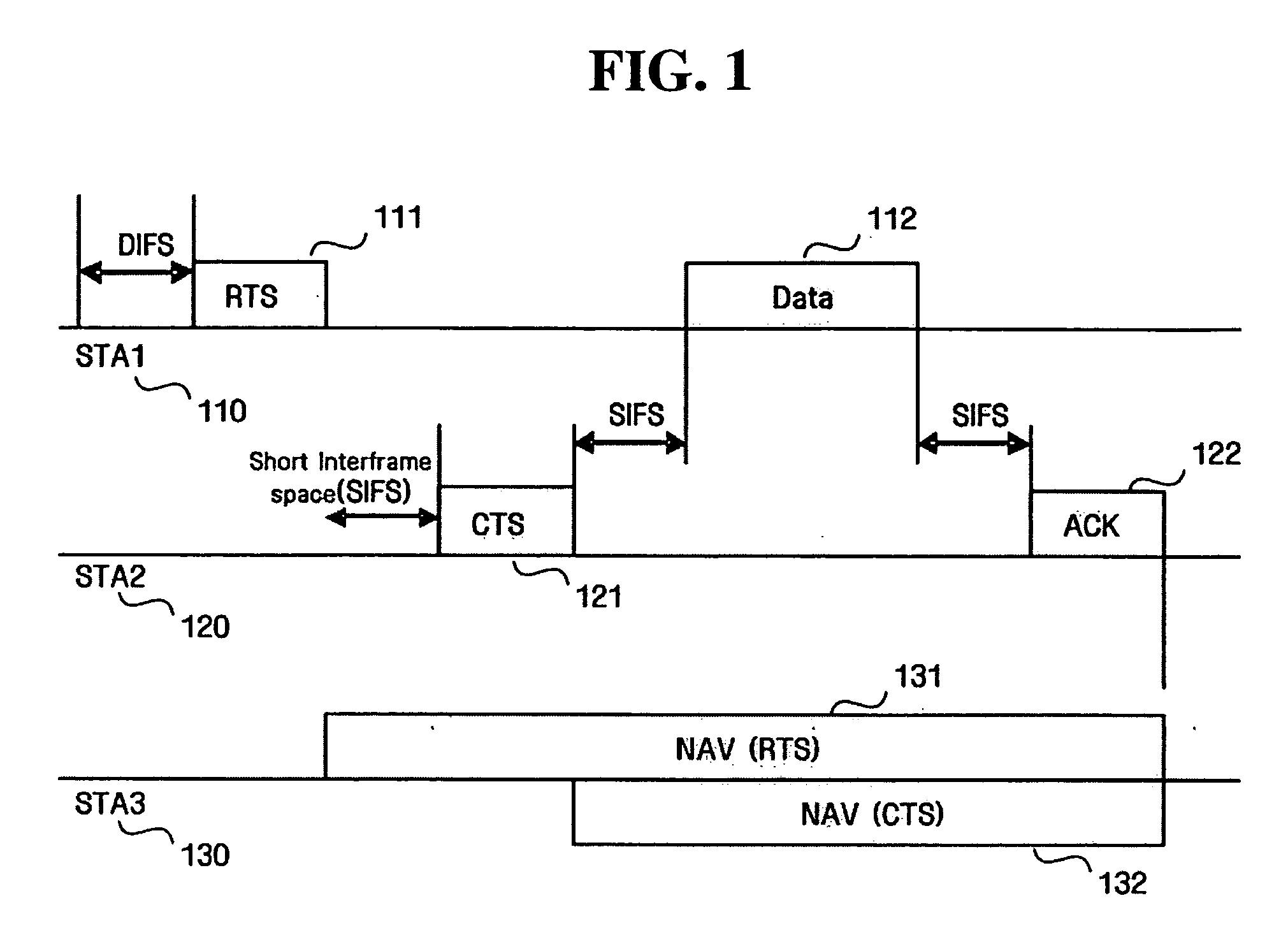
The invention discloses a carrier sense method and a system. According to the method, a transmitting terminal sends an idle channel to assess clear channel assessment (CCA) request frames on a main channel of a transmission channel which needs to be detected; the transmitting terminal sends request to send (RTS) frames on the transmission channel which needs to be detected after sending a point coordination function inter-frame space (PIFS) subsequent to transmission of the CCA request frame; and the transmitting terminal performs data transmission on the transmission channel transmitting clear to send (CTS) frames after receiving an indication that CTS frames are permitted to send. The invention also discloses the carrier sense system, which comprises a transmitting terminal and a receiving terminal. According to the method and the system, the power consumption of the receiving terminal is reduced and reliable CCA results of all transmission channels are provided.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Joint reduction of NEXT and FEXT in xDSL systems
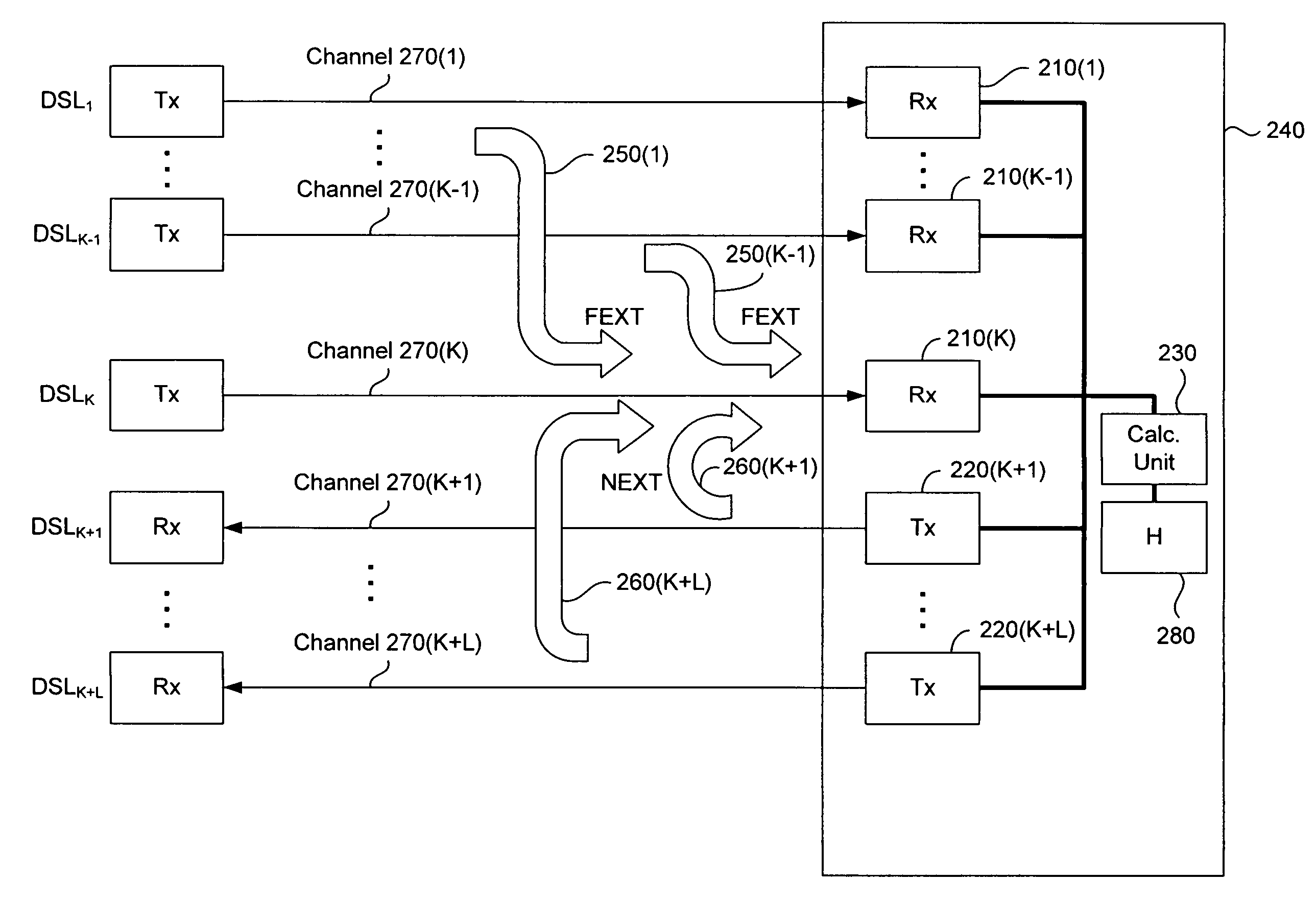
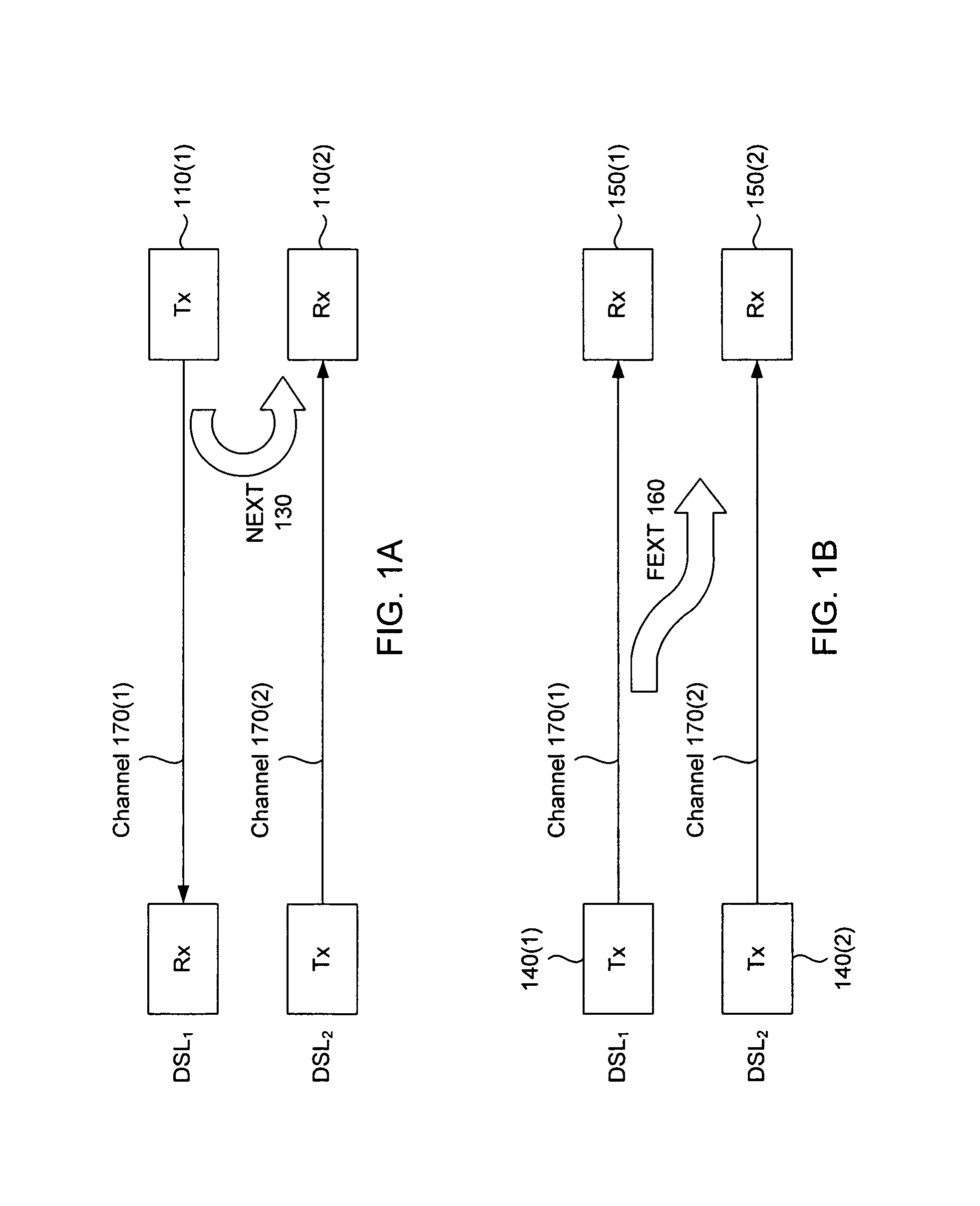
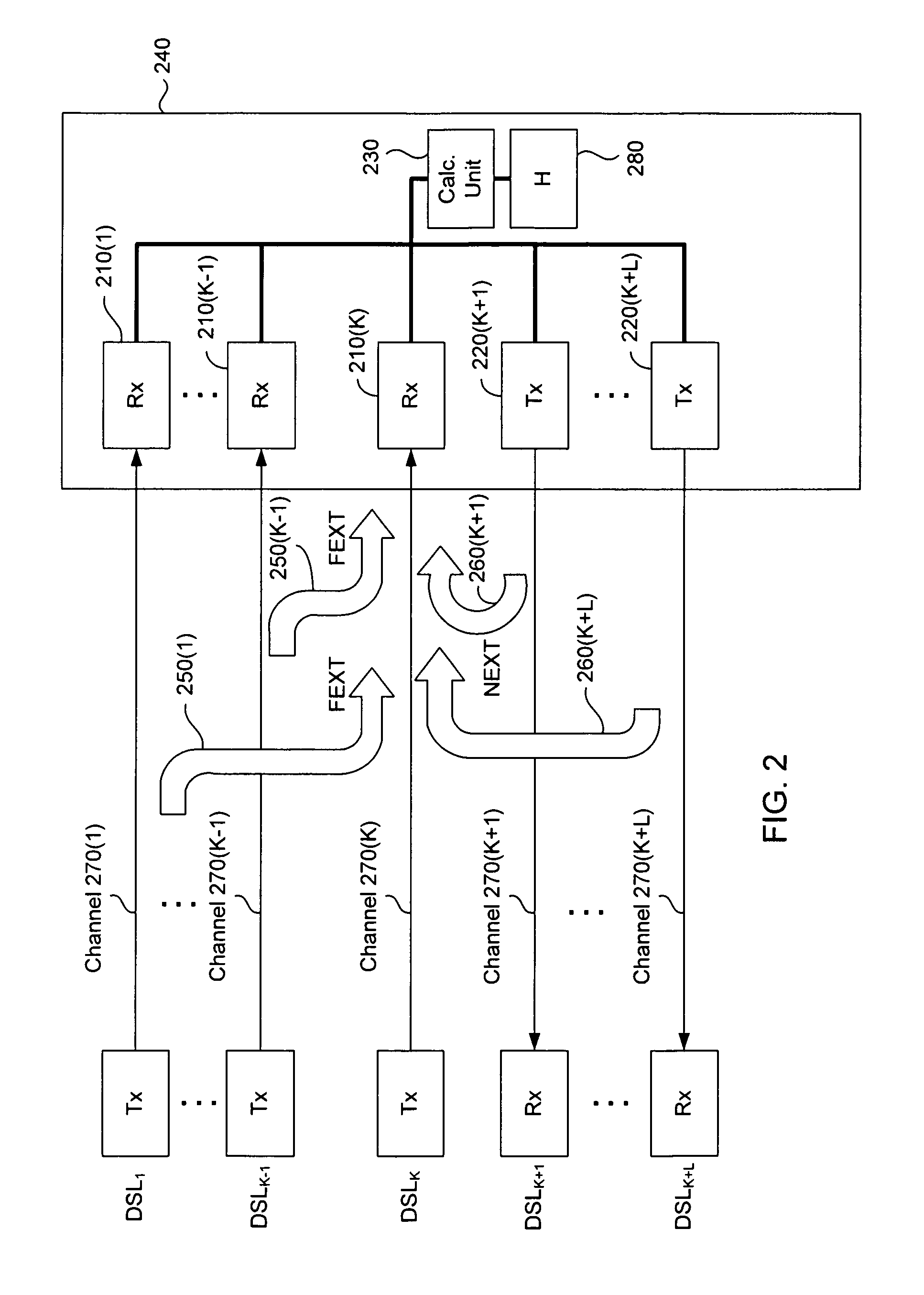
InactiveUS7394752B2Reduce signalingReduce crosstalkFrequency-division multiplex detailsCurrent interference reductionChannel dataCoupling
Methods, apparatus, techniques and computer program products for joint reduction of crosstalk in a synchronized, time division duplexed DSL systems use sequential removal of NEXT interference followed by removal of FEXT interference from a received DSL signal. Crosstalk is removed from a primary signal in a synchronized TDD DSL system having a primary channel that carries the primary signal, at least one NEXT generating channel that generates NEXT interference in the primary signal and at least one FEXT generating channel that generates FEXT interference in the primary signal. Signal data is acquired, where the signal data includes received signal data for the primary channel and at least one FEXT generating channel, transmitted signal data for at least one NEXT generating channel, and channel data comprising channel transfer function data and crosstalk coupling coefficient data for the primary channel, each NEXT generating channel and each FEXT generating channel. After the signal data is acquired, NEXT interference in the primary signal is then removed using the transmitted signal data and the channel data, followed by removal of FEXT interference in the primary signal using vectored DMT FEXT removal, the received signal data and the channel data. In another system in which FEXT generating received signals are not necessarily available, FEXT removal can be achieved using expectation cancellation, the primary signal and the channel data in connection with possible transmitted signal values.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
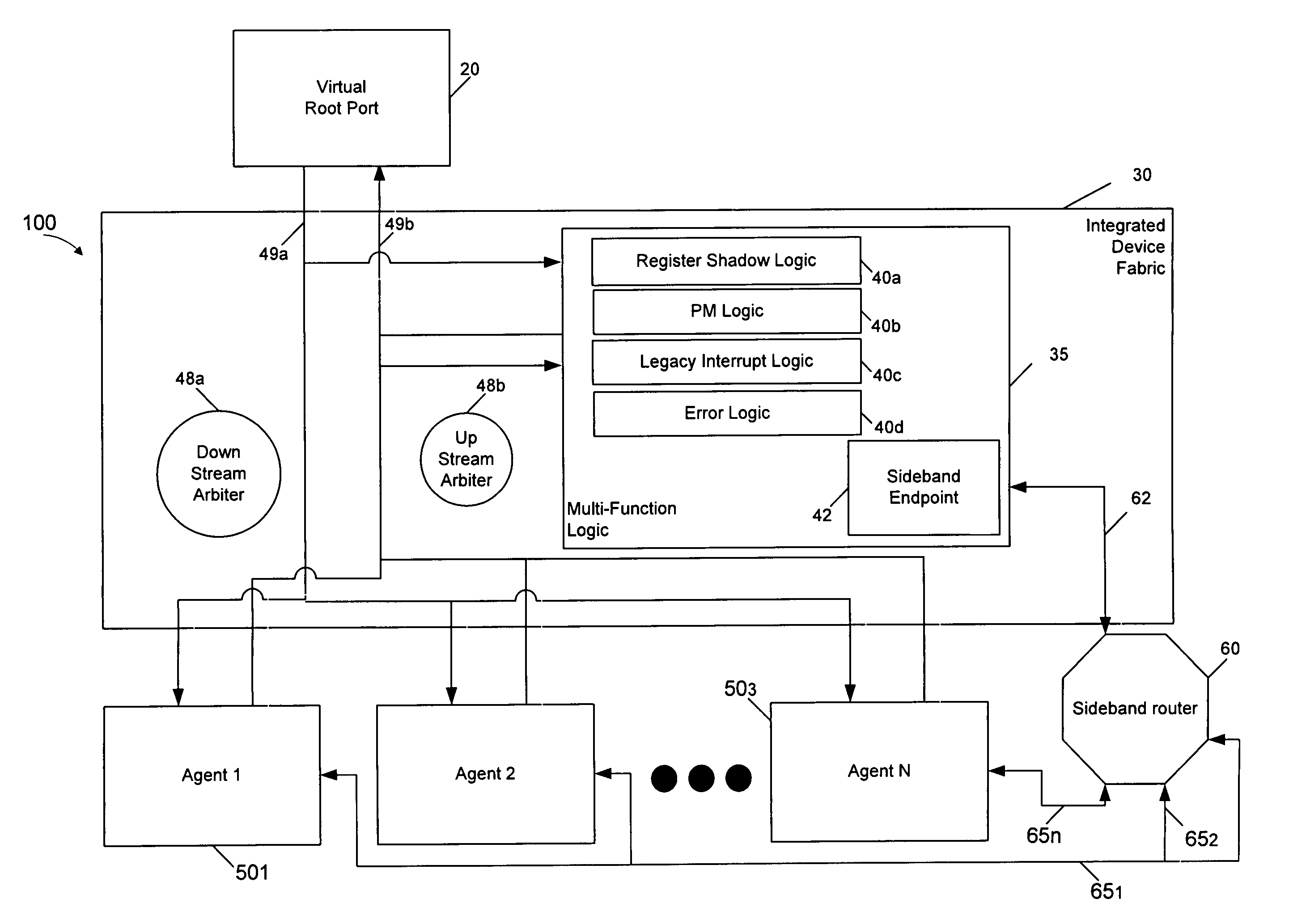
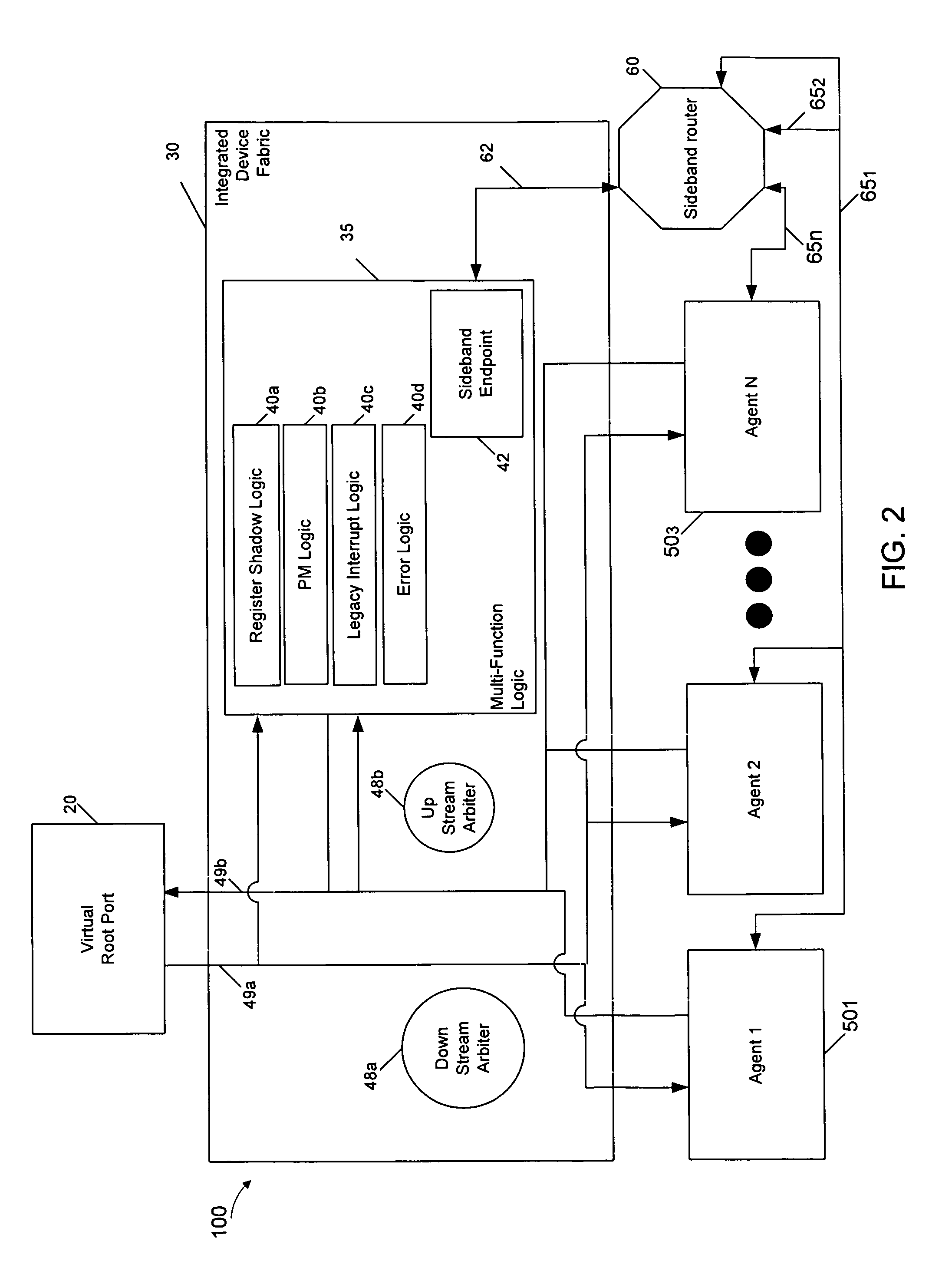
Flexibly integrating endpoint logic into varied platforms
InactiveUS7873068B2Data switching by path configurationHybrid transportIntellectual propertyEngineering
An integrated endpoint having a virtual port coupled between an upstream fabric and an integrated device fabric that includes a multi-function logic to handle various functions for one or more intellectual property (IP) blocks coupled to the integrated device fabric. The integrated device fabric has a primary channel to communicate data and command information between the IP block and the upstream fabric and a sideband channel to communicate sideband information between the IP block and the multi-function logic.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method for using an initial maintenance opportunity for non-contention ranging
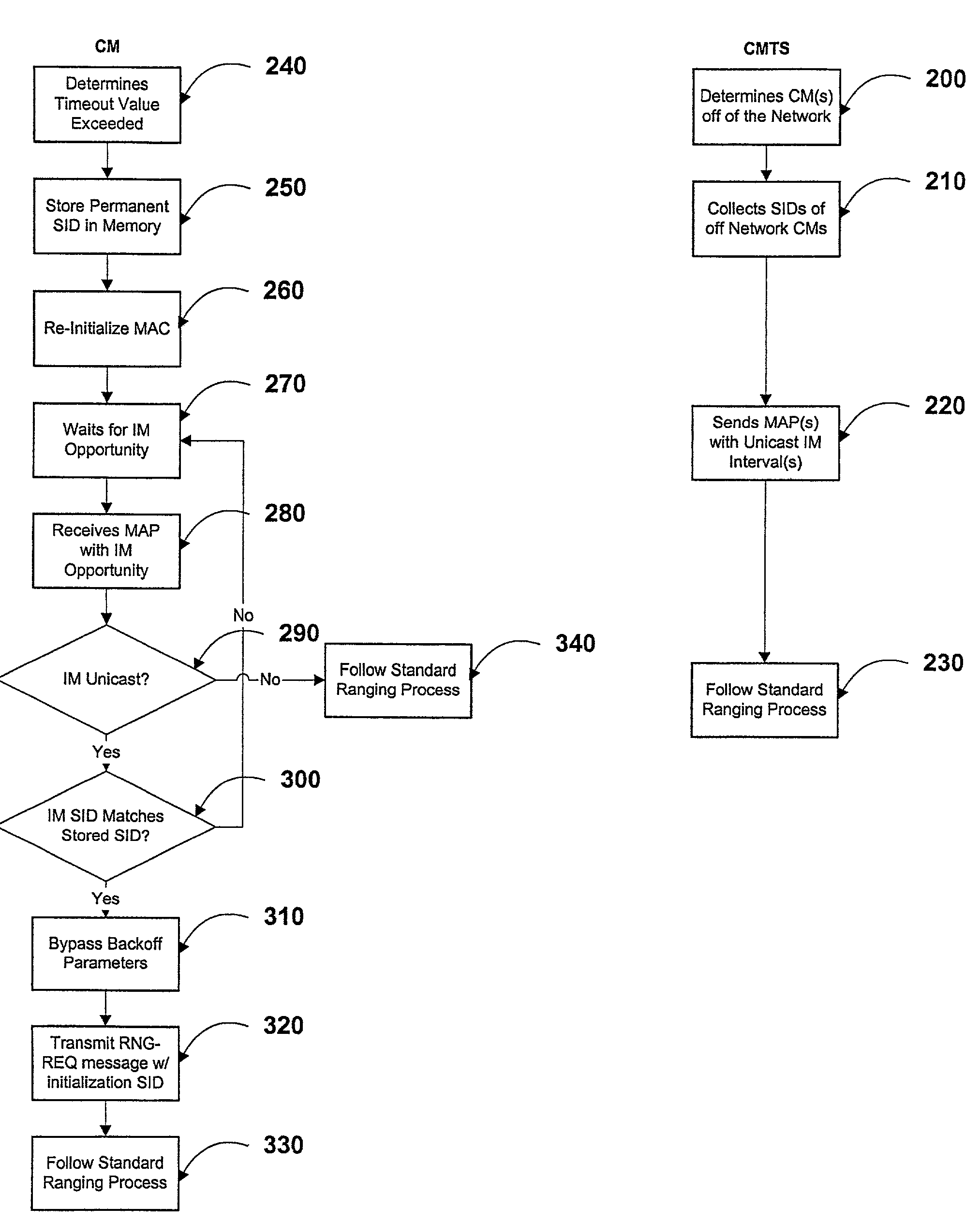
InactiveUS6944881B1Avoid collisionBroadband local area networksTwo-way working systemsModem deviceEngineering
A method of preventing collisions when a cable modem re-registers with a cable modem termination system on a cable television network following failure of a primary communications channel between the cable modem and the cable modem termination system. The method provides a service identifier that is transmitted to the cable modem during initial registration of the cable modem with the cable modem termination system. Upon registration of the cable modem with the cable modem termination system, the cable modem stores the service identifier in memory. After failure of the primary channel, the cable modem reinitializes on the cable network and waits for transmission of a bandwidth allocation map from the cable modem termination system. When the cable modem receives the bandwidth allocation map, it determines if the map contains a unicast initial maintenance opportunity. When the map contains a initial maintenance opportunity having a unicast associated identifier, the cable modem compares the service identifier stored in its memory with a unique service identifier contained in the initial maintenance opportunity information element of the bandwidth allocation map. When the service identifiers match, the cable modem then uses the initial maintenance opportunity having the unicast associated identifier contained in the information element of the bandwidth allocation map to re-register with the network.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
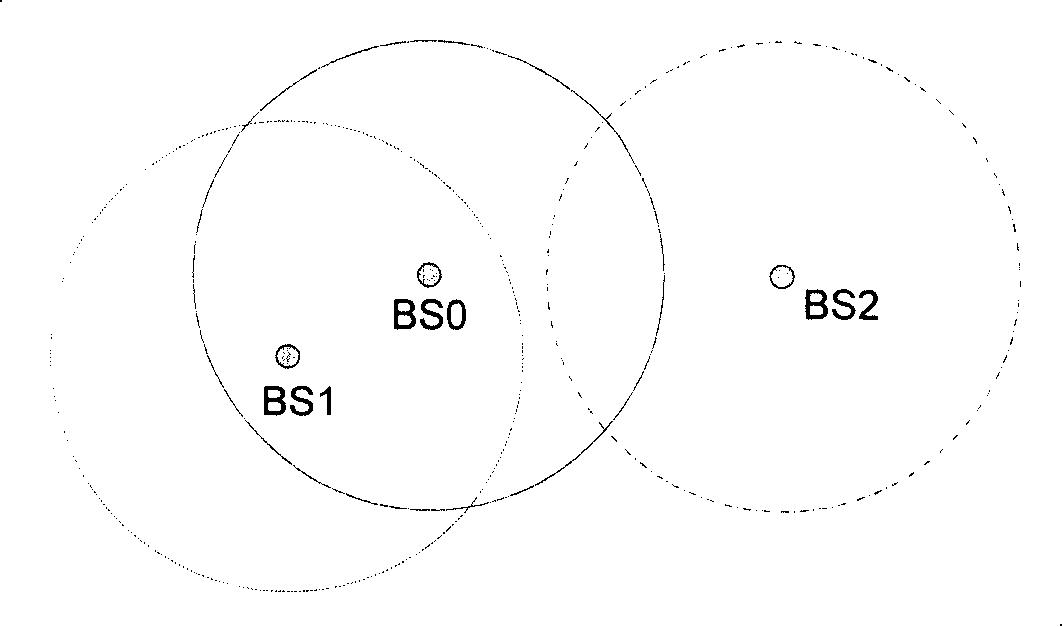
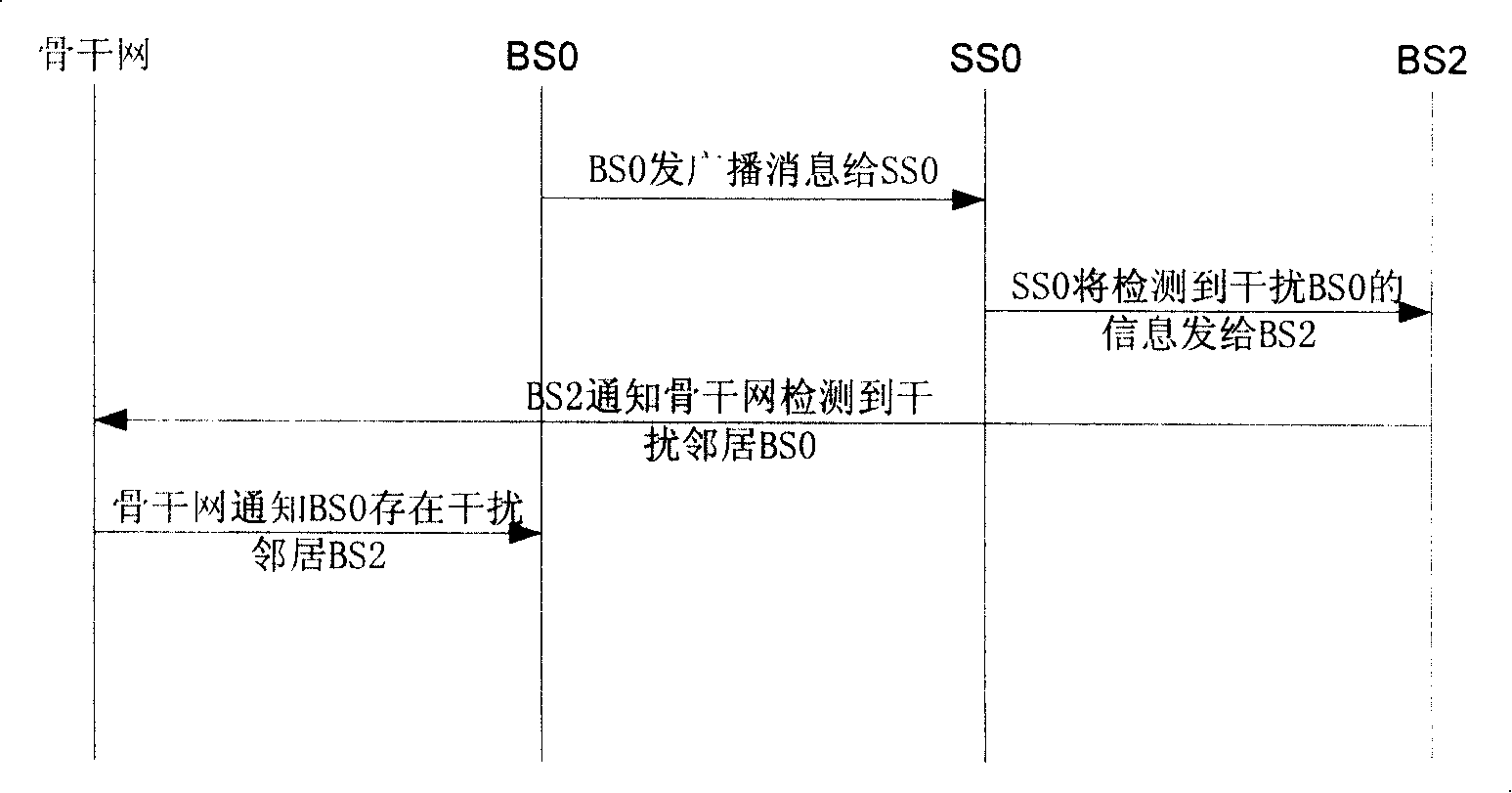
Method, device and system for implementing terminal access in wireless communication system
InactiveCN101179821AEfficient detection of interference situationsImprove access success rateRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless communicationCommunications systemInterference elimination
The invention relates to a terminal access method, device and system in a wireless communication system. In the invention, a base station of the wireless communication system carries out a transceiving operation by using a primary channel and a secondary channel, and a periodicity of the base station is switched between the primary channel and the secondary channel. The method also includes the following steps: after the terminal to be accessed determines that the access operation is not completed through the primary channel of the base station, an interference state of the primary channel of the base station is detected. The detecting result of the interference state is transmitted to the base station by the secondary channel of the base station, and the interference state is eliminated by the base station according to the testing result of the interference state. After an operation of interference elimination, the base station notices the terminal to implement the access operation through the primary channel again. Therefore, the invention is able to improve a success rate of the terminal access in the base station system, and on the other hand, the invention is able to reduce dead zones of the communication system and thereby to improve communication performance of the wireless network.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
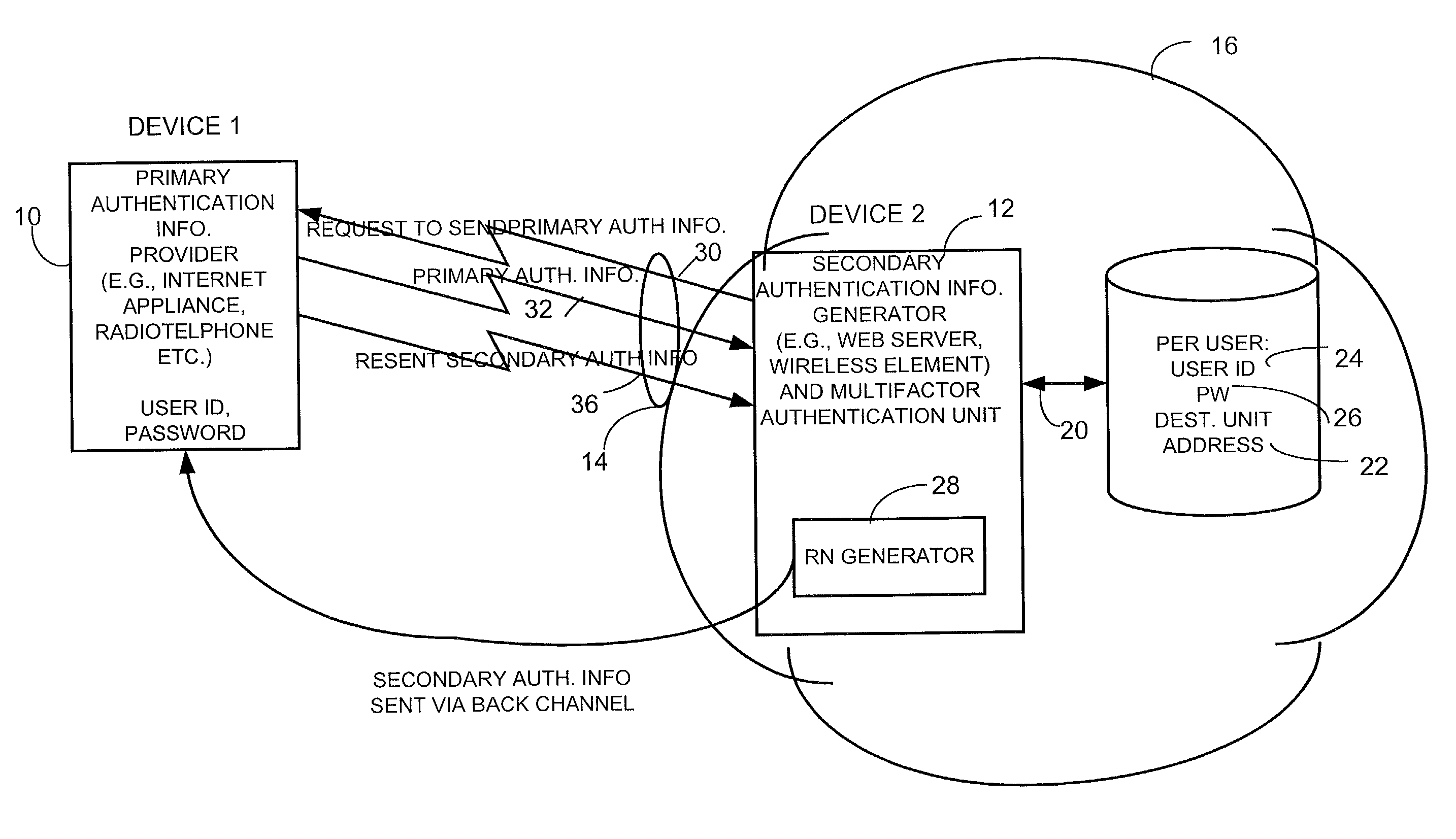
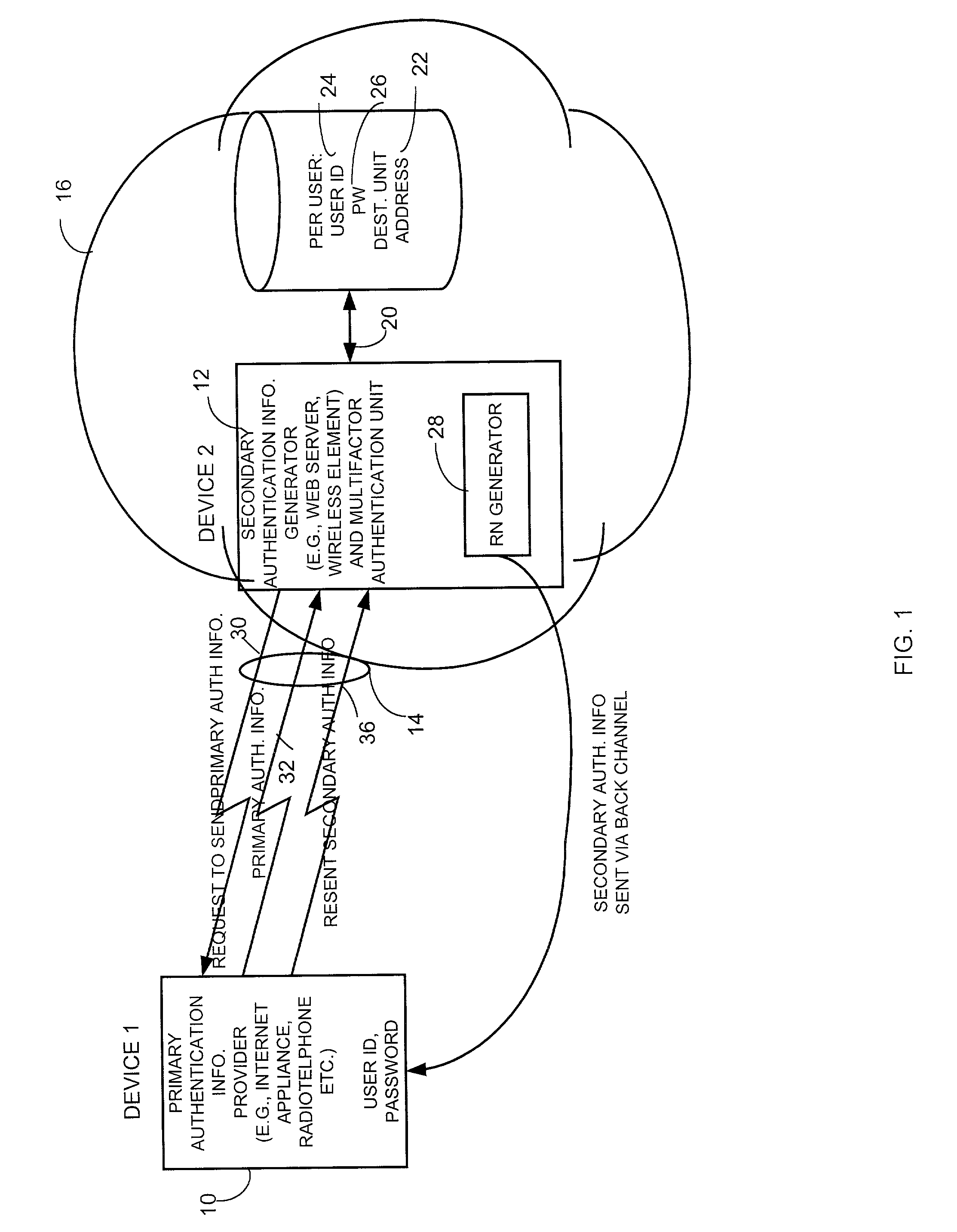
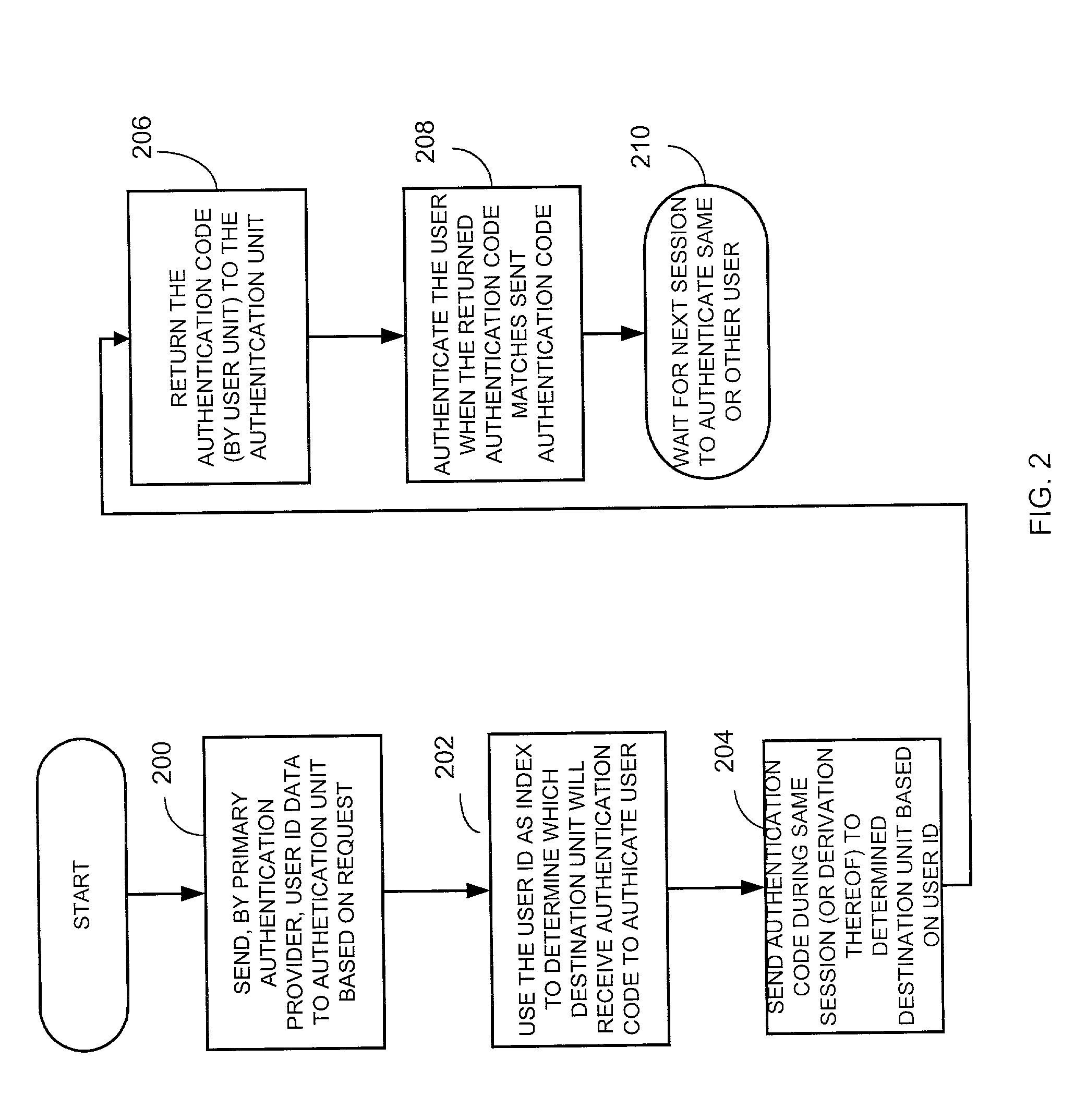
Method and apparatus for providing user authentication using a back channel
ActiveUS7765580B2Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsPasswordThe Internet
A method and apparatus provides user authentication by communicating primary authentication information, such as user identification data and / or password data to an authentication unit via a primary channel such as over the Internet. An authentication code is generated by the authentication unit on a per session basis and is sent to a destination unit via a first secondary channel during the session. The destination unit then retransmits the authentication code, on a second secondary channel, to the first unit in a way that is transparent to a user of the first unit. The first device then send the received re-transmitted authentication code back to the authentication unit via the primary channel during the session.
Owner:ENTRUST
Staggered primary channels for WIFI
InactiveUS20150078298A1Facilitate communicationAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesTelecommunicationsBasic service
Certain aspects of the present disclosure relate generally to wireless communications, and more specifically to systems, methods, and devices for staggered primary channel selection for WiFi. According to certain aspects, a method for wireless communications is provided. The method may be performed, for example, by an access point (AP). The method generally includes obtaining information regarding neighbor basic service sets (BSSs), selecting a primary channel based on the obtained information, and output for transmission a message signaling an intention to communicate using the selected primary channel.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Device and method of providing grant frame for bandwidth scheduling
Devices and methods of limiting wideband STA communication are generally described. The STA receives, over a primary channel, a wakeup frame containing an indication of a SP or CBAP to acquire a wideband TXOP over a wide bandwidth channel including the primary channel and a secondary channel and a control trailer having an indication of the wide bandwidth channel. Prior to the SP / CBAP, the STA opens reception from the primary channel to the wide bandwidth channel. The STA then communicates with another STA over the wide bandwidth channel and subsequently reduces reception from the wide bandwidth channel to the primary channel. The wakeup frame originates from an AP / PCP or the other STA, and contains fields indicating the wakeup frame length and SP or a sensing time length prior to the CBAP.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Mitigation of Interference and Crosstalk in Communications Systems
InactiveUS20080239937A1Effectively competeSubstations coupling interface circuitsInterconnection arrangementsMulti inputDecomposition
Signals in a multi-channel, impaired communication system are post-processed at the receiver. A triangular matrix Decision Feedback Demodulator (DFD) at the receiver extracts channels without requiring delivery of receiver parameters to the transmitter. Multi-Input Multi-Output (MIMO) processing matrices and DFD parameters are computed by first applying matrix transformations to diagonalize the noise covariance matrix of the multiple channels received at the receiver. QR decompositions (i.e., decompositions into orthogonal and triangular matrices) are then applied to the main channels to obtain triangular channel matrices. The noise-diagonalizing transformations and QR decompositions are then combined to form the MIMO postprocessing matrices and DFD parameters. MIMO postprocessing matrices and DFD parameters are computed from training data and then adapted during live data transmission.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
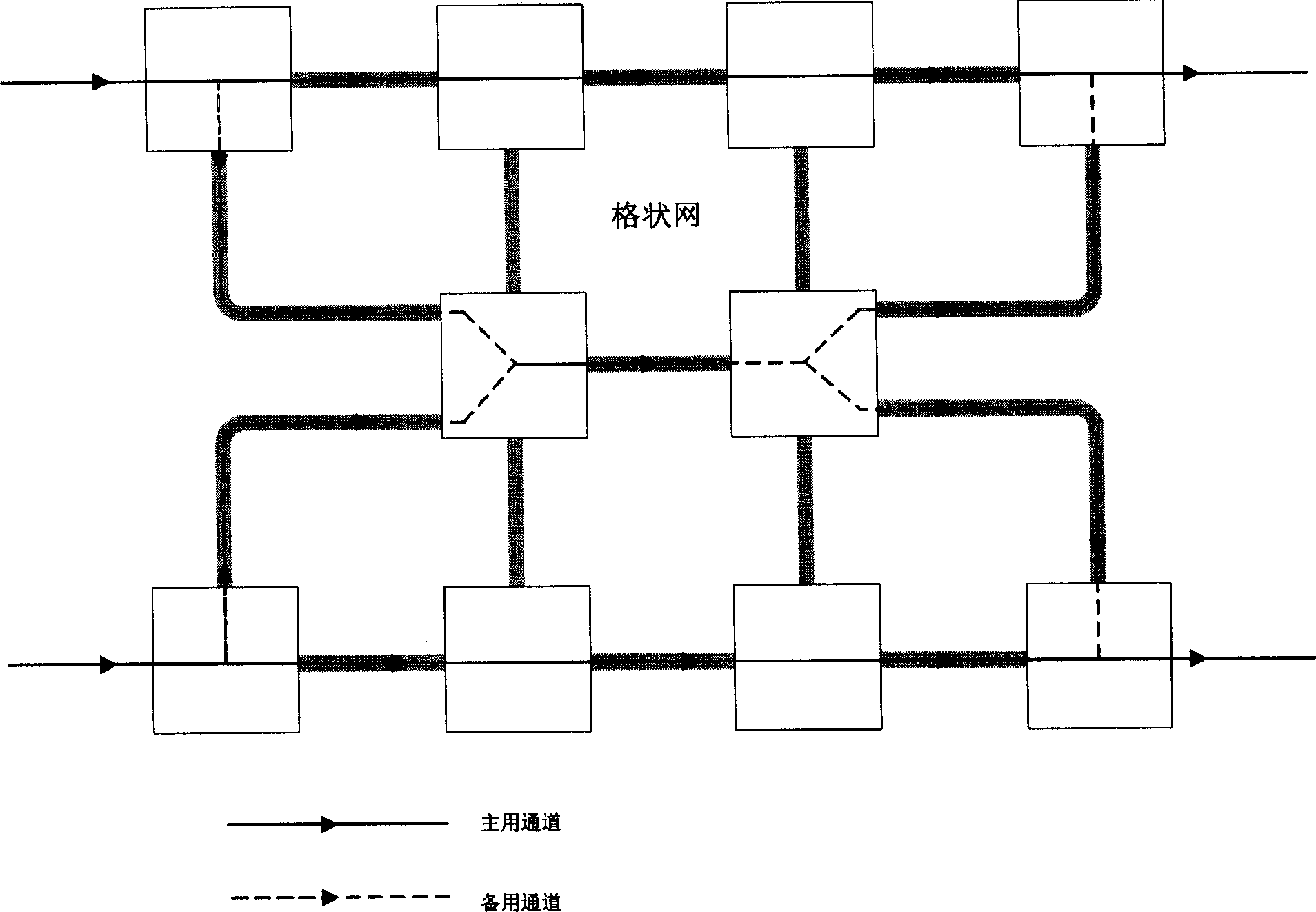
Method of proceeding failure recovery using shared spare passage in lattice shape network
InactiveCN1556637AShorten the timeSignaling process is simpleTransmissionExchange protocolPrimary channel
The invention relates to a method for carrying on failure restoration using shared backup channel in grating network, the method presets a backup channel when creating the primary channel, the backup channel presetting uses share mode, that is to say, the same resources can be used as the preset resources for several backup channels, when the primary channel is failed, it uses the label exchanging protocol to execute the signaling activating process of the backup channel, when one of the shared backup channel is activated, the other backup channels which carry on resources sharing to the activated channel are removed, then calculates these backup channels again. The invention uses sharing protection, upgrades the utilization rate of resources, because of the preset backup channel, the process activating the backup channel is simple and quick.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for performing channel aggregation and medium access control retransmission
InactiveCN103416017ANetwork topologiesInter user/terminal allocationFrequency spectrumMedia access control
A method and apparatus are described for performing channel aggregation to communicate over a non-contiguous spectrum, such as television white space (TVWS), using a plurality of aggregated channels including a primary channel and at least one non-primary channel (e.g., a secondary channel, a tertiary channel or a quaternary channel). Carrier sense multiple access (CSMA) may be performed on the primary channel to obtain access to the primary channel. After waiting an arbitration interframe space (AIFS) and potentially performing backoff on the primary channel, the aggregated channels may be used for transmission. A buffer controller may be used to create, for each of a plurality of access classes (ACs), a logic buffer for each of the channels. A frame controller may be used to provide the buffer controller with aggregated medium access control (MAC) protocol data unit (A-MPDU) frame information, and control aggregation and fragmentation processes.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
Device and method for dispensing at least two mutually reactive components
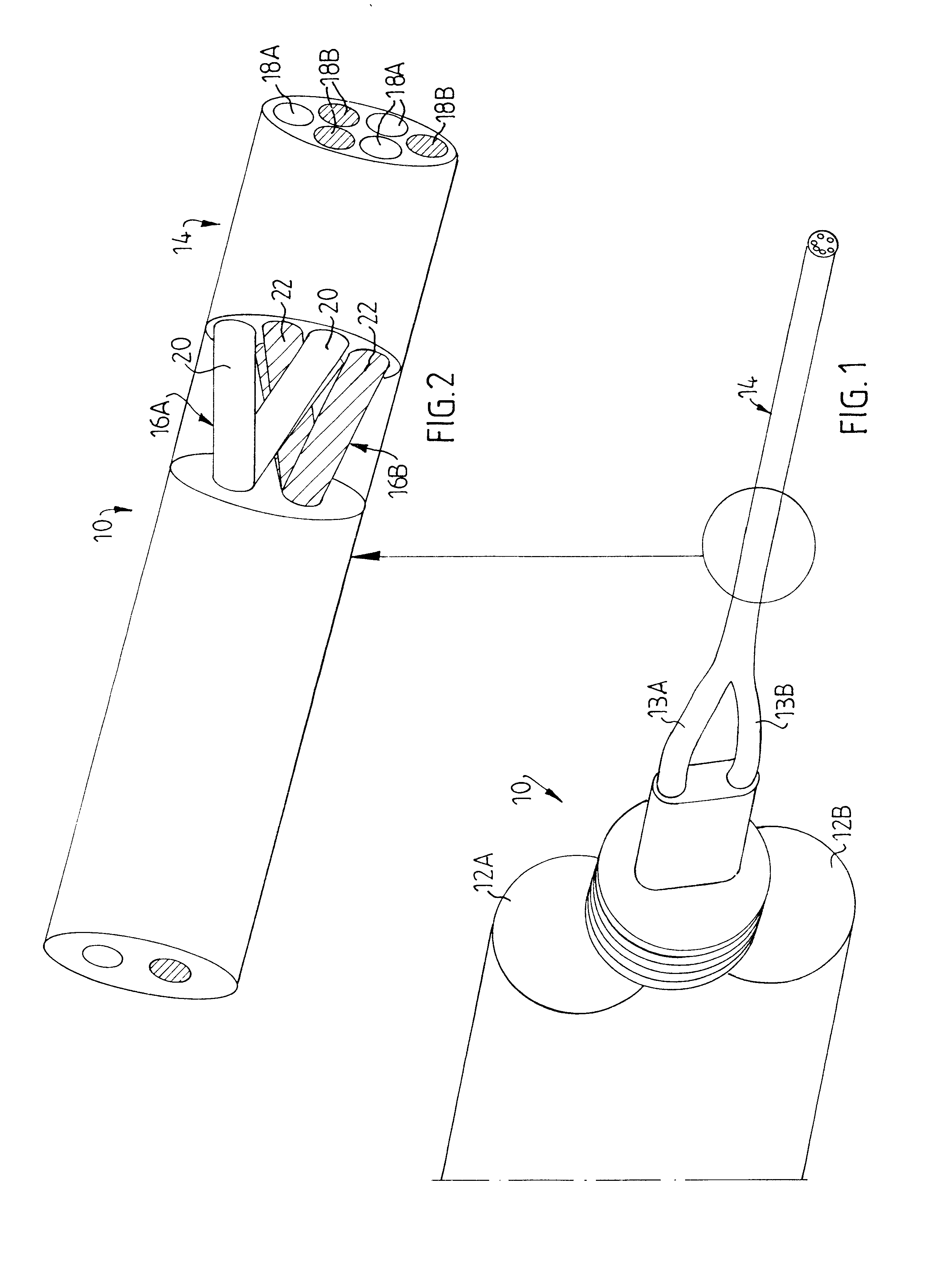
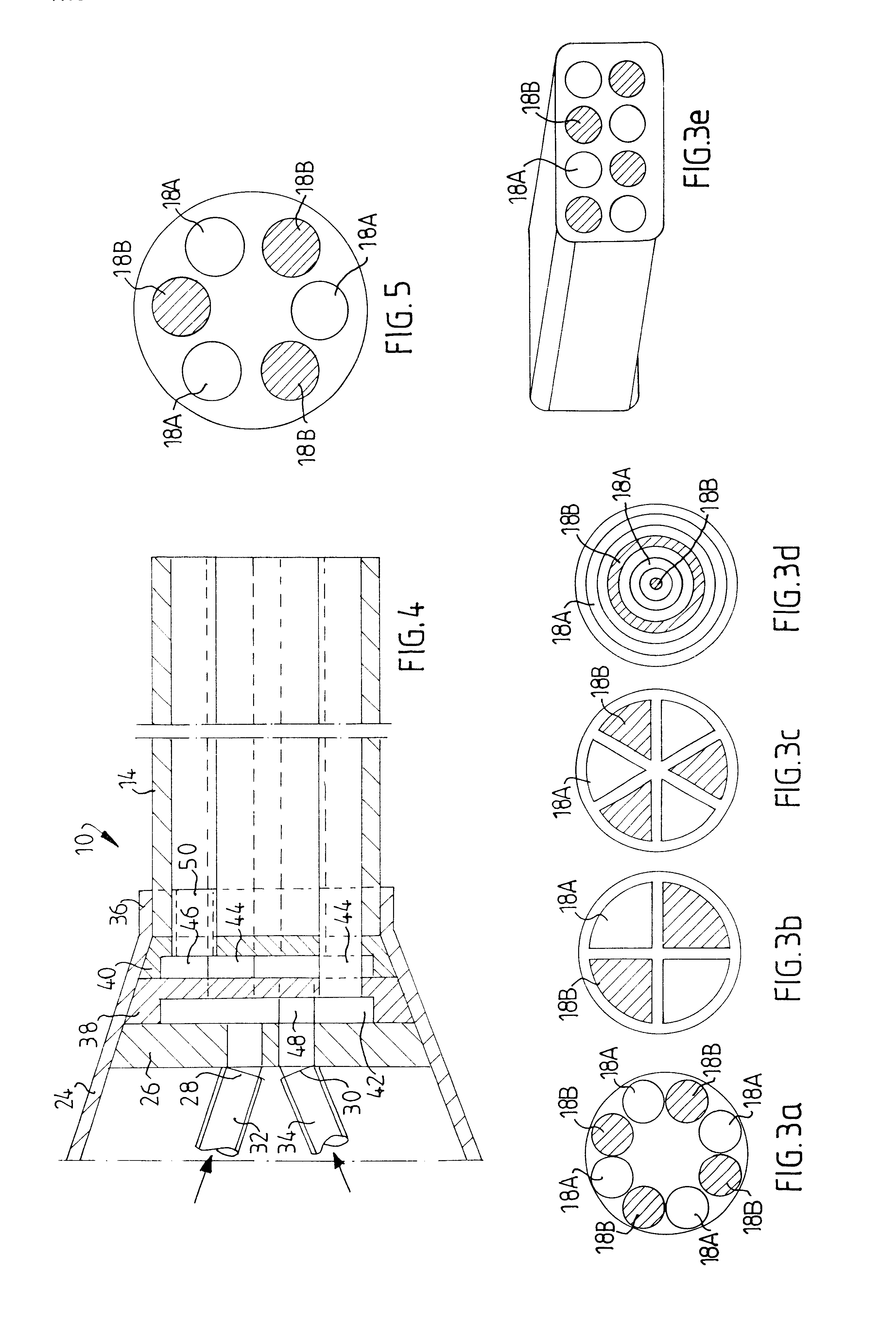
A device for dispensing at least two mutually reactive components, such as fibrinogen and thrombin, comprising a supplier (12A, 12B) having a primary channel for supplying a respective one of said at least two reactive components to a dispenser (14) having secondary channels (18A, 18B) for separately discharging said components at a distal end orifice thereof opening into a target area for external intimate mixing of the respective reactive components outside a distal tip end of said dispenser (14). A distributor (38, 40) is interposed between said supplier and said dispenser for multiplying the number of the respective primary channels with at least a factor 2. Adjacent ones of said secondary channels (18A, 18B) are adjoined to primary channels (32, 34) intended for supply of reactive components of different kind.
Owner:BIOVITRUM AB (PUBL)
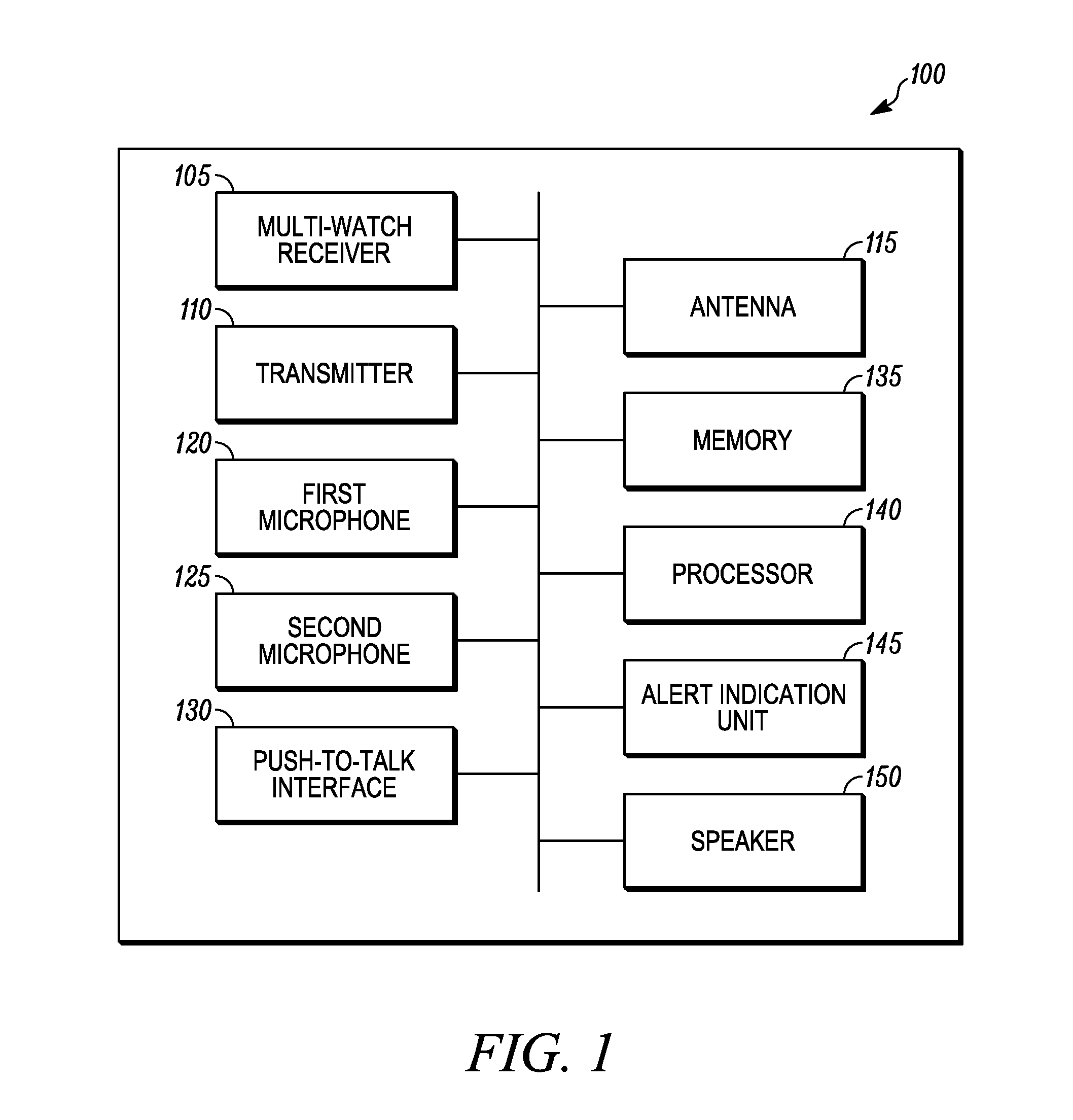
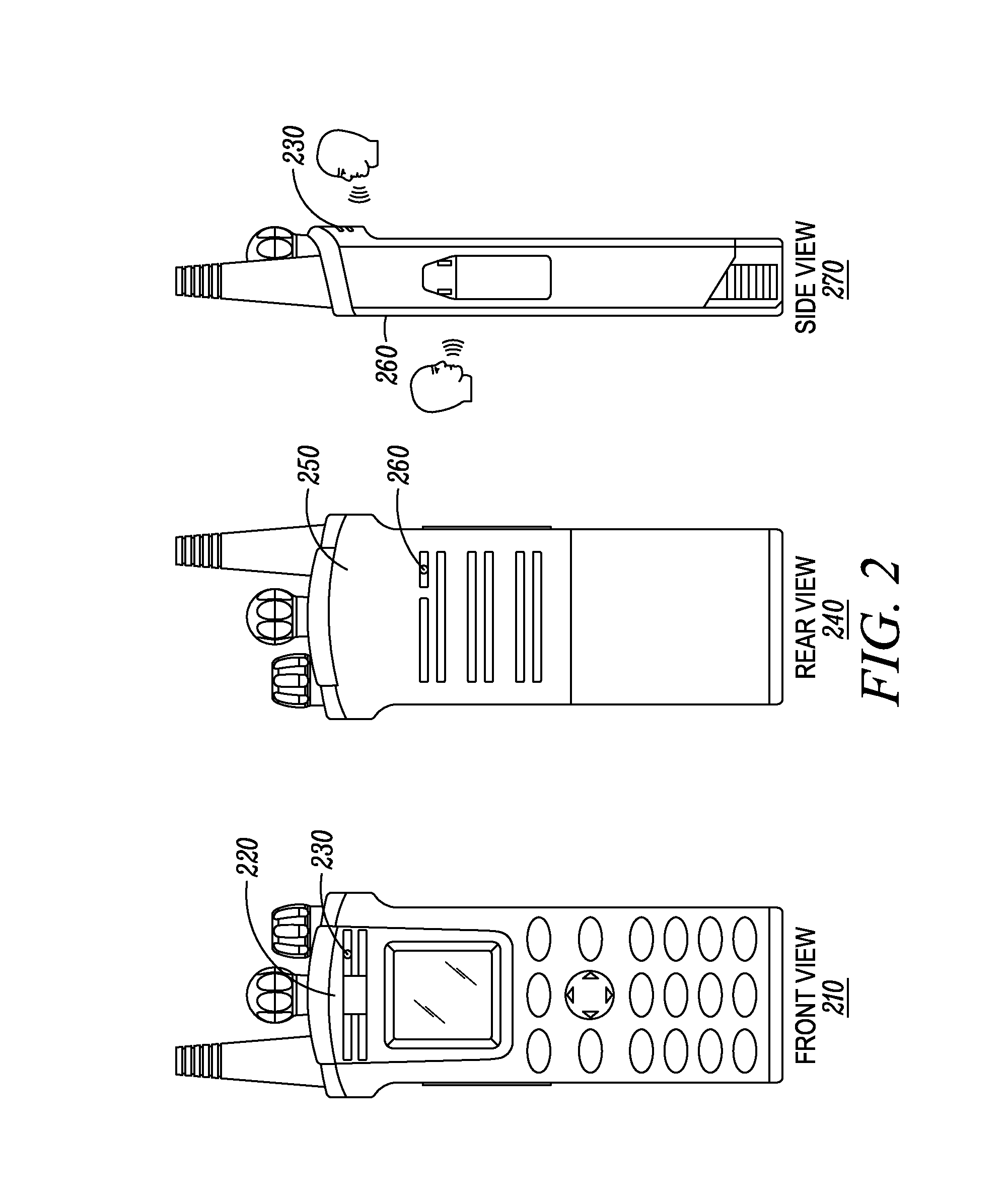
Method for automatically switching to a channel for transmission on a multi-watch portable radio
A method for automatically switching to a channel for transmission on a portable radio is provided. In operation, a first microphone is assigned to respond to communications received on a primary channel and a second microphone is assigned to respond to communications received on a non-primary channel. The portable radio receives independent audio communications simultaneously on the primary channel and the non-primary channel when operating in a multi-watch mode. The portable radio determines a signal gain corresponding to a voice command received at the first and second microphones. When the signal gain for the first microphone is larger than the signal gain for the second microphone, the portable radio switches to a first talk-back channel to respond to communications received on the primary channel. Otherwise, the portable radio switches to a second talk-back channel to respond to communications received on the at least one non-primary channel.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
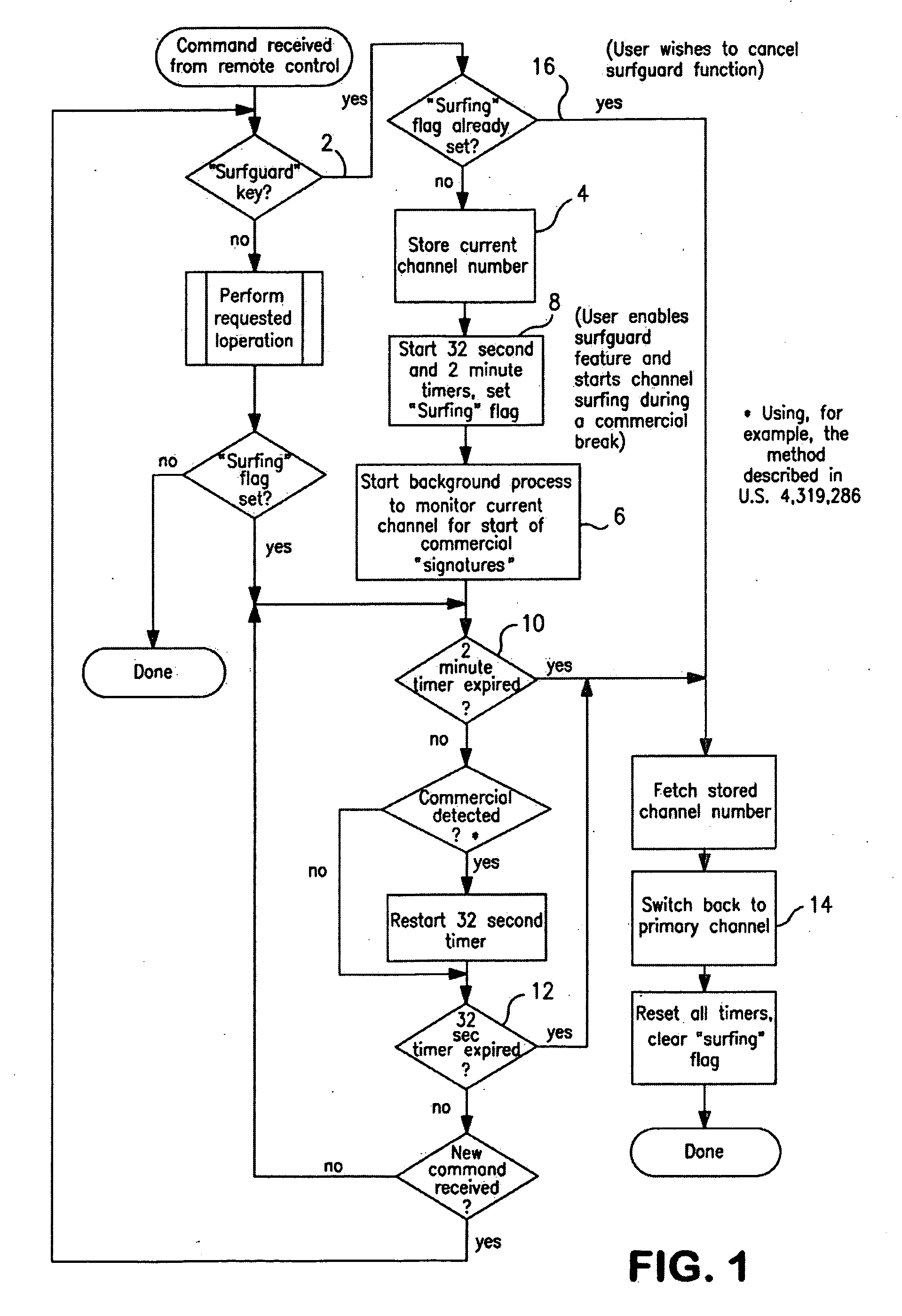
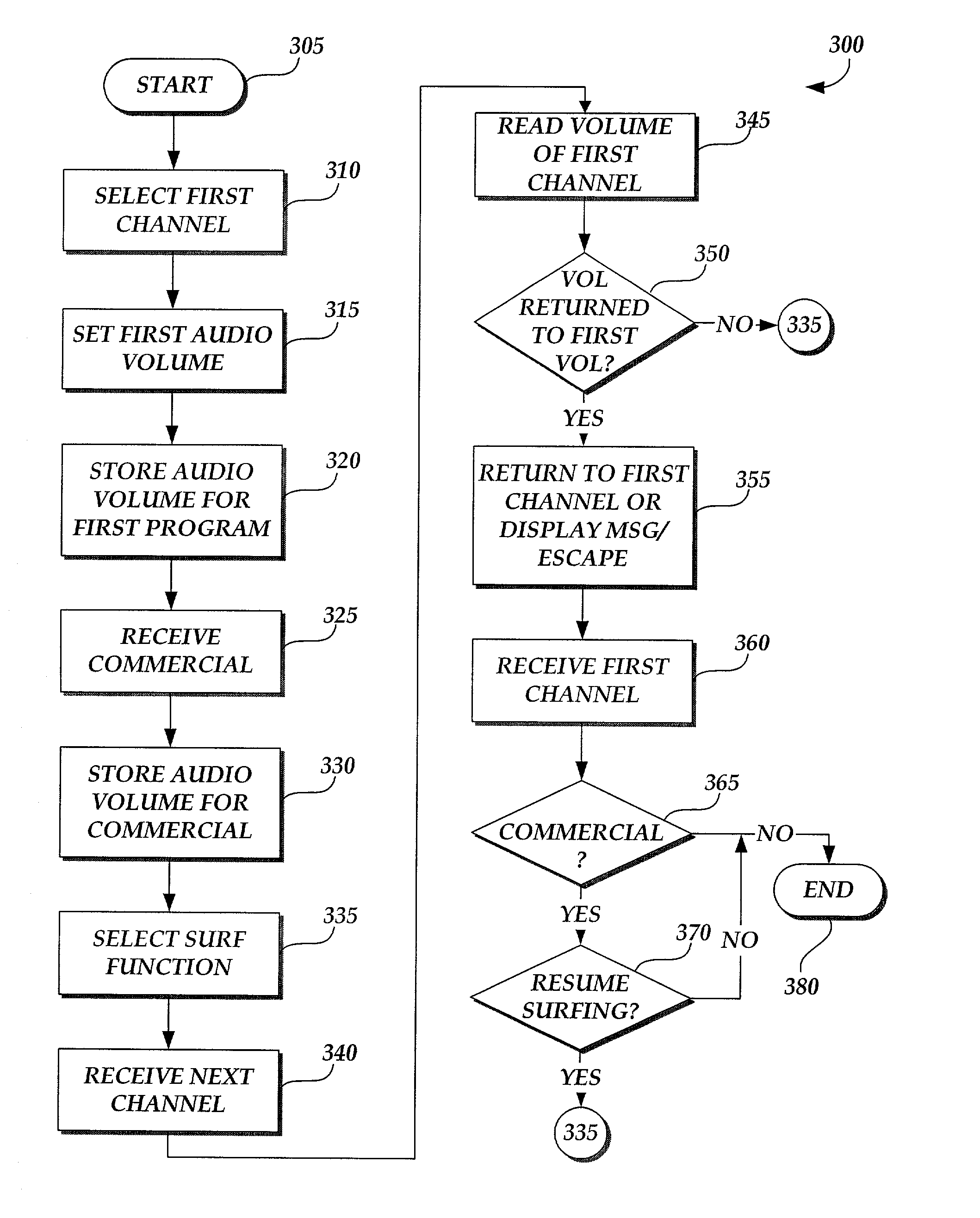
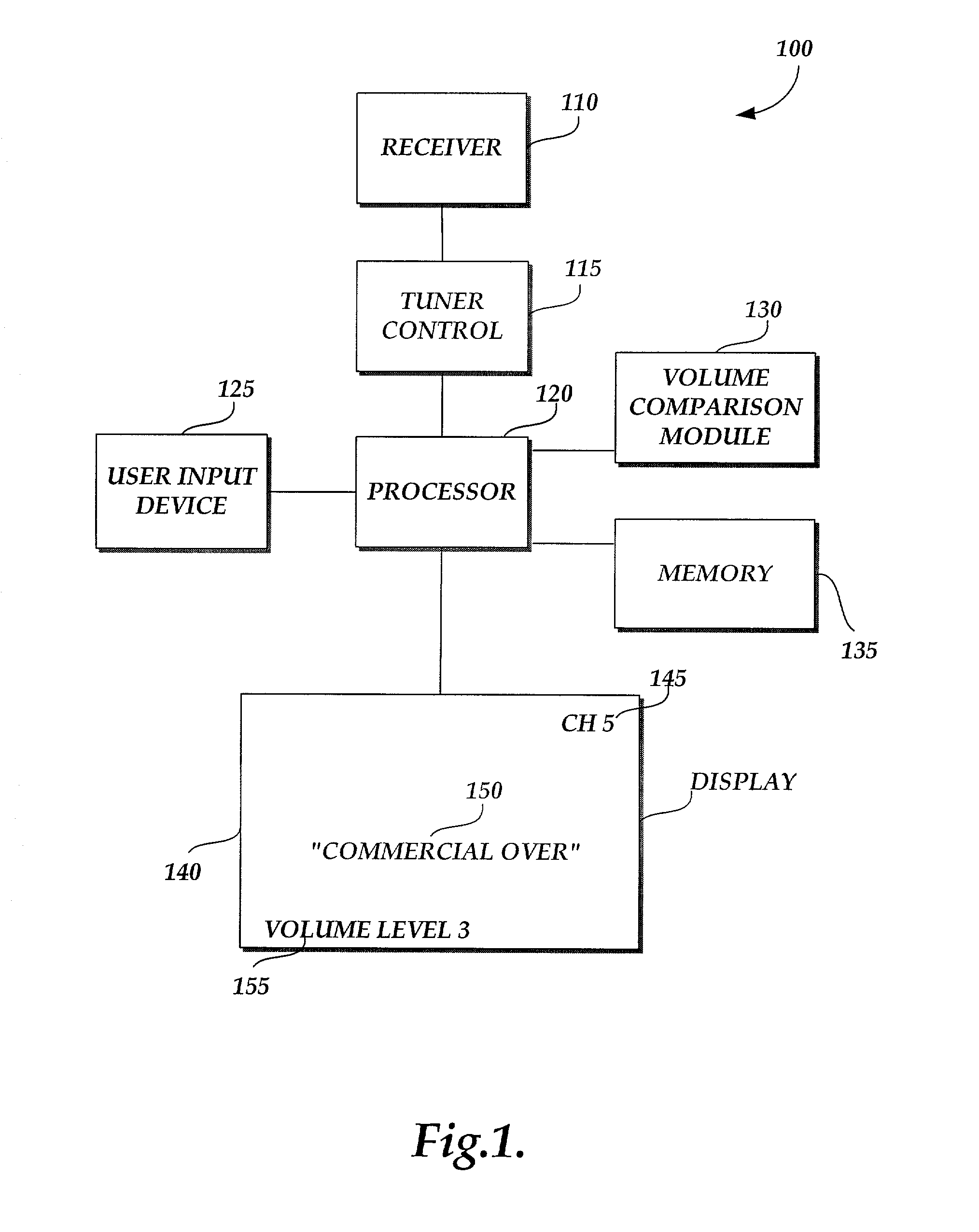
Program restart and commercial ending notification method and system
InactiveUS7012653B1Increase volumeChannel surfing is facilitatedTelevision system detailsColor television detailsTelecommunicationsCommercial broadcasting
A method and system are provided for allowing channel surfing during the presentation of a commercial broadcast by returning the viewer to the desired program channel after the commercial broadcast has concluded. When a commercial broadcast is received that interrupts the presentation of a viewer's desired programming, channel surfing is facilitated based on increased audio volume levels broadcast with the commercial broadcast. During channel surfing, the present audio level of the primary channel presenting the undesired commercial broadcast is monitored. If the audio volume level drops below the level of the commercial broadcast or returns to the level set by the viewer for the desired program prior to receipt of the commercial broadcast, the desired program channel may be reselected to return the viewer to her desired program channel. The viewer may be notified that the commercial broadcast has ended prior to reselection of the desired program channel. Notification may be in the form of a notification message displayed to the viewer.
Owner:BELLSOUTH INTPROP COR
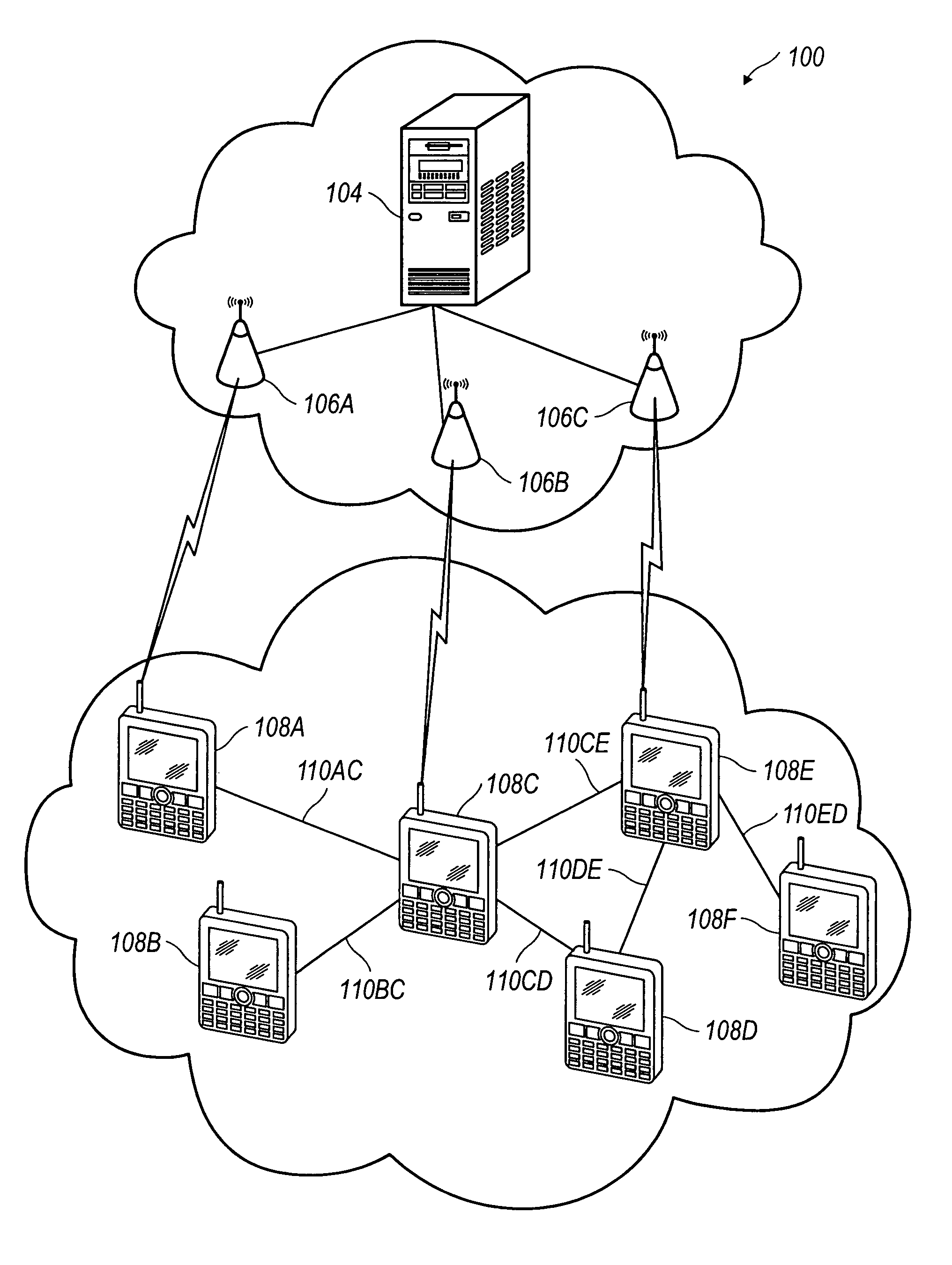
Peer-to-peer collaborative streaming among mobile terminals
ActiveUS7961694B1Improve overall utilizationNetwork topologiesWireless commuication servicesData streamComputer terminal
Systems and methods for collaborative streaming among mobile terminals. Periodically, the mobile terminals may pull a portion of the data stream from a content provider coupled thereto over a primary channel and distribute the pulled data to neighboring mobile terminals, possibly including other mobile terminals pulling portions of the data stream from the content provider and passive mobile terminals that are only receiving pulled data. By transferring data over the secondary channel, the cost to any one terminal to receive the data stream is reduced.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com