Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
420 results about "Radiofrequency coil" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
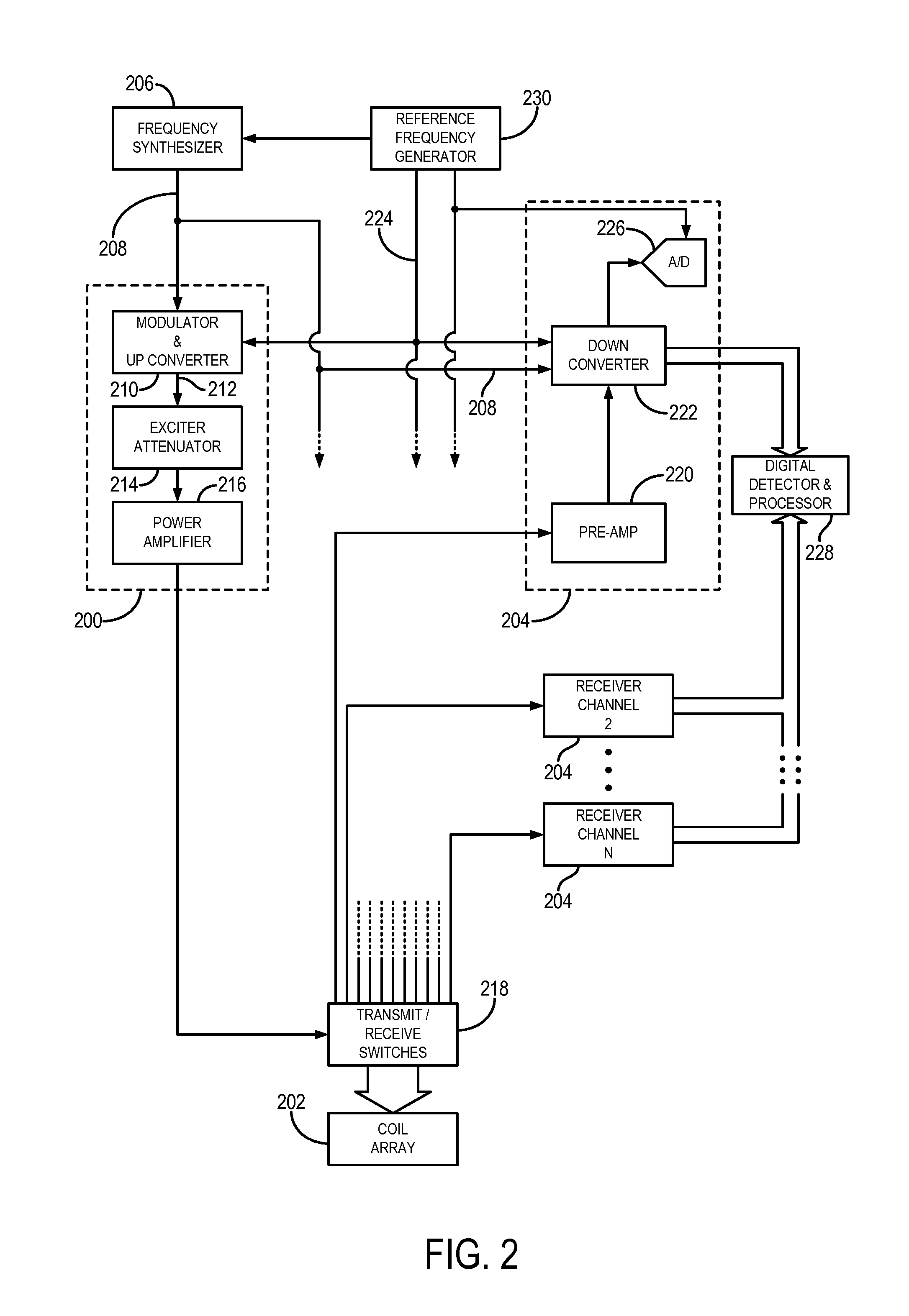
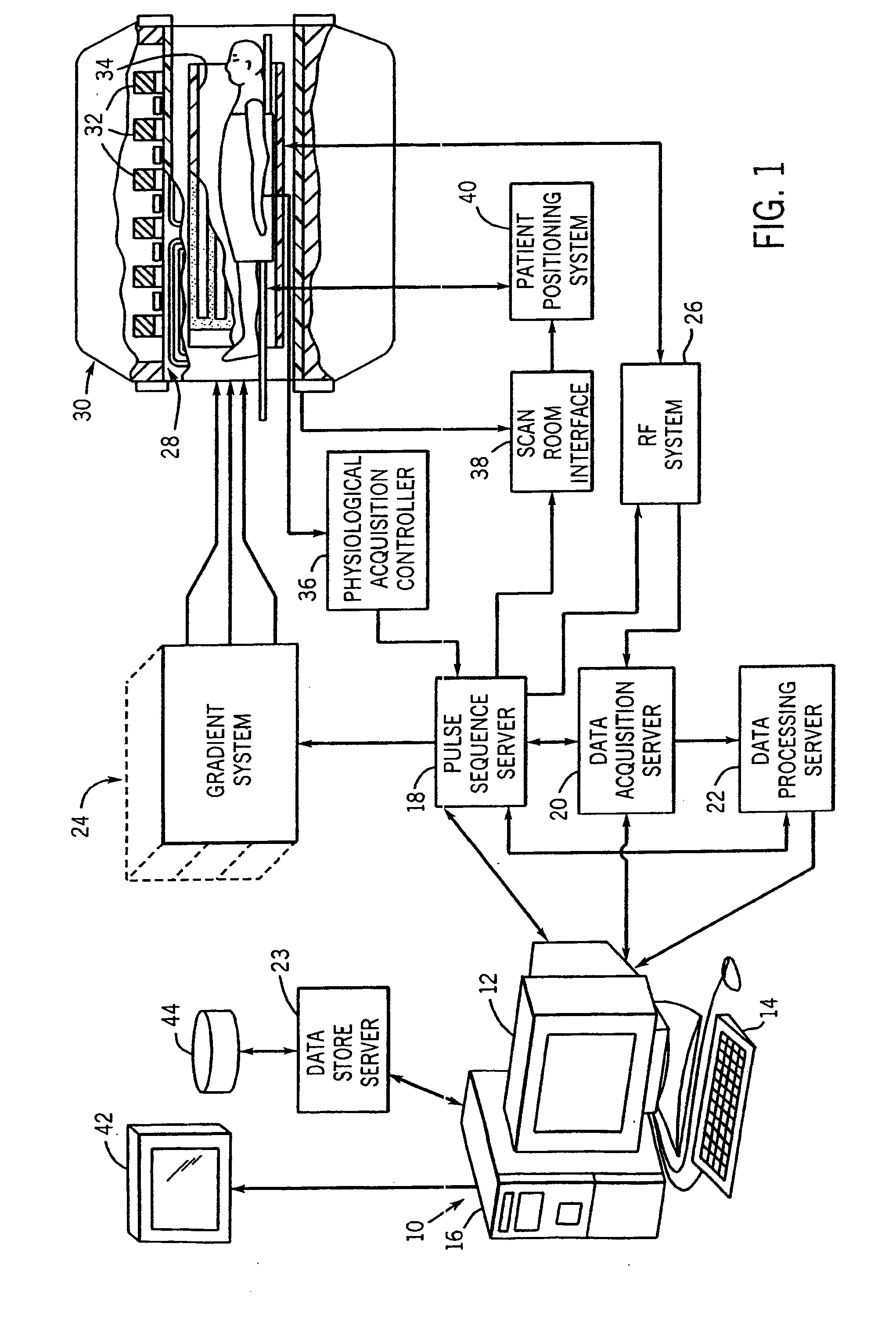
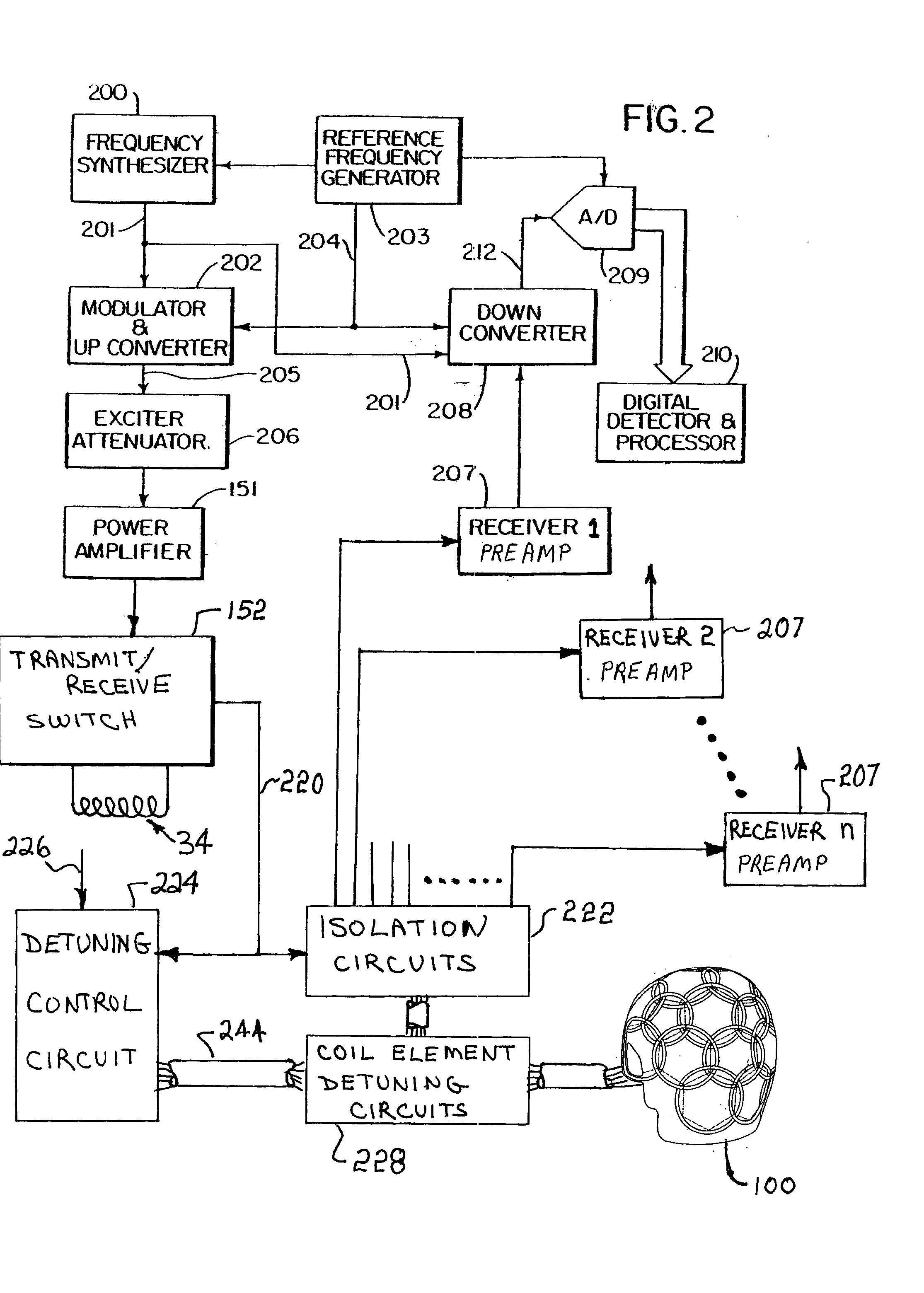
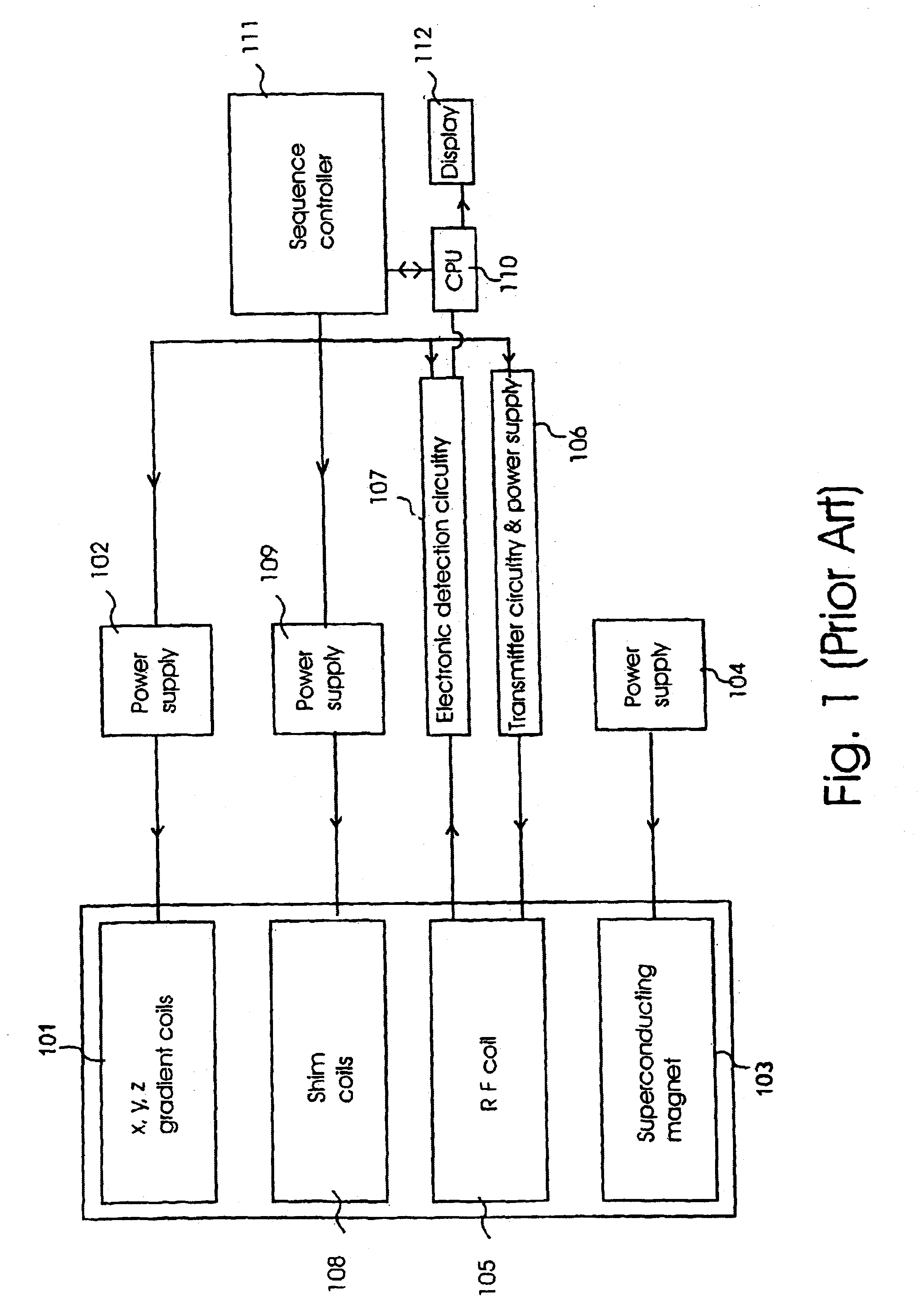
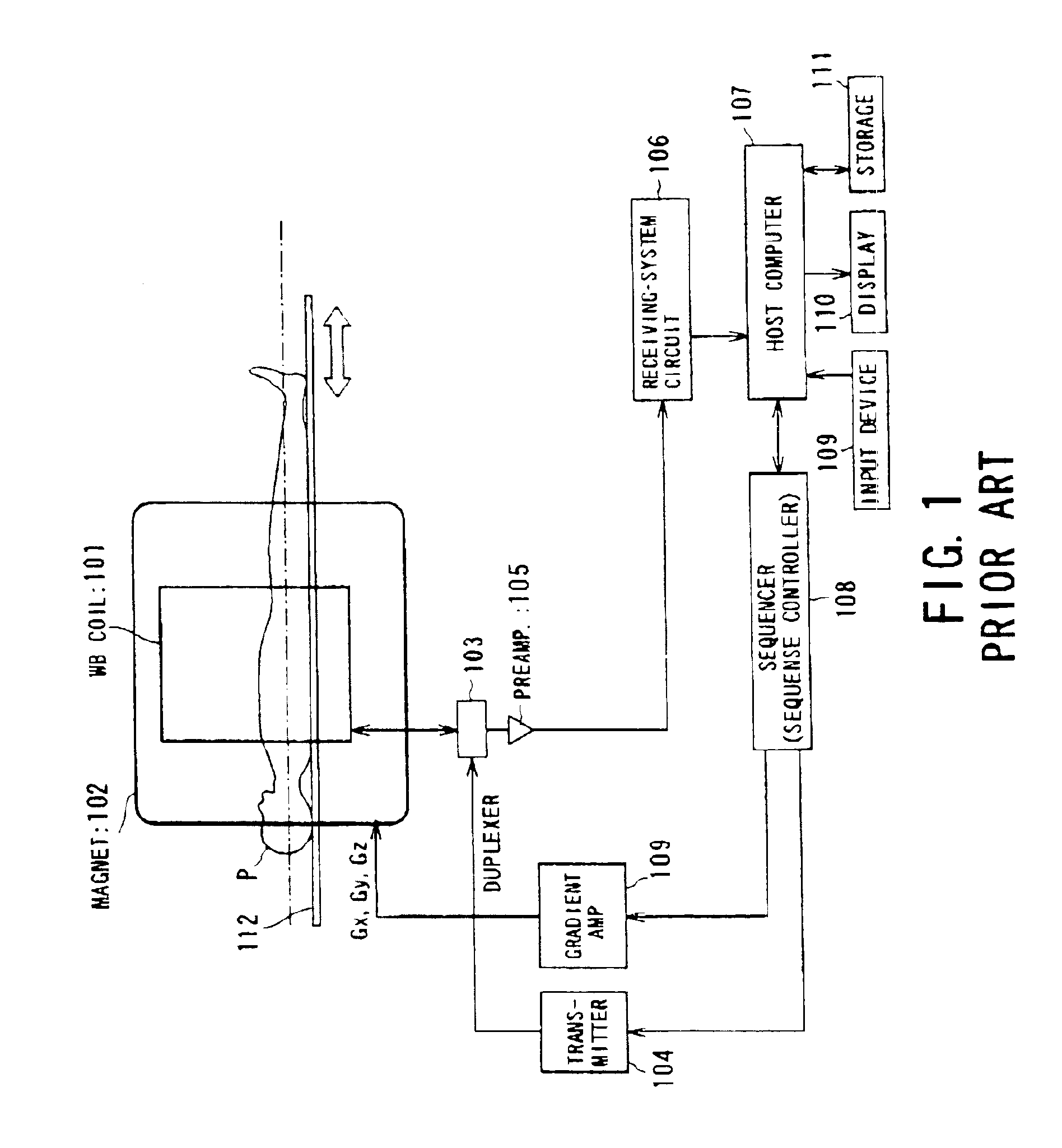
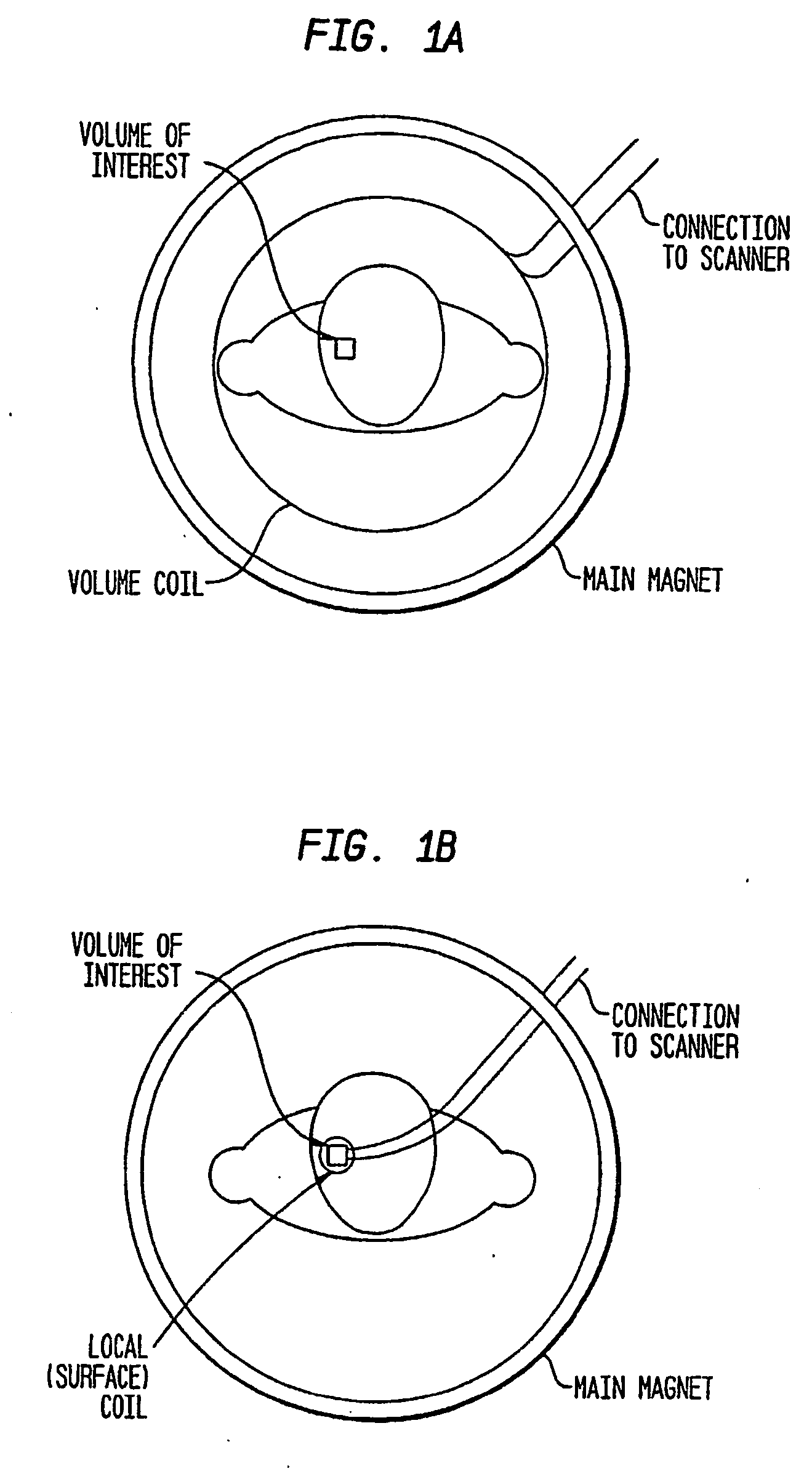
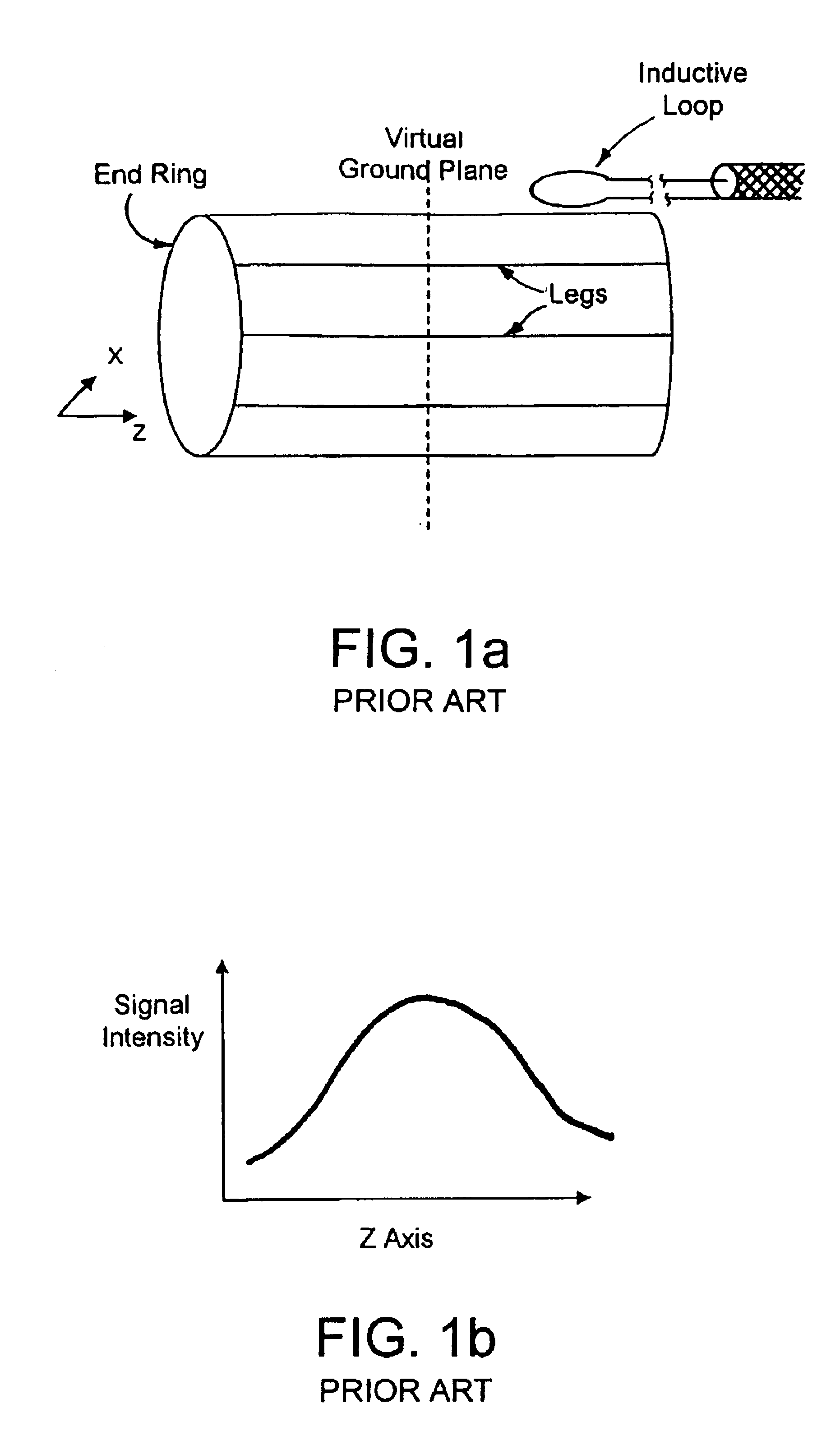
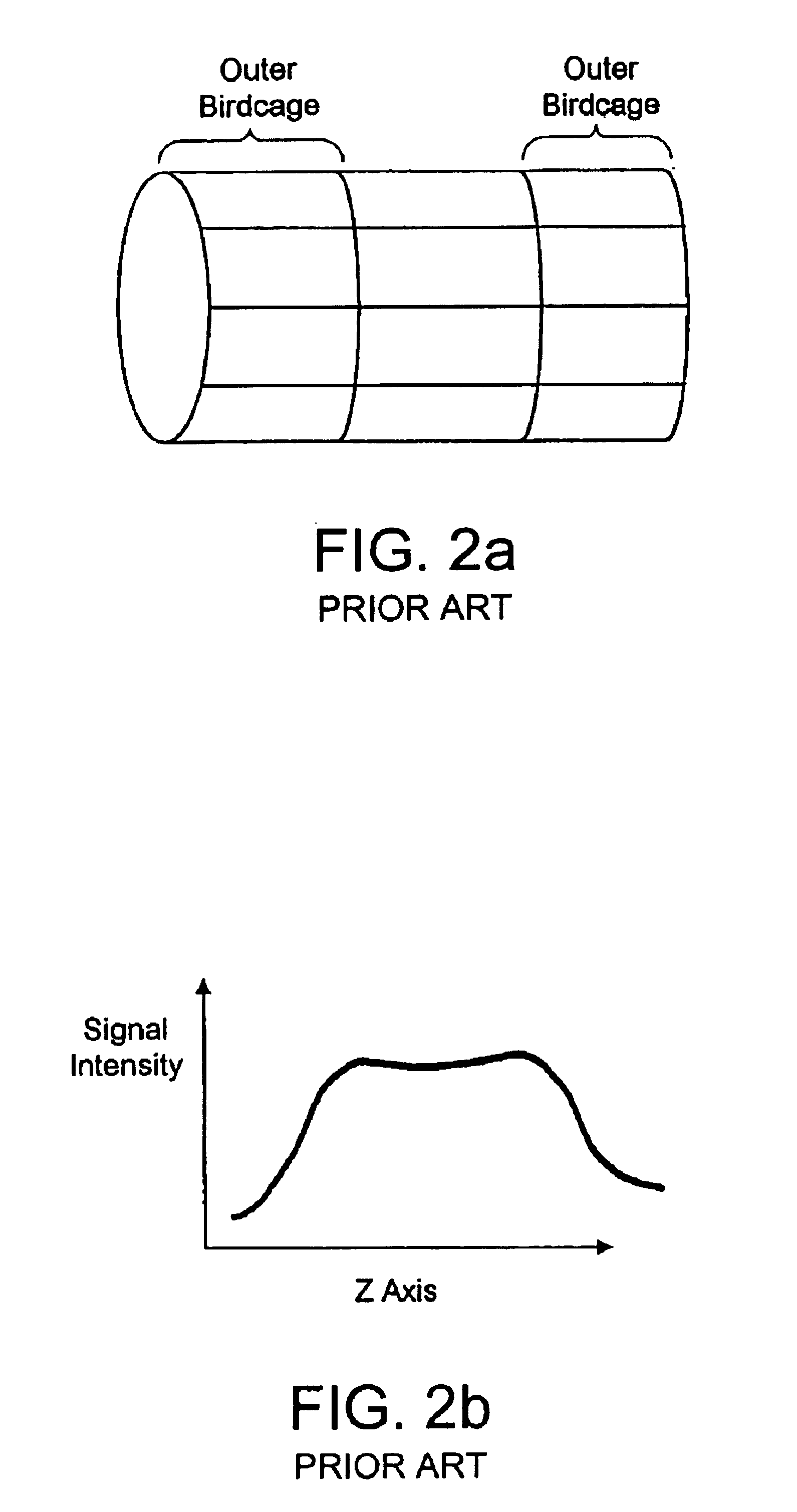
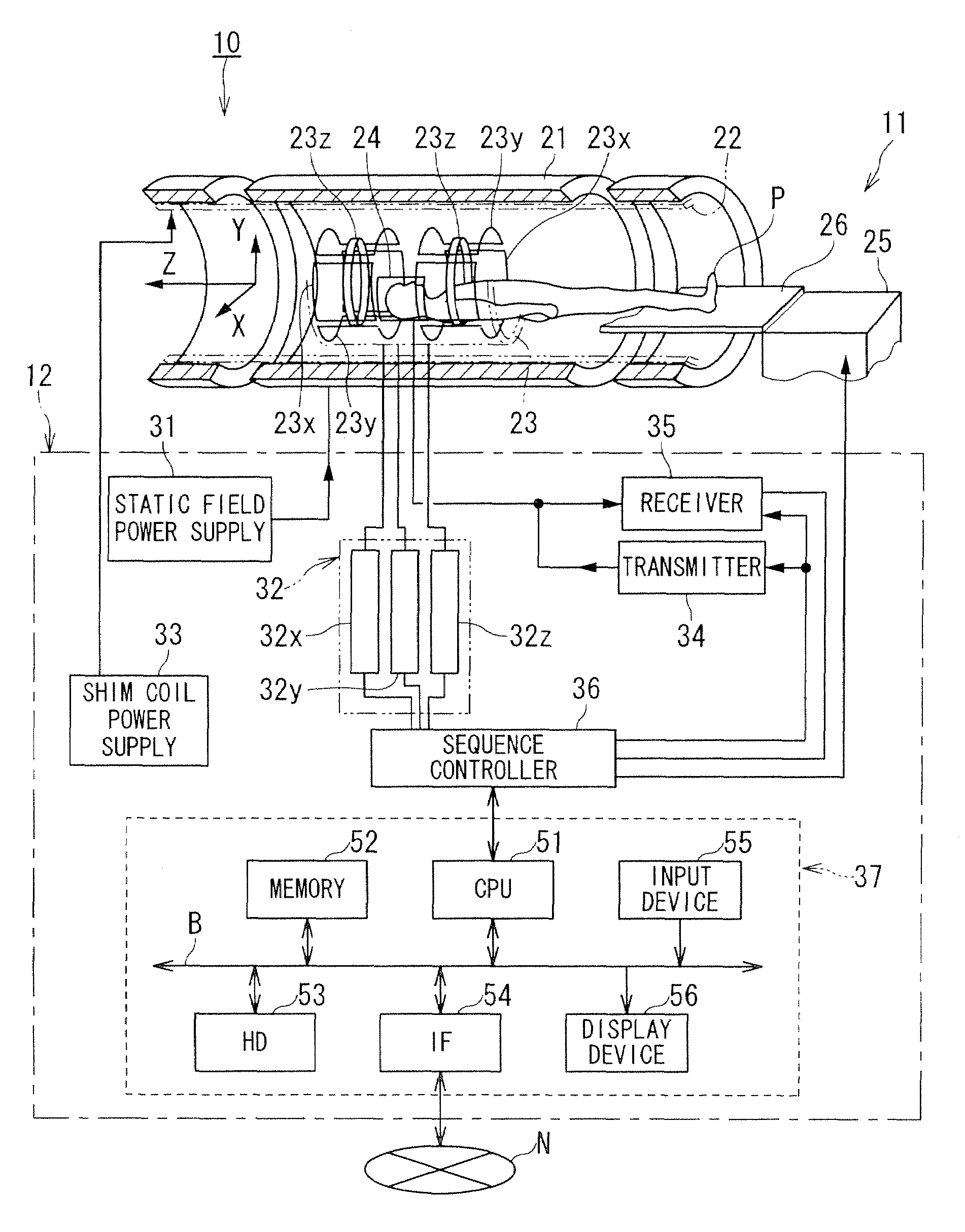
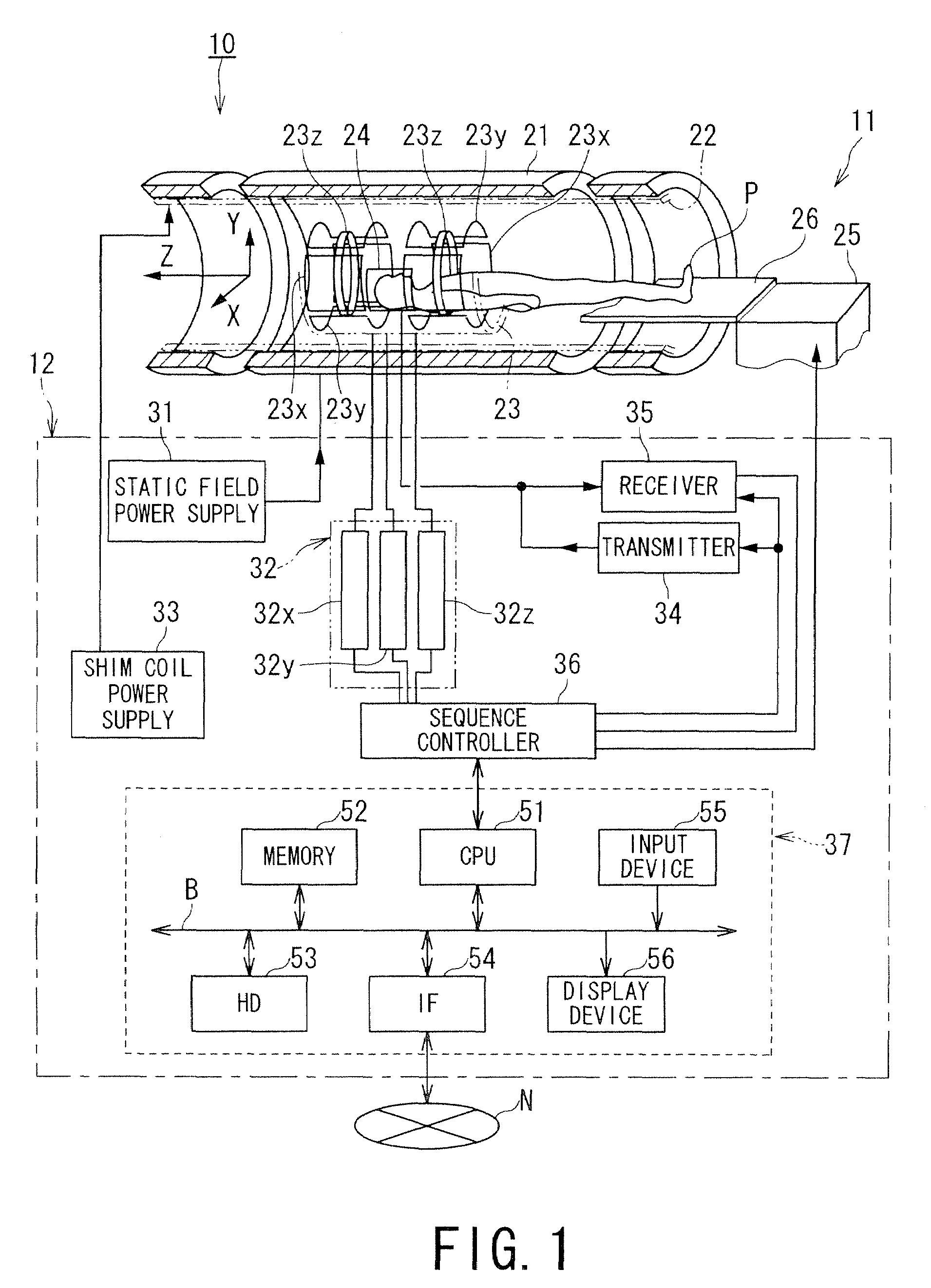
Radiofrequency coils (RF coils) are the receivers, and sometimes also the transmitters, of radiofrequency (RF) signals in equipment used in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The MR signal in MRI is produced by the process of resonance, which is the result of radiofrequency coils. They consist of two electromagnetic coils, the transmitter and receiver, which generate the field and receive the resulting signal. Atomic nuclei of interest in MRI studies have their own resonant frequencies, in the radiofrequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum.
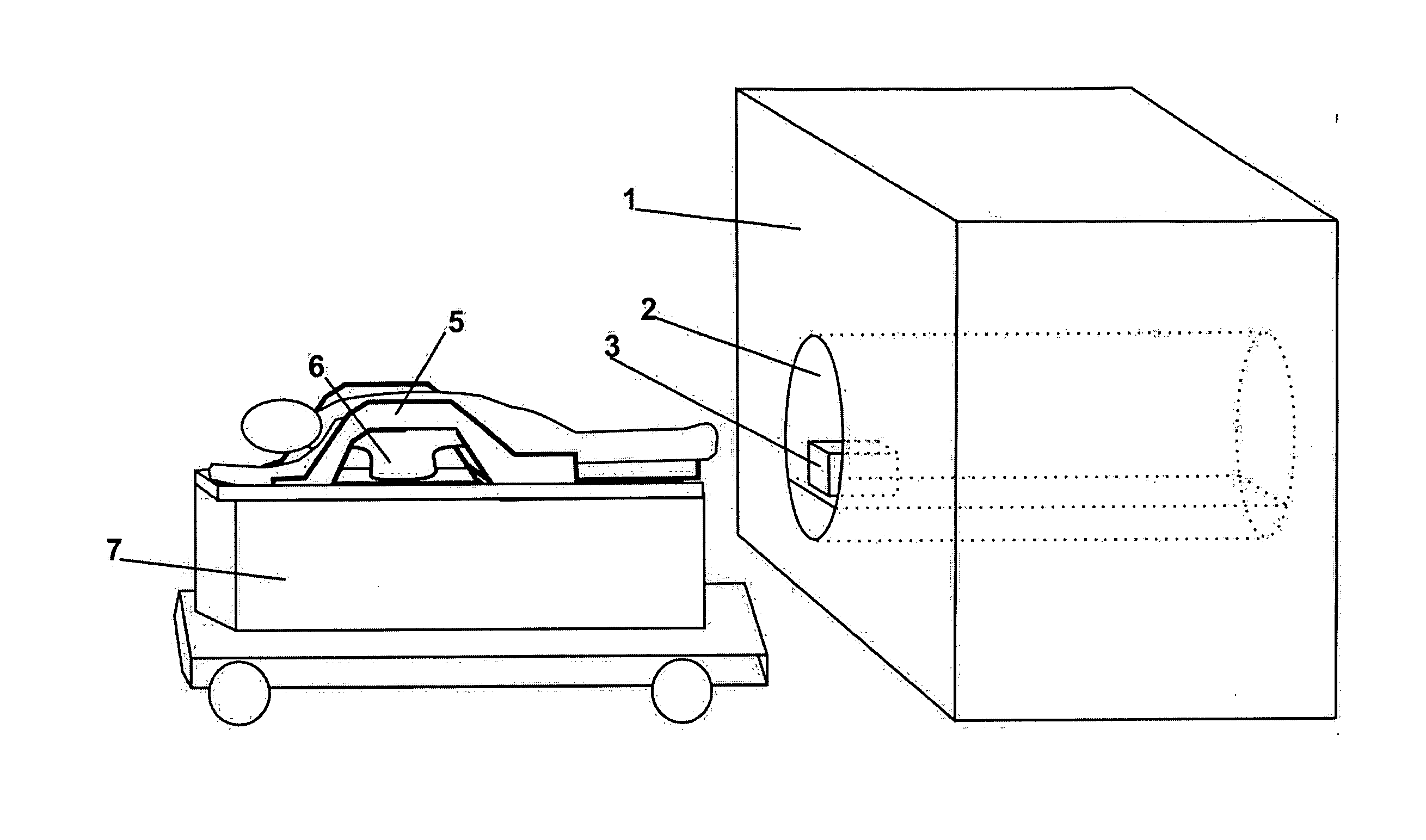
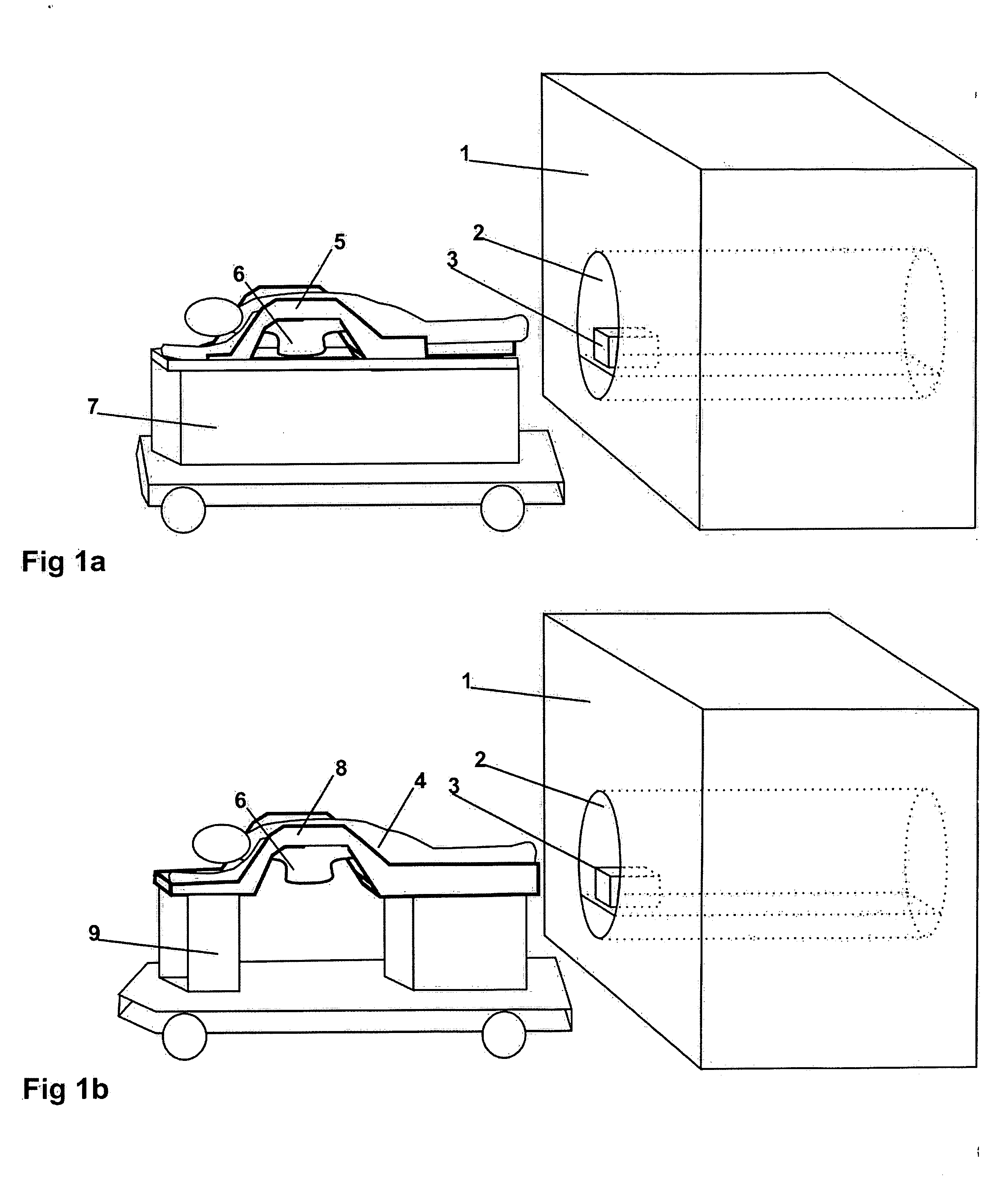
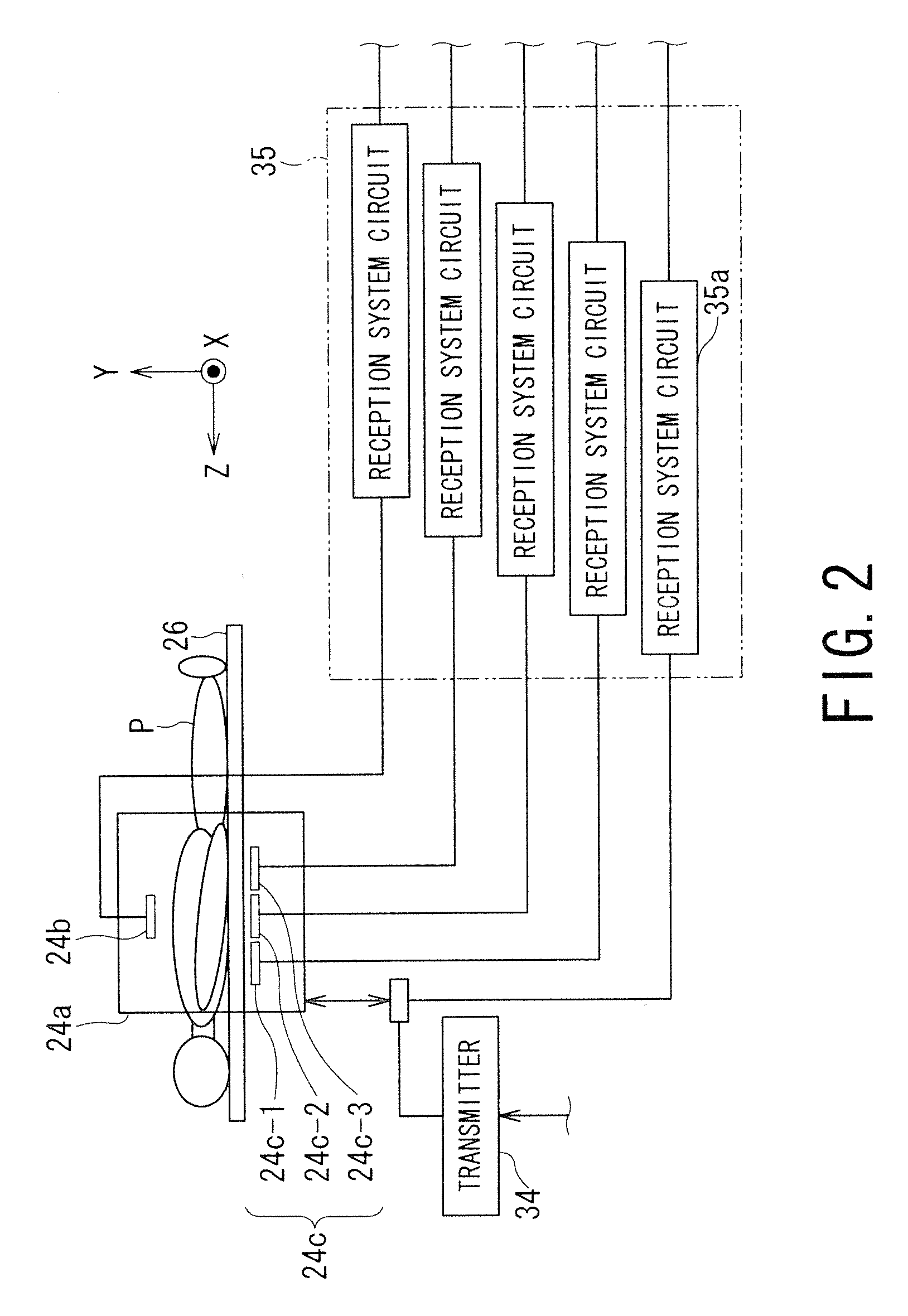
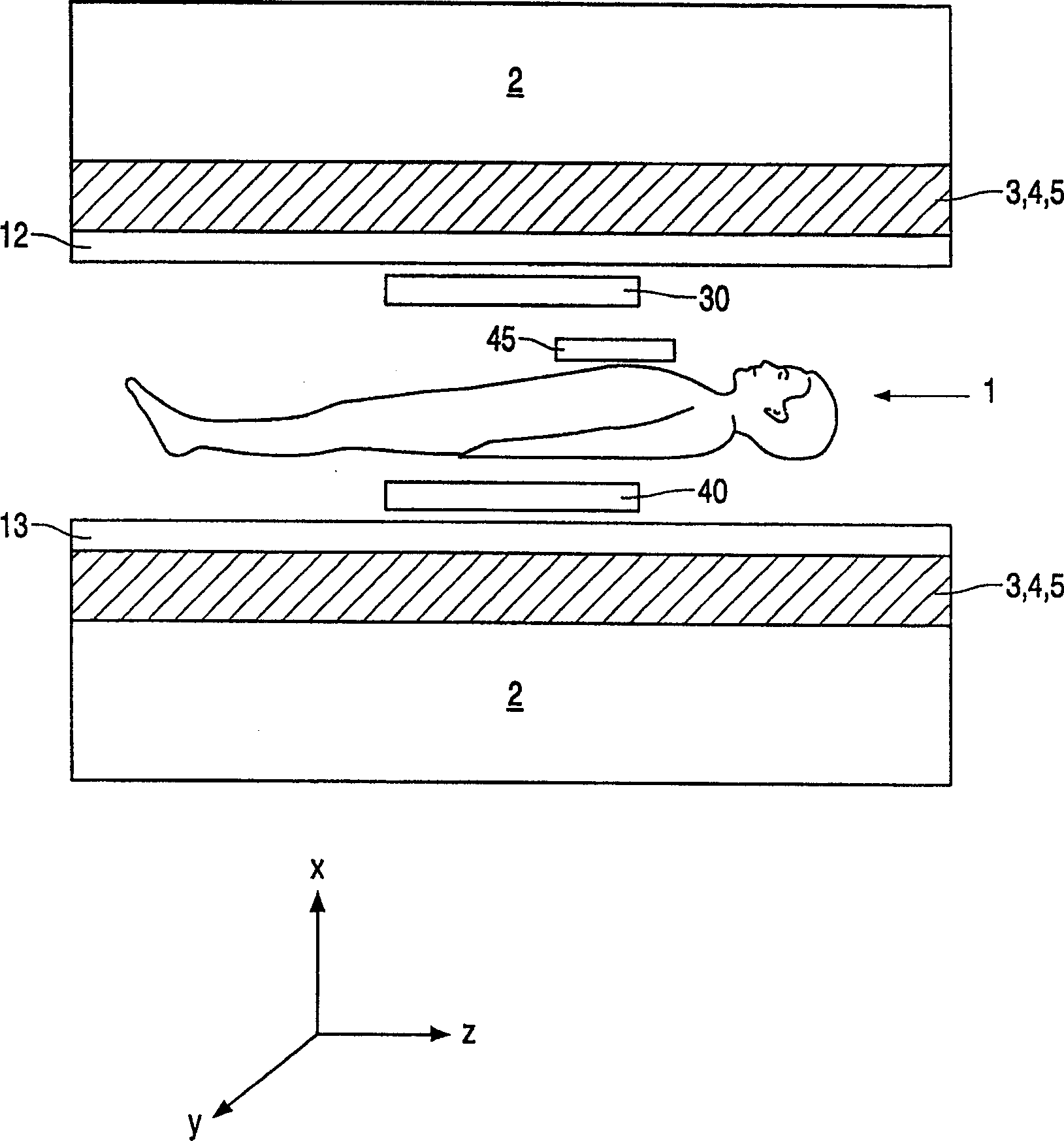
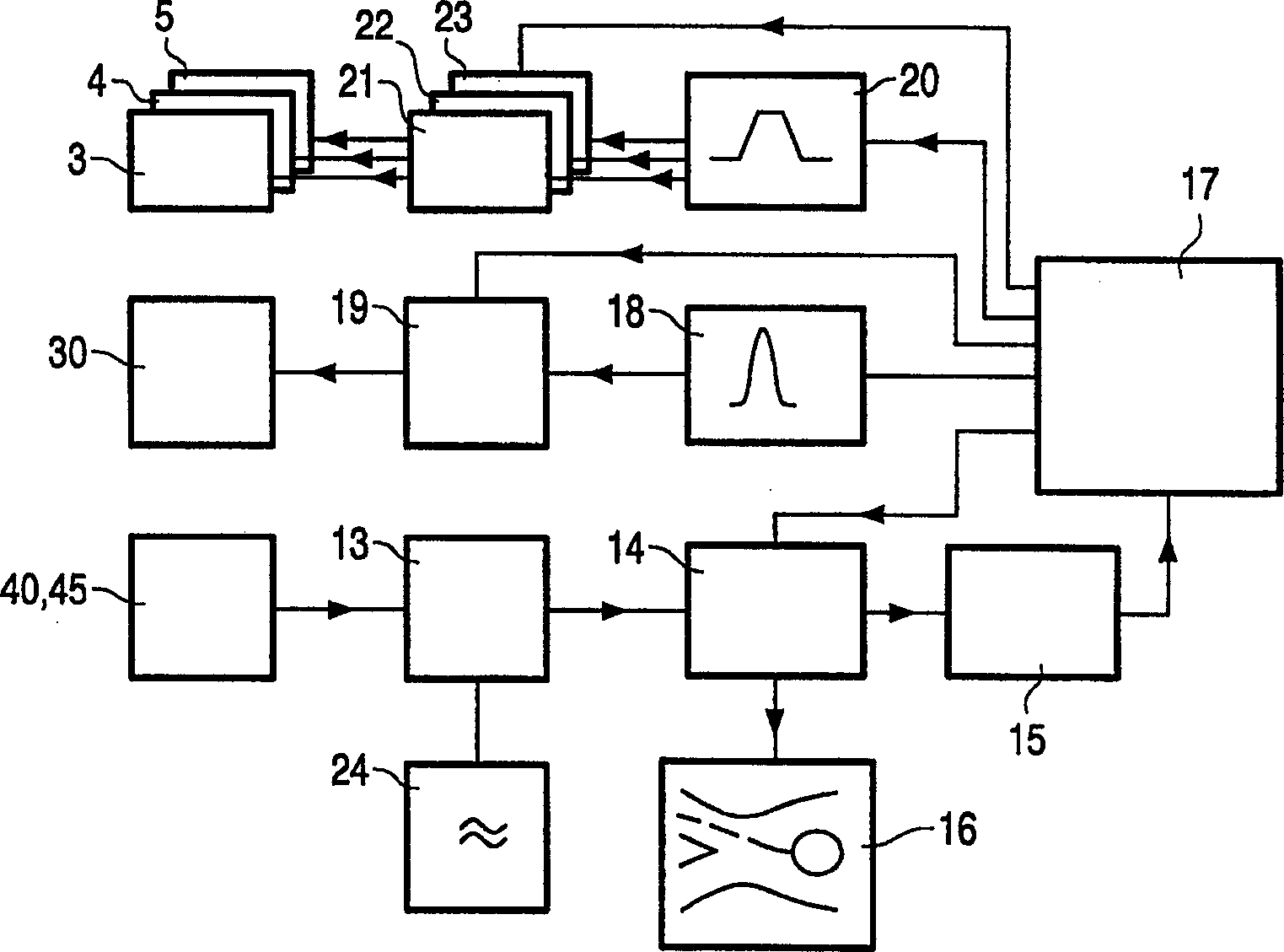
Open architecture imaging apparatus and coil system for magnetic resonance imaging
Apparatus and method for using radio frequency coil systems for magnetic resonance imaging within an open architecture apparatus is provided. The MRI coil system includes a support structure with an open architecture in which secondary support structures, compression systems and plates containing RF coil systems may be introduced. These structures and RF coils can be moved relative to the patient, or removed entirely from the system. In one embodiment the system consists of a tabletop coil system, while another embodiment consists of a dedicated stretcher design.
Owner:INVIVO CORP +1
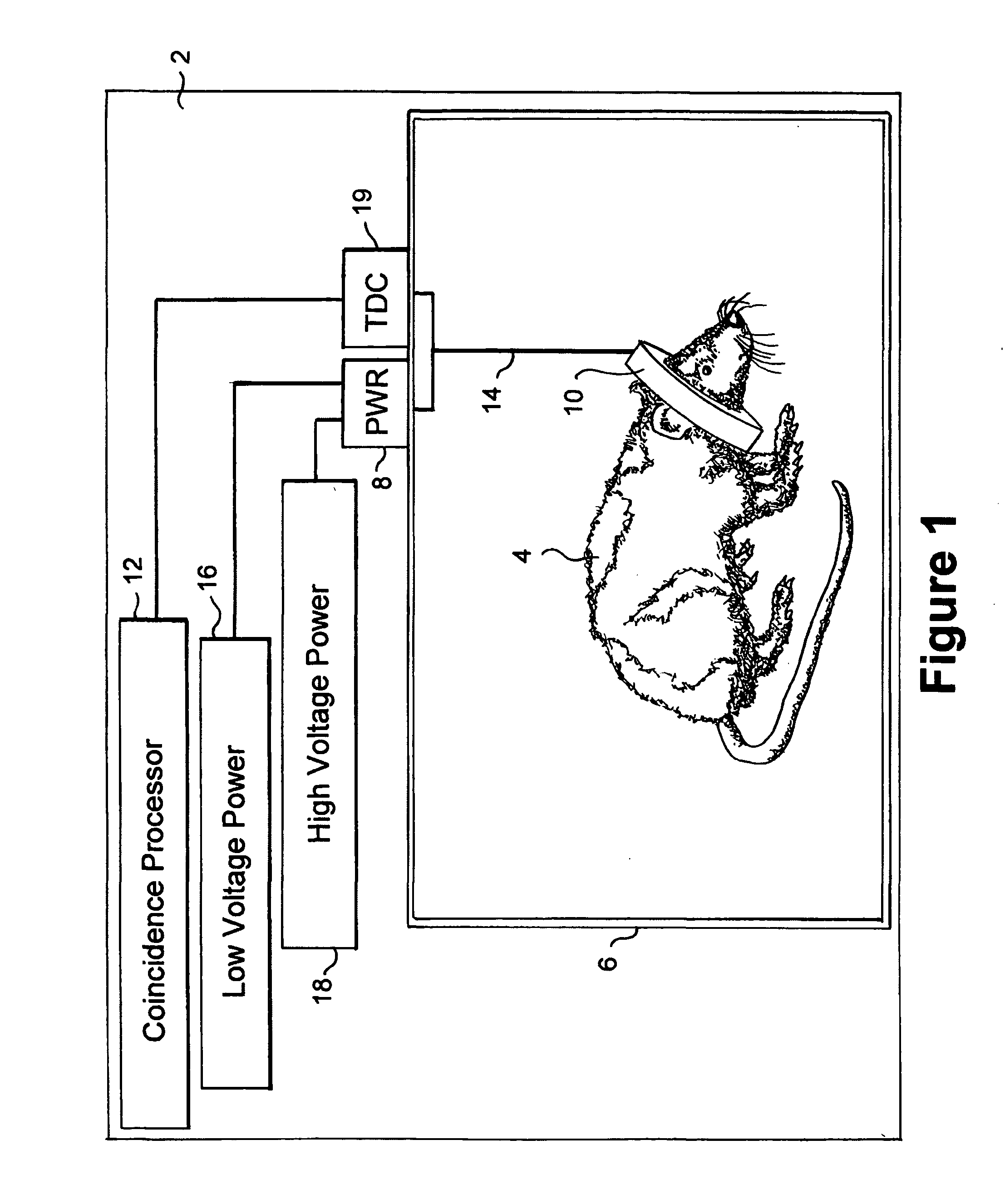
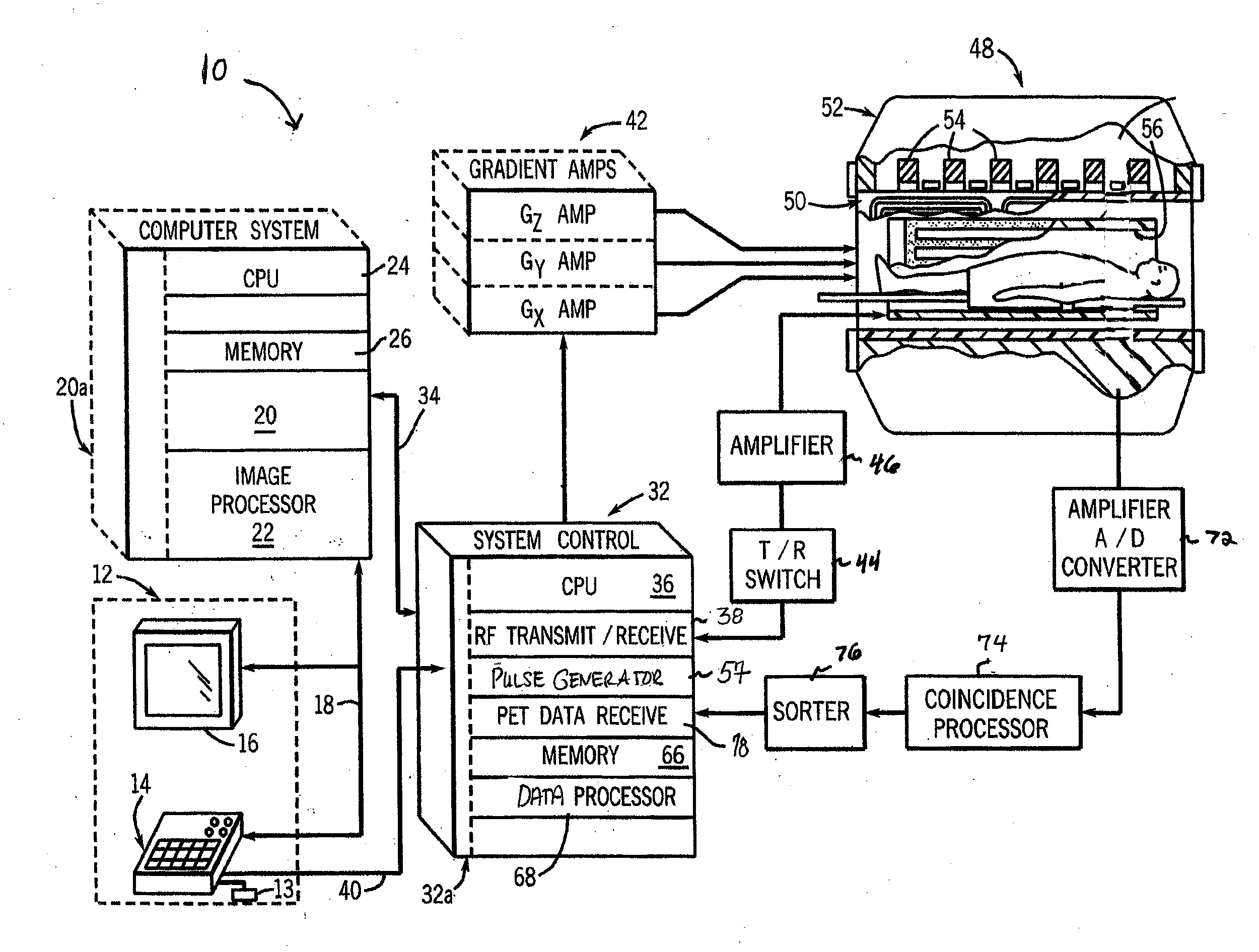
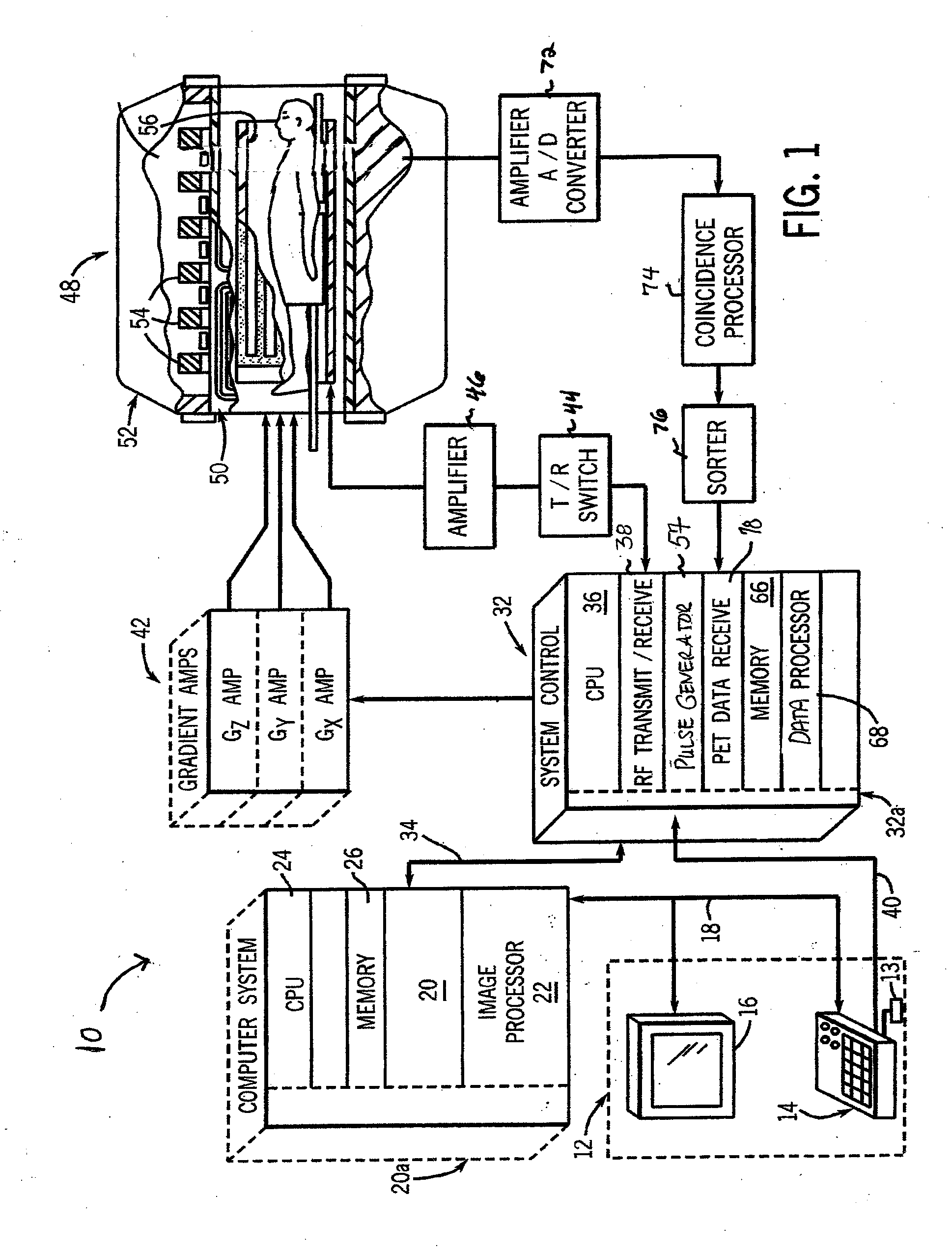
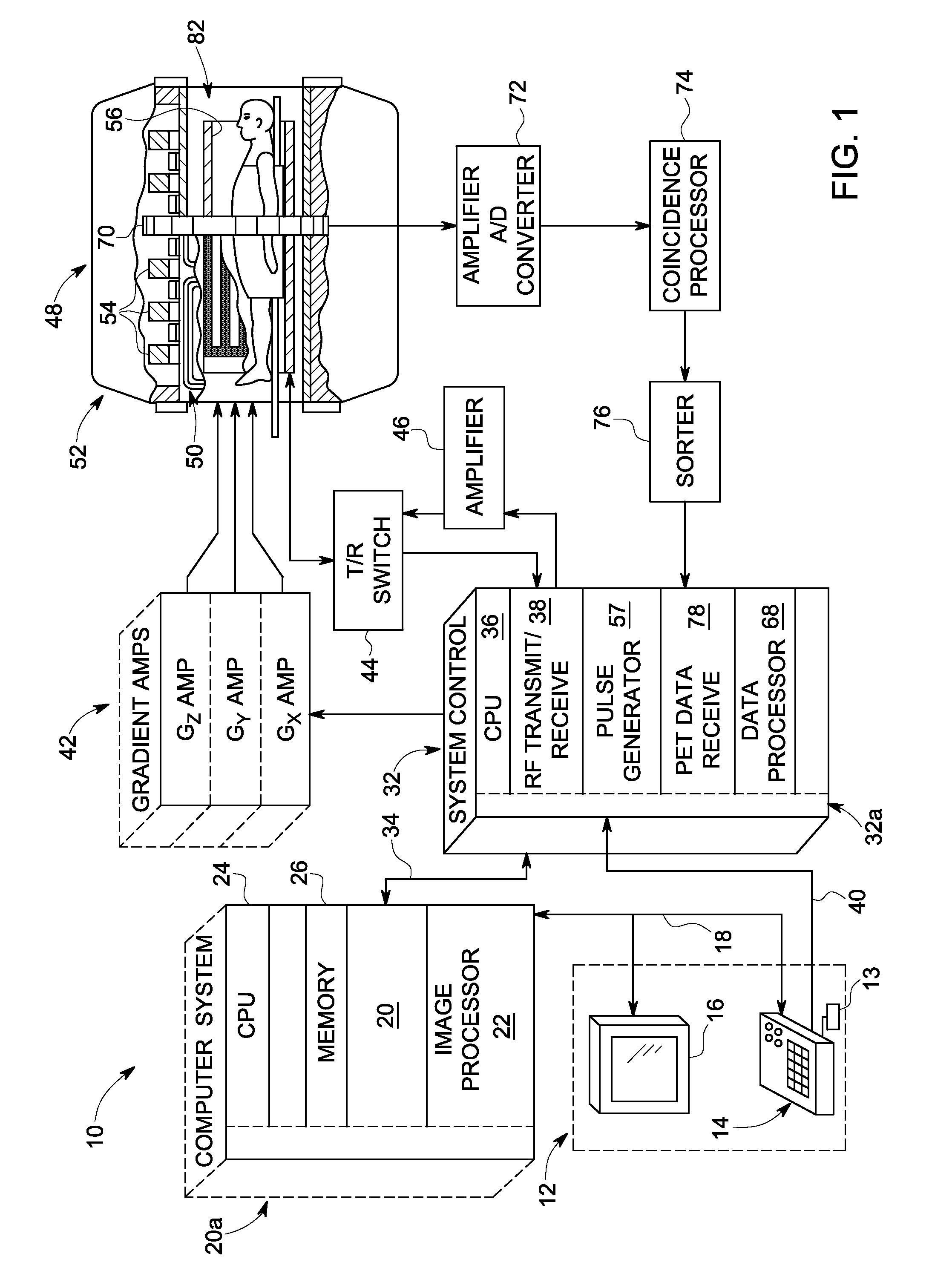
Combined PET/MRI scanner
ActiveUS20050113667A1Reduce power consumptionExtension of timeMagnetic measurementsMaterial analysis by optical meansAudio power amplifierPhoton detection
A combined PET / MRI scanner generally includes a magnet for producing a magnetic field suitable for magnetic resonance imaging, a radiofrequency (RF) coil disposed within the magnetic field produced by the magnet and a ring tomograph disposed within the magnetic field produced by the magnet. The ring tomograph includes a scintillator layer for outputting at least one photon in response to an annihilation event, a detection array coupled to the scintillator layer for detecting the at least one photon outputted by the scintillator layer and for outputting a detection signal in response to the detected photon and a front-end electronic array coupled to the detection array for receiving the detection signal, wherein the front-end array has a preamplifier and a shaper network for conditioning the detection signal.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
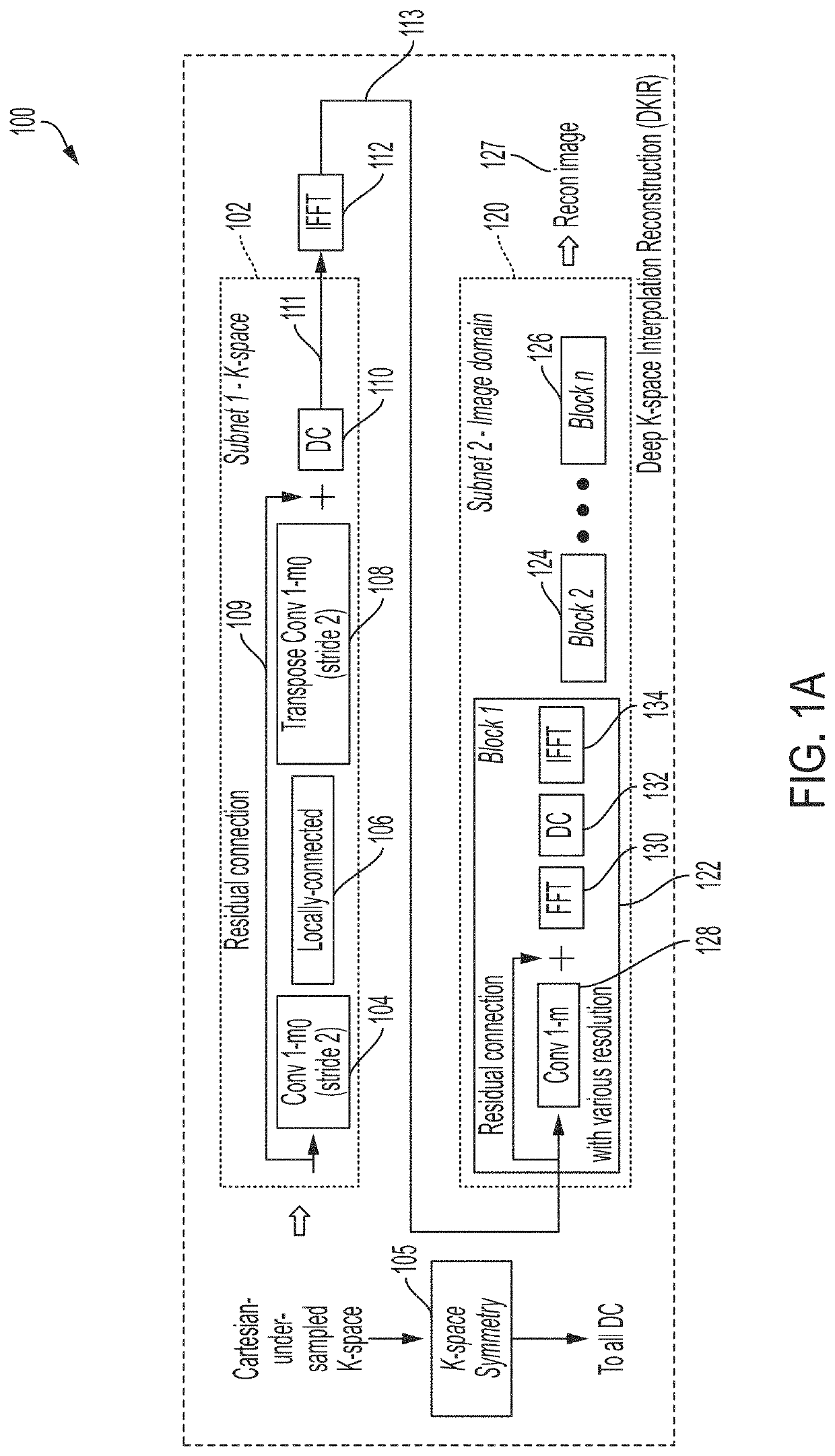
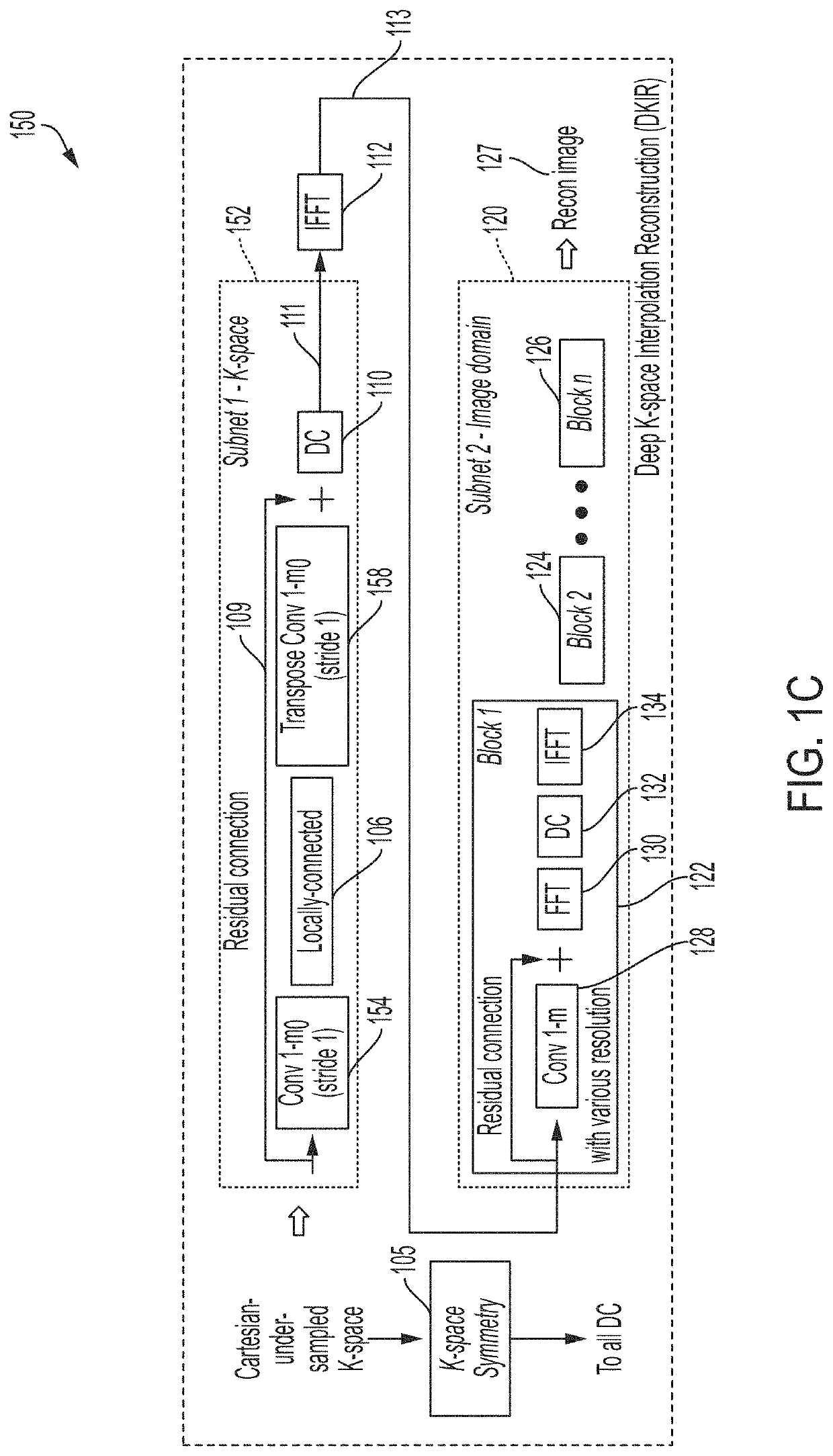
Deep learning techniques for magnetic resonance image reconstruction
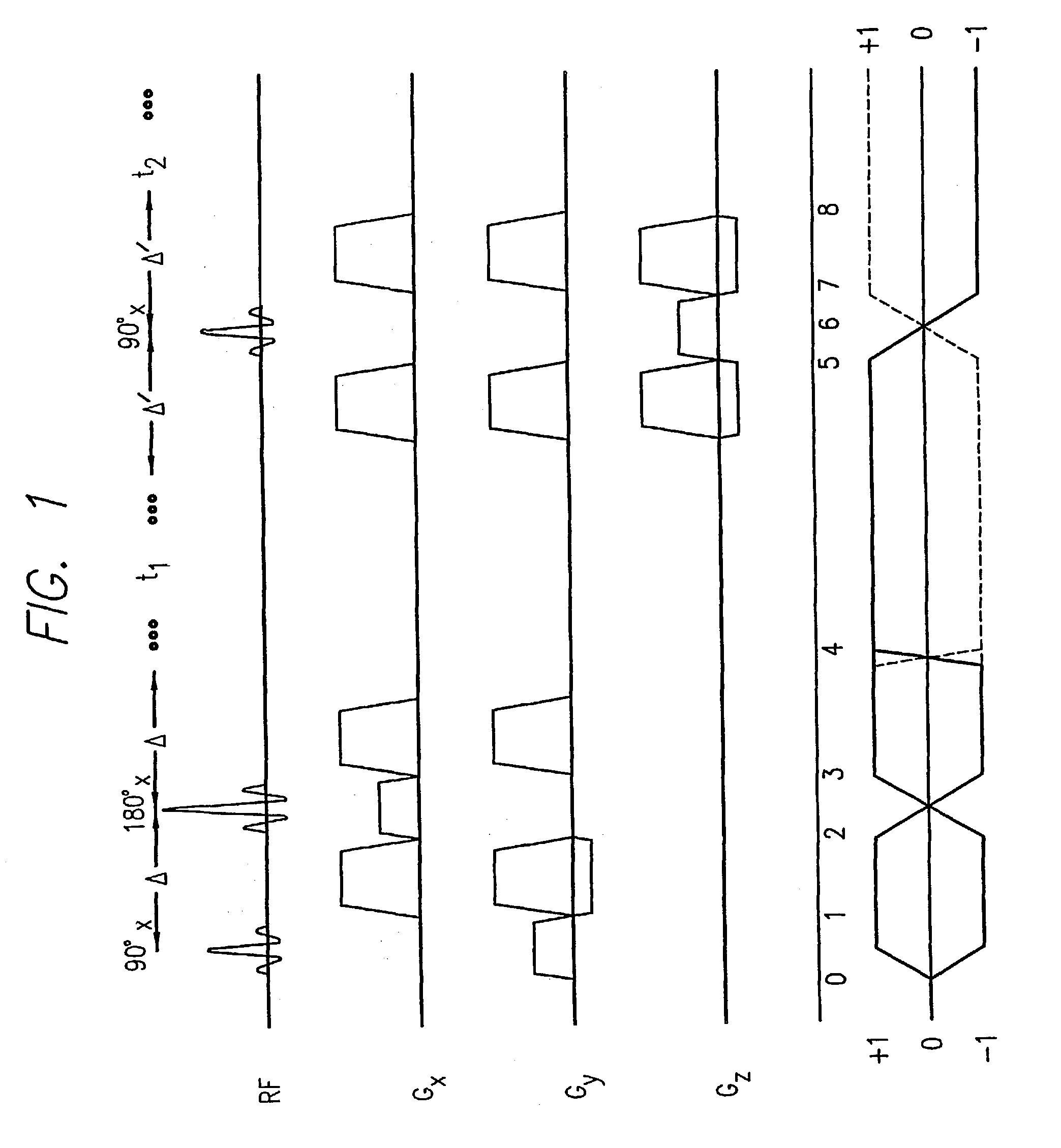
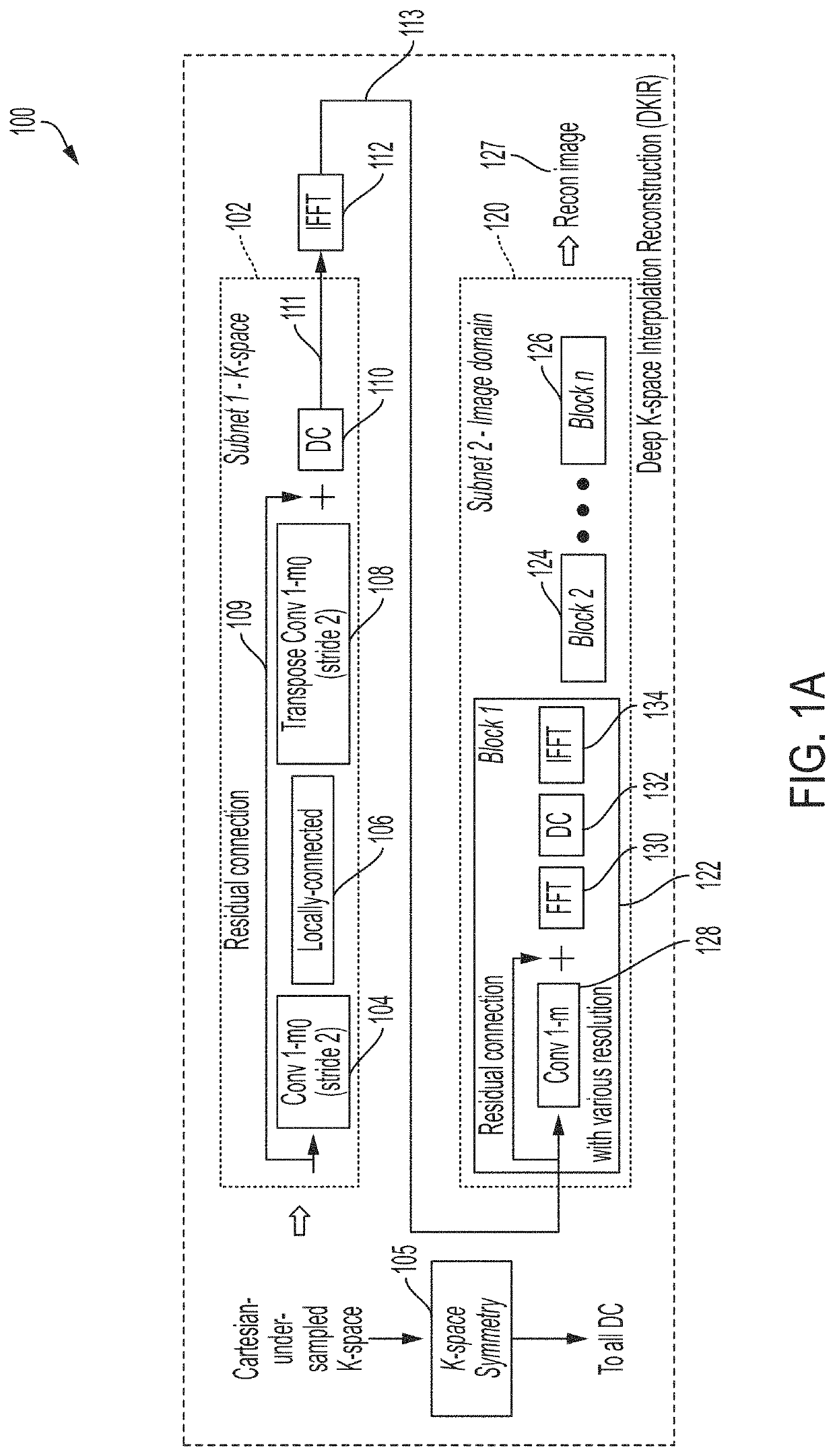
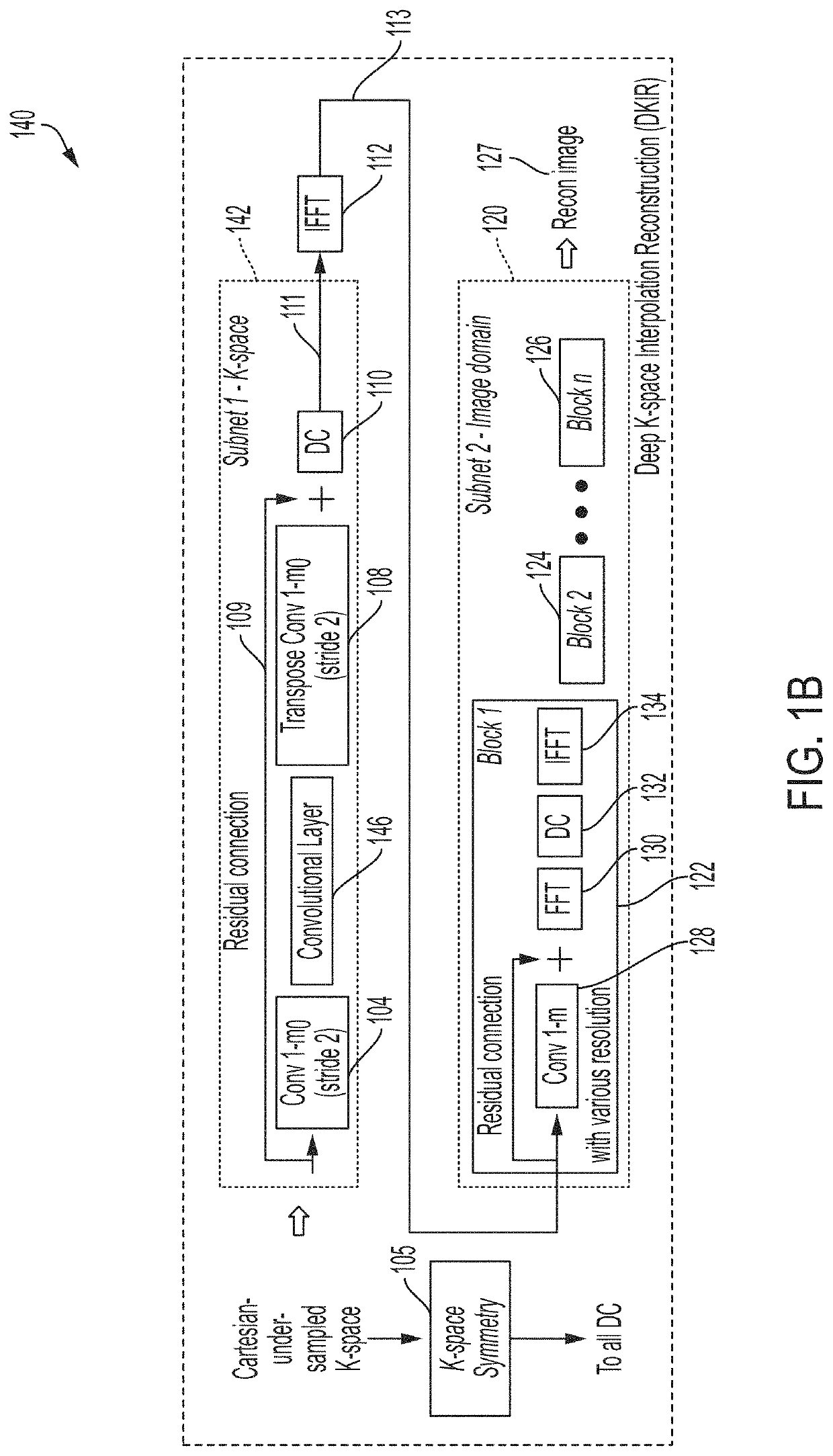
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system, comprising: a magnetics system comprising: a B0 magnet configured to provide a B0 field for the MRI system; gradient coils configured to provide gradient fields for the MRI system; and at least one RF coil configured to detect magnetic resonance (MR) signals; and a controller configured to: control the magnetics system to acquire MR spatial frequency data using non-Cartesian sampling; and generate an MR image from the acquired MR spatial frequency data using a neural network model comprising one or more neural network blocks including a first neural network block, wherein the first neural network block is configured to perform data consistency processing using a non-uniform Fourier transformation.
Owner:HYPERFINE OPERATIONS INC
Method for simultaneous multi-slice magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20110254548A1Reliable separationLarge possible separationMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic gradientMulti slice
A method for multi-slice magnetic resonance imaging, in which image data is acquired simultaneously from multiple slice locations using a radio frequency coil array, is provided. By way of example, a modified EPI pulse sequence is provided, and includes a series of magnetic gradient field “blips” that are applied along a slice-encoding direction contemporaneously with phase-encoding blips common to EPI sequences. The slice-encoding blips are designed such that phase accruals along the phase-encoding direction are substantially mitigated, while providing that signal information for each sequentially adjacent slice location is cumulatively shifted by a percentage of the imaging FOV. This percentage FOV shift in the image domain provides for more reliable separation of the aliased signal information using parallel image reconstruction methods such as SENSE. In addition, the mitigation of phase accruals in the phase-encoding direction provides for the substantial suppression of pixel tilt and blurring in the reconstructed images.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Magnetic resonance imaging system and RF coil
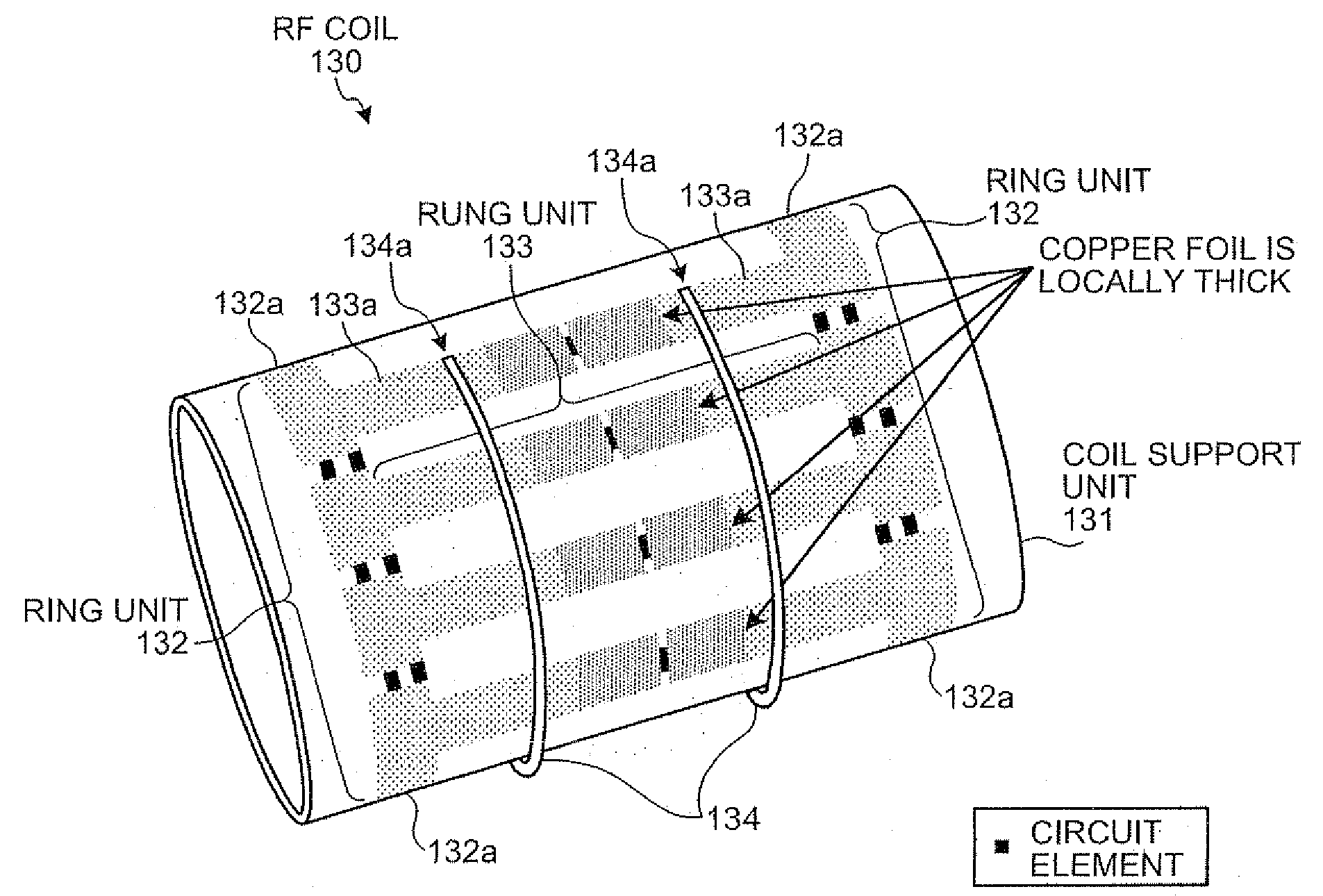
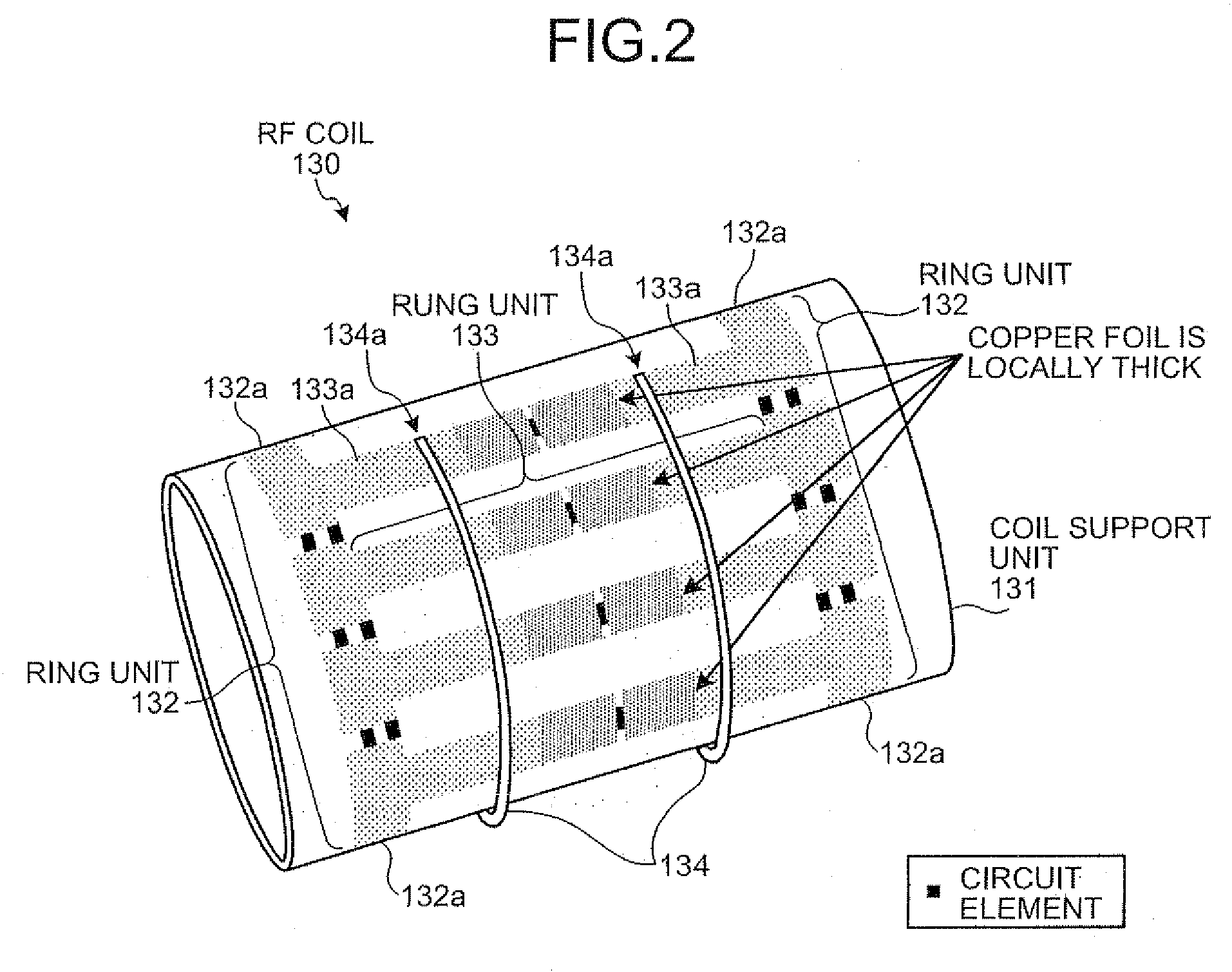
ActiveUS20090134875A1Dissipate heat generatedElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceRadio frequencyRadiofrequency coil
When an RF coil in a magnetic resonance imaging system includes a plurality of conductive members and circuit elements connected to the conductive members, at least part of each of the conductive members is formed to a thickness so as to dissipate heat generated from the circuit elements. Moreover, the magnetic resonance imaging system is configured to include a cooling unit that circulates cooling air over the surfaces of the circuit elements provided in the RF coil.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Shaped MRI Coil Array
ActiveUS20080007250A1Minimize mutual inductanceMutual inductance is minimizedElectrocardiographyMagnetic measurementsRadio frequencyEngineering
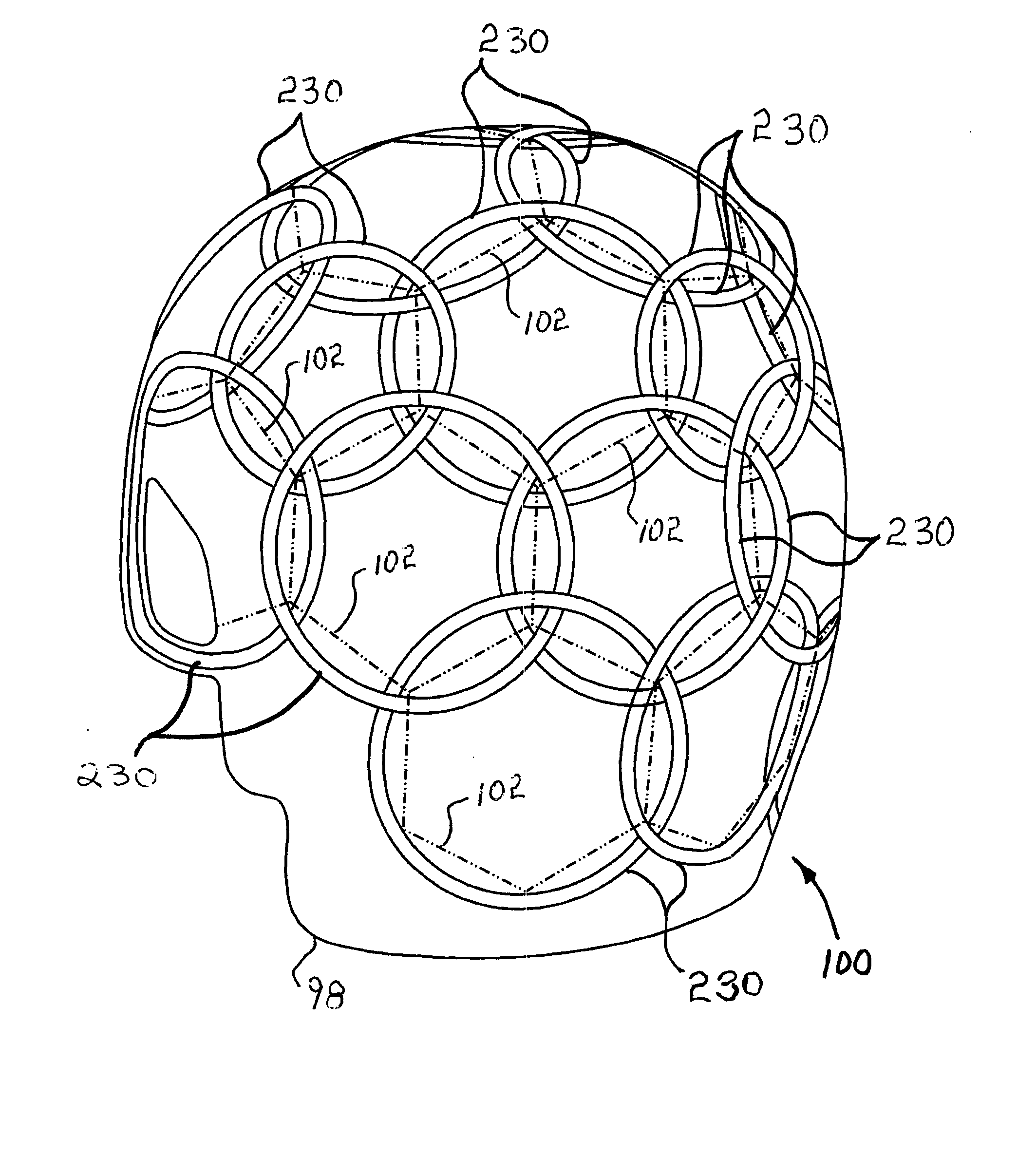
An MRI rf coil array is comprised of a large number of separate coil elements that are supported on a substrate that is shaped to the contour of the anatomy being imaged. The coil elements overlap each other to reduce mutual inductance and their location is determined by tiling the surface of the substrate with regular, substantially same sized polygons. The center of each coil element is aligned with the center of a polygon. By using a mixture of different polygons, such as hexagons and pentagons, an arrangement of coil elements may be formed that cover a surface with non-zero Gaussian curvature where each coil is overlapped with its neighbors such that their mutual inductance is nulled.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Localized two-dimensional shift correlated MR spectroscopy of human brain
InactiveUS7200430B2Measurements using NMR spectroscopyDiagnostic recording/measuringWhole bodySpectroscopy
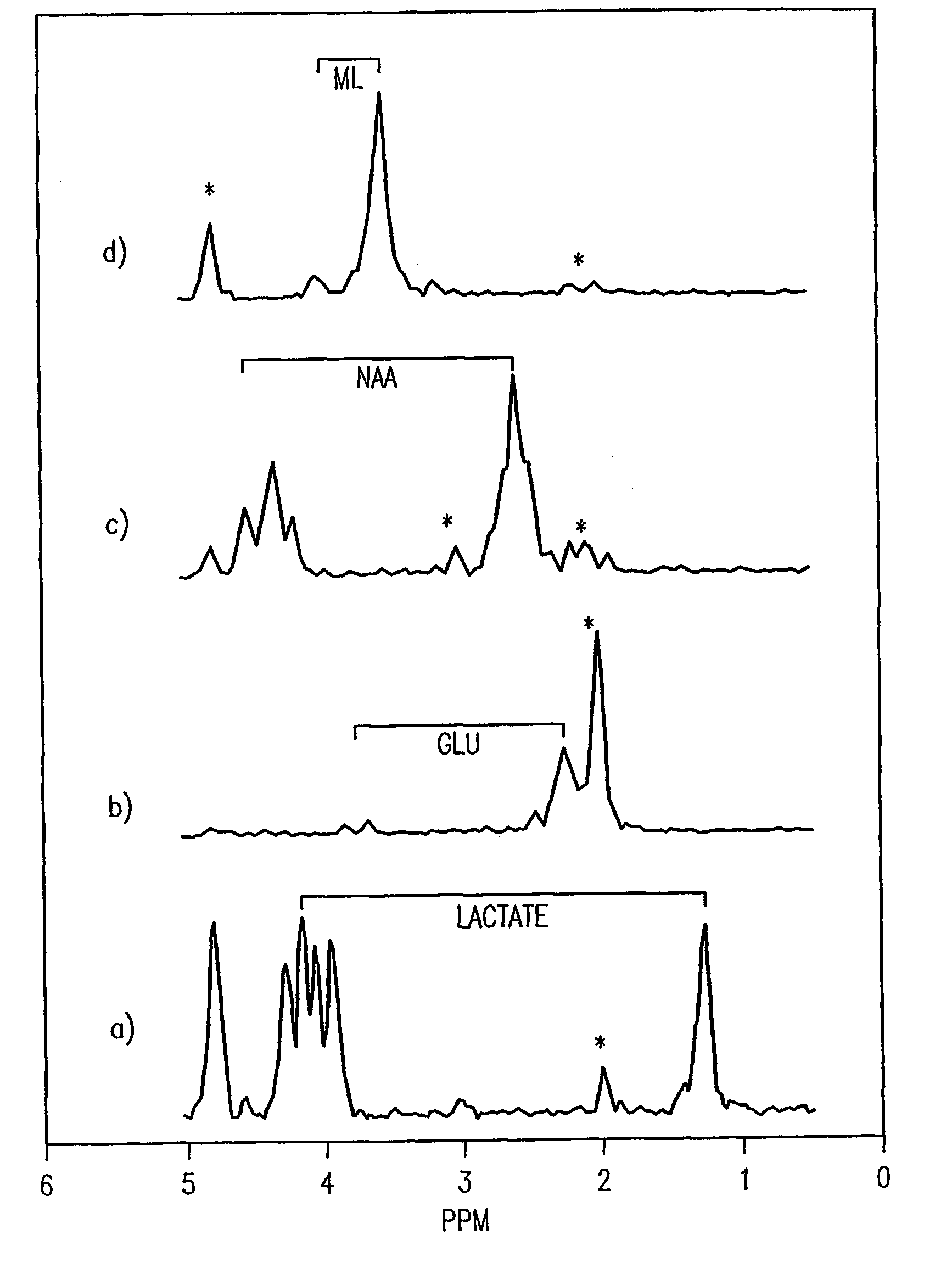
A two-dimensional (2D) chemical shift correlated MR spectroscopic (COSY) sequence integrated into a new volume localization technique (90°-180°-90°) for whole body MR Spectroscopy. Using the product operator formalism, a theoretical calculation of the volume localization as well as the coherence transfer efficiencies in 2D MRS is presented. A combination of different MRI transmit / receive rf coils is used. The cross peak intensities excited by the proposed 2D sequence are asymmetric with respect to the diagonal peaks. Localized COSY spectra of cerebral frontal and occipital gray / white matter regions in fifteen healthy controls are presented.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Deep learning techniques for magnetic resonance image reconstruction
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system, comprising: a magnetics system comprising: a B0 magnet configured to provide a B0 field for the MRI system; gradient coils configured to provide gradient fields for the MRI system; and at least one RF coil configured to detect magnetic resonance (MR) signals; and a controller configured to: control the magnetics system to acquire MR spatial frequency data using non-Cartesian sampling; and generate an MR image from the acquired MR spatial frequency data using a neural network model comprising one or more neural network blocks including a first neural network block, wherein the first neural network block is configured to perform data consistency processing using a non-uniform Fourier transformation.
Owner:HYPERFINE OPERATIONS INC
Open architecture imaging apparatus and coil system for magnetic resonance imaging
Apparatus and method for using radio frequency coil systems for magnetic resonance imaging within an open architecture apparatus is provided. The MRI coil system includes a support structure with an open architecture in which secondary support structures, compression systems and plates containing RF coil systems may be introduced. These structures and RF coils can be moved relative to the patient, or removed entirely from the system. In one embodiment the system consists of a tabletop coil system, while another embodiment consists of a dedicated stretcher design.
Owner:INVIVO CORP +1
System and apparatus for detecting gamma rays in a pet/mri scanner
ActiveUS20080265887A1Material analysis by optical meansElectric/magnetic detectionPhotodetectorRadio frequency
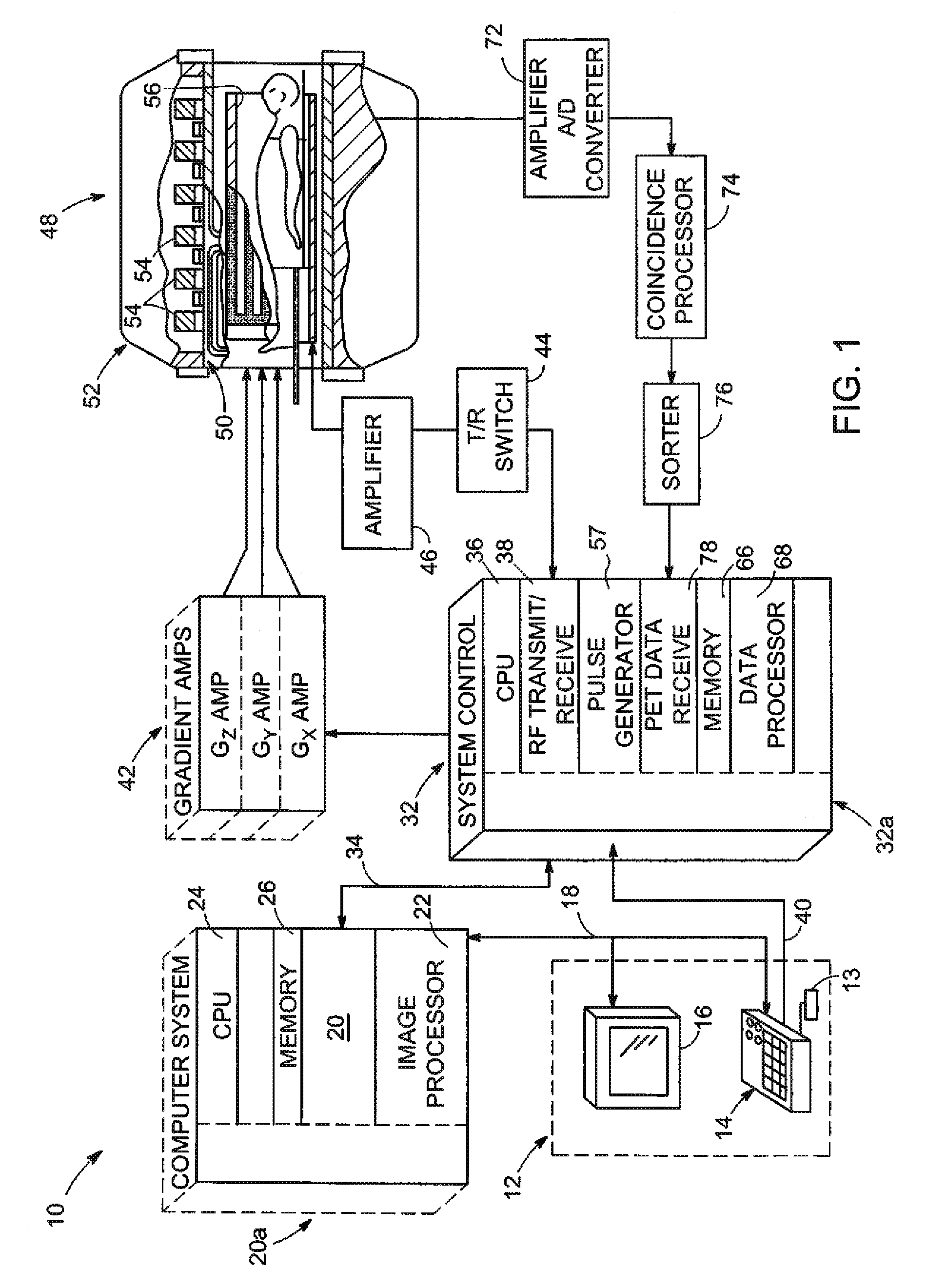
A gamma ray detector ring for a combined positron emission tomography (PET) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system is integrated into a radio frequency (RF) coil assembly such that the detector ring is integrated with a RF shield. Each gamma ray detector in the detector ring includes a scintillator component that emits light when a gamma ray is detected and a photodetector component designed to be sensitive to the frequency of light produced by the scintillator. A RF shield may be integrated into a detector ring such that the RF shield is positioned between the scintillator and photodetector components of each detector, thereby saving valuable radial space within the imaging system. Multiple such detector rings may be located adjacent to one another to increase axial coverage and enable three-dimensional PET imaging techniques.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
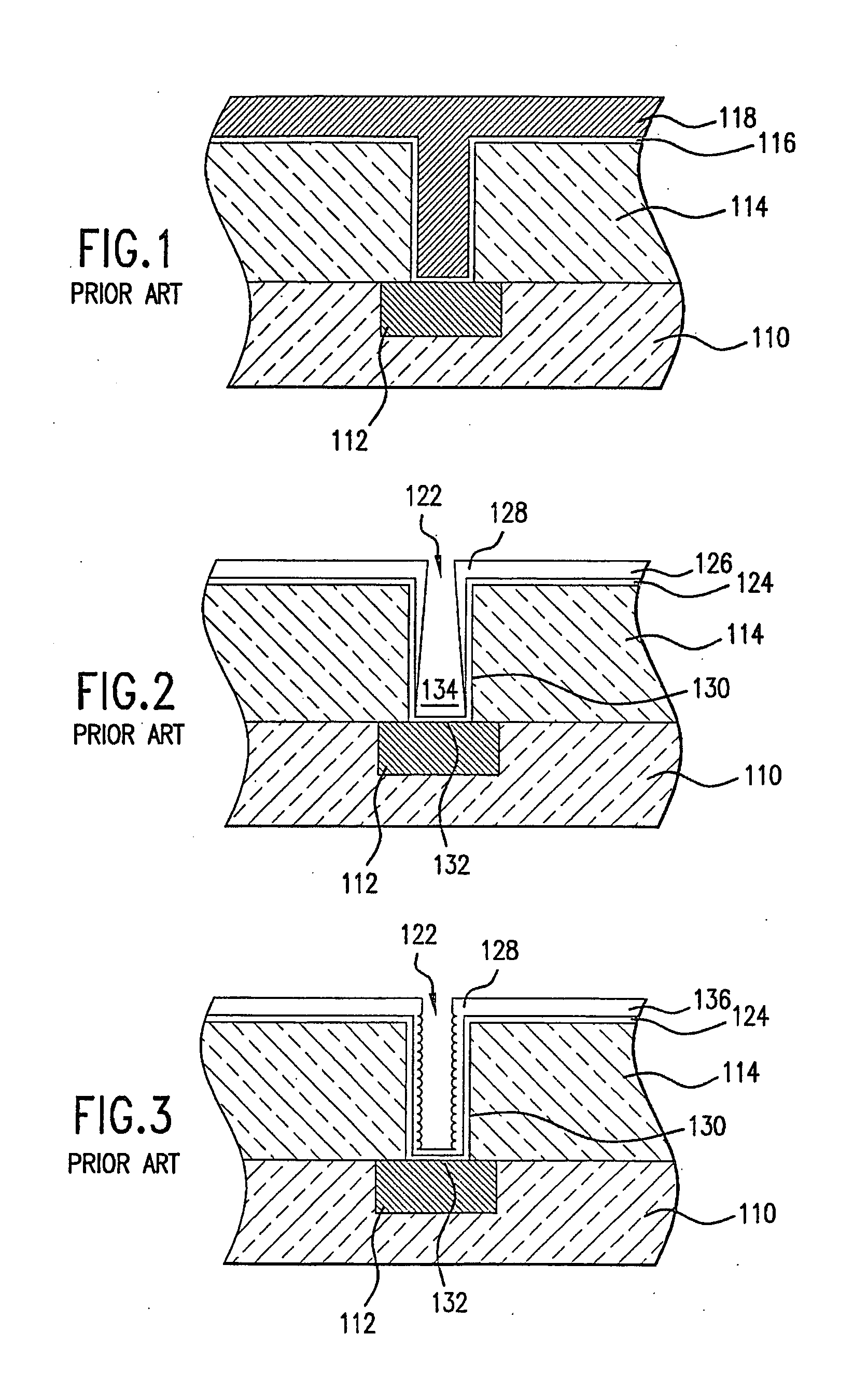
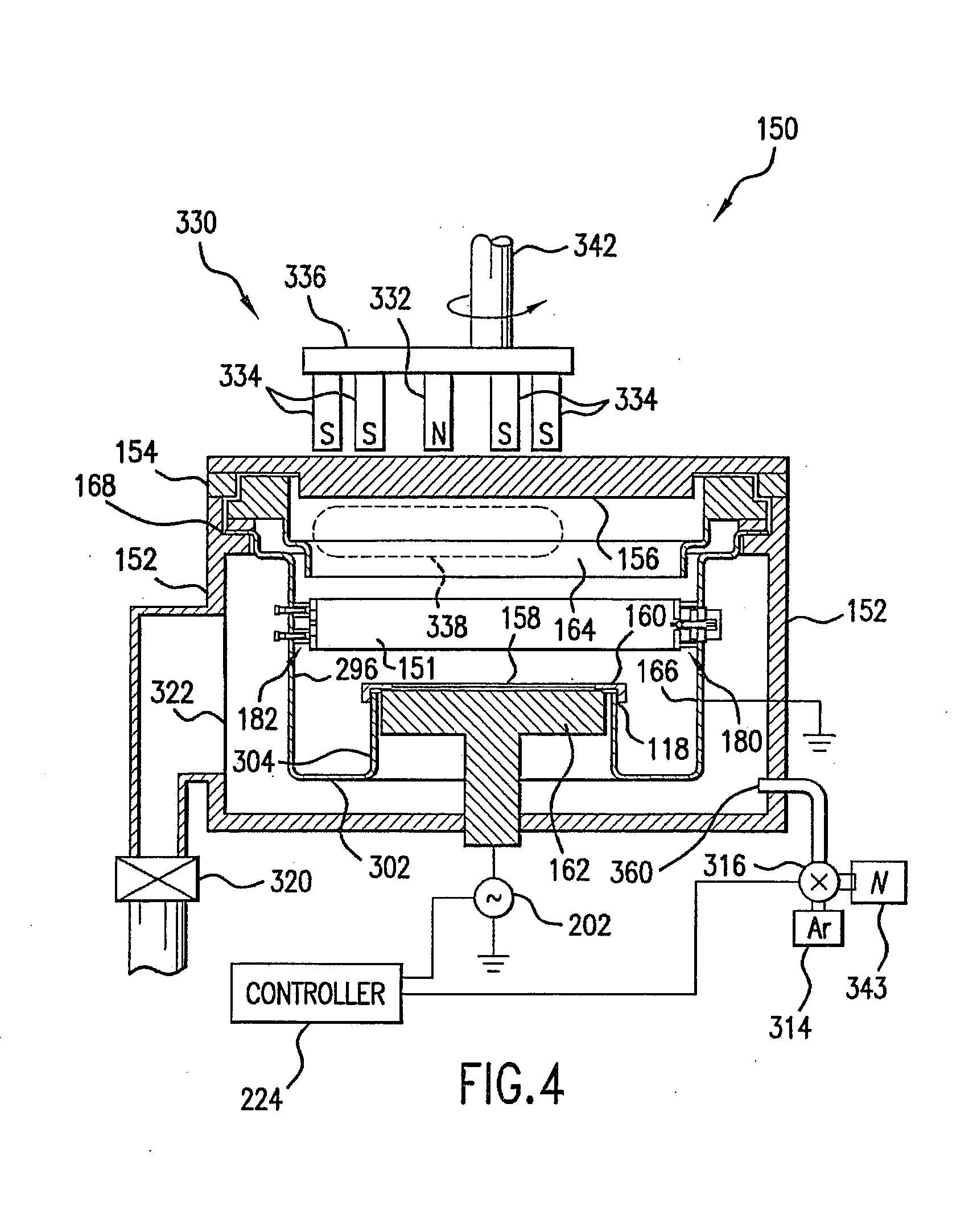
Self-ionized and inductively-coupled plasma for sputtering and resputtering
InactiveUS20050255691A1Raise the ratioReduce layer thicknessElectric discharge tubesSolid-state devicesRadio frequency energyMagnetic poles
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for simultaneous multi-slice magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS8405395B2Reliable separationLarge possible separationMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic gradientMulti slice
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Thermal buffering of cross-coils in high-power NMR decoupling
InactiveUS6320384B1Improve thermal conductivityElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceDielectricMagnetic susceptibility
A transverse rf saddle coil (30) for use in NMR is affixed in intimate thermal conract on one surface of a ceramic coilform (23) of high thermal conductivity. The probe is mostly for use with solid samples at high fields where the axis of the coilform is not alignedwith the main field. An orthogonal rf coil (1) is mounted in intimate thermal contact to the first saddle coil (30) via a ceramic spacer or coilform (2). The coilform is cooled by high-velocity gas flow and is also often associated with bearing exhaust gas from a high speed sample spinner. The two coils are tuned to different rf frequencies with circuits capable of supporting high rf currents. The rf coils (30, 1) may be magnetically compensated and expansion controlled, and passive geometric compensation of magnetic susceptibility effects from a sample spinner stator may also be incorporated. Novel coil mounting techniques, including metallurgical bonds to ceramics and capturing by dielectric clam-shells, are also disclosed.
Owner:DOTY SCI
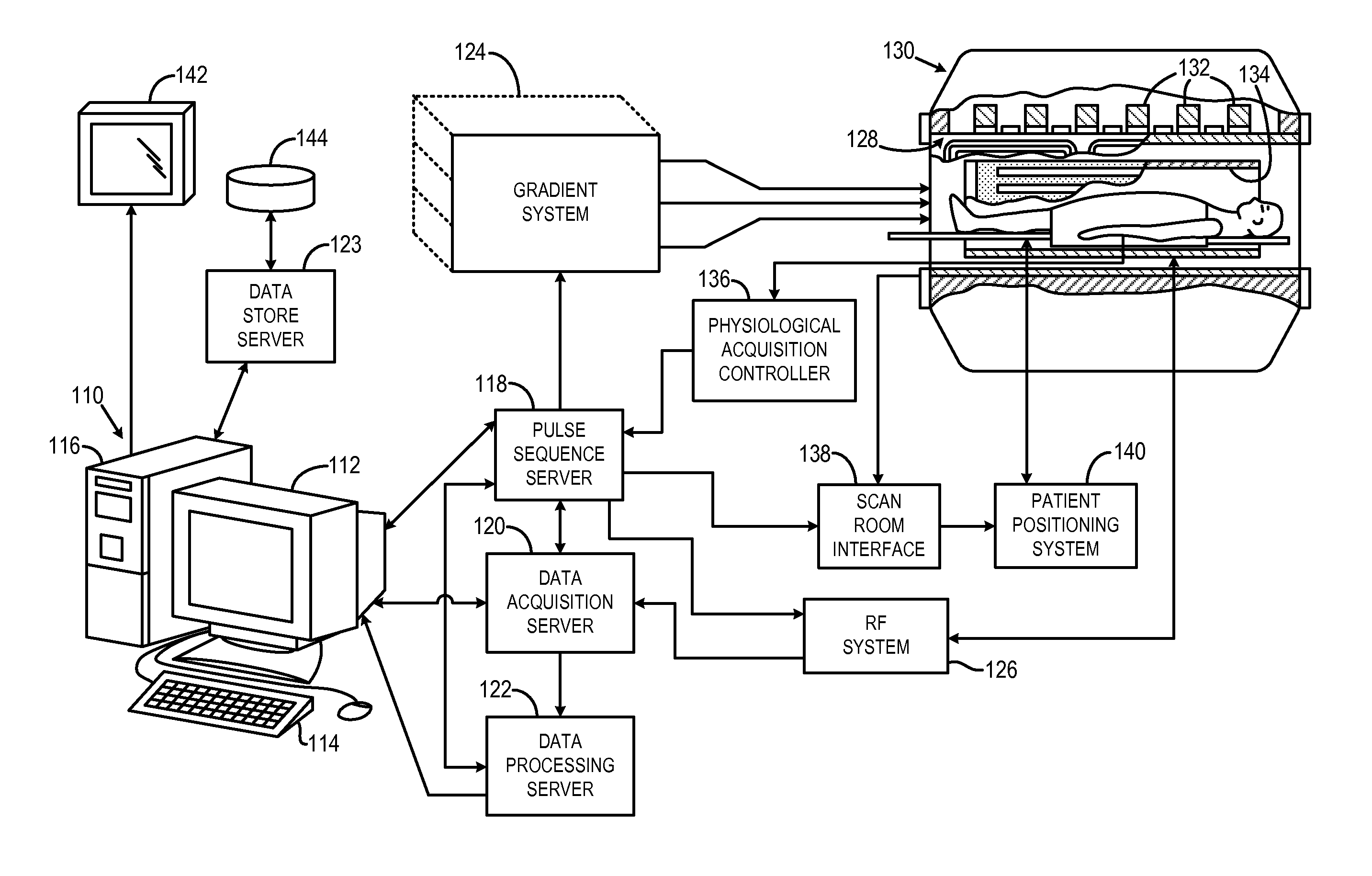
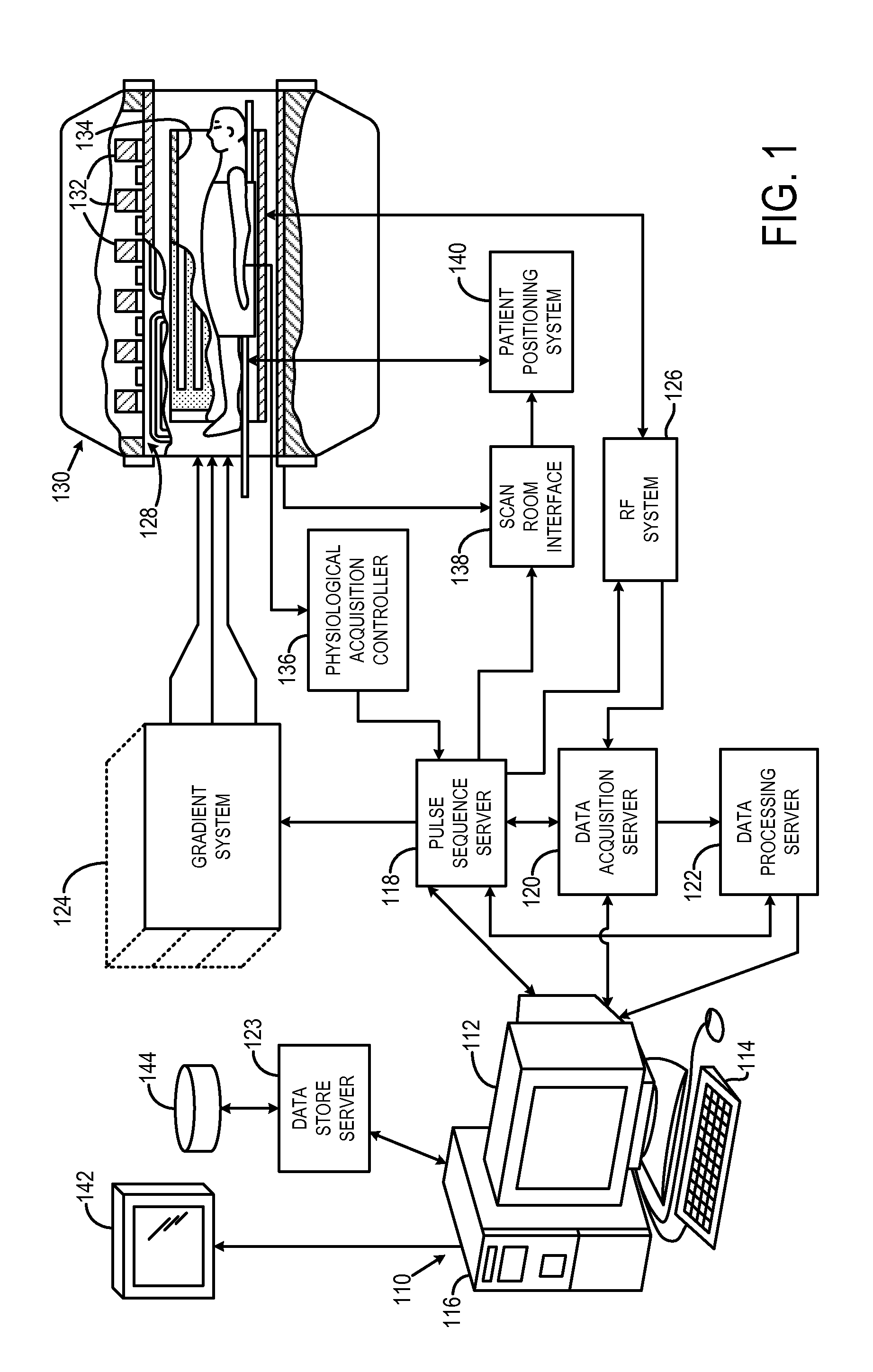
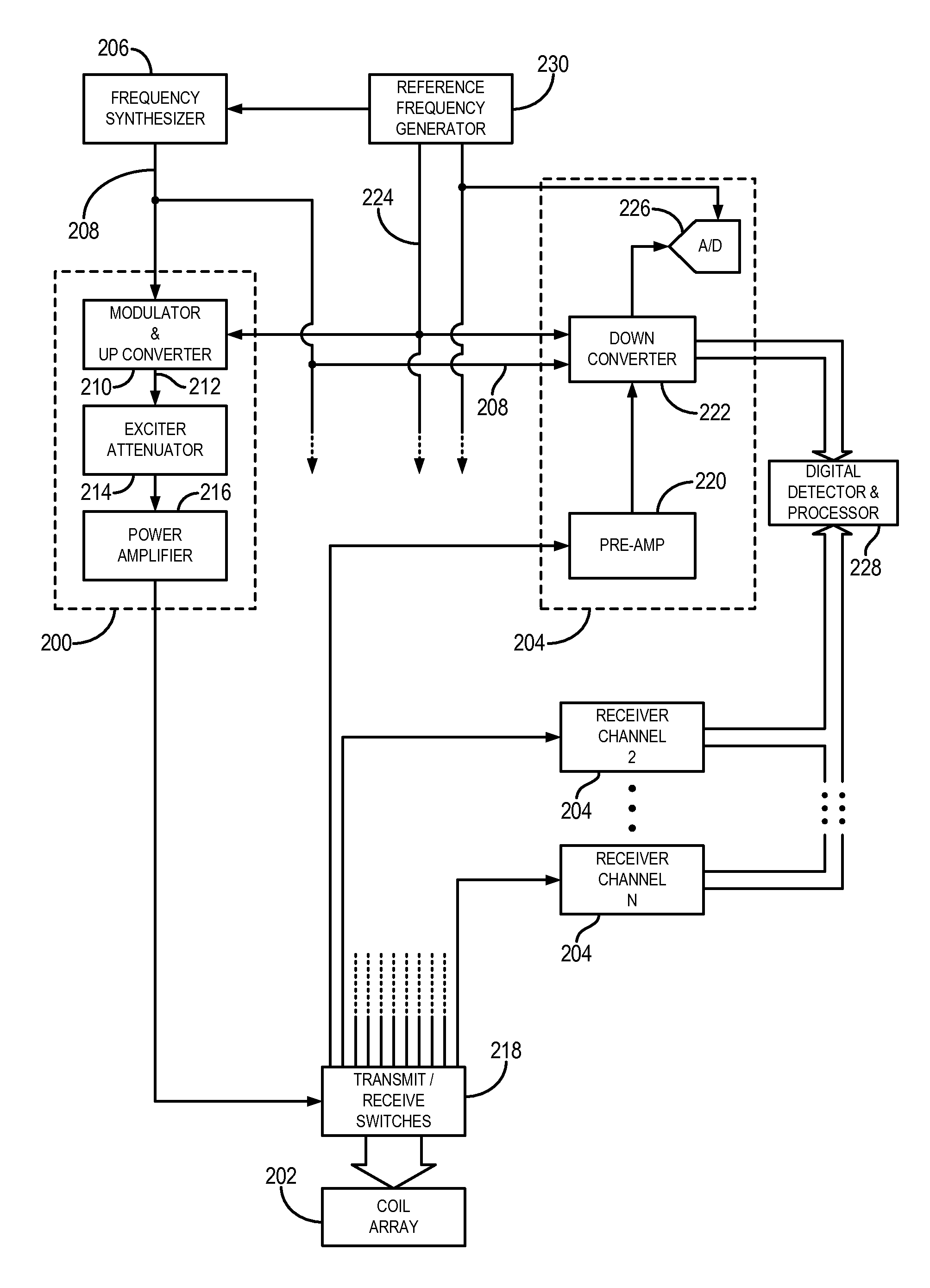
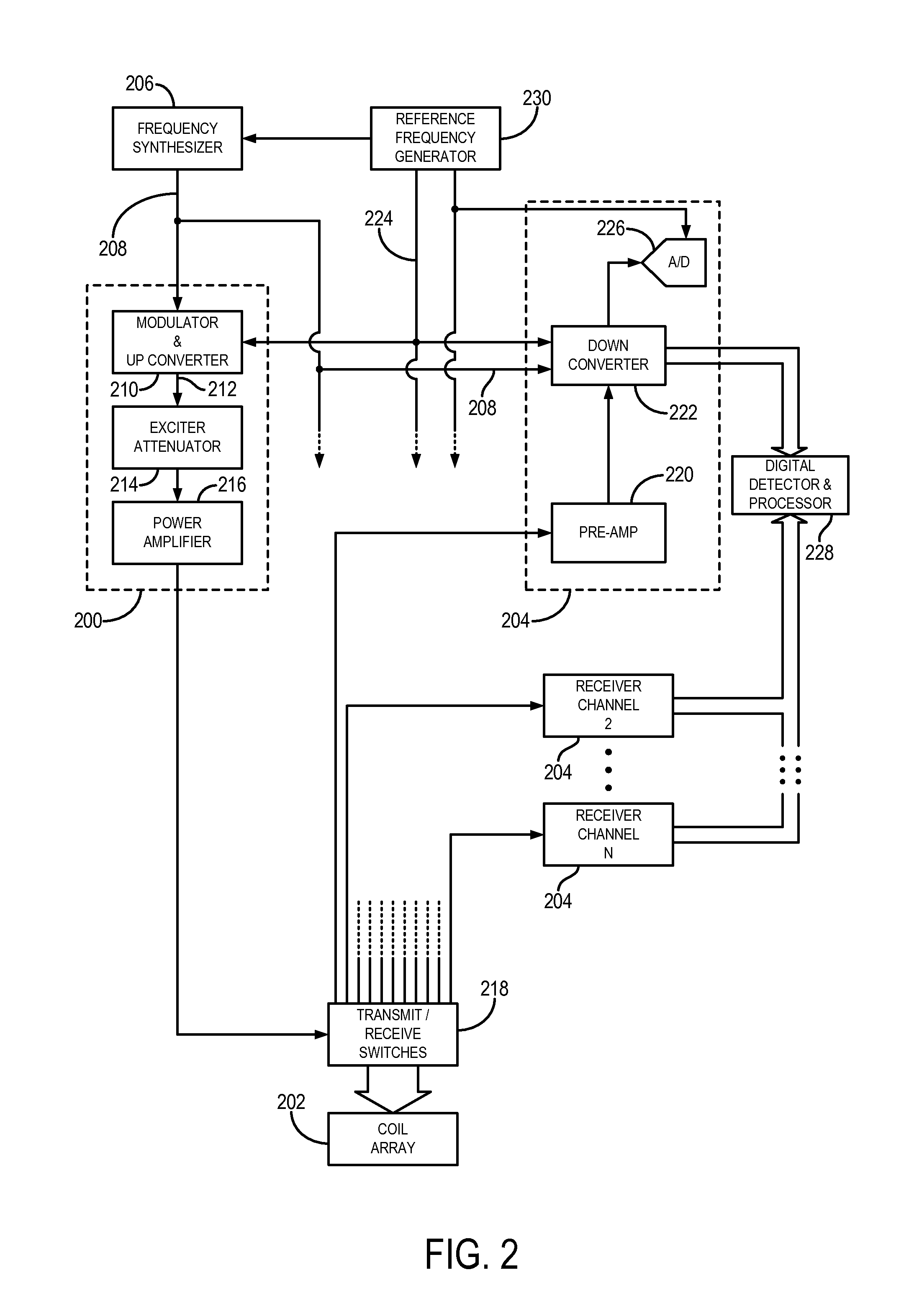
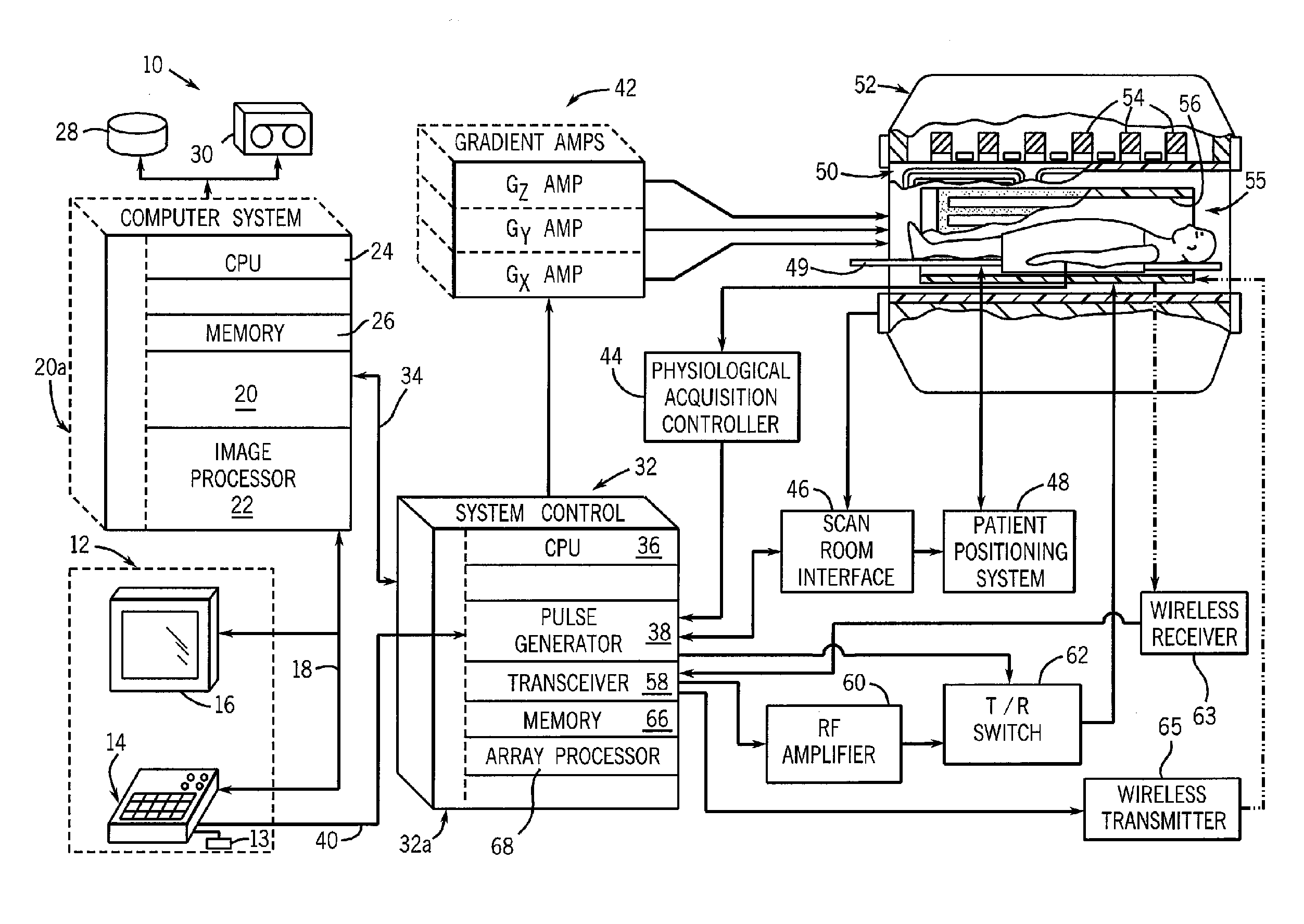
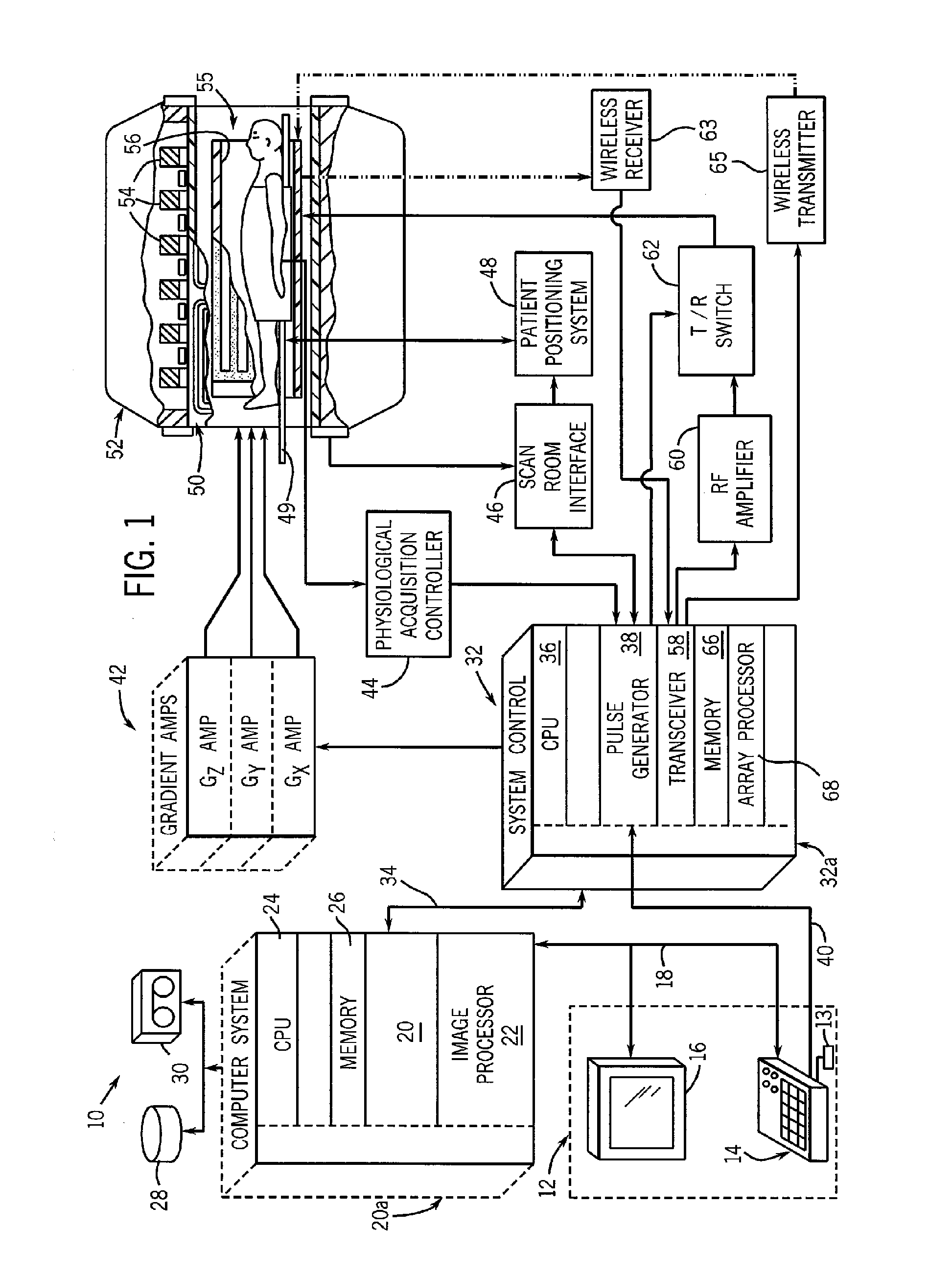
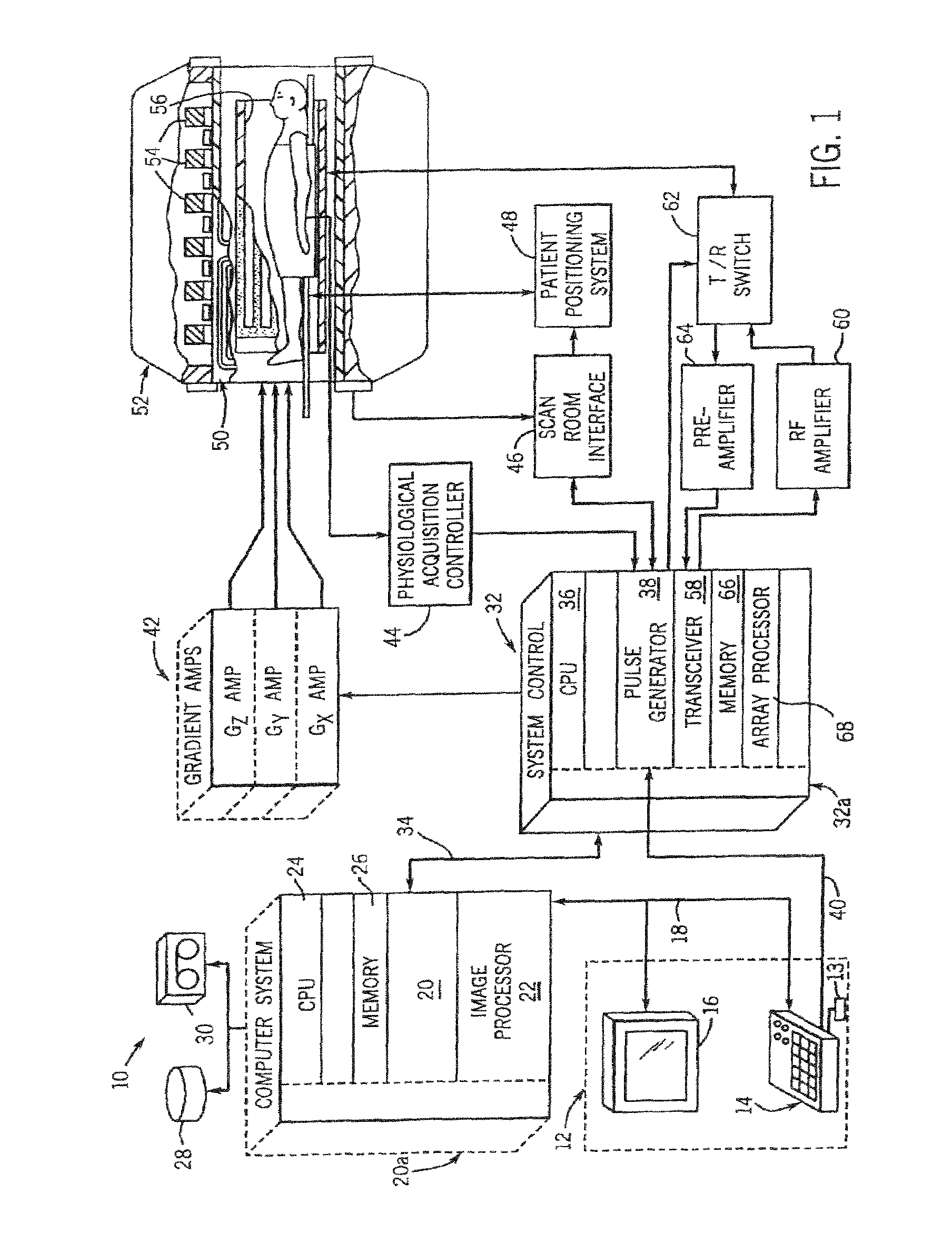
Methods & apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging
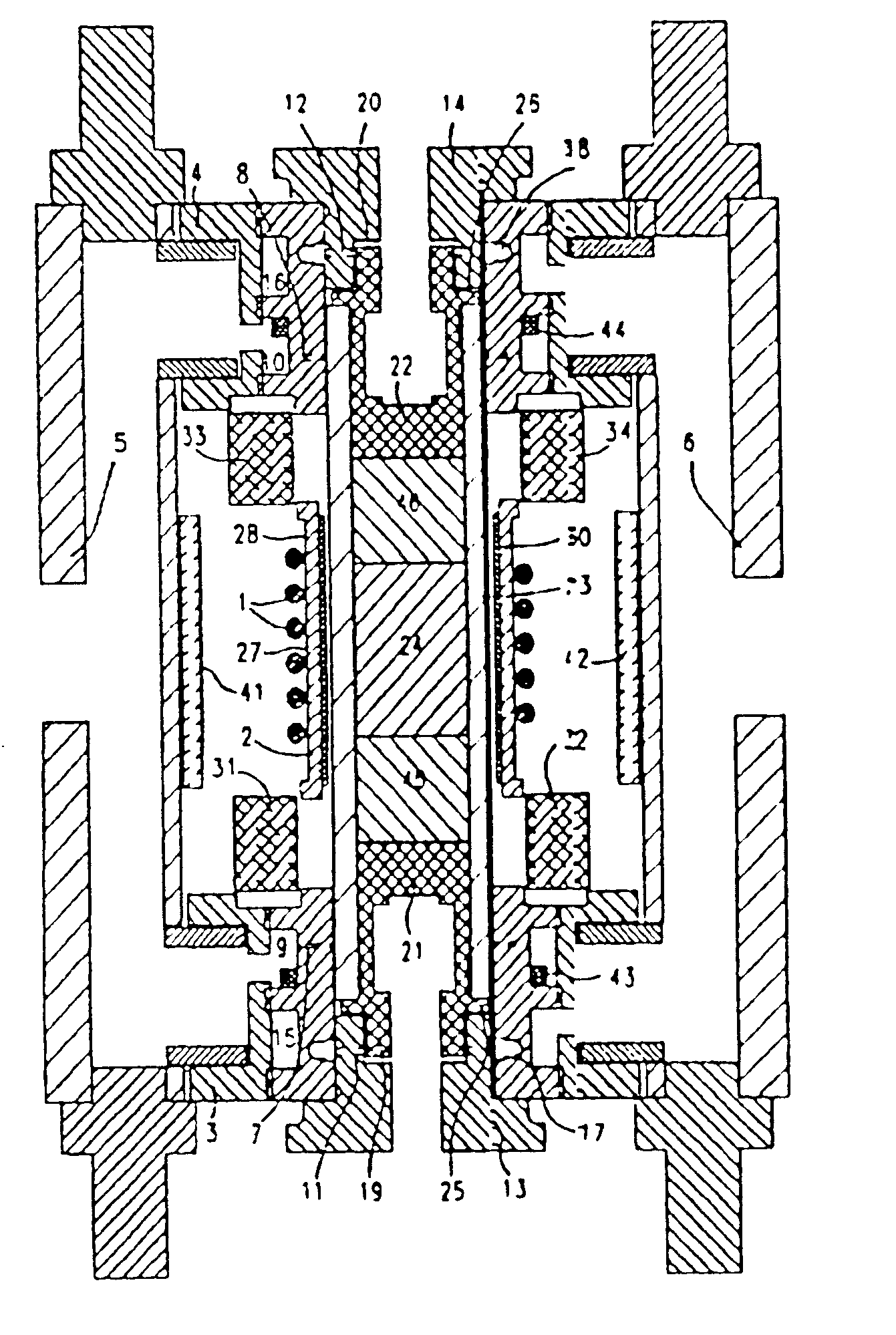
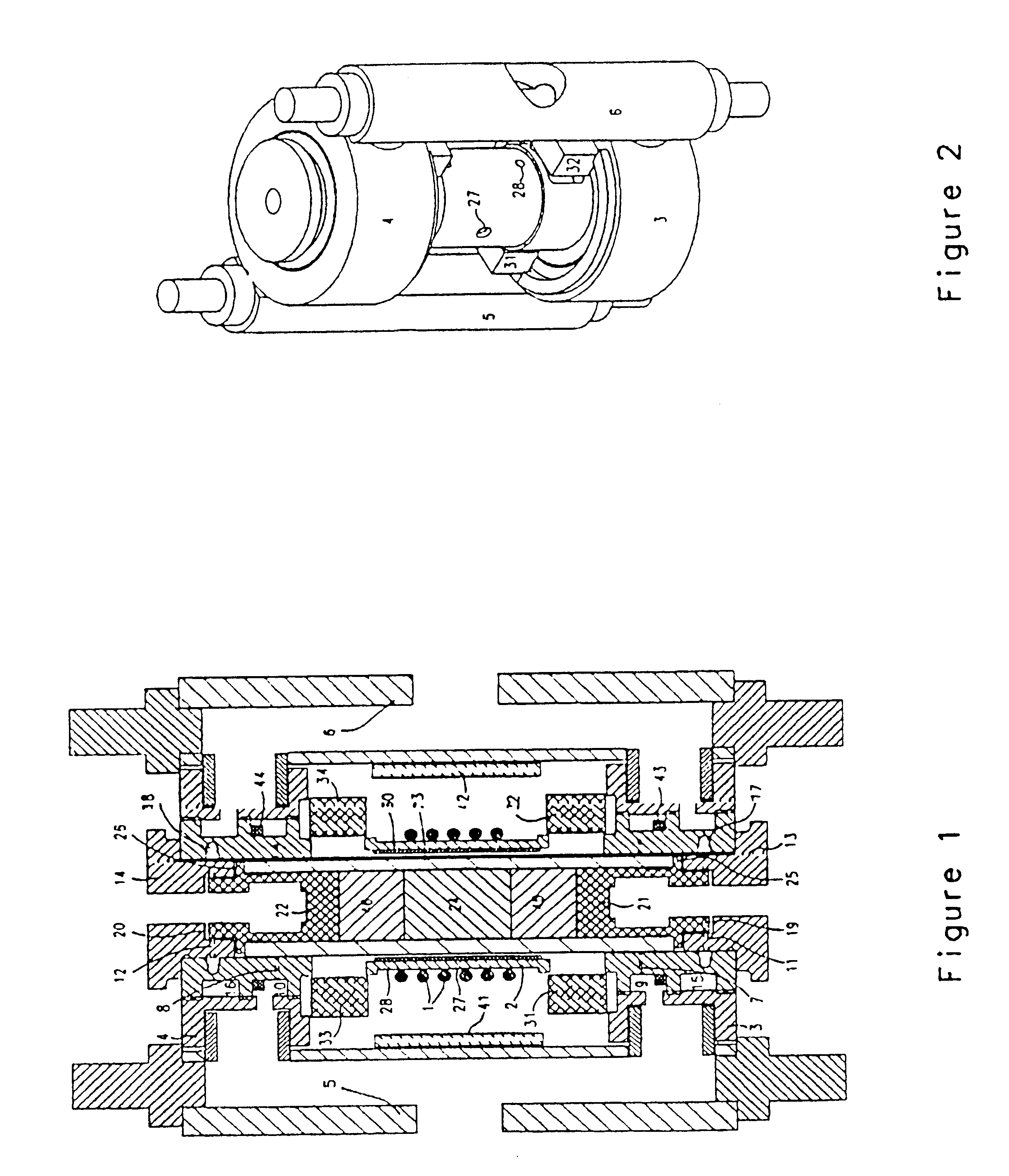
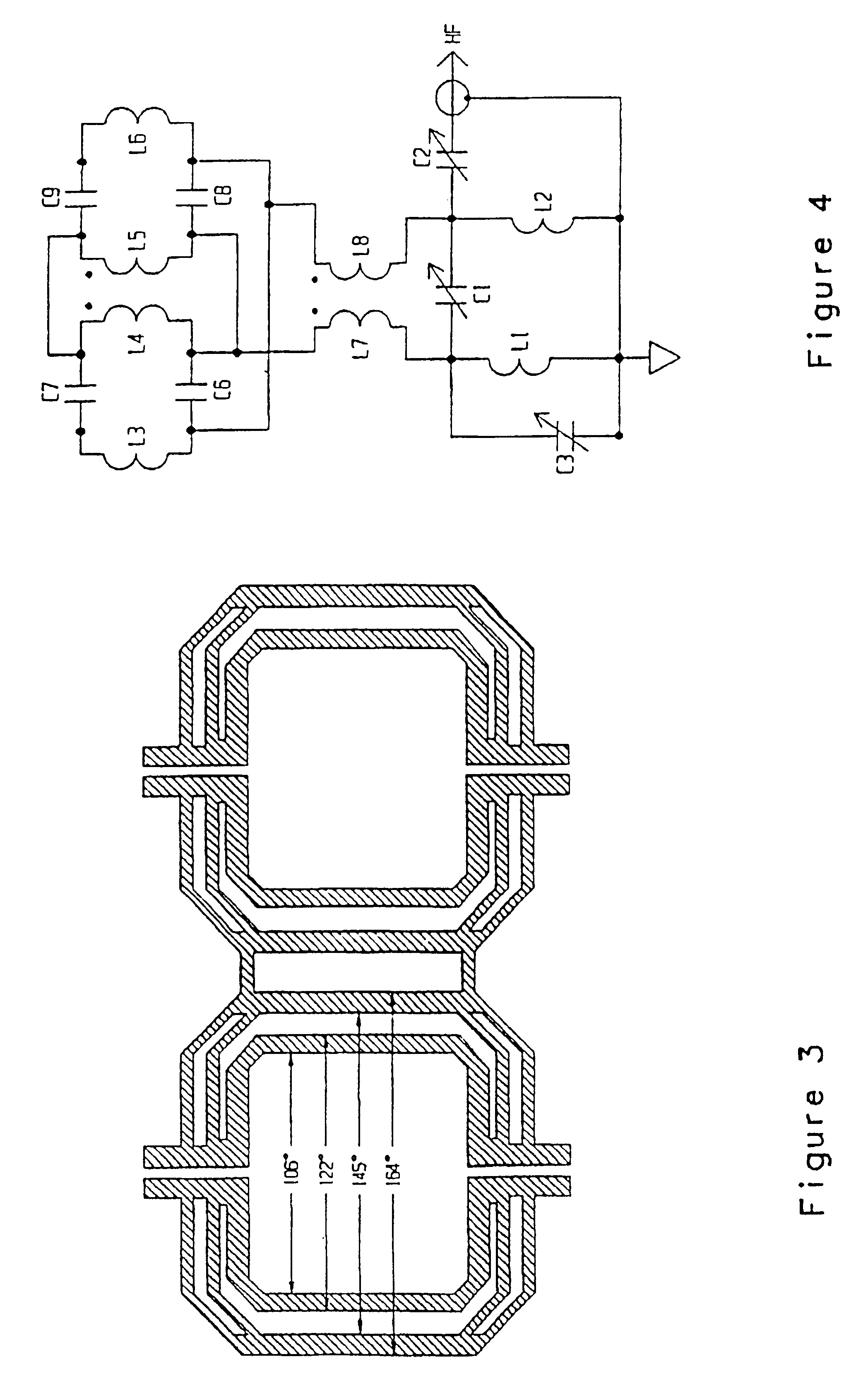
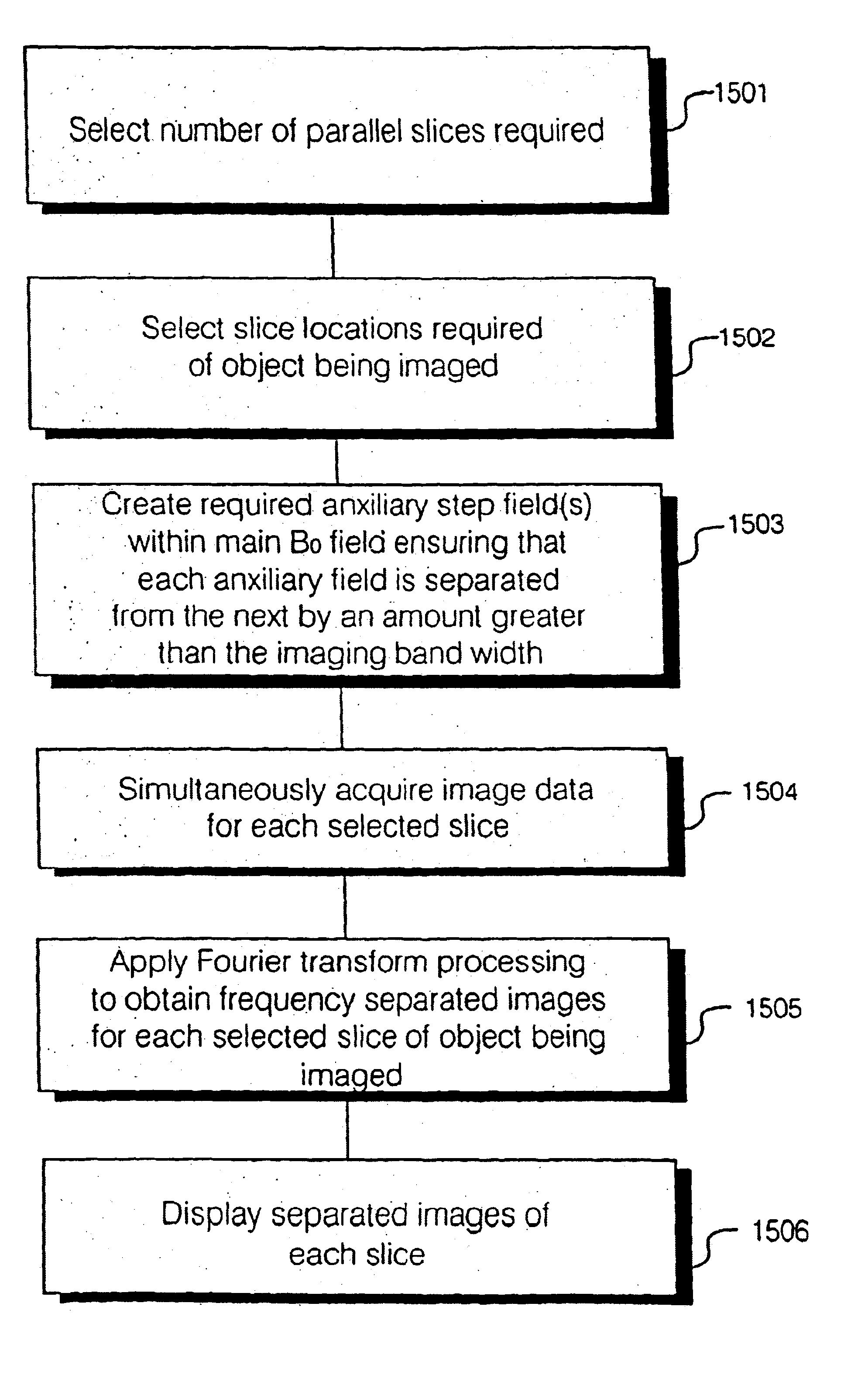
InactiveUS6980001B2Shorten Image Acquisition TimeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMagnetizationPhysical entity
A parallel magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) apparatus configurable to image a physical entity comprises:a main magnetic flux source for providing a uniform fixed magnetic field, B0;an RF array system comprising a plurality of RF coils and receivers, said RF system configured for:generating rotating RF excitation magnetic fields B1; andreceiving RF signals due to precessing nuclear magnetization on multiple spatially distinct radio frequency coils and associated receiver channels, said RF system being configured to operate in accordance with a B1 sensitivity encoding technique;a control processor for controlling imaging functionality, collecting image data and effecting data processing of the captured image data the control processor being configured with post processing capability for the B1 sensitivity encoding technique;an image display means for displaying processed image data as resultant images; andan auxiliary magnetic field means capable of producing at least one auxiliary uniform B0 step magnetic field imaging region within the main B0 magnetic field;wherein:the auxiliary magnetic field, means is configured to operate in combination with the RF coil system and the B1 sensitivity encoding technique, the imaging apparatus thereby providing faster image acquisition than that attributed to the speed up factor provided solely by the B1 sensitivity encoding technique.The invention also includes a method of imaging using this apparatus.Furthermore, the invention also includes a method and apparatus for three-dimensional MR imaging using a 1D Multiple Acquisition Micro B0 array coupled with a 2D Multiple Acquisition Micro B0 array.
Owner:UNIV OF SHEFFIELD AT WESTERN BANK THE
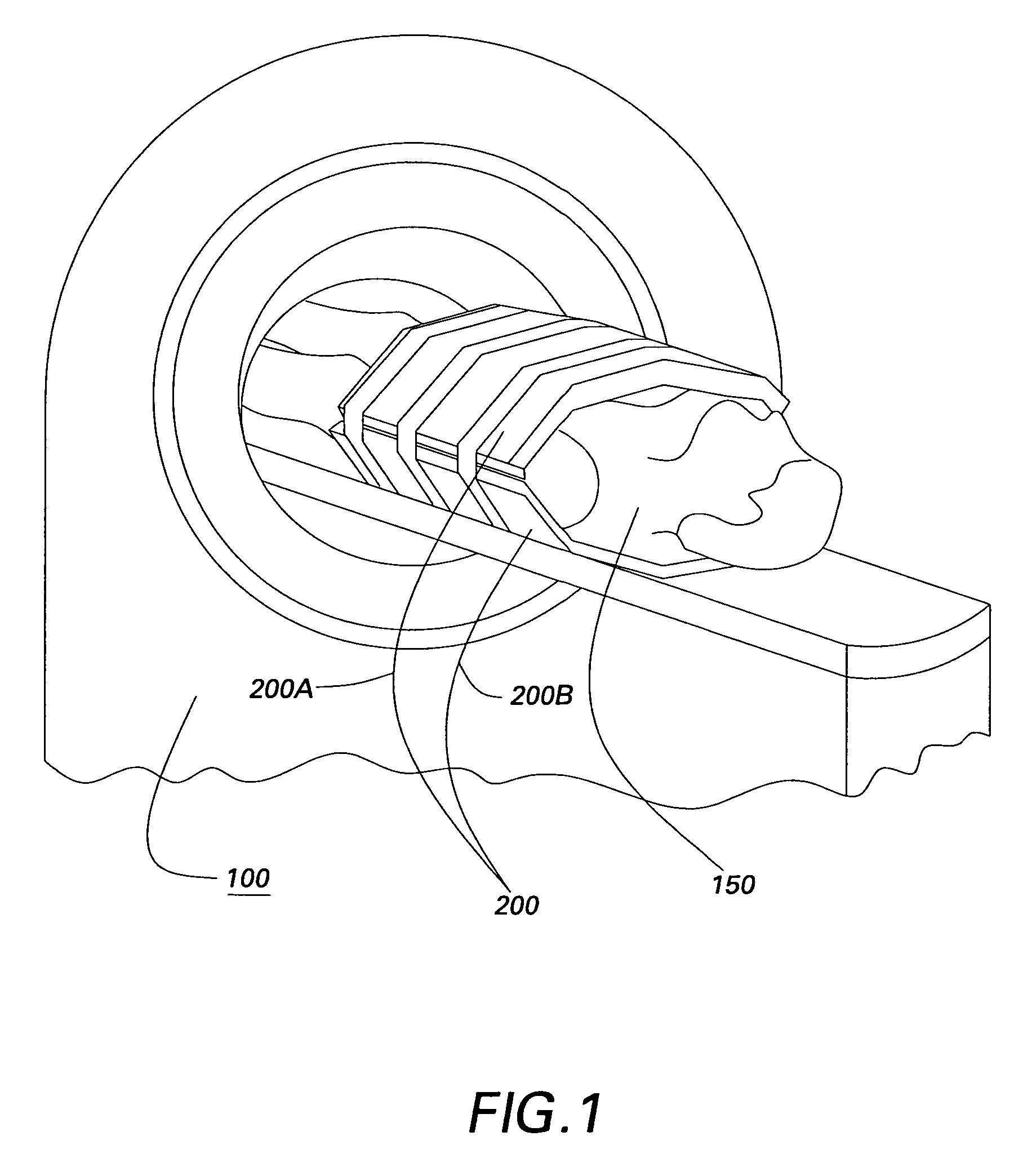
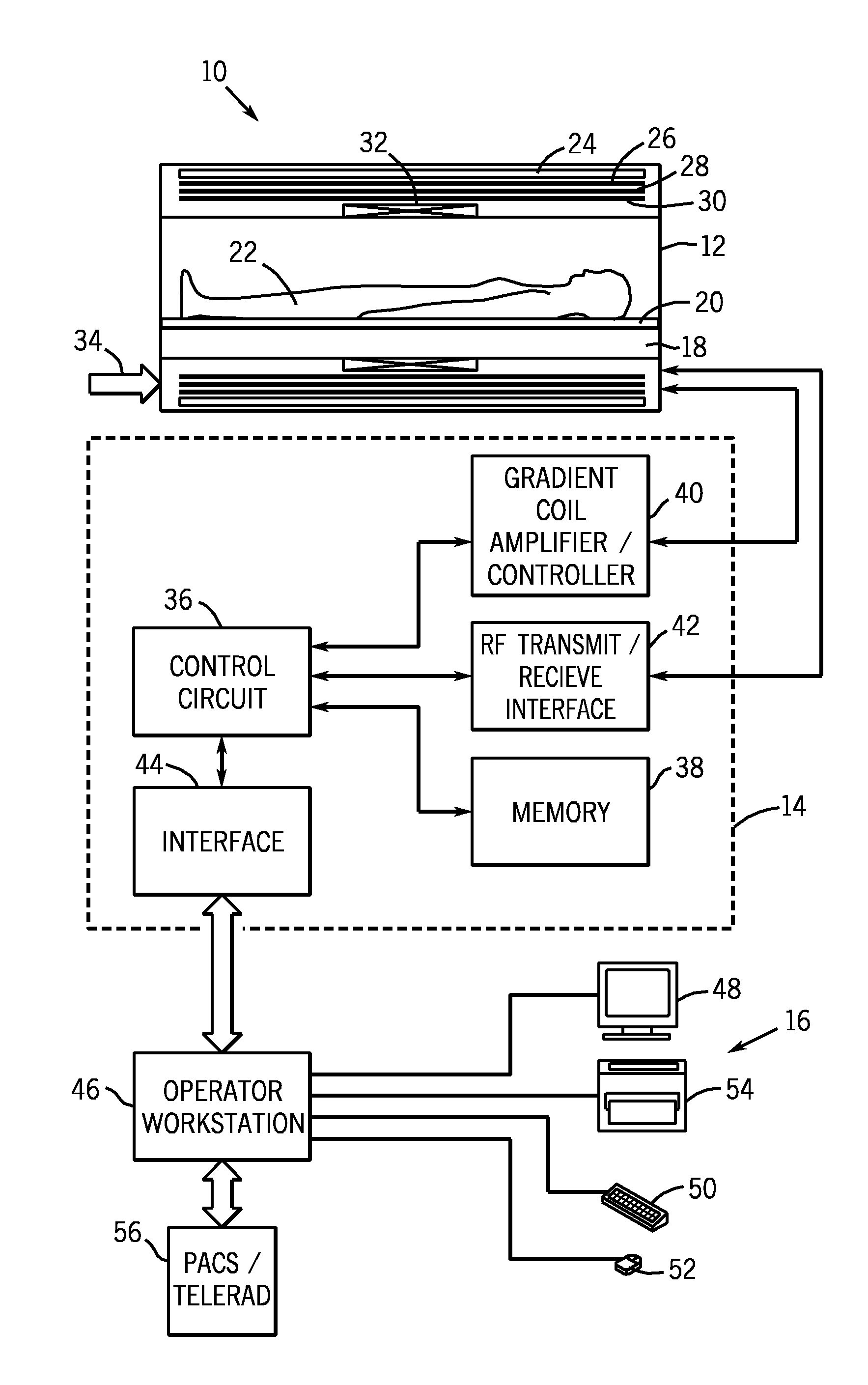
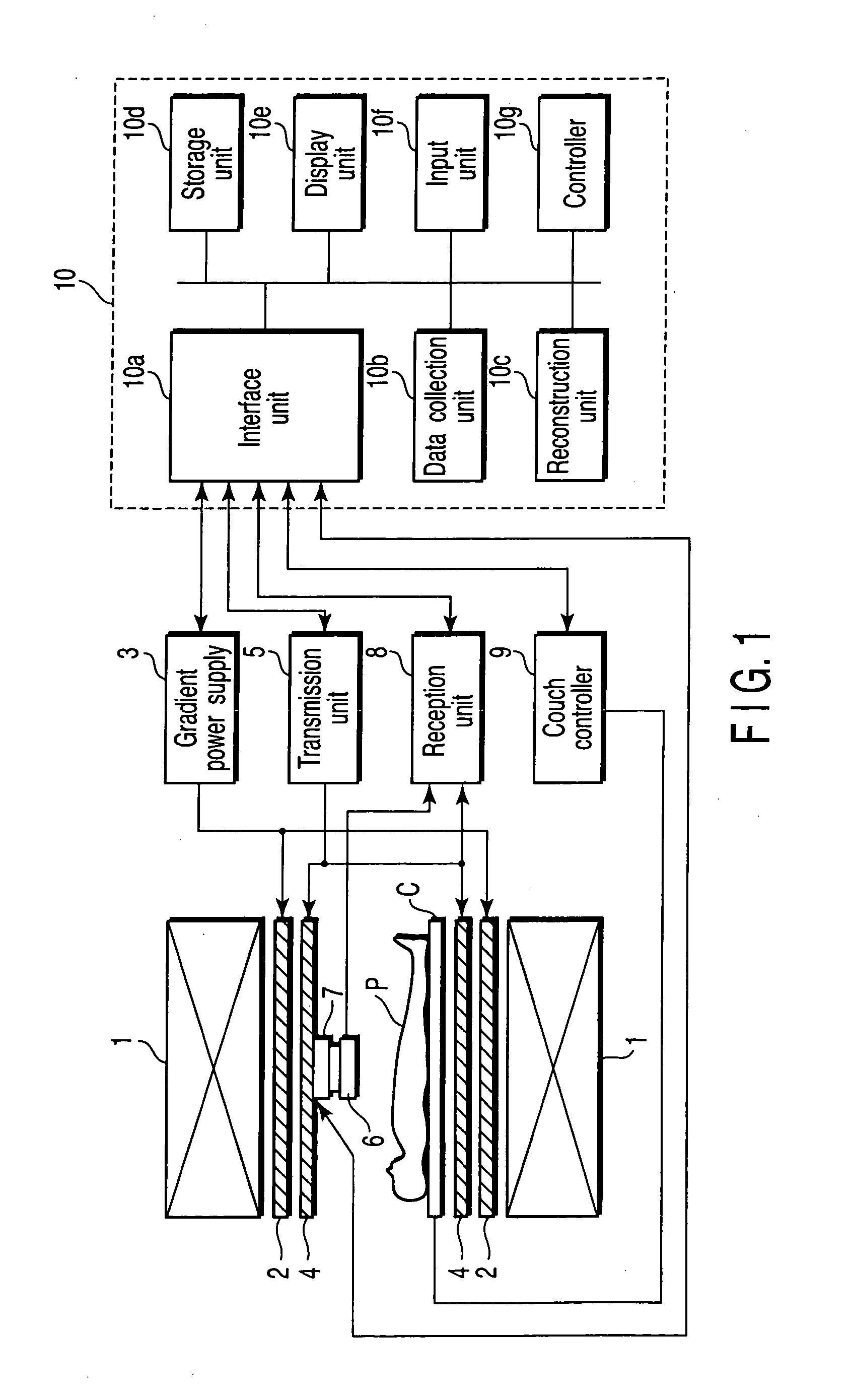
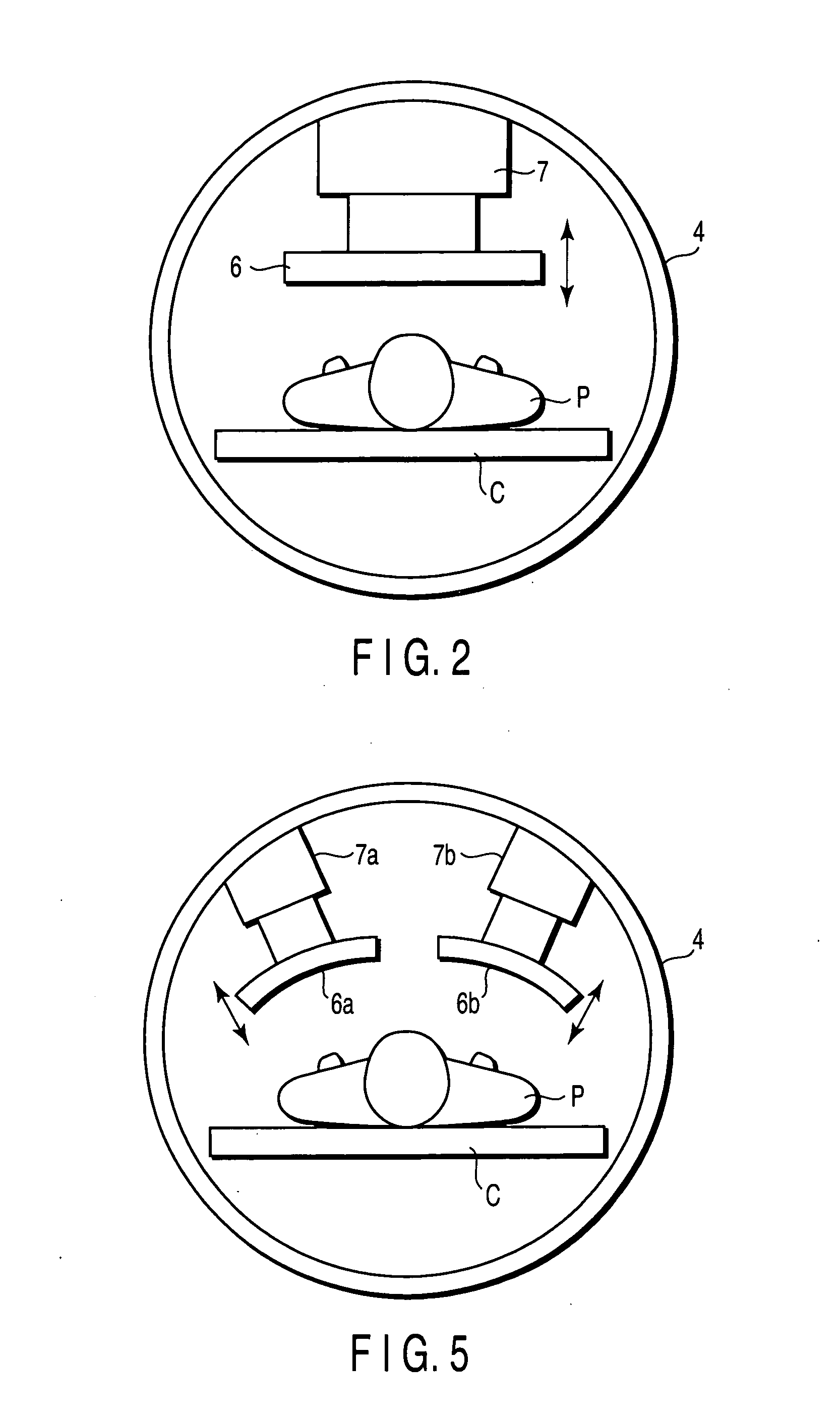
Magnetic resonance imaging involving movement of patient's couch
InactiveUS6946836B2Improve accuracyWork lessMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceEngineering
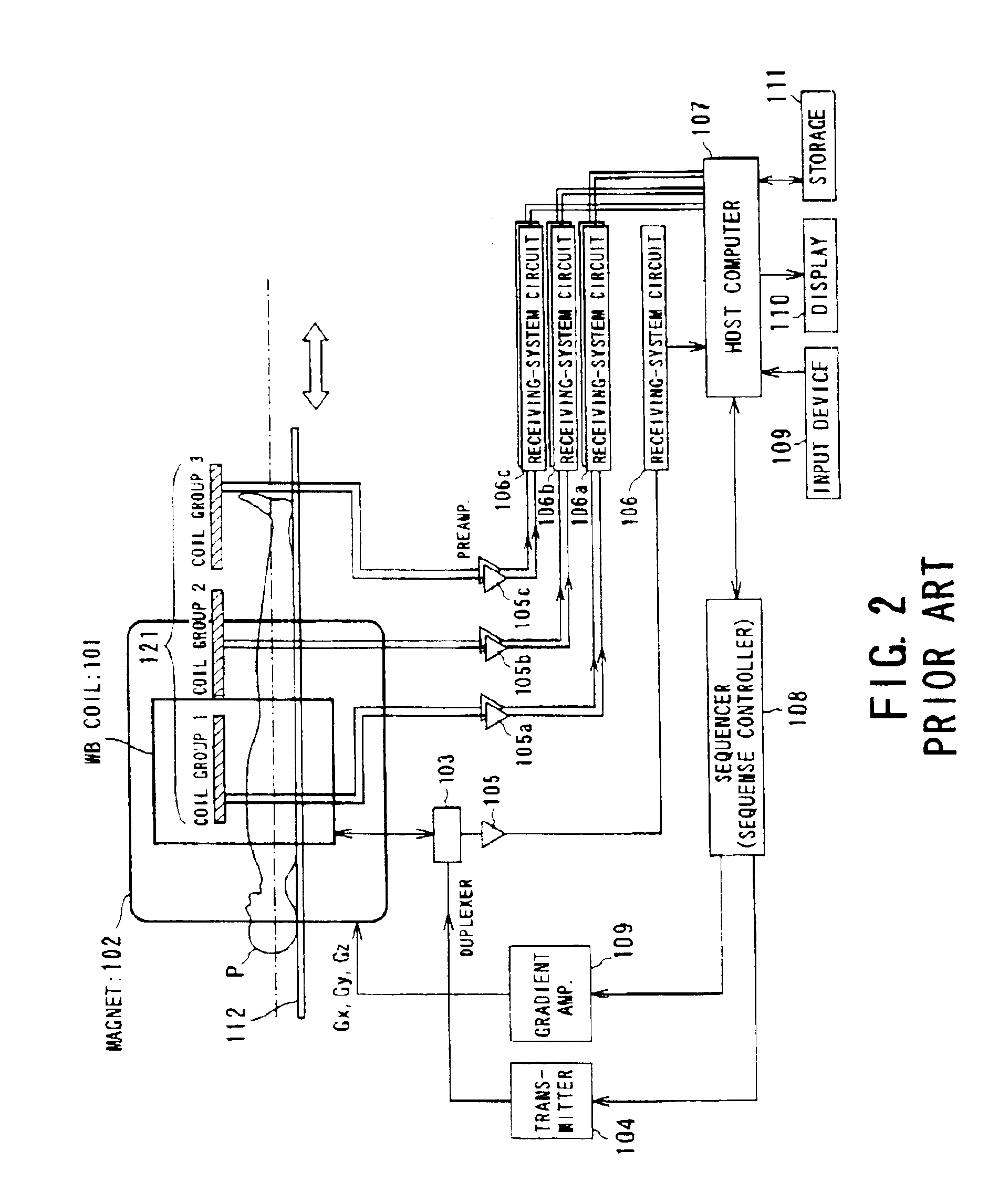
A magnetic resonance imaging system performing various types of imaging that involves movement of a patient's couch. The system has a patient's couch having a tabletop movable in a predetermined direction passing through a static magnetic field as well as reception multiple RF coils consisting of for example a plurality of coil groups. The tabletop is automatically moved in its longitudinal direction in accordance with a length of each coil group in the predetermined direction. At each moved position, scanning is performed on a given pulse sequence. An echo signal is received through the multiple RF coils, then switched over by an input switchover unit to be sent to a receiving-system circuit. The echo signal is subjected to given processing in this circuit so that it is converted to echo data. The echo data are produced into an MR image by a host computer.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
System and apparatus for detecting gamma rays in a PET/MRI scanner
ActiveUS7667457B2X/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentElectric/magnetic detectionPhotodetectorRadio frequency
A gamma ray detector ring for a combined positron emission tomography (PET) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system is integrated into a radio frequency (RF) coil assembly such that the detector ring is integrated with a RF shield. Each gamma ray detector in the detector ring includes a scintillator component that emits light when a gamma ray is detected and a photodetector component designed to be sensitive to the frequency of light produced by the scintillator. A RF shield may be integrated into a detector ring such that the RF shield is positioned between the scintillator and photodetector components of each detector, thereby saving valuable radial space within the imaging system. Multiple such detector rings may be located adjacent to one another to increase axial coverage and enable three-dimensional PET imaging techniques.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
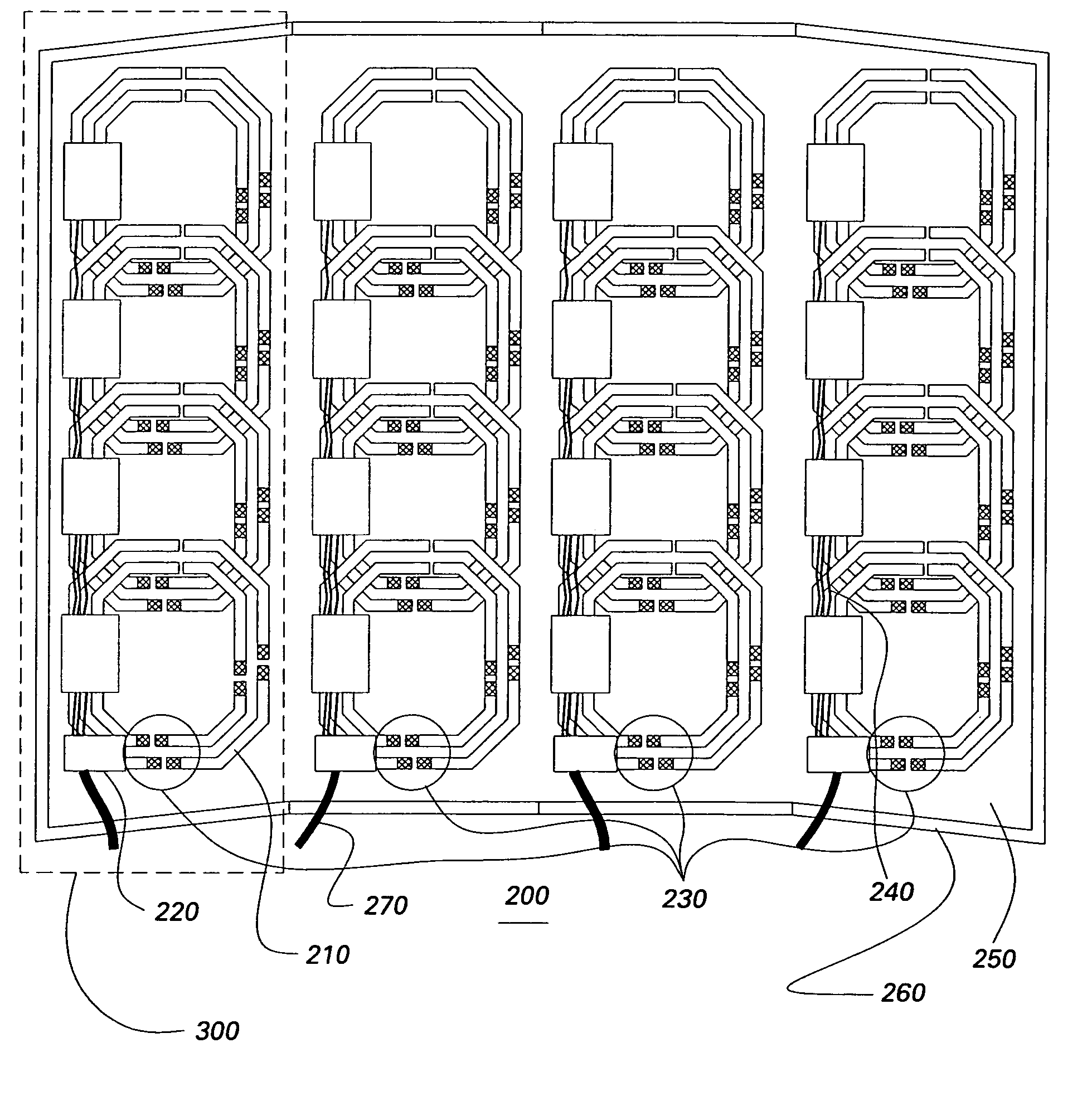
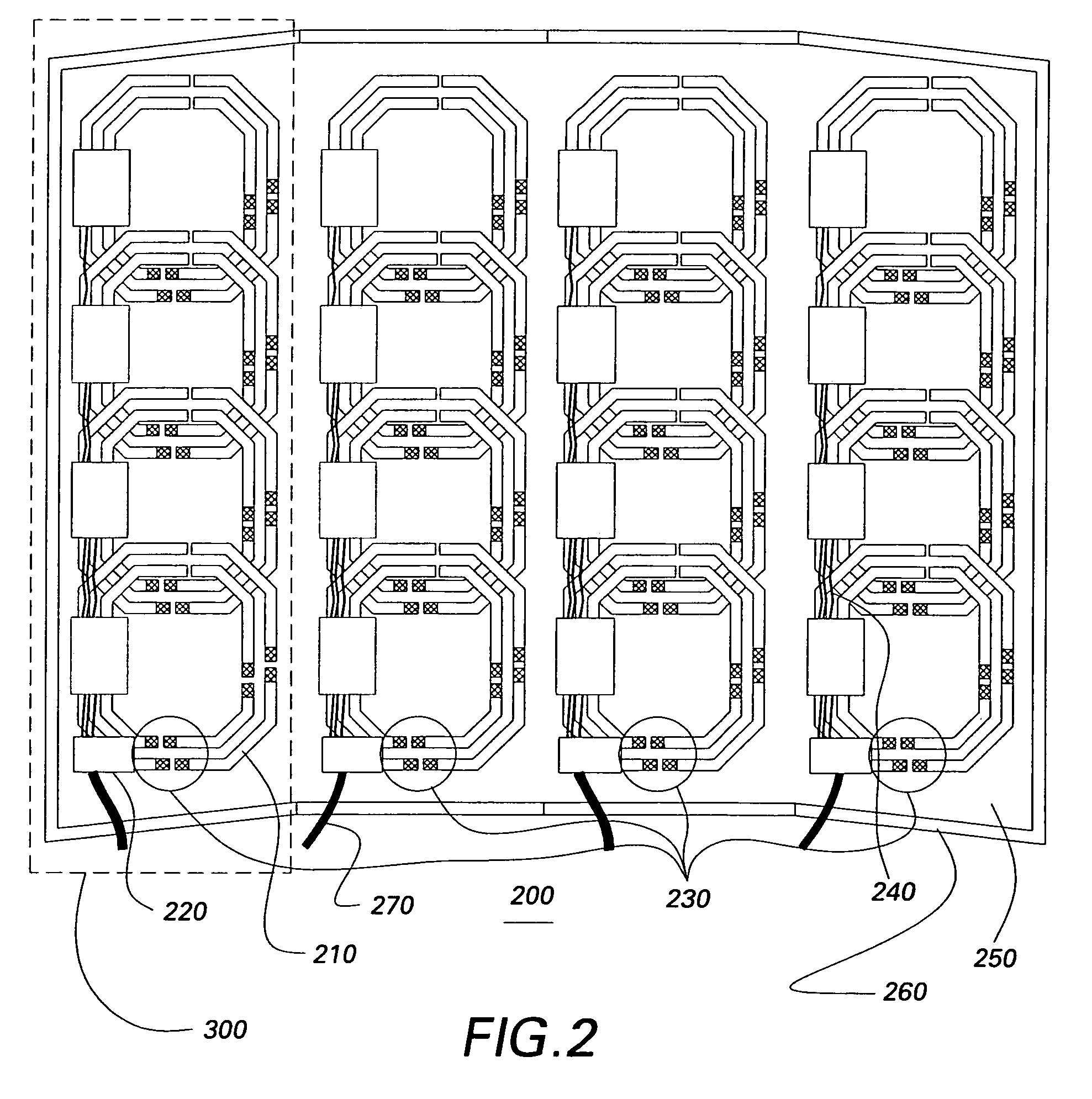
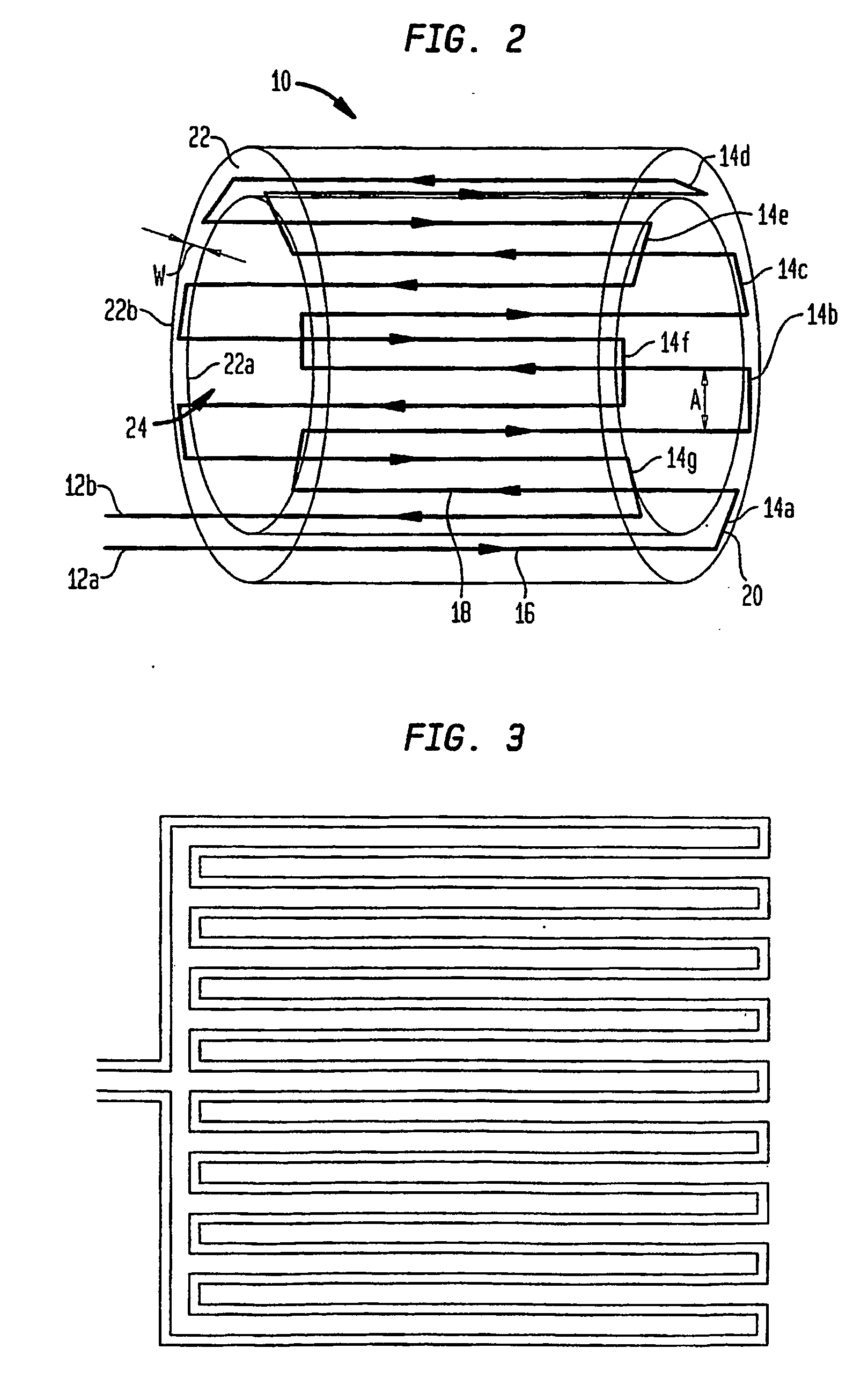
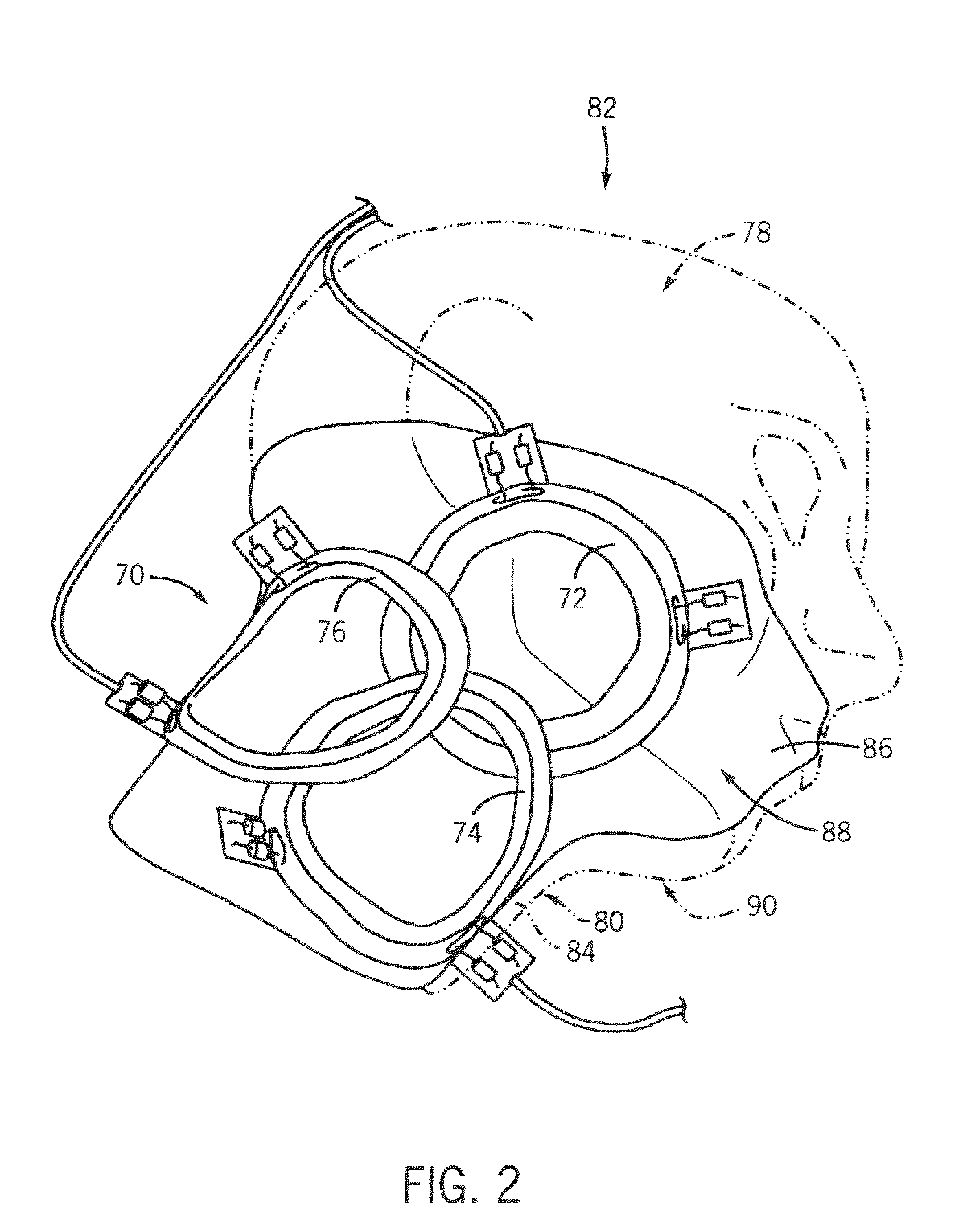
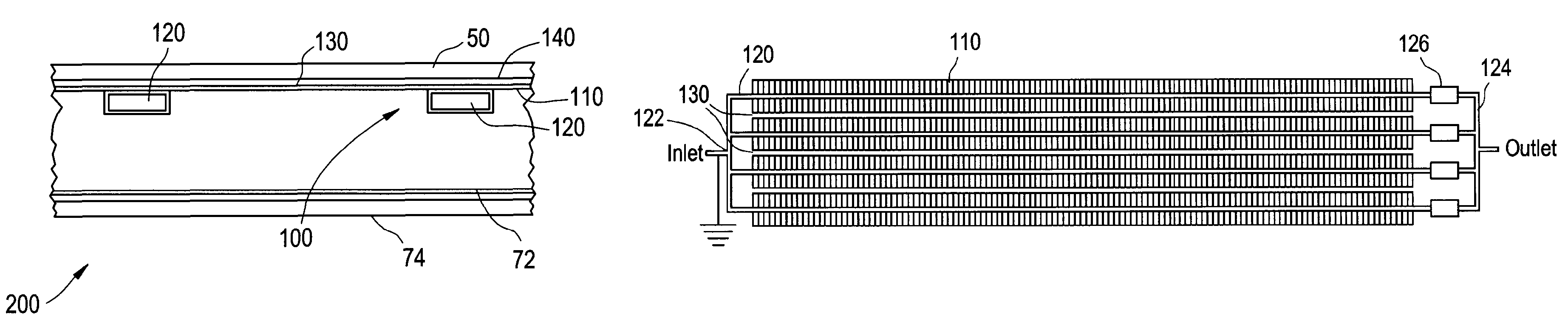
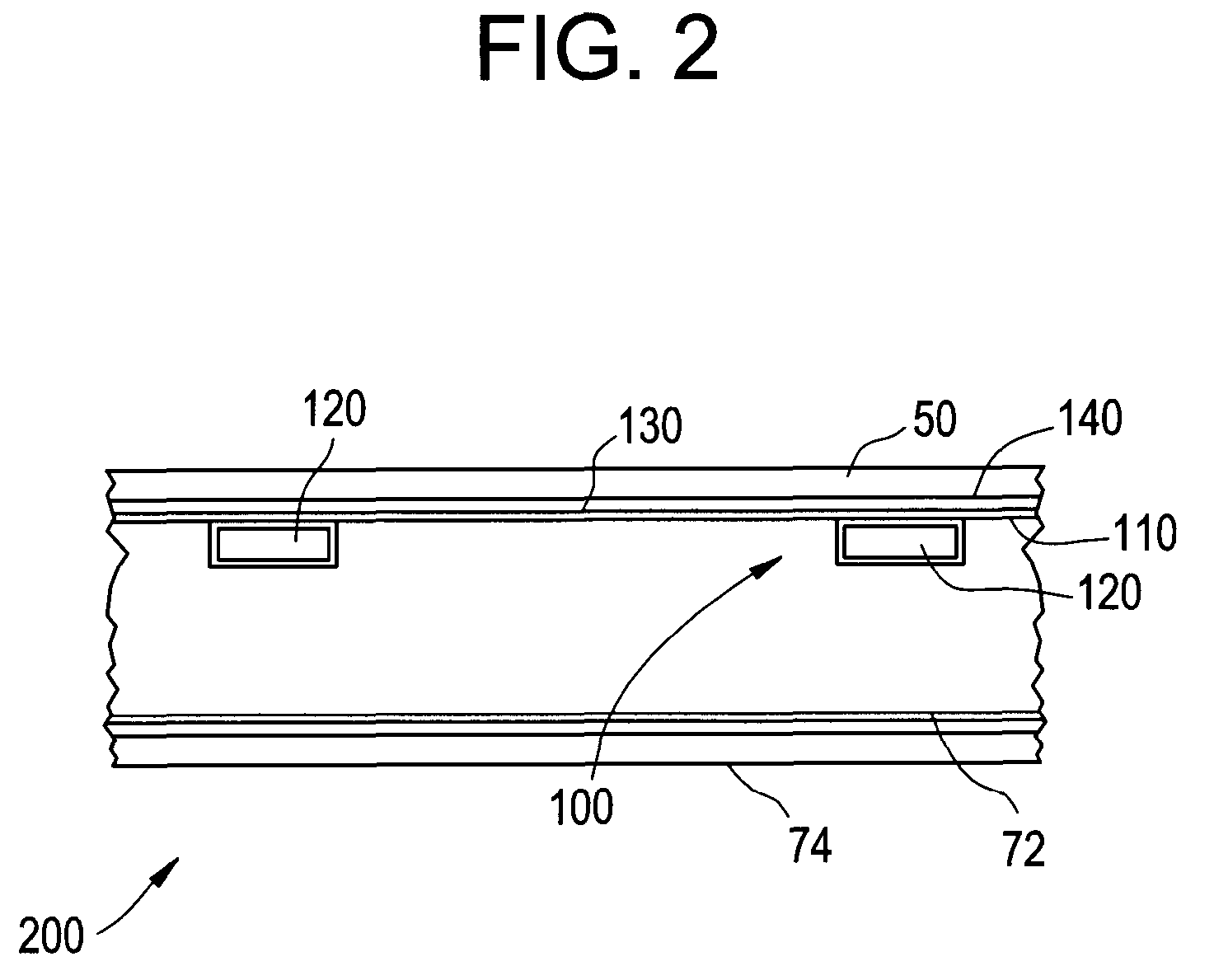
Multi-turn element RF coil array for multiple channel MRI
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
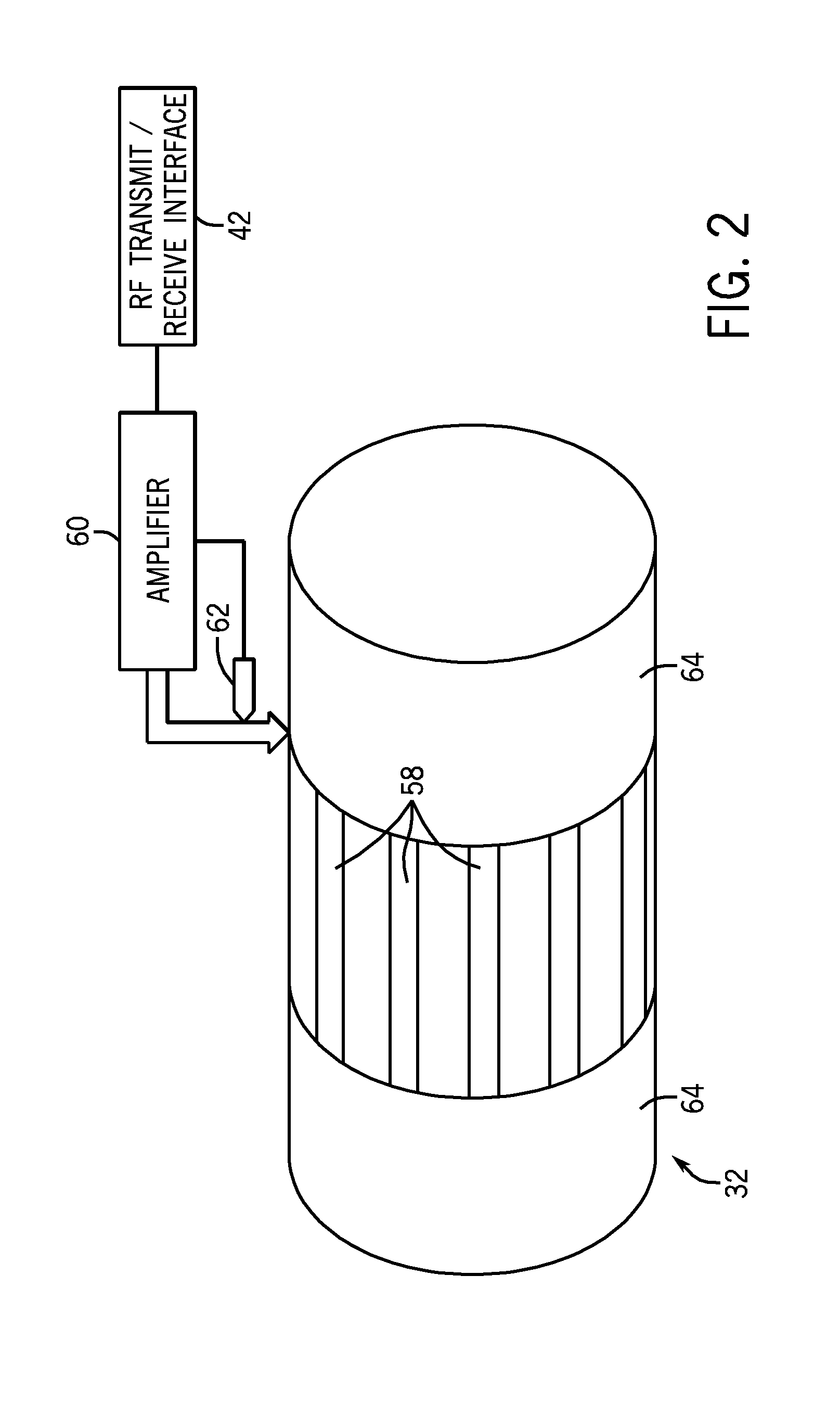
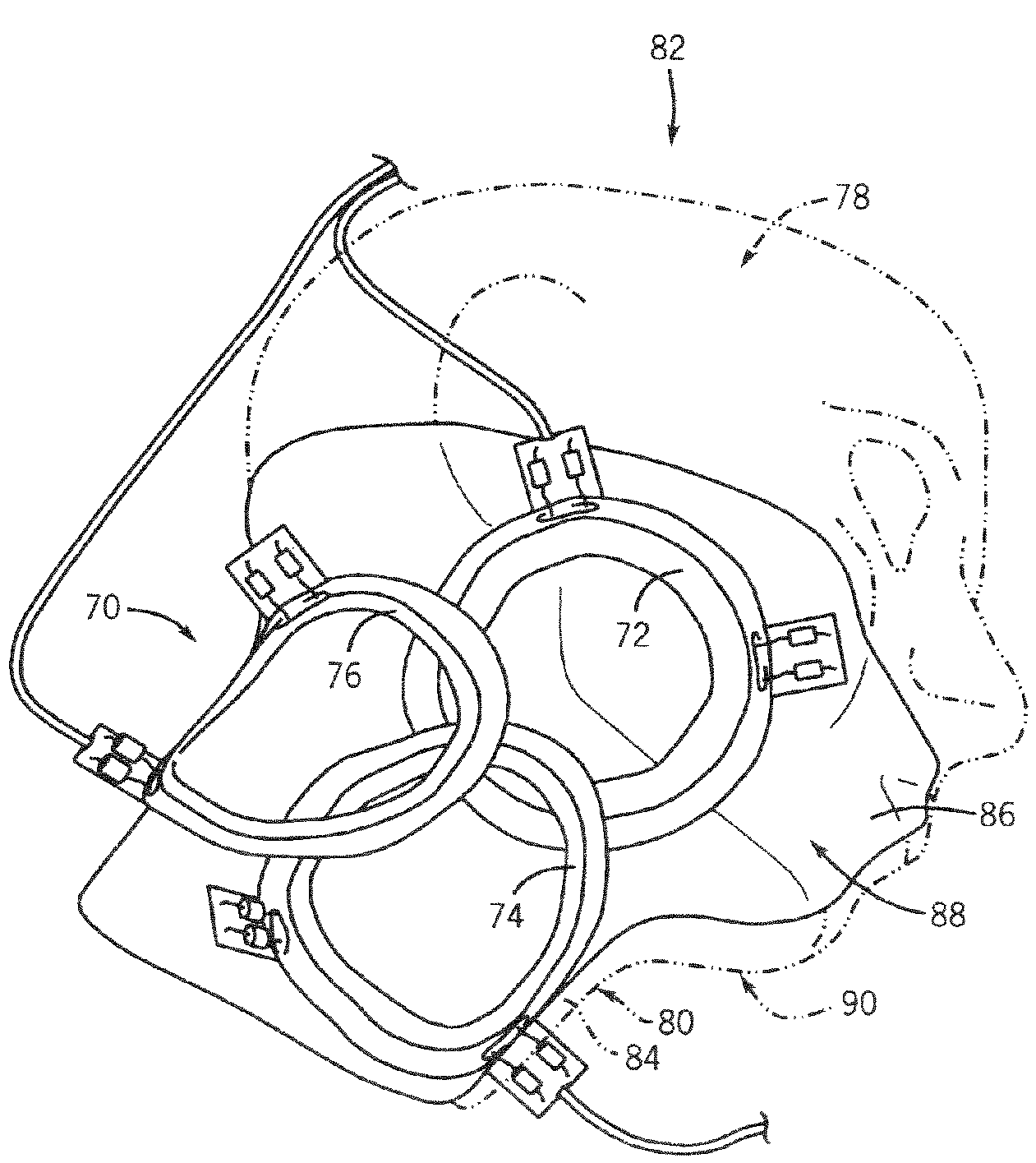
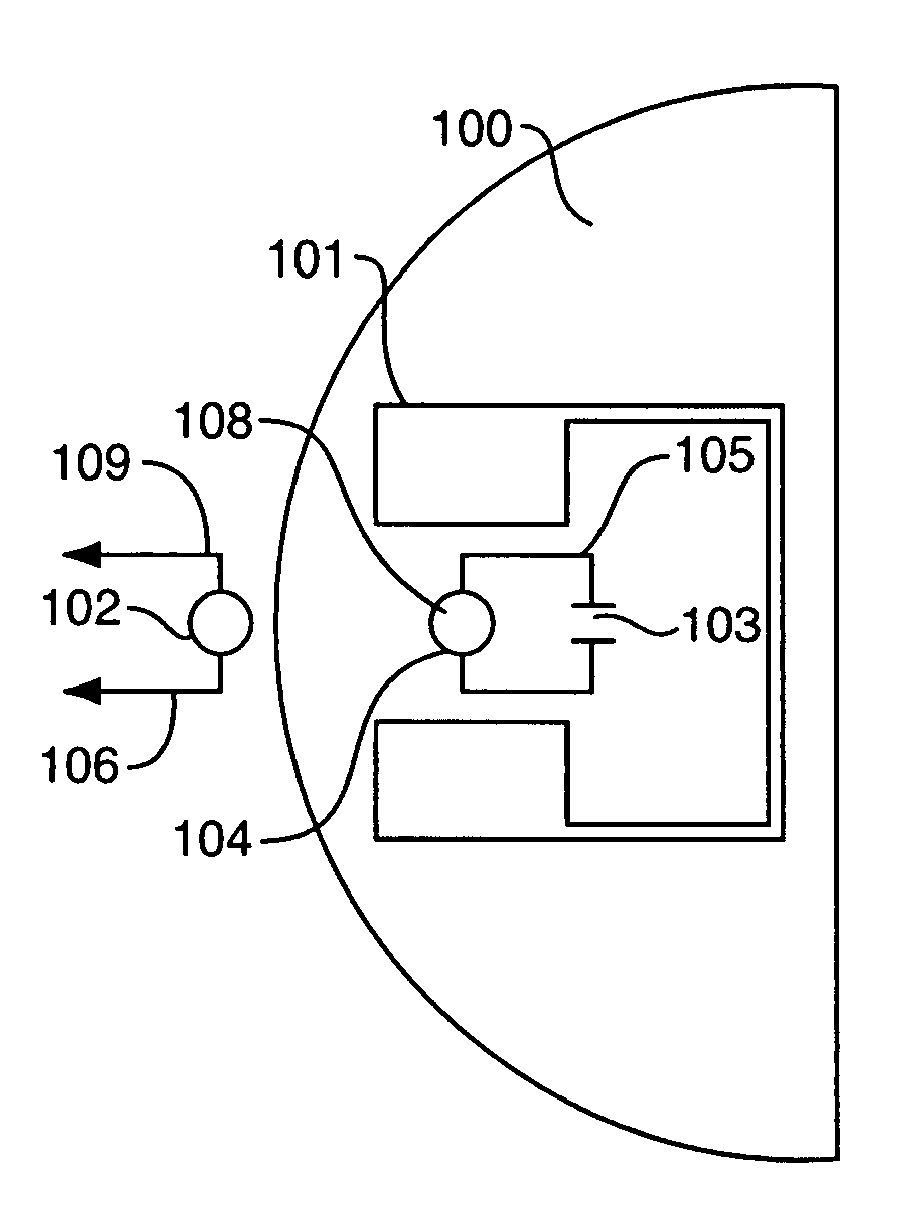
Radiofrequency coil and catheter for surface nmr imaging and spectroscopy
In one aspect, the present invention provides a cylindrical meanderline coil that can significantly improve the performance and usefulness of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) catheter radiofrequency (RF) coils by shaping the spatial dimensions of the volume of excitation and reception of signal. This can provide improved accuracy in defining the volume of excitation and reception of the subject or specimen, and increase the signal to noise ratio of a received signal. In another aspect, the invention provides an intravascular catheter having a coil at its tip for generating and / or detecting magnetic excitations. A preamplifer coupled to the catheter in proximity of the coil allows amplifying signals generated and / or detected by the coil. Although in one application, a coil and / or a catheter of the invention can be employed, for example, for MR spectroscopy or imaging of biological tissue, such as atherosclerotic plaques arterial walls in the human body, the invention provides similar advantages in any situation where a magnetic resonance or other magnetic induction signal is to be received from a thin cylindrical shell or sector of a cylindrical shell.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
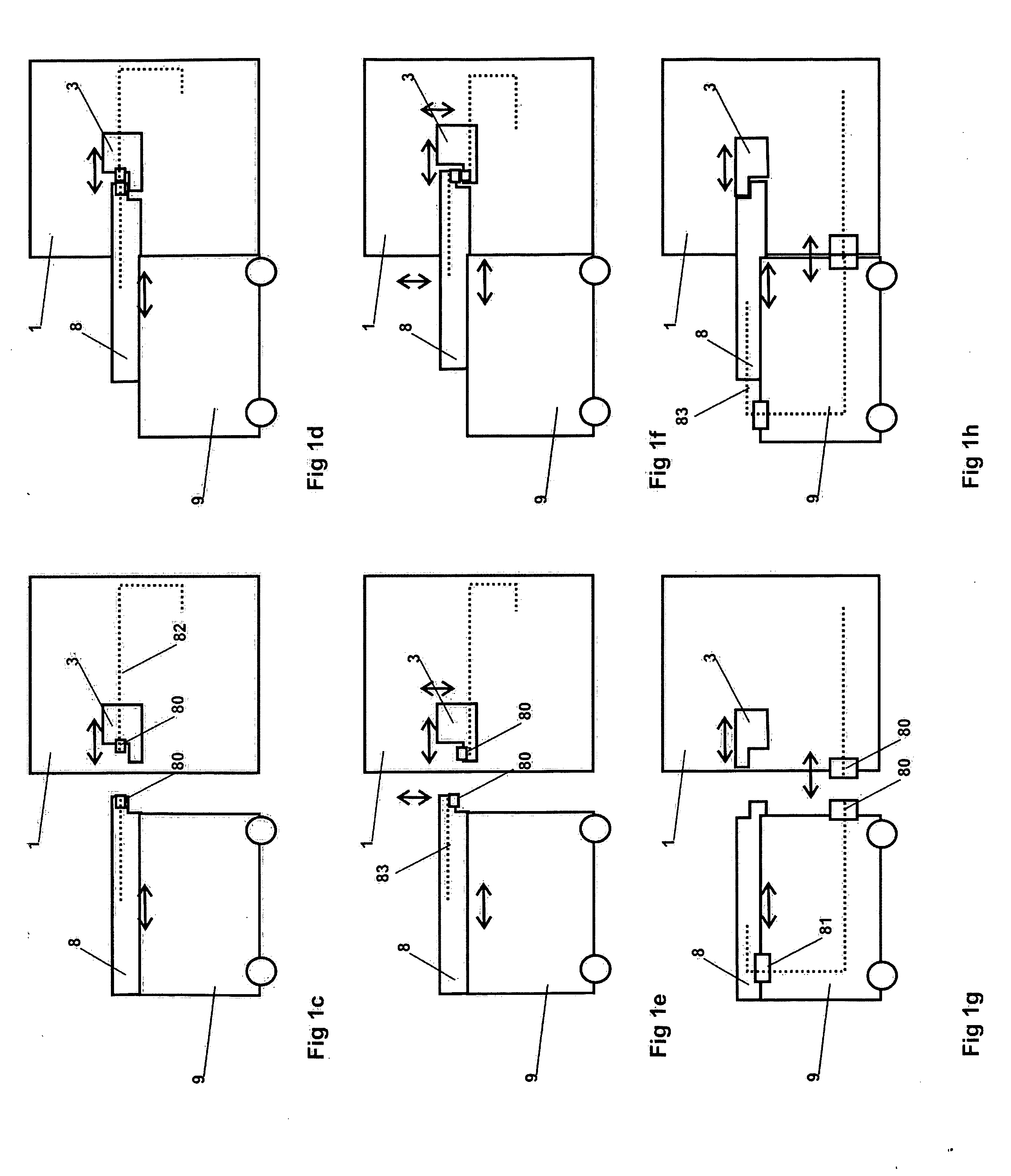
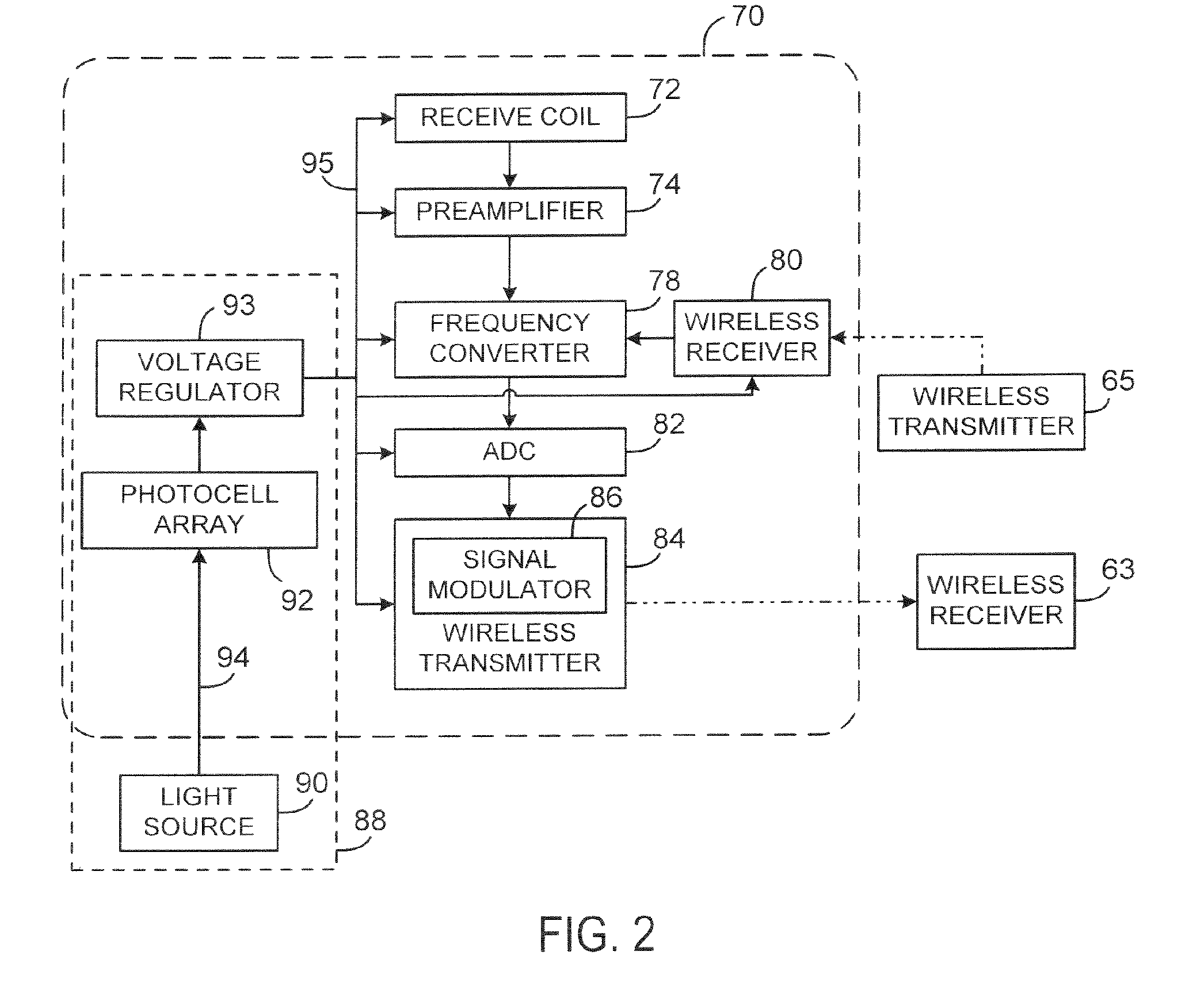
Wireless RF coil power supply
ActiveUS20060226841A1Magnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionElectrical batteryA d converter
A system wirelessly supplies electrical power to an RF coil and an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) for an MRI system. The system supplies power to at least operate the RF coil and ADC without the use of a battery and without use of a wired connection external to the bore of the magnet.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Using s-parameter measurements to manage SAR and transmit gain
ActiveUS20100244840A1Electric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceAudio power amplifierEngineering
Systems and methods for controlling a magnetic resonance imaging system are provided. In one embodiment, a magnetic resonance imaging system includes a radio frequency coil with a plurality of conductive coil elements, control circuitry that determines, based at least in part on a measurement of scattering parameters, a plurality of forward voltages that will cause power deposition into an object within a predetermined specific absorption rate, and an amplifier configured to apply the determined plurality of forward voltages respectively to the plurality of coil elements. The control circuitry may determine the plurality of forward voltages based at least in part on an unloaded measurement of scattering parameters and a loaded measurement of scattering parameters.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
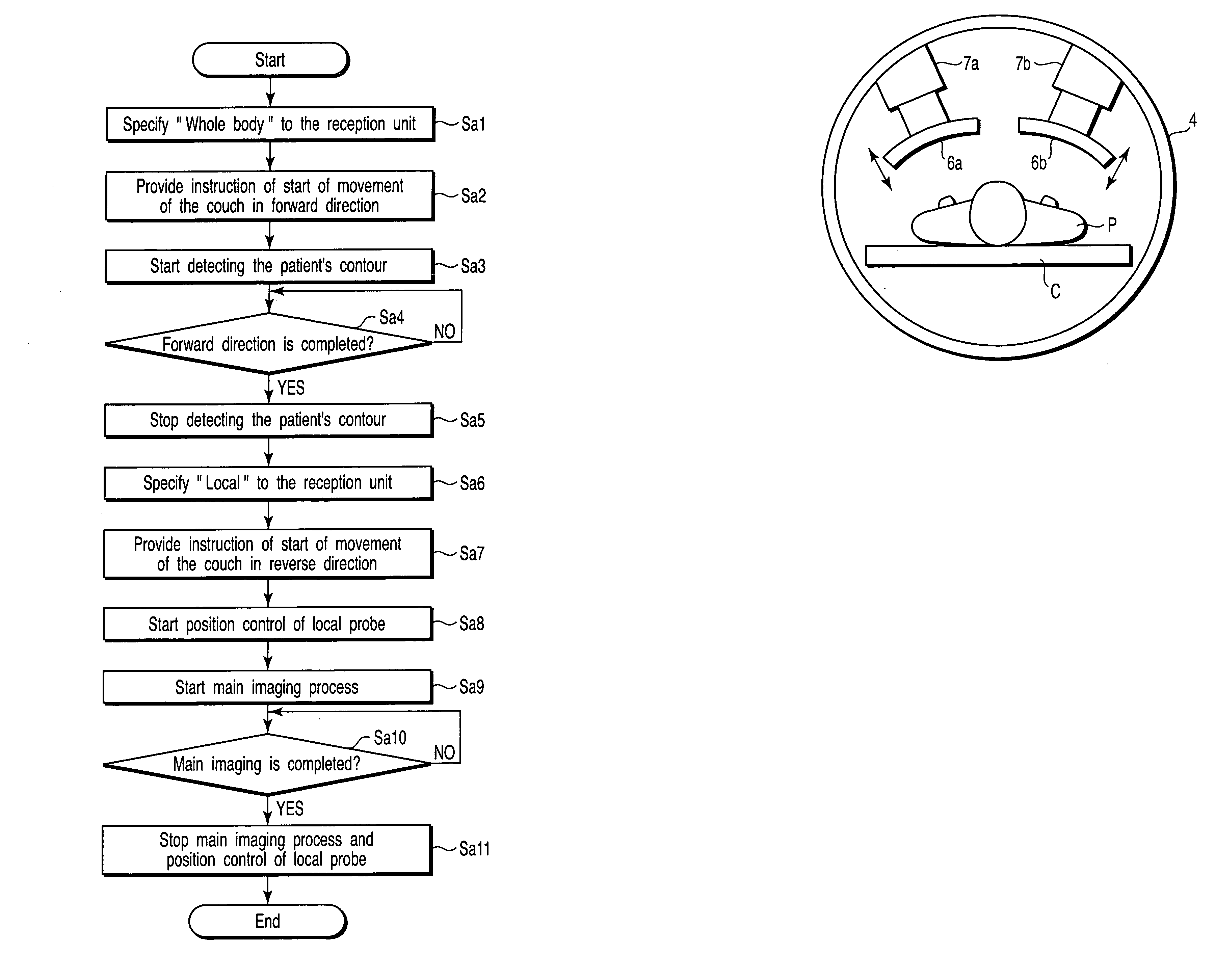
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and image generation method therein
ActiveUS20050122108A1Quality improvementMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionRadio frequencyRadiofrequency coil
A magnetic resonance imaging apparatus of the invention comprises a static magnetic field generation unit which generates a static magnetic field in a gantry, a gradient magnetic field generation unit which applies a gradient magnetic field to a object in the static magnetic field, a radio frequency coil which receives a magnetic resonance signal from the object to which the gradient magnetic field is applied, a contour detection unit which detects a contour of the object, a coil movement unit which moves the radio frequency coil on the basis of the detected contour while the radio frequency coil is placed near and far relative to the object, and an image generation unit which generates a magnetic resonance image on the basis of the received magnetic resonance signal.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
6-channel array coil for magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS7382132B1Easy to detectHigh resolutionMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionCoil arrayHigh resolution image
A method and apparatus for acquiring high resolution MR images of a carotid artery. A six-channel RF coil array has three RF coils placed in an overlapping pattern and positioned adjacent to a first region-of-interest (ROI) of an imaging patient. The six-channel RF coil also has three RF coils placed in an overlapping pattern and positioned adjacent to a second ROI of an imaging patient.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO +1
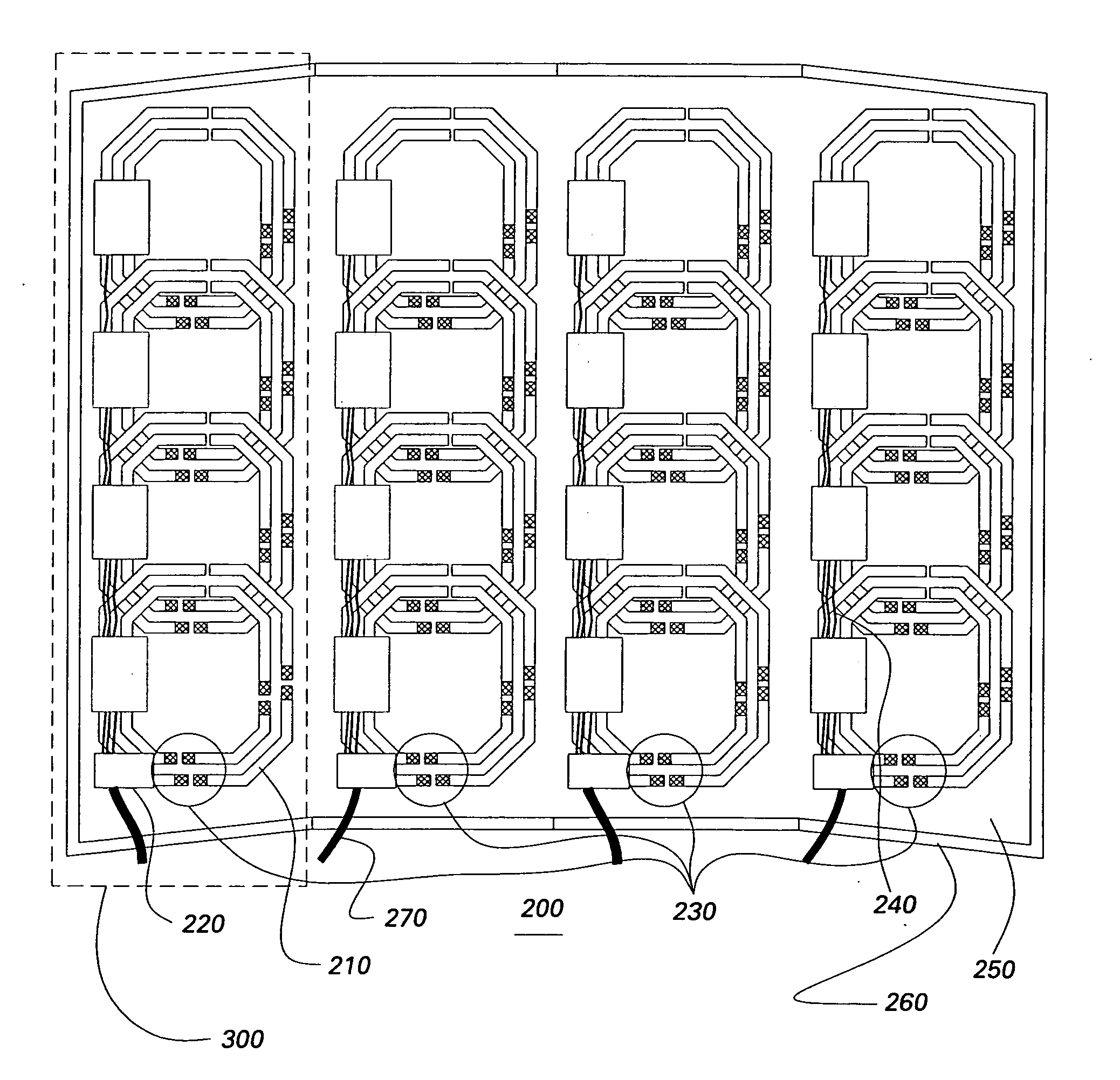
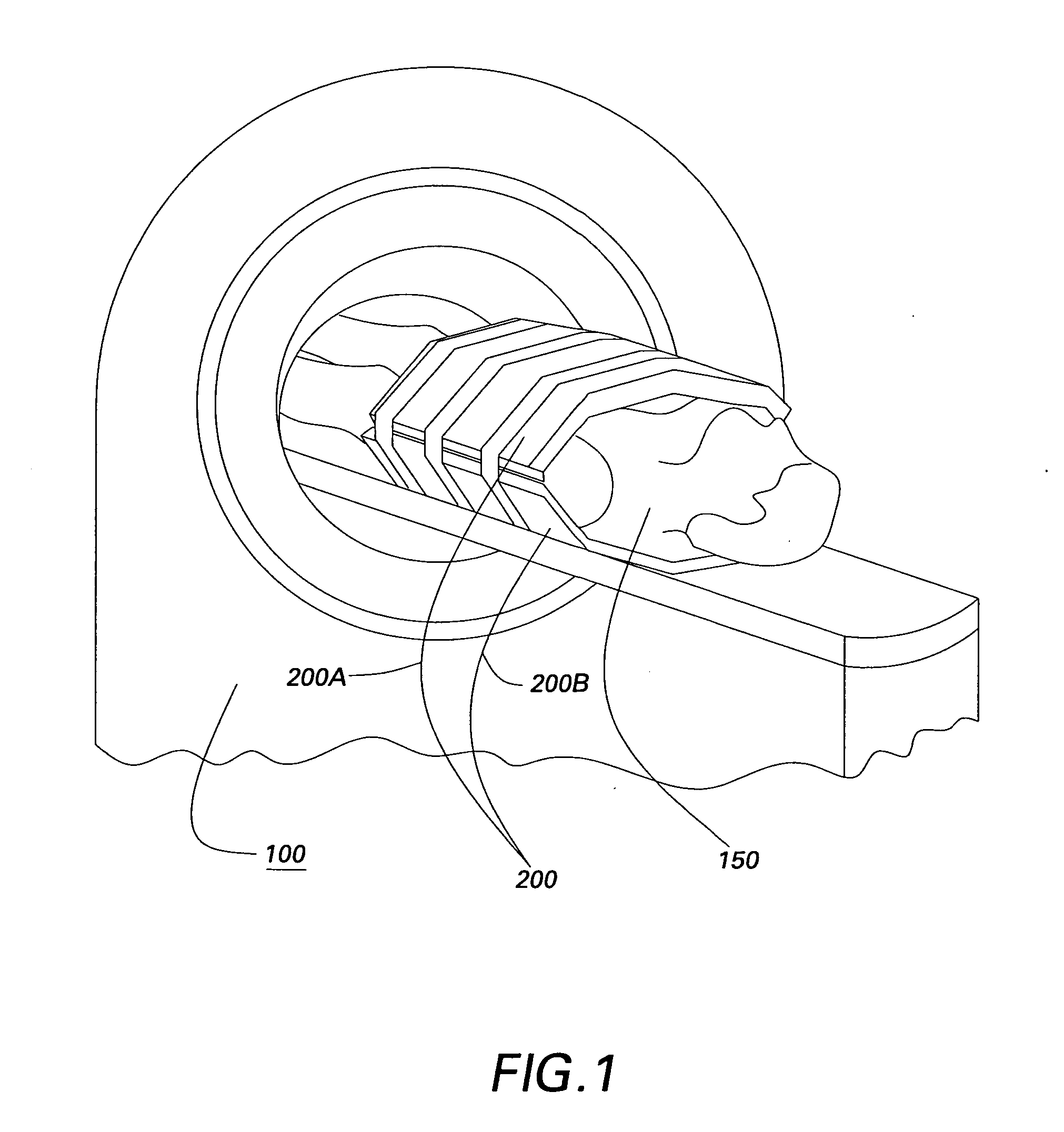
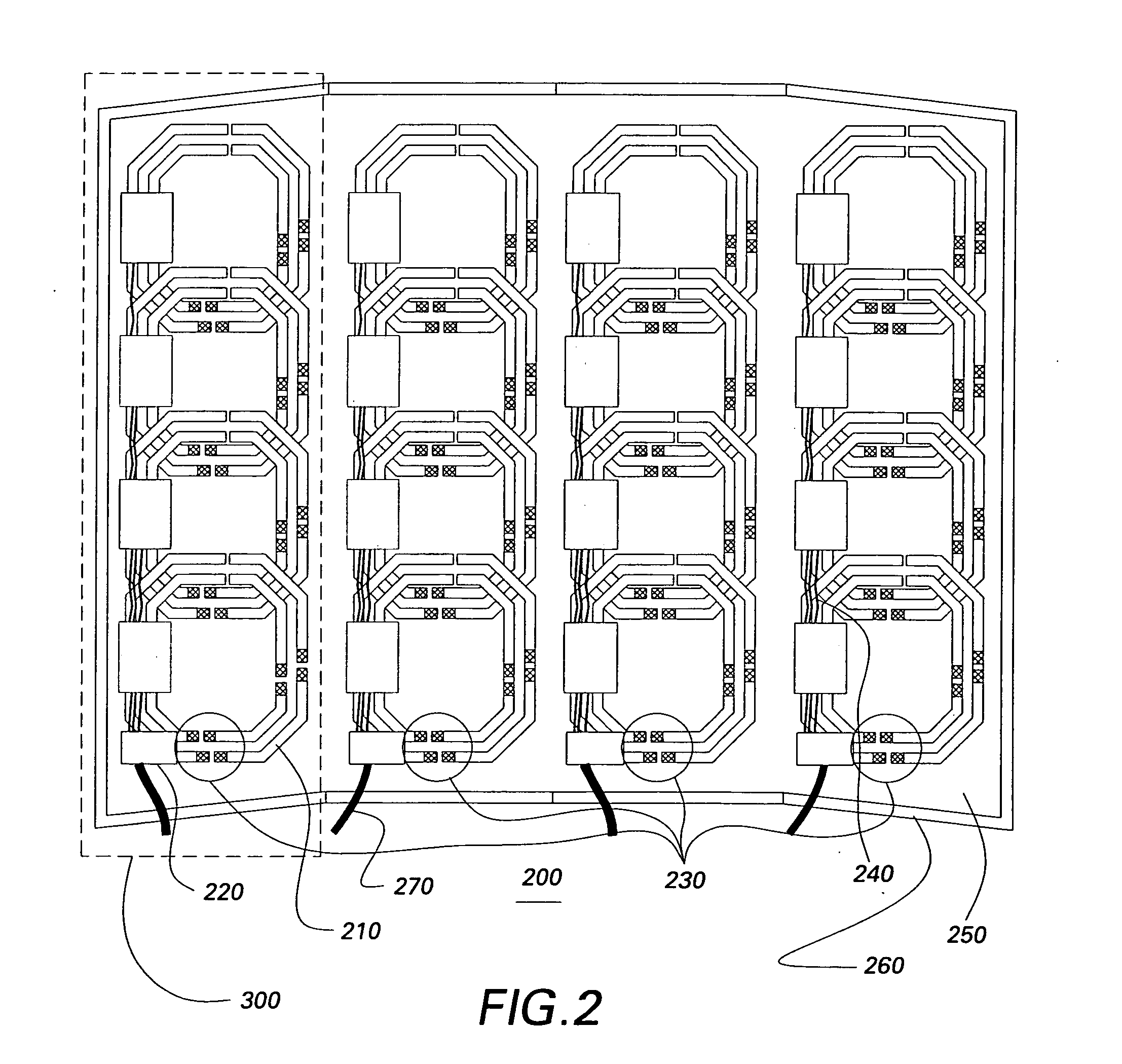
Multi-turn element RF coil array for multiple channel MRI
InactiveUS20050253582A1High QHigh load rateDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsCoil arraySurface coil
An RF coil assembly for use in a multiple receive-channel MRI system is provided. The RF coil assembly is configured as a multi-turn-element RF coil assembly 200 to operate as a surface-coil array in cooperation with the MRI system 100 which is configured to operate in a multiple-channel receive mode.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Gradient bore cooling providing RF shield in an MRI system
InactiveUS7397244B2Electric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceVolumetric imagingRadio frequency
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) device for imaging a volume includes a main magnet for generating a magnetic field, an insulator sheet formed into a tube extending along an axis, a gradient coil disposed on an outside surface defining the tube for manipulating the magnetic field generated by the main magnet to image the volume, and a cooling circuit disposed between the gradient coil and a RF coil. The cooling circuit is disposed on an opposite inside surface defining the tube, wherein the cooling circuit shields the gradient coil from the RF coil while cooling the gradient coil.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
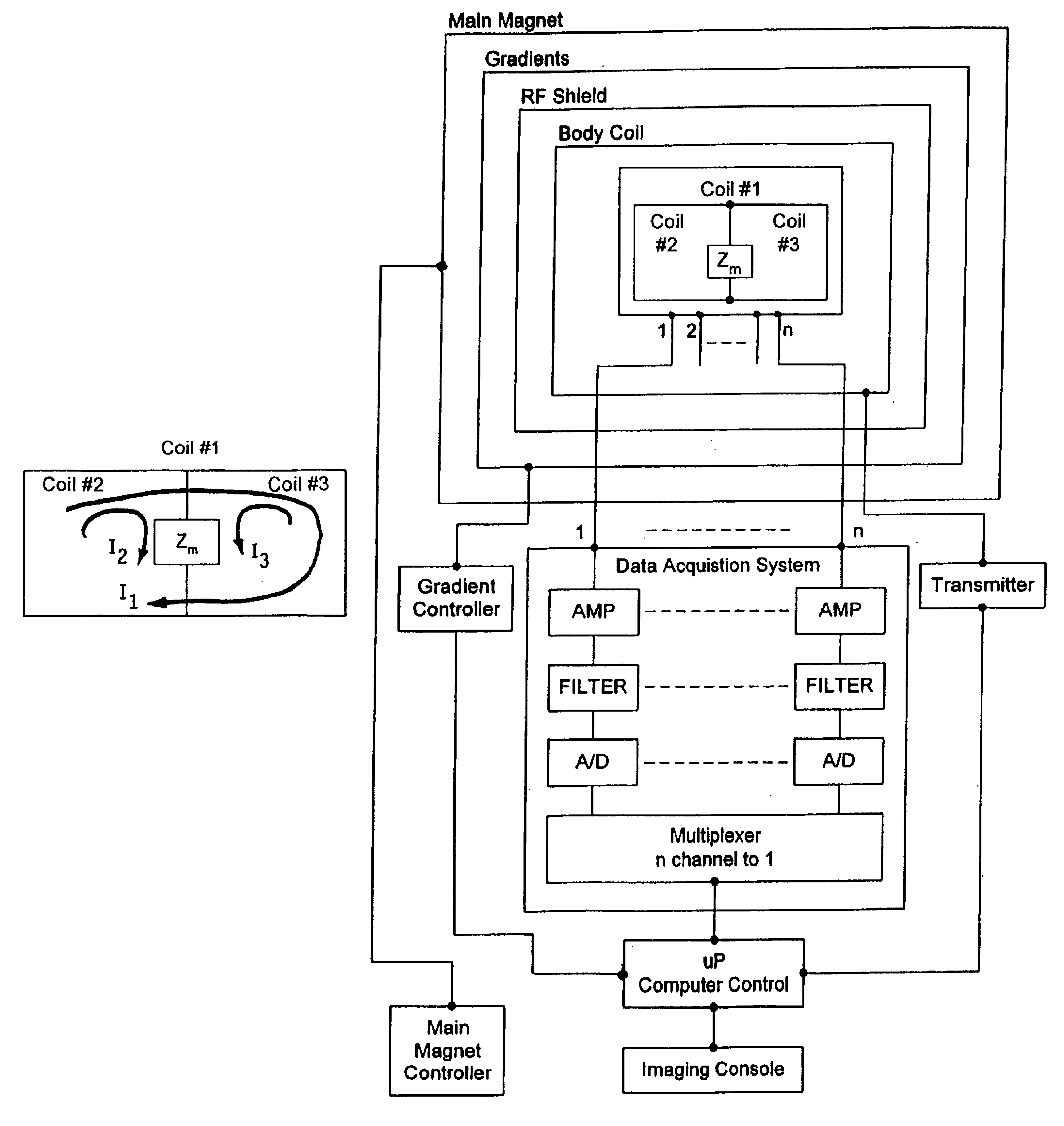
Radio-frequency coil array for resonance imaging analysis
InactiveUS6850064B1Improve signal-to-noise ratioHigh resolutionElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceCoil arrayImaging analysis
An RF coil array is provided with increased S / N over the entire imaging FOV. The array design includes a first RF coil spanning the entire FOV, second and third RF coils which together span the entire FOV such that the entire system provides improved S / N over the imaging FOV. An aspect of the invention is the unusual combination of coils in one integrated structure, that are well isolated from one another and maintain preferred current distributions and mode orientations.
Owner:ADVANCED IMAGING
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20080015430A1Avoid performancePrecise positioningMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringStatic fieldMovement control
A magnetic resonance imaging apparatus has a static field magnet, gradient coils, a gantry including an opening and storing the static field magnet the gradient coils, a bed structure for advancing and retreating a table-top, on which an object can be placed, with respect to the opening, a lower coil formed by a radio frequency coil disposed below the table-top, and a movement control unit configured to control the lower coil to be movable.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
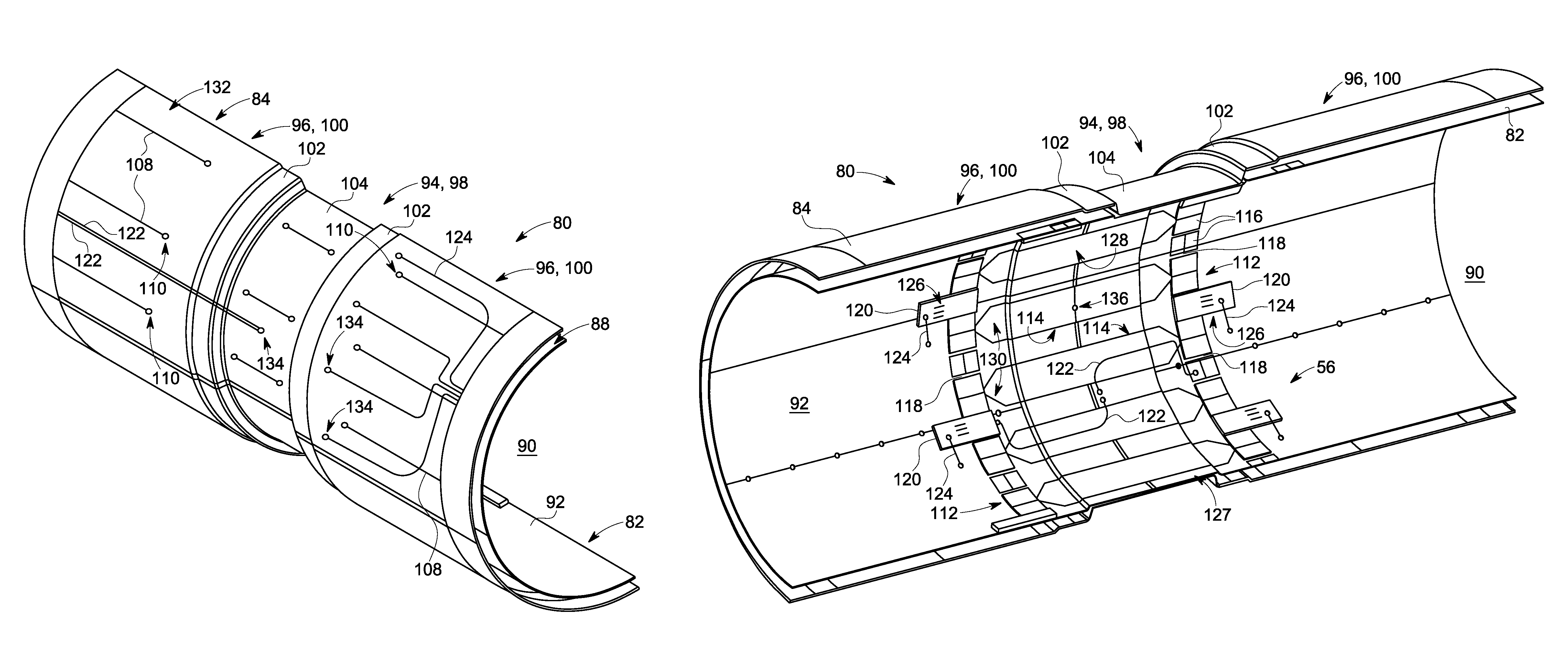
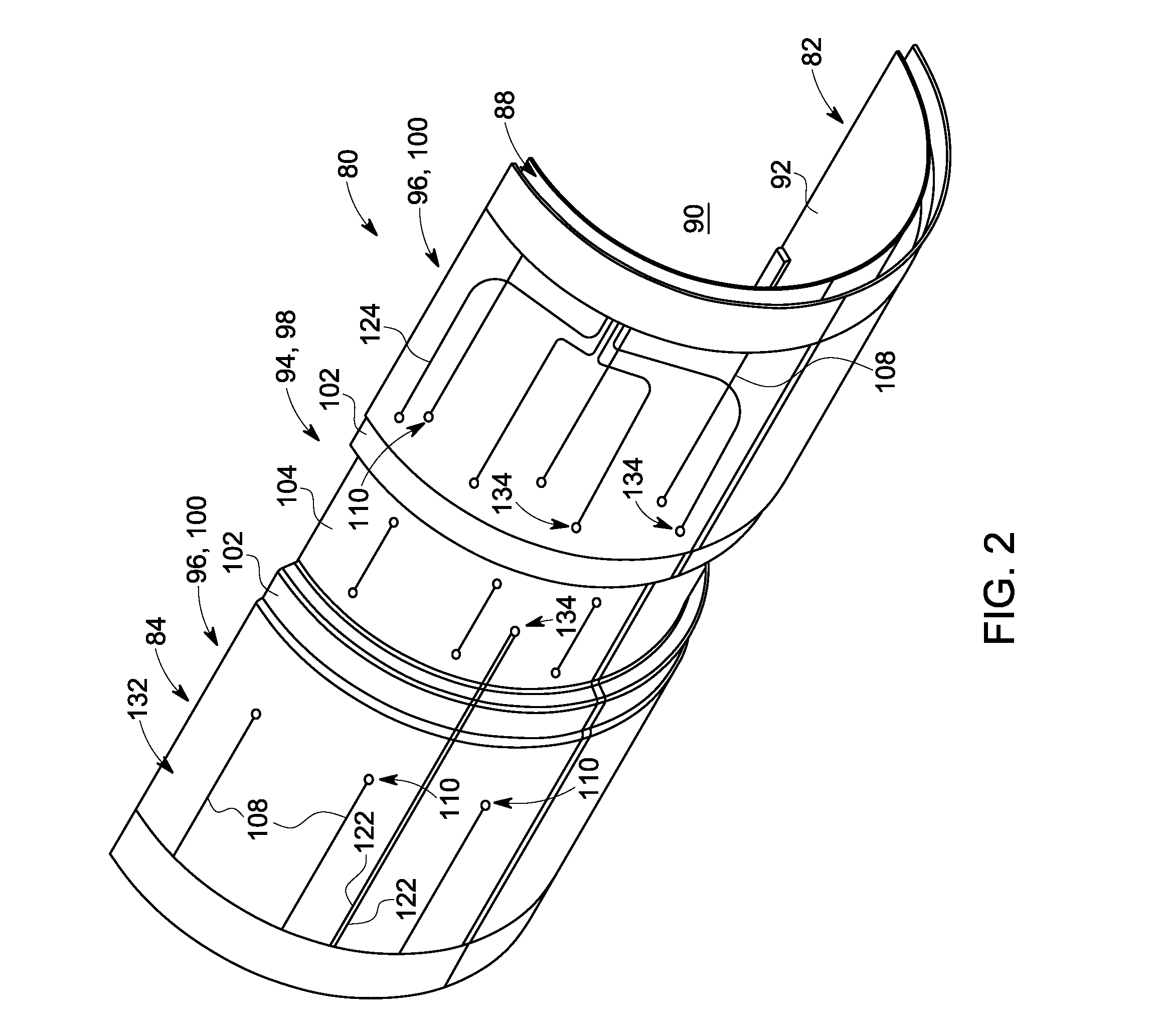
Structured RF coil assembly for MRI scanner
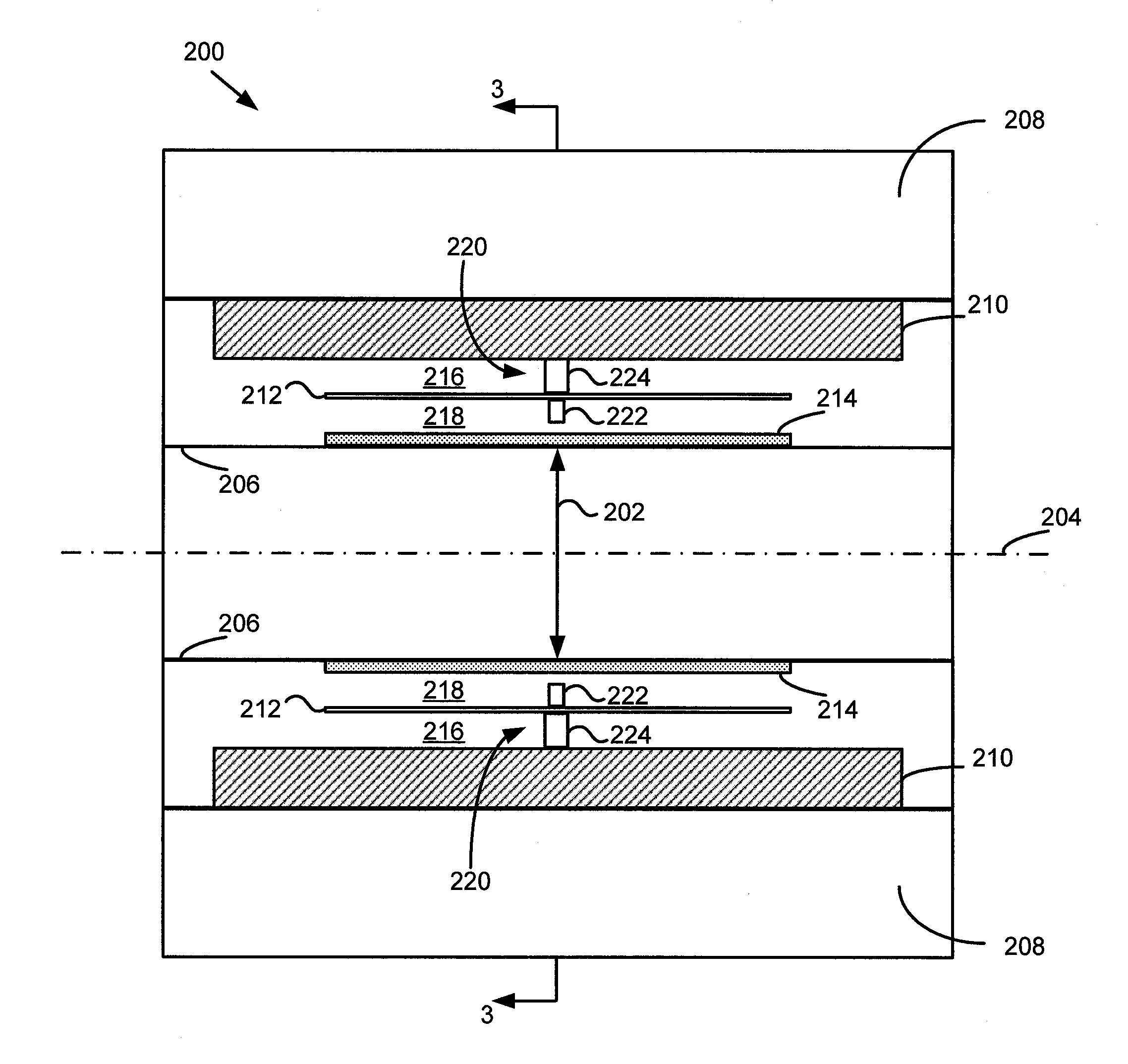
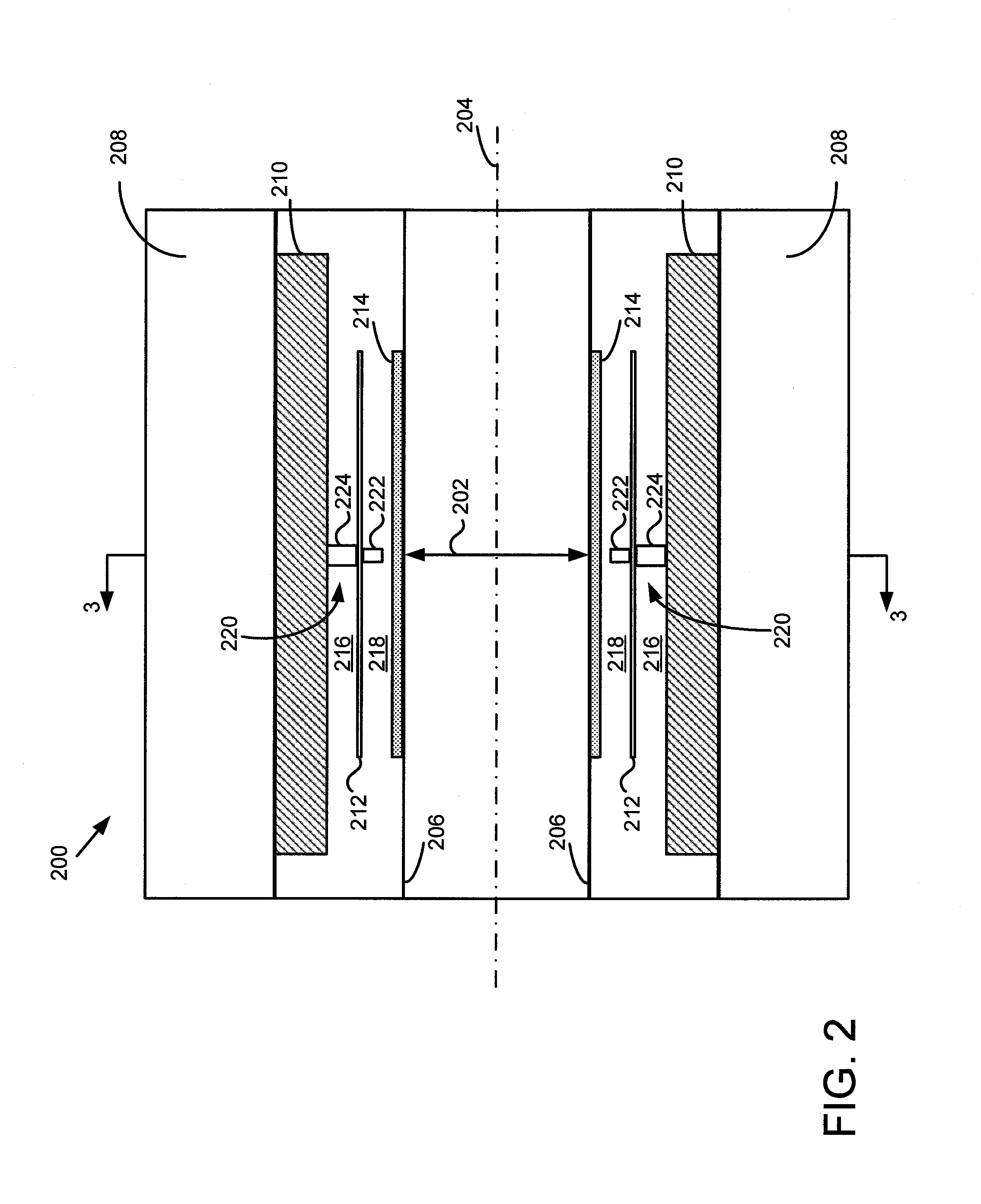
An imaging apparatus that incorporates an RF coil assembly and RF shield as part of a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system is disclosed. The imaging apparatus includes an MRI system having a plurality of gradient coils, an RF coil former having inner and outer surfaces, an RF shield positioned on the outer surface of the RF coil former so as to be formed about the RF coil former, and an RF coil positioned on the inner surface of the RF coil former, with the RF coil coupled to a pulse generator to emit an RF pulse sequence and receive resulting MR signals from a subject of interest. The RF coil former comprises a generally cylindrical member having an indented portion indented in a radial direction inwardly from the outer surface, with the RF shield conforming to the RF coil former so as to also have an indented portion.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
RF coil system for magnetic resonance image forming device
InactiveCN1420363AFast imagingNo loss of image qualityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsImaging qualityComputer-aided
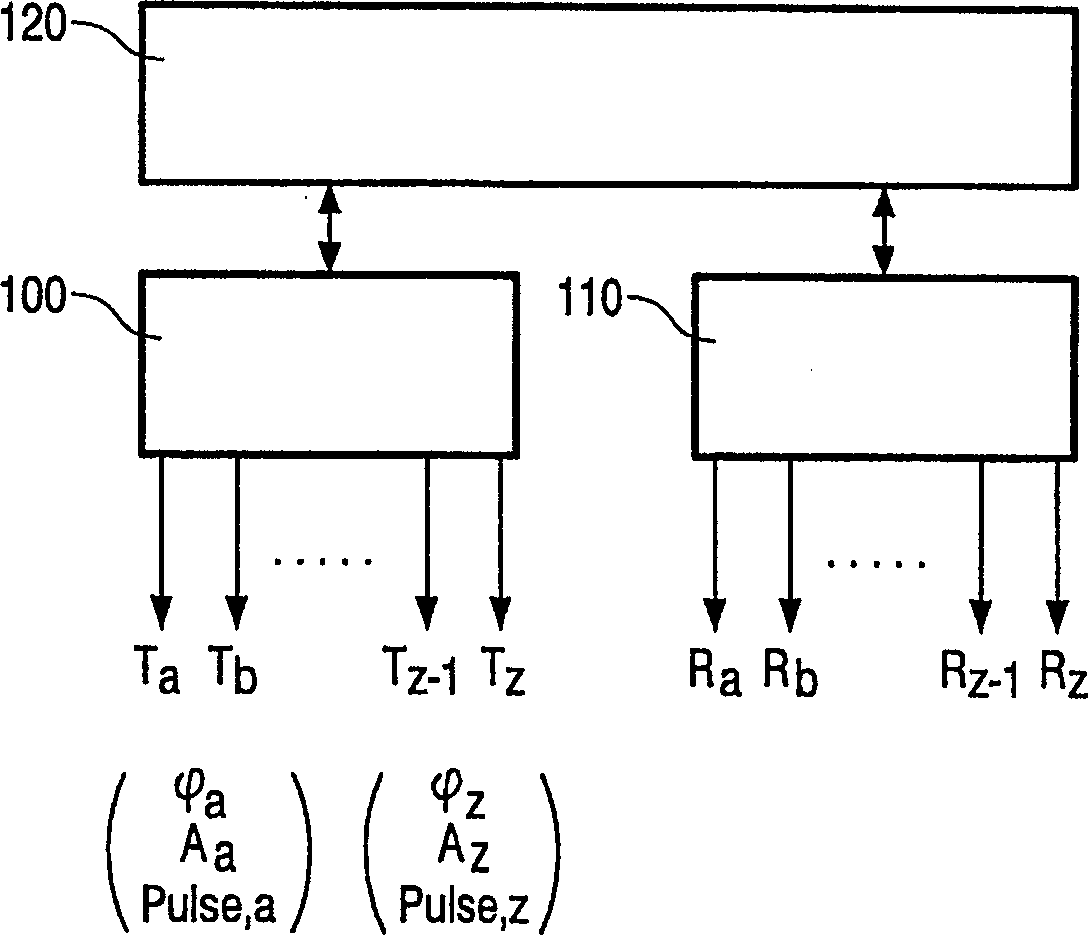
An RF coil system for a magnetic resonance imaging apparatus whereby a substantially computer-aided and hence automatically optimized image quality in respect of signal-to-noise ratio and resolution can be achieved in dependence on the type and size of the object to be imaged, without time-consuming replacement or manual positioning of the RF coil system being necessary. To this end, the coil system (A) includes a plurality of single RF coils (Sx) which are essentially decoupled from one another and have a different size and / or different position, as well as a control device with a plurality of transmission units which are associated with a respective RF coil and whereby one or more RF coils can be selected and supplied with an RF pulse having an independently adjustable amplitude and / or phase and / or pulse shape. The invention also relates to a magnetic resonance imaging apparatus provided with such an RF coil system.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
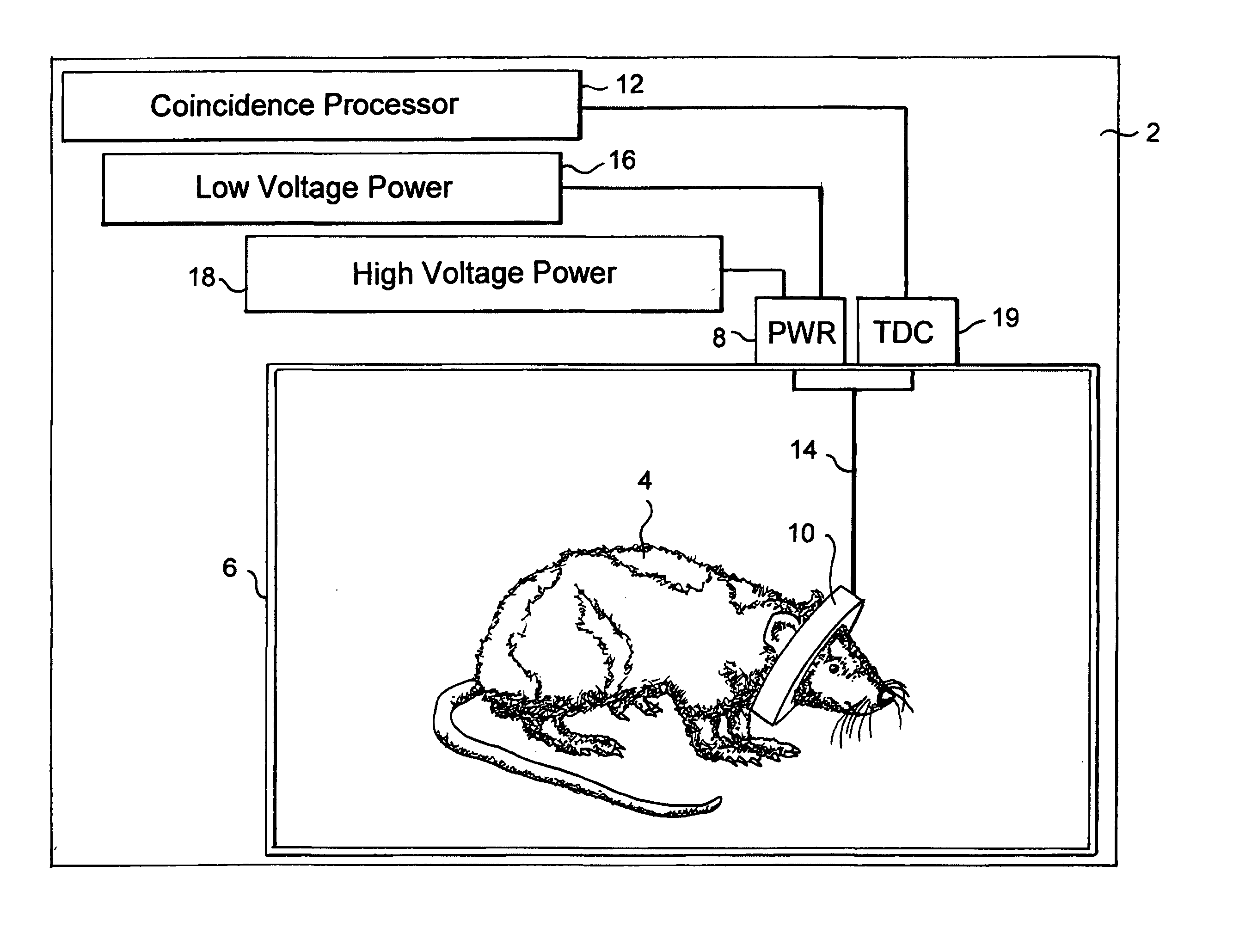
Magnetic resonance system with implantable components and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20120223705A1Diagnostic recording/measuringAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceResonance measurementProton magnetic resonance
Nuclear magnetic resonance systems and methods of use thereof are provided. The systems employ implantable radiofrequency coils (105) and optionally implantable magnets (101). The systems can employ weak permanent magnets and / or permanent magnets that provide magnetic fields that are much less homogeneous than in conventional systems. This allows, for example, for inexpensive and simple probeheads for nuclear magnetic resonance relaxometry with suitable biosensors. The methods of the present invention allow in-vivo magnetic resonance measurements and, in particular, monitoring of analytes and determination of medical diagnostic information, for example, based on determined magnetic resonance parameters.
Owner:T2 BIOSYST
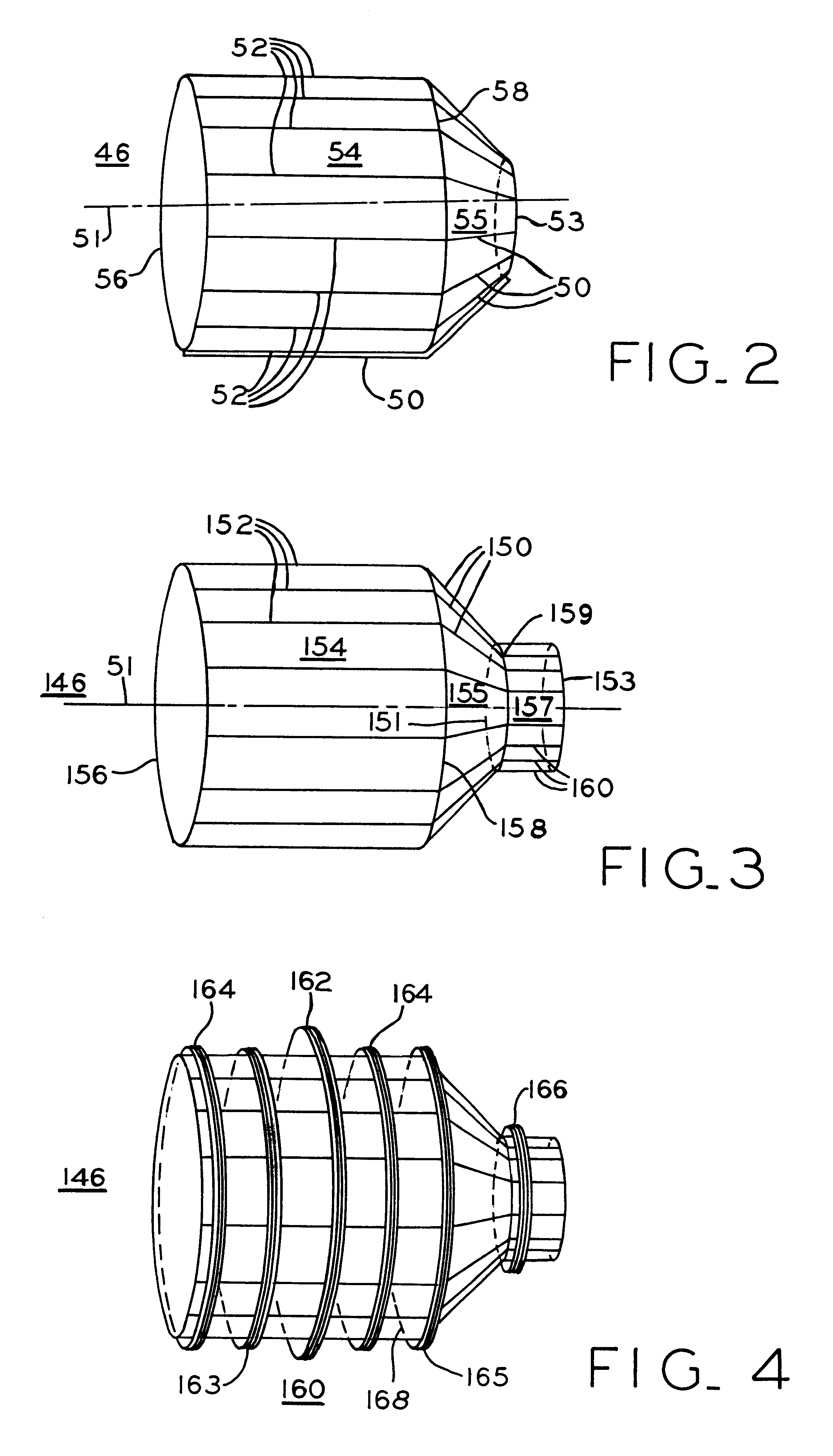
Magnetic resonance imaging head coil
InactiveUS6313633B1Improve homogeneityImprove image qualityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsElectrical conductorHomogeneous magnetic field
A short radio frequency coil for magnetic resonance imaging of the head to provide a homogeneous magnetic field including parallel conductors forming a first cylindrical portion with end rings supporting the conductors which then continue at an angle to form the frustum of a cone and further continuing to form a reduced diameter second cylindrical portion. A third conductive end ring of reduced diameter positioned at the open end of the second cylindrical portion supports the end of the conductors and provides a reduced diameter opening. An asymmetrical coil surrounds portions of the radio frequency coil including the first cylindrical and frustum of a cone portions.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com