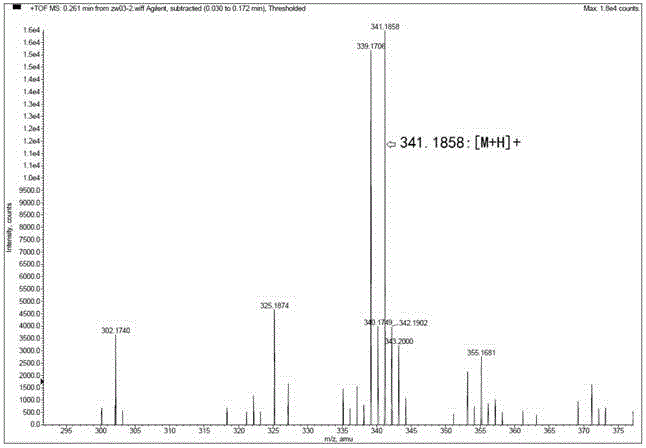
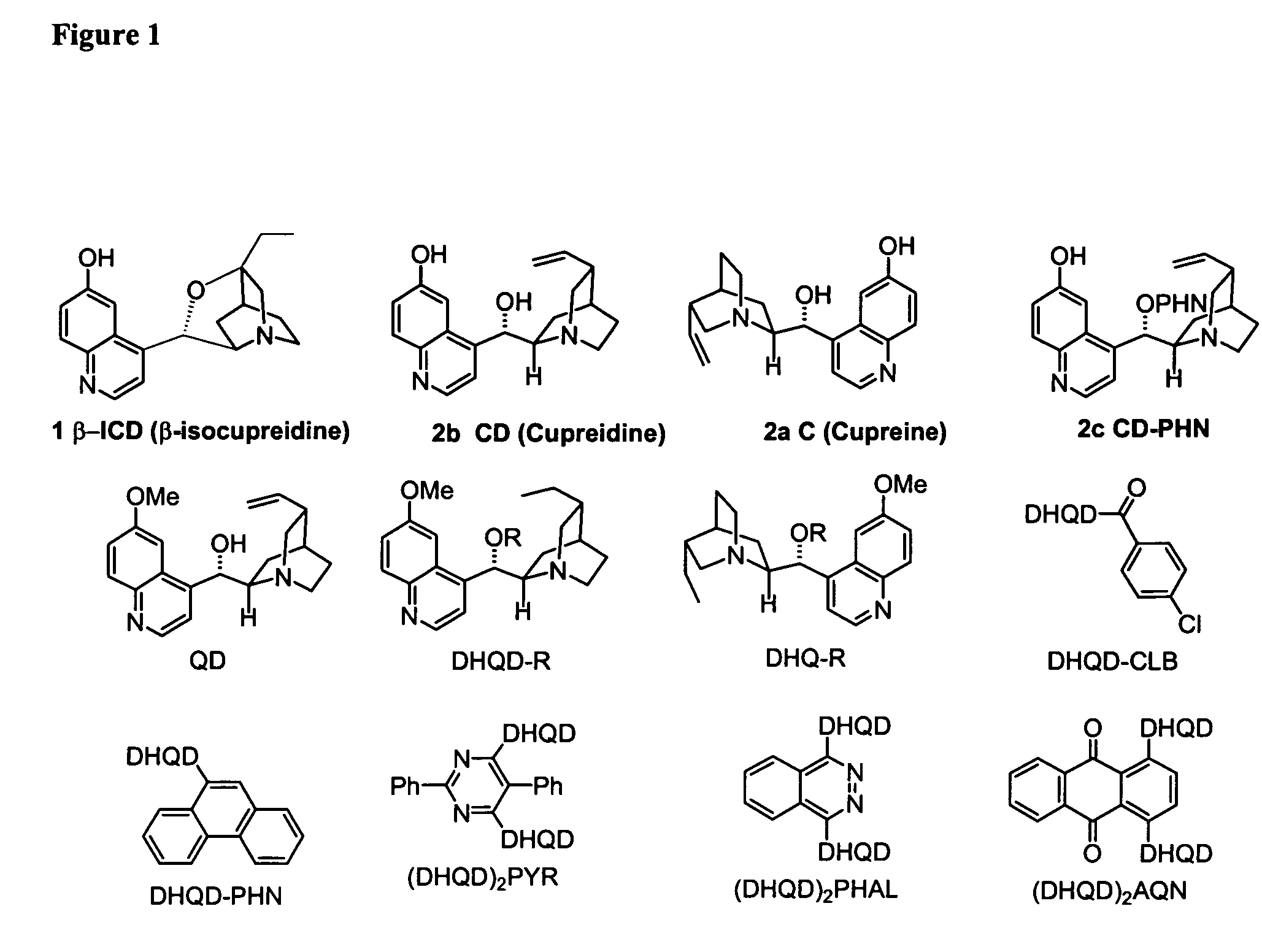
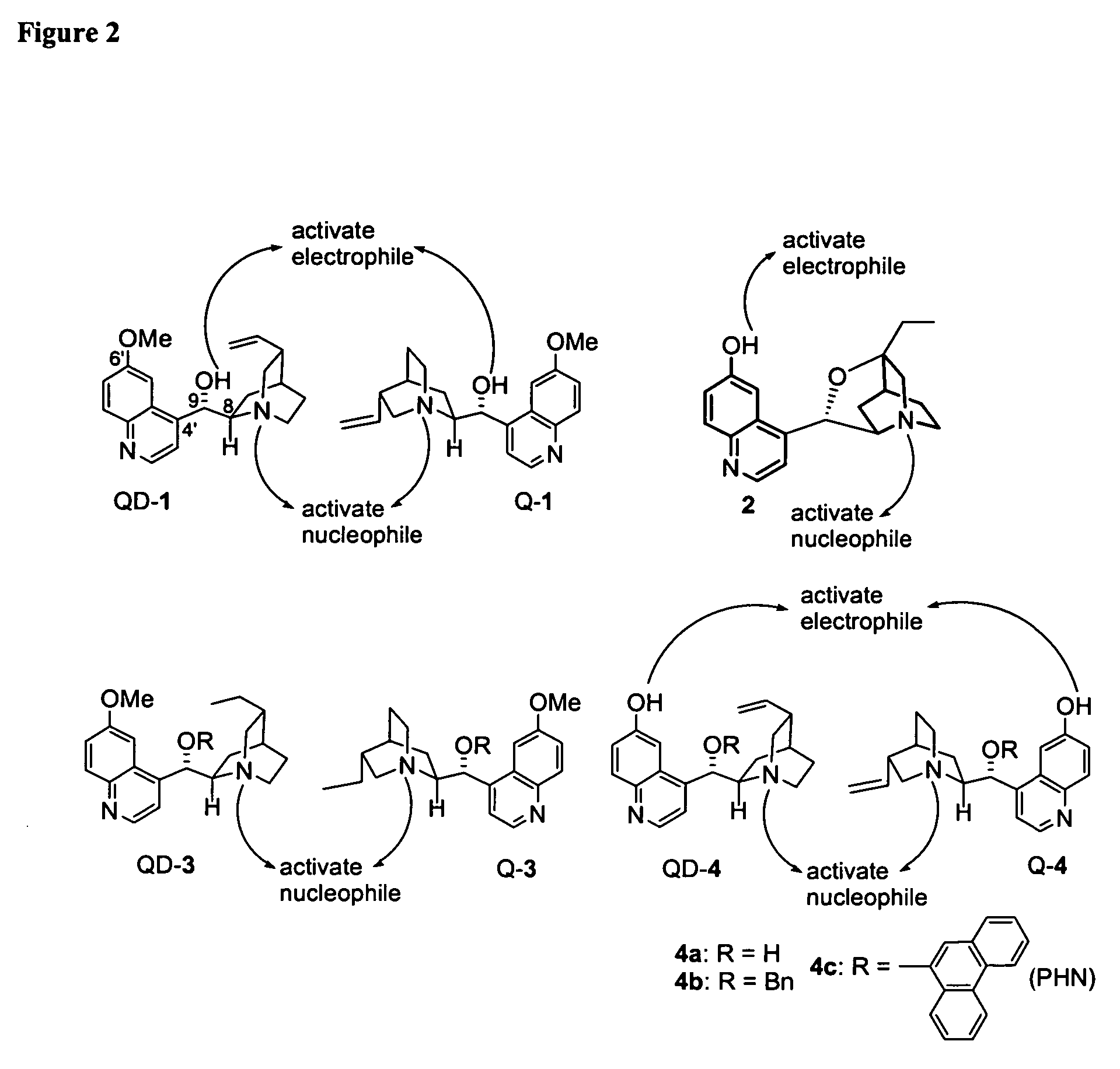
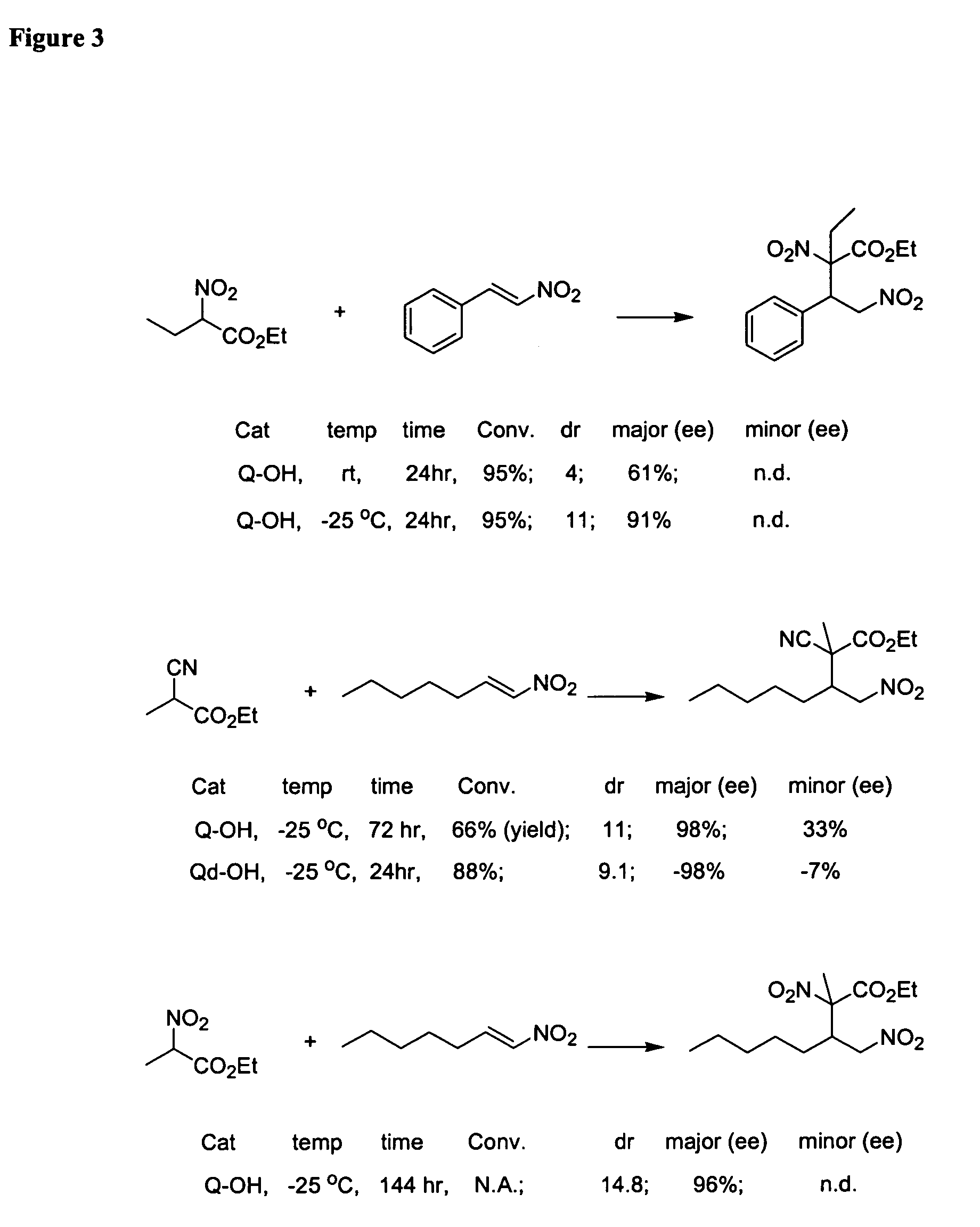
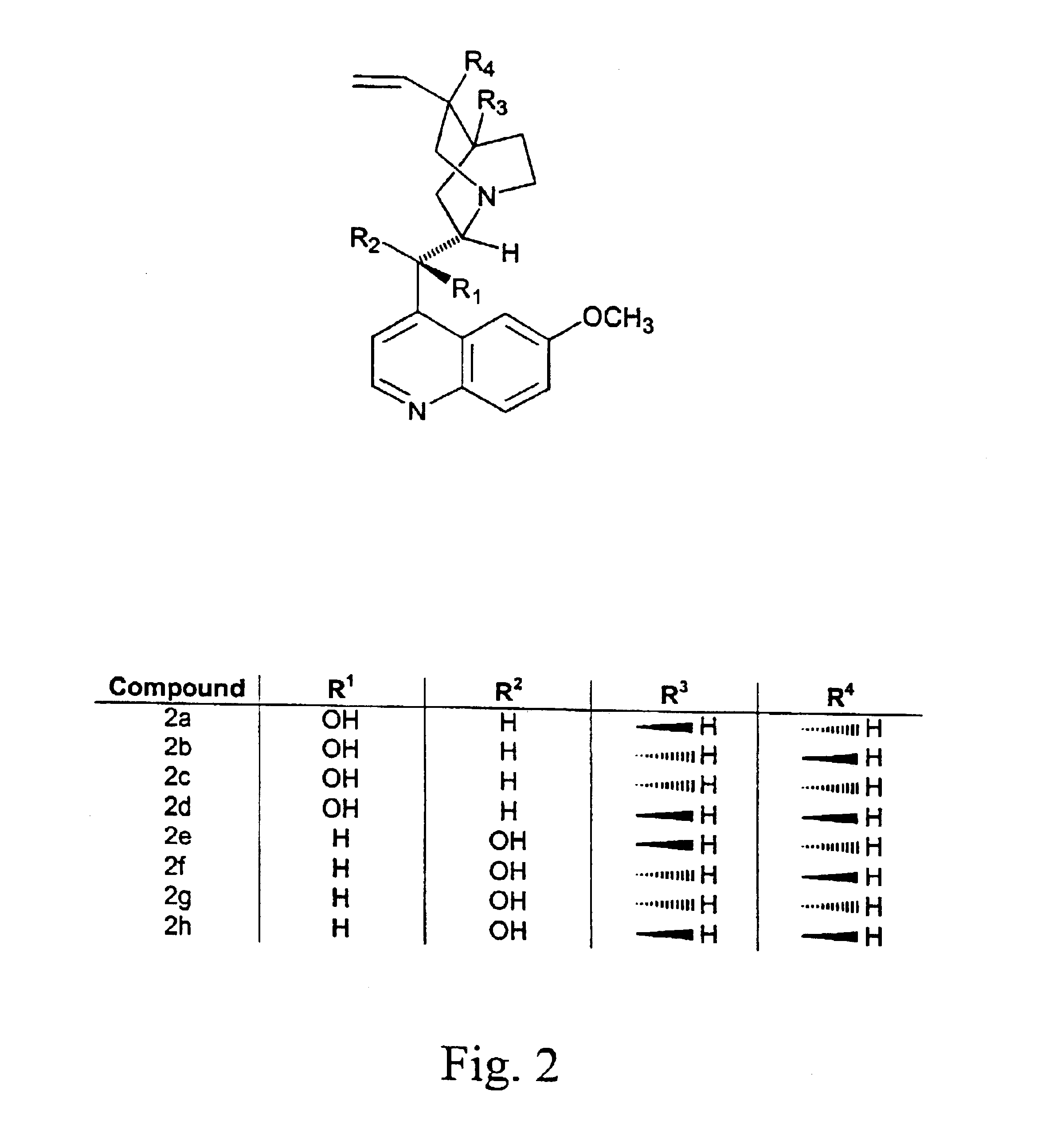
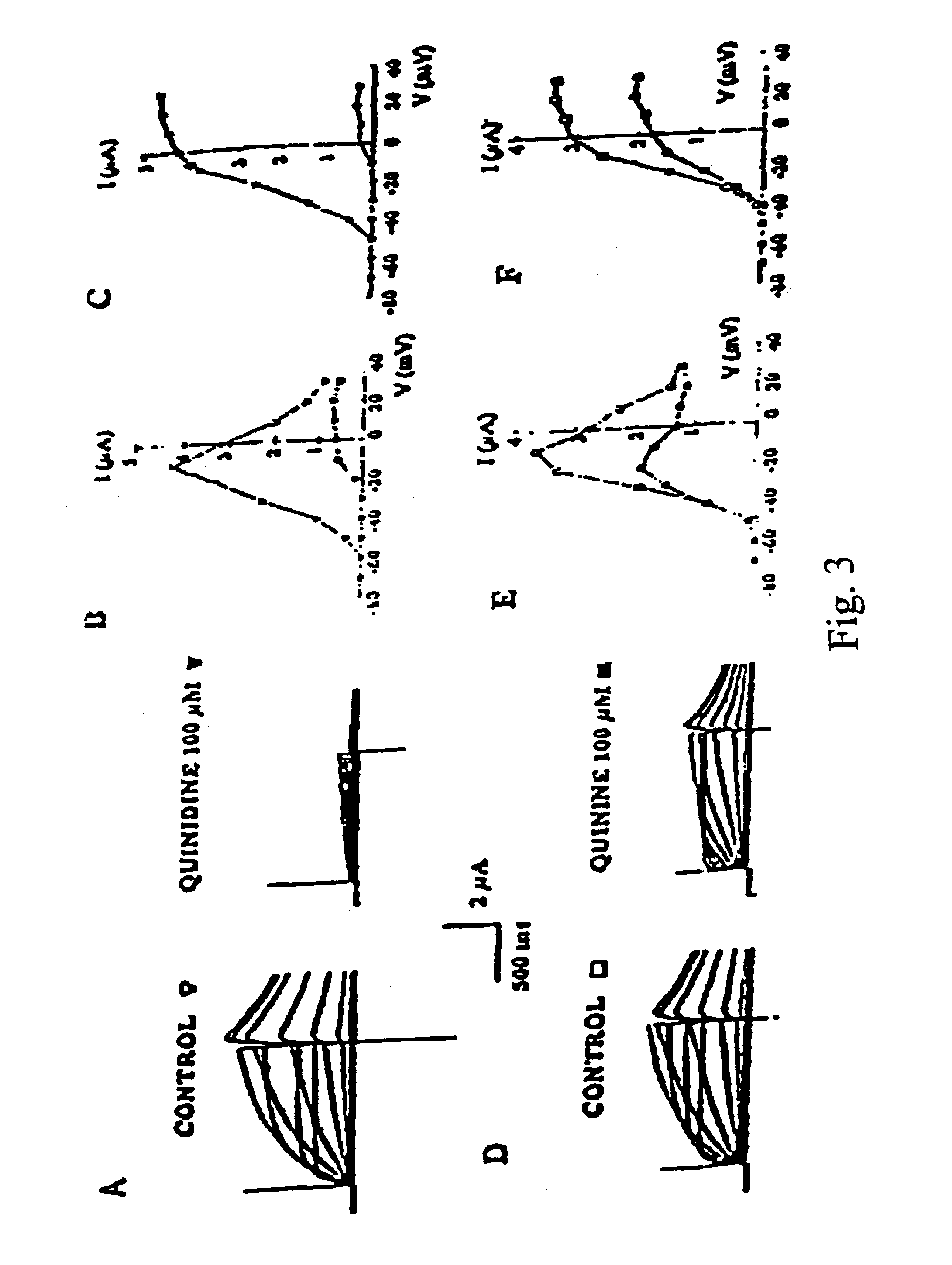
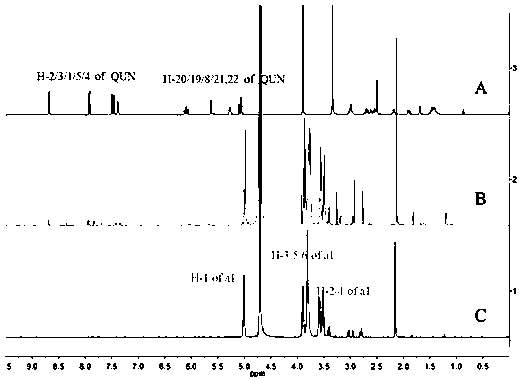
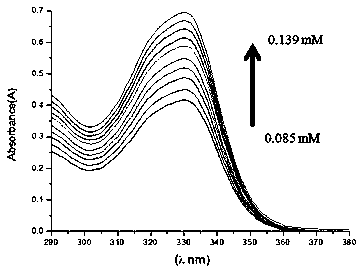
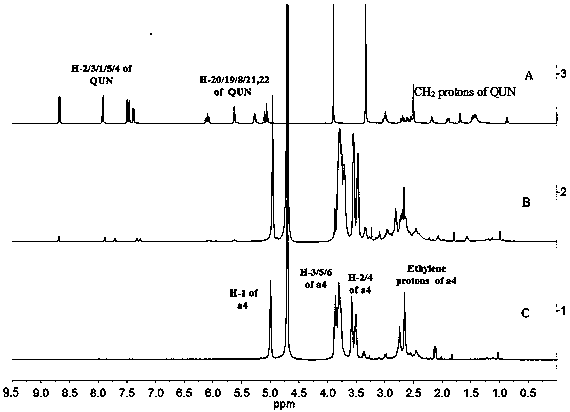
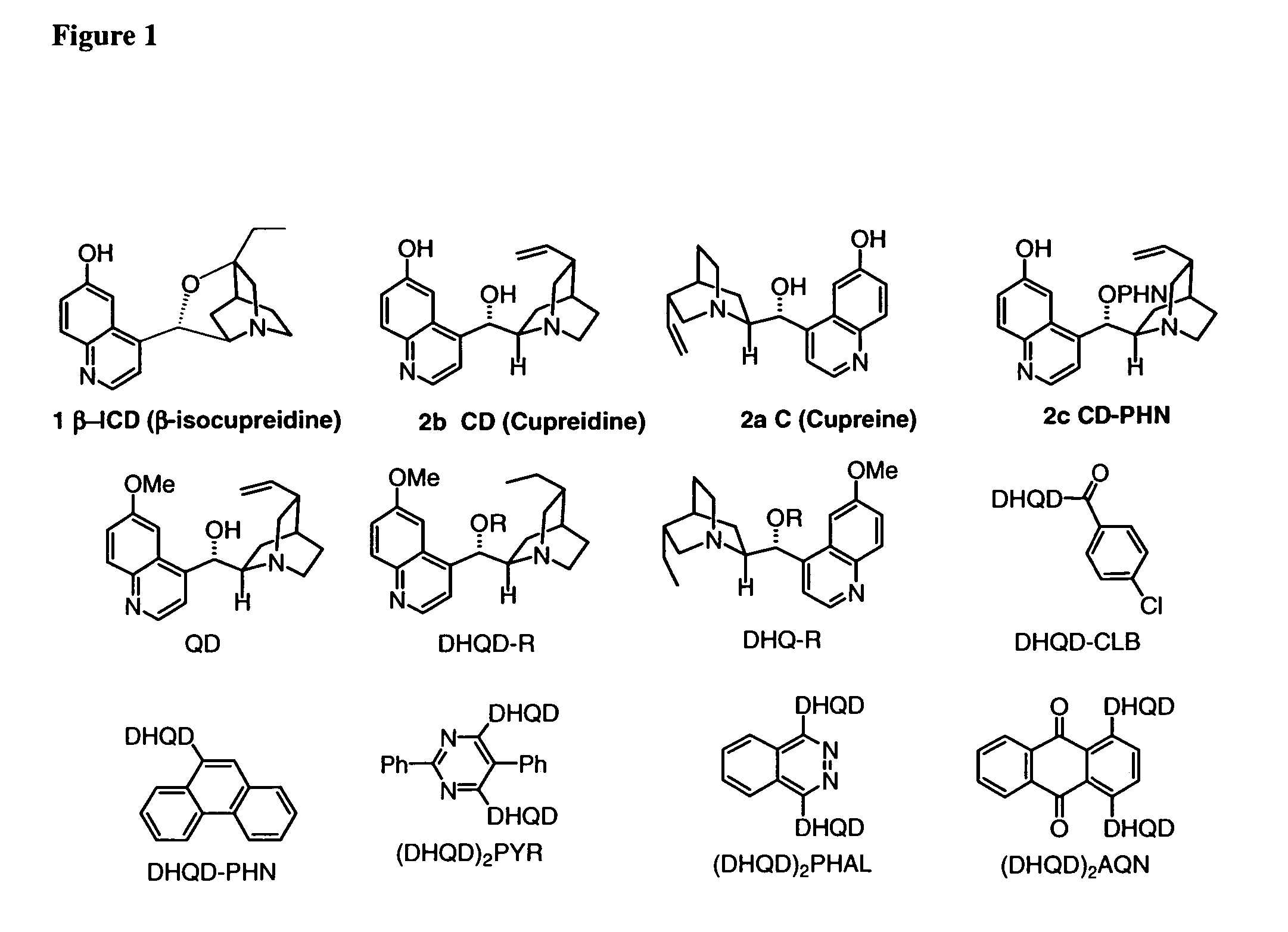
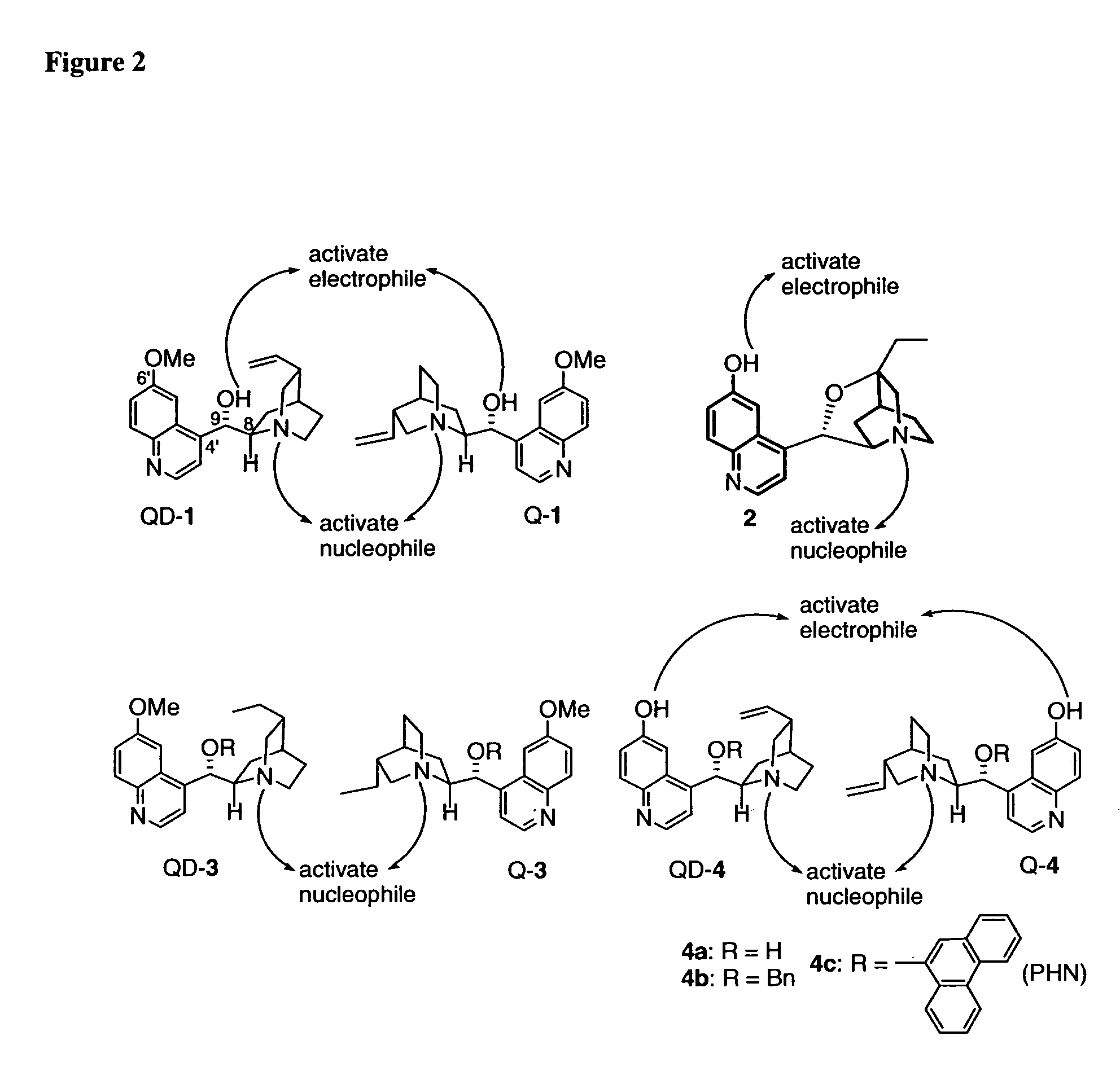
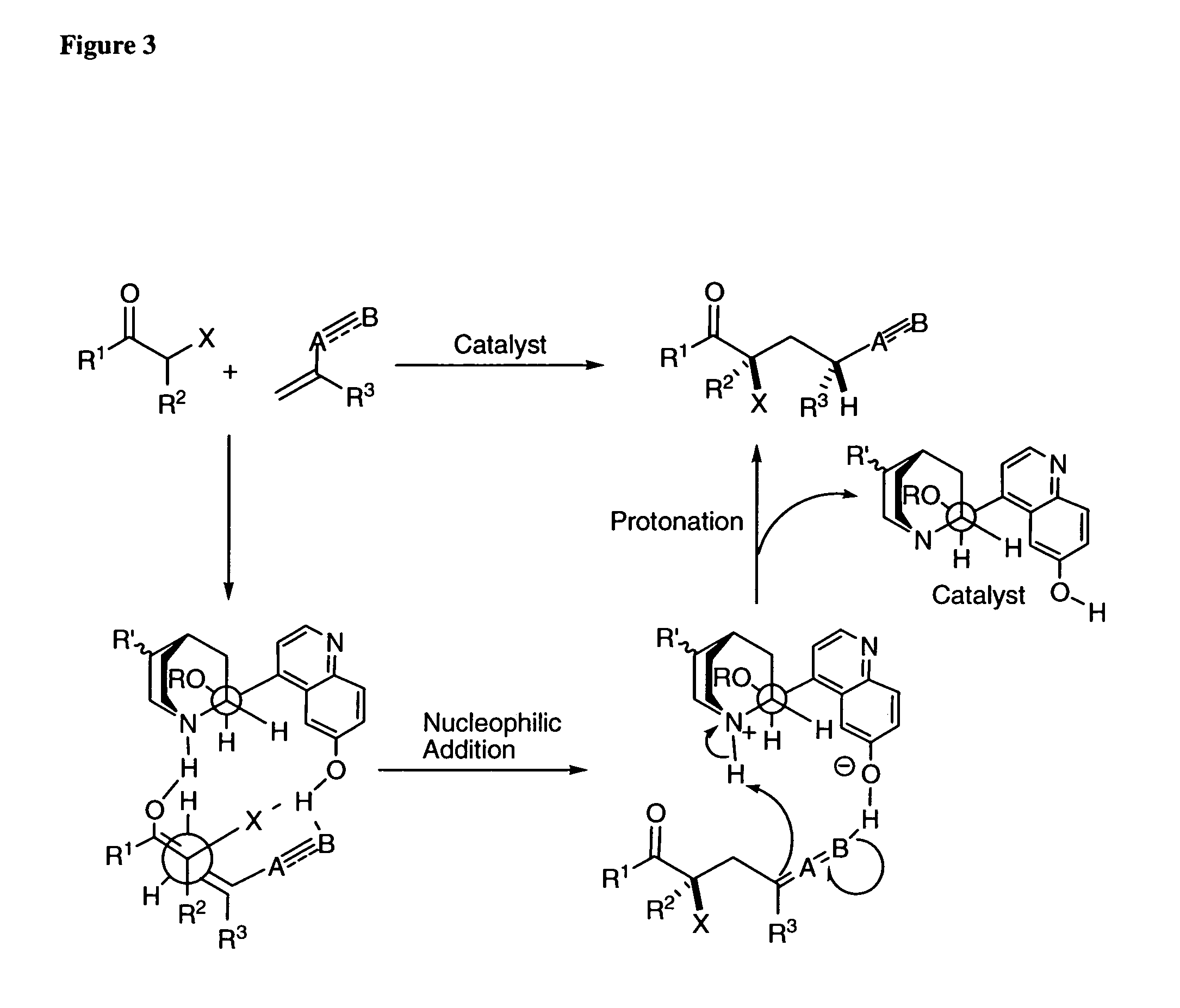
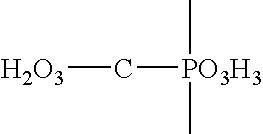Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
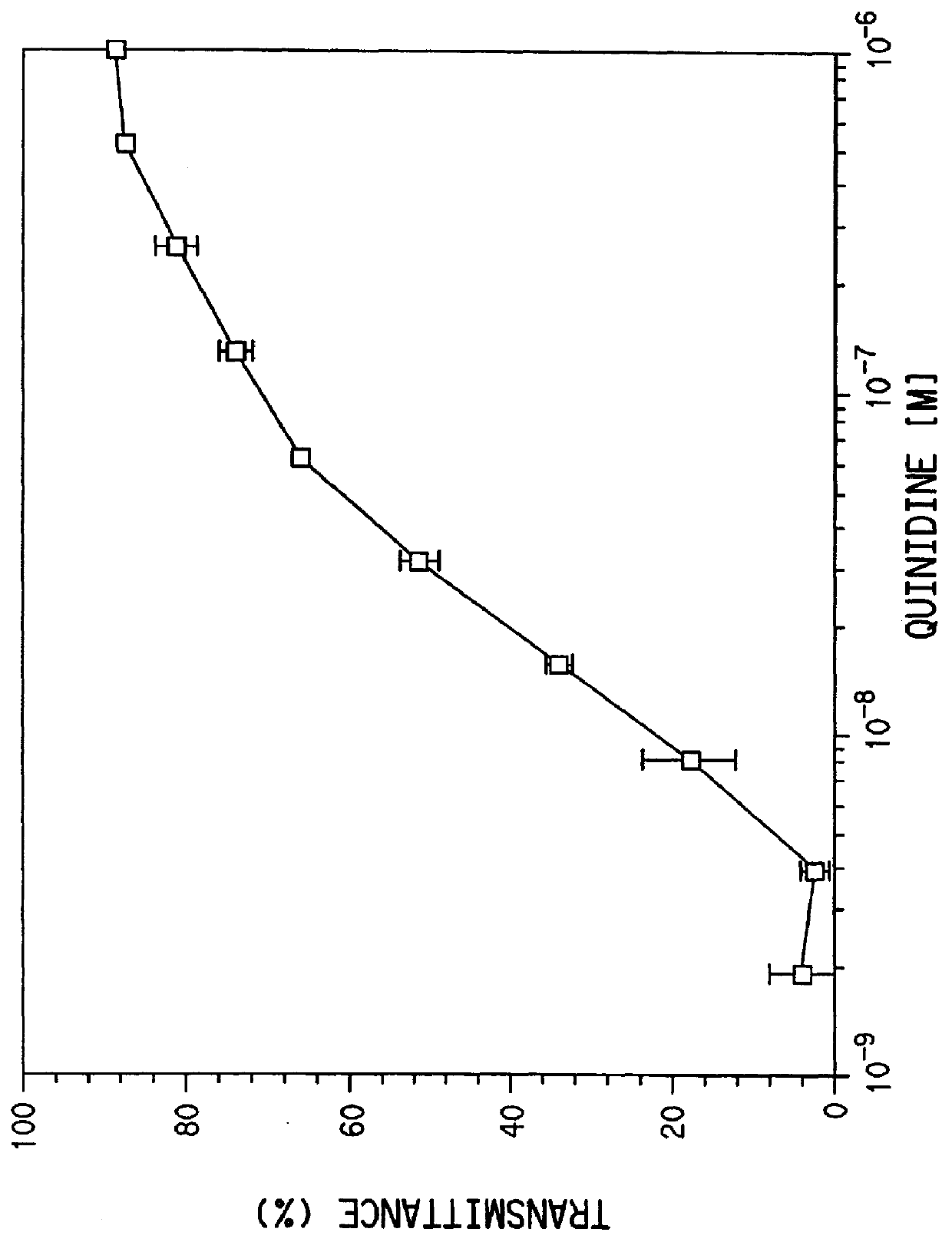
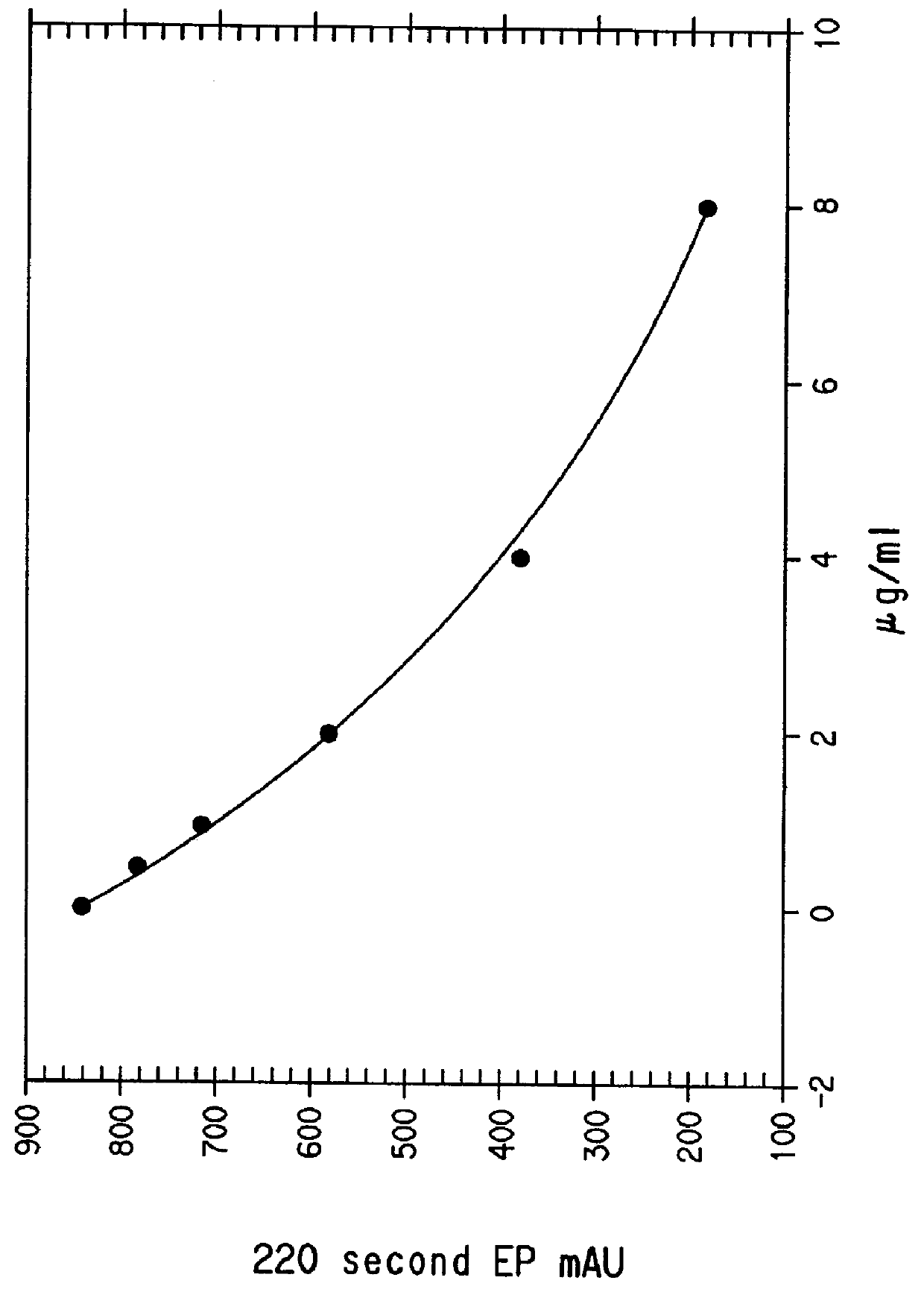
55 results about "Quinidine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
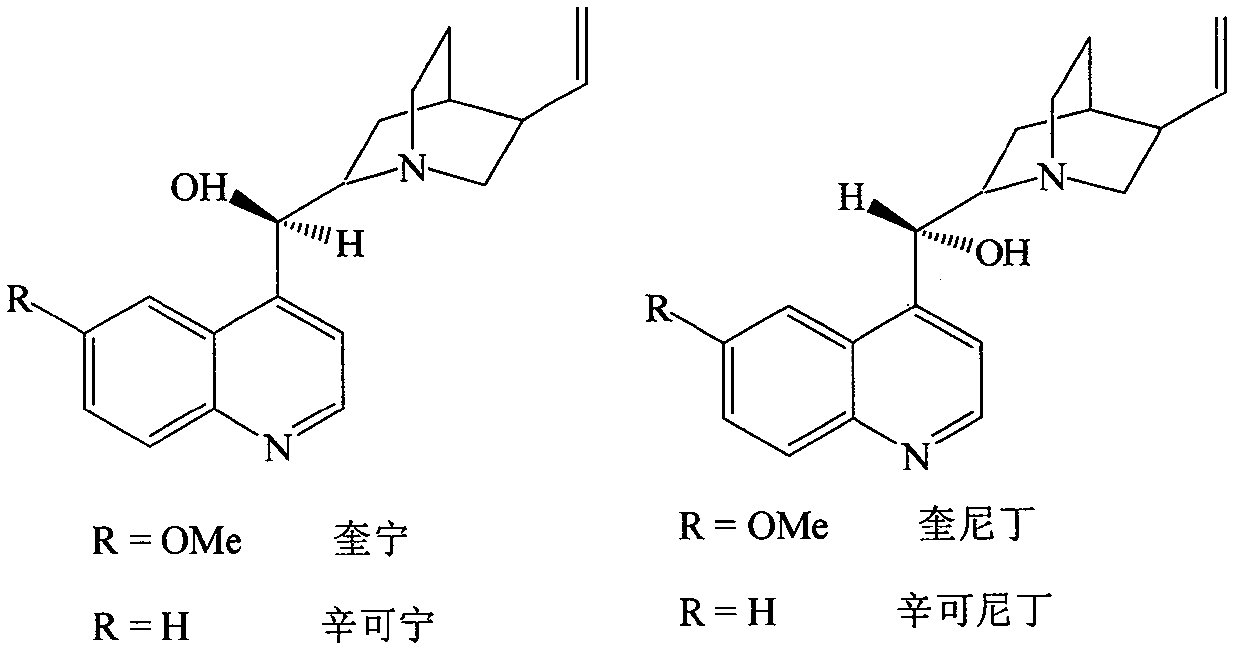
Quinidine is a medication that acts as a class I antiarrhythmic agent (Ia) in the heart. It is a stereoisomer of quinine, originally derived from the bark of the cinchona tree. The drug causes increased action potential duration, as well as a prolonged QT interval.
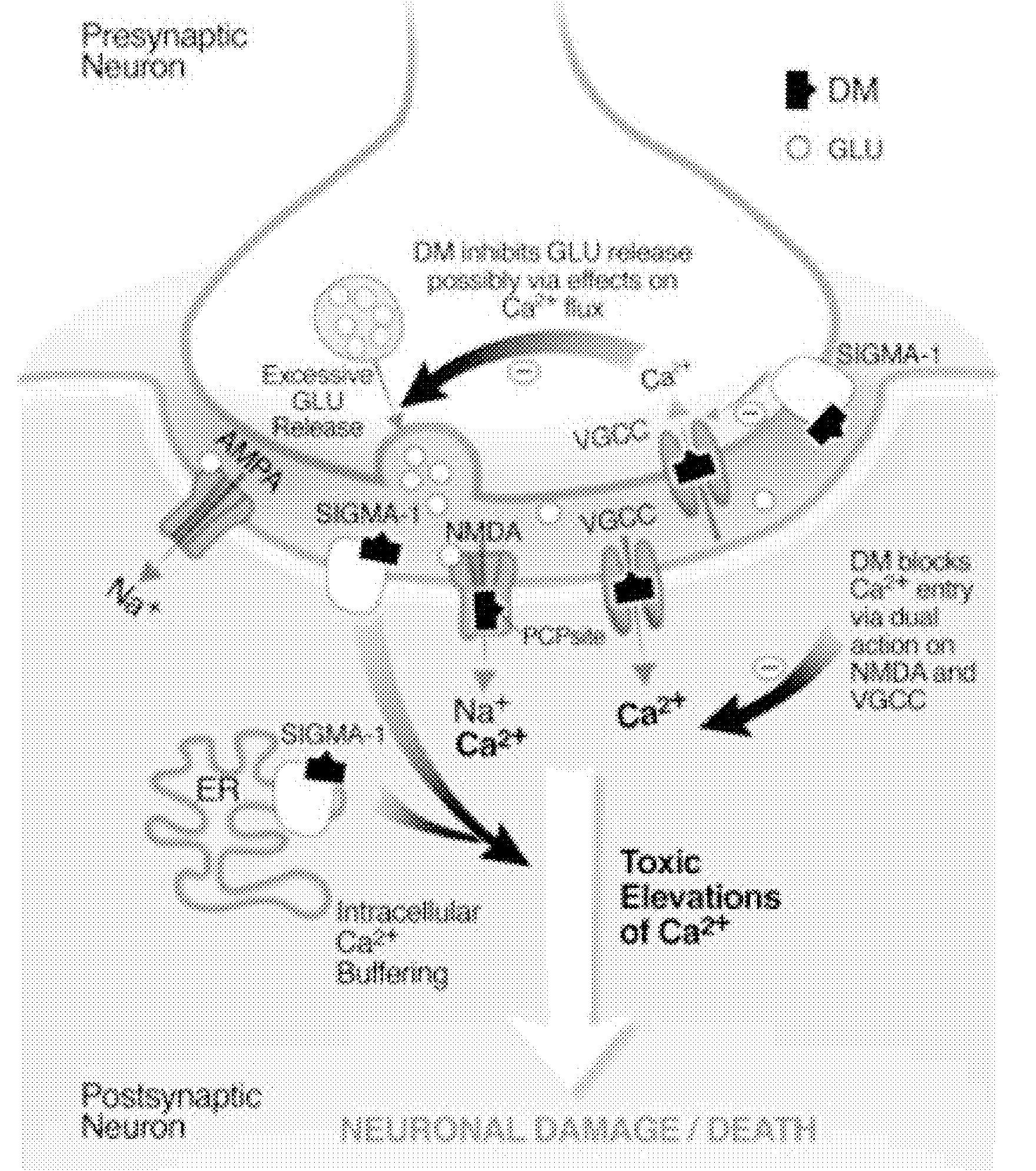
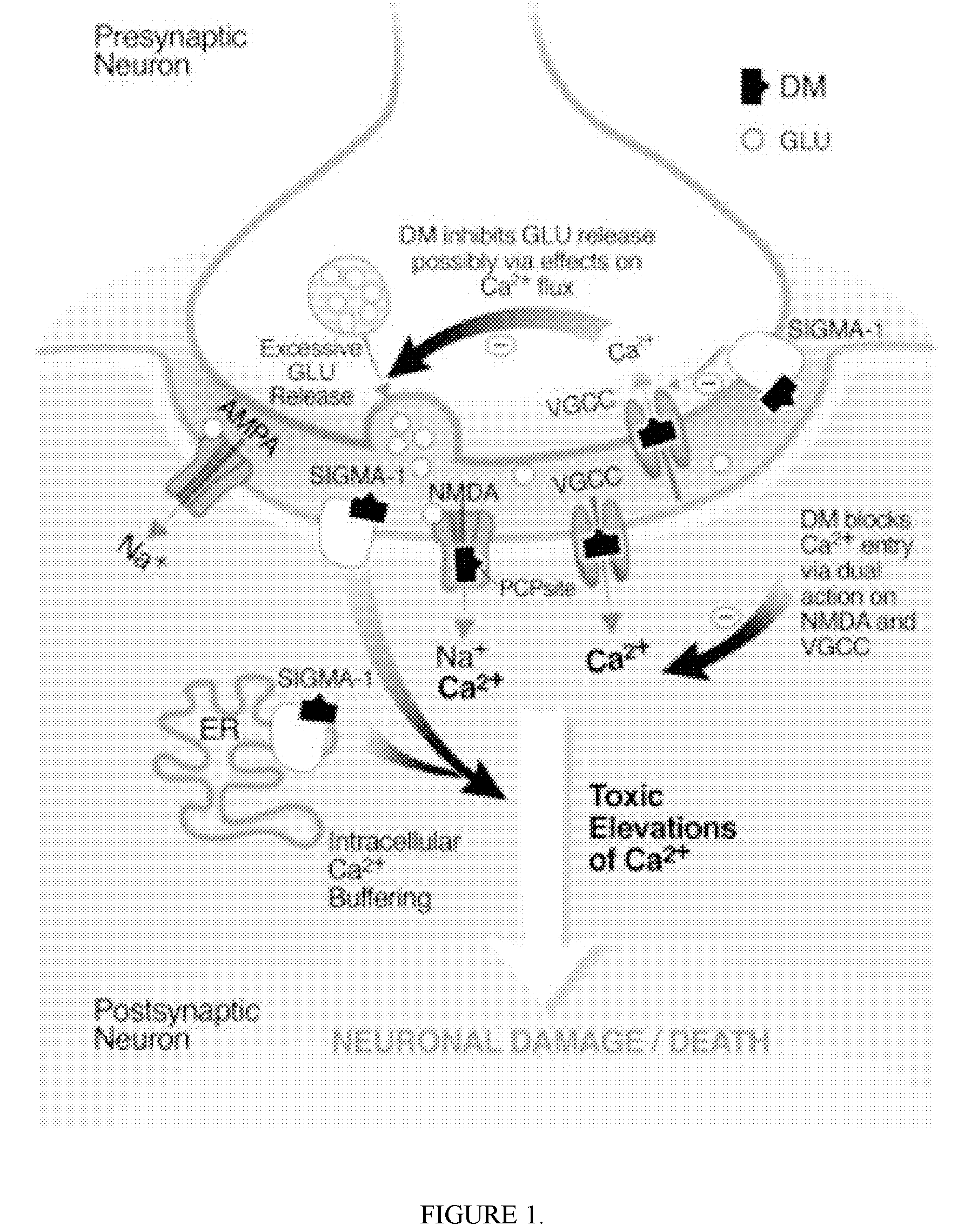
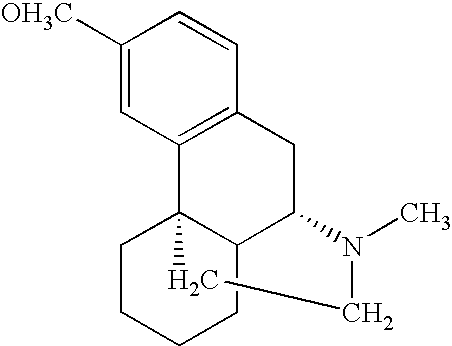
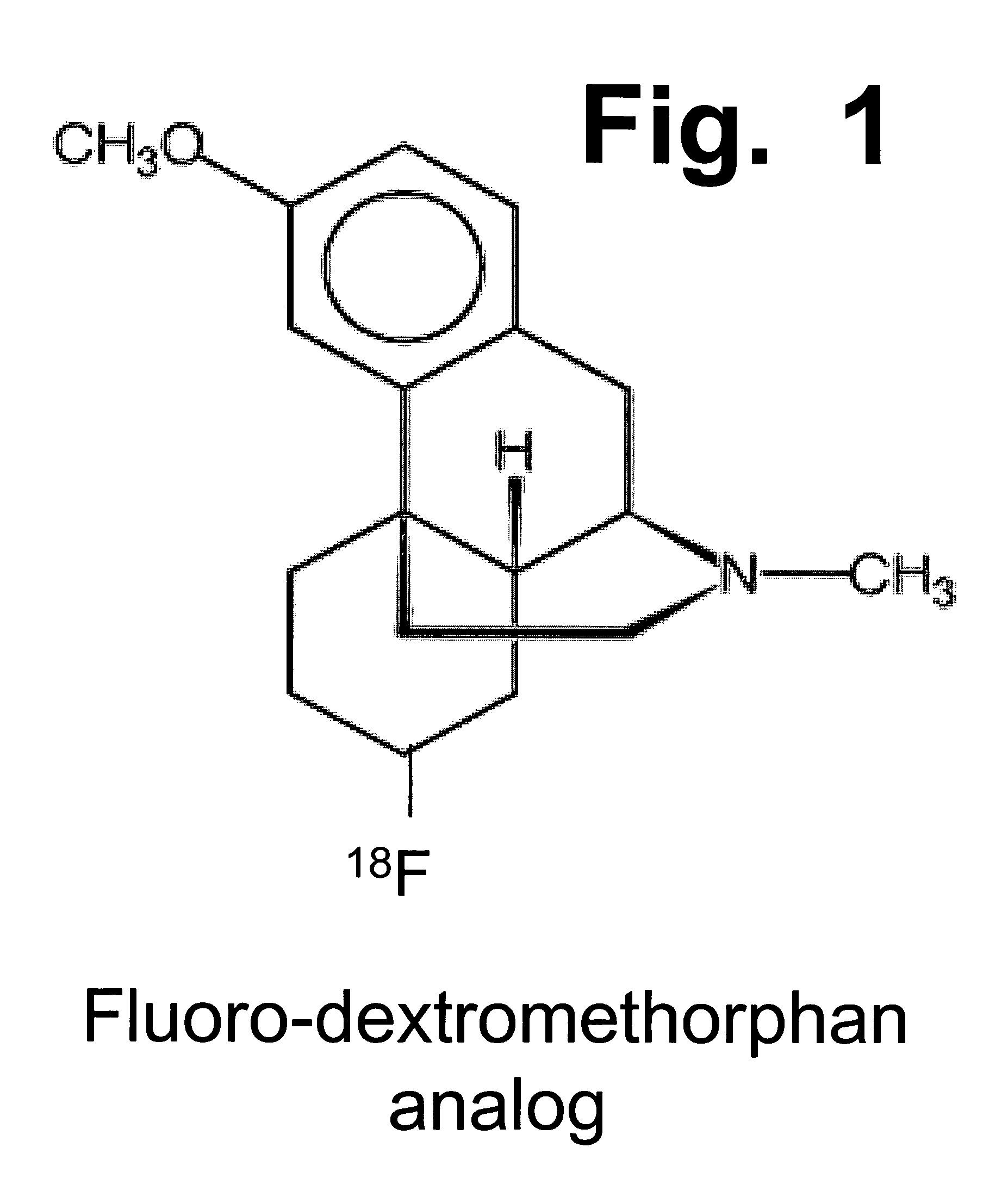
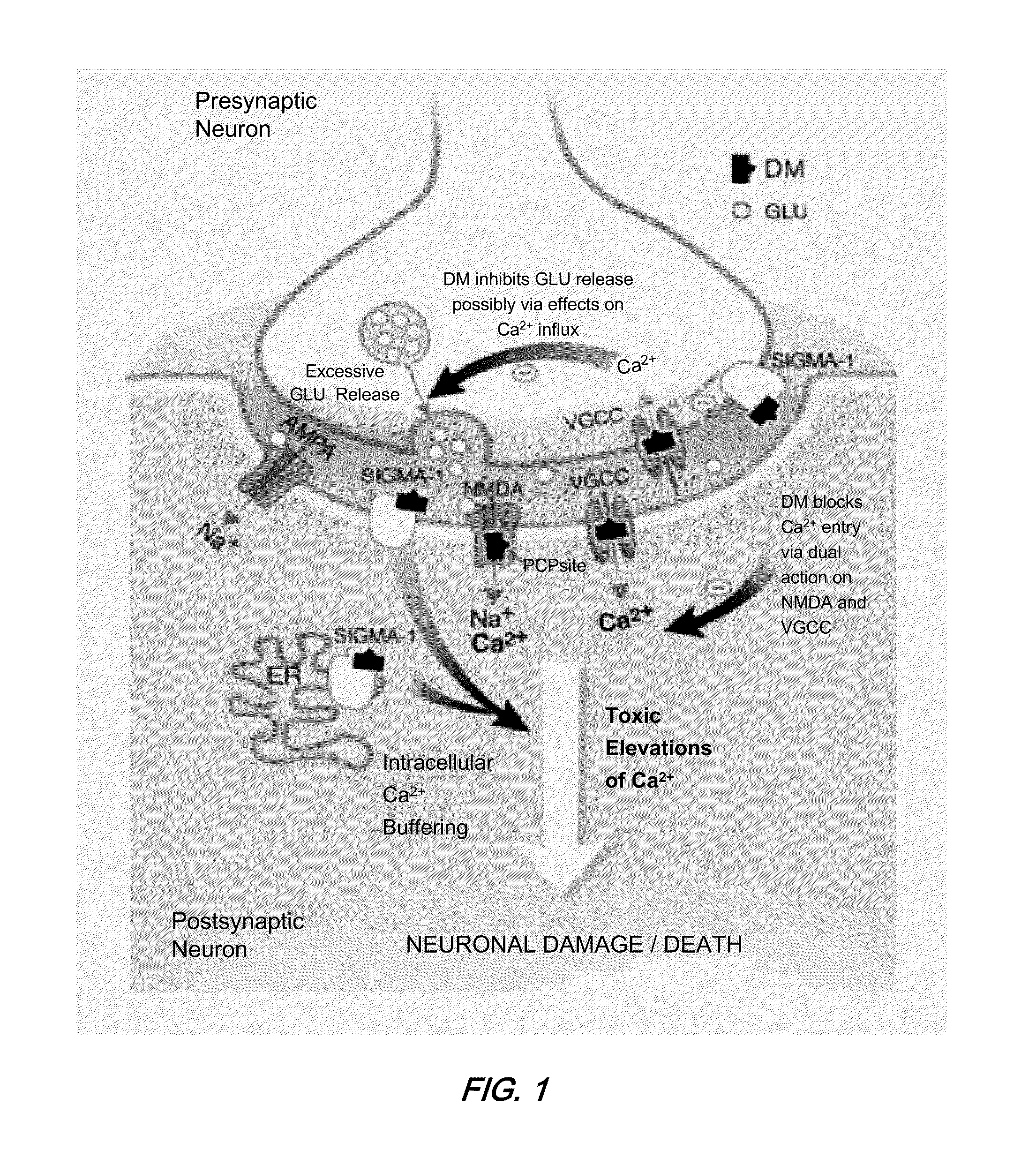
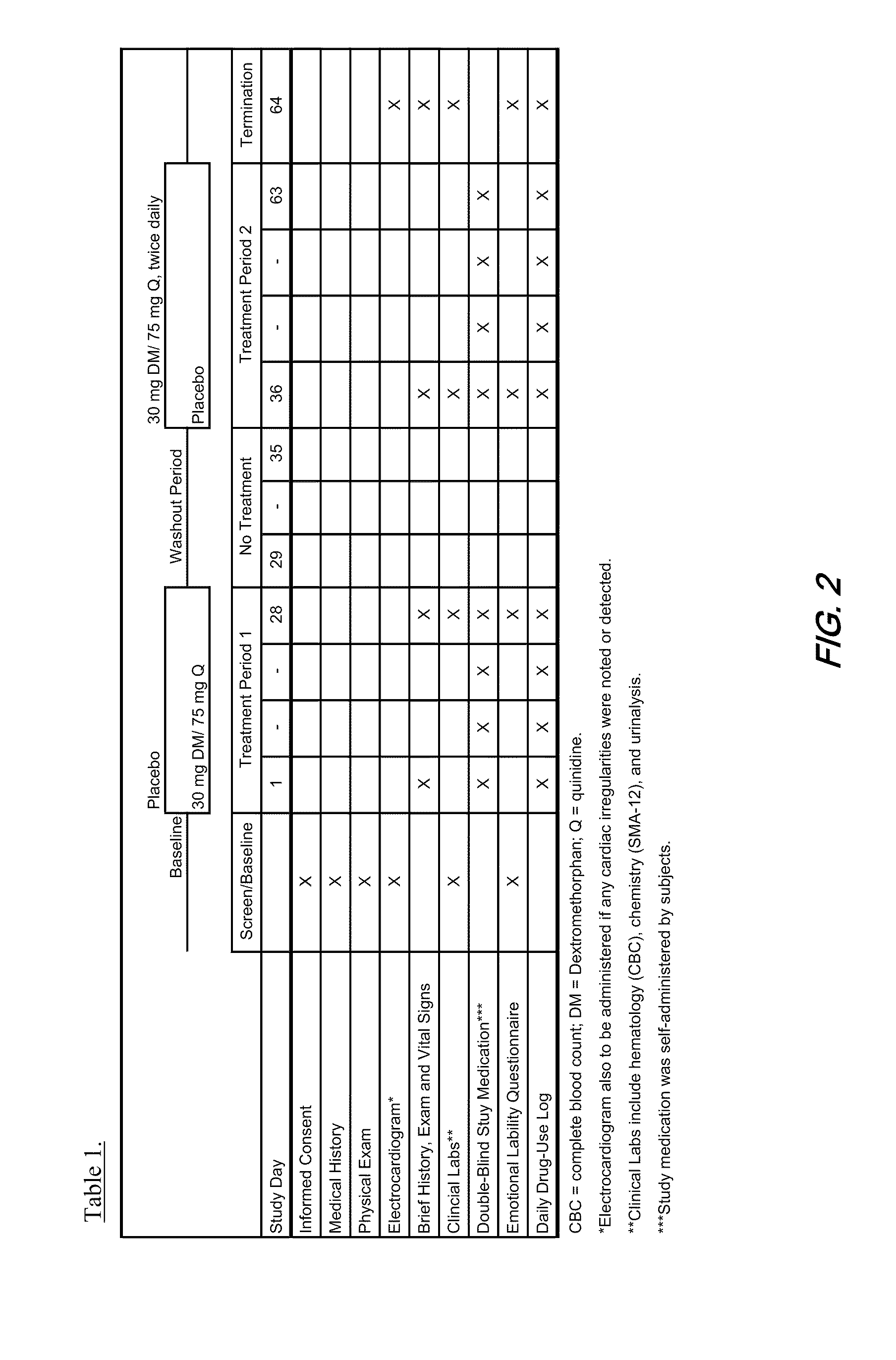
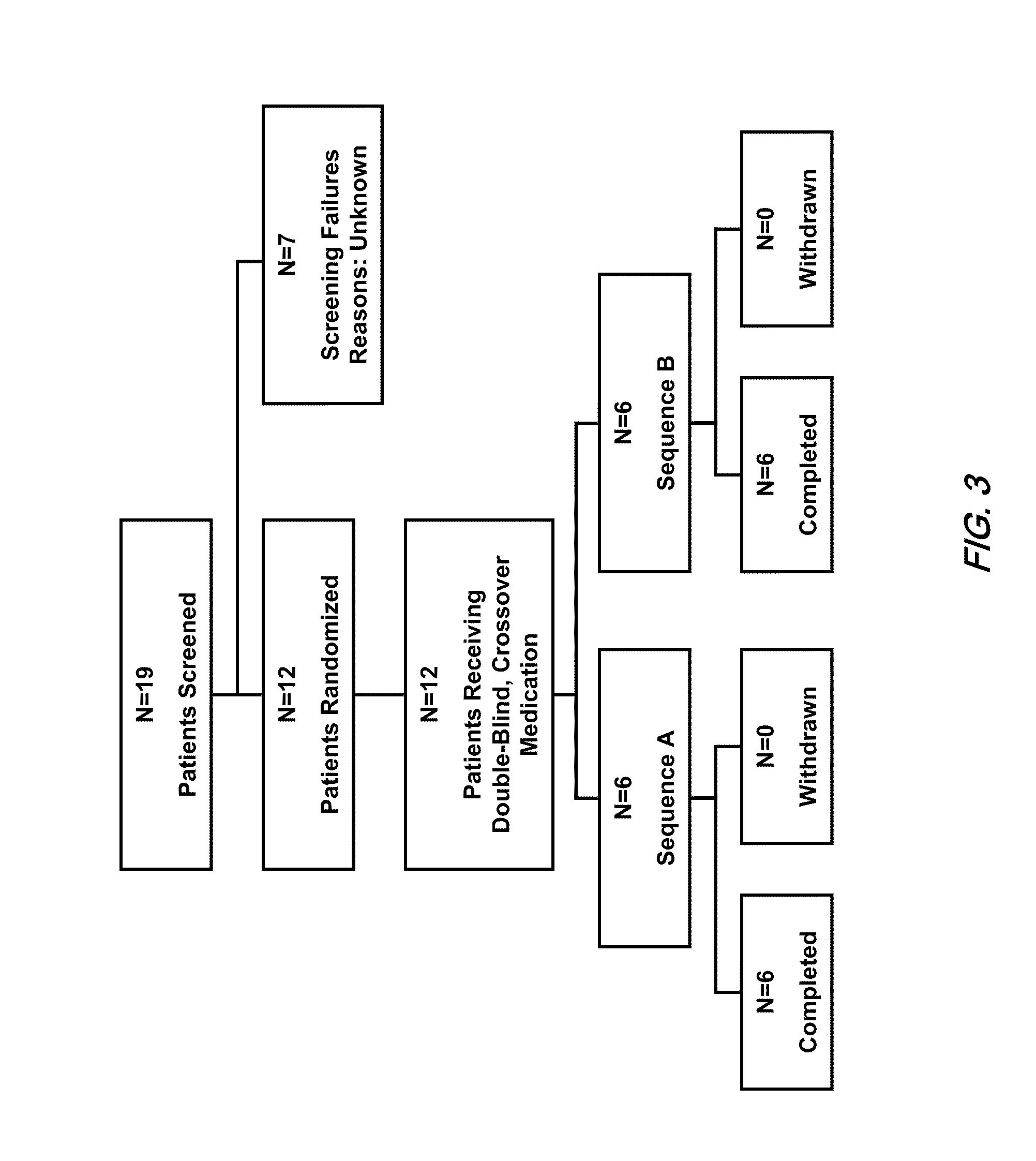
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising dextromethorphan and quinidine for the treatment of neurological disorders
Pharmaceutical compositions and methods for treating neurological disorders by administering same are provided. The compositions comprise dextromethorphan in combination with quinidine.
Owner:AVANIR PHARMA
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising dextromethorphan and quinidine for the treatment of depression, anxiety, and neurodegenerative disorders
Pharmaceutical compositions and methods for treating depression, anxiety, and neurodegenerative diseases and cognitive disorders, such as dementia and Alzheimer's disease, by administering same are provided. The compositions comprise dextromethorphan in combination with quinidine.
Owner:AVANIR PHARMA
Dextromethorphan and an oxidase inhibitor for treating intractable conditions
Methods are disclosed for increasing the effectiveness of dextromethorphan in treating chronic or intractable pain, for treating tinnitus and for treating sexual dysfunction comprising administering dextromethorphan in combination with a therapeutically effective dosage of a debrisoquin hydroxylase inhibitor. A preferred combination is dextromethorphan and the oxidative inhibitor quinidine.
Owner:AVANIR PHARMA
Enhancement of impaired motor and mental functions, using dextromethorphan and oxidase enzyme inhibitor
InactiveUS20070191411A1Improve abilitiesImprove motor controlBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseClinical trial
During clinical trials on patients suffering from neurological disorders, it has been observed that some patients obtain dramatic improvements in motor control and / or higher mental functioning, when they receive a combination of dextromethorphan and quinidine, at suitable dosages. Improved motor control has been exemplified to date by improved ability to swallow and / or speak, among victims of stroke, head injury, or ALS. Improved higher mental functioning has been exemplified better job performance, increased ability to analyze and solve problems, and increased ability to have successful and satisfying interactions with other people. These types of effects can be seen in a relatively brief time period, such as within several days to a week.
Owner:CENT FOR NEUROLOGIC STUDY
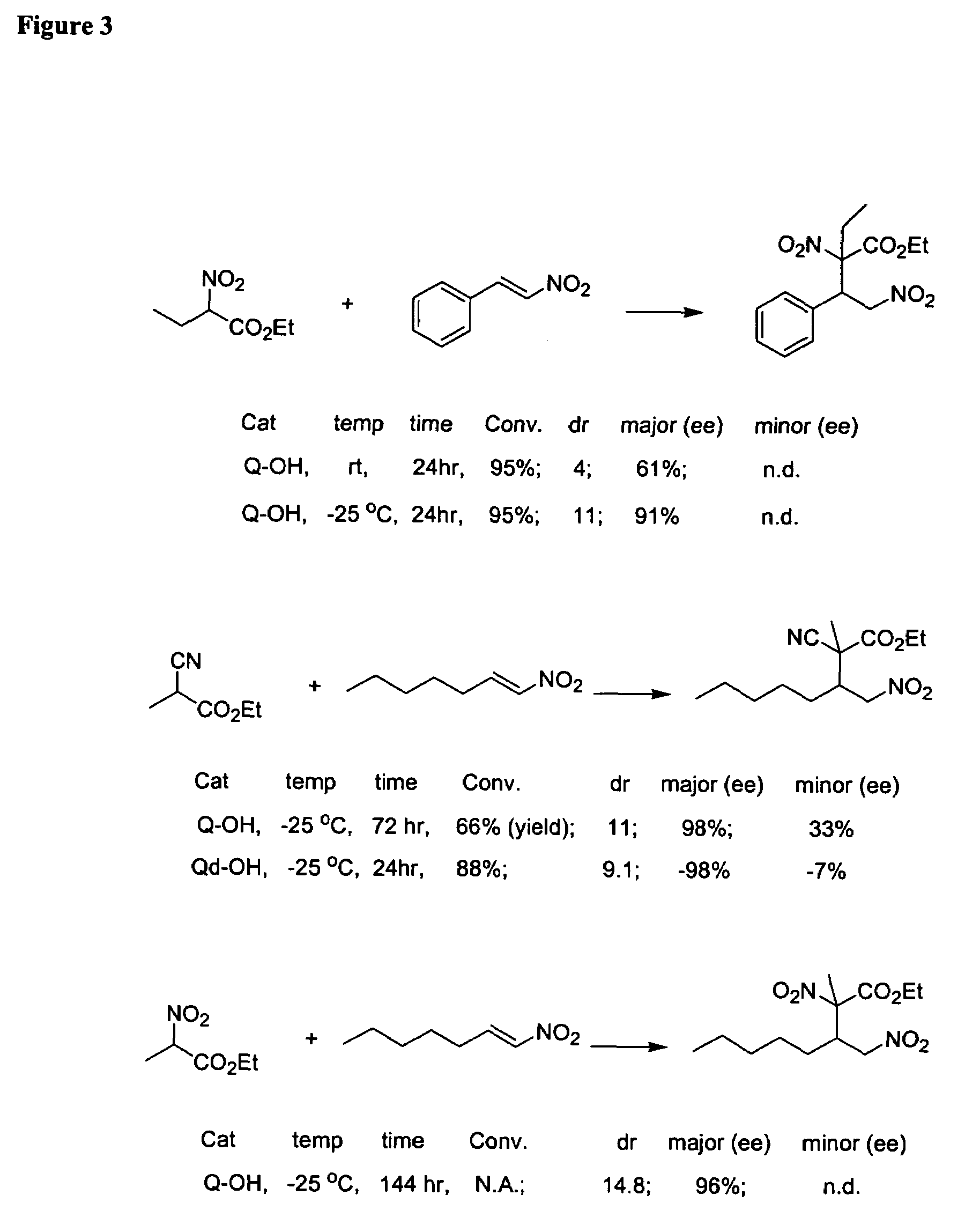
Preparation method of alpha-hydroxy-beta-dicarbonyl compound using cinchona alkaloid derivative as catalyst
InactiveCN103333069AOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationReaction temperatureQuinidine
The invention discloses a preparation method of an alpha-hydroxy-beta-dicarbonyl compound using a cinchona alkaloid derivative as a catalyst. In the condition that the cinchona alkaloid derivative is used as the catalyst, a compound is caused to be in contact with oxidants including oxygen, hydrogen peroxide, and alkyl hydroperoxide; the compound and the oxidant in contact are mixed and stirred in an inert solvent for reaction; after the reaction is ended, the alpha-hydroxy-beta-dicarbonyl compound is obtained by separation, wherein the inert solvent comprises halogenated hydrocarbon, aromatic hydrocarbon, alkane and the like; the dosage molar ratio of the peroxide, which is used as the oxidant, to a beta-dicarbonyl compound is 1-30; the dosage of the catalyst III is 0.5-50mol%; the reaction temperature is minus 78 to 50 DEG C. According to the novel preparation method of the alpha-hydroxy-beta-dicarbonyl compound using the cinchona alkaloid derivative as the catalyst disclosed by the invention, cinchona alkaloid quinine and cinchona alkaloid quinindium, which are main alkaloids in the bark of cinchona and congener, are widely applied to organic unsymmetrical catalytic reaction.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
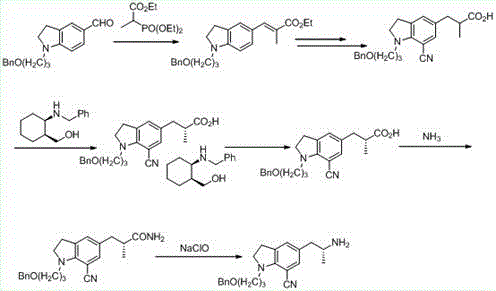
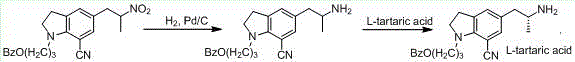
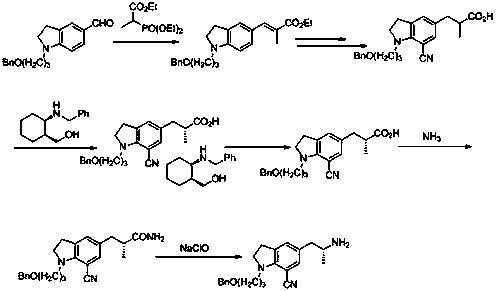
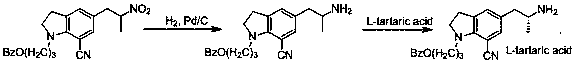
Preparation method of indoline derivative for synthesizing silodosin
ActiveCN106380438AHigh optical purityChemical cost reductionOrganic chemistryBenzoic acidPalladium on carbon
The invention provides a preparation method of an indoline derivative for synthesizing silodosin. Indoline is taken as a starting raw material and reacts with benzoic acid and 1-chloro-3-bromopropane to prepare a compound (1); a reaction is carried out in a Vilsmeier agent, and a formyl group in introduced to the 5th position to prepare a compound (2); the compound (2) and nitroethane undergoes an asymmetric Henry reaction in the catalysis of quinidine-copper acetate to prepare a compound (3); the compound (3) is subjected to acetylation through acetic anhydride to prepare a compound (4); a cyano group is introduced to the 7th position to prepare a compound (6); and two functional groups are reduced through palladium-on-carbon hydrogenation in one step to obtain a high-chiral-purity target compound: (R)-1-[1-(3-benzoyloxypropyl)-5-(2-aminopropyl)-7-cyano]indoline. In the early stage of the method, cheap quinidine is used to perform an asymmetric Henry reaction for introduction of chiral centers, thereby avoiding resolution in the latter stage. The method is reasonable in design, simple to operate, effectively improved in yield and reduced in cost, and therefore is suitable for massive production.
Owner:江苏宇田医药有限公司
Cinchona alkaloids compound and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a cinchona alkaloids compound with a new macrocyclic structure, and a preparation method thereof. The cinchona alkaloids compound is prepared with cinchona alkaloids quinidine as a substrate. According to the preparation method, quinidine is subjected to a halogen cyclization reaction, such that the new macrocyclic structure is obtained. Related derivatives can be obtained through the changes on the C11-locus. The cinchona alkaloids compound provided by the invention can be used as a novel chiral catalyst or a ligand. The preparation method is simple, and yield is high.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Asymmetric Michael and Aldol additions using bifunctional cinchona-alkaloid-based catalysts
InactiveUS20060014956A1Silicon organic compoundsCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationLeaving groupKetone
One aspect of the present invention relates to quinine-based and quinidine-based catalysts. Another aspect of the invention relates to a method of preparing a derivatized quinine-based or quinidine-based catalyst comprising 1) reacting quinine or quinidine with base and a compound that has a suitable leaving group, and 2) converting the ring methoxy group to a hydroxy group. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a method of preparing a chiral, non-racemic compound from a prochiral electron-deficient alkene or azo compound or prochiral aldehyde or prochiral ketone, comprising the step of: reacting a prochiral electron-deficient alkene or azo compound or prochiral aldehyde or prochiral ketone with a nucleophile in the presence of a catalyst; thereby producing a chiral, non-racemic compound; wherein said catalyst is a derivatized quinine or quinidine. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a method of kinetic resolution, comprising the step of: reacting racemic chiral alkene with a nucleophile in the presence of a derivatized quinine or quinidine.
Owner:BRANDEIS UNIV
Film coated tablet for improved upper gastrointestinal tract safety
InactiveUS20070071822A1Protection is in progressInhibition releaseBiocideTetracycline active ingredientsIrritationUpper gastrointestinal
A novel oral dosage to be delivered to the stomach comprising a safe and effective amount of an active ingredient selected from the group consisting of emepronium bromidebromide, doxycycline, and other tetracyclines / antibiotics, iron preparations, quinidine, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, alprenolol, ascorbic acid, captopril, theophylline, zidovoudine (AZT), bisphosphonates and mixtures thereof and pharmaceutically-acceptable excipients, wherein said oral dosage form is a generally oval form and film coated to facilitate rapid esophageal transit and avoid irritation in the mouth, buccal cavity, pharynx, and esophagus.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
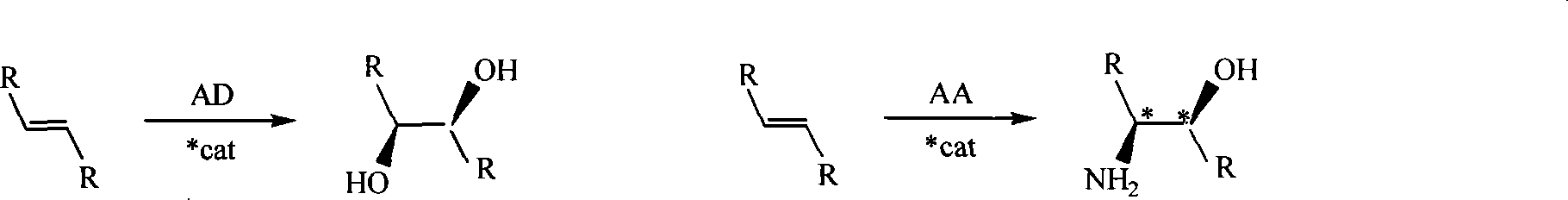
Optically active isomers of quinine and quinidine and their respective biological action
The present invention provides methods for purifying, identifying and using optically active isomers of quinine and quinidine as well as compositions comprising such optically active isomers. Such optically active isomers having desired actions on cardiac sodium and potassium channel function substantially separable from undesirable effects on GI motility can be useful for more effective therapy of cardiac arrhythmias. Also disclosed are methods for assaying the levels of such isomers present in the biological fluids.
Owner:ACADEMIC PHARMA
Withaferin compositions for prevention of aging
ActiveUS20180125865A1Prevent agingBlocking in networkNervous disorderDigestive systemApigeninCell survival
The present invention provides gero-protective pharmaceutical compositions and methods, the compositions being adapted to enhance at least one of cell survival and cell metabolism in a mammalian subject, the pharmaceutical compositions include at least two of Withaferin a or its structural analogs, coumestrol, ginsenoside, quinidine, silymarin, licochalcone a, lipoic acid and apigenin, in a pharmaceutically effective amount.
Owner:INSILICO MEDICINE IP LTD
Inclusion compound of quinidine and amine cyclodextrin
InactiveCN108239185AGood solubilization effectImprove solubilityAntipyreticAnalgesicsSolubilitySolvent
The invention discloses an inclusion compound of quinidine and amine cyclodextrin, belonging to the technical field of pharmacy. According to the invention, the amine cyclodextrin in the inclusion compound is amino-substituted beta-cyclodextrin; the inclusion compound of the amine cyclodextrin and the quinidine is prepared through a solvent method or an ultrasonic method; the amine cyclodextrin and the quinidine are adopted to form the inclusion compound; except for the inclusion effect of the cavity of the cyclodextrin with the quinidine, the cyclodextrin can form an alkali environment in anaqueous solution and forms an ion interaction with hydroxy of the quinidine; meanwhile, amino can form a cation in water and generates a hydrogen-bond interaction with a nitrogen atom on a quinidine molecule, thereby facilitating reinforcing water-solubility and stability of the inclusion compound. The inclusion compound provided by the invention has high stability and good water-solubility, and is expected to improve the bioutilizability of the quinidine. Meanwhile, the preparation method for the inclusion compound provided by the invention is simple and convenient, has mild conditions, facilitates operation and is applicable to industrial application.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Asymmetric carbon-carbon-bond-forming reactions catalyzed by bifunctional cinchona alkaloids
InactiveUS7582764B2Carbamic acid derivatives preparationCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationThioureaDiimide
One aspect of the present invention relates to quinine-based and quinidine-based catalysts. In certain embodiments, the quinine-based and quinidine-based catalysts contain a hydroxy group at the 6′ position. In certain embodiments, the quinine-based and quinidine-based catalysts contain an O-aryl group or an O-aroyl group at the C9 position. In certain embodiments, the quinine-based and quinidine-based catalysts contain an optionally substituted O-diazene group or an optionally substituted O-benzoyl group at the C9 position. In certain embodiments, the quinine-based and quinidine-based catalysts contain a thiourea at the C9 position. In certain embodiments, the quinine-based and quinidine-based catalysts contain an NH(═S)NH-aryl group at the C9 position. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a method of preparing a chiral, non-racemic compound from a prochiral electron-deficient alkene or prochiral imine, comprising the step of: reacting a prochiral alkene or imine with a nucleophile in the presence of a catalyst; thereby producing a chiral, non-racemic compound; wherein said catalyst is a derivatized quinine or quinidine. In certain embodiments, the nucleophile is a malonate or β-ketoester. In certain embodiments the nucleophile is an alkyl or aryl or aralkyl 2-cyano-2-alkylacetate. In certain embodiments the nucleophile is an alkyl or aryl or aralkyl 2-cyano-2-alkylacetate.Another aspect of the present invention relates to a method of kinetic resolution, comprising the step of: reacting a racemic aldehyde or racemic ketone with a nucleophile in the presence of a derivatized quinine or quinidine, thereby producing a non-racemic, chiral compound. In certain embodiments, the kinetic resolution is dynamic.
Owner:BRANDEIS UNIV
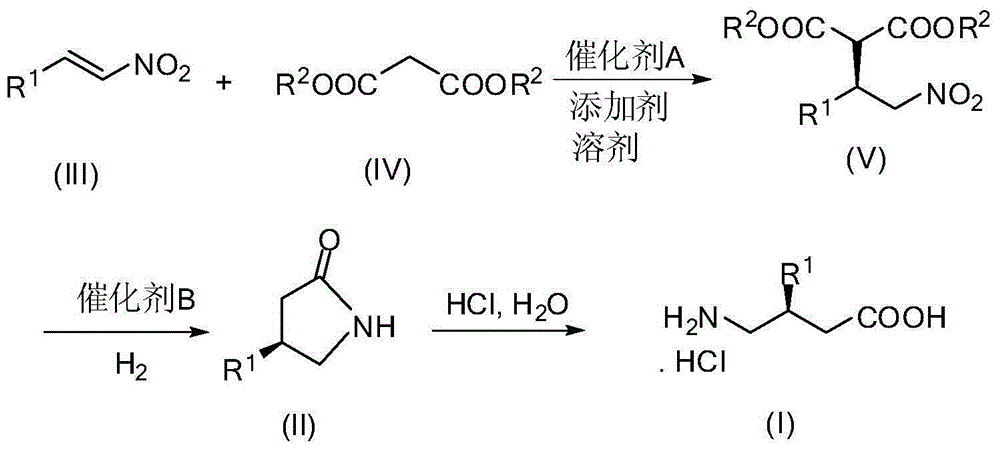
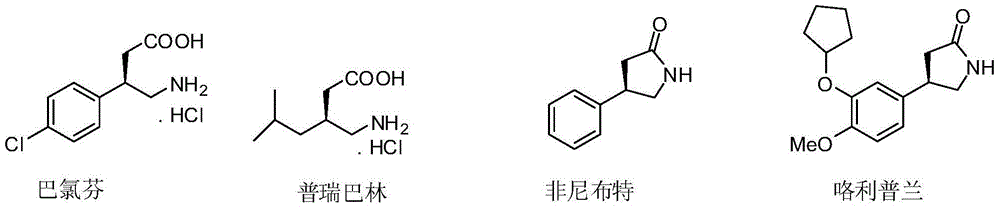
Method for synthesizing gamma-aminobutyric acid chiral compound
InactiveCN104557583AHigh yieldHigh enantioselectivityOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationHydrogenGamma-Aminobutyric acid
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing a gamma-aminobutyric acid chiral compound. The method comprises the following steps of: adding nitroolefin and malonate to a solvent in the presence of a catalyst A and an additive; carrying out conjugate addition reaction on nitroolefin and malonate to selectively obtain a compound V; carrying out hydrogenation reduction reaction on the compound V under the action of a catalyst B and hydrogen, decarboxylation and amidation to obtain a compound II; carrying out acidolysis on the compound II to obtain a compound I. According to the method, a gamma-aminobutyric acid chiral drug prepared by taking a low-cost easily-prepared quinidine derivative as a catalyst and alkali as an additive is high in yield and high in enantioselectivity. The method disclosed by the invention is moderate in reaction condition and easy to operate and is a green synthesis process for synthesizing gamma-aminobutyric acid chiral drugs.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Synthetic method for 2-hydroxyl-1-indanone compounds
ActiveCN108129306AMild reaction conditionsLow costOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationQuinidineSolvent
The invention belongs to the technical field of organic chemistry, and specifically relates to a synthetic method for 2-hydroxyl-1-indanone compounds. The method uses an indanone compound as a raw material, a peroxide as an oxidant and a quinidine or a quinine derivative as a catalyst, in the presence of a solvent, the indanone compound and the peroxide are subjected to an asymmetric hydroxylation, and therefore the 2-hydroxyl-1-indanone compounds with stereoselectivity are obtained. Compared with a previous method, the method provided by the invention has the advantages that the catalyst canbe quantitatively recovered, the reaction conditions are mild, the costs are low, the yield is high, and the stereoselectivity is strong, and is suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:金华奥布朗医药科技有限公司
Process for preparing MeO-Peg-protected dihydroquinine or dihydroquinidine derivatives, new dihydroquinine or dihydroquinidine derivatives and their use
InactiveUS6326327B1Molecular sieve catalystsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsDihydroquinidineDihydroquinine
Owner:DEGUSSA AG
Method for preparing quinindium and cinchonine
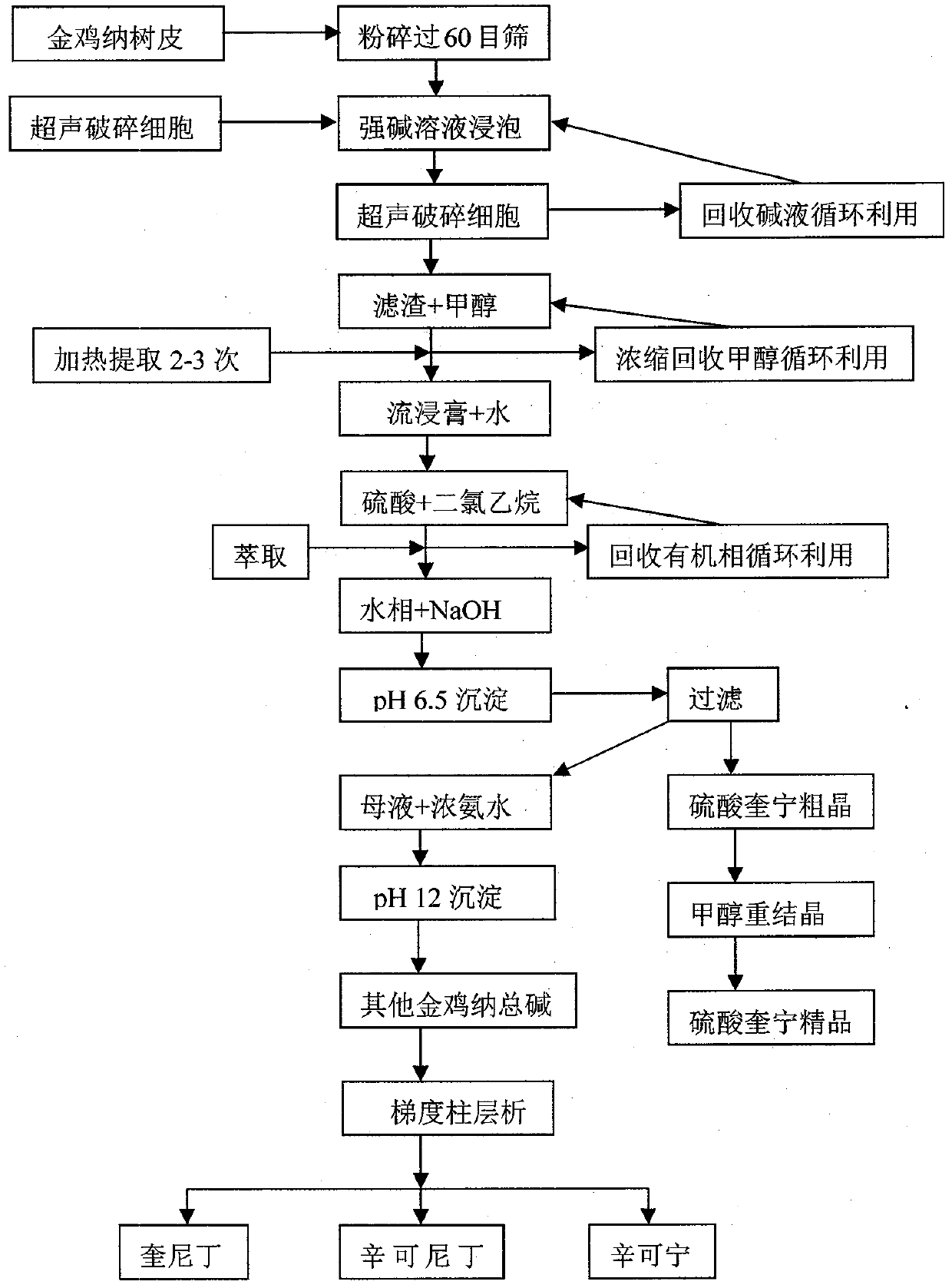
InactiveCN102212064AAchieve purificationThe preparation method is economical, simple and convenientOrganic chemistryFiltrationPeruvian Bark
The invention discloses a method for preparing quinindium and cinchonine. The method comprises the following steps: separating out quinine from a total alkaloid of Peruvian bark through a sulfate precipitation method so as to obtain a filtrate containing other alkaloids; basifying the filtrate until the pH value is not less than 10, collecting the obtained precipitate and drying the precipitate so as to obtain a raw material A; dissolving the raw material A with an organic solvent, filtering, separating an indissoluble substance from the filtrate; dissolving the indissoluble substance with a proper amount of alcohol solvent, adding activated carbon for decoloring, and then carrying out filtration and crystallization so as to obtain the cinchonine; and concentrating the filtrate until the volume of filtrate is 1 / 5-1 / 10 of the original volume, standing until a solid is separated out, dissolving the solid with a proper amount of alcohol solvent, adding the activated carbon for decoloring, and then carrying out filtration and crystallization so as to obtain the quinindium. The method is economical, simple and convenient and is in favor of amplification production; and the yield is high.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising dextromethorphan and quinidine for the treatment of neurological disorders
Pharmaceutical compositions and methods for treating neurological disorders by administering same are provided. The compositions comprise dextromethorphan in combination with quinidine.
Owner:AVANIR PHARMA
Asymmetric Michael and Aldol additions using bifunctional cinchona-alkaloid-based catalysts
Owner:BRANDEIS UNIV
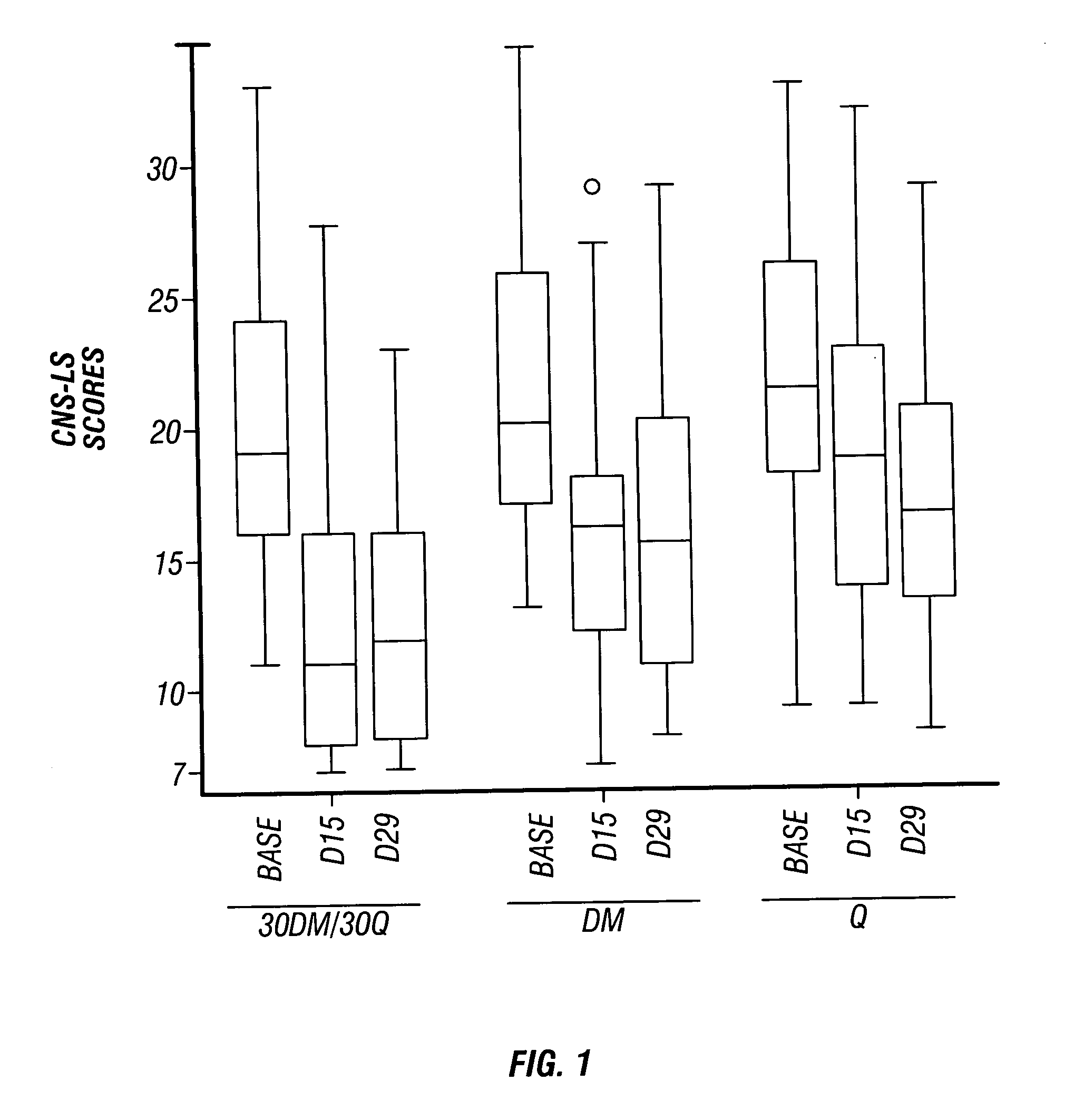
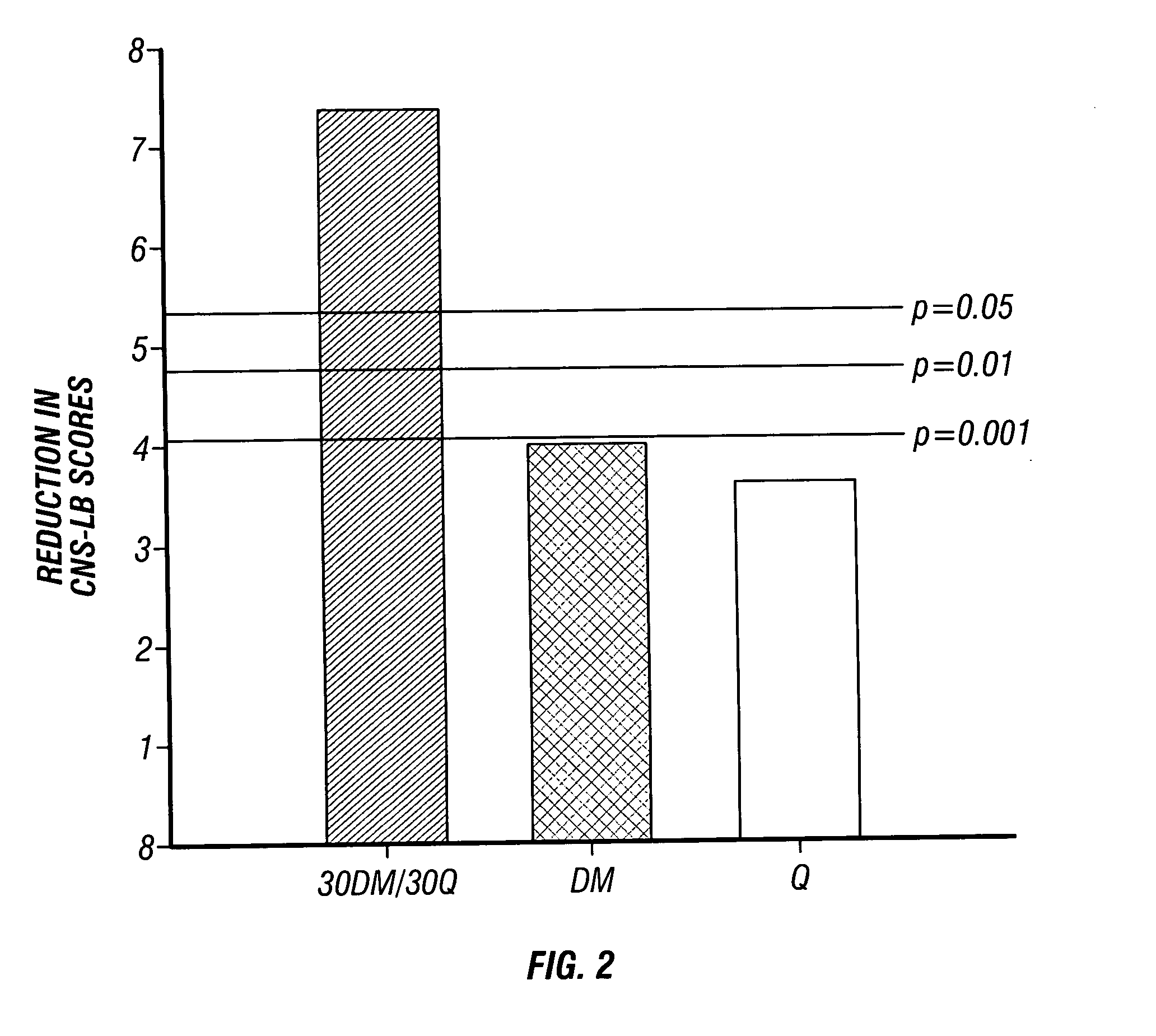
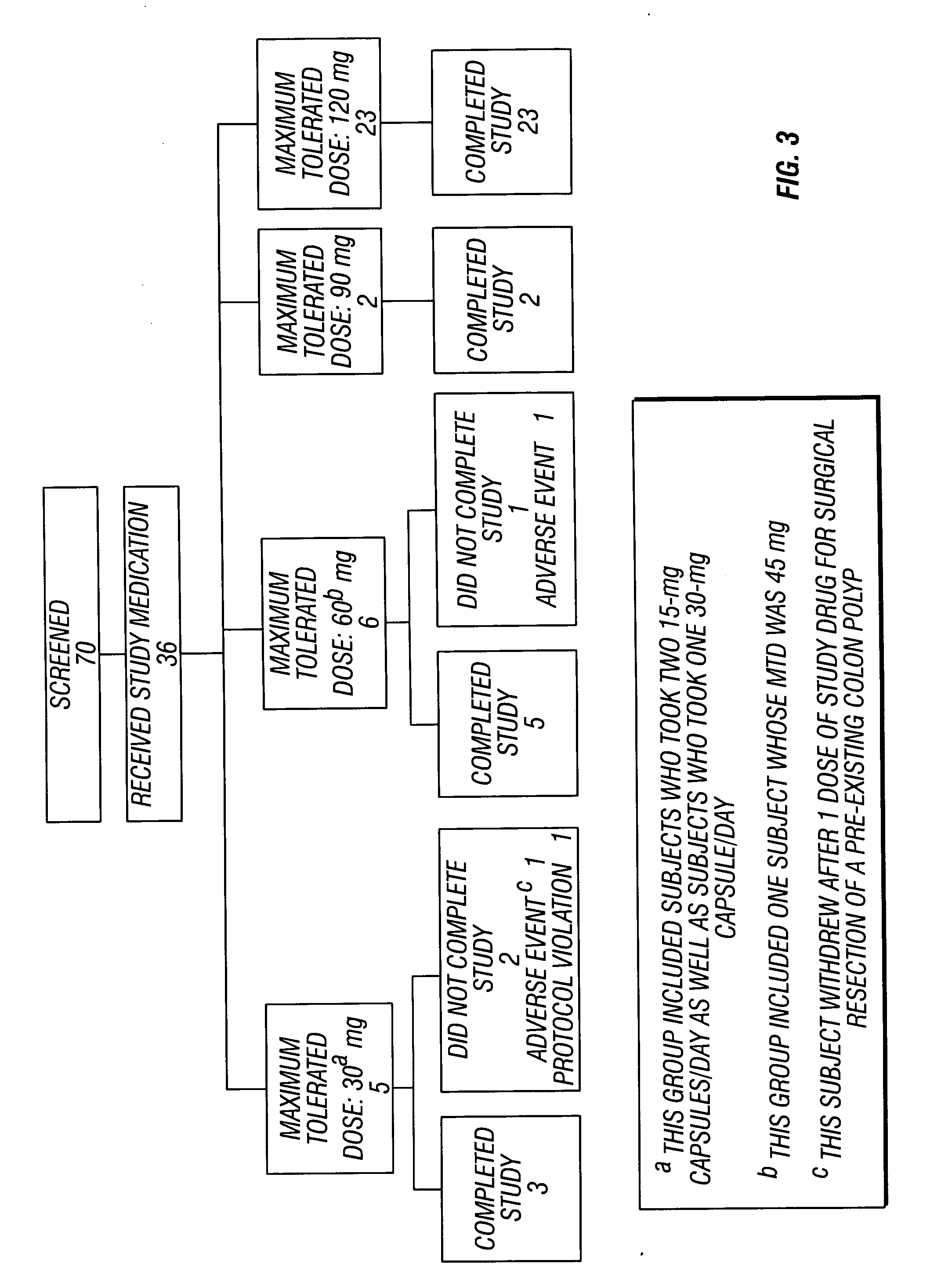
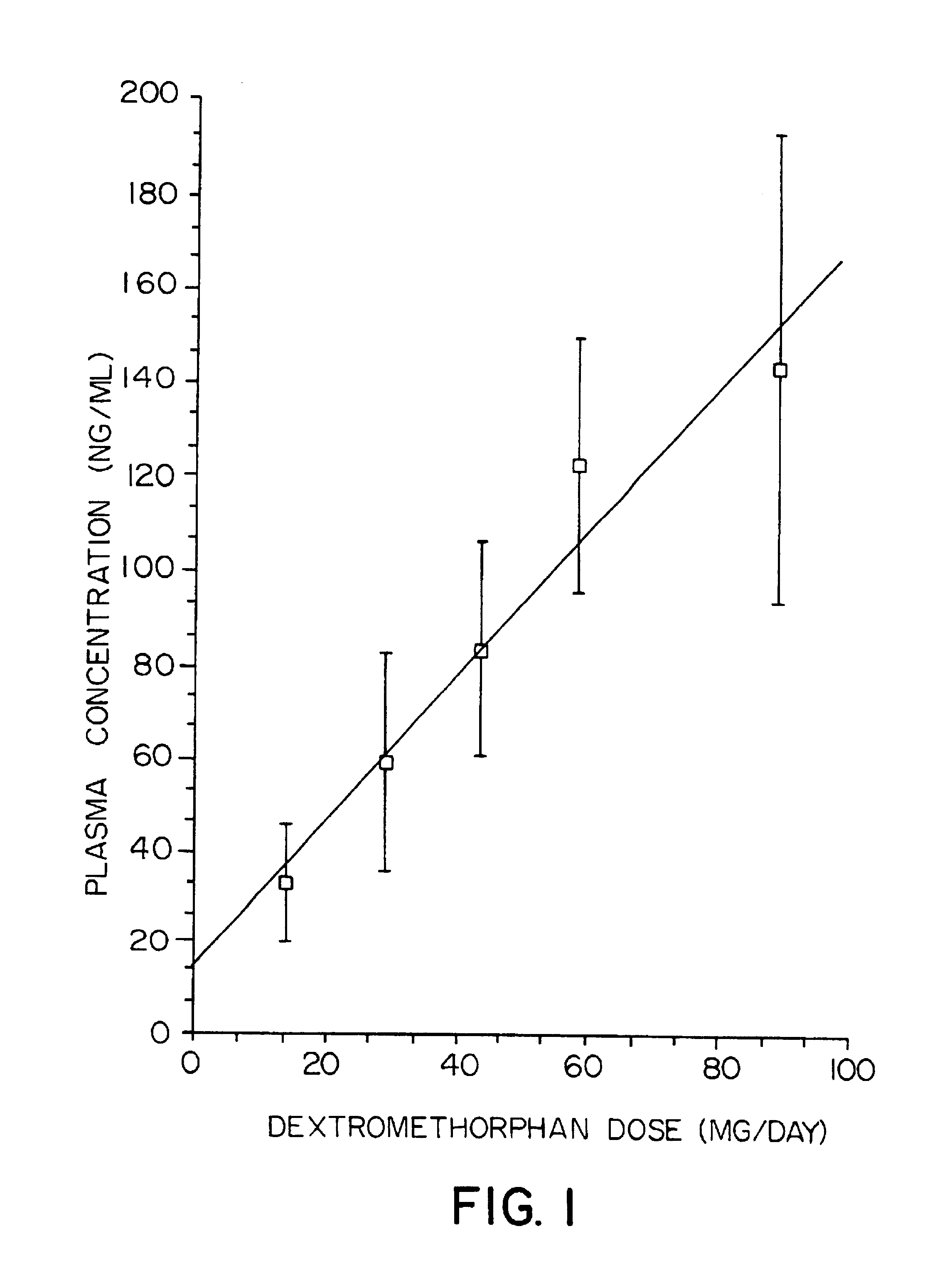
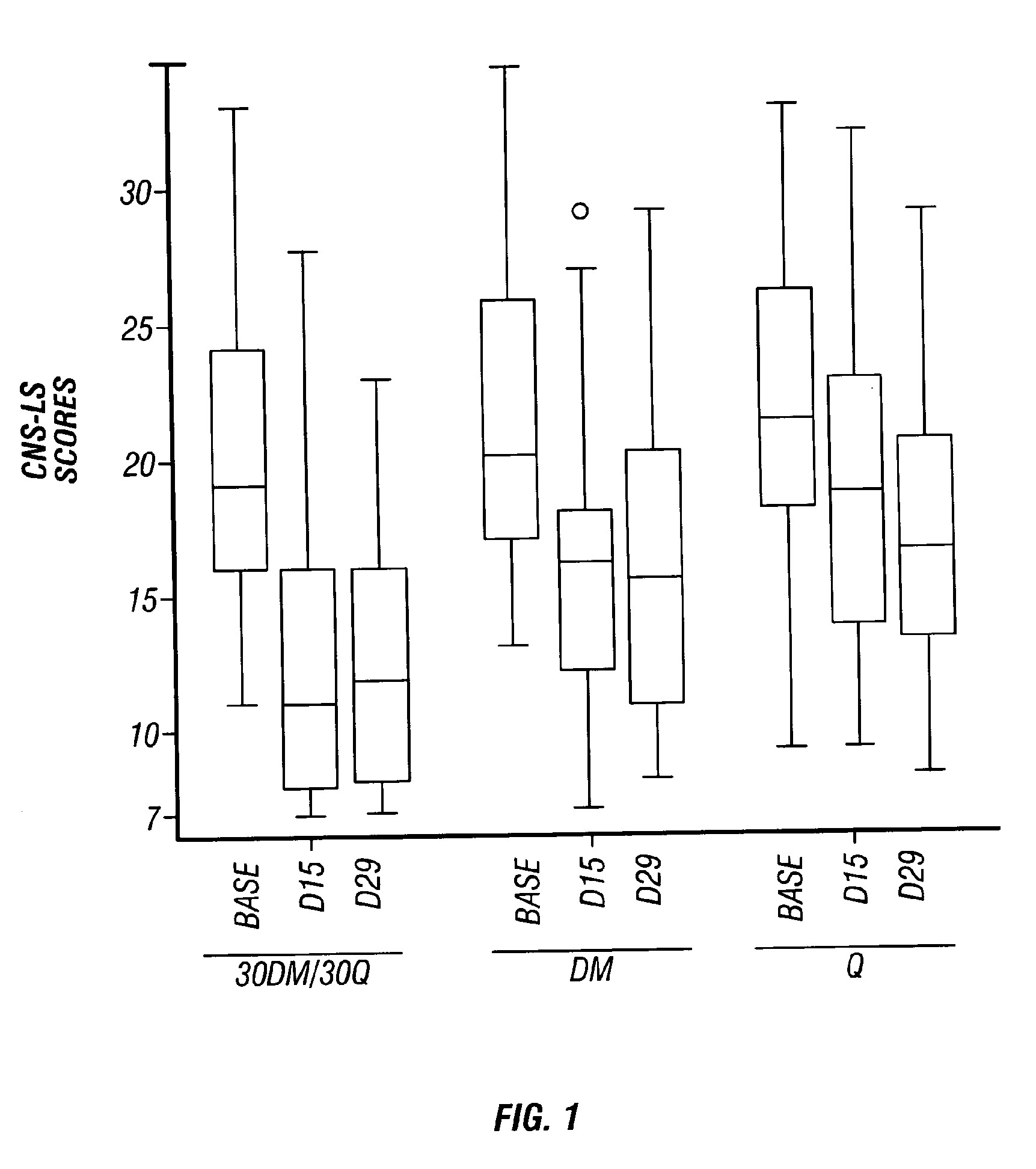
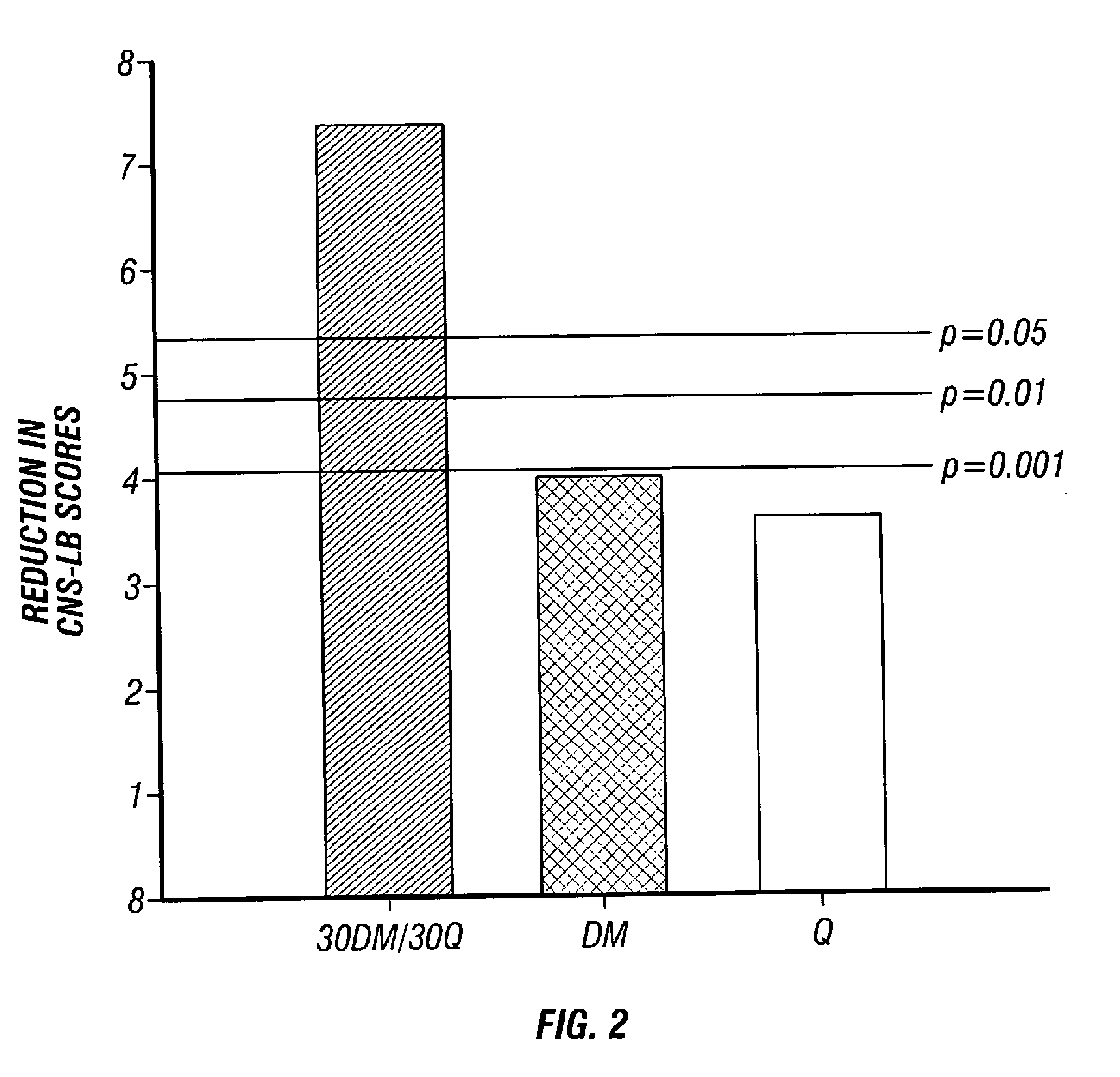
Method of reducing CNS and gastrointestinal side affects associated with long-term dextromethorphan/low-dose quinidine combination therapy
InactiveUS20110212987A1Reduce gastrointestinal side effectsRelieve nauseaBiocideNervous disorderSide effectQuinidine
Pharmaceutical compositions and methods for treating neurological disorders by administering same are provided. The compositions comprise dextromethorphan in combination with quinidine. This invention also provides methods of reducing CNS and gastrointestinal side effects associated with a long term, dextromethorphan / low-dose quinidine combination therapy.
Owner:AVANIR PHARMA
Pharmaceutical Compositions Comprising Dextromethorphan and Quinidine for the Treatment of Depression, Anxiety, and Neurodegenerative Disorders
Pharmaceutical compositions and methods for treating depression, anxiety, and neurodegenerative diseases and cognitive disorders, such as dementia and Alzheimer's disease, by administering same are provided. The compositions comprise dextromethorphan in combination with quinidine.
Owner:AVANIR PHARMA
Industrialized production method for efficiently extracting, separating and purifying serial cinchona alkaloid from cinchona bark
InactiveCN102558169AGood extraction recoverySuitable for large-scale industrial productionOrganic chemistryAntipyreticFood additiveBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention discloses a method for preparing serial cinchona alkaloid with effects of malaria resistance, arrhythmia resistance and the like by adopting cinchona bark as a raw material. The method utilizes advanced ultrasonic cell disruption and extraction, simple extraction separation and high-purity column purification process to generate quinine sulfate, quinidine, cinchonidine and cinchonine, of which the purities are all higher than 99.5%. Compared with the traditional method, the method has higher extraction recovery and environment-friendly and low-carbon process flow, and is better applicable to industrial mass production of active ingredients at the grade of GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice and food additives).
Owner:江苏斯威森生物医药工程研究中心有限公司
Method for synthesizing cinchona alkaloids microwave radiation non-solvent
InactiveCN101245063AQuick responseMild reaction conditionsOrganic chemistryOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsSolvent freeDihydroquinine
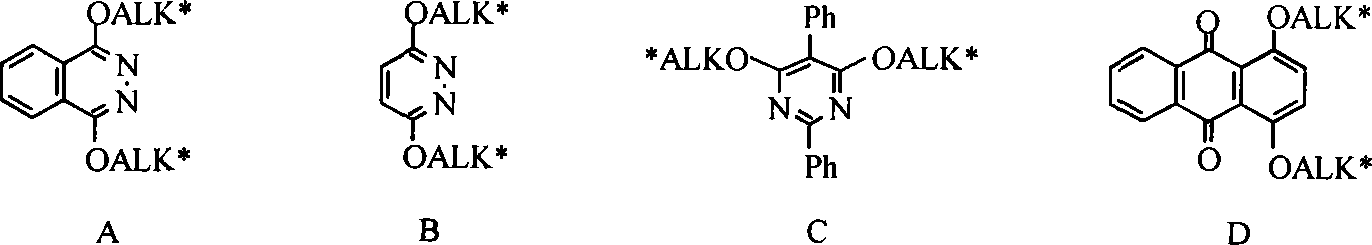
The invention discloses a method of the solvent-free synthesis of cinchona alkaloid derivatives by adopting microwave radiation with the catalysis of a phase transfer catalyst. According to the method of the invention, 1, 4-dichloro-2, 3-naphthyridine, 3, 6-dichloropyridazine, 4, 6-dichloropyrimidines, 2, 5-diphenyl-4, 6-dichloropyrimidines or phthalic acid can react with quinine, hydroquinine, quinidine, dihydro quinidine, cinchonine or cinchonidine according to a mol ratio of 1:3 to 3:1 to obtain the cinchona alkaloid derivatives. Under the action of microwave, the synthetic process of the cinchona alkaloid derivatives can become simple and safe in operation, short in reaction time, and mild in reaction condition; more particularly, toxic organic solvents such as methylbenzene and DMF with a high boiling point, etc. are not adopted in the course of the reaction, thus being in line with the megatrend of green chemistry, furthermore, monosubstituted products and disubstituted products can be obtained with high yield by the control of reaction time and power.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Process for preparing MeO-Peg-protected dihydroquinine or dihydroquinidine derivatives, new dihydroquinine or dihydroquinidine derivatives and their use
InactiveUS6180551B1Molecular sieve catalystsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsDihydroquinidineDihydroquinine
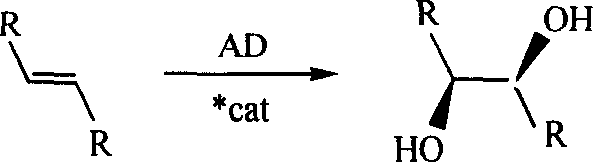
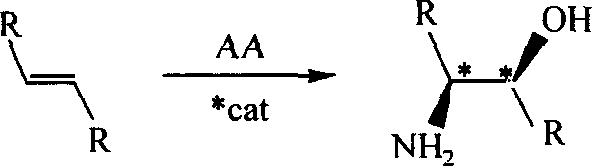
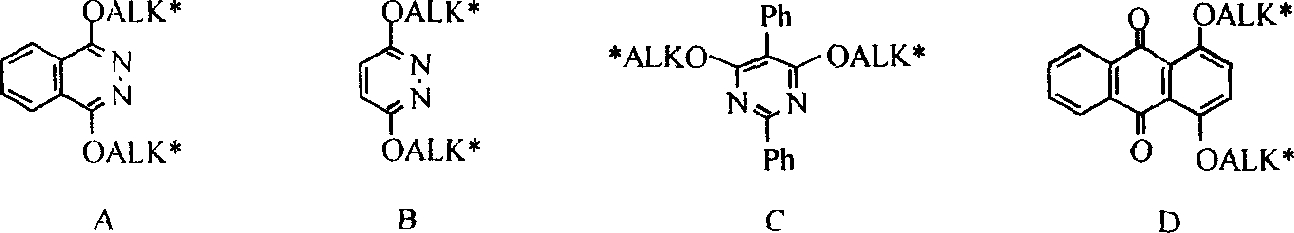
Process for the formation of MeO-Peg-protected dihydroquinine or dihydro quinindine derivatives, new dihydroquinine-or dihyroquinidine derivatives as well as the use thereof. It is known that dihydroquinine or dihydroquinidine derivatives can be successfully used as ligands in the enantioselective dihydroxylation. The new disclosed ligand systems based on dihydroquinine / quinidine, unlike the prior art ligands, can be recycled after enantioselective dihydroxylation by precipitating and filtering the reaction medium, and be reused in the reaction medium. Also disclosed are the ligand systems (I) and (IV), process for preparing the same and their use in the enantioselective dihydroxiation of double bonds.
Owner:DEGUSSA AG
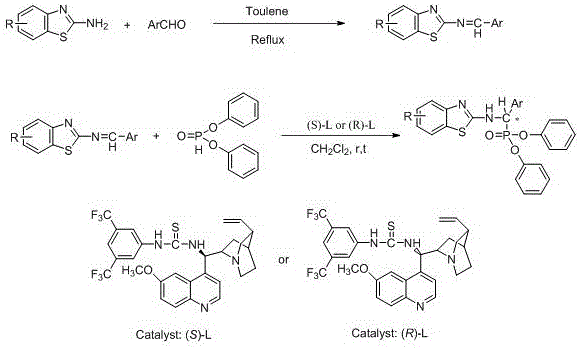
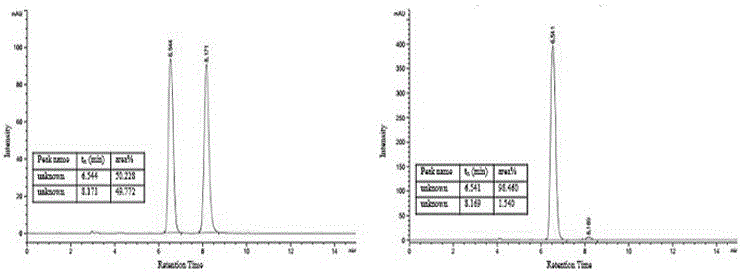
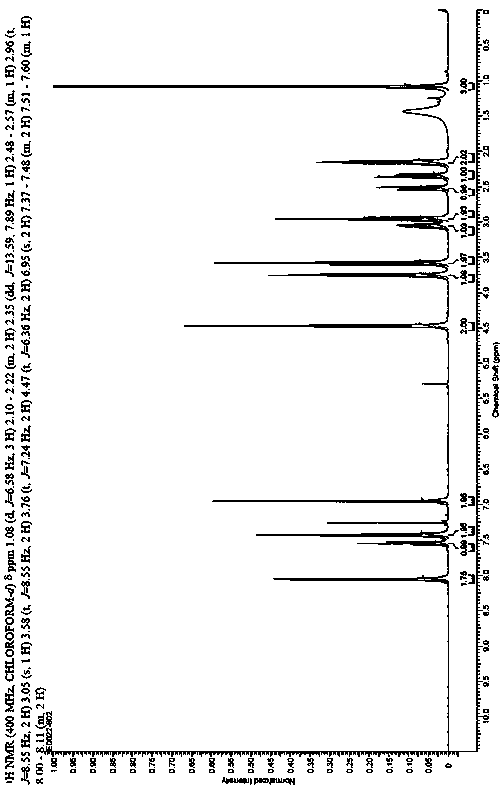
Chiral alpha-amino phosphonate ester compounds having anti-virus activity and containing benzothiazole heterocycle, preparation and applications thereof
ActiveCN104987350ARaw materials are easy to getMild reaction conditionsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsDisinfectantsTobacco mosaic virusThiourea
The present invention discloses a class of chiral alpha-amino phosphonate ester compounds having anti-virus activity and containing benzothiazole heterocycle, preparation and applications thereof, wherein the structure of the compound is represented by the following general formula (I). According to the present invention, thiourea or thiourea quinidine is adopted as a chiral catalyst, a 4A molecular sieve is adopted as a cocatalyst, and dichloromethane is adopted as solvent to rapidly synthesize the high yield and high optical activity chiral alpha-amino phosphonate ester compound containing benzothiazole heterocycle at a room temperature; and especially treatment, protection and activity passivation of the compound R-4h on cucumber mosaic virus are superior to the commercial agent ningnanmycin, treatment, protection and activity passivation of the compound R-4q on tobacco mosaic virus are superior to the commercial agent ningnanmycin, and the compounds R-4h and R-4q provide good inhibition effects on tobacco mosaic virus (TMV), cucumber mosaic virus (CMV), Southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus (SRBSDV) and the like, have good universality, and can be used for anti-plant virus chiral pesticide preparation. The formula (1) is defined in the specification.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
A kind of preparation method for the indoline derivative of synthetic silodosin
ActiveCN106380438BHigh optical purityChemical cost reductionOrganic chemistryBenzoic acidPalladium on carbon
Owner:江苏宇田医药有限公司
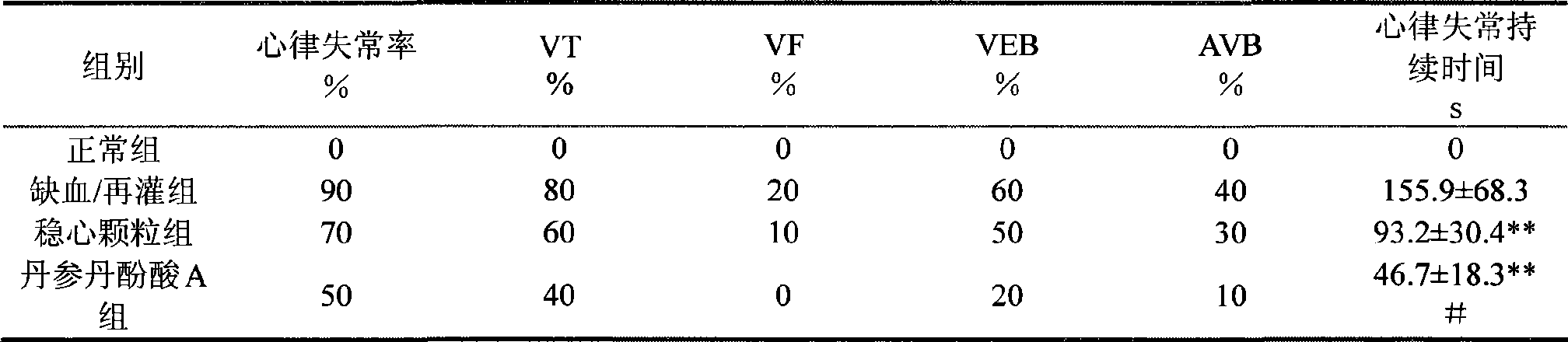
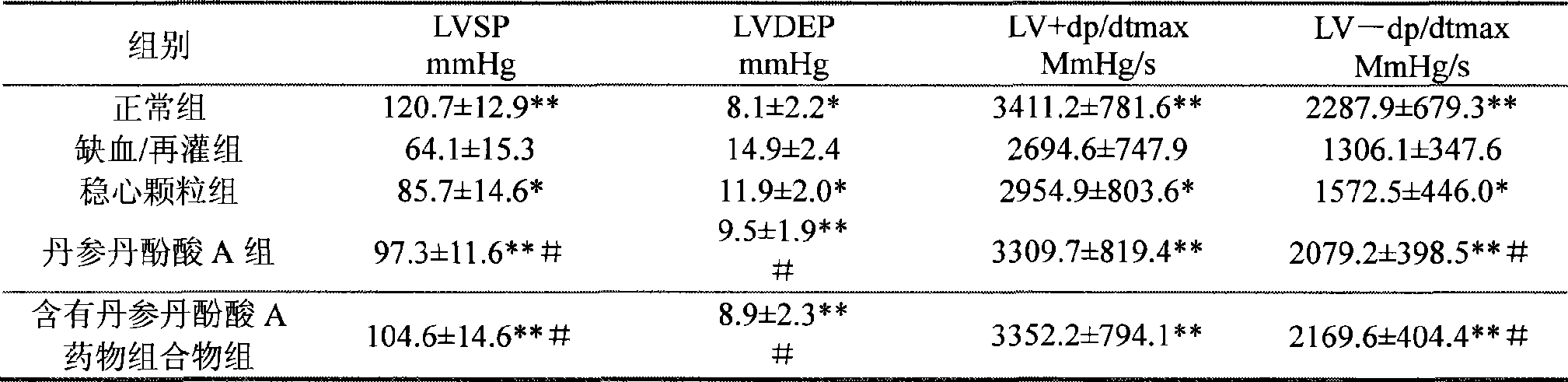
Use of salvianolic acid A and medicine composition thereof from Salia miliiorrhiza Bge.
The present invention discloses salvianolic acid A and a novel use of pharmaceutical composition comprising salvianolic acid A. The invention is characterized by the application of salvianolic acid A in preparing the medicament for treating arrhythmia, and the application of pharmaceutical composition composed of salvianolic acid A, ginseng, ophiopogon root, cornus officinalis, quinidine, lignocaine, etc. in preparing the medicament for treating arrhythmia. The pharmaceutical and clinical researches show that the salvianolic acid A and pharmaceutical composition comprising salvianolic acid A have excellent treating function for arrhythmia.
Owner:PHARMA RES INST OF BENCAO TIANYUAN OF BEIJING
Acid absorbing agent for preparing cinchona alkaloids ligand
InactiveCN1733762ASimple and fast operationQuantitatively accurateOrganic chemistryDihydroquinidineQuinidine
The invention discloses the use of CaH2 in synthesizing cinchona alkaloid ligand, wherein the ligand has a structure disclosed in the specification. CaH2 can be used as the acid binder in synthesizing cinchona alkaloid ligand. monosubstituted product or disubstituted product including hydroquinine, Quinidine, Dihydroquinidine and their derivatives.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Quinidine conjugates and their use in immunoassays
InactiveUS6140530ACarbamic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationQuinidineImmunogenicity
This invention relates to quinidine derivatives and immunogenic conjugates and reporter conjugates prepared therefrom. The immunogenic conjugates and reporter conjugates are useful for eliciting antibodies and for performing immunoassays for quinidine. A particle agglutination immunoassay for quinidine is also provided.
Owner:DADE BEHRING
Dextromethorphan quinidine orally disintegrating tablet and application thereof
ActiveCN114469882AEasy to swallowGood taste masking effectOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderUse medicationOrally disintegrating tablet
The invention provides a dextromethorphan quinidine orally disintegrating tablet as well as a preparation method and application of the dextromethorphan quinidine orally disintegrating tablet. The flavoring agent is added into the orally disintegrating tablet, so that the problem that dextromethorphan and quinidine are extremely bitter and numb in taste is solved, the prepared orally disintegrating tablet is easy to disintegrate, the problem that patients suffering from nervous system diseases are difficult to swallow is solved, and meanwhile, the medication experience of the patients is greatly improved. Meanwhile, the dextromethorphan quinidine orally disintegrating tablet provided by the invention is simple in preparation process and suitable for industrial mass production.
Owner:BEIJING JITAI PHARM TECH CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com