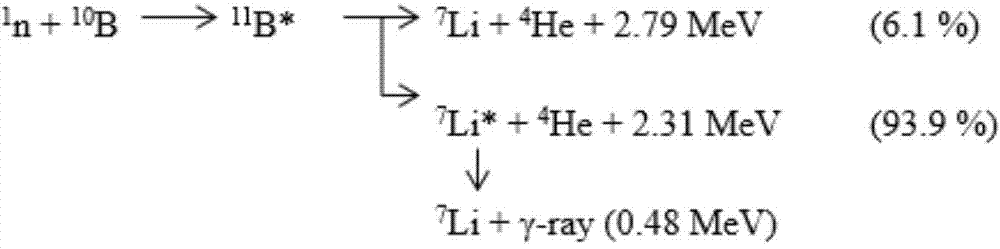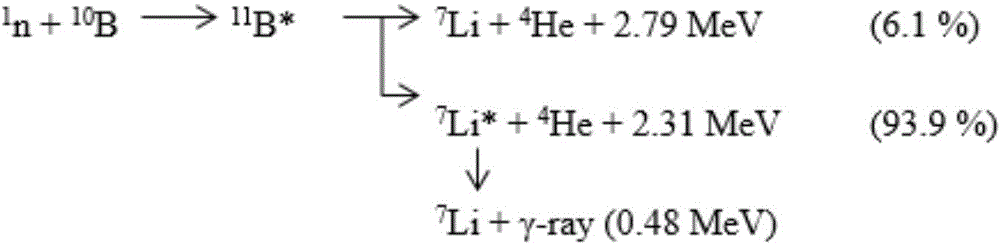Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1491 results about "Radiation shield" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
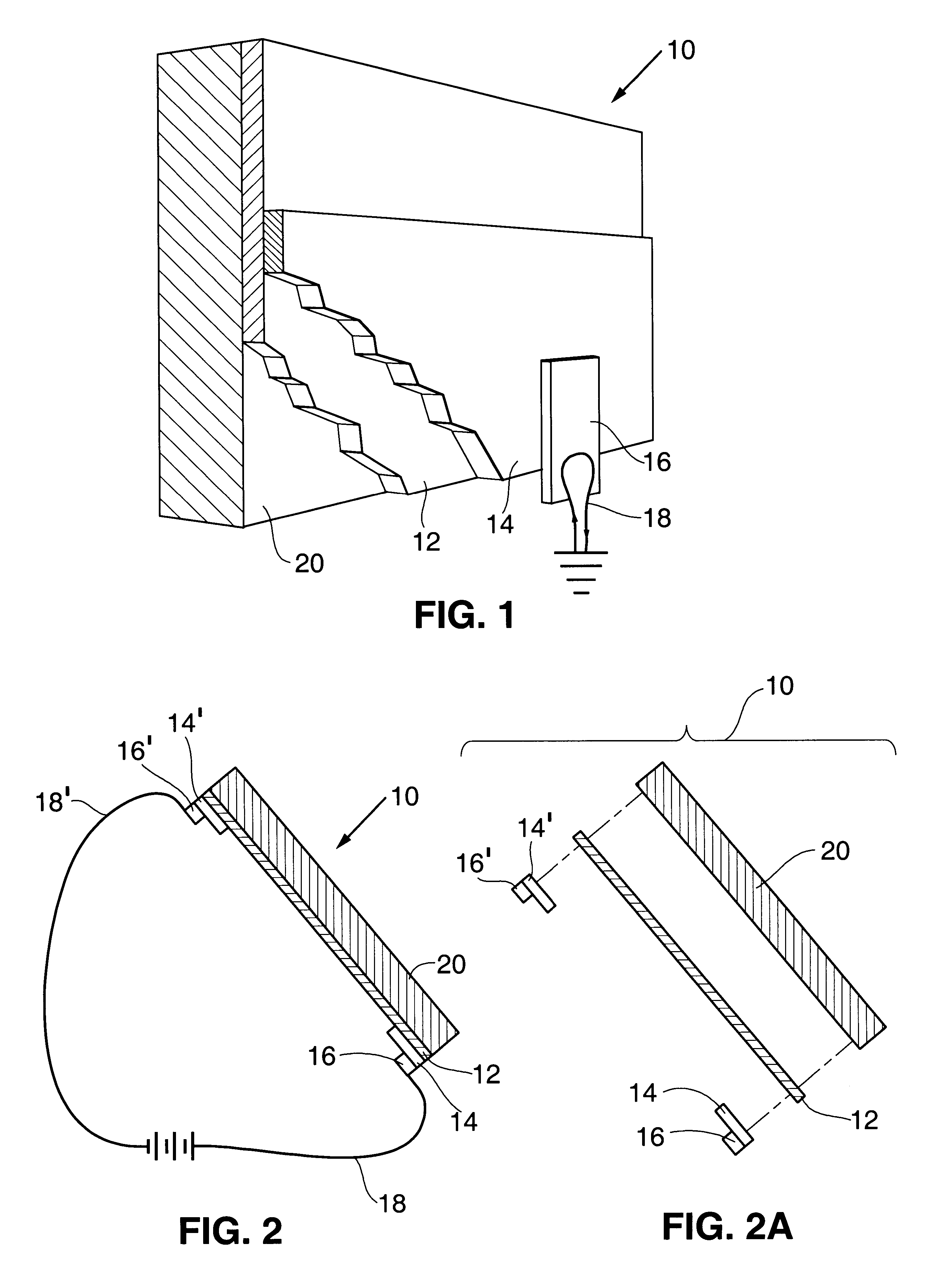
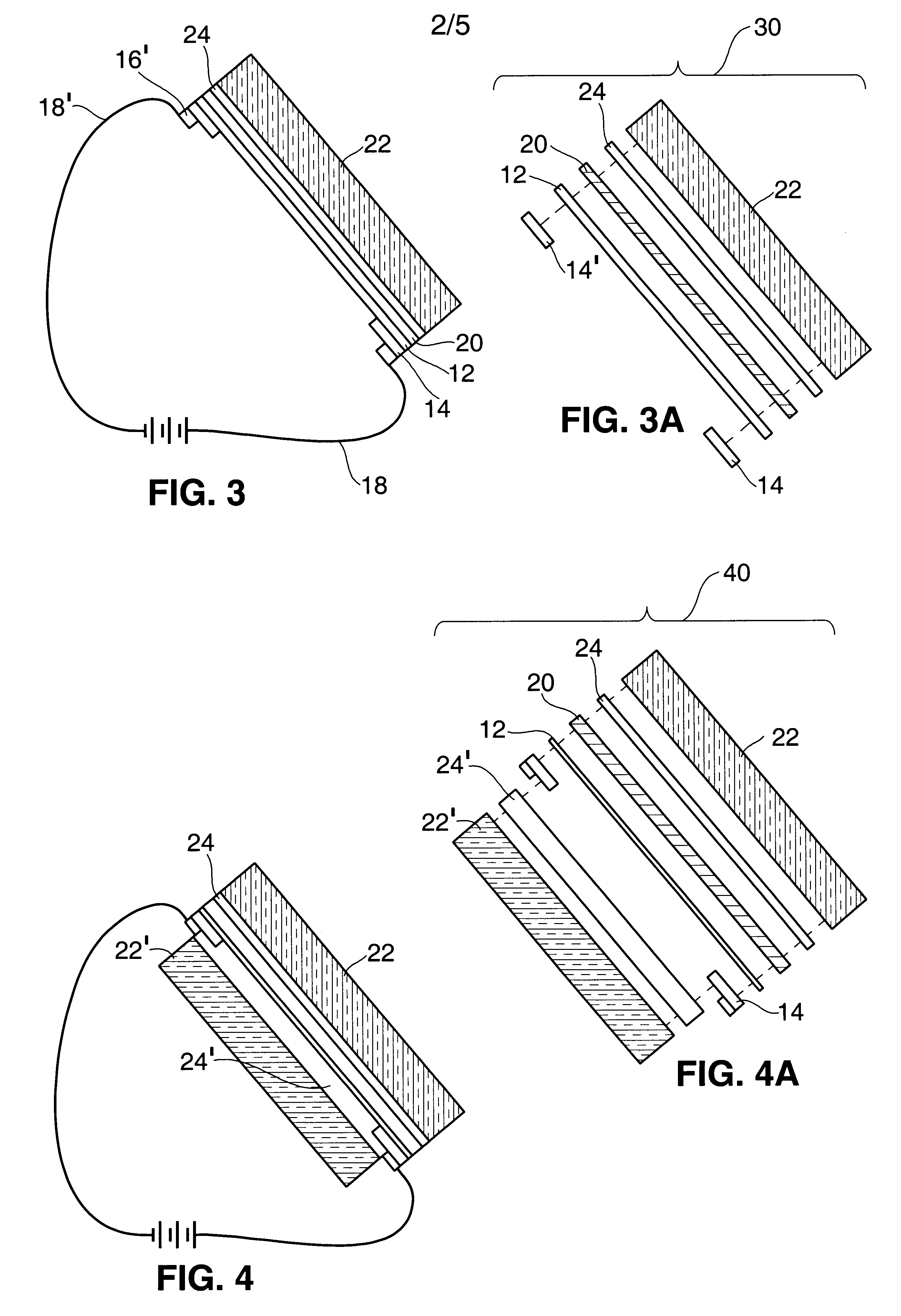
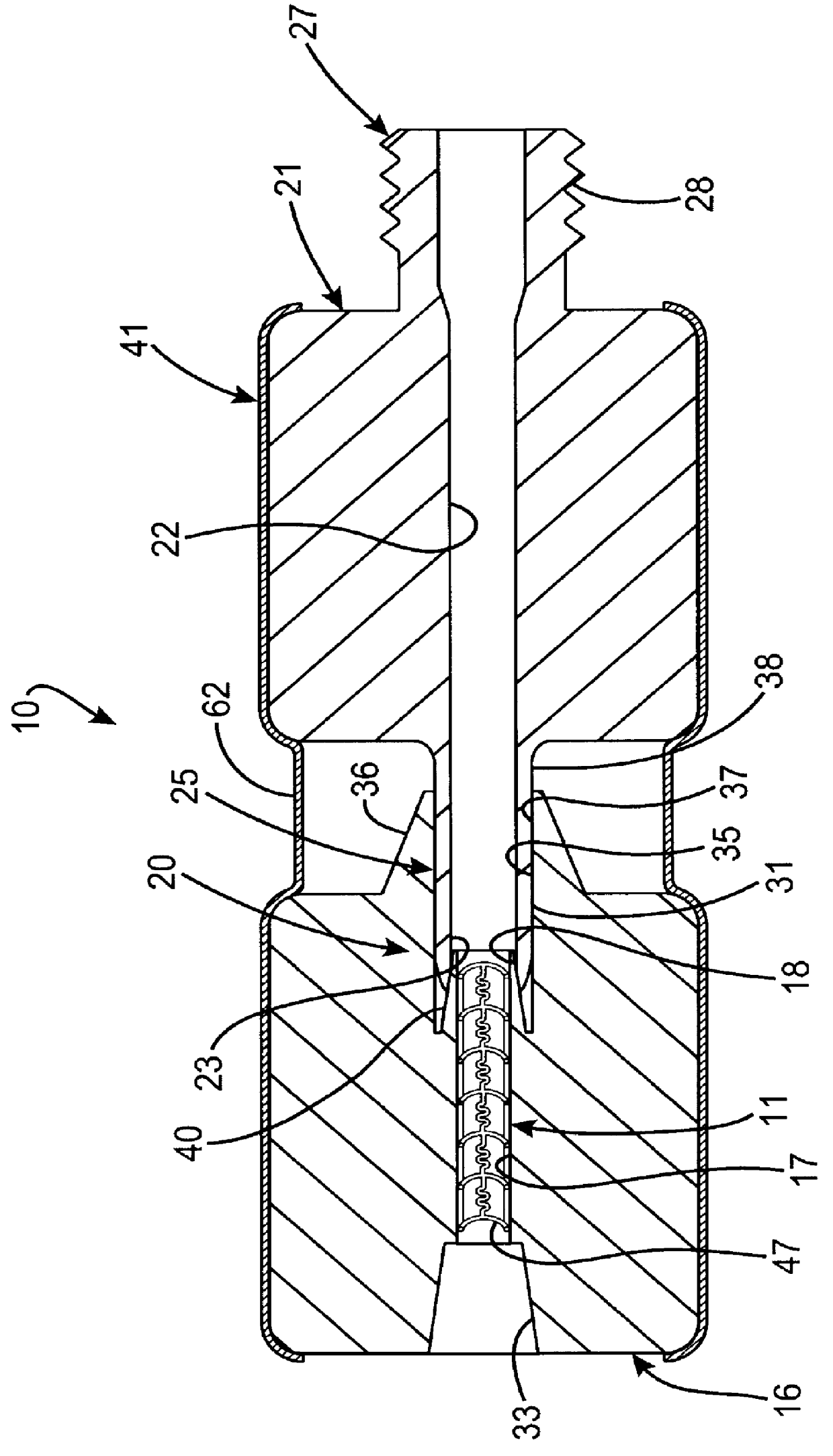
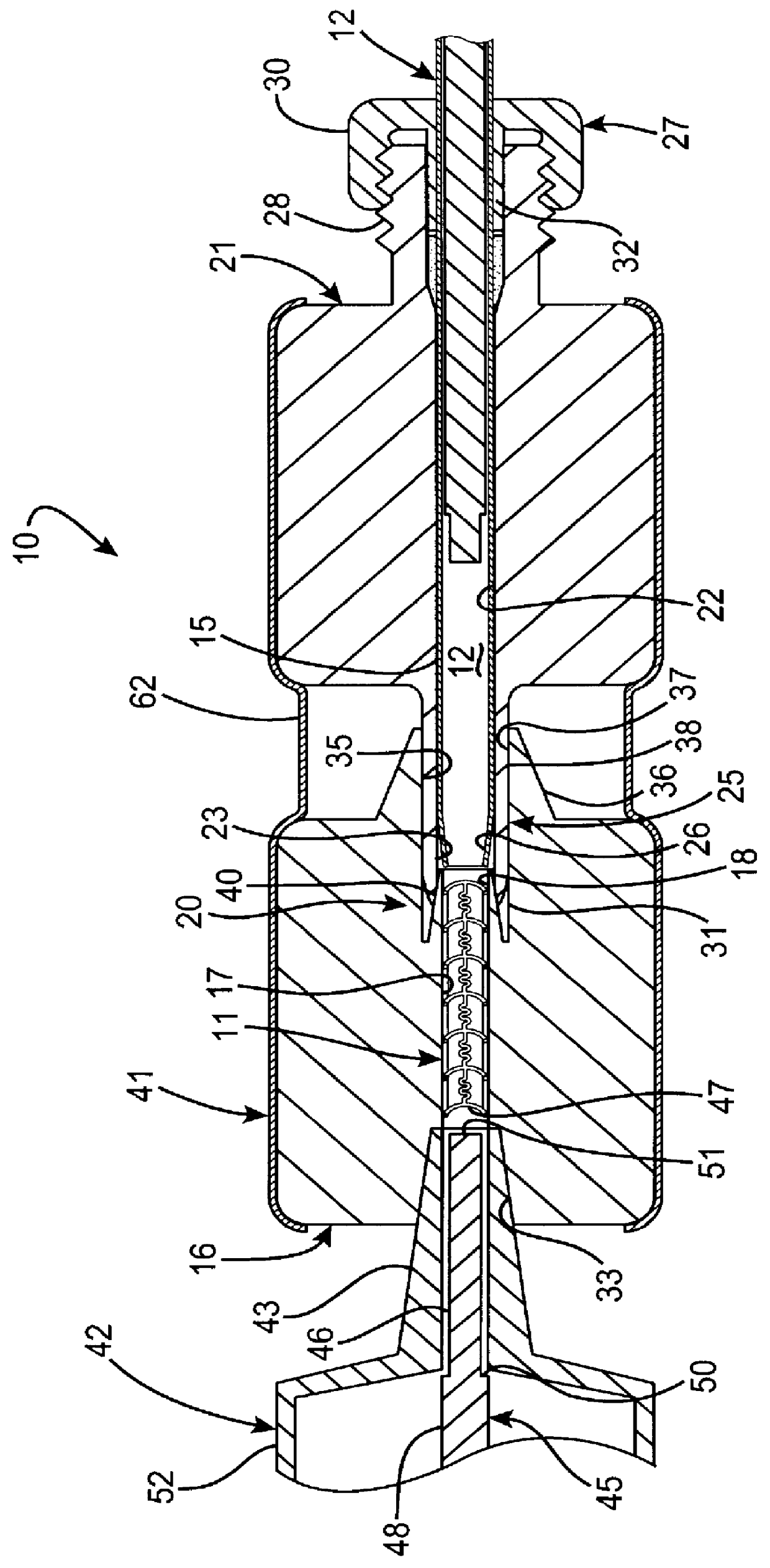
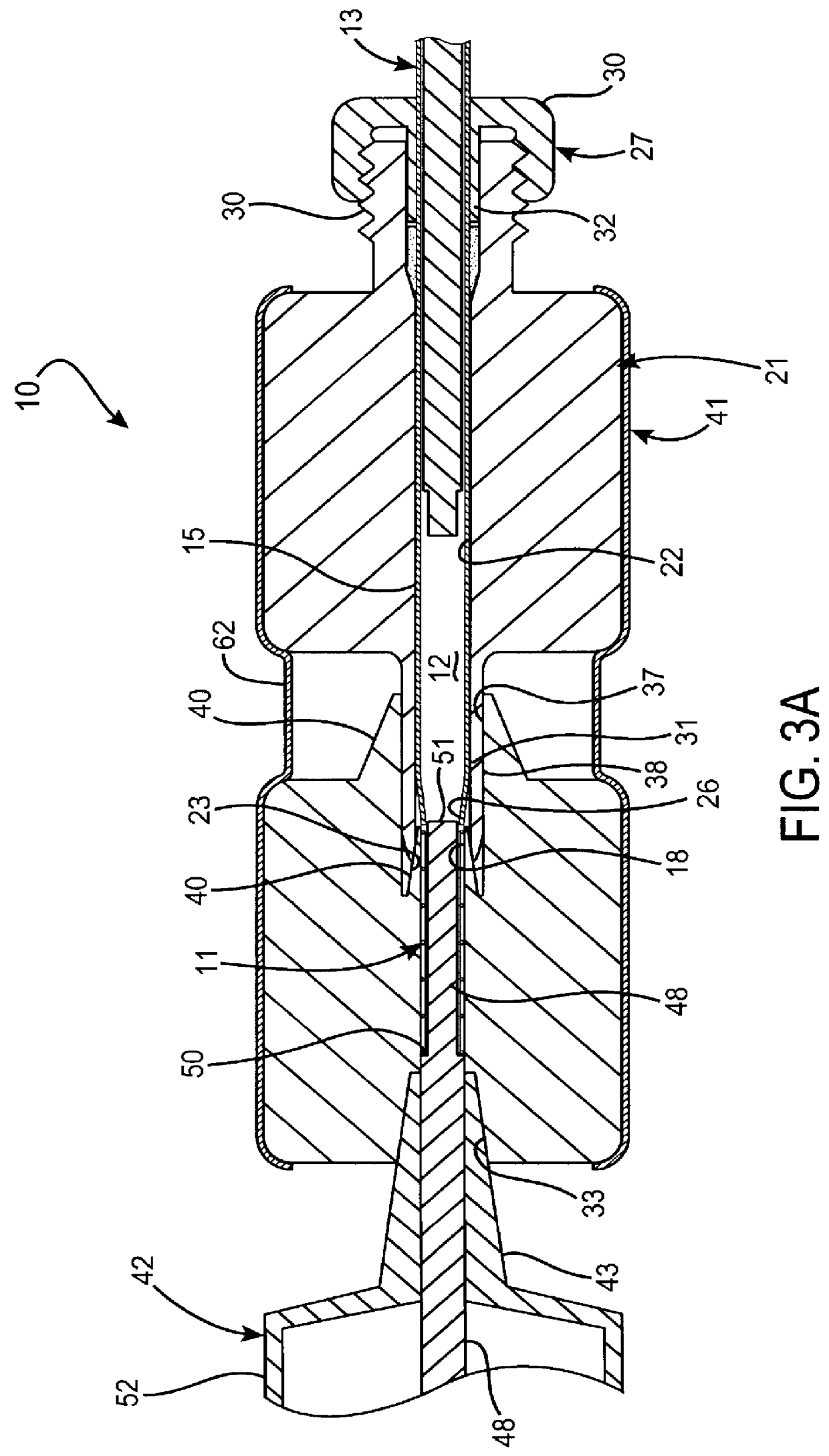
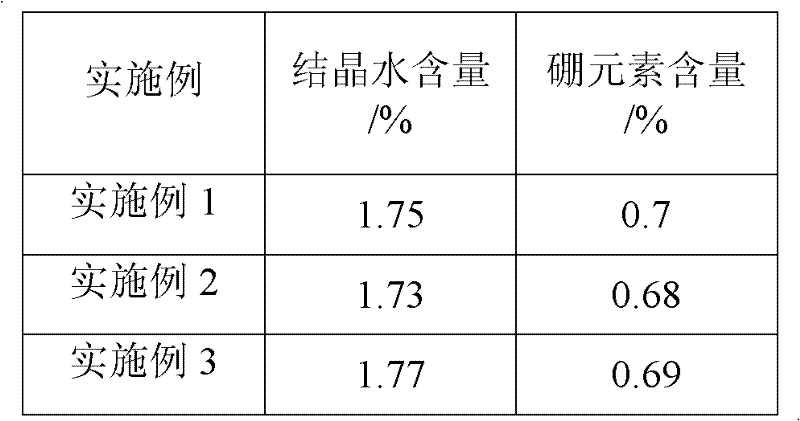
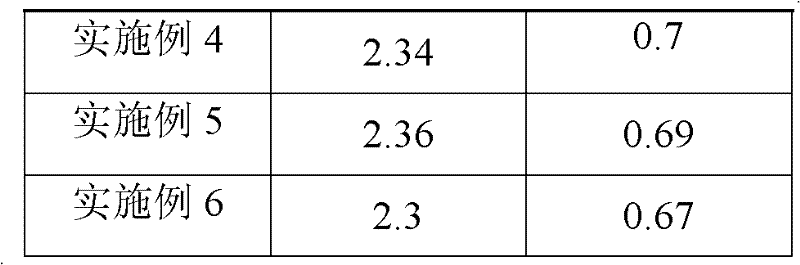
Radiation shield
ActiveUS20190051544A1Reduce heat fluxQuality improvementGaseous chemical processesElectric discharge tubesSusceptorHeat flux
A radiation shield and an assembly and a reactor including the radiation shield are disclosed. The radiation shield can be used to control heat flux from a susceptor heater assembly and thereby enable better control of temperatures across a surface of a substrate placed on a surface of the susceptor heater assembly.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Radiant shield
InactiveUS20080314892A1Thermometer detailsDrying solid materials with heatTemperature controlMetallurgy
A radiant shield and a furnace employing a radiant shield for controlled heating and treatment of material using infrared radiation. The furnace is capable of improved temperature control where material treated by the furnace may interfere with the quality of a measured temperature signal and temperature control based on that signal.
Owner:DESPATCH INDS
Self-contained, portable inspection system and method
InactiveUS6843599B2Rapidly deployableCost-effectively and accurately on uneven surfaceX-ray apparatusMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationComputer moduleEngineering
The inspection methods and systems of the present invention are mobile, deployable, and capable of scanning a wide variety of receptacles cost-effectively and accurately on uneven surfaces. The inspection system comprises an inspection module that, in a preferred embodiment, is in the form of a mobile trailer capable of being towed and transported to its intended operating site with the help of a tug-vehicle. The tug-vehicle preferably includes at least one source of electromagnetic radiation, a hydraulic lift system to load and unload the radiation source, and at least one radiation shield plate positioned on the back of the driver cabin of the tug-vehicle.
Owner:RAPISCAN SYST INC (US)
Vacuum deposition of bus bars onto conductive transparent films
InactiveUS6204480B1Suitable for processingWindowsConductive layers on insulating-supportsElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrical connection
Vacuum deposition processes such as sputter-depositing are employed to deposit electrically conductive bus bars onto thin film transparent conductor sheets. These assemblies provide efficient and durable electrical connections to the conductor sheets which can be laminated into glazing structures such as automotive windshields to provide resistance heating for defogging and deicing or the provide an electrical connection for in-window antennas and in window radiation shields.
Owner:SOUTHWALL TECH INC
Dispensing and injection system for radiopharmaceuticals
InactiveUS20050203329A1Enhanced Radiation ProtectionEasy to effect automatic controlIn-vivo radioactive preparationsInfusion devicesSaline waterRadiation shield
Disclosed is a dispensing and injection system for radiopharmaceuticals, wherein a dosage calibrator is arranged inside a radiation-shielded hermetic chamber for detecting the radioactivity of radiopharmaceuticals contained in a vial. At least one saline water cartridge is arranged inside the casing and includes an internal passage, radiopharmaceuticals discharge end, a radiopharmaceuticals injection end, a and saline water reservoir outlet end. The saline water cartridge forms a saline water reservoir. A movable dispensing and injection mechanism controls radiopharmaceuticals dispensing operation of a syringe and controls movement of the syringe between a radiopharmaceuticals dispensing position and an injection position. When the movable dispensing and injection mechanism moves the syringe to the radiopharmaceuticals dispensing position, the syringe withdraws a predetermined amount of radiopharmaceuticals from the vial. When moved to the injection position, the syringe injects the withdrawn radiopharmaceuticals into the radiopharmaceuticals injection end of the saline water cartridge. After the radiopharmaceuticals is injected into a patient, the saline water stored in the saline water reservoir of the saline water cartridge is withdrawn for effecting flushing process.
Owner:SHIH CHI DAU
Shaped biocompatible radiation shield and method for making same
InactiveUS7109505B1Reduce low energy radiationPrevent regenerationRadiation/particle handlingElectrode and associated part arrangementsRadiosurgeryProximate
A radiation applicator system is structured to be mounted to a radiation source for providing a predefined dose of radiation for treating a localized area or volume, such as the tissue surrounding the site of an excised tumor. The applicator system includes an applicator and an adapter. The adapter is formed for fixedly securing the applicator to a radiation source, such as a radiosurgery system which produces a predefined radiation dose profile with respect to a predefined location along the radiation producing probe. The applicator includes a shank and an applicator head, wherein the head is located at a distal end of the applicator shank. A proximate end of the applicator shank couples to the adapter. A distal end of the shank includes the applicator head, which is adapted for engaging and / or supporting the area or volume to be treated with a predefined does of radiation. The applicator can include a low energy radiation filter inside of the applicator head to reduce undesirable low energy radiation emissions. A biocompatible radiation shield may be coupled to the outer surface of the applicator head to block radiation emitted from a portion of the radiation probe, in order to shield an adjacent location or vital organ from any undesired radiation exposure. A plurality of applicators having applicator heads and radiation shields of different sizes and shapes can be provided to accommodate treatment sites of various sizes and shapes.
Owner:CARL ZEISS STIFTUNG DOING BUSINESS CARL ZEISS
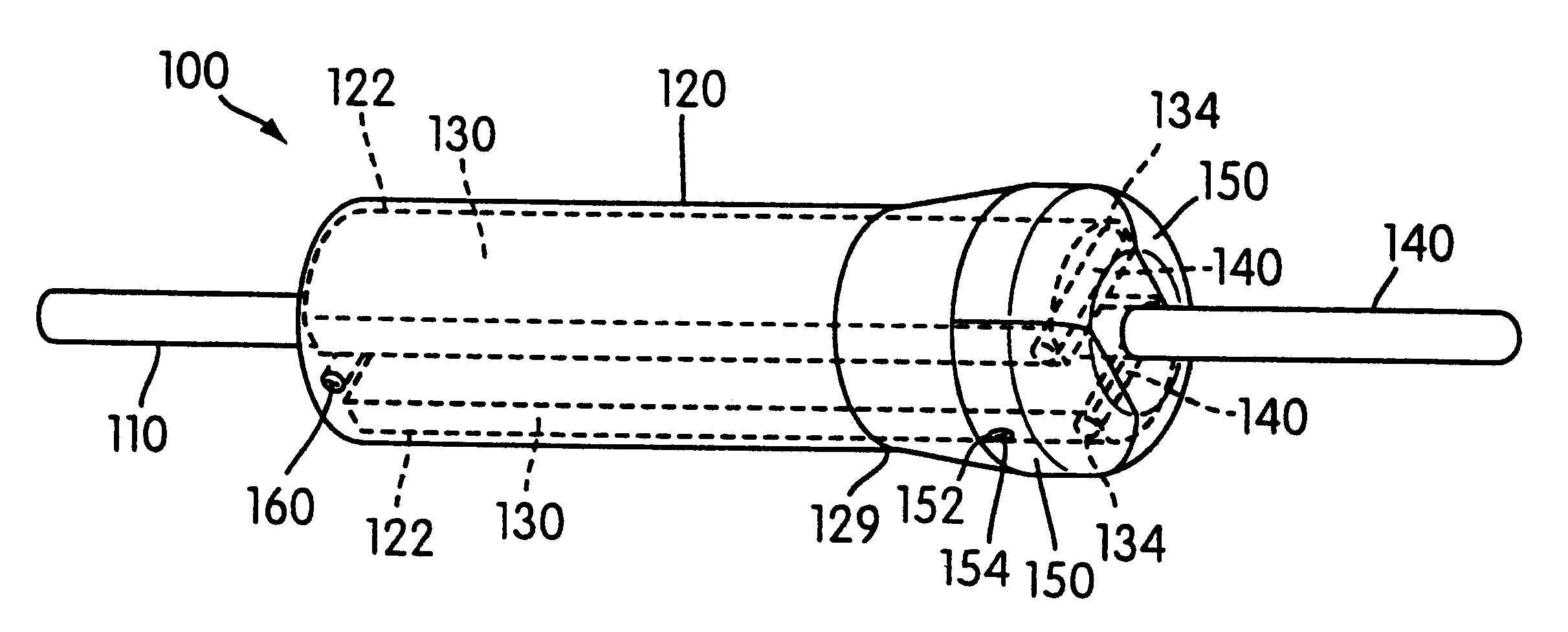
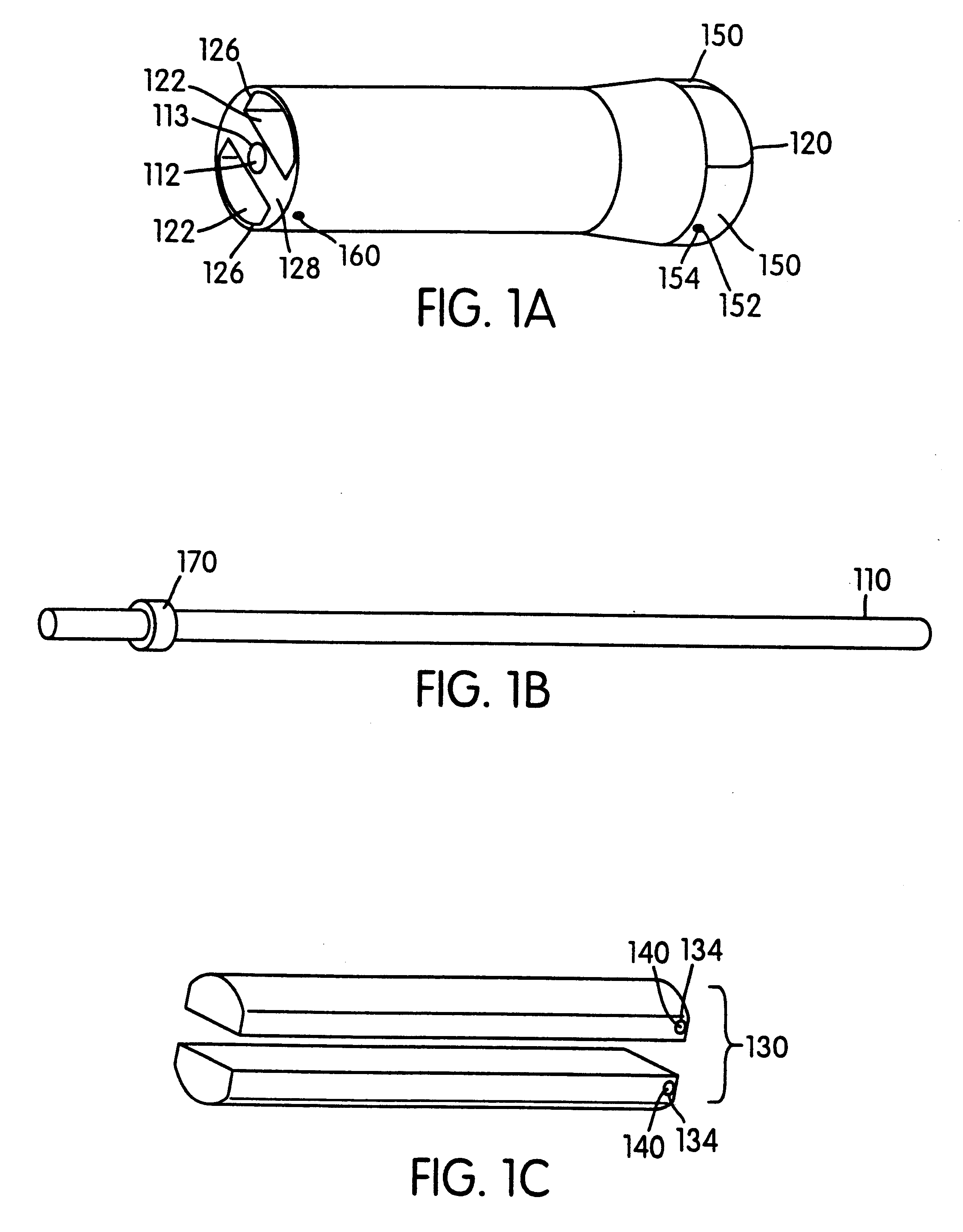
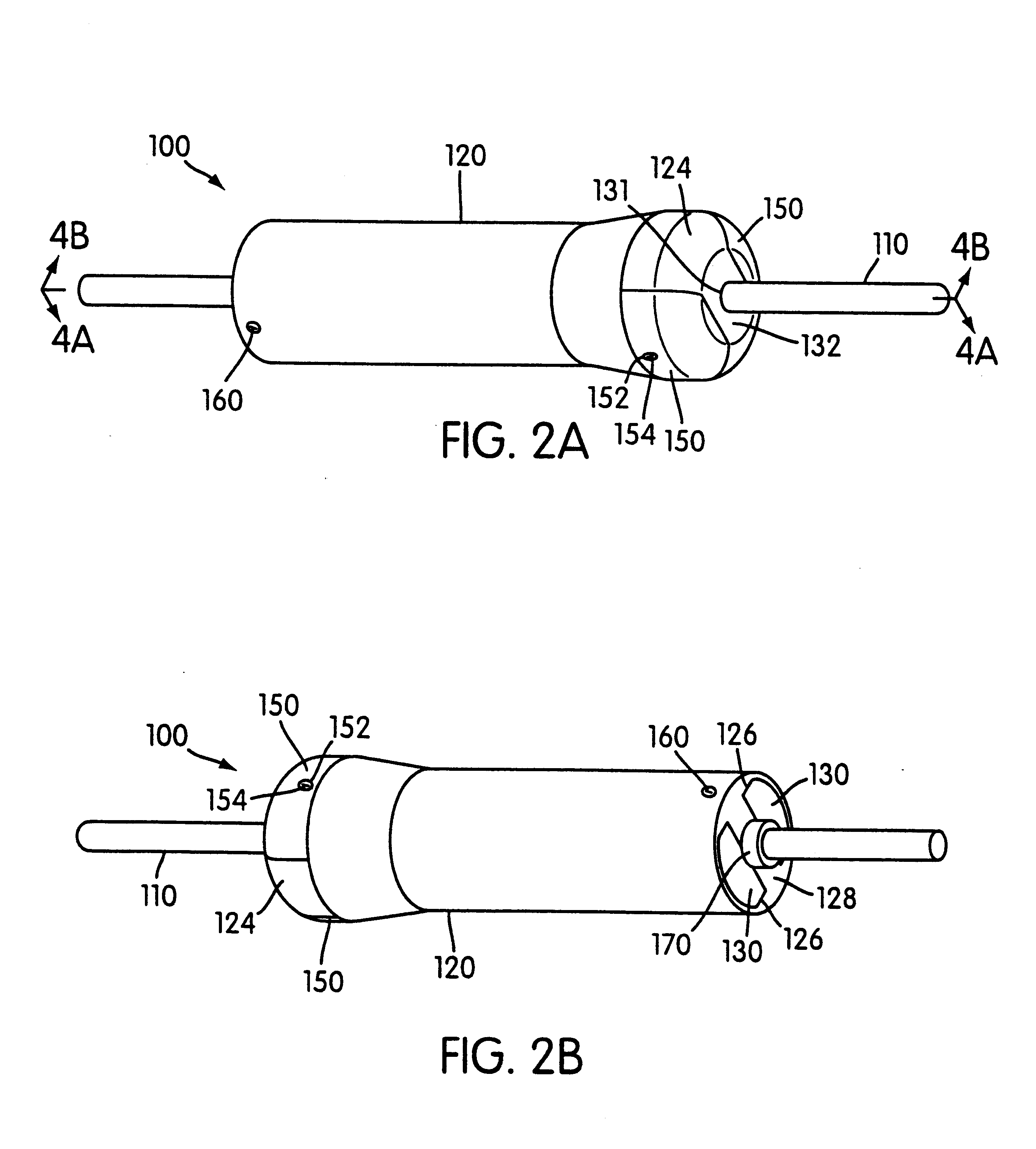
Cylindrical roller stent crimper apparatus with radiation shield
A stent loading apparatus for loading a deformable stent onto a deployment device. The stent loading apparatus includes an elastic member defining a passage therein formed for longitudinal receipt of the deformable stent in an uncrimped condition. A first member includes a first compression region; and a second member includes a second compression region positioned substantially adjacent the first compression region at a first position. At this first position, the elastic member and the deformable stent in the uncrimped condition may be received between the opposed first and second compression regions. The first compression region and the second compression region are further configured to provide rolling support and compression of the elastic member during relative movement between the first position and a second position for rolling radial compression of the deformable stent onto the deployment device.
Owner:ISOSTENT
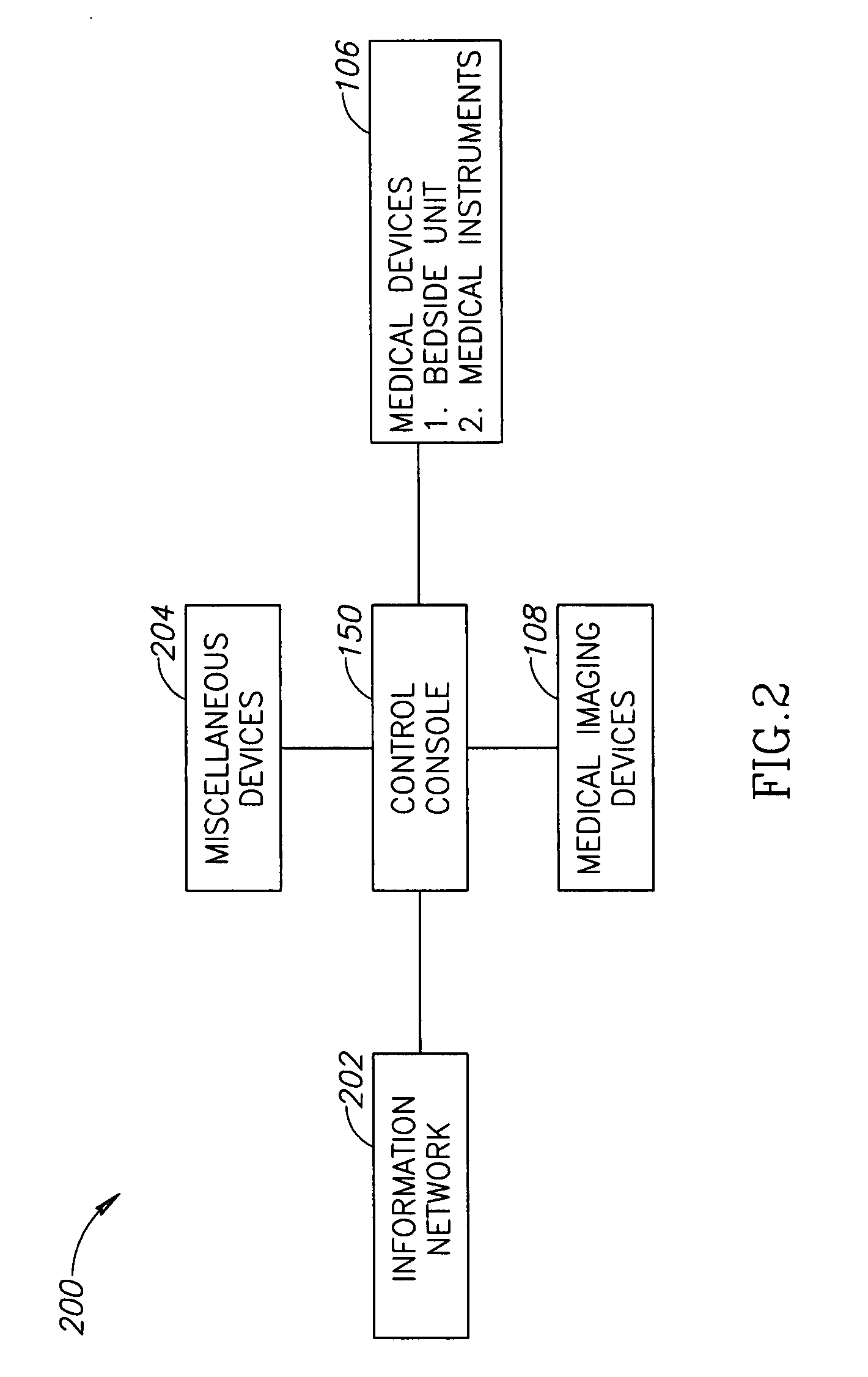
Protected control console apparatuses
ActiveUS20080217564A1Improve visibilityElectric signal transmission systemsElectrode and associated part arrangementsCommunication interfaceEngineering
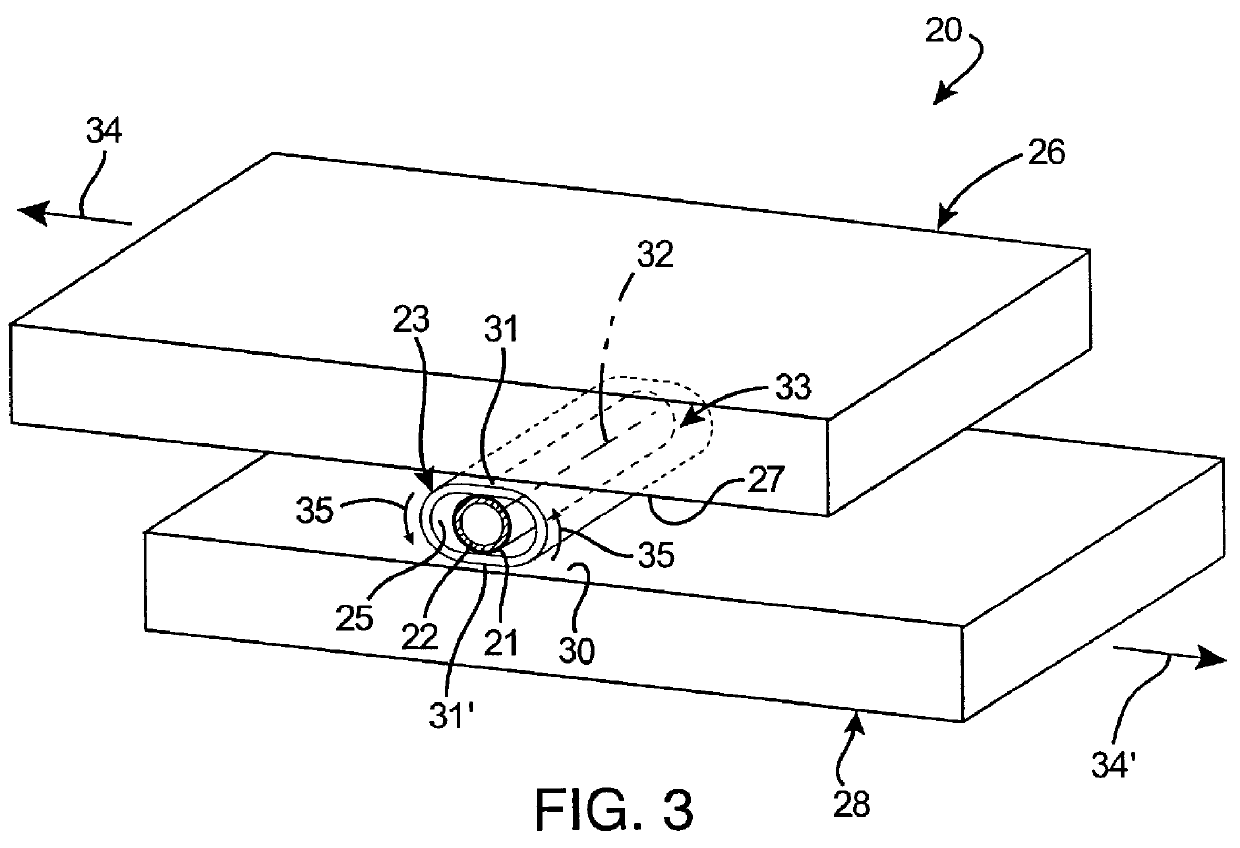
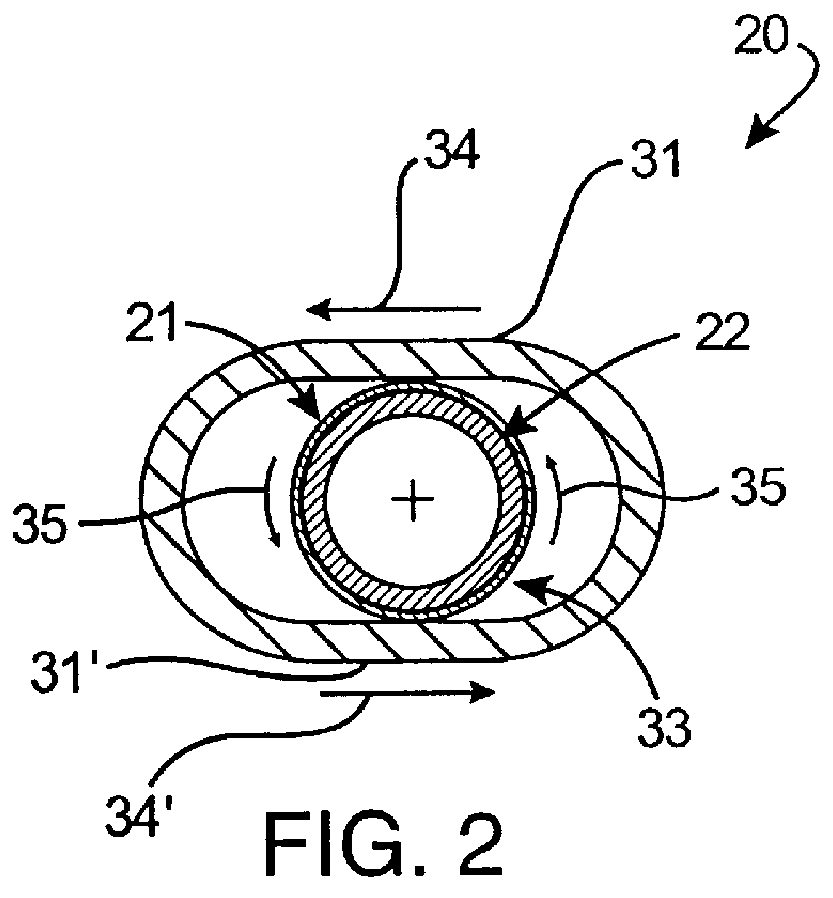
An apparatus for control of a procedure, comprising: a communications interface; a control console, wherein the control console is adapted to provide control commands via the communications interface to at least one of: at least one imaging device or at least one medical instrument used to perform the procedure; and, at least one radiation shield attached to the control console and positioned between the control console and a patient on which the procedure is being performed, wherein the apparatus is separately movable from at least one of the at least one imaging device, the patient or the at least one medical instrument.
Owner:CORINDUS
Stent loading assembly for a self-expanding stent
A stent loading apparatus for loading a self-expanding radioactive stent into a bore of a deployment device in a compressed condition including a storage device defining an elongated first passage formed and dimensioned for sliding receipt of the stent therein. The first passage extends through the storage device and terminates at a stent transfer opening of a proximal coupling end thereof. A radiation shield defines an elongated second passage which terminates at a distal opening of a distal coupling end thereof. The distal coupling end of the radiation shield and the proximal coupling end of the storage device cooperate to align the distal opening of the shield in receiving communication with the stent transfer opening of the storage device. The second passage of the shield is formed and dimensioned for receipt of the deployment device therein in a manner positioning a mouth of the deployment device bore substantially adjacent the stent transfer opening of the storage device. Upon urging of the stent in a direction toward the shield, the radioactive stent may be slideably transferred from the first passage and into the mouth of the bore for retainment therein in the compressed condition.
Owner:ISOSTENT
Deterministic computation of radiation doses delivered to tissues and organs of a living organism
InactiveUS20050143965A1Improve computing efficiencyHigh solution accuracyDosimetersComputation using non-denominational number representationInternal radiationIntensity modulation
Various embodiments of the present invention provide methods and systems for deterministic calculation of radiation doses, delivered to specified volumes within human tissues and organs, and specified areas within other organisms, by external and internal radiation sources. Embodiments of the present invention provide for creating and optimizing computational mesh structures for deterministic radiation transport methods. In general these approaches seek to both improve solution accuracy and computational efficiency. Embodiments of the present invention provide methods for planning radiation treatments using deterministic methods. The methods of the present invention may also be applied for dose calculations, dose verification, and dose reconstruction for many different forms of radiotherapy treatments, including: conventional beam therapies, intensity modulated radiation therapy (“IMRT”), proton, electron and other charged particle beam therapies, targeted radionuclide therapies, brachytherapy, stereotactic radiosurgery (“SRS”), Tomotherapy®; and other radiotherapy delivery modes. The methods may also be applied to radiation-dose calculations based on radiation sources that include linear accelerators, various delivery devices, field shaping components, such as jaws, blocks, flattening filters, and multi-leaf collimators, and to many other radiation-related problems, including radiation shielding, detector design and characterization; thermal or infrared radiation, optical tomography, photon migration, and other problems.
Owner:TRANSPIRE
Inverse ratio of gamma-ray and neutron emissions in the detection of radiation shielding of containers
InactiveUS7116235B2Reduce instabilityTrolley cranesX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentNeutron emissionGamma ray
Owner:VERITAINER ASSET HLDG LLC
Inverse ratio of gamma-ray and neutron emissions in the detection of radiation shielding of containers
InactiveUS20050275545A1Reduce instabilityTrolley cranesX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentNeutron emissionGamma ray
The presence of radiation shielding material concealing illegitimate content in a container is detected by obtaining each of measured gamma-ray data and measured neutron data from the container, and comparing the measured gamma-ray and neutron data to expected gamma-ray and neutron data. An anomaly between the measured data and the expected data is an indicum of the presence of such material shielding such illegitimate content.
Owner:VERITAINER ASSET HLDG LLC
Ionic shield for devices that emit radiation
InactiveUS20020089464A1Antenna supports/mountingsAntenna couplingsRadiation shieldCellular telephone
A radiation shield, for use in association with a device, such as a cellular telephone, having a radiation emitter, comprising a barrier positioned between a source of radiation and an object to be shielded, the barrier including means for converting radiation into ionic motion, to, in turn, dissipate the radiation and preclude the radiation from reaching an object to be shielded. The invention further comprises methods associated with the shielding of a user from radiation.
Owner:CERAMTEC
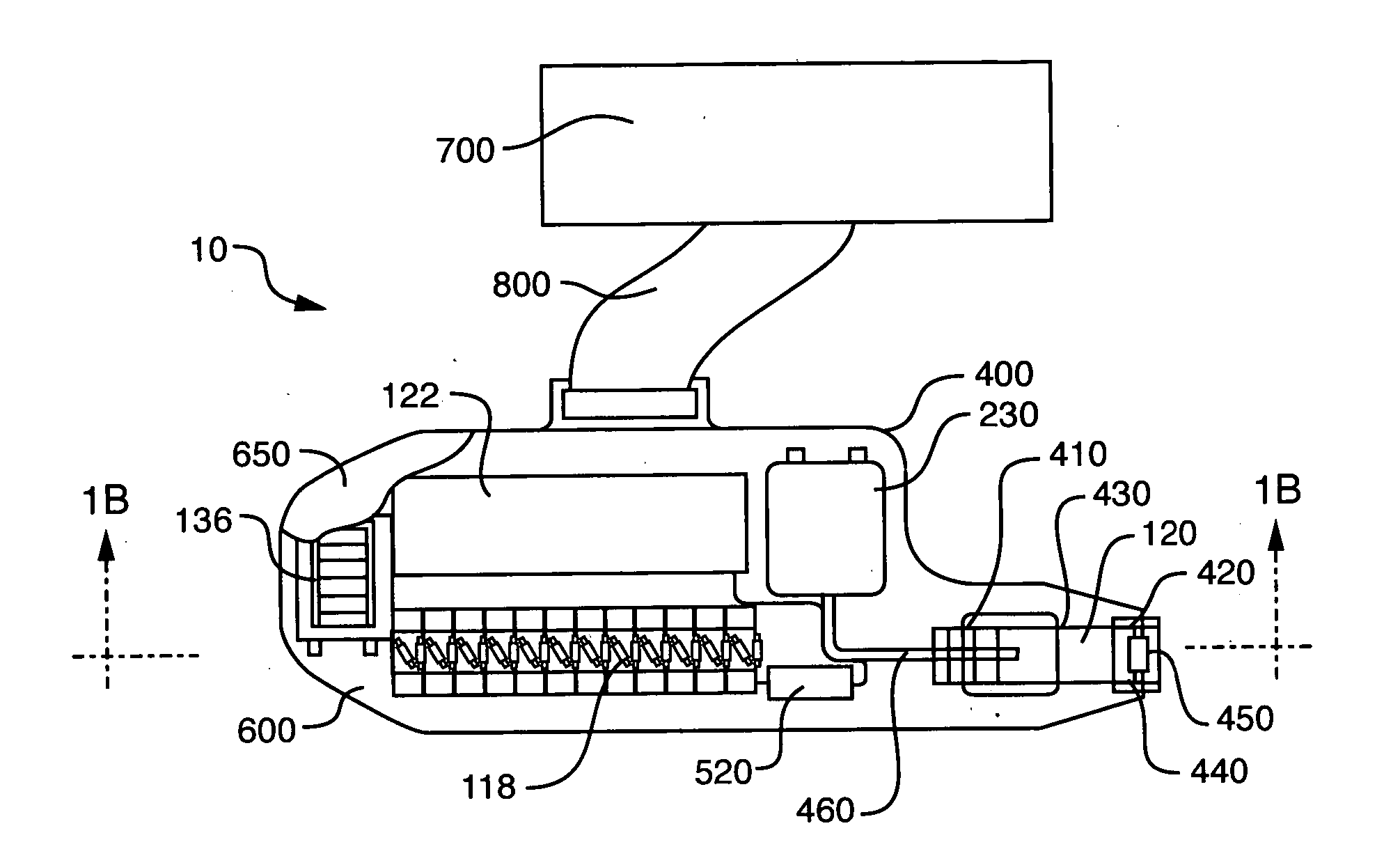
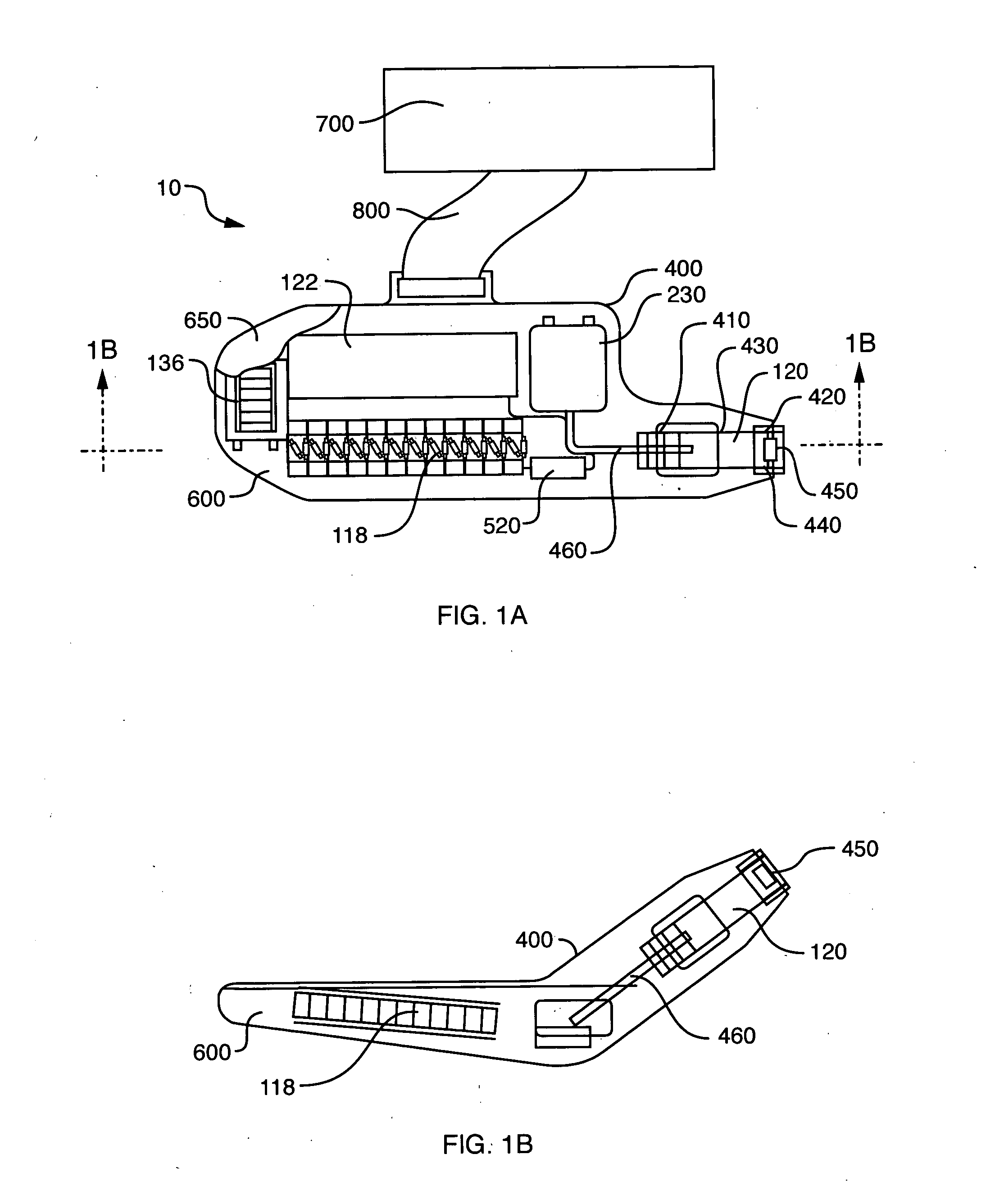
Integrated X-ray source module
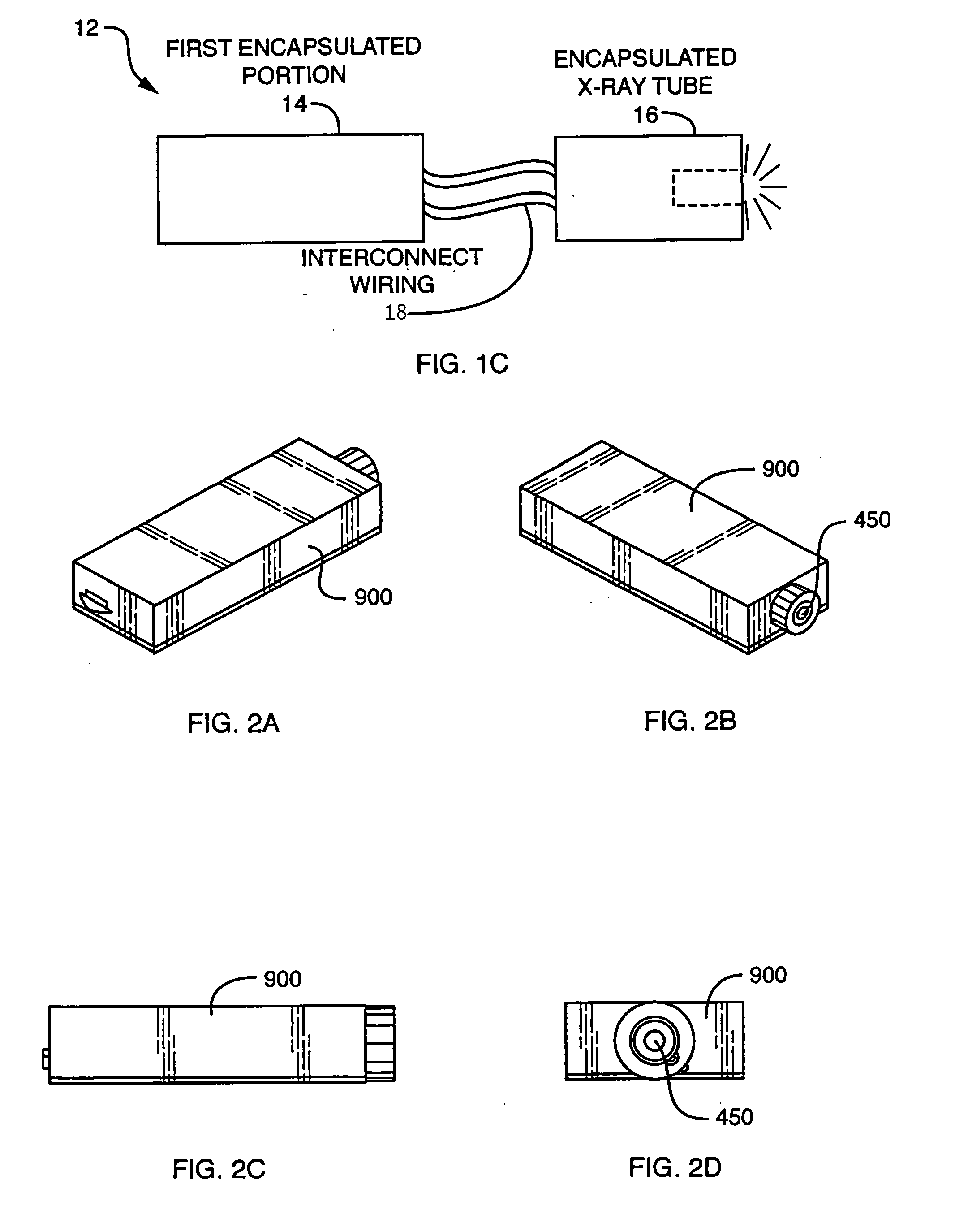
Described is a self-contained, small, lightweight, power-efficient and radiation-shielded module that includes a miniature vacuum X-ray tube emitting X-rays of a controlled intensity and defined spectrum. Feedback control circuits are used to monitor and maintain the beam current and voltage. The X-ray tube, high-voltage power supply, and the resonant converter are encapsulated in a solid high-voltage insulating material. The module can be configured into complex geometries and can be powered by commercially available small, compact, low-voltage batteries.
Owner:NEWTON SCI
Beam shaper for neutron-capture therapy
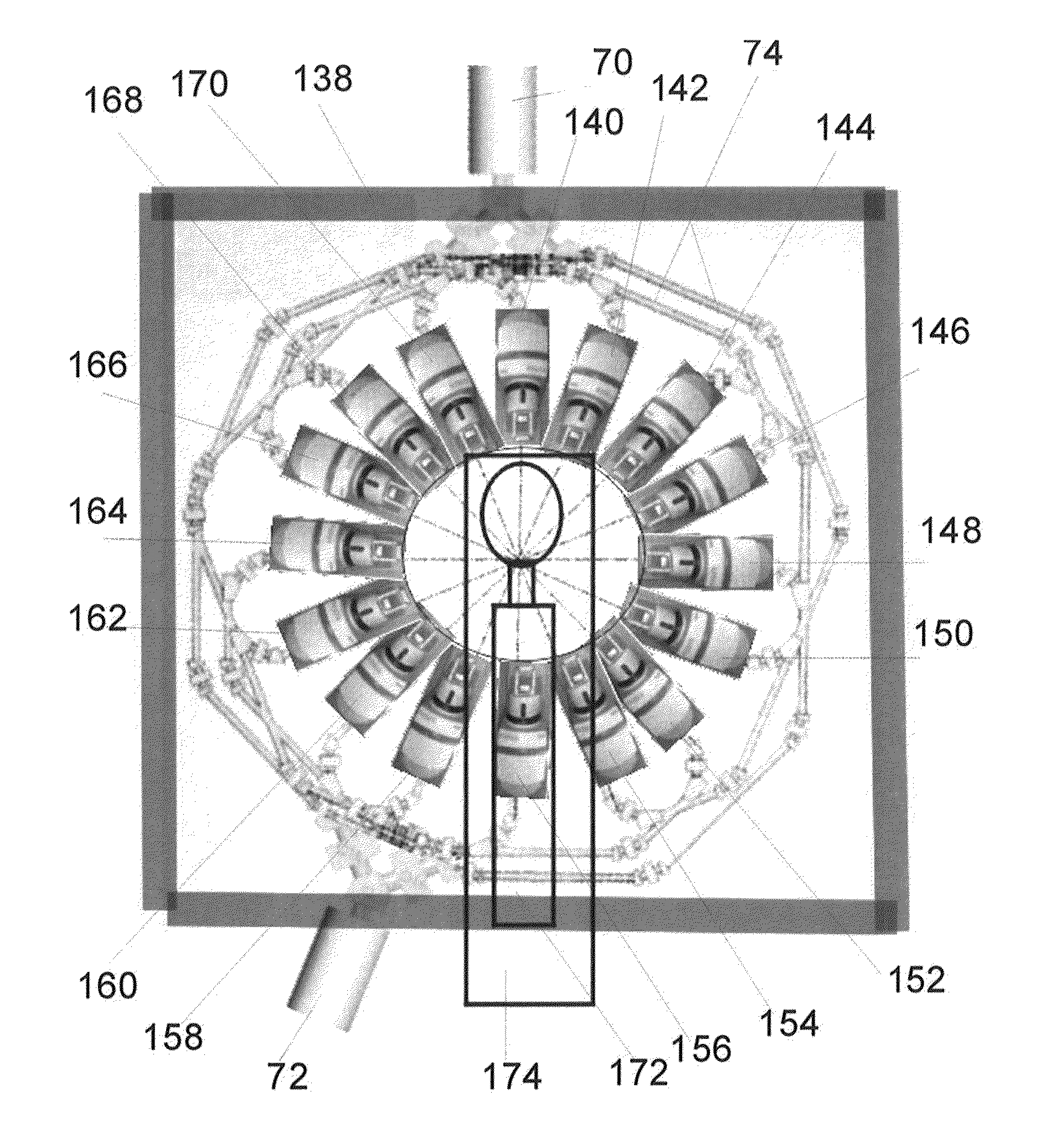
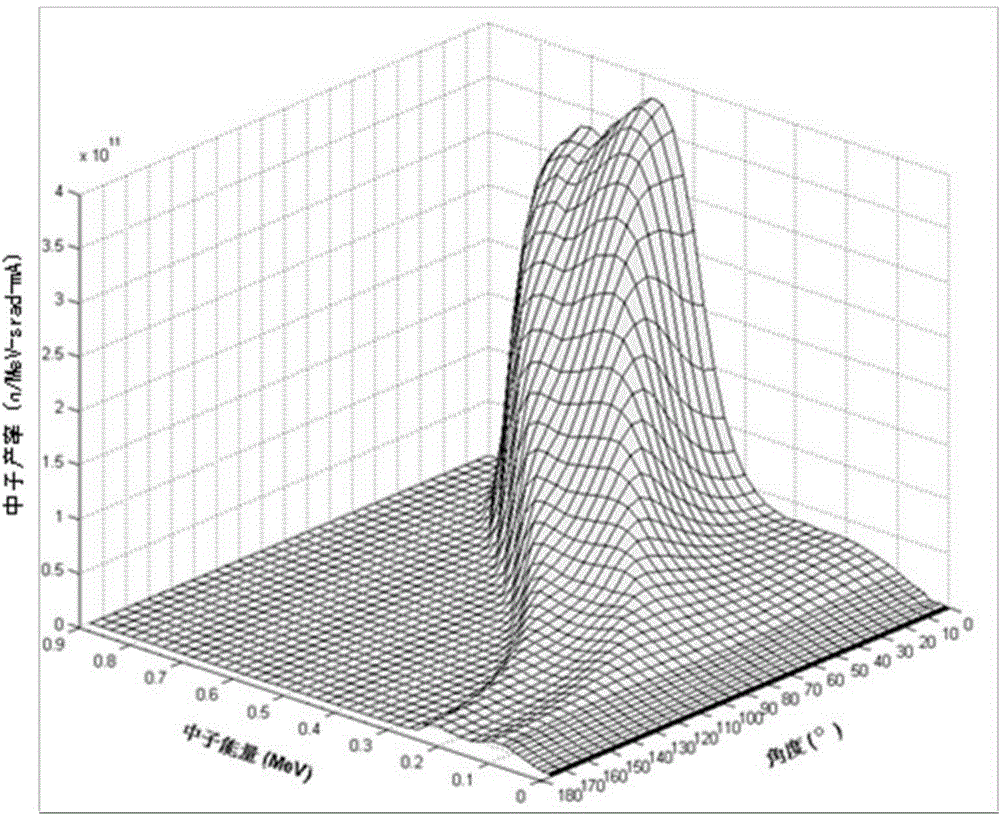
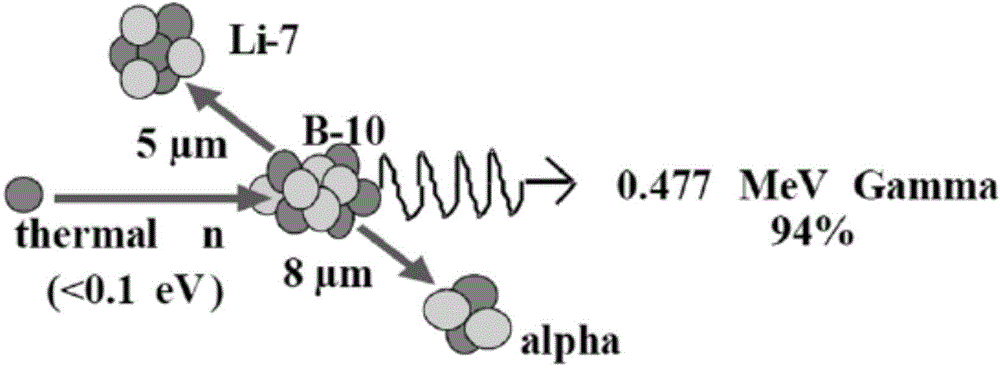
The invention provides a beam shaper for neutron-capture therapy in order to improve flux and quality of a neutron source. The beam shaper comprises a target, a slowing body adjacent to the target, a reflector wrapping the slowing body, a thermal neutron absorber adjacent to the slow body, a radiation shield arranged in the beam shaper and a beam outlet. The target generates nuclear reaction with a proton beam incident from a beam inlet so as to generate neutrons, the neutrons form a neutron beam which defines a main axis, the slowing body slows down the neutrons generated from the target to an epithermal neutron energy region, the reflector guides the neutrons deviating from the main axis to the main axis so as to improve intensity of the epithermal neutron beam, a gap passage is arranged between the slowing body and the reflector so as to improve epithermal neutron flux, the thermal neutron absorber is used for absorbing the thermal neutron so as to avoid causing overmuch dosed with shallow normal tissue during therapy, and the radiation shield is used for shielding leaked neutrons and photon so as to reduce normal tissue dose in a non-radiation region.
Owner:NEUBORON MEDTECH
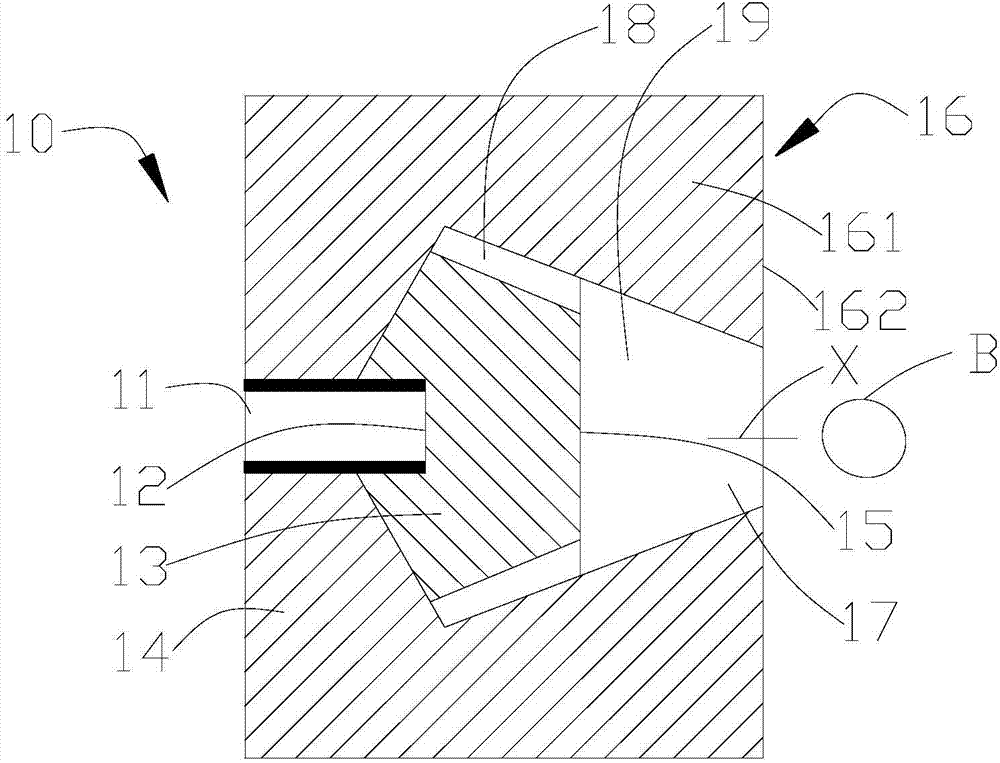
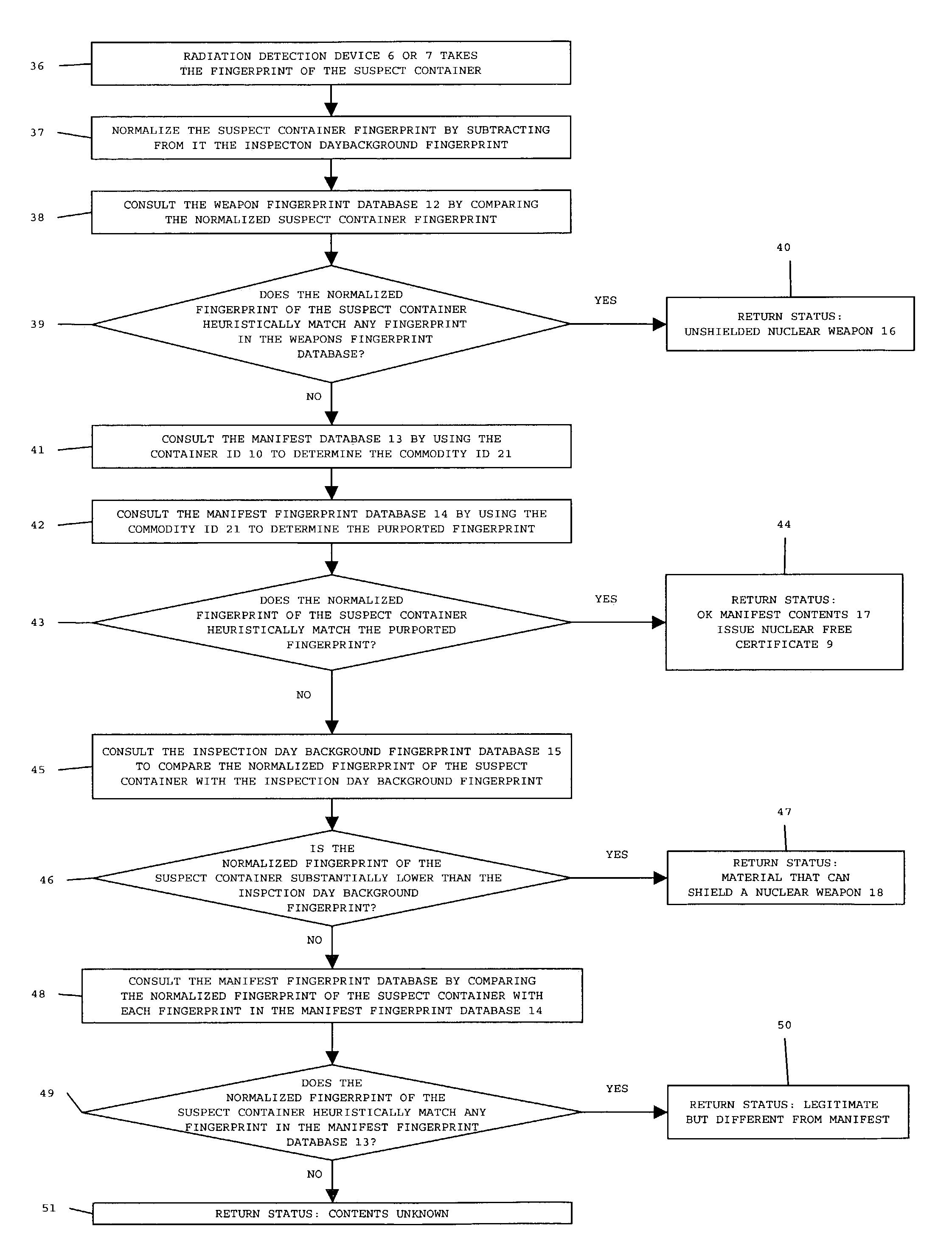
Apparatus and method for detecting radiation or radiation shielding in containers
InactiveUS7026944B2Inspection is accurateTrolley cranesX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentRadioactive agentEngineering
A computer program, database and method for the detection of fissile or radioactive material or radiation shielding material in a container works with detection devices brought into proximity to containers so that the presence of fissile or radioactive material, or shielding materials to conceal the presence of such fissile or radioactive materials, may be detected. A comparison may then be made of the output of the detector to a threshold to determine subsequent action regarding the shipping container. The threshold may be based on the output of known, dangerous radioactive materials, known legitimate contents or empty containers.
Owner:VERITAINER ASSET HLDG LLC
Lethal and sublethal damage repair inhibiting image guided simultaneous all field divergent and pencil beam photon and electron radiation therapy and radiosurgery
InactiveUS7835492B1Improve modulationIncrease radiation intensityIrradiation devicesX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyRadiosurgeryC banding
A medical accelerator system is provided for simultaneous radiation therapy to all treatment fields. It provides the single dose effect of radiation on cell survival. It eliminates the inter-field interrupted, subfractionated fractionated radiation therapy. Single or four beams S-band, C-band or X-band accelerators are connected to treatment heads through connecting beam lines. It is placed in a radiation shielding vault which minimizes the leakage and scattered radiation and the size and weight of the treatment head. In one version, treatment heads are arranged circularly and connected with the beam line. In another version, a pair of treatment heads is mounted to each ends of narrow gantries and multiple such treatment heads mounted gantries are assembled together. Electron beam is steered to all the treatment heads simultaneously to treat all the fields simultaneously. Radiating beam's intensity in a treatment field is modulated with combined divergent and pencil beam, selective beam's energy, dose rate and weight and not with MLC and similar devices. Since all the treatment fields are treated simultaneously the dose rate at the tumor site is the sum of each of the converging beam's dose rate at depth. It represents the biological dose rate. The dose rate at d-max for a given field is the individual machine dose rate. Its treatment options includes divergent or pencil beam modes. It enables to treat a tumor with lesser radiation toxicities to normal tissue and higher tumor cure and control.
Owner:SAHADEVAN VELAYUDHAN
Multicomponent vaginal cylinder system for low dose rate brachytherapy or gynecological cancers
InactiveUS6641518B2Medical devicesX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyVaginaRadiation shield
A multicomponent vaginal cylinder system composed of a tandem capable of housing one or more radiation sources, one or more removable ovoid cartridges, each cartridge capable of housing a radiation source, and a vaginal cylinder structure having corresponding hollow cavities to accommodate the insertions of the tandem and the ovoid cartridges. Radiation shielding may be removably attached to portions of the vaginal cylinder structure to shield tissues from unwanted radiation. A method for using this vaginal cylinder system to treat gynecological cancers is also disclosed.
Owner:MIAMI THE UNIV OF
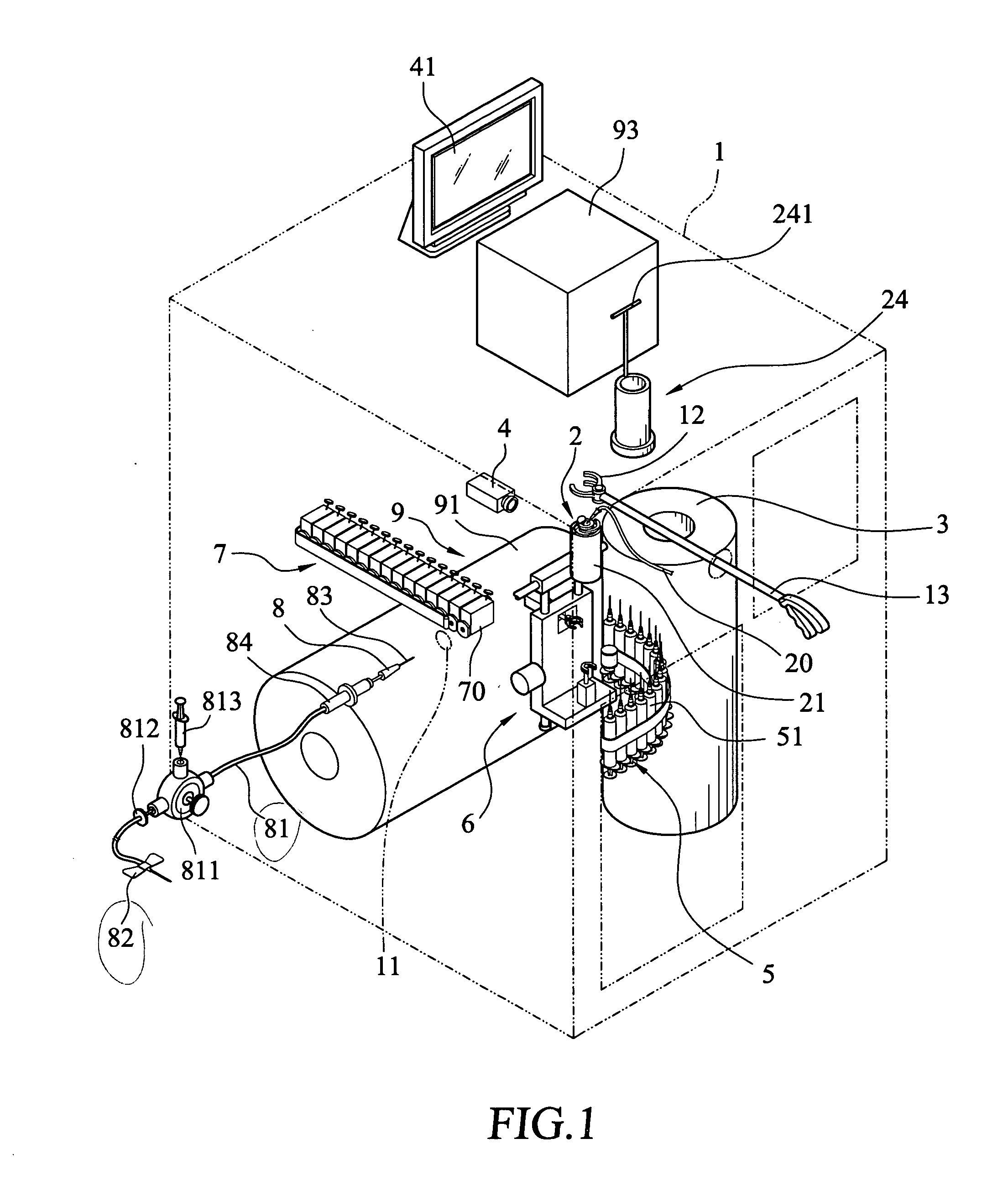
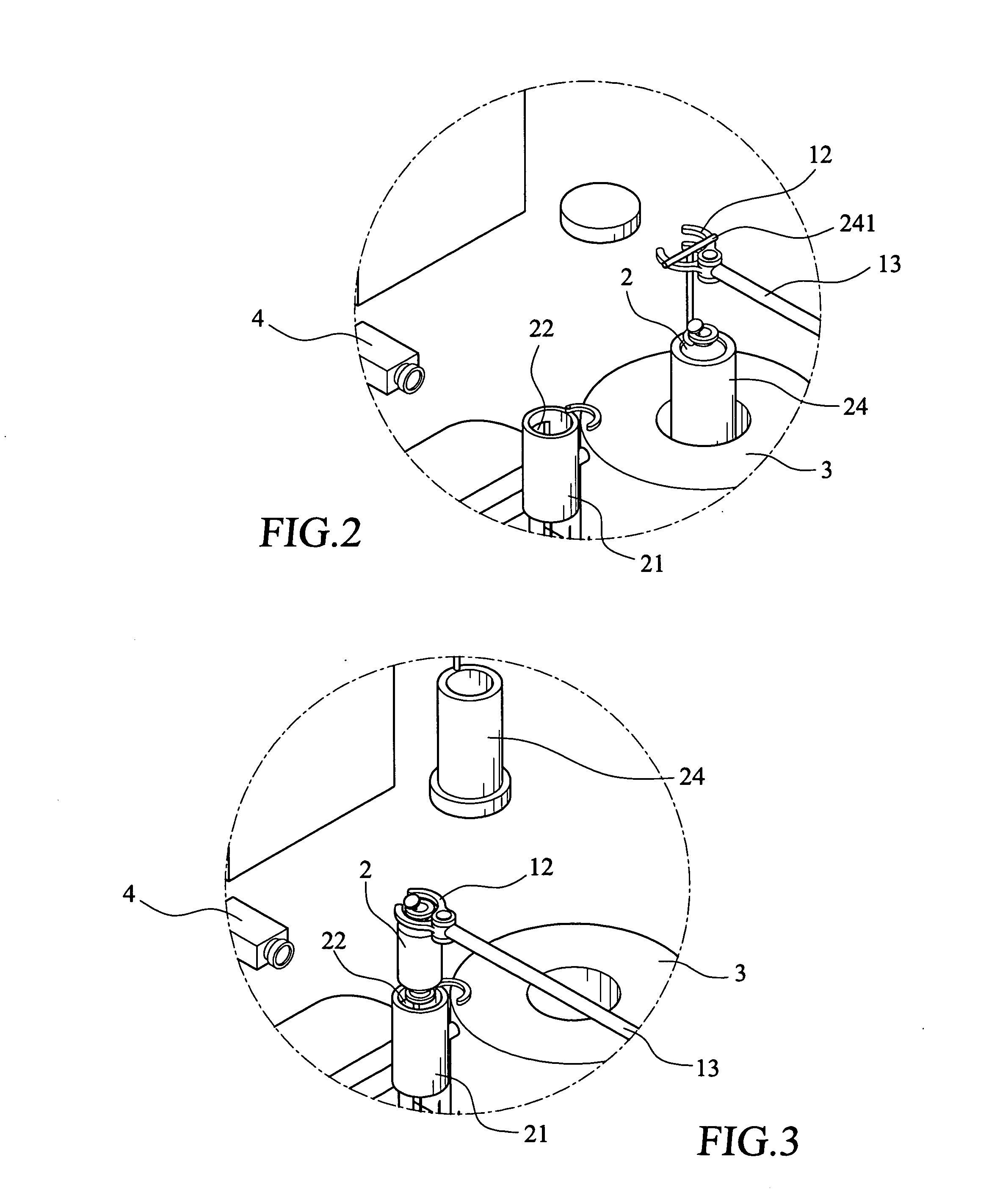
Process and device for preparing radiopharmaceutical products for injection
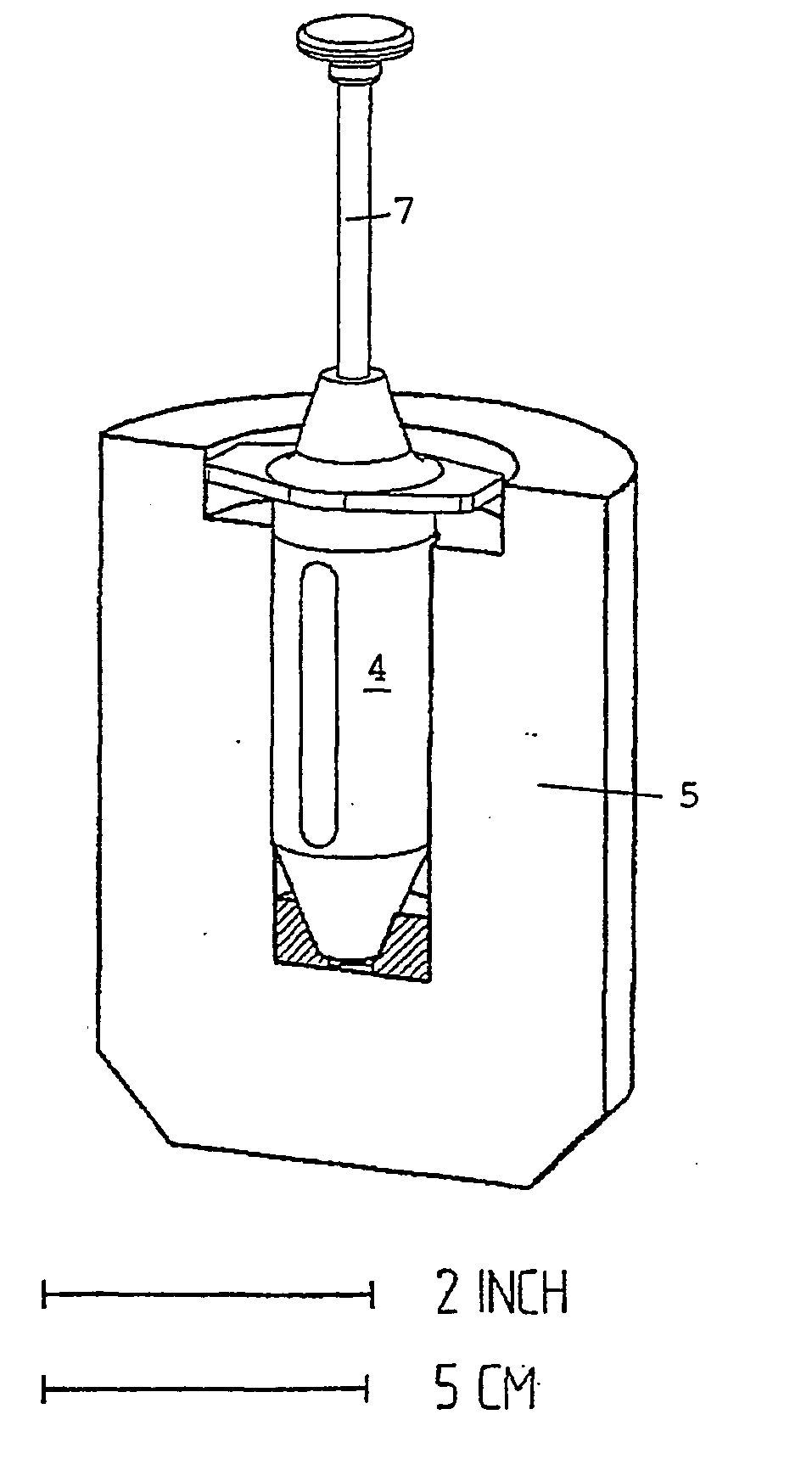
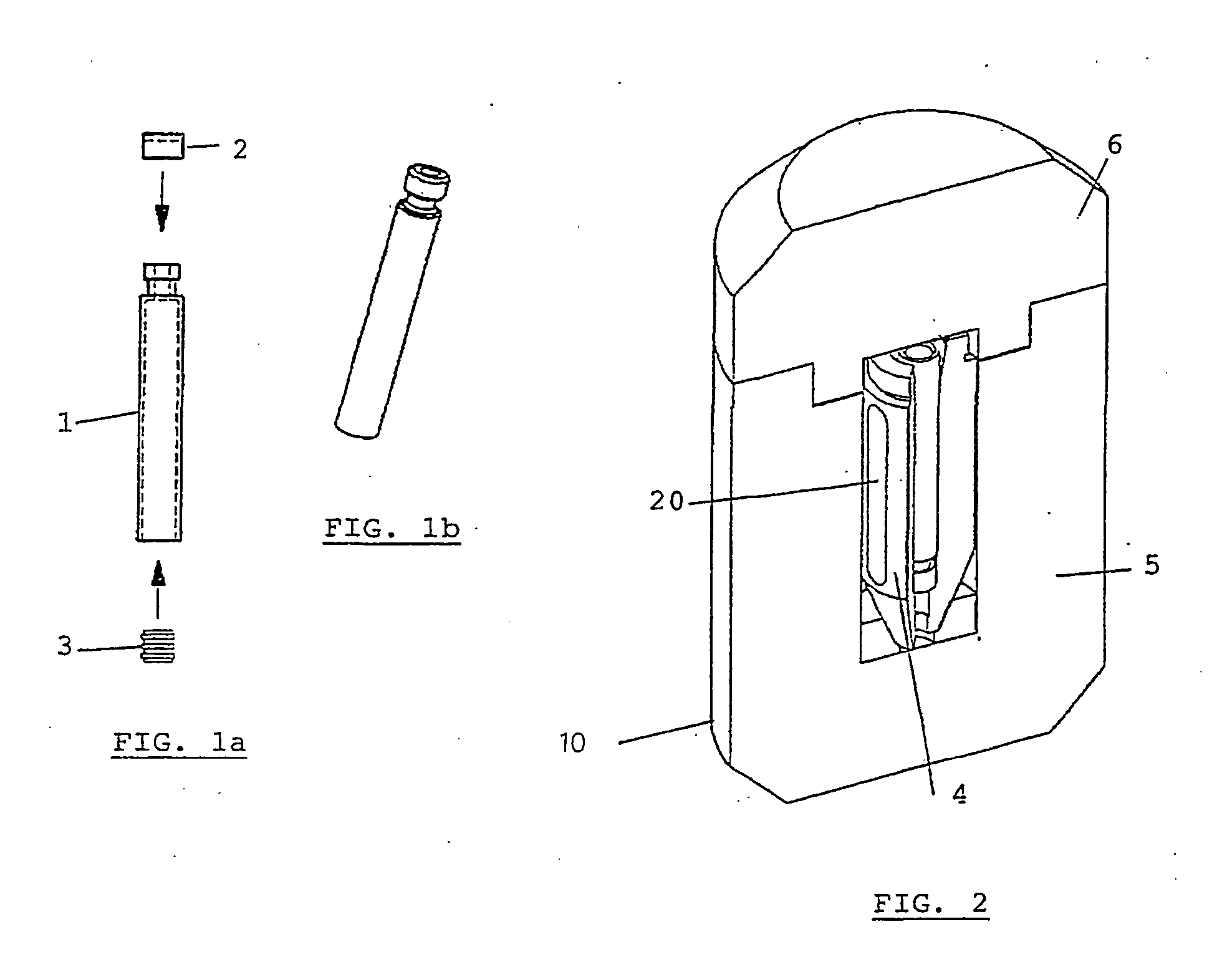
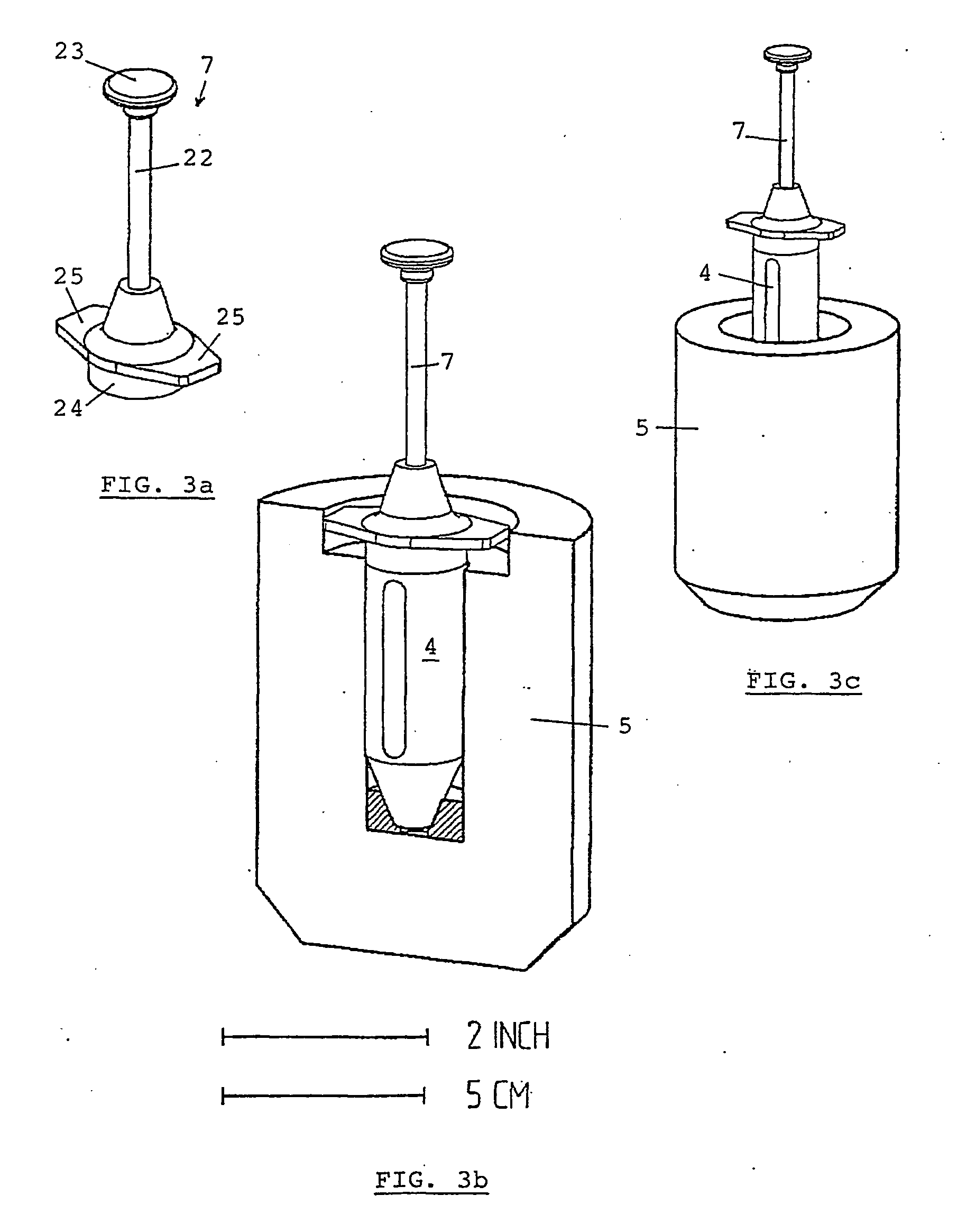
InactiveUS20040084340A1Reduce needAmpoule syringesDispensing apparatusRadiopharmaceutical CompoundChemical compound
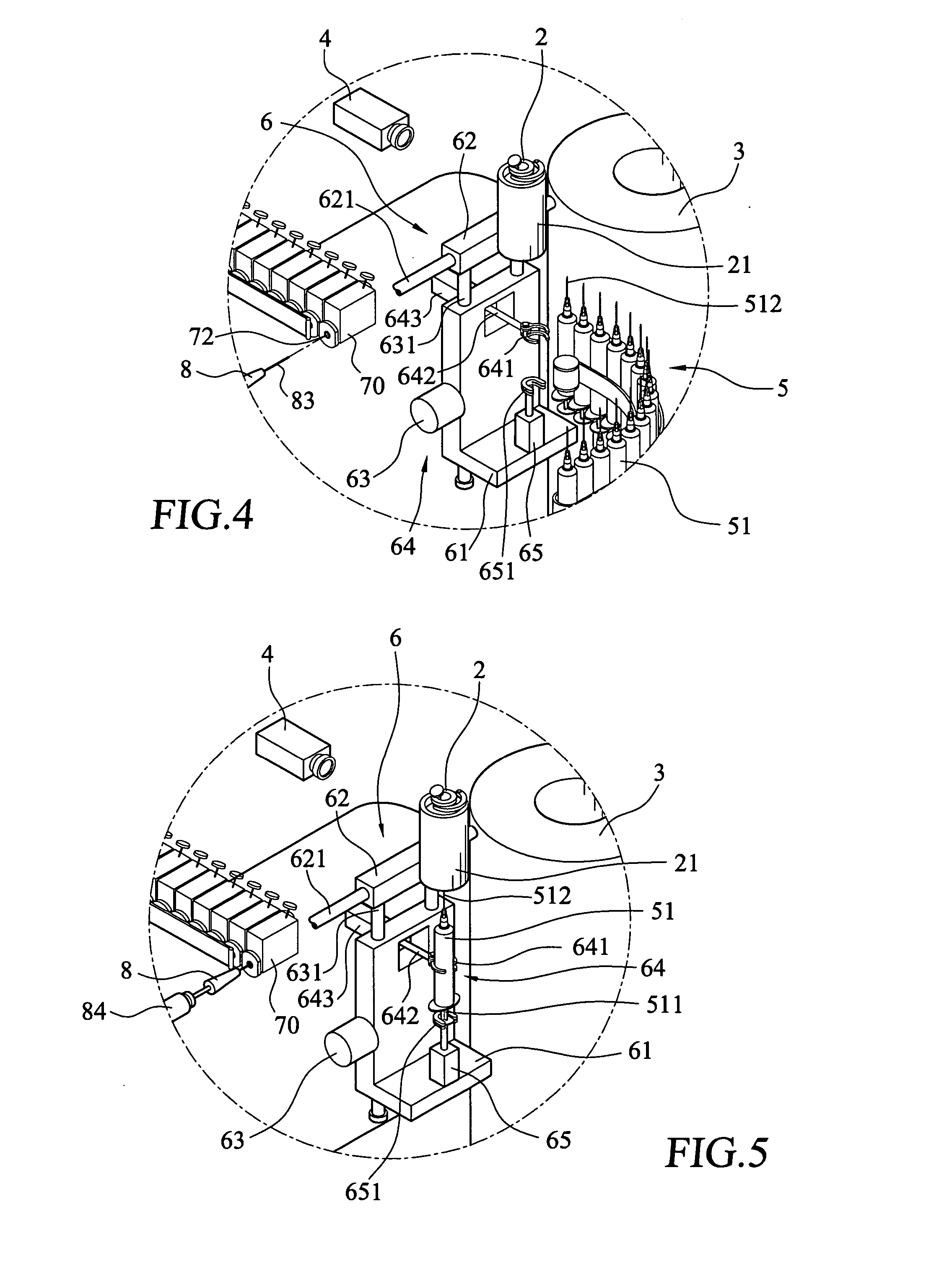
Method for preparing, packaging and handling an individual dose of a radiopharmaceutical compound, comprising the following steps: filling a cartridge (1) with said dose of radiopharmaceutical compound via a first end, the second end being closed by means of a component serving as a piston (3); closing said cartridge (1) at said first end by means of a closure device (2); placing said cartridge (1) in a radiation shielding device (10), comprising an inner part (4) and an outer part (5), said inner part serving as radiation shielding for an operator and said outer part serving as a transportation shielding container; closing said container by means of an appropriate shielding lid (6); transporting said container up to the place at which an injection of said radiopharmaceutical compound will take place; removing the shielding lid (6) of the container; fixing a plunger (7) to the cartridge piston (3); extracting the cartridge and the inner part (4) of the radiation shielding device (10) from the outer part (5) serving as a container, and placing injection means (30) on the cartridge end which has the setting closure device (2).
Owner:MORELLE JEAN LUC
In orbit space transportation and recovery system
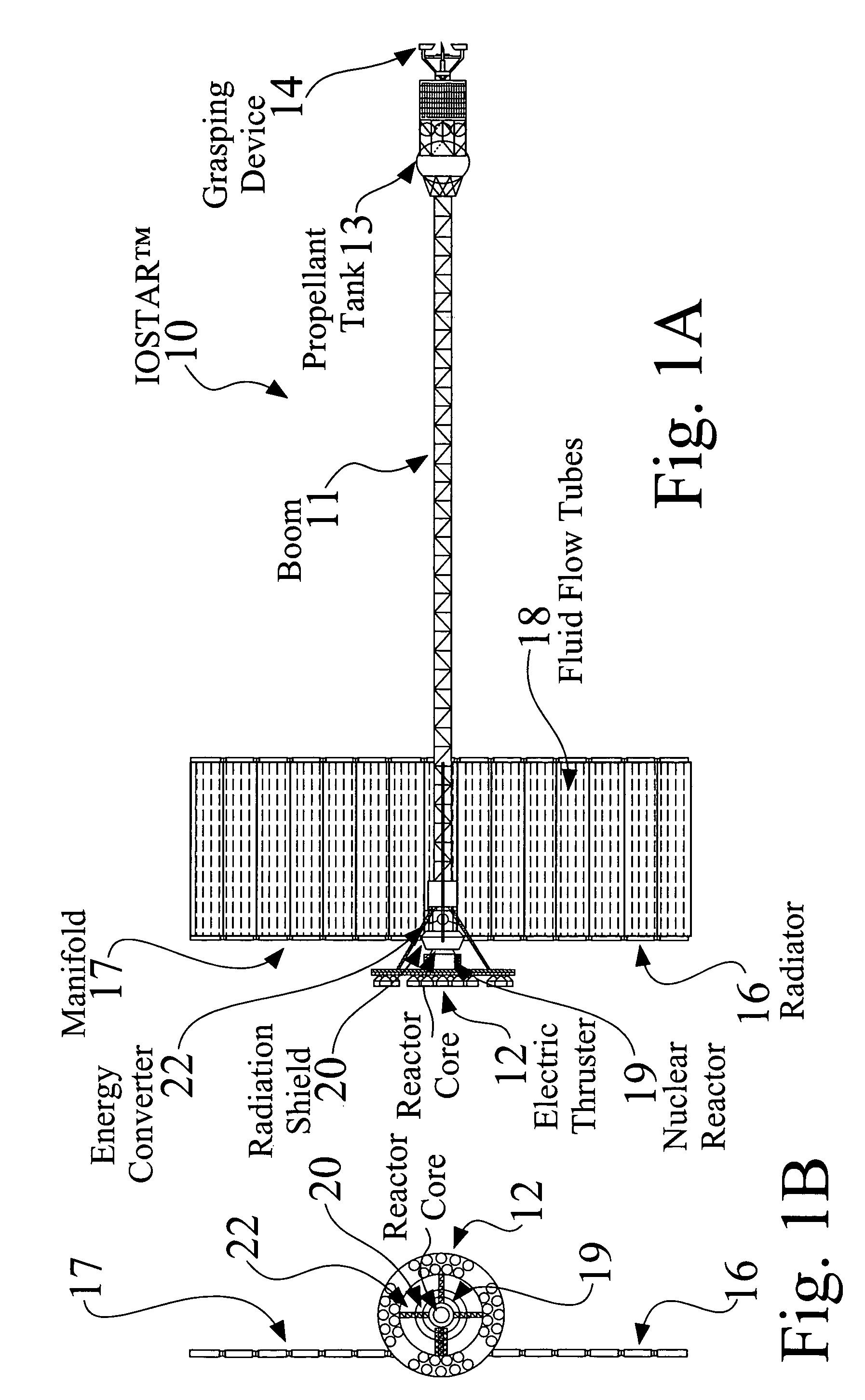
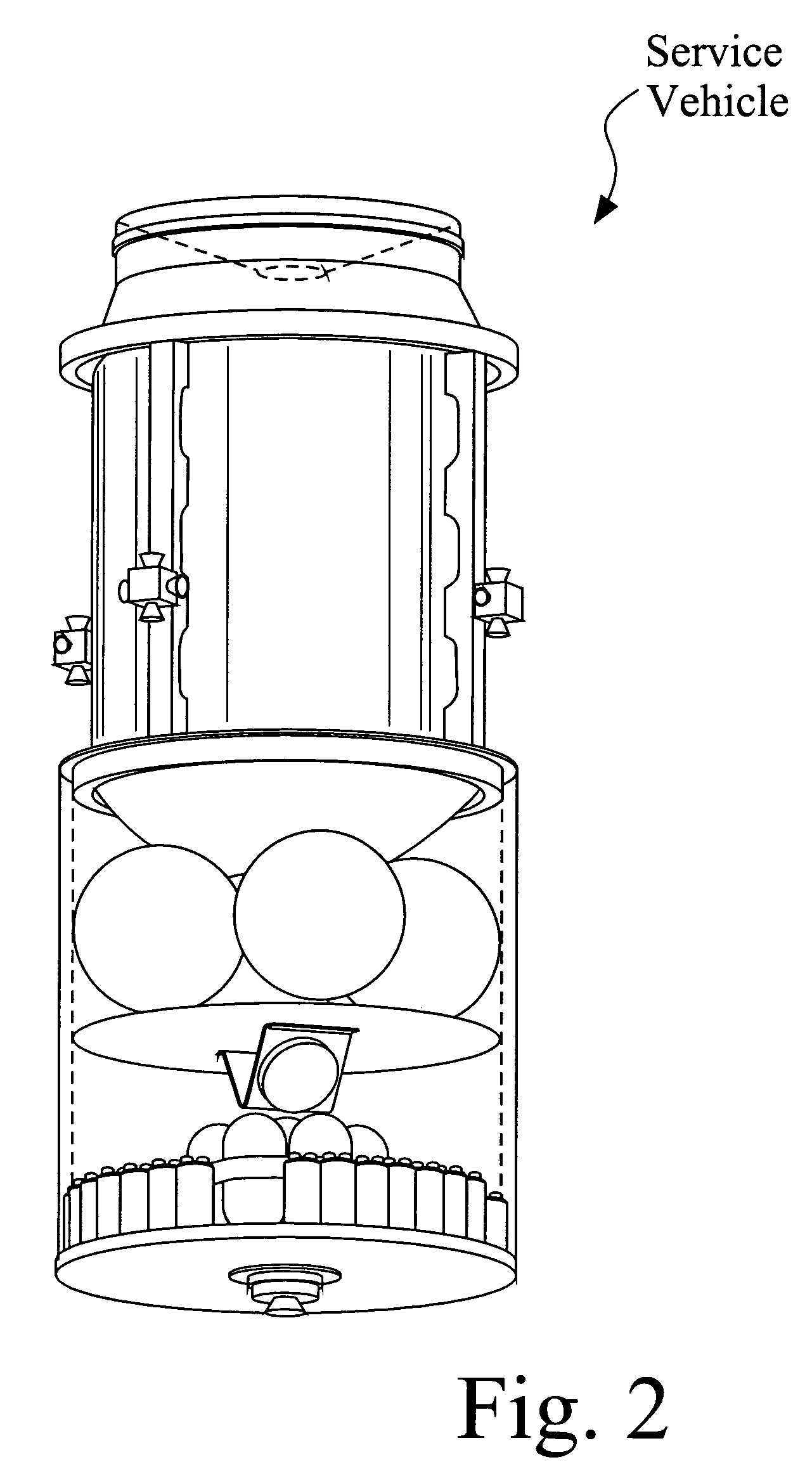
InactiveUS7216833B2Low costCosmonautic environmental control arrangementLaunch systemsNuclear reactorPropellant tank
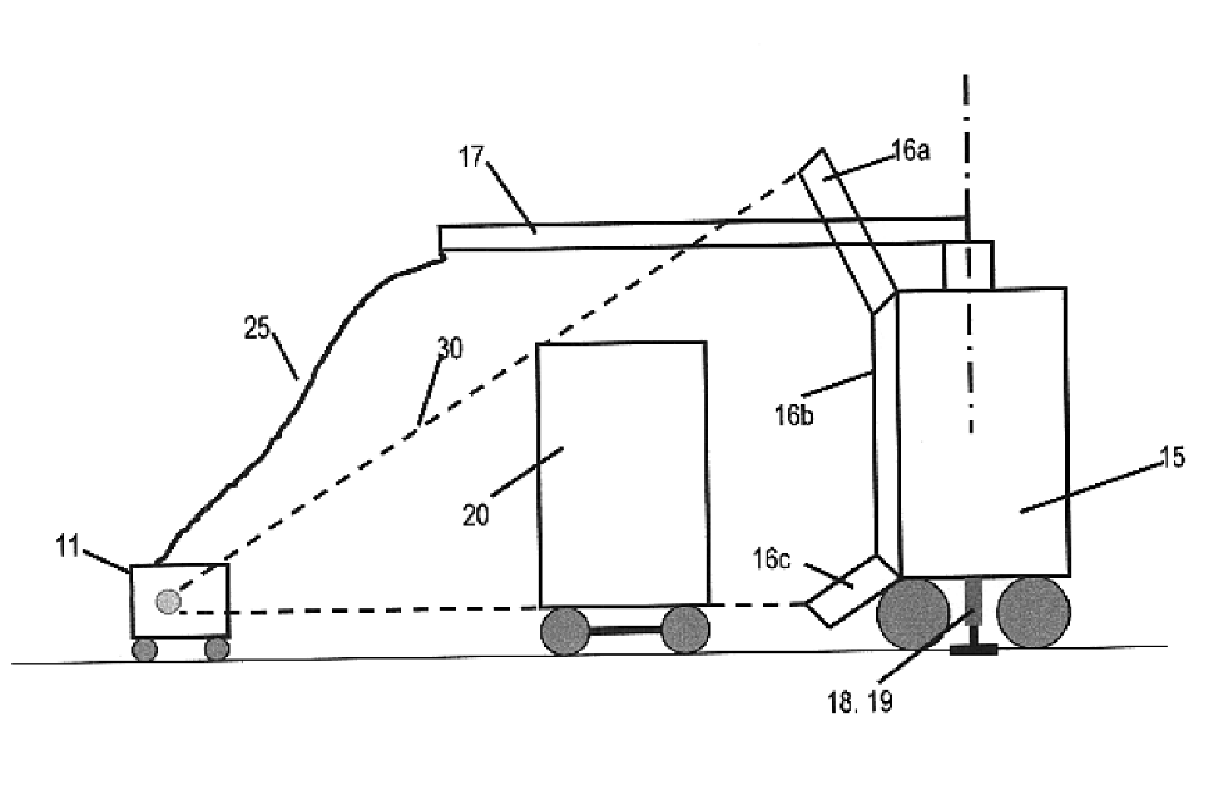
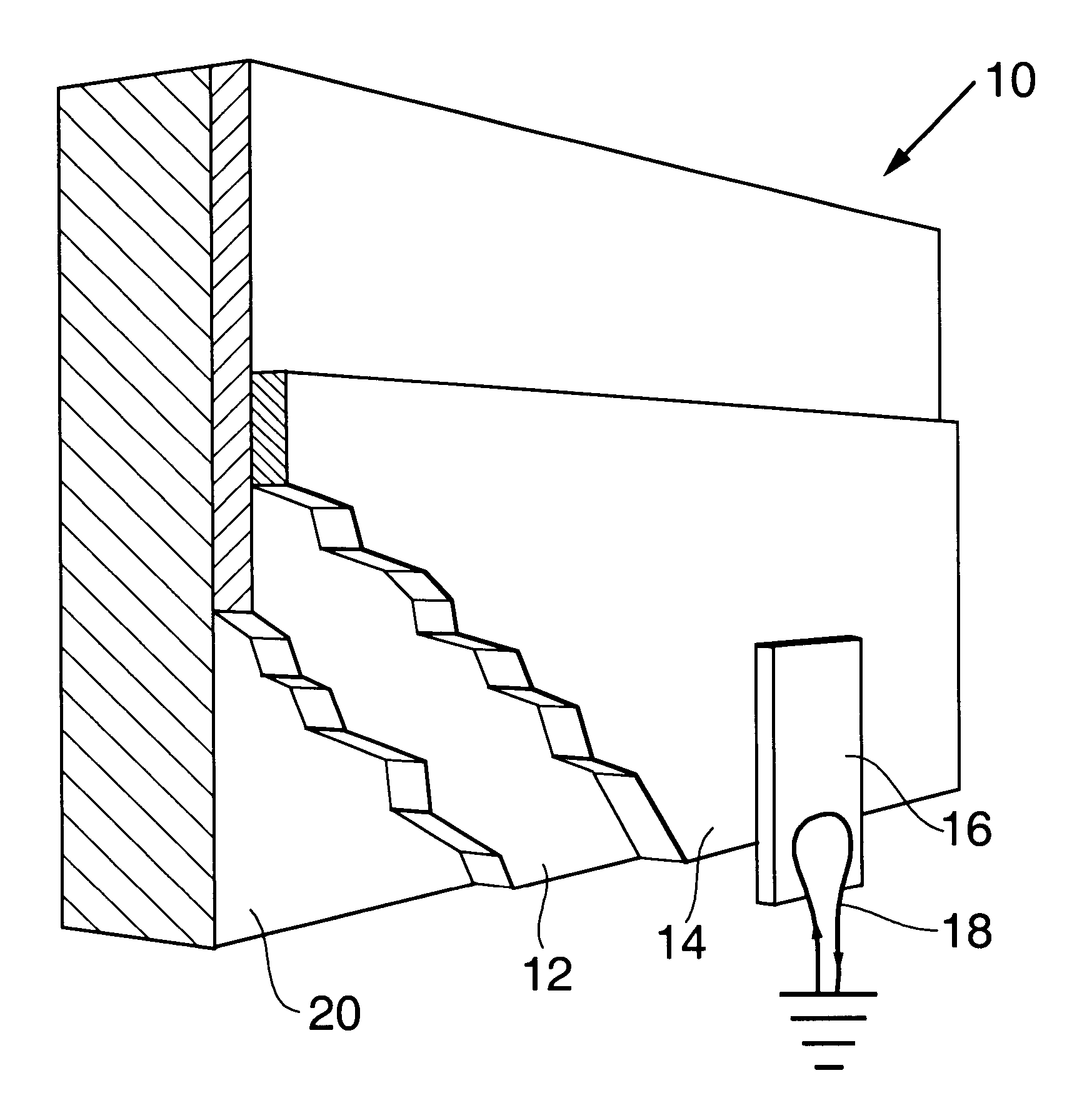
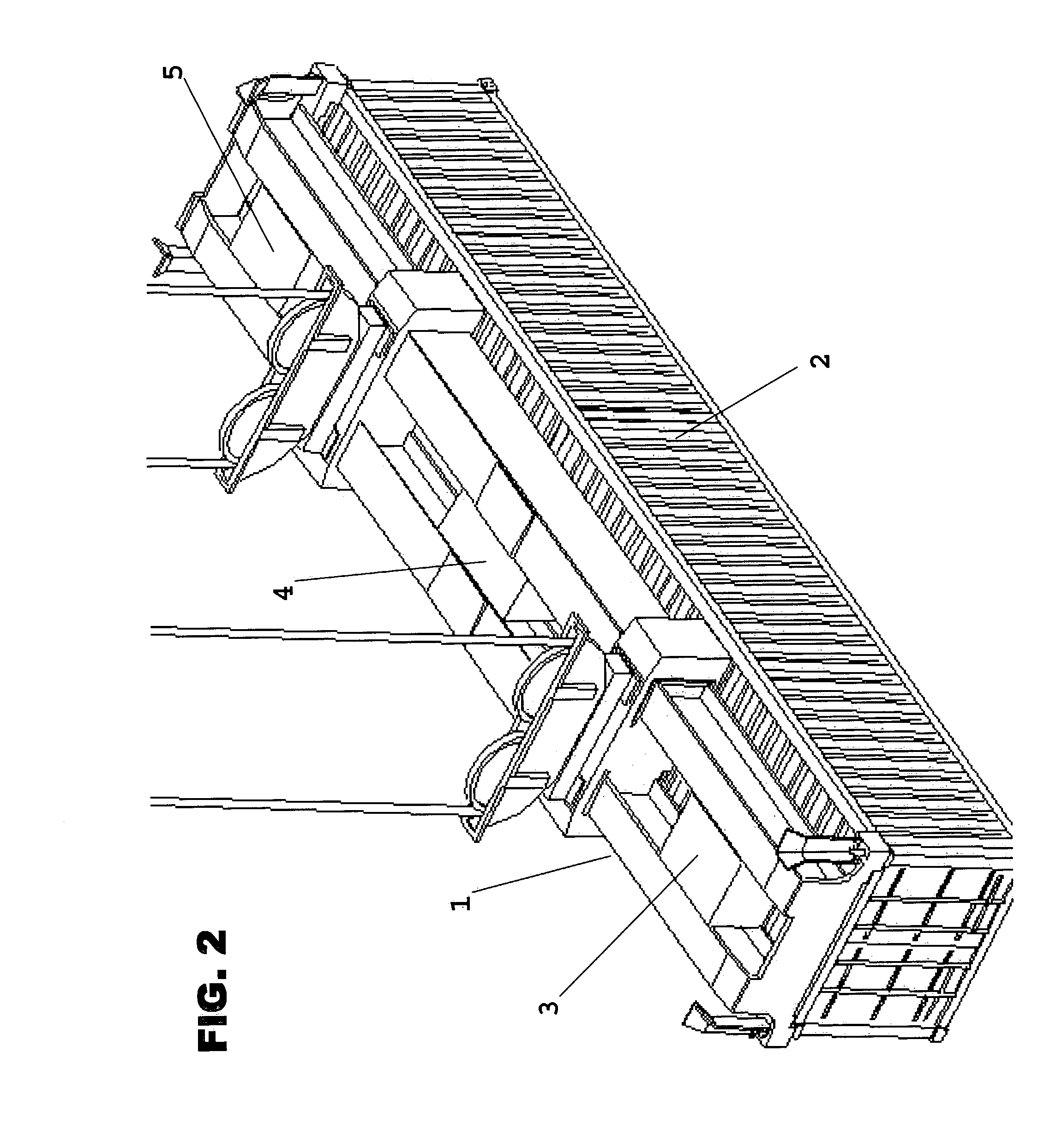
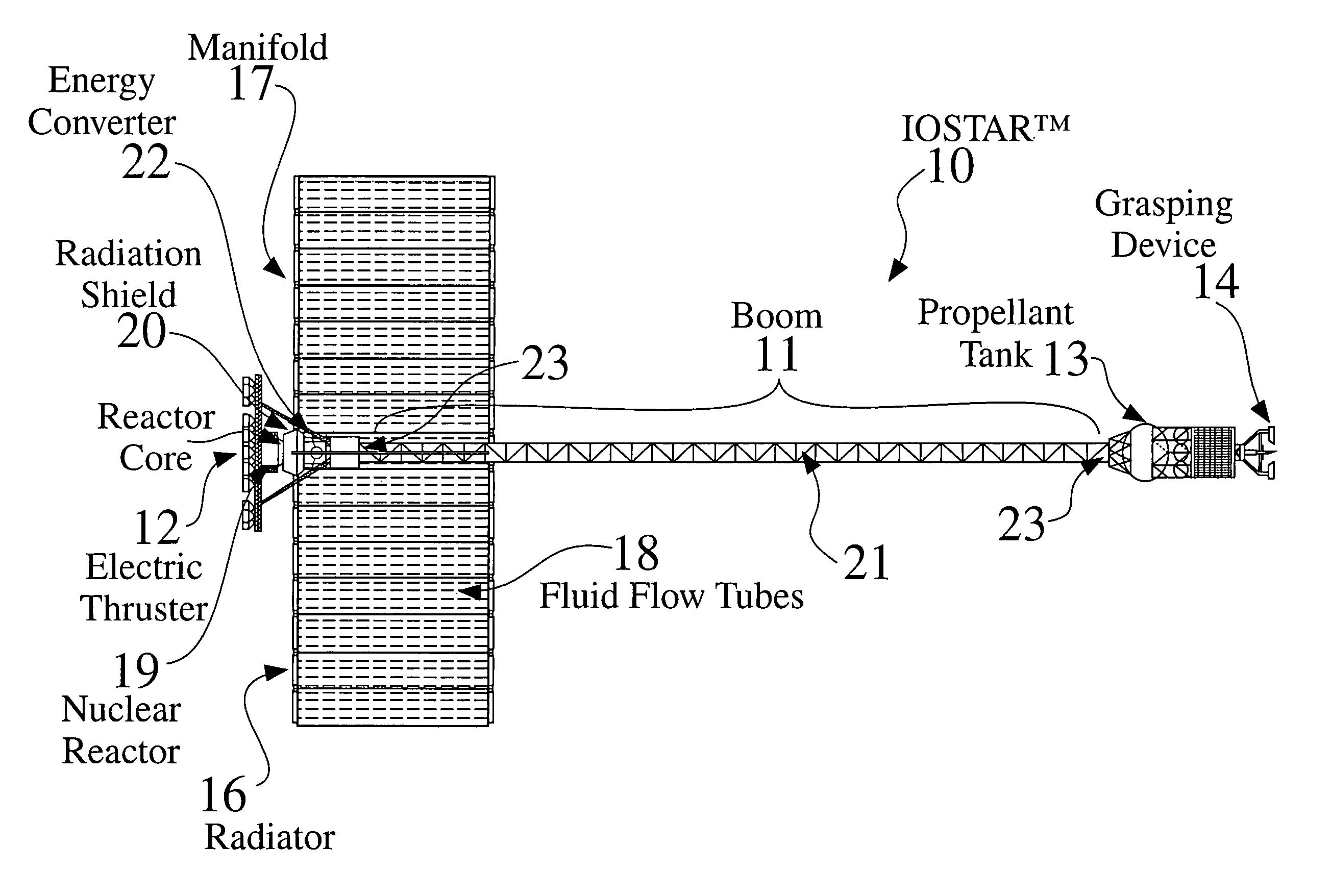
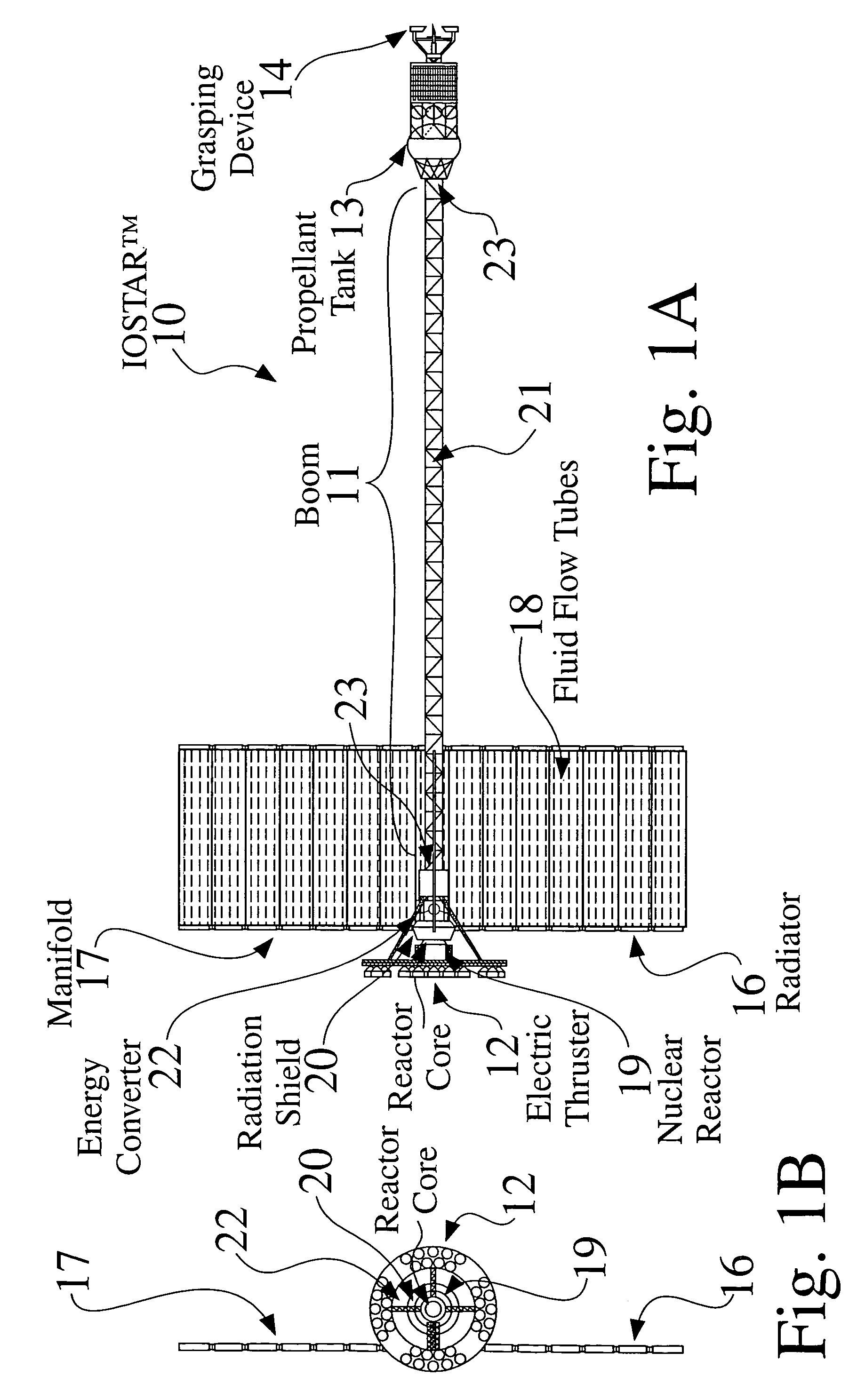
An In Orbit Transportation & Recovery System (IOSTAR™) (10). One preferred embodiment of the present invention comprises a space tug powered by a nuclear reactor (19). The IOSTAR™ includes a collapsible boom (11) connected at one end to a propellant tank (13) which stores fuel for an electric propulsion system (12). This end of the boom ( 11) is equipped with docking hardware (14) that is able to grasp and hold a satellite (15) and as a means to refill the tank (13). Radiator panels (16) mounted on the boom (11) dissipate heat from the reactor (19). A radiation shield (20) is situated next to the reactor (19) to protect the satellite payload (15) at the far end of the boom (11). The IOSTAR™ (10) will be capable of accomplishing rendezvous and docking maneuvers which will enable it to move spacecraft between a low Earth parking orbit and positions in higher orbits or to other locations in our Solar System.
Owner:IOSTAR CORP
Integrated Multilayer Insulation
ActiveUS20100251653A1Reduce the total massImprove automationCeilingsCosmonautic vehiclesAtmospheric pressureRadiation shield
A multilayer insulation with an array of rigid posts is provided. In particular, the posts are comprised of multiple post elements that are interconnected to radiation shields or sheets comprising the layers of the integrated multi-layer insulation structure. The post elements maintain spacing between adjacent sheets, thus maintaining a volume between the sheets. The post elements within a post can be attached to one another to form an integrated post structure. Moreover, neighboring posts can be interconnected to one another by beams. The post elements can also be configured so that, when the IMLI structure is not subjected to atmospheric pressure, the elements within a post are separated from one another to form gaps, thereby reducing heat transfer between layers.
Owner:BALL AEROSPACE & TECHNOLOGIES
Integrated X-ray source module
Described is a self-contained, small, lightweight, power-efficient and radiation-shielded module that includes a miniature vacuum X-ray tube emitting X-rays of a controlled intensity and defined spectrum. Feedback control circuits are used to monitor and maintain the beam current and voltage. The X-ray tube, high-voltage power supply, and the resonant converter are encapsulated in a solid high-voltage insulating material. The module can be configured into complex geometries and can be powered by commercially available small, compact, low-voltage batteries.
Owner:NEWTON SCI
In orbit space transportation and recovery system
InactiveUS7070151B2Low costCosmonautic radiation protectionLaunch systemsNatural satelliteNuclear reactor
An In Orbit Transportation & Recovery System (IOSTAR™) (10) One preferred embodiment of the present invention comprises a space tug powered by a nuclear reactor (19). The IOSTAR™ includes a collapsible boom (11) connected at one end to a propellant tank (13) which stores fuel for an electric propulsion system (12). This end of the boom (11) is equipped with docking hardware (14) that is able to grasp and hold a satellite (15) and as a means to refill the tank (13). Radiator panels (16) mounted on the boom (11) dissipate heat from the reactor (19). A radiation shield (20) is situated next to the reactor (19) to protect the satellite payload (15) at the far end of the boom (11). The IOSTAR™ (10) will be capable of accomplishing rendezvous and docking maneuvers which will enable it to move spacecraft between a low Earth parking orbit and positions in higher orbits or to other locations in our Solar System.
Owner:IOSTAR CORP
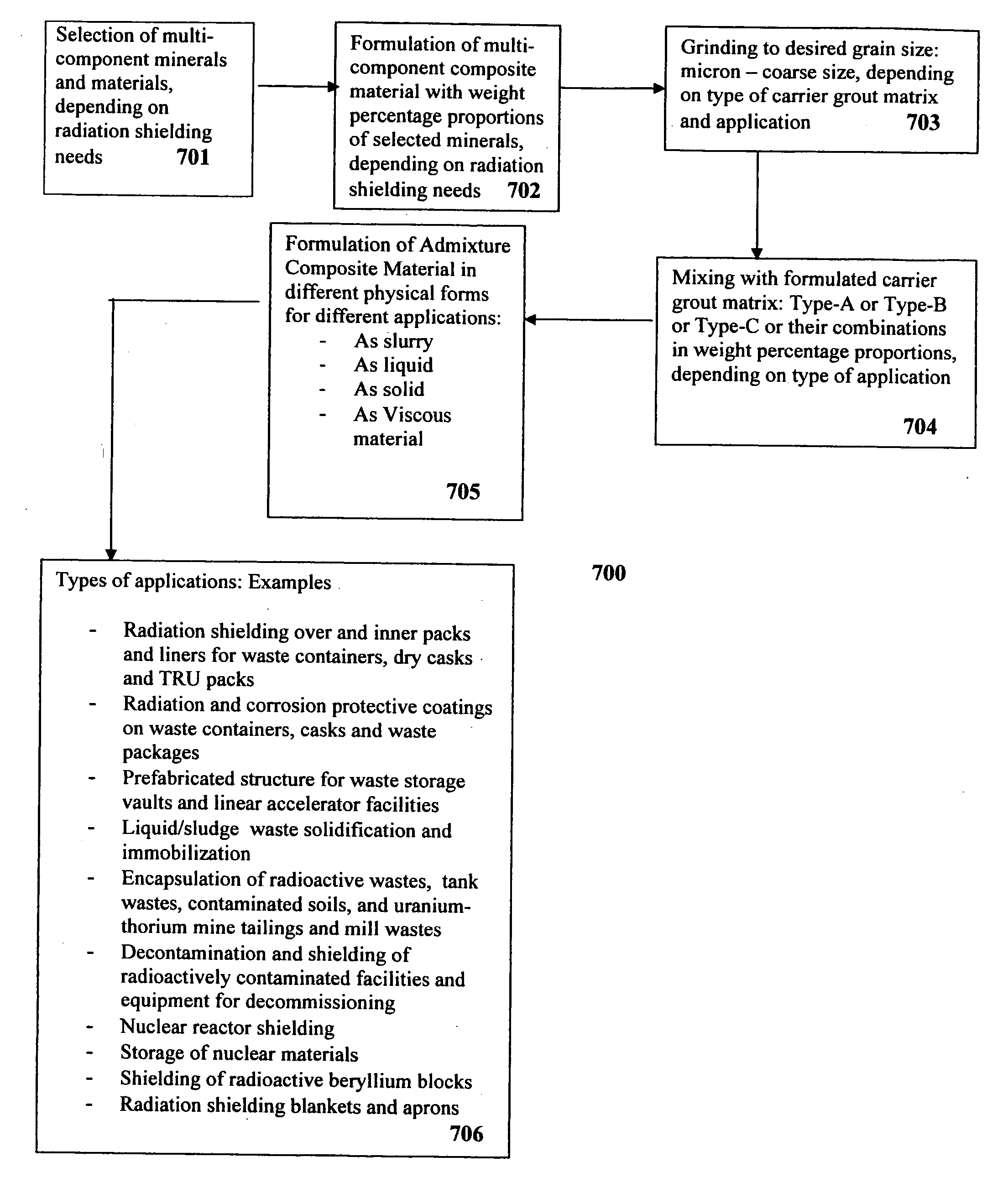
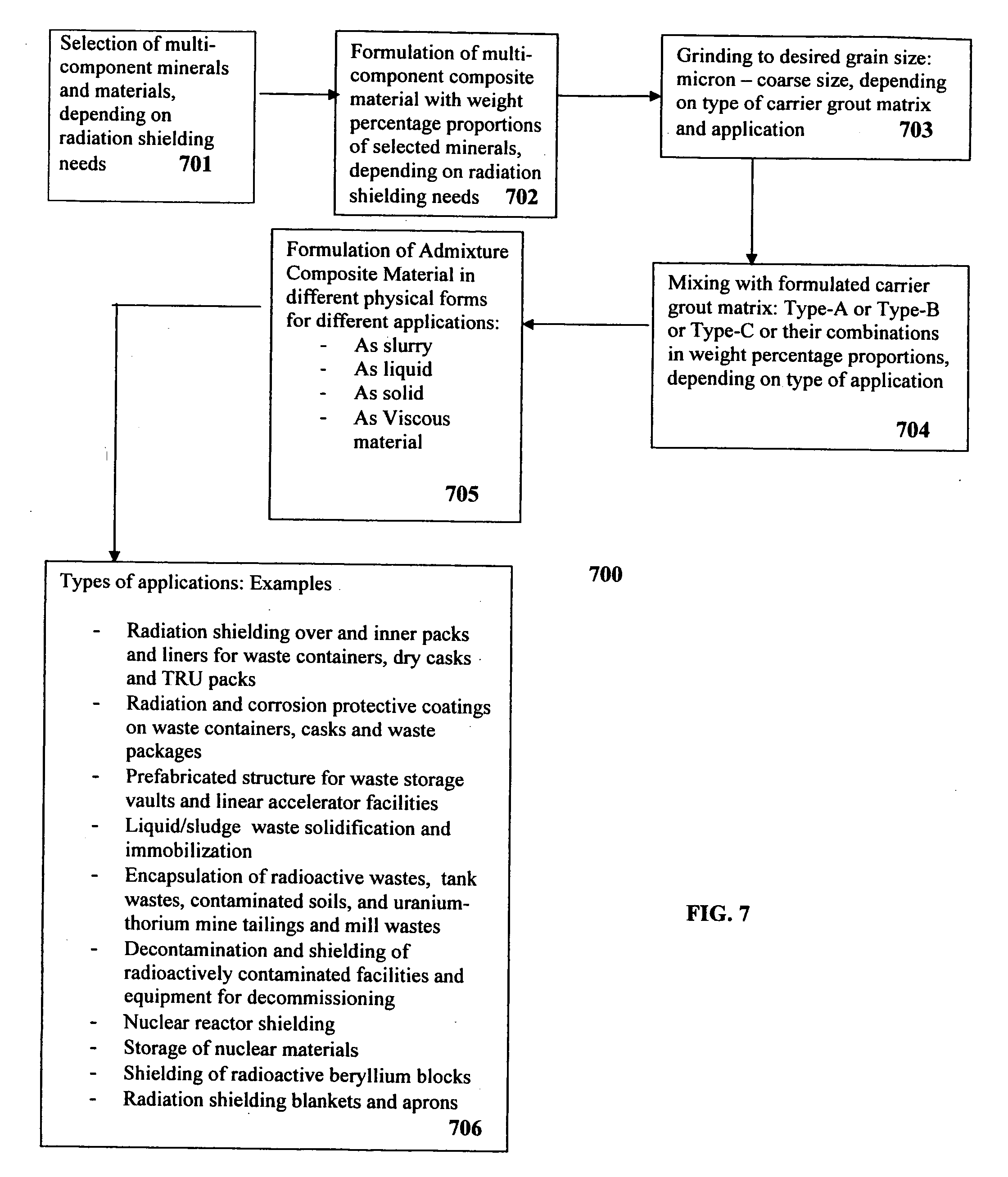
Composite materials and techniques for neutron and gamma radiation shielding
ActiveUS20050258405A1Safe and cost-effective managementIncrease volumeDiffusing elementsNuclear engineering solutionsPolymer modifiedRadioactive waste
This invention deals with multi-component composite materials and techniques for improved shielding of neutron and gamma radiation emitting from transuranic, high-level and low-level radioactive wastes. Selective naturally occurring mineral materials are utilized to formulate, in various proportions, multi-component composite materials. Such materials are enriched with atoms that provide a substantial cumulative absorptive capacity to absorb or shield neutron and gamma radiation of variable fluxes and energies. The use of naturally occurring minerals in synergistic combination with formulated modified cement grout matrix, polymer modified asphaltene and maltene grout matrix, and polymer modified polyurethane foam grout matrix provide the radiation shielding product. These grout matrices are used as carriers for the radiation shielding composite materials and offer desired engineering and thermal attributes for various radiation management applications.
Owner:SAYALA DASHARATHAM
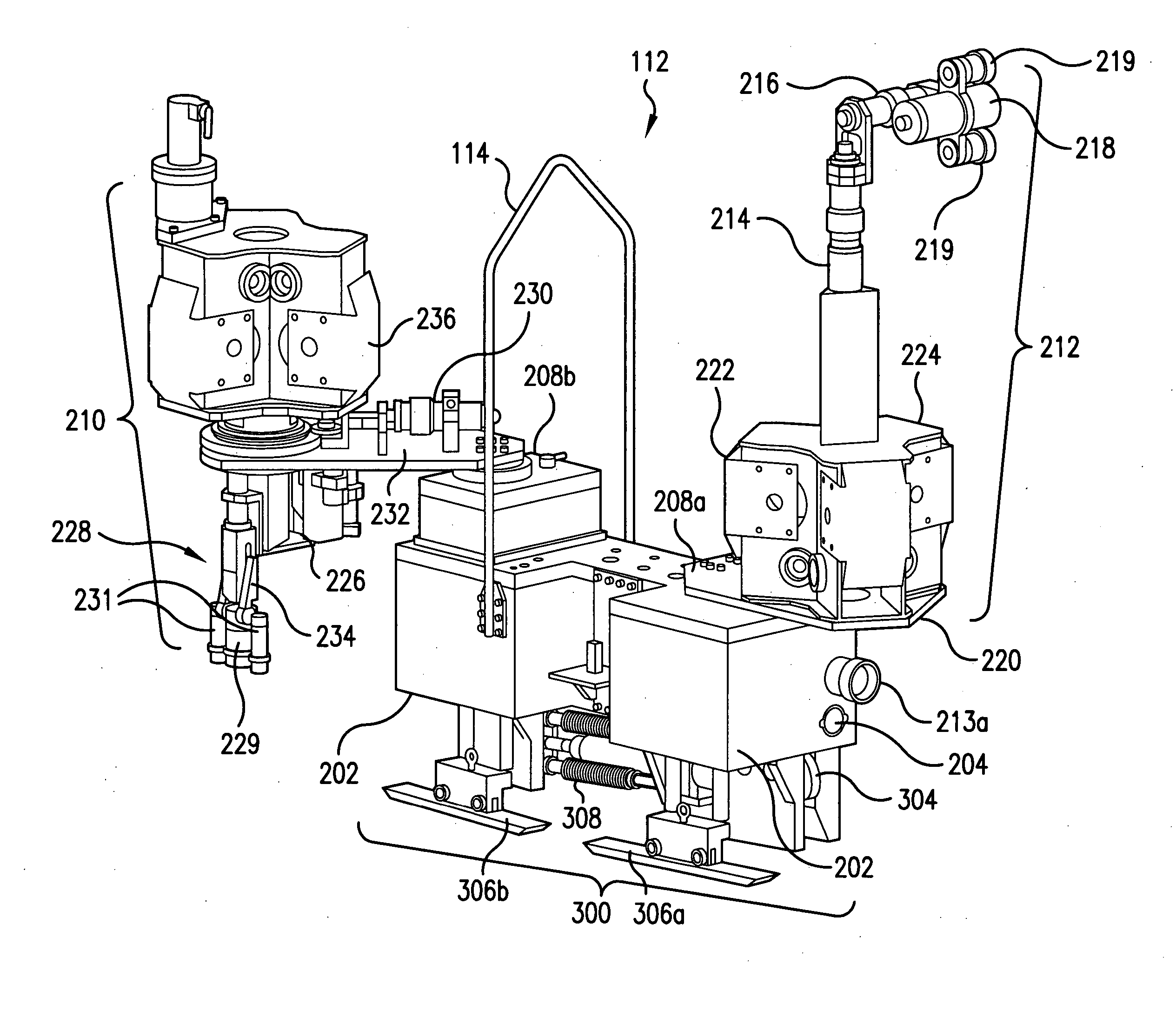
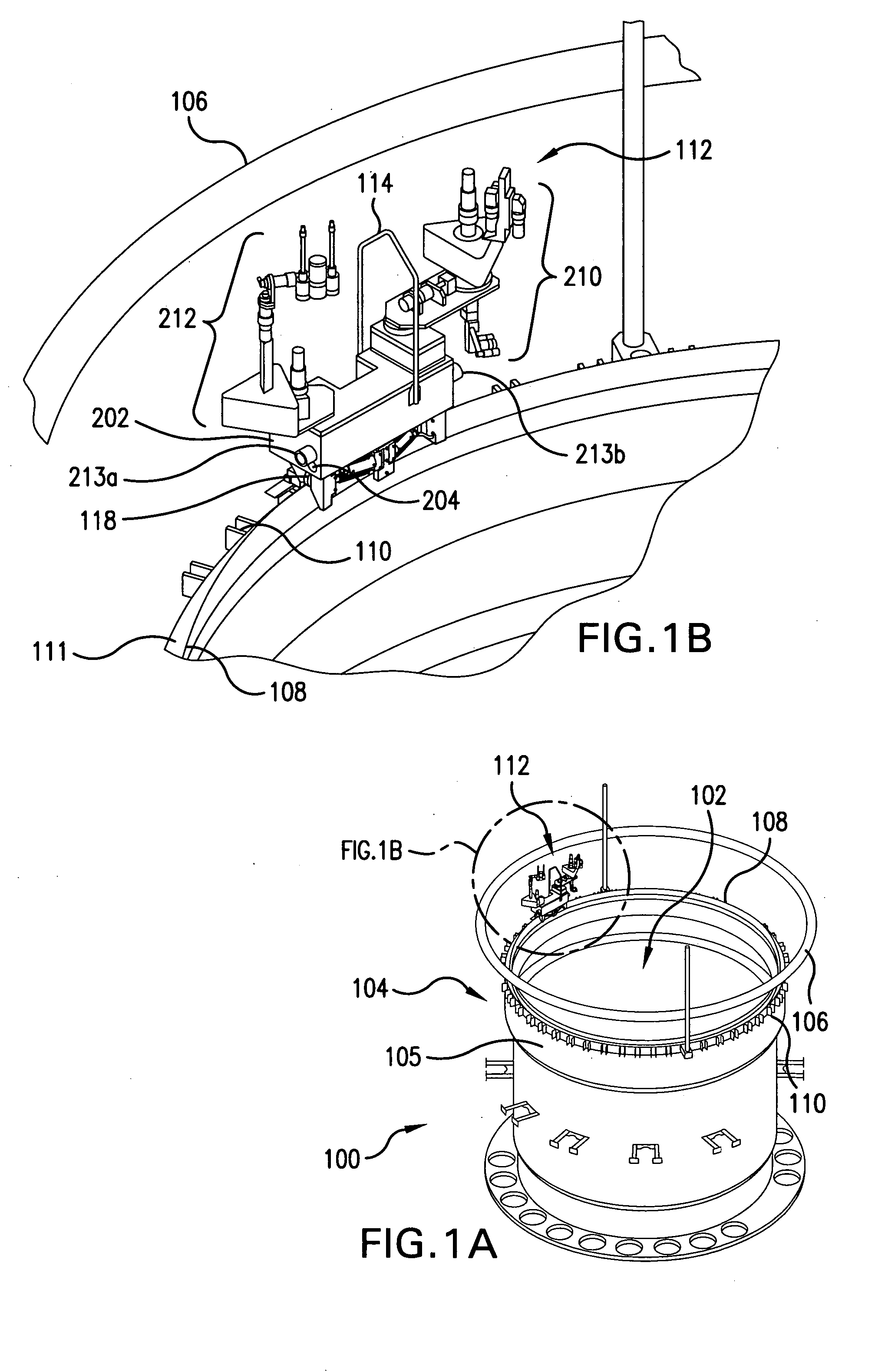
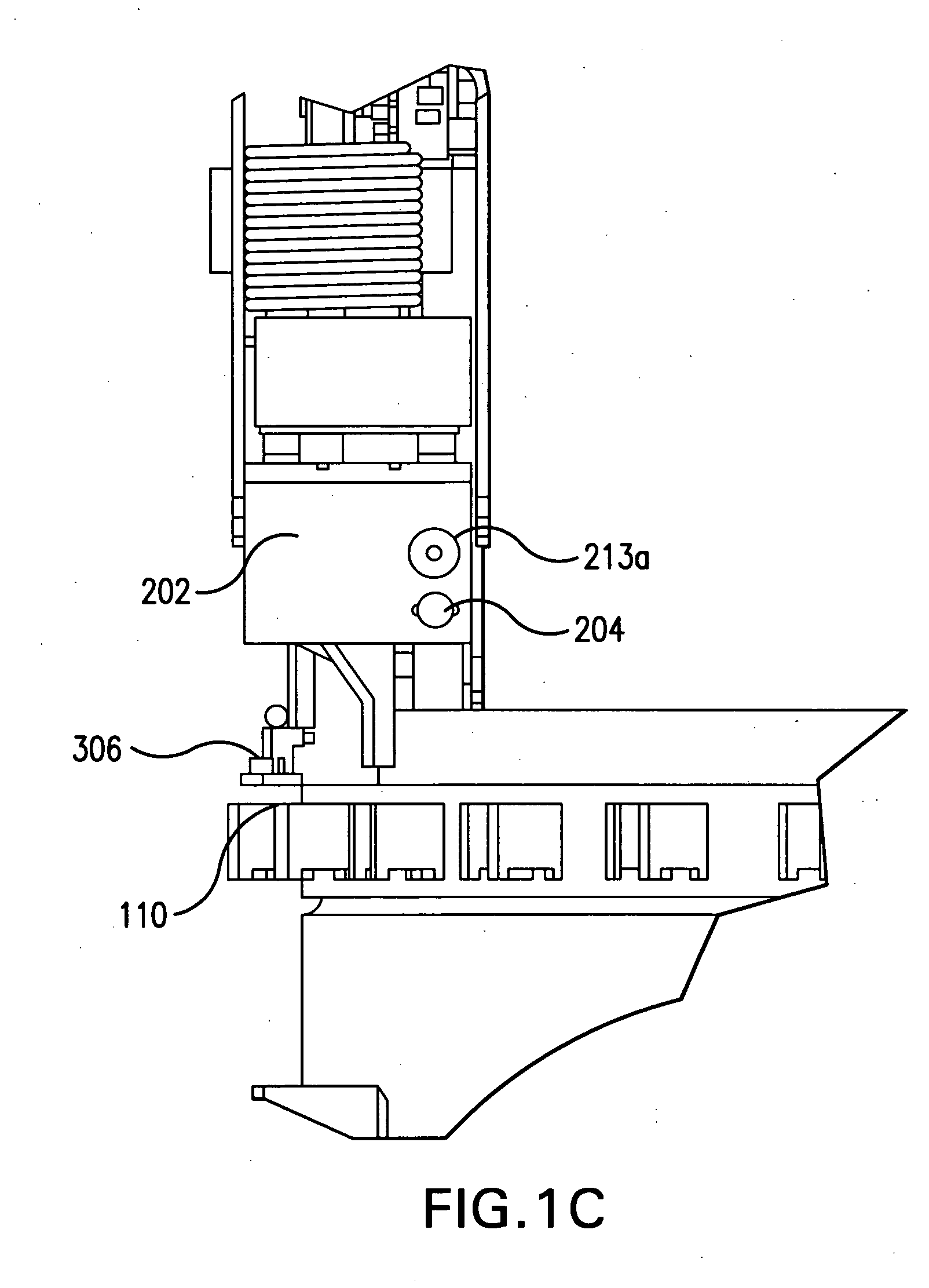
Apparatus and method for inspecting areas surrounding nuclear boiling water reactor core and annulus regions
InactiveUS20070146480A1Shorten the construction periodConserve costNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringElectrical controlEngineering
A remotely controlled apparatus (112) for inspecting the core (102) and annulus (104) areas of nuclear boiling water reactors (100) includes a circumferential drive mechanism for propelling the apparatus (112) on the steam dam (108) of the reactor (100). The inspection apparatus (112) uses a set of driver rollers (314) that grip the side of the steam dam (108) and provide propulsion for the apparatus. A pinch-roller assembly with high-tension springs (308) and pneumatic air cylinders (310) is utilized for removably securing a set of pinch rollers (312) to the side of the steam dam opposite the side of the driver rollers (314). A set of rollers (304) are adapted to rest on top of the steam dam (108), supporting the weight of the apparatus (112) and enabling the apparatus to move around the steam dam (108). Two positioning guide rails (306) aid in the balance of the apparatus (112), especially when it is stationary. The apparatus (112) has a watertight main body (202), which houses the electrical control wiring and circuitry. The main body (202) has a front camera (204) and a rear camera (205) used to direct the movements of the apparatus (112). The main body also has two turret-type telescoping mast assemblies (208) with telescoping masts 210 and 212, which are capable of extending at a selected distance above and below the main body (202). The mast assemblies 210 and 212 support inspection equipment such as radiation-shielded EVT-1-capable video cameras and radiation-tolerant fiberscopes. The apparatus (112) and its inspection tools are remotely controlled via control consoles with video monitors from a low-dose, non-contaminated enclosure located remotely from a boiling water reactor.
Owner:EXELON CORP
Compositions of suspended non-aggregated carbon nanotubes, methods of making the same, and uses thereof
InactiveUS7365100B2Improved strength and weight and strength to weight ratioMaterial nanotechnologyOther chemical processesCapacitanceElectricity
The invention is directed, in part, to stable compositions of suspended carbon nanotubes, methods of making them, and uses thereof. The invention provides methods of producing high and low concentrations of highly dispersed carbon nanotubes suspended in a liquid. The carbon nanotube suspensions are of use in generating products with improved strength, weight, strength to weight ratio, electrical and thermal versatility, radiation shielding, capacitance, dielectric properties, selective ion flow, catalytic activity and biological applications. The invention provides for industrial processing of materials comprising carbon nanotubes such as, but not limited to, fibers, films, synthetic membranes, coatings, drug delivery systems, and molecular circuitry components.
Owner:VERSILANT NANOTECH +1
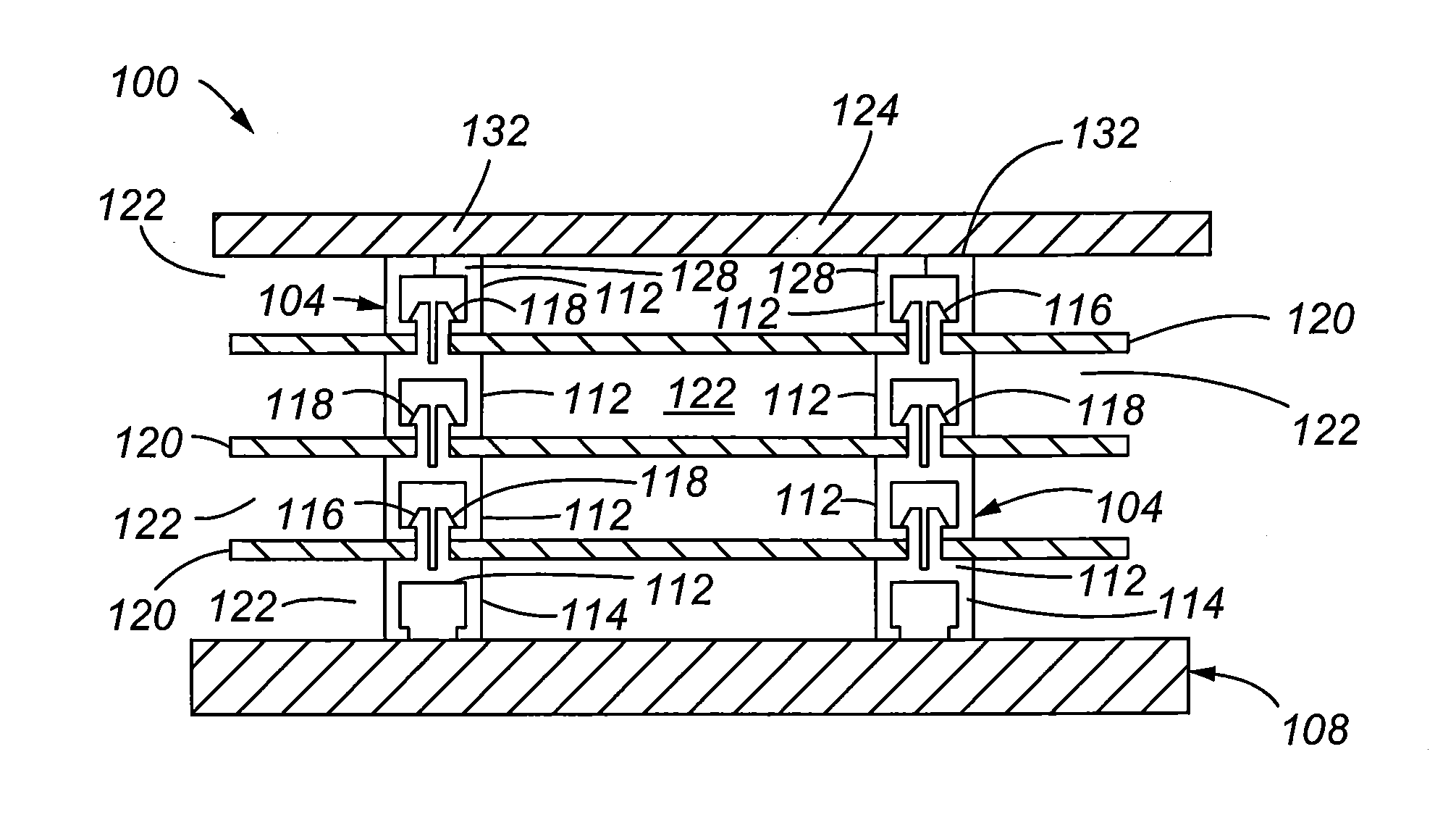
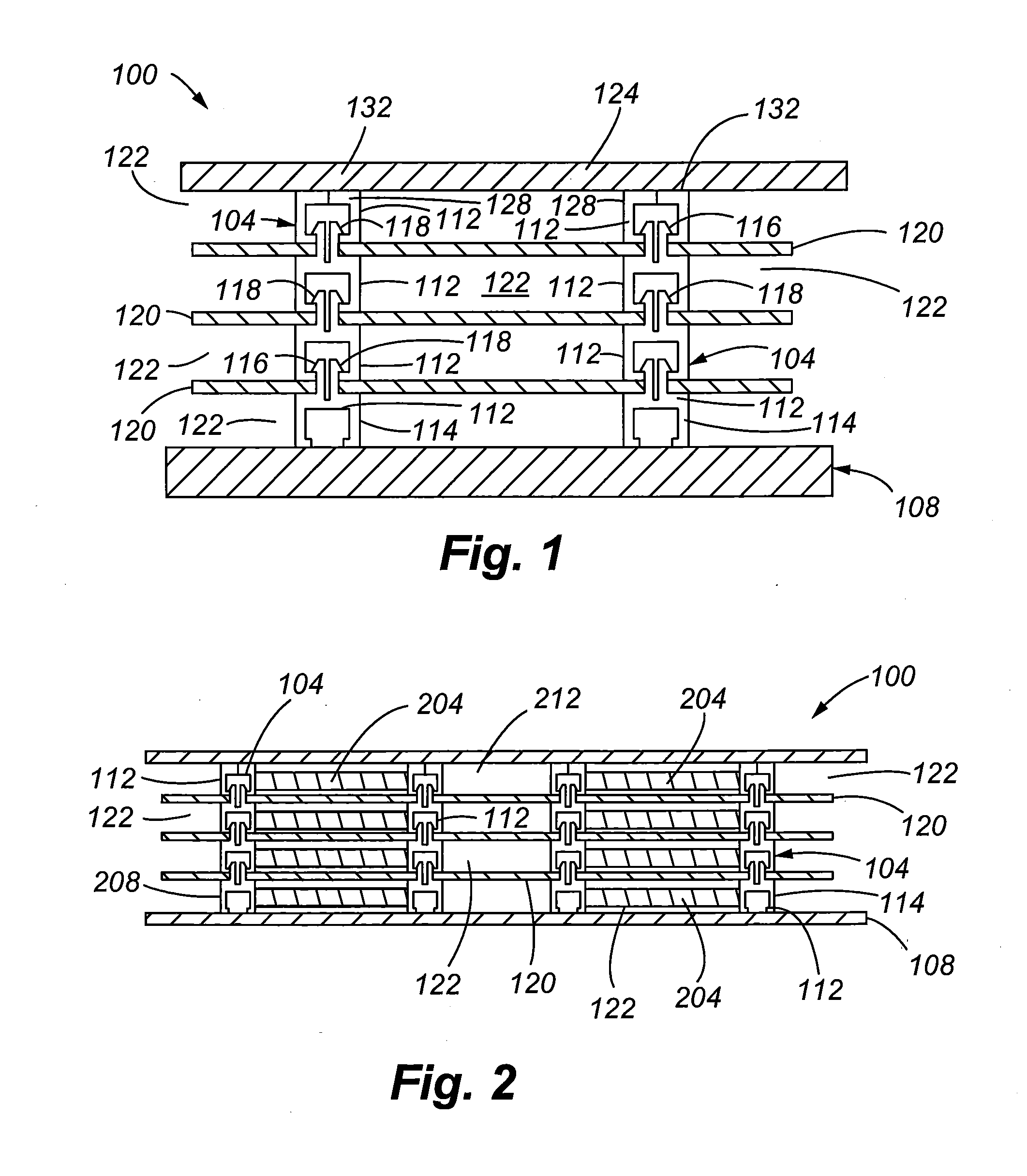
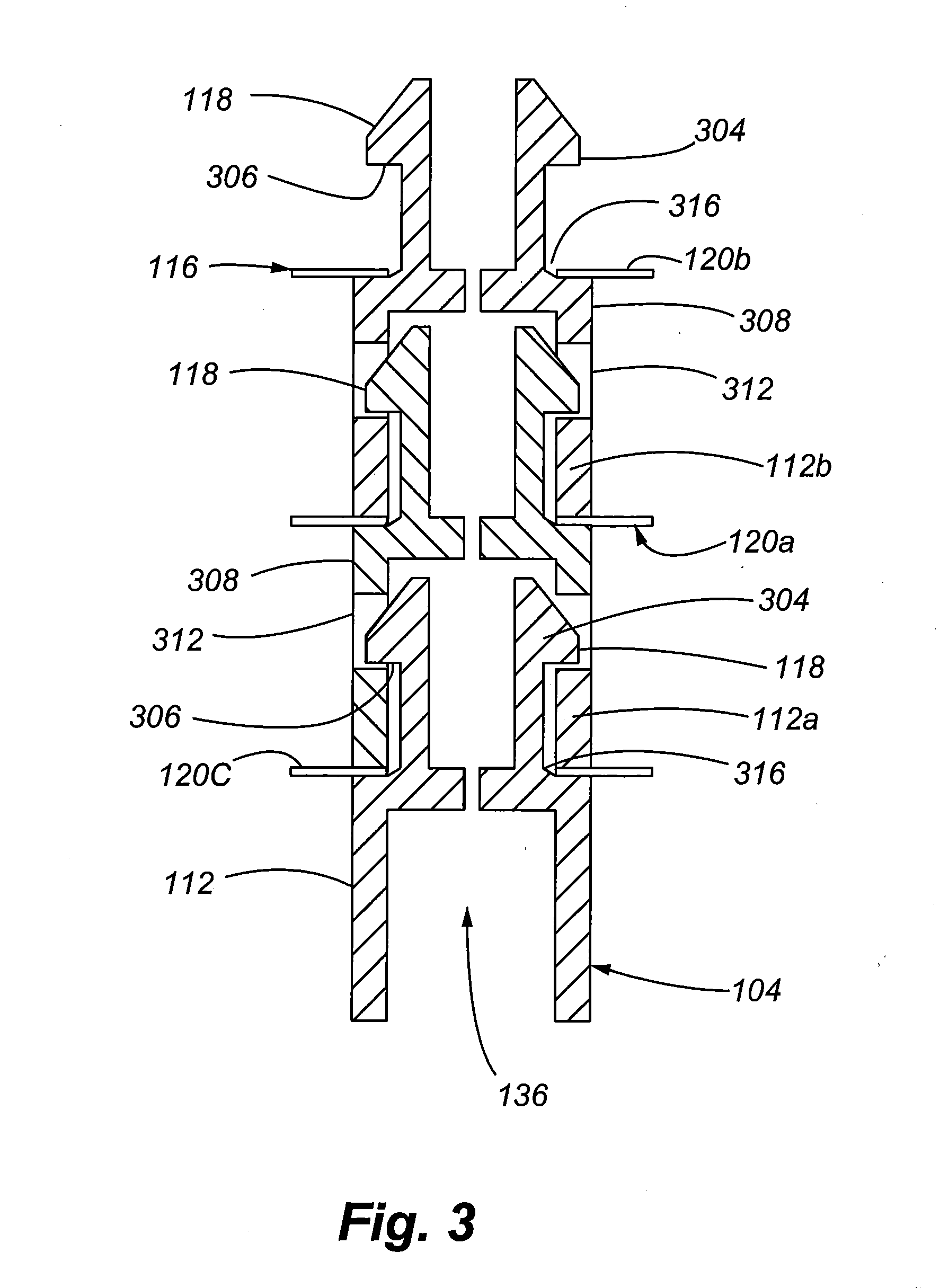
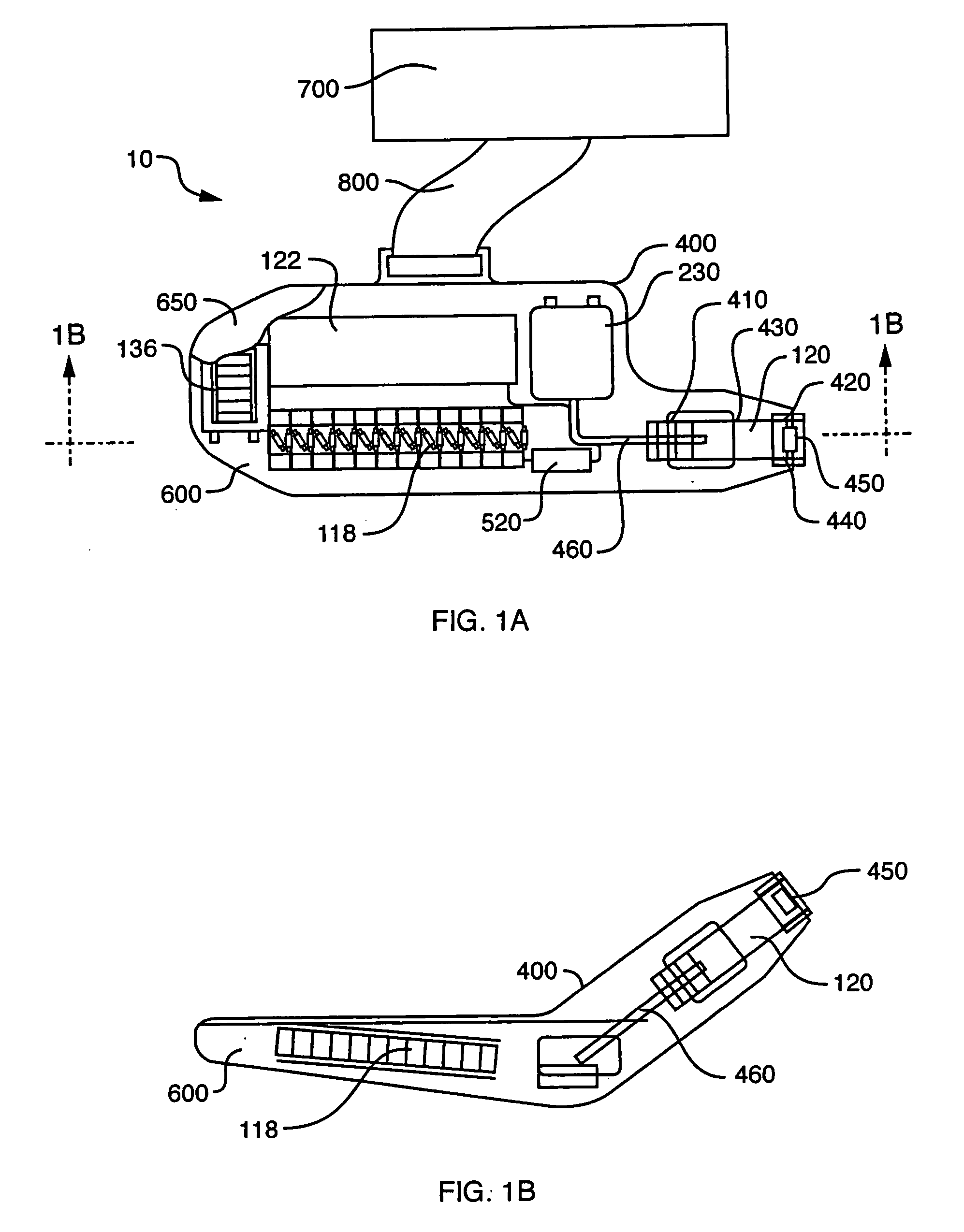
Integrated radiation shield
InactiveUS6392246B1Environment safetyEasy to integrateConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsPortable shielded containersEngineeringIsotope
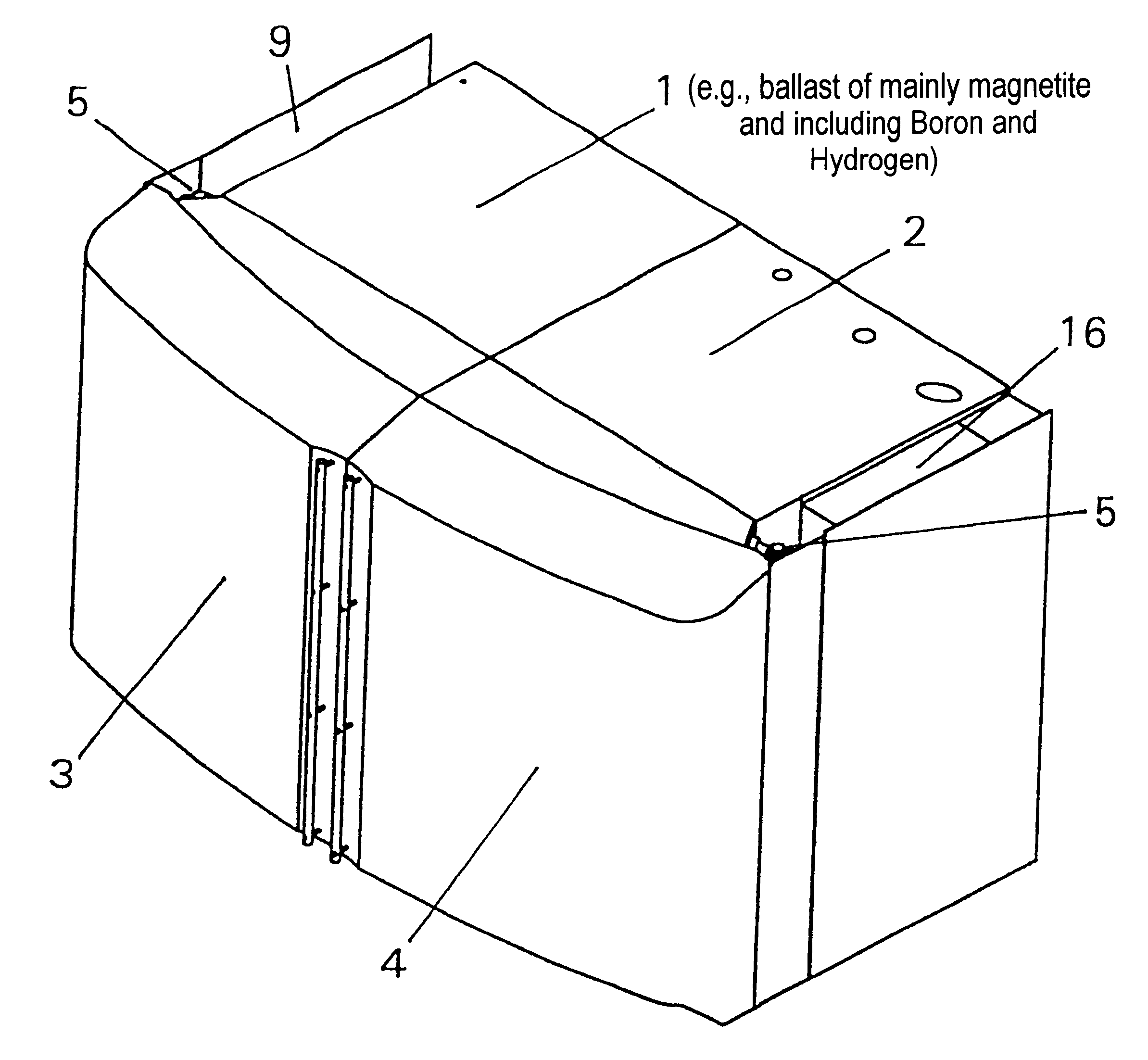
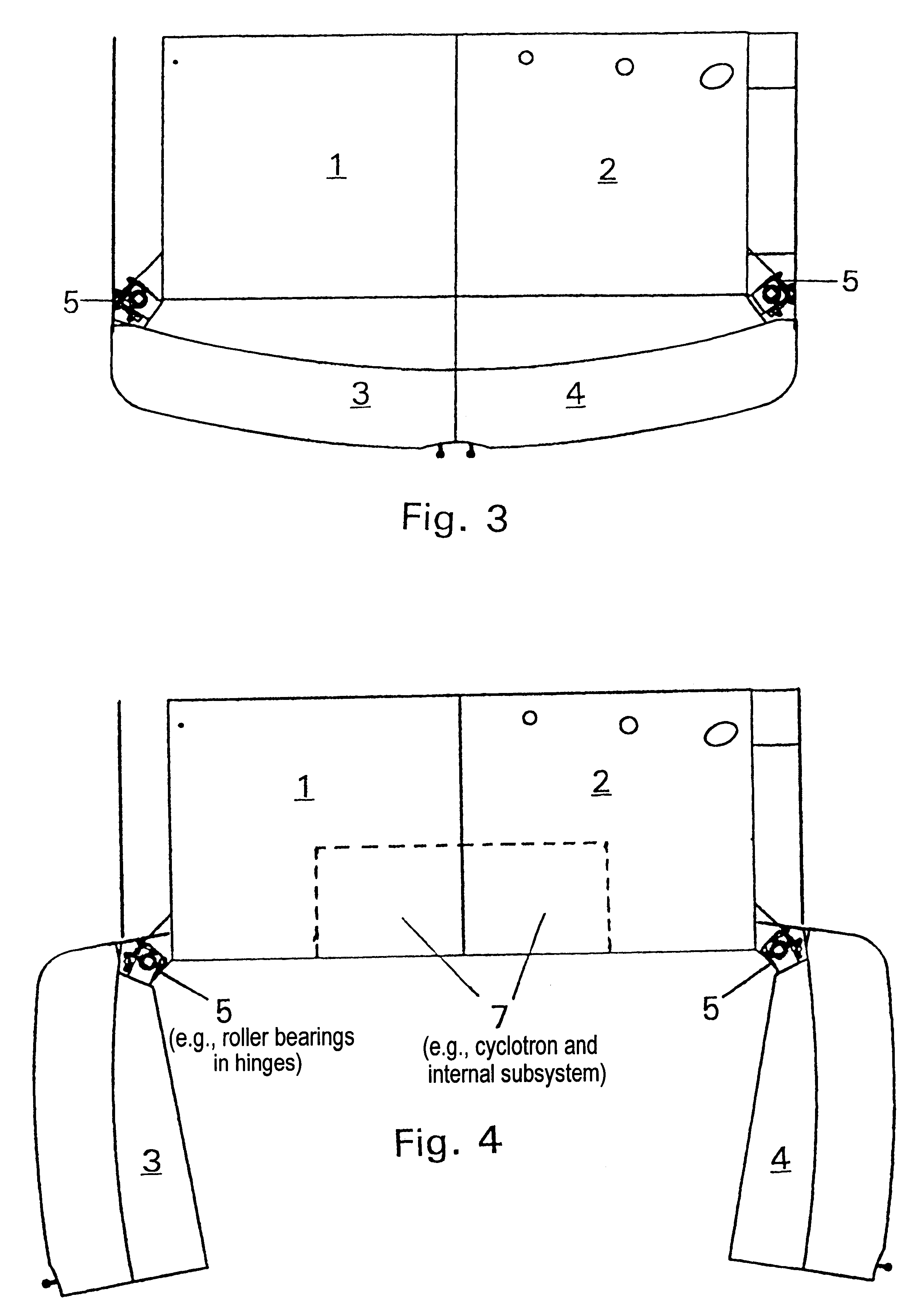
An apparatus is disclosed that forms a basic integrated radiation shield for a PET isotope production system to create a safe environment. The apparatus and the system combine several subsystems to provide a high degree of integration and a nice aesthetic impression. The apparatus contains a cyclotron system and contains integrated target media handling for gas targets and water dispensing systems for water targets. A compartment including first and second additional radiation shields, respectively, that contains additional processing systems. The apparatus forms a closed radiation-proof system by means of a casing formed of four molded sections. A first and second section constitute a main body containing;the cyclotron system and a third and a fourth section constituting a pair of tight doors for encompassing the cyclotron into a sealed radiation shield. The first section additionally contains a Waste Gas Delay Line embedded in its shielding material.
Owner:GEMS PET SYST
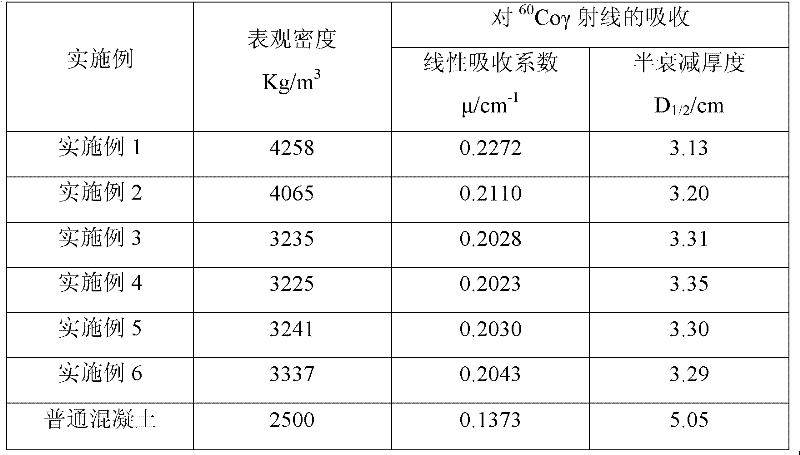
Radiation shield concrete and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102219459AReduce water-cement ratioLow shrinkageSolid waste managementShieldingSlagSuperplasticizer
The invention relates to radiation shield concrete and a preparation method thereof. The radiation shield concrete is characterized by comprising a cementing material, coarse aggregates, fine aggregates, steel fibre, a high-efficiency slushing agent and water; the cementing material is composed of ordinary portland cement and inorganic mineral admixtures; the inorganic mineral admixtures are siliceous dust and coal ash; the fine aggregates are natural sand, boron glass powder and steel slag powder; the coarse aggregates are steel sections or a mixture of the steel sections and steel slag; the proportions of various types of components are as follows: 500 kg / m<3> of cementing material, 1400-2215 kg / m<3> of coarse aggregates, 750-950 kg / m<3> of fine aggregates, and 155-200 kg / m<3> of water; the high-efficiency slushing agent is 0.5-1.0% of the total weight of the cementing material by weight; and the steel fibre is 1.0-1.5% of the total volume of the concrete by volume. The radiation shield concrete has good mechanical property and lasting quality, good shielding effect on gamma rays, good effect on shielding neutron rays, can be used or comprehensively recycling wastes and has low cost.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Methods for tissue irradiation with shielding
InactiveUS20070191667A1Reduce and minimize damaging irradiationUniform irradiationCannulasX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyDistal portionRadiation damage
Devices and methods are disclosed for treatment to tissue surrounding a body cavity or other intracorporeal site, such as after removal of tissue, e.g. cancer. Such a device includes a treatment location on a distal portion of the device with one or more radiation shielding components that partially encircle a radiation source at the treatment location to control emitted radiation from the radiation source. The device minimizes radiation damage to healthy tissue surrounding the body cavity or other site while irradiating tissue not shielded by the radiation shielding components. A device embodying features of the invention can include a sealing member at a location on a shaft of the device proximal to a treatment location to seal the passageway leading to the body cavity.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Beam shaping body for neutron capture therapy
In order to improve the flux and the quality of a neutron source, the invention provides a beam shaping body for neutron capture therapy. The beam shaping body comprises a beam inlet, a target, a retarding body adjacent to the target, a reflecting body surrounding the external of the retarding body, a thermal neutron absorber adjacent to the retarding body, and a radiation shield and a beam outlet formed in the beam shaping body, wherein the target has nuclear reaction with proton beam entering from the beam inlet, so as to produce a neutron; the neutron forms a neutron beam; the neutron beam defines a main axis; the retarding body slows down the neutron produced by the target to an epithermal neutron energy region; the retarding body is designed to a shape containing at least one cone; the reflecting body guides the neutron deviated from the main axis back to the main axis, so as to improve the strength of an epithermal neutron beam; the thermal neutron absorber is used for absorbing a thermal neutron, so as to prevent the thermal neutron from causing excessive dosage with a superficial normal tissue during therapy; the radiation shield is used for shielding leaked neutron and photon, so as to reduce the normal tissue dosage of a non-irradiated region.
Owner:NEUBORON MEDTECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com