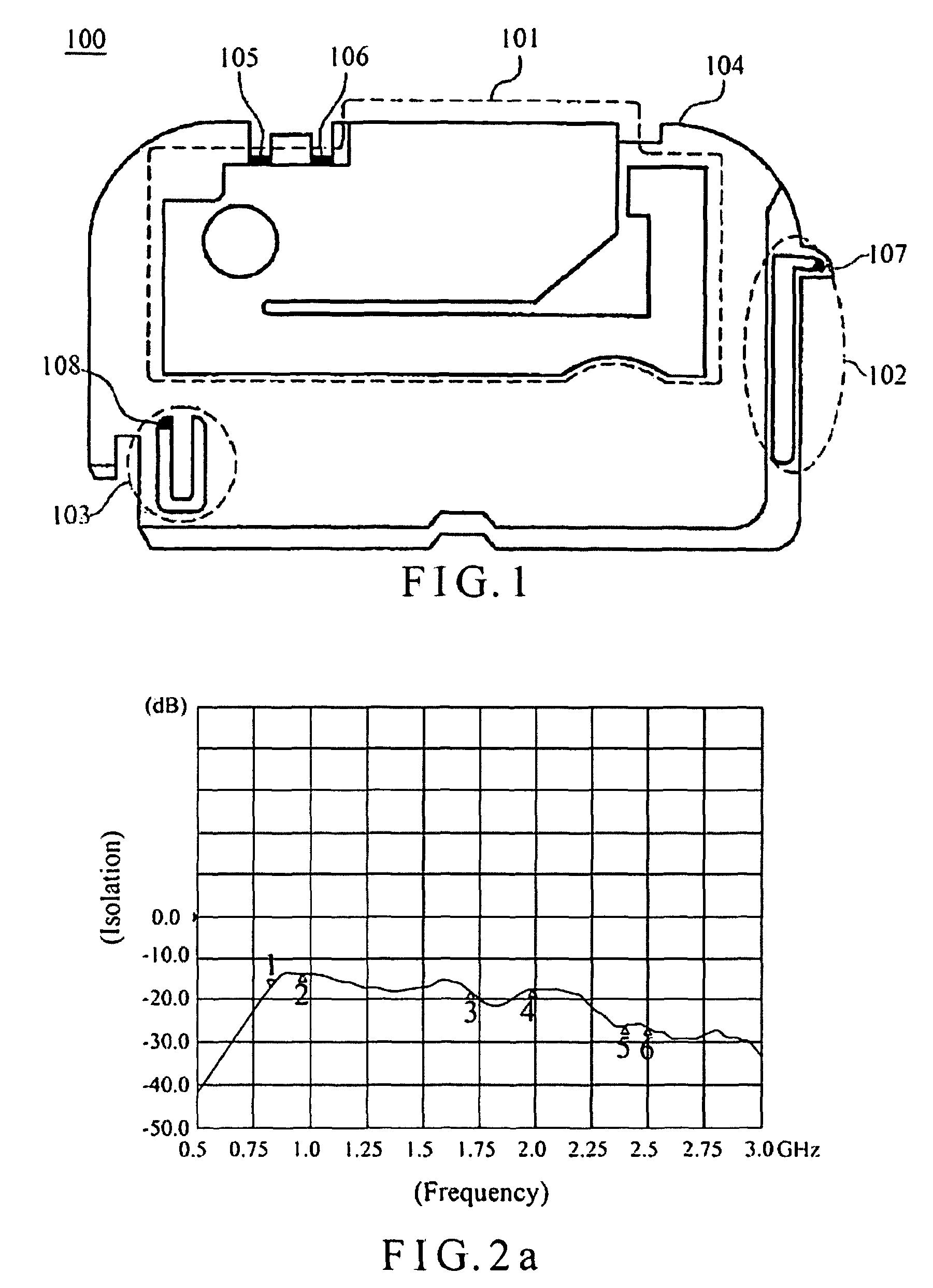
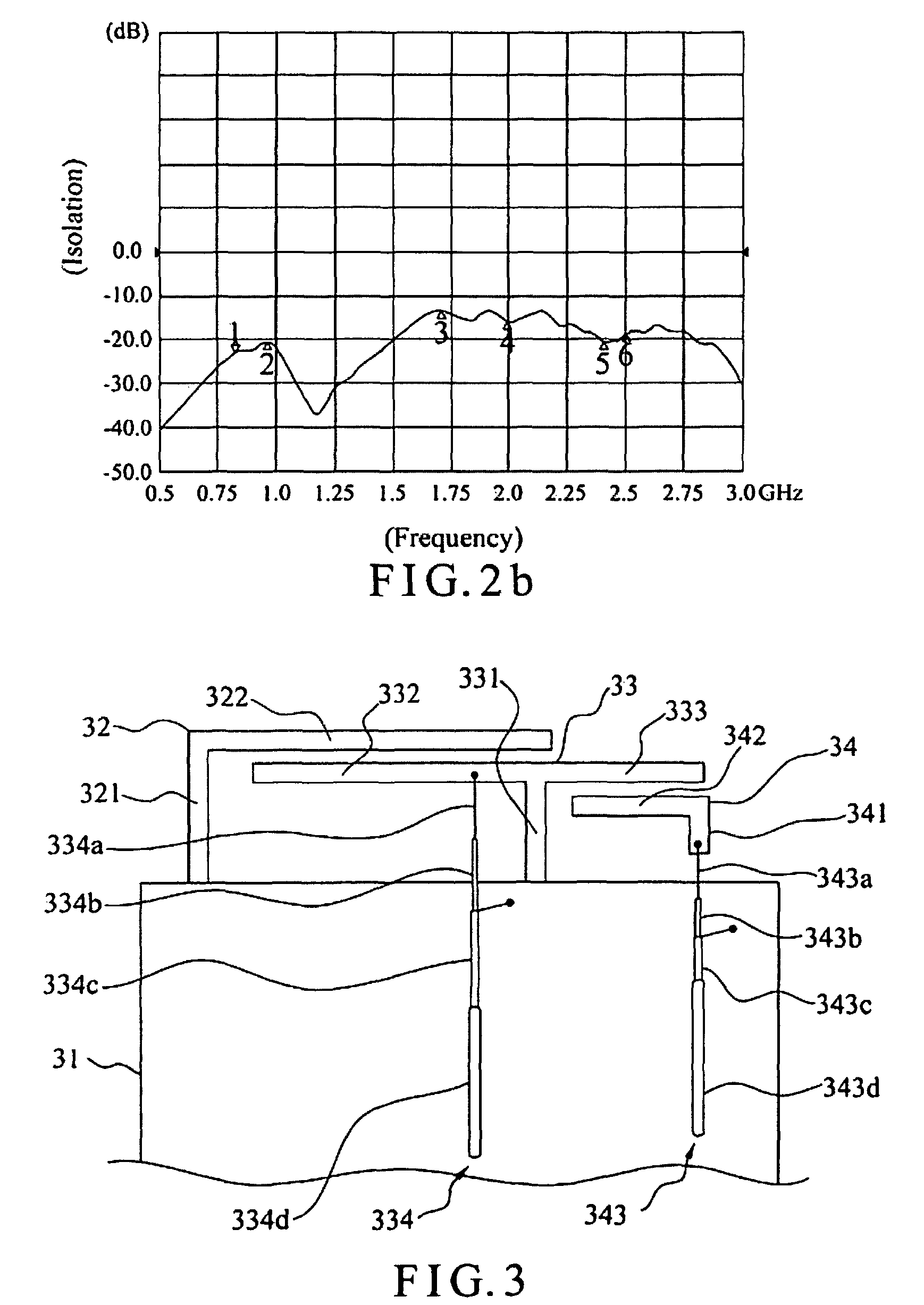
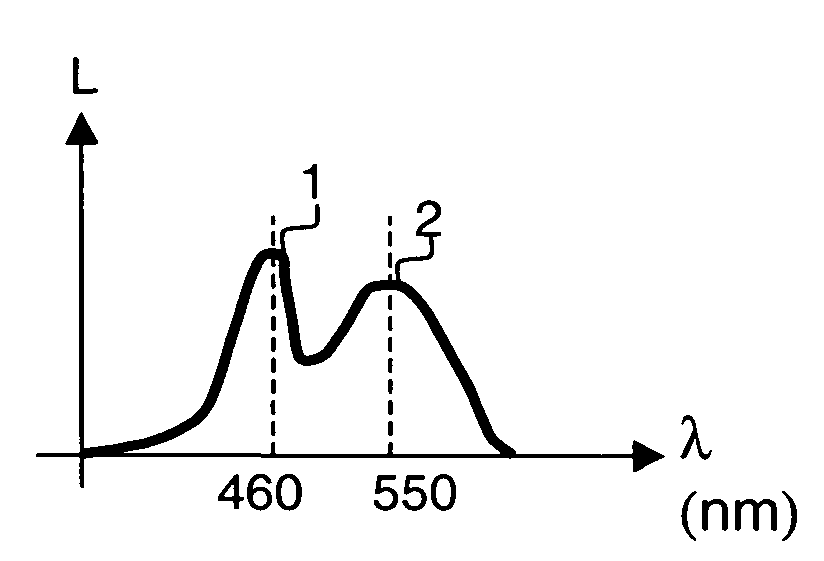
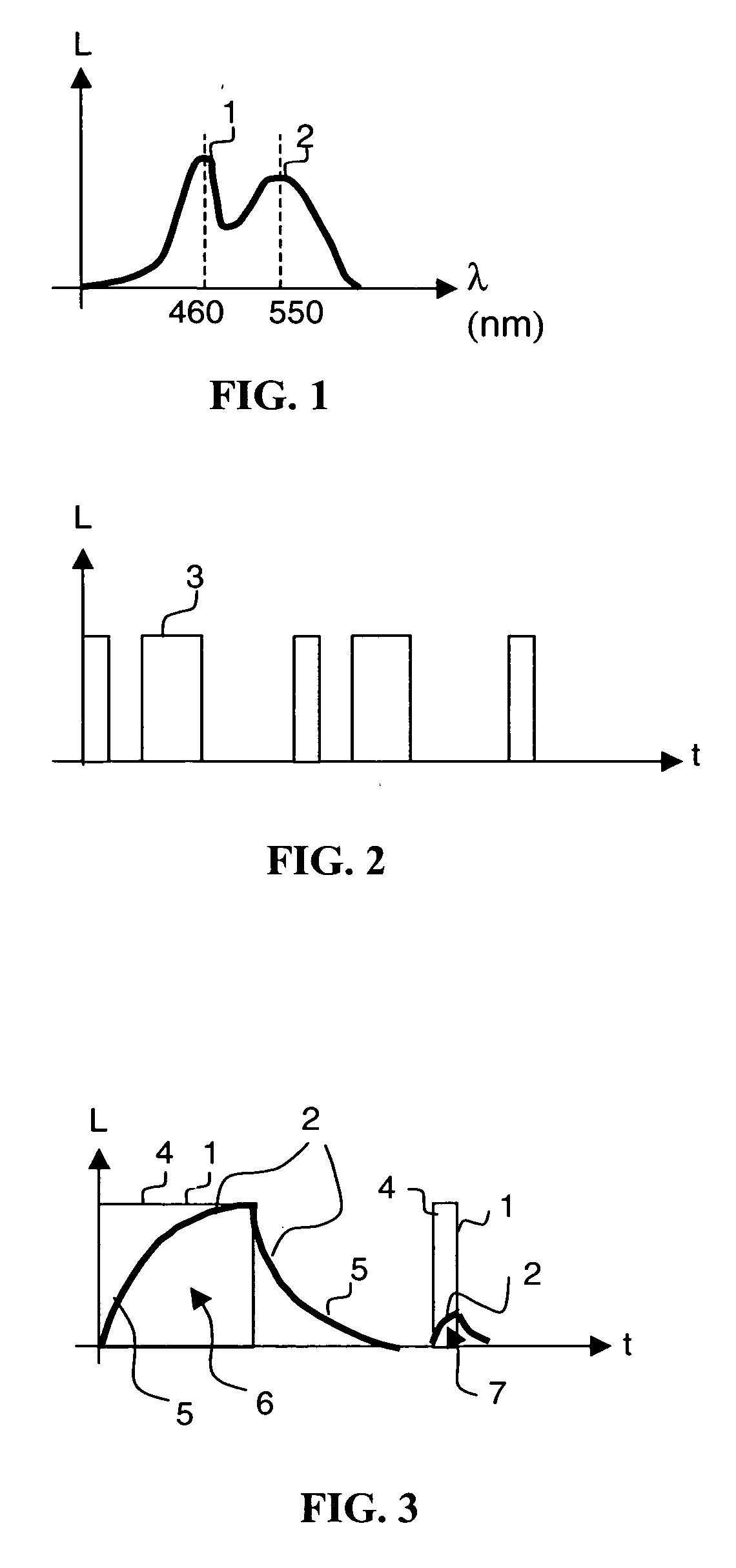
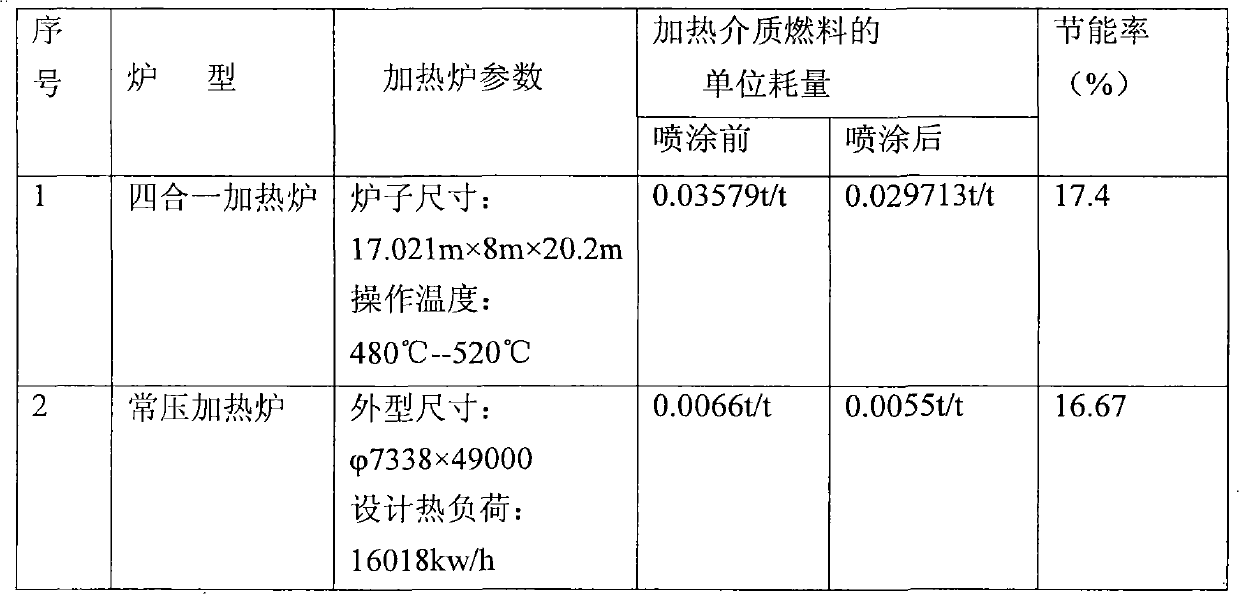
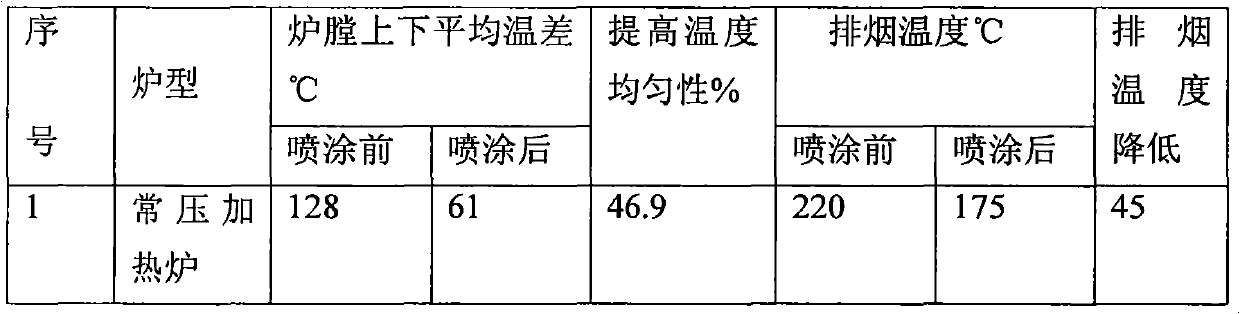
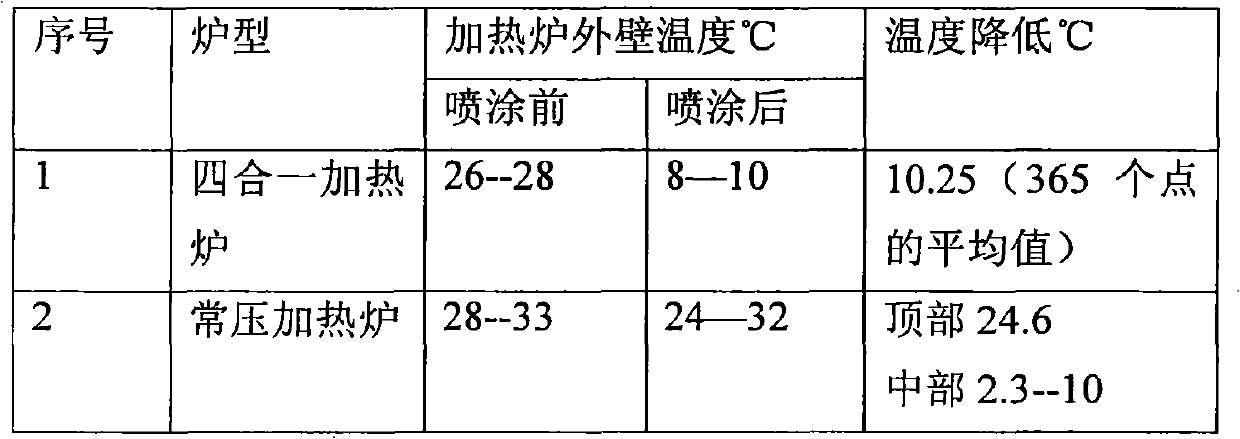
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
281 results about "Secondary radiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
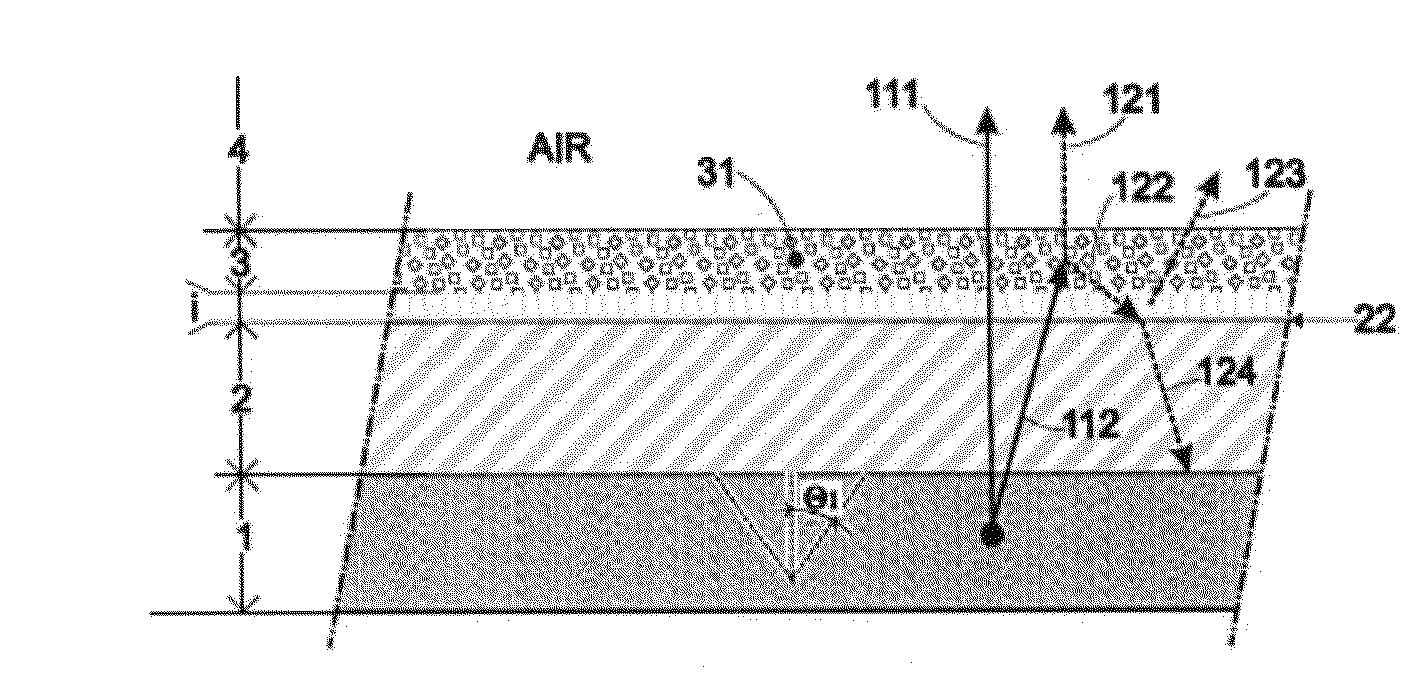
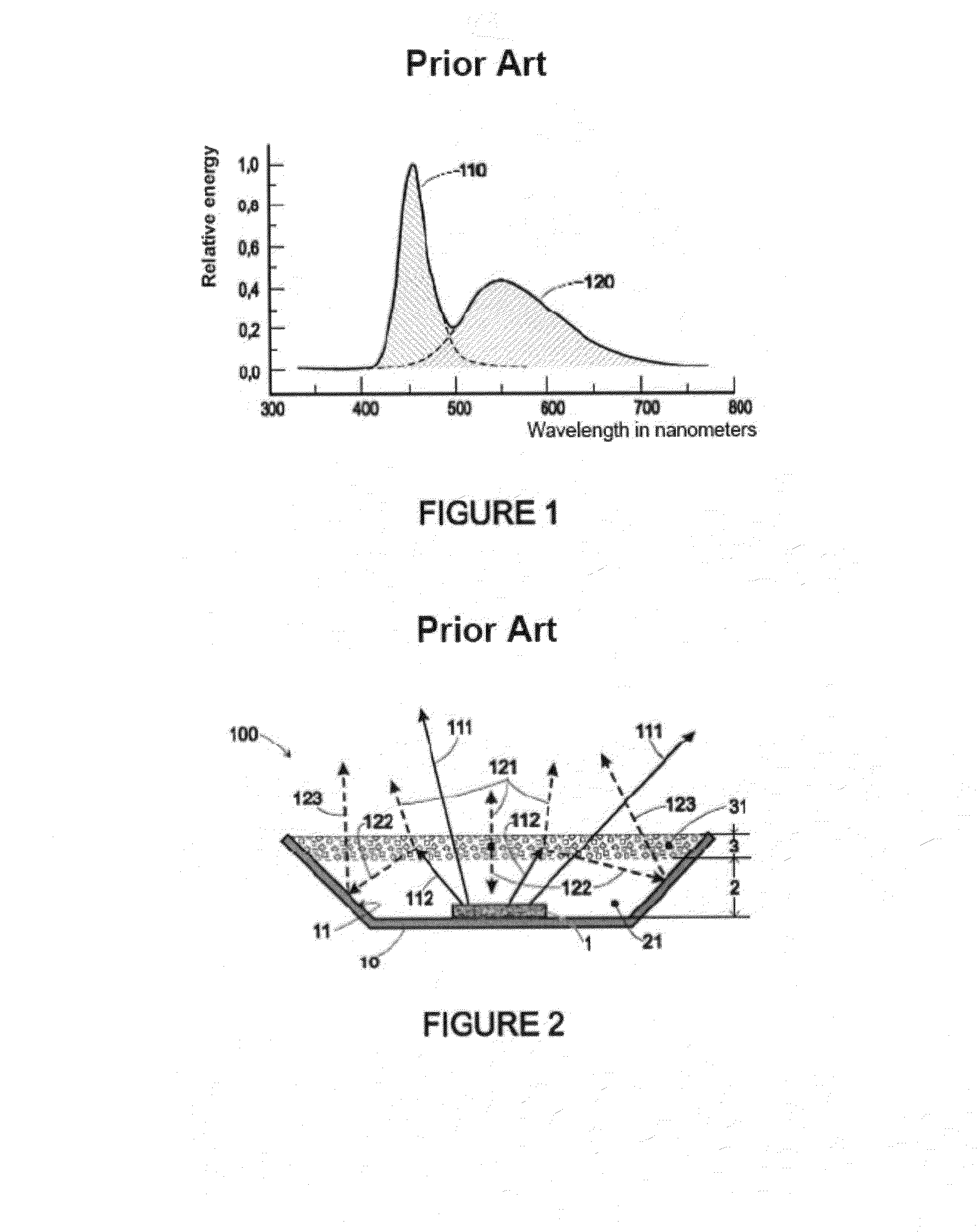
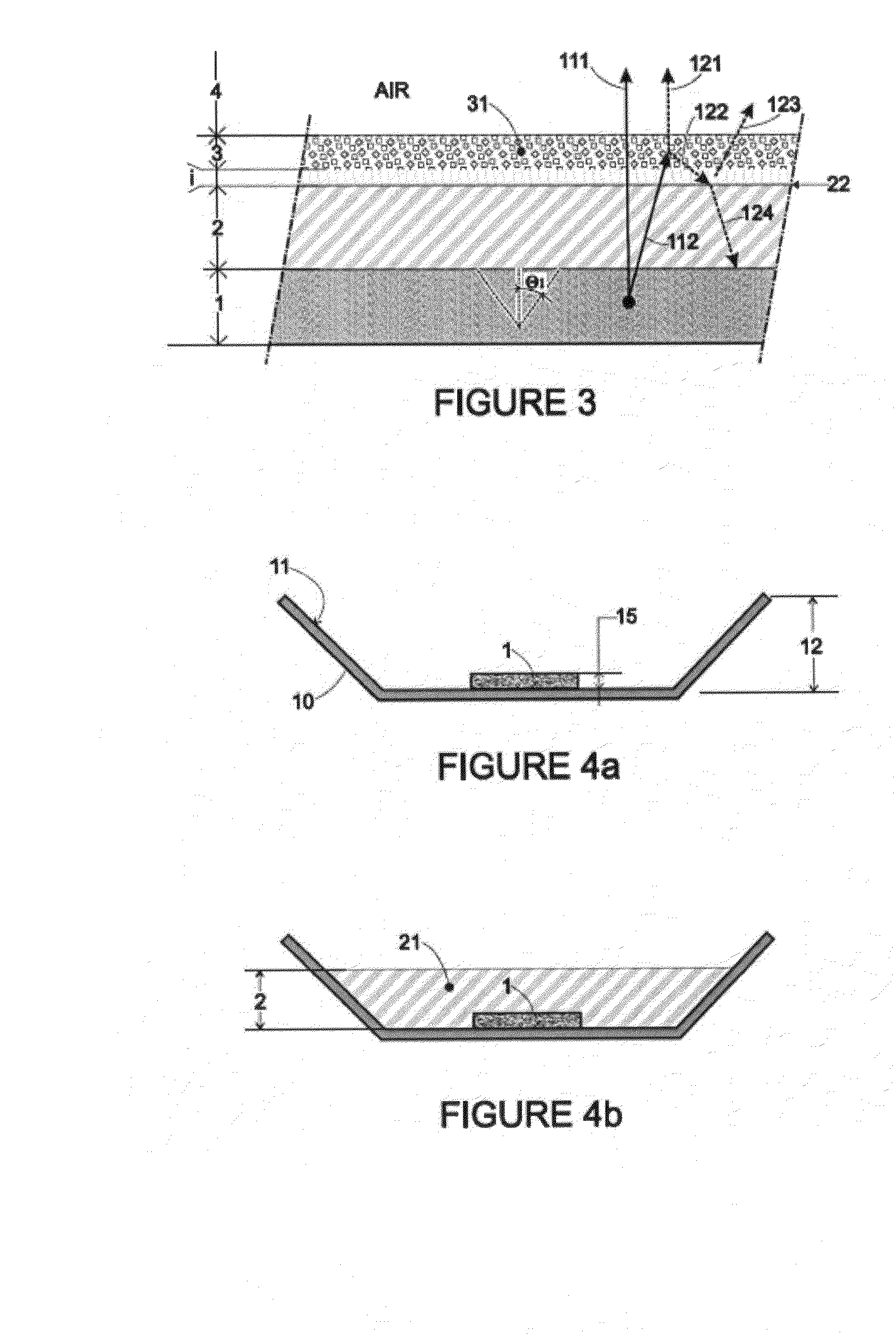
Secondary radiation is a phenomenon that has its origins in the use of X-rays. As X-rays are used for scans on just about any type of substance, the presence of emissions builds up a level of subtle radiation residue that is then emitted is a random manner by the substance in question.
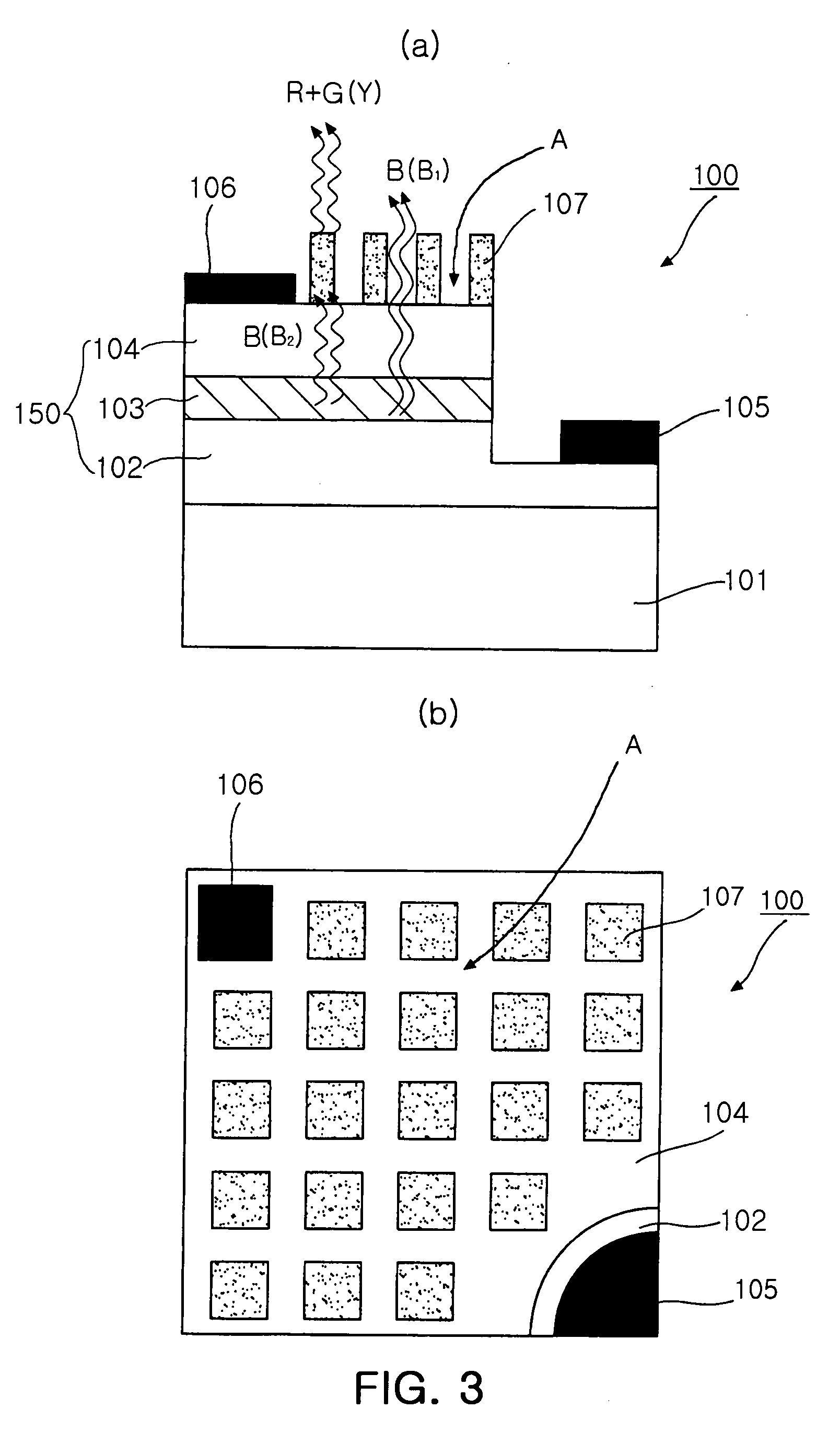
Light source having an LED and a luminescence conversion body and method for producing the luminescence conversion body
ActiveUS20040145308A1Efficient luminescence conversionDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsDopantSecondary radiation
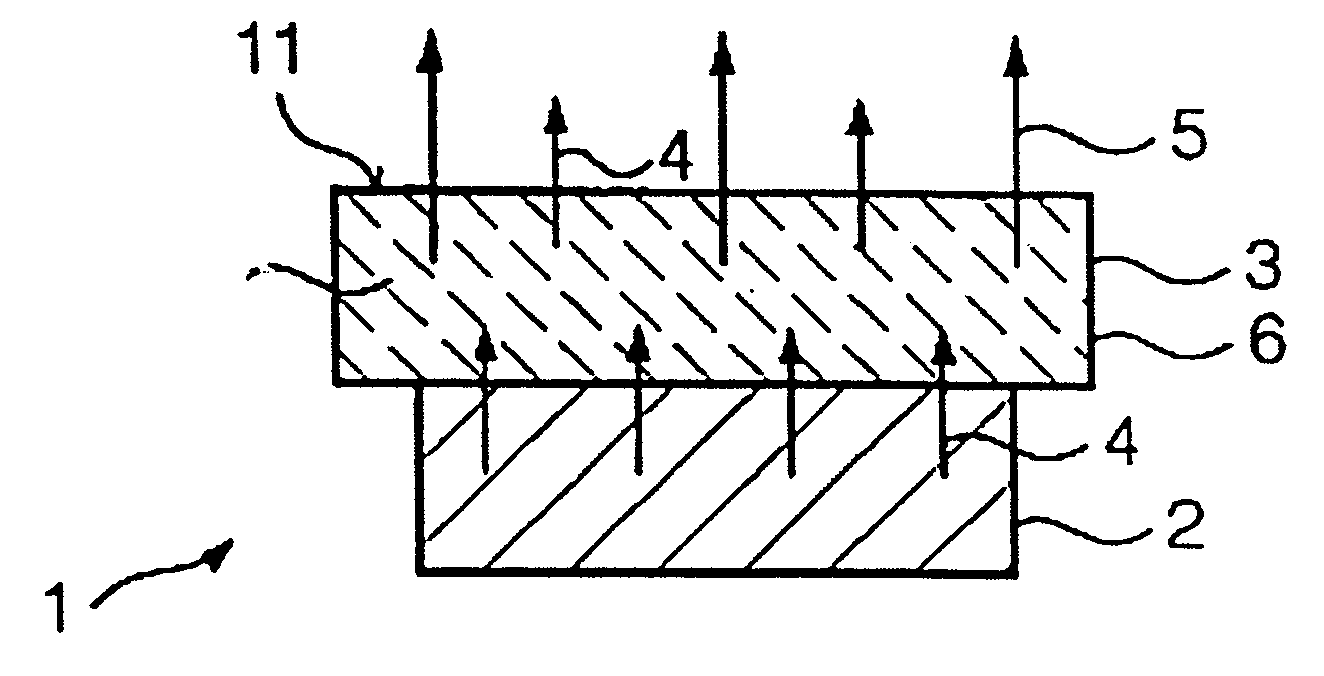
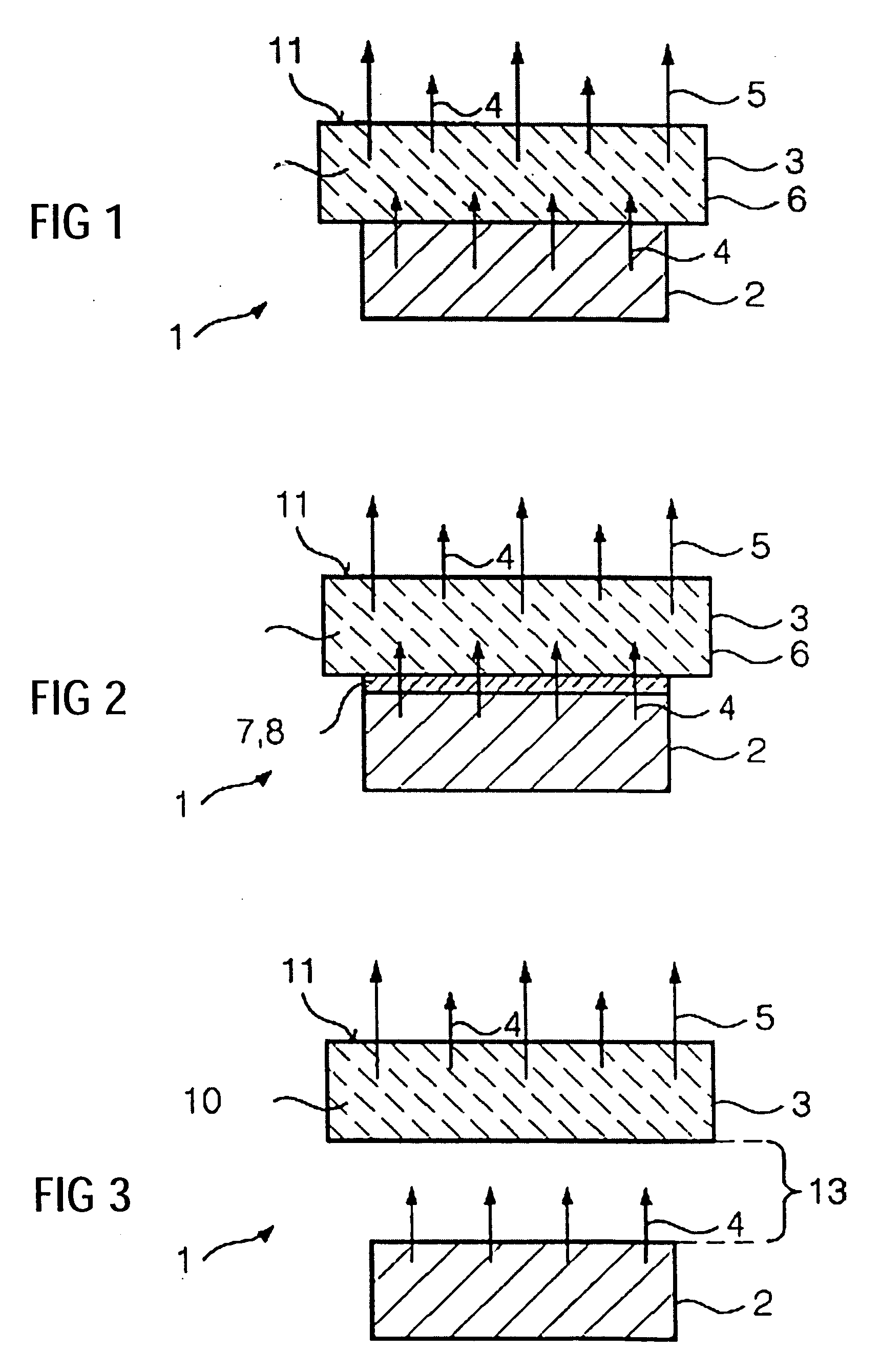
The invention relates to a light source (1), having at least one LED (2) for emitting a primary radiation (4) and at least one luminescence conversion body (3) having at least one luminescent material for converting the primary radiation (4) into a secondary radiation (5). The luminescence conversion body is a polycrystalline ceramic body. The LED is based on GaInN and emits blue primary radiation. The ceramic body comprises for example a luminescent material based on a cerium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet. This luminescent material emits yellow secondary radiation. Blue primary radiation and yellow secondary radiation penetrate through the luminescence conversion body and are perceived as white light by the observer. In order to produce the luminescence conversion body, provision is made of a polycrystalline ceramic body which is united with a solution of a dopant. By means of a thermal treatment, the dopant (activator) diffuses into the ceramic body, the luminescent material being formed.
Owner:OSRAM OPTO SEMICONDUCTORS GMBH
White light emitting device
InactiveUS20070228931A1Easily adjusting color balanceUniform luminous propertiesDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsSecondary radiationLength wave
A high quality white light emitting device capable of adjusting color balance easily. A substrate is provided. A light emitting structure includes an n-type semiconductor layer, an active layer and a p-type semiconductor layer sequentially formed on the substrate. Here, the light emitting structure emits primary radiation. Wavelength conversion film elements absorb a portion of the primary radiation and convert the absorbed portion of the primary radiation into secondary radiation of a different wavelength. The wavelength conversion film elements define an open region for selectively transmitting the primary radiation therethrough.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Light source having an LED and a luminescence conversion body and method for producing the luminescence conversion body
ActiveUS7554258B2Efficient luminescence conversionDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsDopantSecondary radiation
A light source, having at least one LED for emitting a primary radiation and at least one luminescence conversion body having at least one luminescent material for converting the primary radiation into a secondary radiation. The luminescence conversion body is a polycrystalline ceramic body which itself acts partly or completely as luminescent material by virtue of at least part of the base material which forms the ceramic body being activated by a dopant.
Owner:OSRAM OPTO SEMICON GMBH & CO OHG
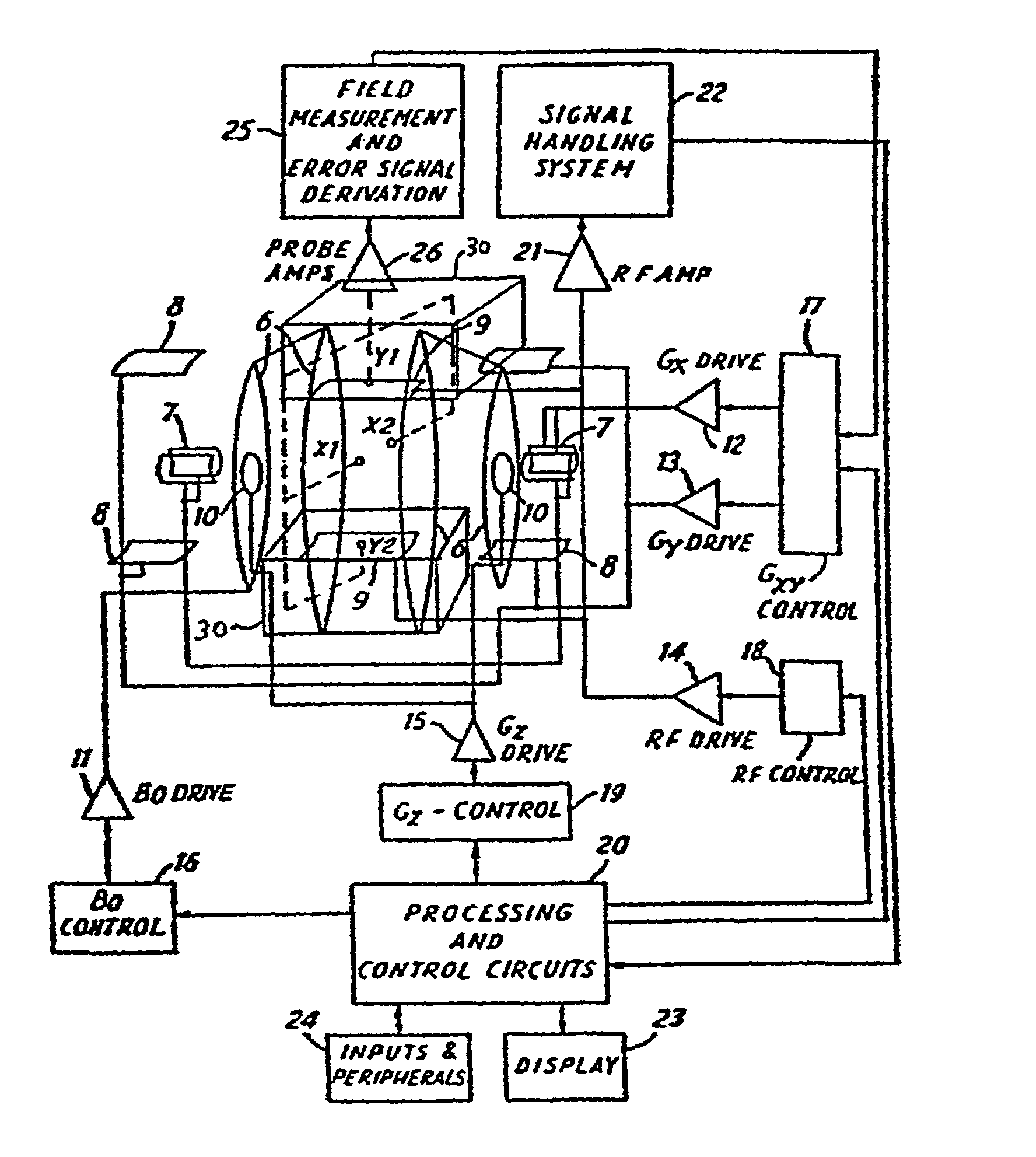
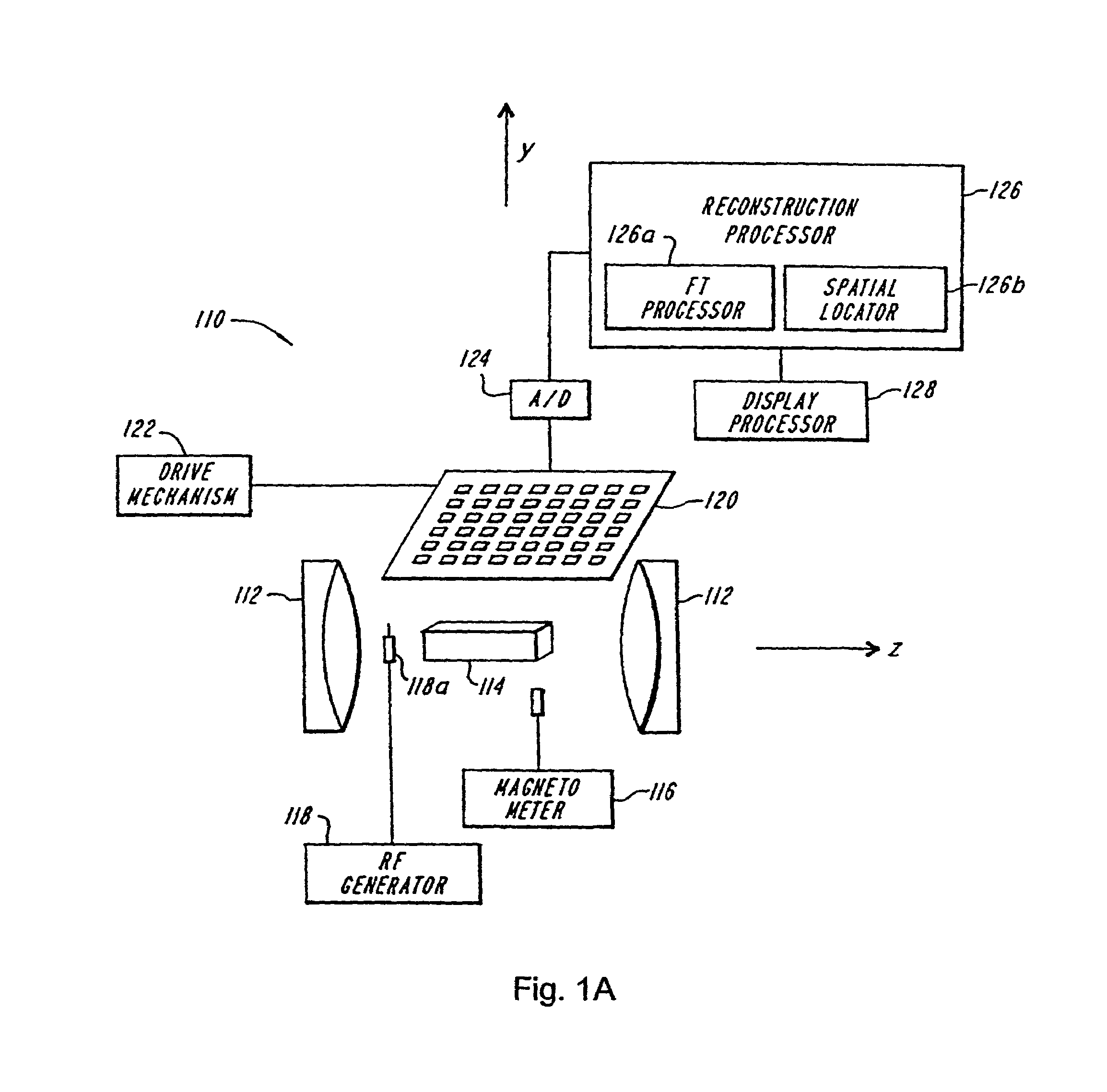
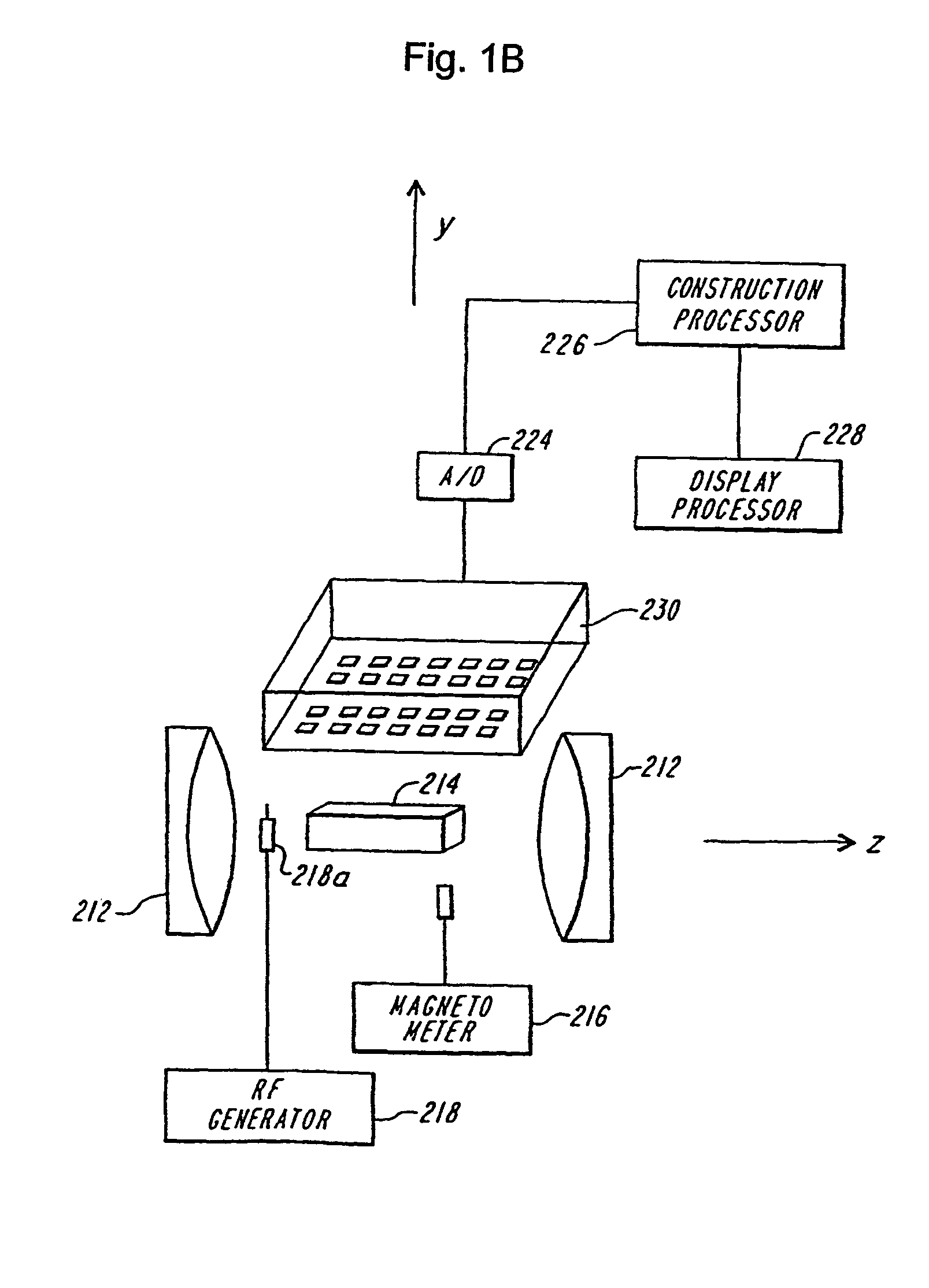
4 dimensional magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS7382129B2Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionPhase correlationVoxel
Provided are apparatus and methods for forming a multidimensional image of inanimate or animate objects which utilize a magnetization source (112) to magnetize a volume of an object to be imaged, a radiation source (118) for applying a radiation field to the object to be imaged, an output signal detector (120) for producing output signals in response to the secondary radiation at a plurality of spatial locations outside of the object as a function of time, processors (126, 126a and 126b) for determining a plurality of Fourier components, for associating the Fourier components due to each voxel (14) by phase, and for converting each set of components into a voxel location, and an image processor (128) for producing an image.
Owner:MILLS RANDELL L
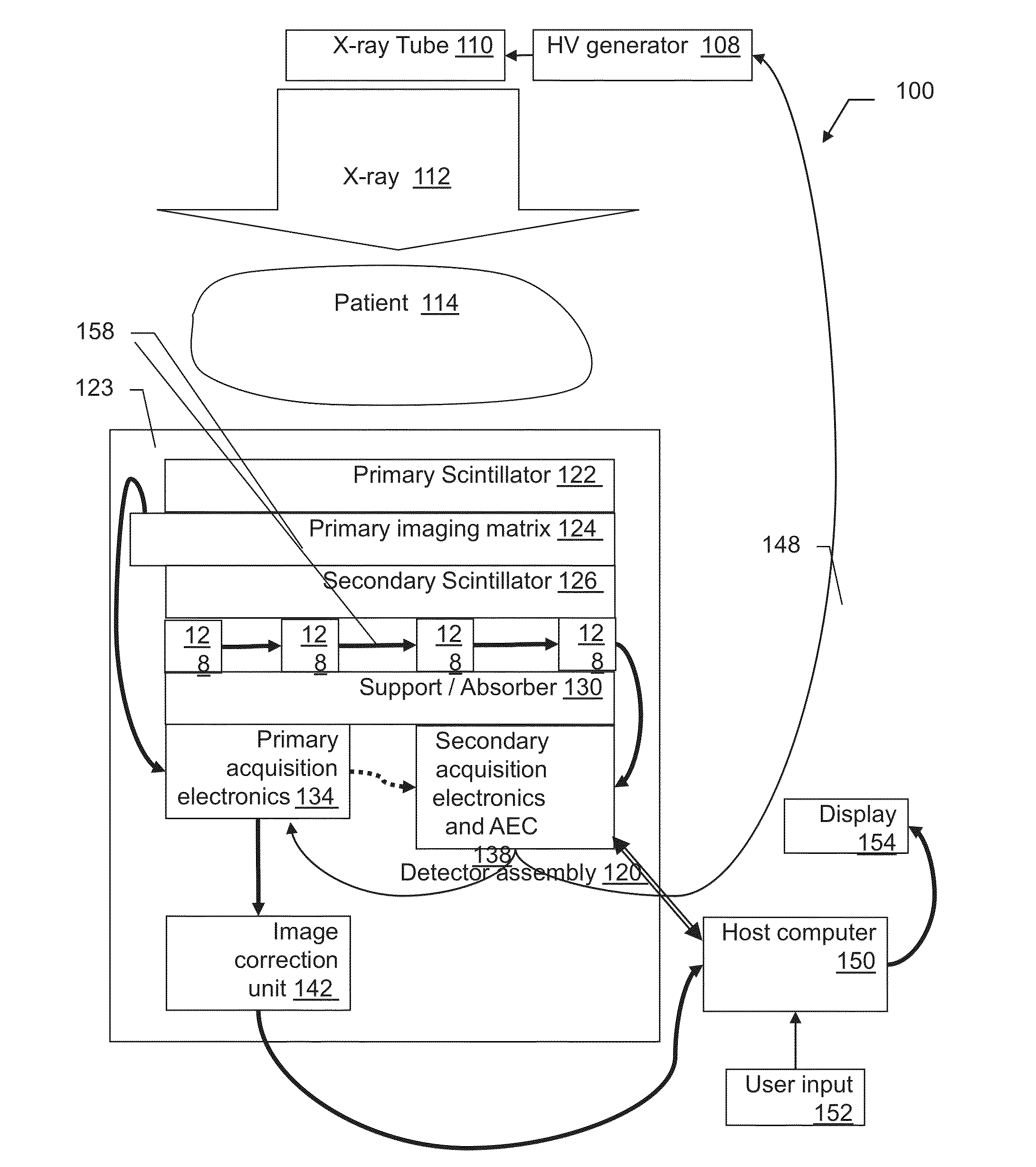
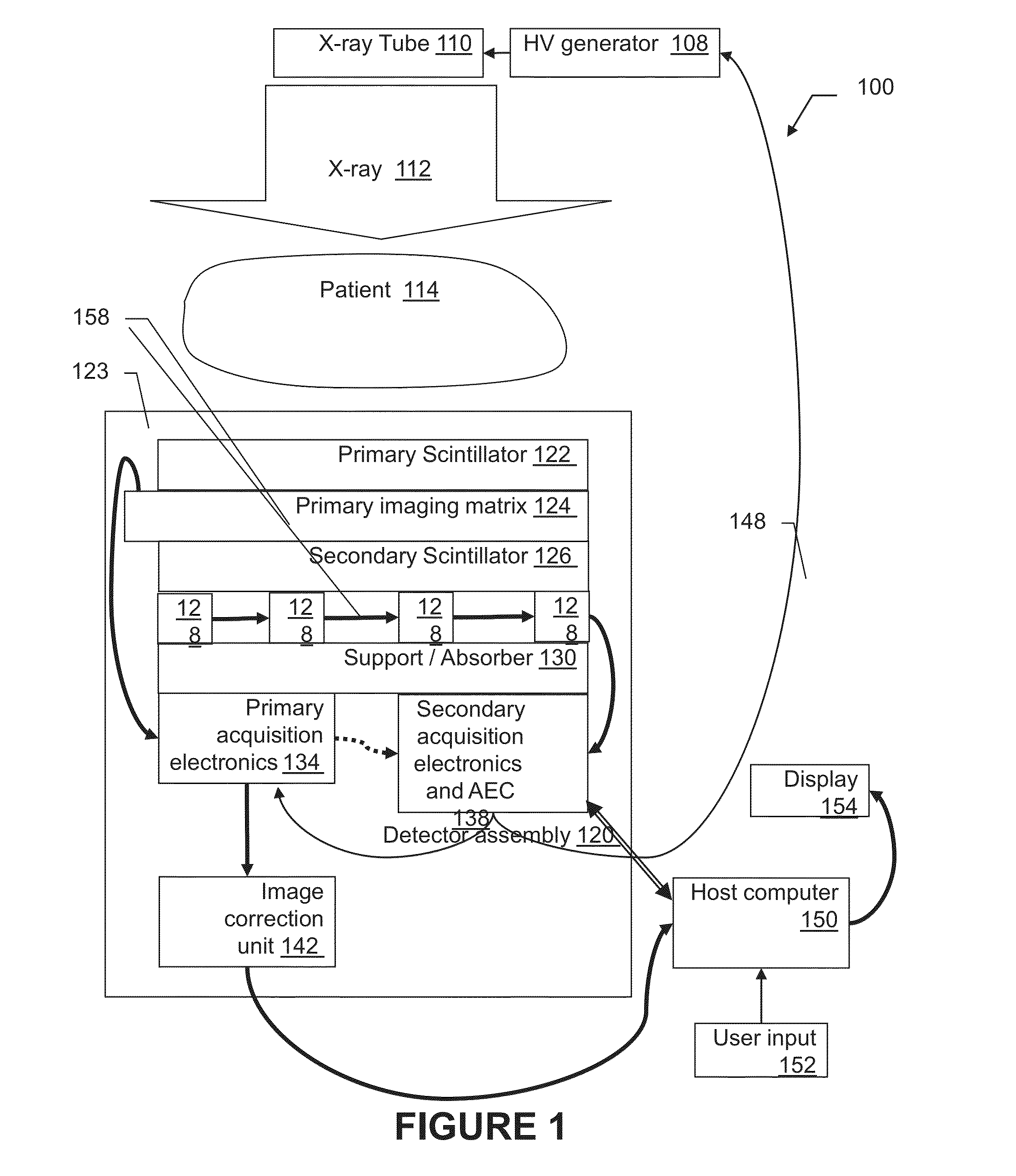
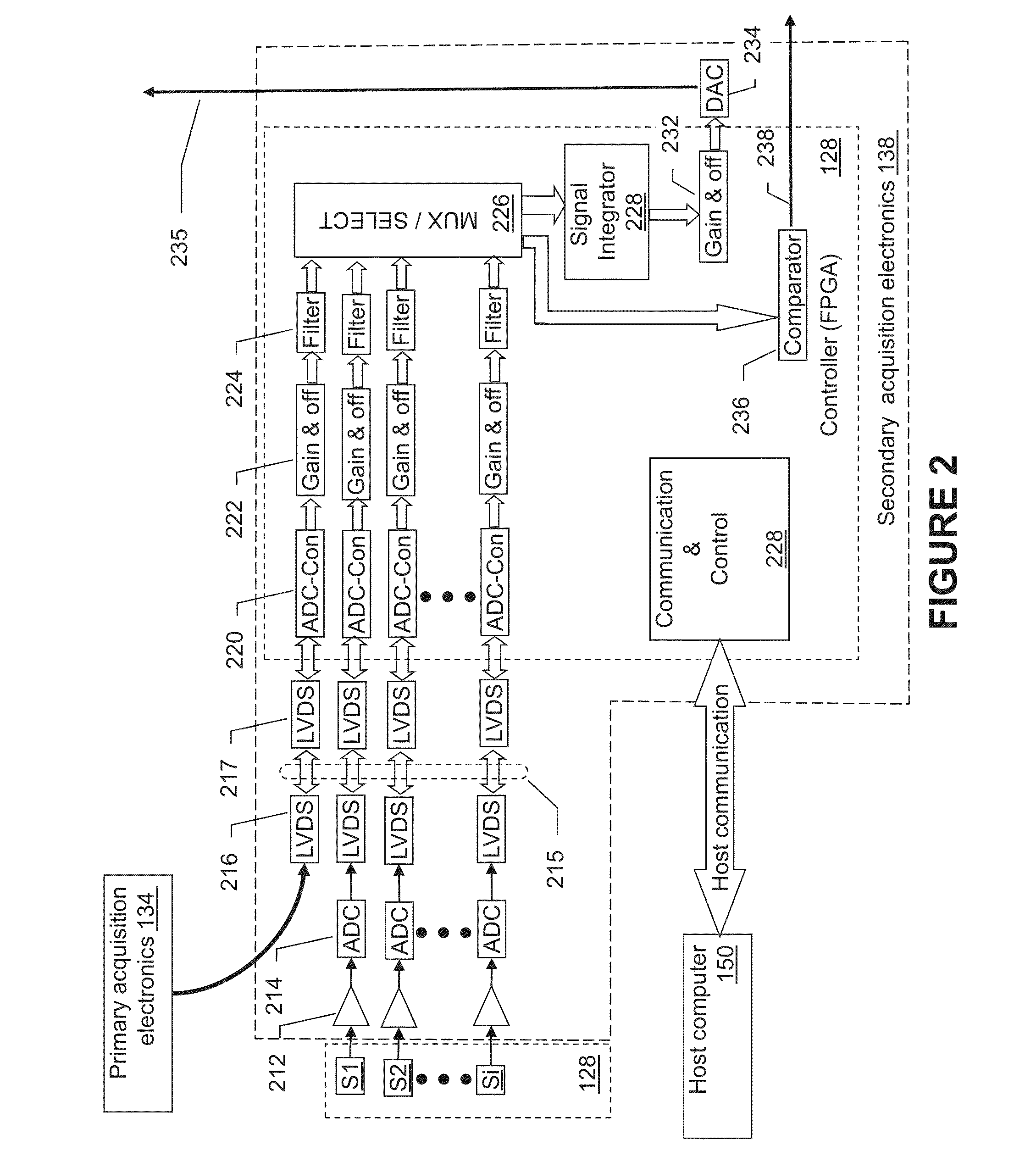
X-ray radiation detector with automatic exposure control
ActiveUS20130126742A1Material analysis by optical meansPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsCMOSSignal correction
An apparatus and method for radiation detection is herein described. The apparatus consists of two radiation-detection arrays: A primary radiation-detection array, based on scintillator-CMOS design, and a secondary radiation-detection array, mounted on the back of said primary array. A method of controlling the detection operation is described, where output of the secondary array is exploited for controlling the acquisition-start and acquisition-stop of the primary array. Further, the apparatus is equipped with fast memory for storage of correction tables, and with a processor for fast computation of the correction. A method of calibration is also describes with tables for: offset correction, gain correction, and for defect-pixel correction. These tables are evaluated by the fast processor and stored on the fast memory. A method of real-time evaluation of the signal corrections is described, which depends on the acquisition-start and acquisition-stop timings and which results a clean, artifact-free image.
Owner:CMT - MEDICAL TECHNOLGIES
Preparation method of silicon rubber foam material
The invention discloses a preparation method of a silicon rubber foam material, which is characterized by mixing 100 parts of silicon rubber, 12-85 parts of white carbon black, 2-15 parts of constitution controller, 3-15 parts of foaming agent, 0-5 parts of blowing promoter and 0-8 parts of cross-linking agent promoter and forming, radiating the silicon rubber by electron beams or gamma rays to generate cross-linking reaction, heating the foaming agent for decomposing and foaming, immediately utilizing the electron beams or the gamma rays to carry out secondary radiation crosslinking after foaming the silicon rubber to further improve the comprehensive properties of the silicon rubber foam material. The silicon rubber foam material can be used for sealing, damping, insulation, sound insulation and thermal insulation materials.
Owner:WUJIANG LANGKE CHEM FIBER
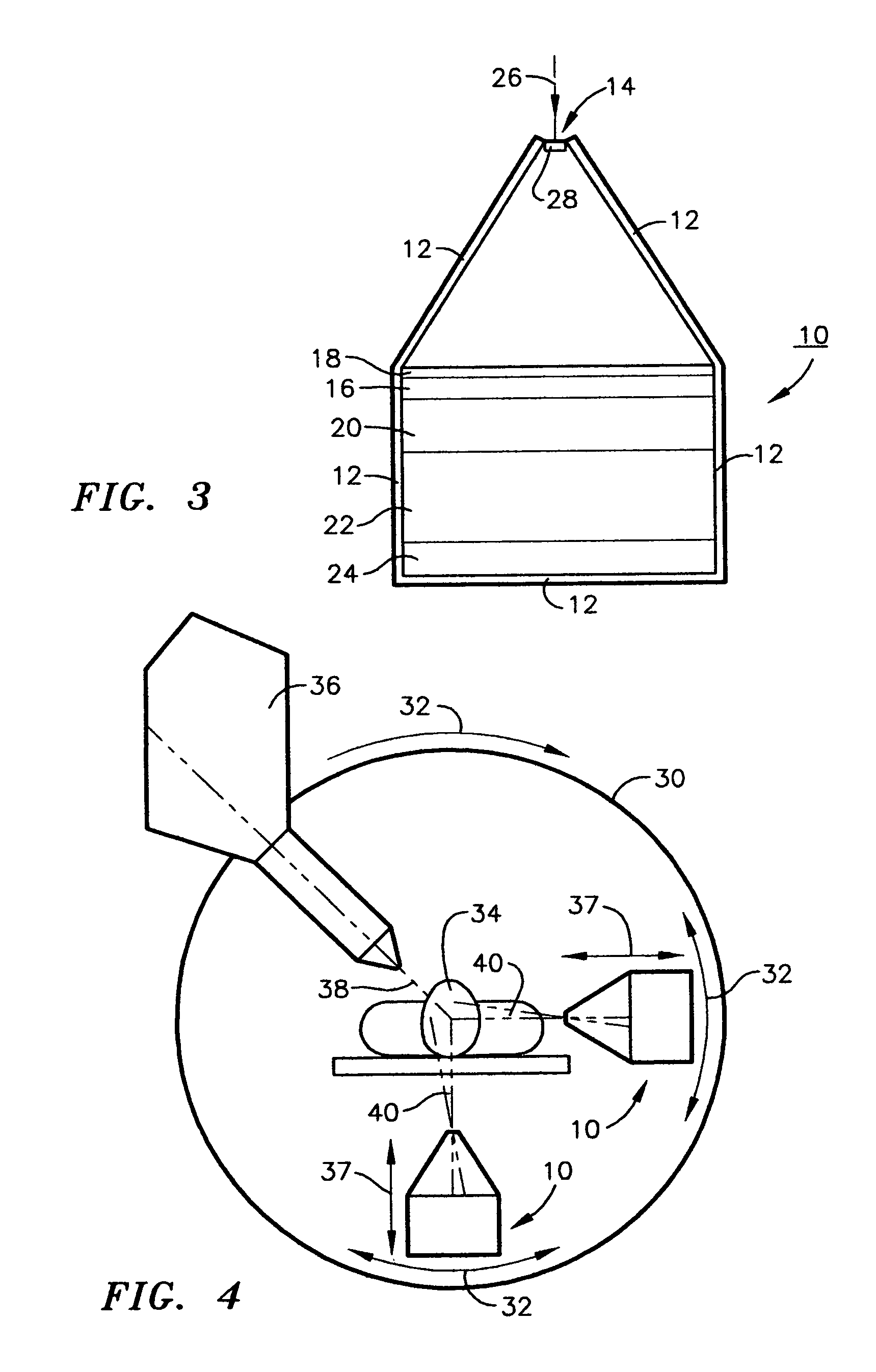
Patterned-media magnetic recording disk with optical contrast enhancement and disk drive using optical contrast for write synchronization
ActiveUS20100091618A1Increase contrastCombination recordingPatterned record carriersRadiation exposureNon magnetic
A patterned-media magnetic recording disk drive uses an optical system for clocking the write data and a patterned-media disk that has discrete magnetizable data islands with nonmagnetic spaces between the islands, wherein the nonmagnetic spaces contain optical contrast material. The optical contrast material may be optically absorptive material, fluorescent material, or a metal layer that generates surface plasmons when excited by radiation of a specific wavelength. Radiation from a primary radiation source is directed to a near-field transducer maintained near the disk surface and a radiation detector detects radiation reflected back from the transducer. If the disk has fluorescent material or a metal layer in the nonmagnetic spaces, then a secondary radiation source irradiates the fluorescent material or metal layer with radiation of a specific wavelength to cause the fluorescent material to emit radiation or the metal layer to generate surface plasmons. As the disk rotates, reflected optical power from the transducer varies depending on whether an island or space is under the transducer. The output signal from the radiation detector output controls the write clock.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
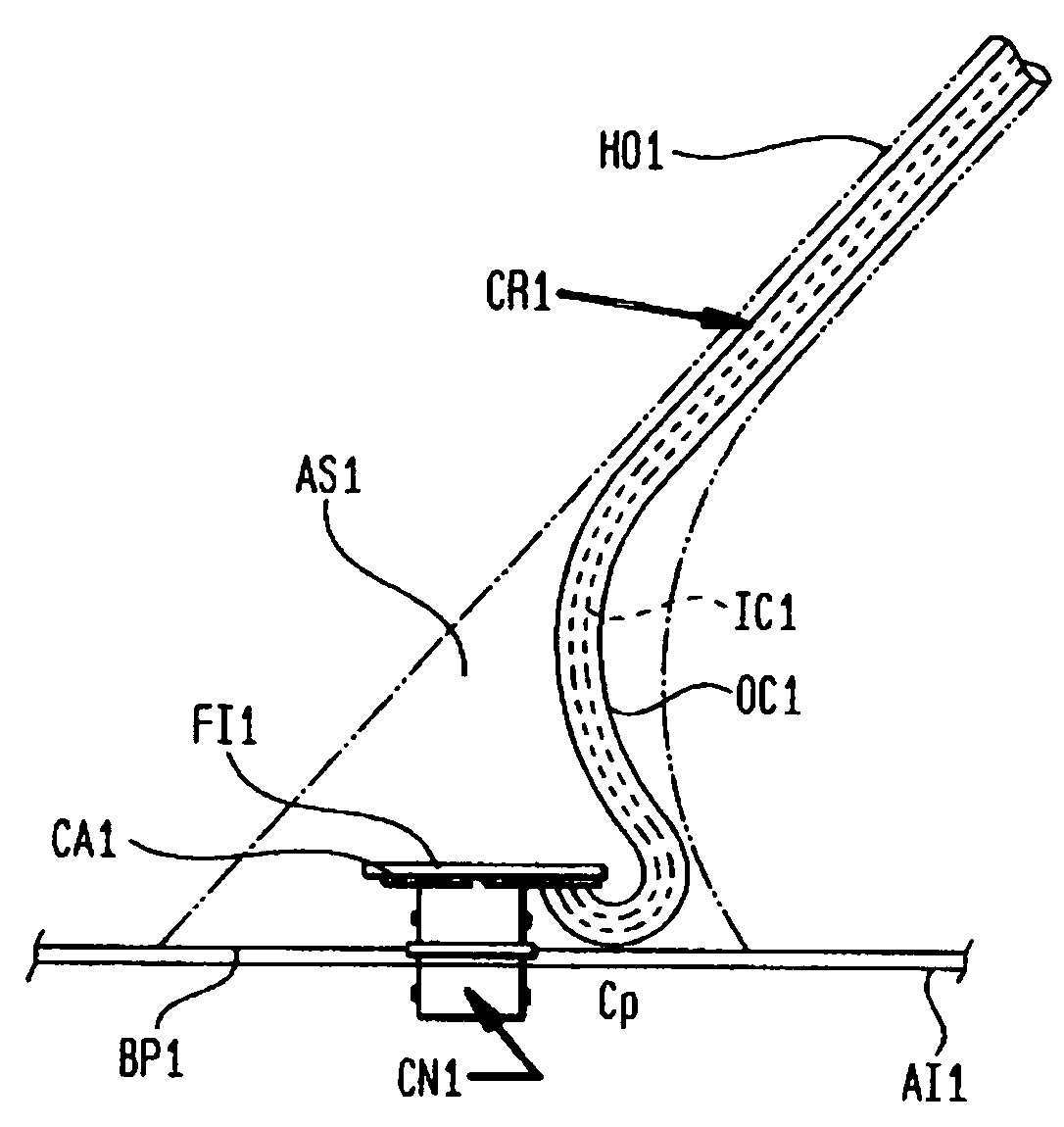
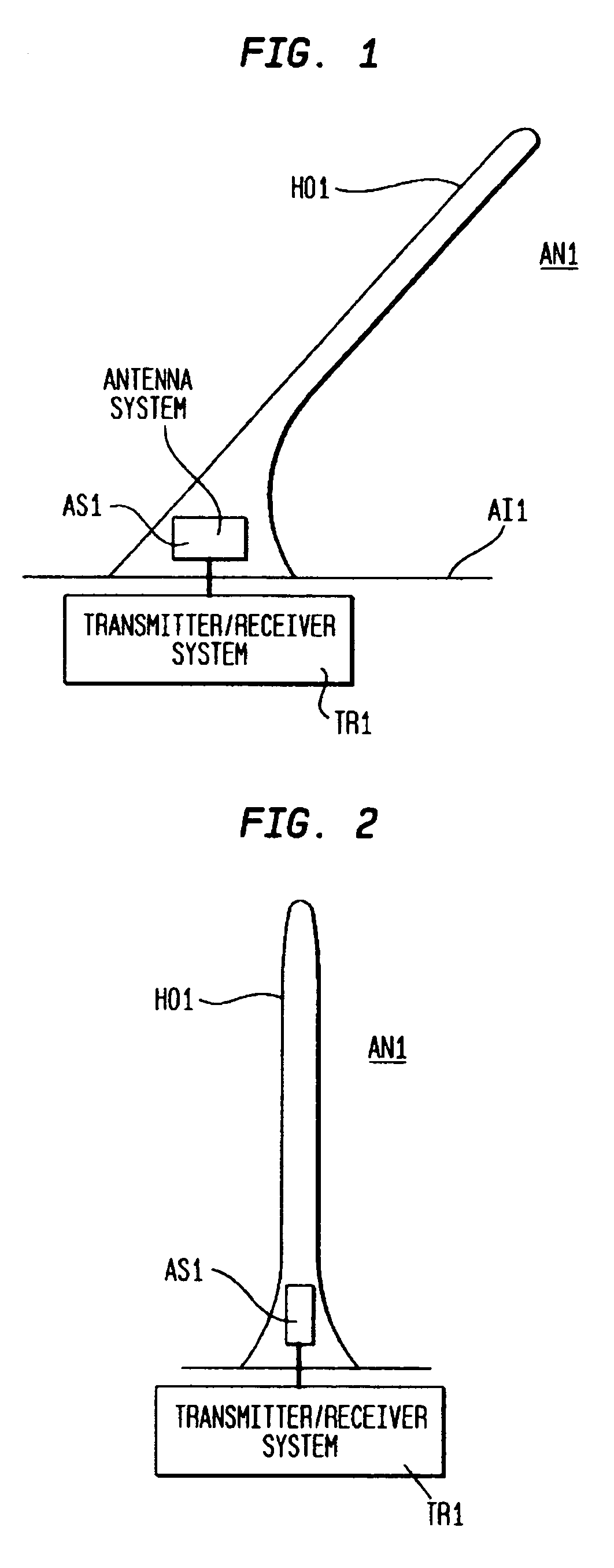
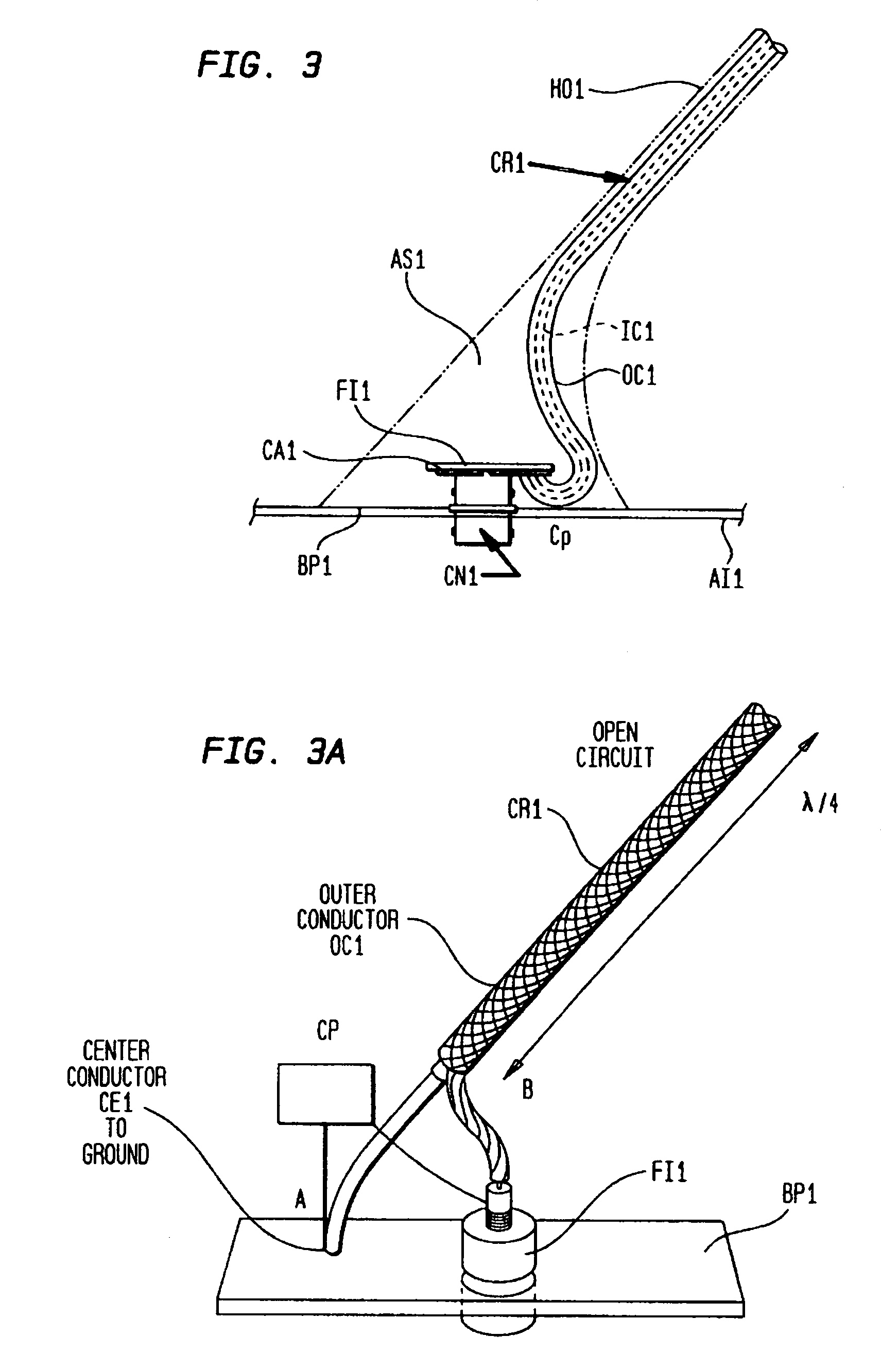
Combination aircraft antenna assemblies
InactiveUS7053845B1Antenna supports/mountingsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesSecondary radiationFlight vehicle
Owner:COMANT INDS
Multi-antenna module
InactiveUS7973726B2Reduce spacingEasy to assembleSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsCapacitanceElectrical conductor
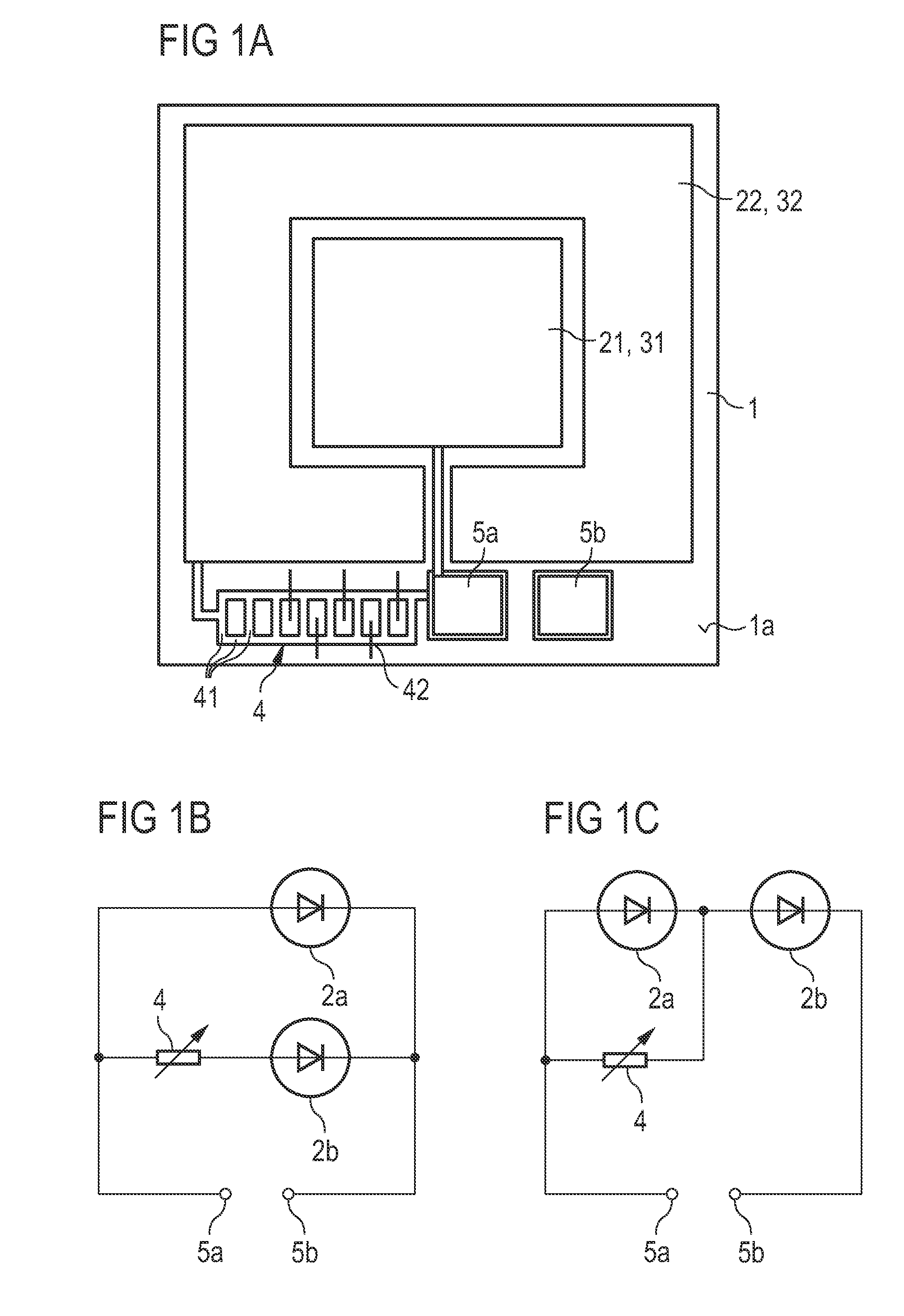
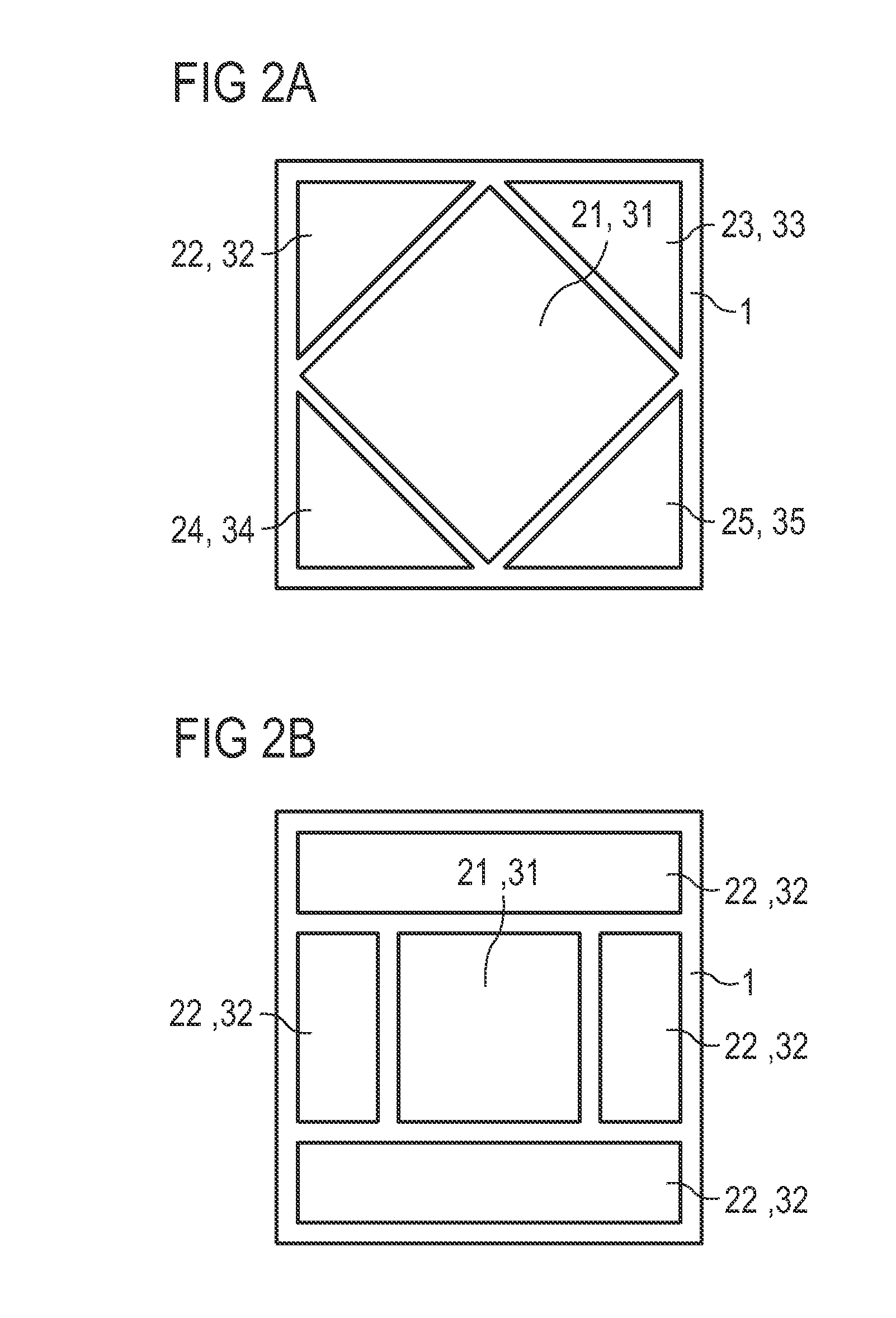
A multi-antenna module comprises a ground plane, a primary conductor, a secondary conductor and a plurality of coupling conductors, wherein the framework of the parallel primary radiation arm and secondary radiation arm can infinitely expand the number of antenna units in the same antenna structure. The capacitive coupling effect of parallel radiation arms and the inductance of the radiation arms themselves can effectively reduce the signal interference between antennae, whereby a plurality of antennae can be integrated to achieve antenna miniaturization. The primary conductor, the secondary conductor and the coupling conductors are all connected to the same ground plane, whereby the layout space is reduced, and the multi-antenna module is easy-to-assemble for various electronic devices.
Owner:ADVANCED CONNECTEK INC
Electroluminescent diode lighting device comprising a communication device and installation comprising one such device
ActiveUS20060071613A1Improve transfer rateQuality improvementPhotometry using reference valueElectroluminescent light sourcesEffect lightEngineering
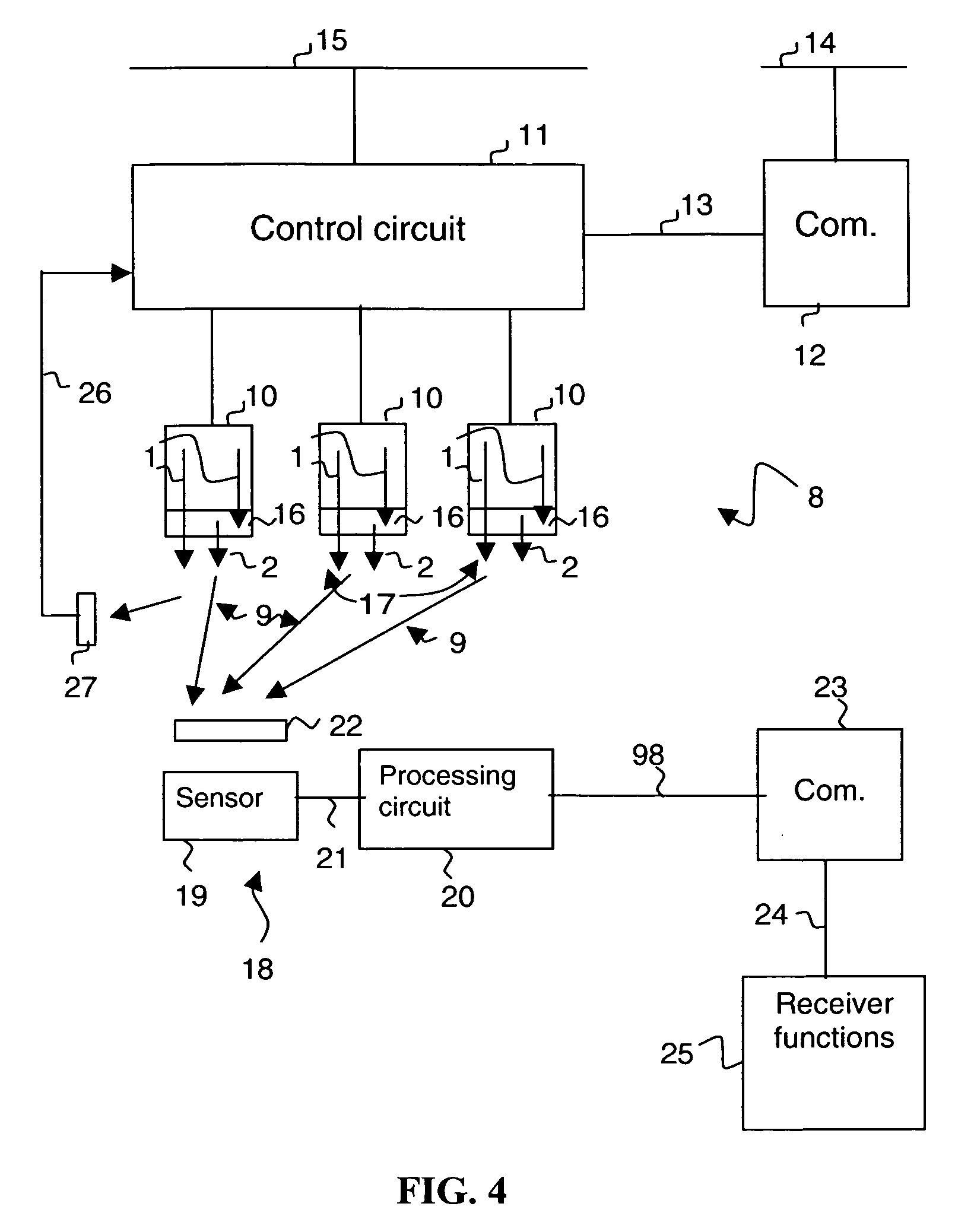
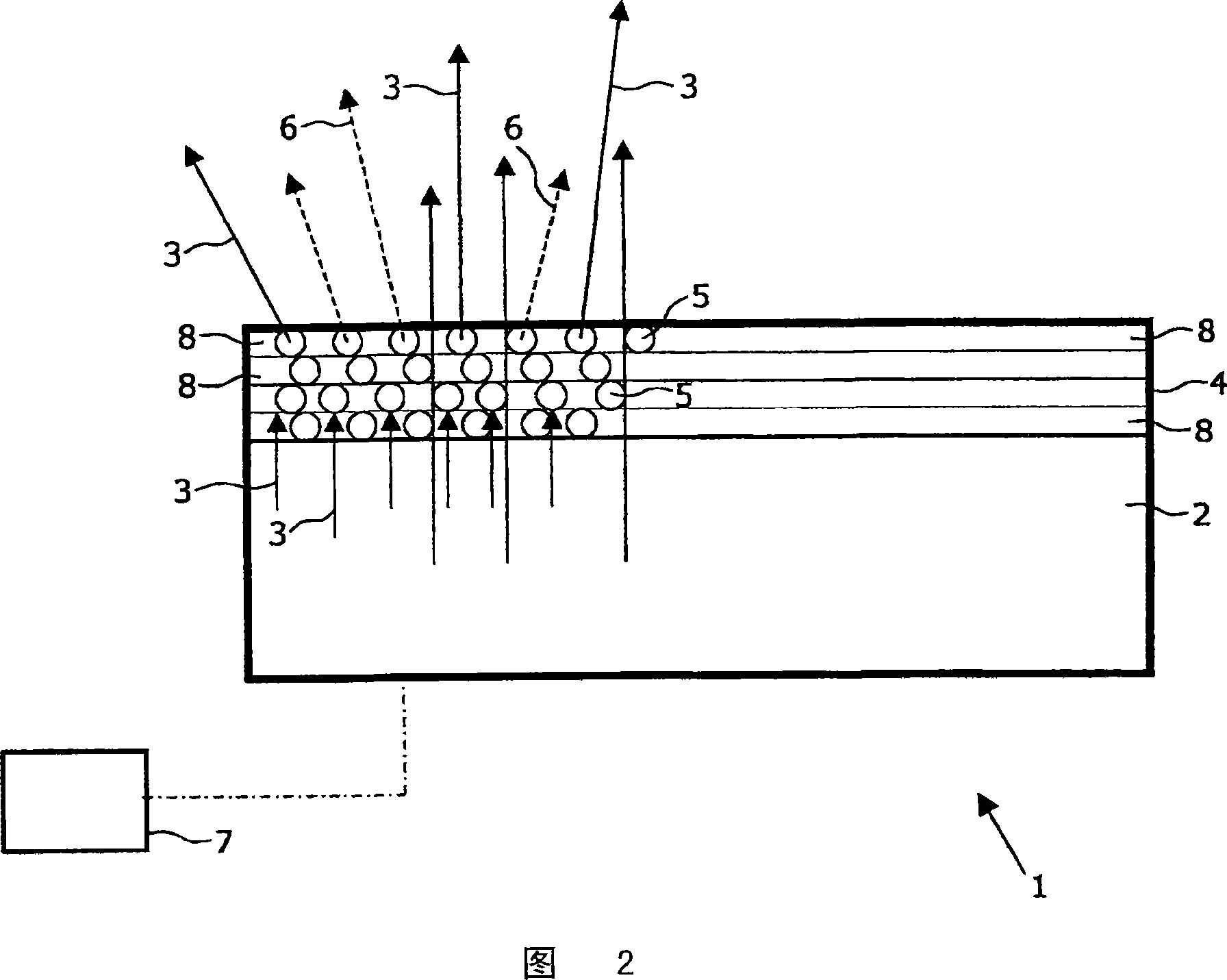
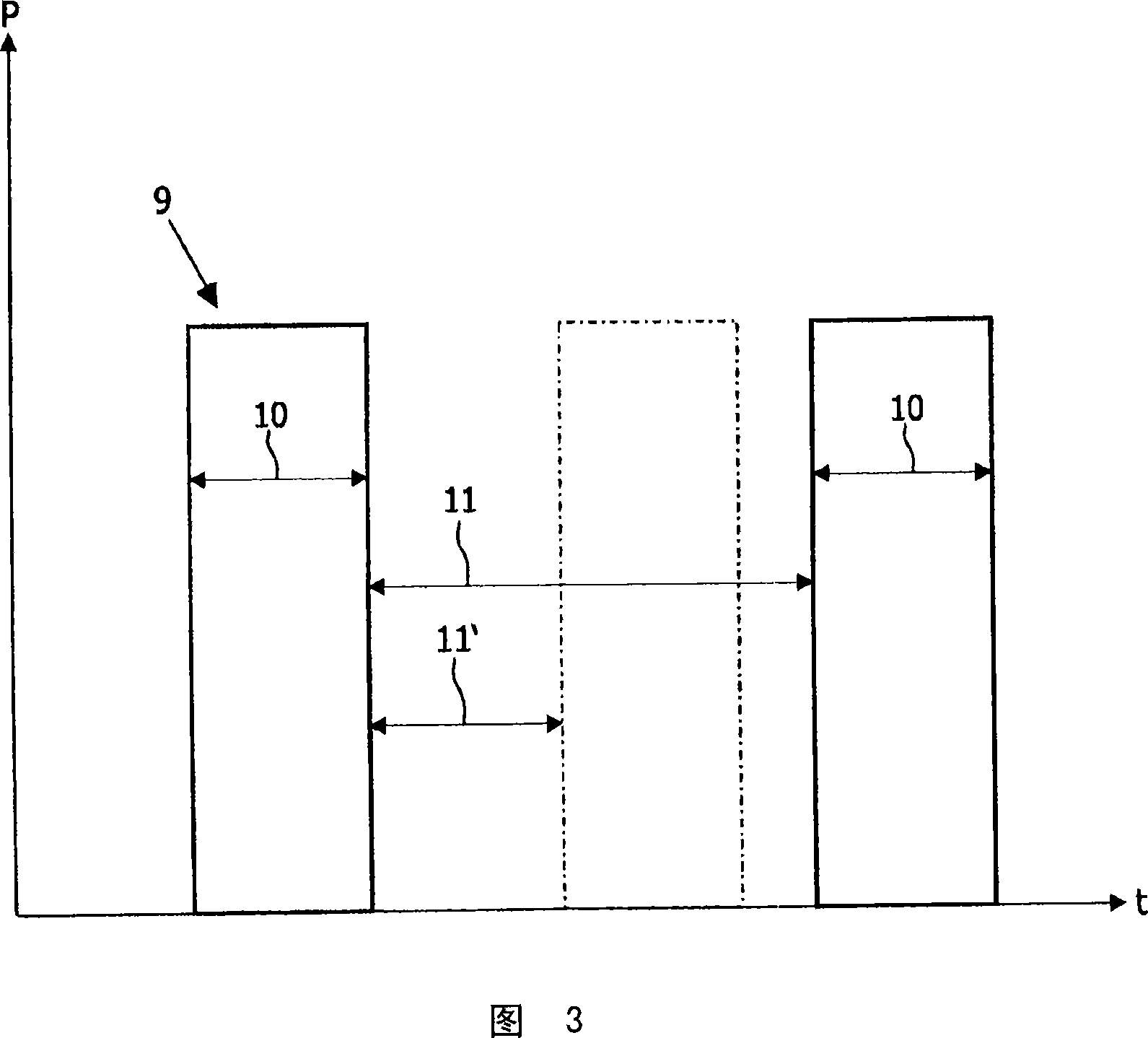
The lighting device comprises at least one emitter (10) of white light (9) produced by an initial radiation (1) and a secondary radiation (2), an electronic control circuit (11) to control the lighting, and a communication circuit (12). The electronic circuit (11) controls power supply of the light emitter to emit a modulating light signal (3, 4, 31, 36) of said initial radiation according to a communication signal (13). Said modulating light signal is designed to be received by a light signal receiver (18) sensitive to the initial radiation (1). A lighting installation comprises a power supply line, at least one lighting device (8) and at least one electrical apparatus (95, 96) connected to a receiver (18) comprising a sensor (19) sensitive to the initial radiation (1).
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC IND SAS
Biomass supercritical water gasification hydrogen production absorption reactor thermally driven by solar energy
ActiveCN101597025AReduce heat lossIncrease the concentration ratioEnergy inputHydrogen productionHeat fluxHeat flow
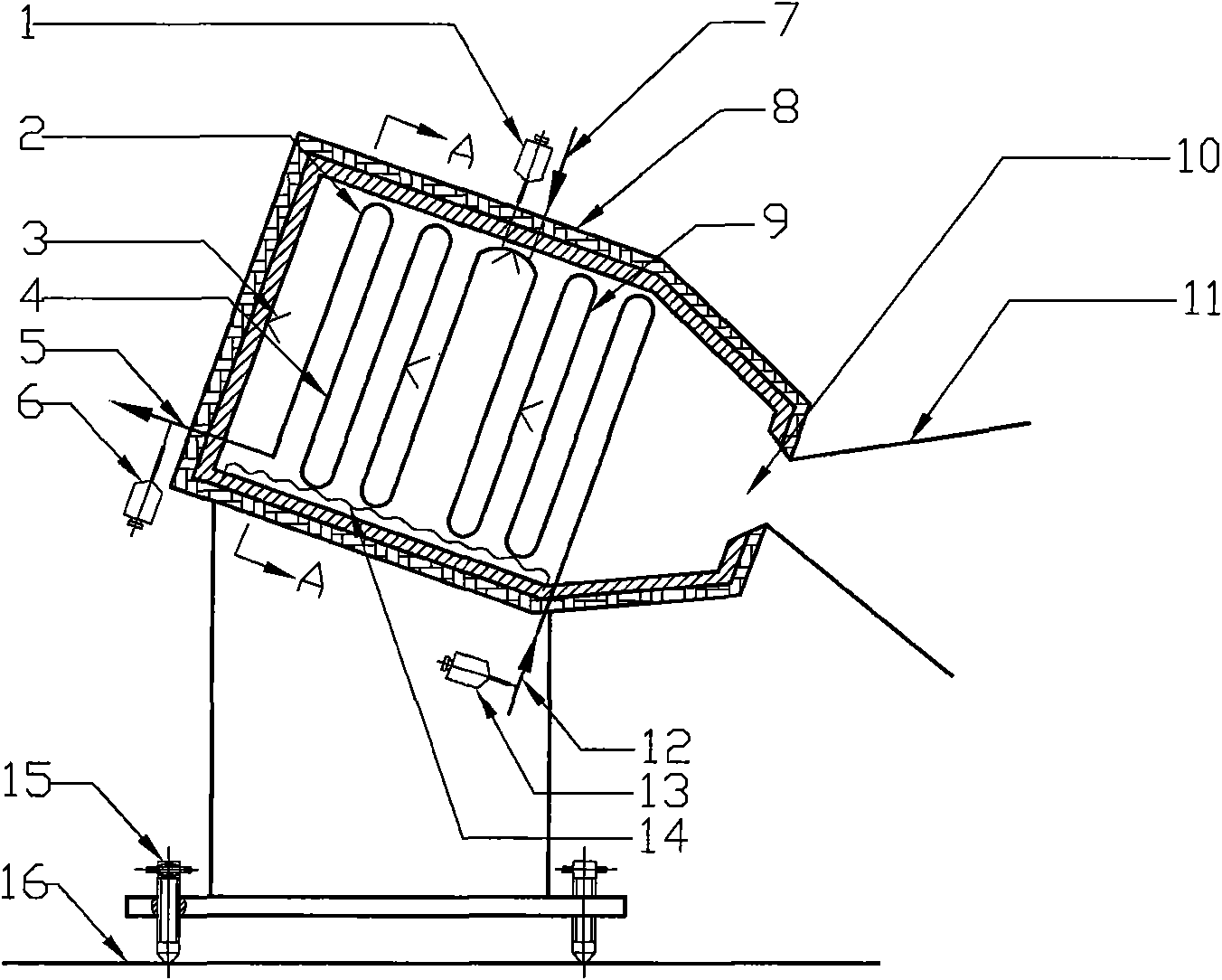
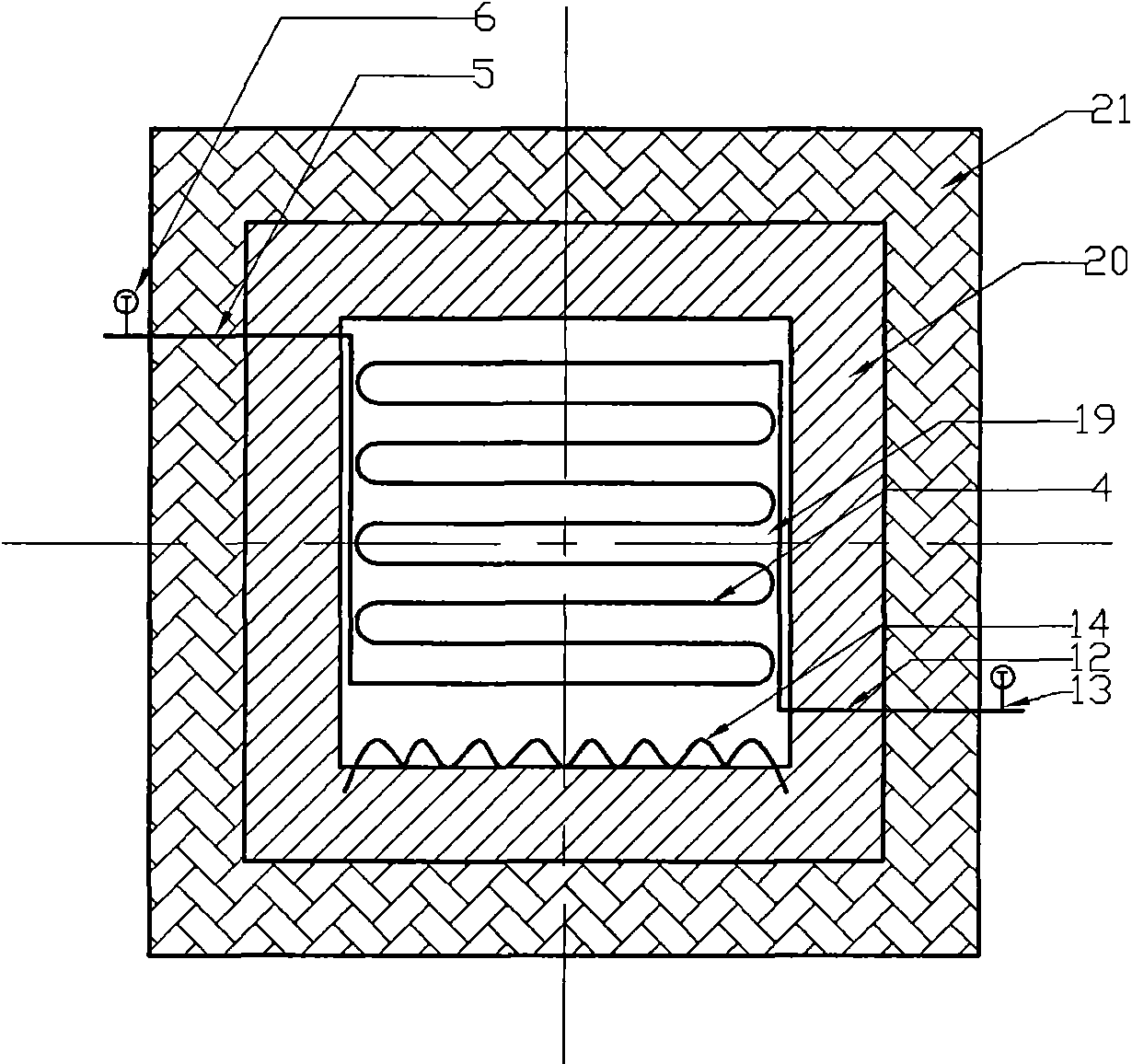
The invention discloses a biomass supercritical water gasification hydrogen production absorption reactor thermally driven by solar energy. An absorption reactor cavity is connected with a conical surface solar energy secondary condenser, thus effectively improving heat flux density at the daylight opening of the absorption reactor; the absorption reactor cavity is internally provided with a coiler flow biomass supercritical water reactor, biomass and supercritical water continuously flow in a reaction tube to absorb and focus solar energy direct radiation and cavity inner wall secondary radiation for gasification hydrogen production reaction; the coil flow reactor is divided into a preheating section and a reaction section, thus realizing fast warming of biomass material; the inner wall of the absorption reactor is built by laying firebricks and coated with silicate heat insulation cotton; and the inclined angle of the absorption reactor can be adjusted by a pedestal adjusting screw rod. The absorption reactor, being one core part of the biomass supercritical water gasification hydrogen production devices thermally driven by solar energy, can realize continuous gasification hydrogen production of various biomasses in supercritical water and has the characteristics of low cost, safety and high efficiency.
Owner:陕西中核交大超洁能源技术有限公司
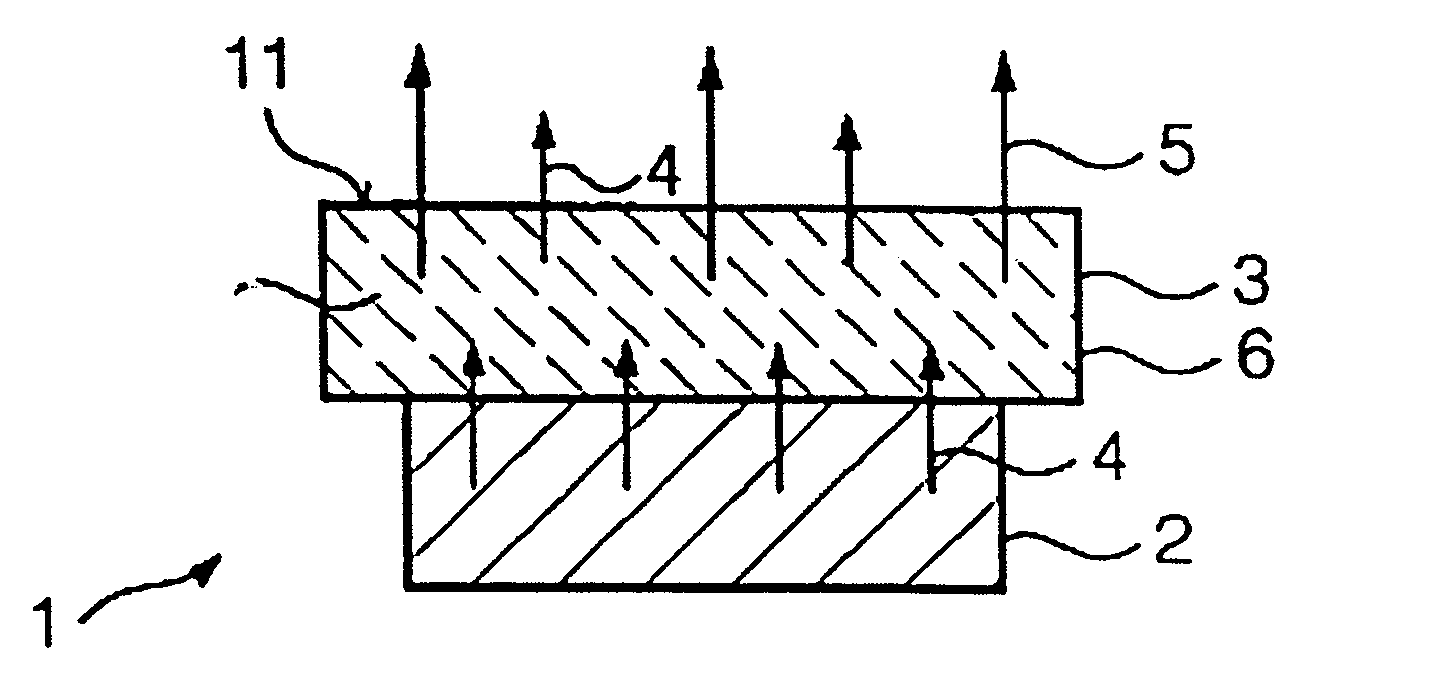
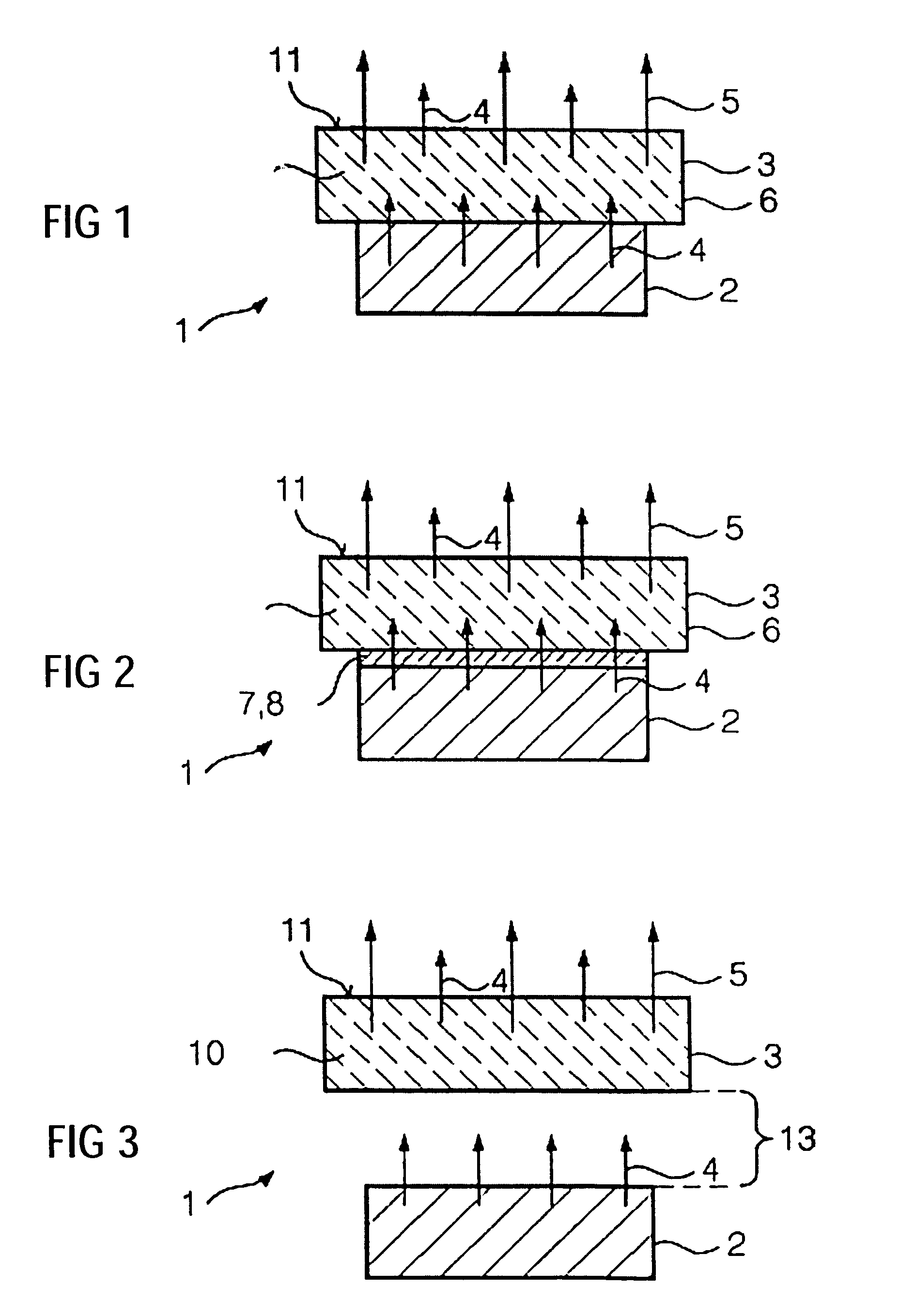
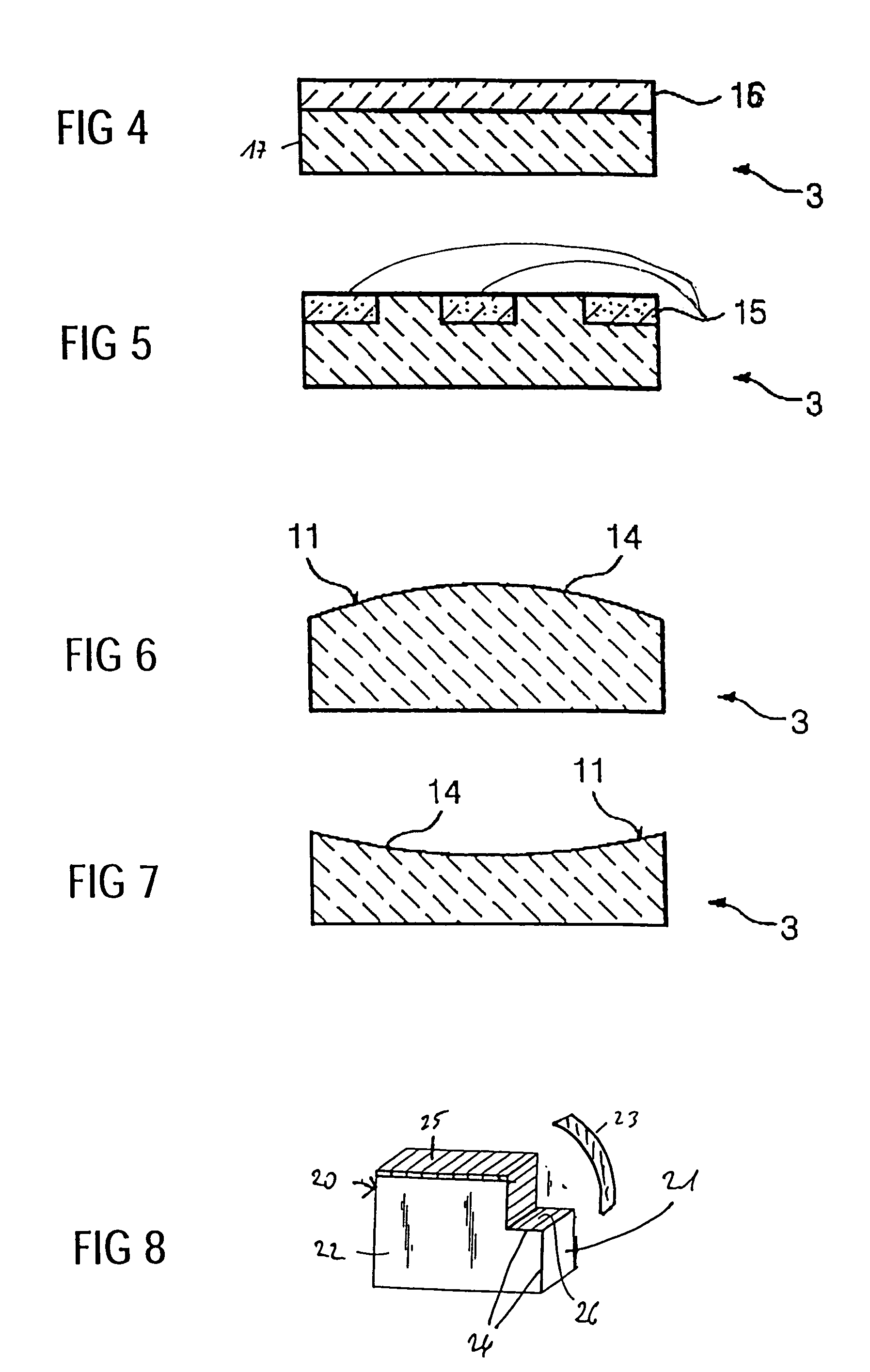
Light source and method for producing light modifiable in colour and/or luminosity
ActiveCN101243557AIncrease brightnessBrightness doesn't changeElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesSecondary radiationLuminosity
The present invention relates to a light source, which produces light leaving the light source with modifiable color and luminosity, with at least one light emitting diode for emitting primary radiation, comprising a layer connected with said diode, wherein said layer includes at least one luminescent material for converting the primary radiation into a secondary radiation.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Multi-antenna module
InactiveUS20090231200A1Reduce distractionsReduce space of antennaSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsCapacitanceElectrical conductor
A multi-antenna module comprises a ground plane, a primary conductor, a secondary conductor and a plurality of coupling conductors, wherein the framework of the parallel primary radiation arm and secondary radiation arm can infinitely expand the number of antenna units in the same antenna structure. The capacitive coupling effect of parallel radiation arms and the inductance of the radiation arms themselves can effectively reduce the signal interference between antennae, whereby a plurality of antennae can be integrated to achieve antenna miniaturization. The primary conductor, the secondary conductor and the coupling conductors are all connected to the same ground plane, whereby the layout space is reduced, and the multi-antenna module is easy-to-assemble for various electronic devices.
Owner:ADVANCED CONNECTEK INC
Radiation-Emitting Semiconductor Component
InactiveUS20120193657A1Efficient use ofReduce productionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesSecondary radiationLight-emitting diode
A radiation-emitting semiconductor component includes a light-emitting diode chip with at least two emission regions that can be operated independently of each other and at least two differently designed conversion elements. During operation of the light-emitting diode chips each of the emission regions is provided for generating electromagnetic primary radiation. Each emission region has an emission surface by which at least part of the primary radiation is decoupled from the light-emitting diode chip. The conversion elements are provided for absorbing at least part of the primary radiation and for re-emitting secondary radiation. The differently designed conversion elements are disposed downstream of different emission surfaces. An electric resistance element is connected in series or parallel to at least one of the emission regions.
Owner:OSRAM OPTO SEMICONDUCTORS GMBH
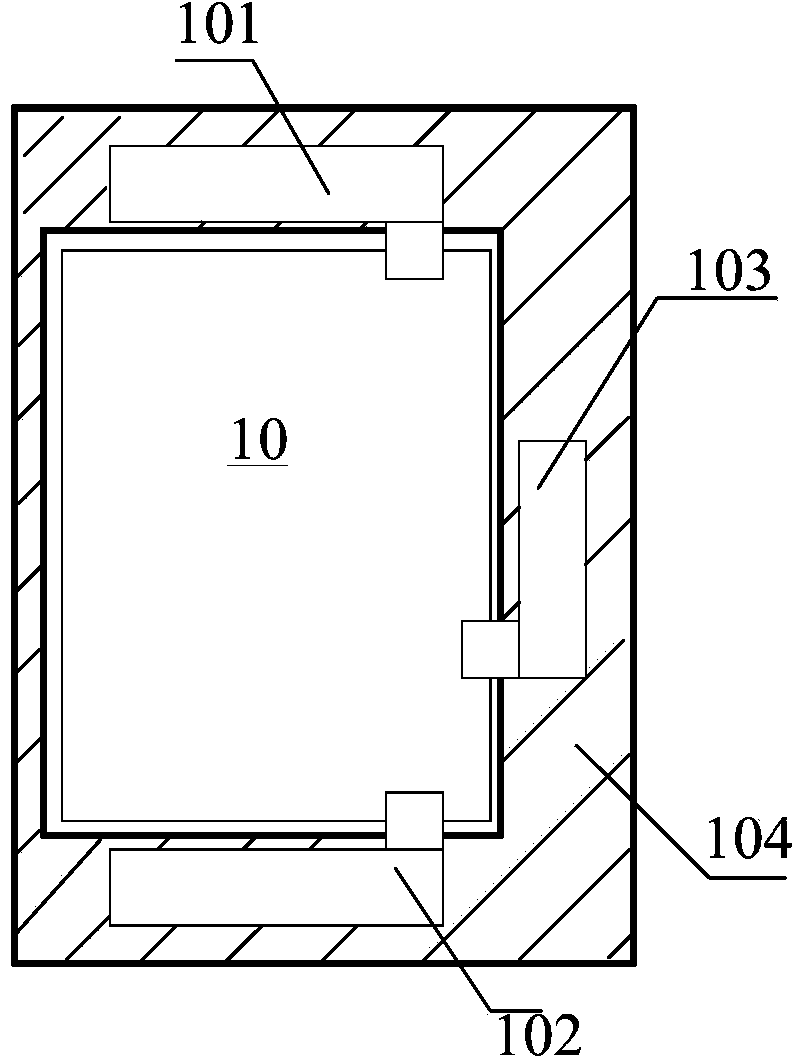
Ceramic coating used for heating furnace
InactiveCN102020475AExtended service lifeHas high temperature oxidation resistanceEmissivityRadiance
The invention relates to ceramic coating used for a heating furnace. The ceramic coating comprises the following components: ceramic micro powder, an inorganic bonding agent and a linear thermal expansivity regulator. The invention also provides a method for preparing the ceramic coating for the heating furnace. The ceramic coating has the characteristics of having improved radiance and thermal shock resistance, being efficient and energy-saving, prolonging the service life of furnace linings and furnace tubes, improving temperature uniformity and the like, as defined below: (1) the energy consumption is reduced, the energy is saved by more than 3 percent and pollutant discharge is reduced; (2) the temperature uniformity in the heating furnace is improved: (3) the metallurgy stability of the furnace tube of the heating furnace is improved, the coking and scaling of the furnace tub are delayed, and the absorbing capacity of the furnace tube can be maximized; (4) the emissivity of the surface of the refractory lining layer can be maximized so as to increase the secondary radiation of radiant heat (energy) and increase the efficiency of the radiant section; and (5) the outer wall temperature and the exhaust gas temperature of the heating furnace can be reduced by more than 5 percent.
Owner:北京安泰恒业科技有限公司
Wireless terminal
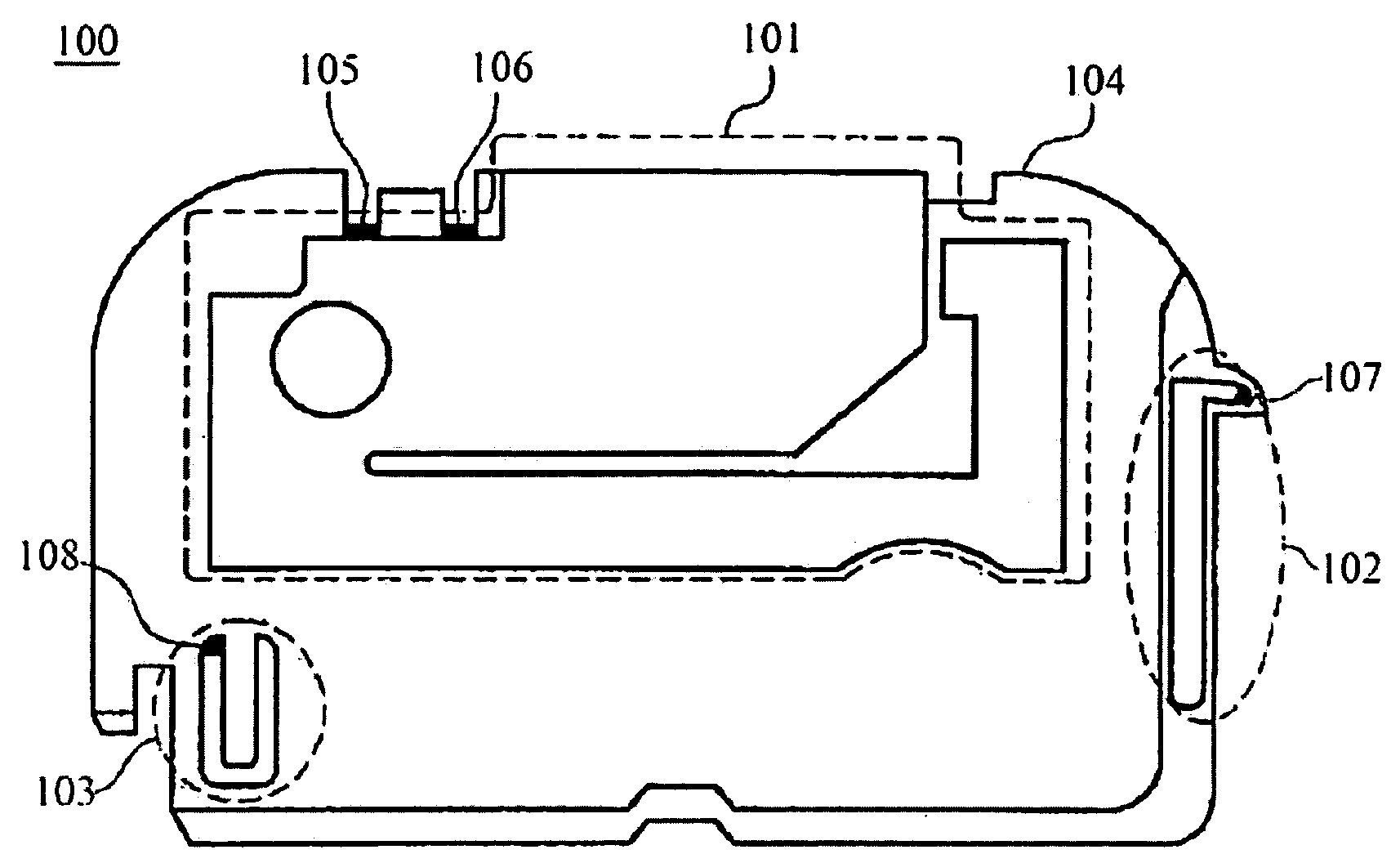
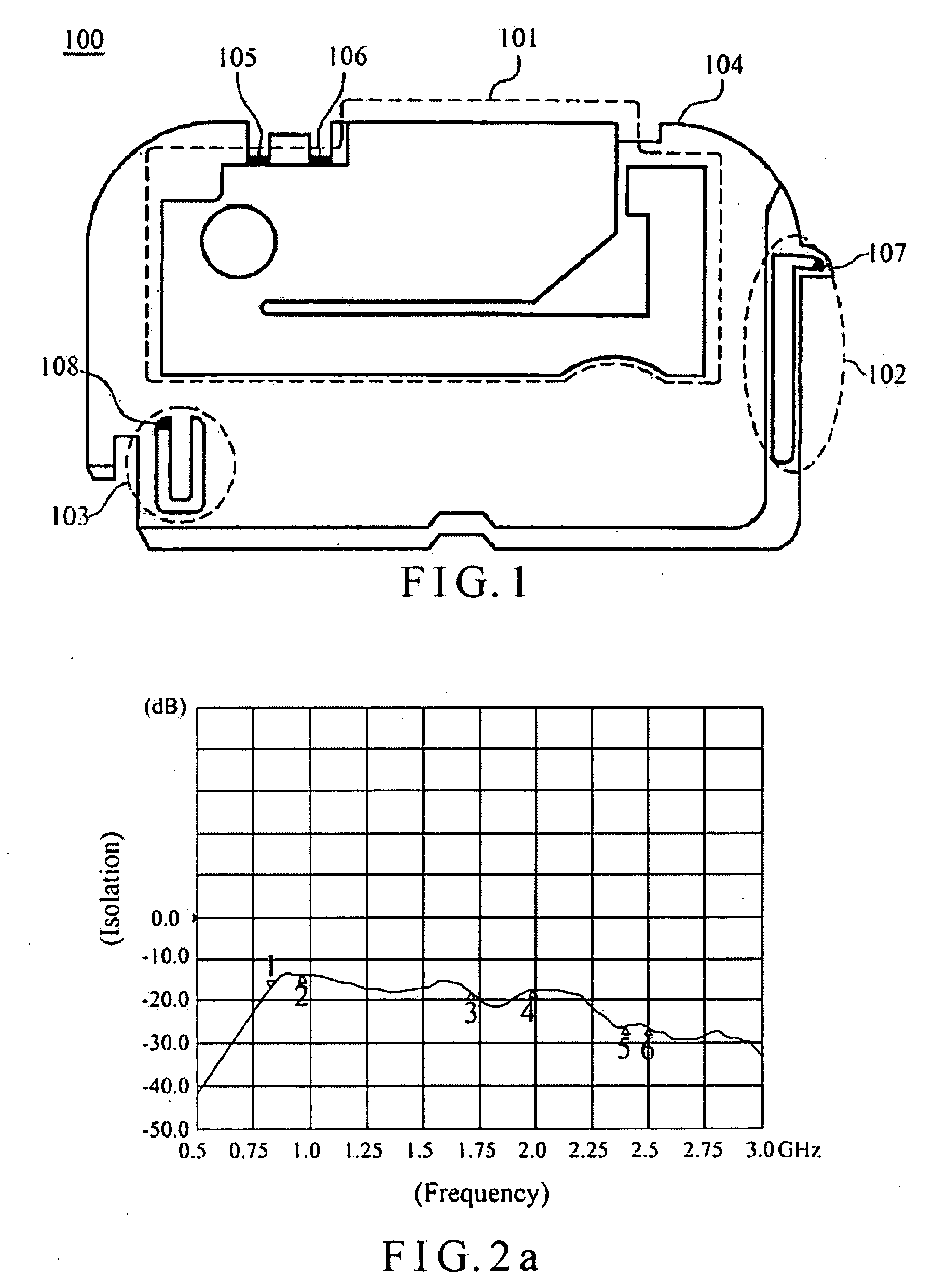
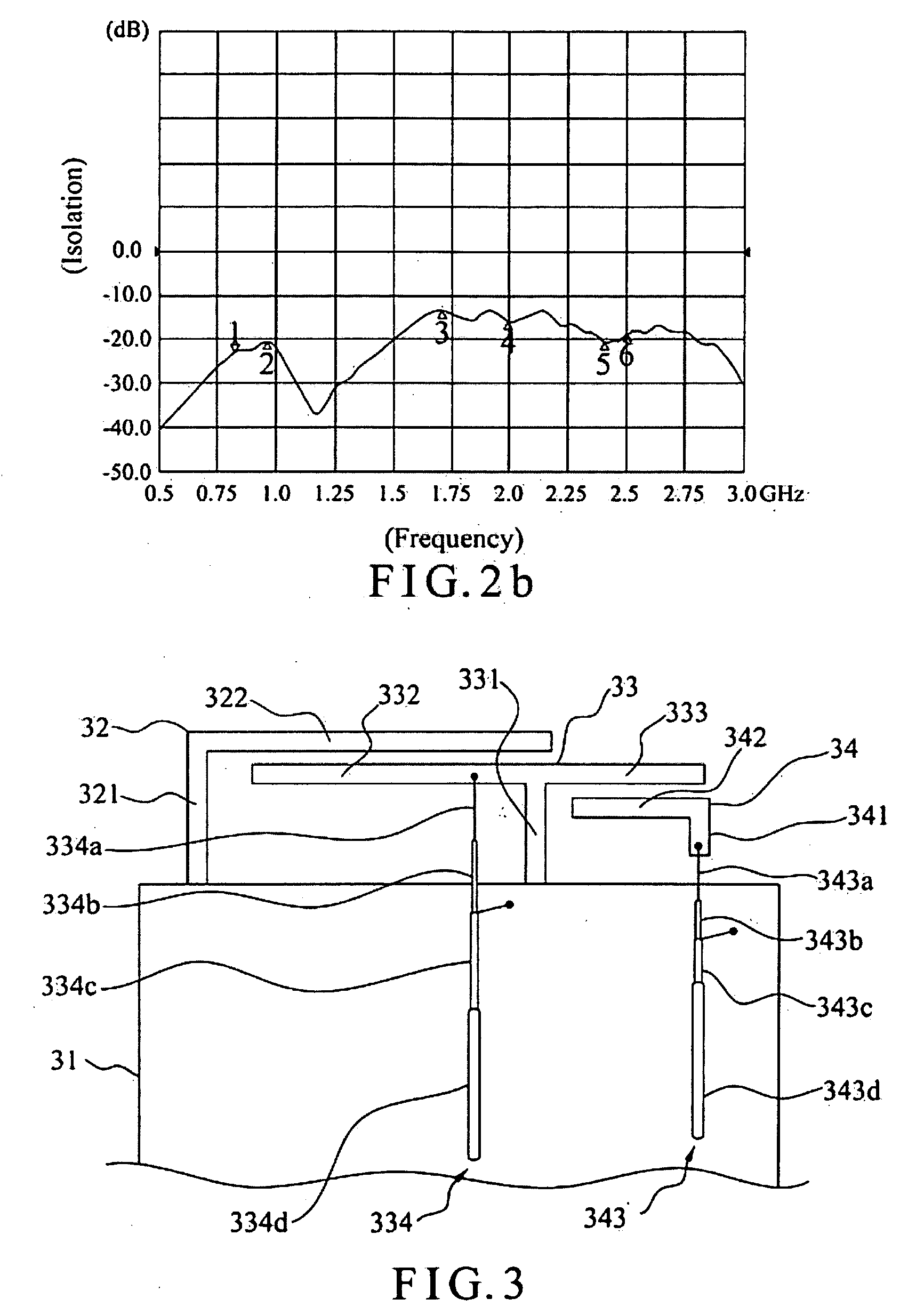
ActiveCN103636064AImprove isolationImprove radiation efficiencySimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsSecondary radiationEngineering
The present invention discloses a wireless terminal. The wireless terminal includes a first antenna, a second antenna, a printed circuit board, a support and a resonator, wherein the first antenna is located at a side of the printed circuit board, the second antenna is located at the other side of the printed circuit board, the printed circuit board is used as a metal ground of the first antenna and the second antenna, the resonator is located on the support, a grounding point of the resonator is located on the printed circuit board, and a clearance zone is disposed between the plurality of antennae and the printed circuit board. The wireless improves an isolation degree of the plurality of anteenae, and the clearance zone is disposed between the resonator and the PCB, so that the resonator is enable to radiate the energy of the antenna in a better way, and the energy of the antenna flow into the resonator is avoided to be comsumped in the resonator, secondary radiation of antenna energy is achieved, and radiation efficiency of the antenna is improved.
Owner:HUAWEI DEVICE CO LTD
Single-feed source periodically arranged groove slot panel antenna
The invention provides a single-feed source periodically arranged groove slot panel antenna, which consists of a grounding plate and a plurality of periodically arranged groove structures loaded on two sides of a slot source, and a distance between a slot and a neighbouring groove is less than a groove period. Different from the radiation mechanism of a traditional periodically arranged groove structure, the grooves of the invention cannot be taken as a secondary radiation source any more, because the phase of an electric field at the grooves is opposite to the phase of the electric field at the slot. Another novel electromagnetic oscillation mode that two neighbouring grooves are integrally taken as the secondary radiation source which radiates energy to the space is generated on the surface of the antenna. The novel antenna has the characteristics of more compact structure and more flexible design, and is smaller in the compression angle of an H surface and antenna gain is improved to some extent compared with the traditional groove slot antenna with the same groove number.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
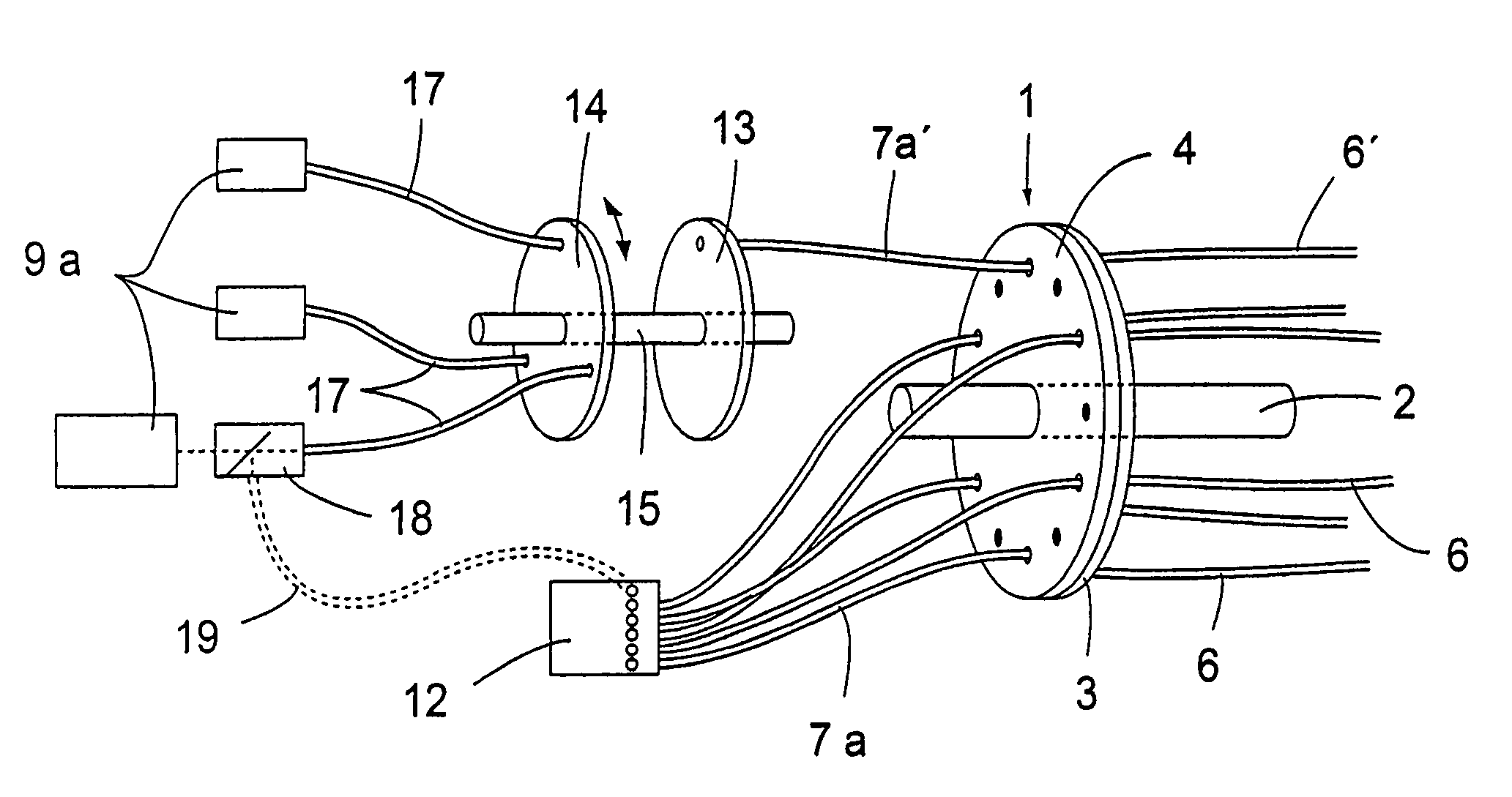
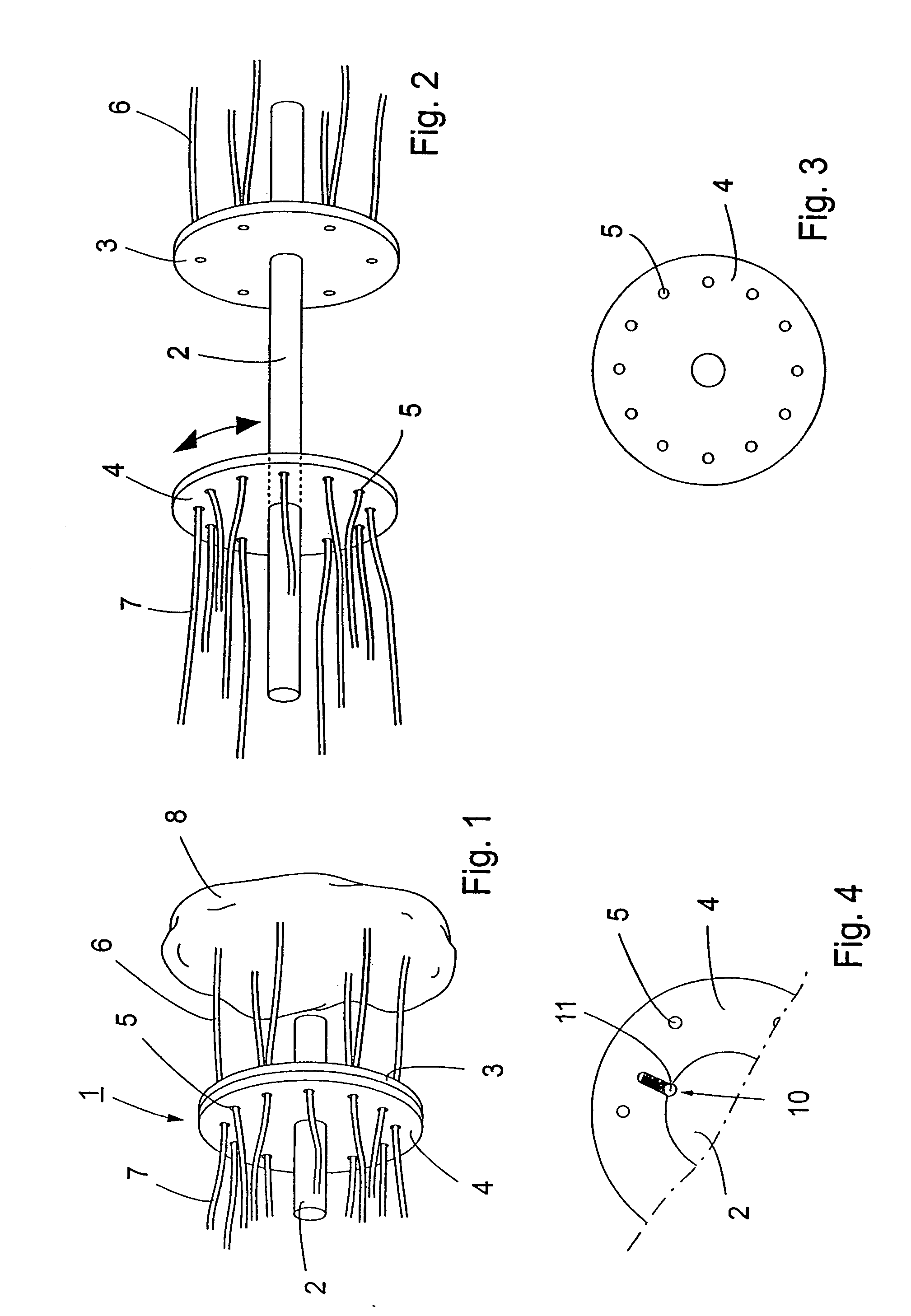
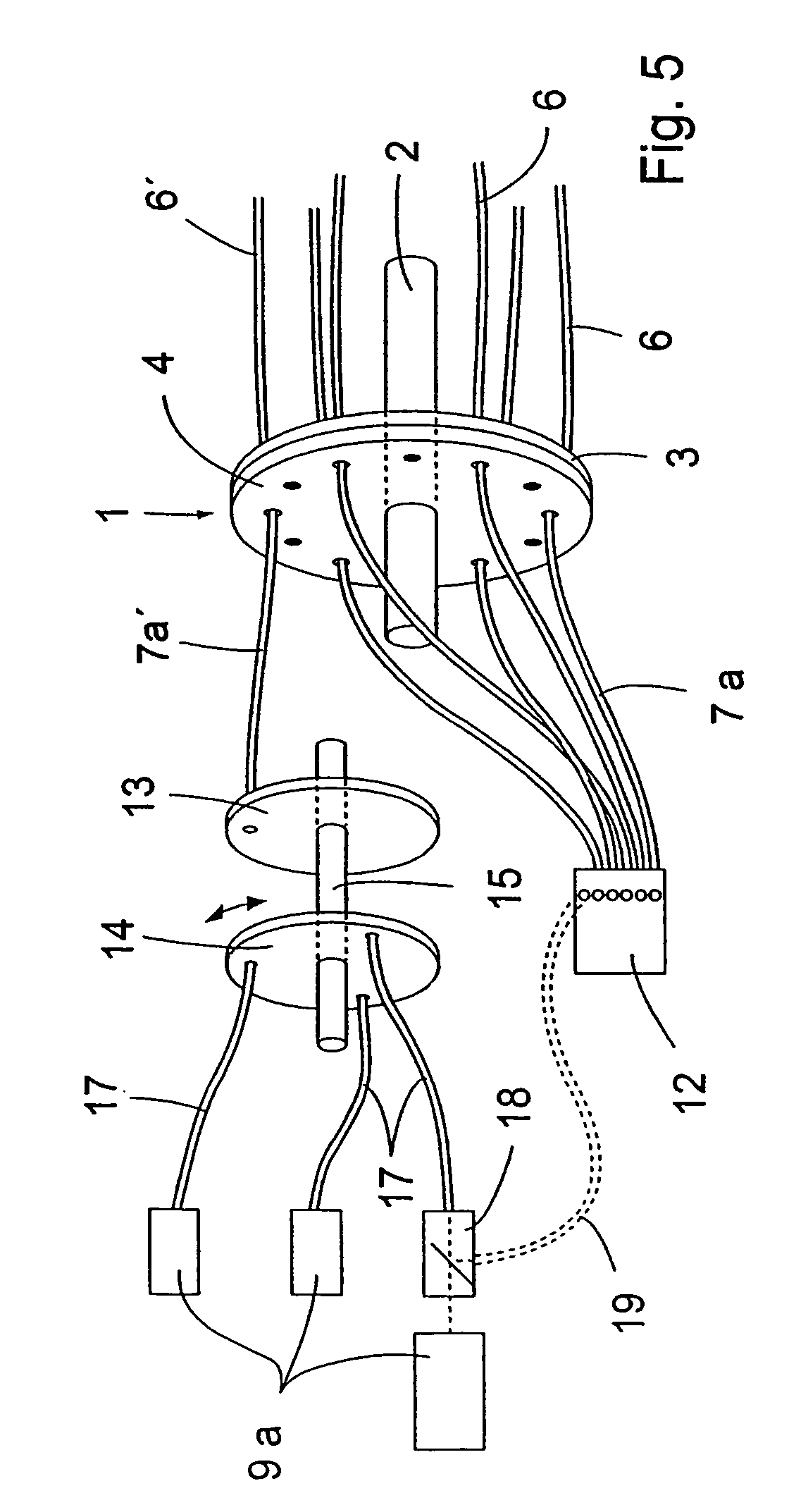
Therapy and diagnosis system and method with distributor for distribution of radiation
InactiveUS7037325B2Easy to calculateEffective treatmentSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsCircular discElectrical conductor
A distributor for a system for interactive interstitial photodynamic and photothermal tumor therapy and tumor diagnosis, comprises a plurality of primary radiation conductors arranged for conducting radiation to and from the tumor site, a plurality of secondary radiation conductors, two flat discs abutting against each other, wherein a first of said discs is fixed and the second of said discs is turnable relatively to the other disc, and each disc has holes arranged on a circular line. The proximal ends of the primary radiation conductors are fixed in the holes of the fixed disc and distal ends of the secondary radiation conductors are fixed in the holes of the turnable disc, whereby the primary and the secondary radiation conductors by rotation of the turnable disc are connectable to each other in different constellations.
Owner:SUNE SVANBERG +1
Method for producing the image of the internal structure of an object with X-rays and a device for its embodiment
InactiveUS20050031078A1Improve accuracyReduce usageHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionHandling using diaphragms/collimetersFluorescenceX-ray
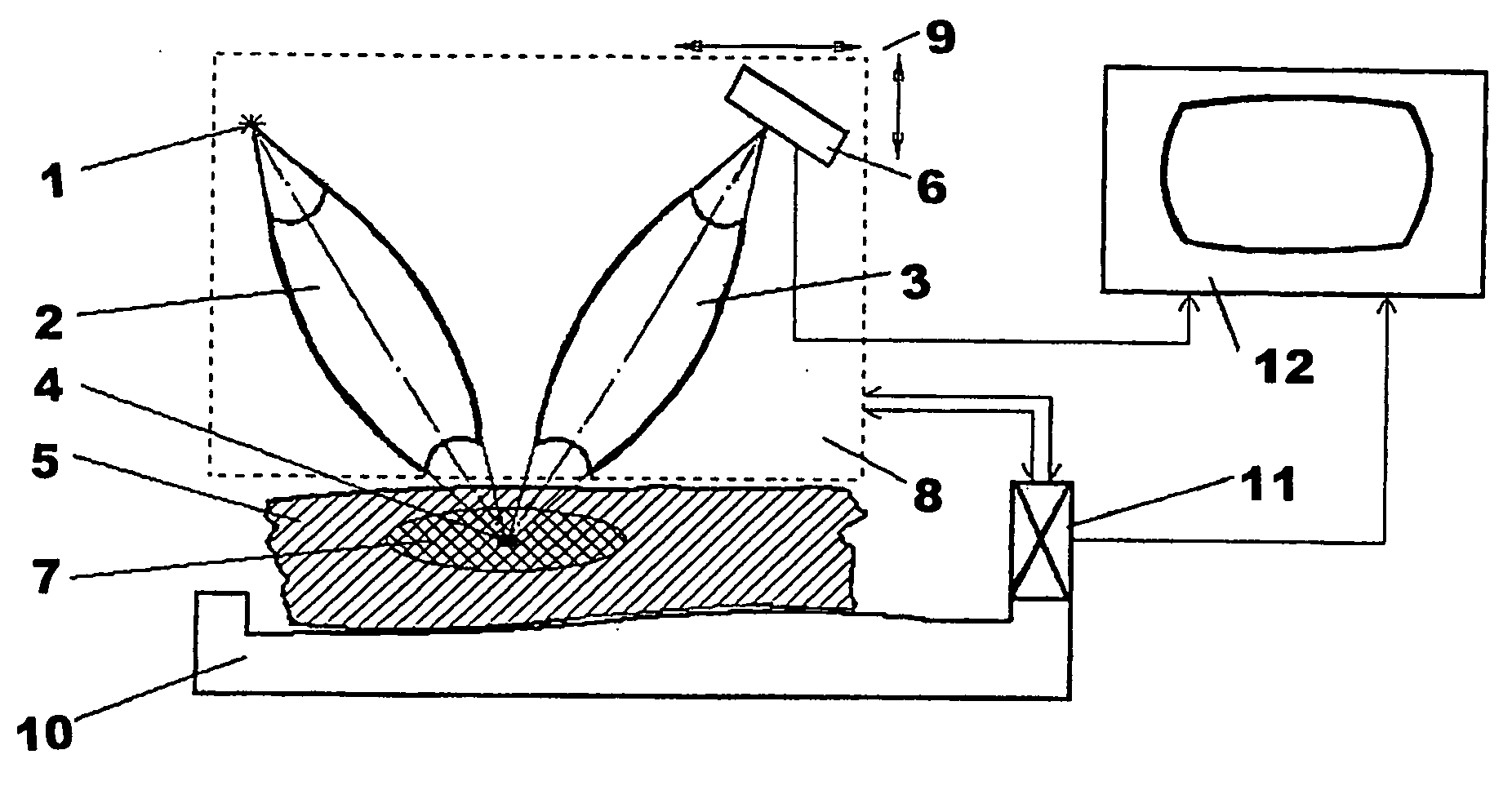
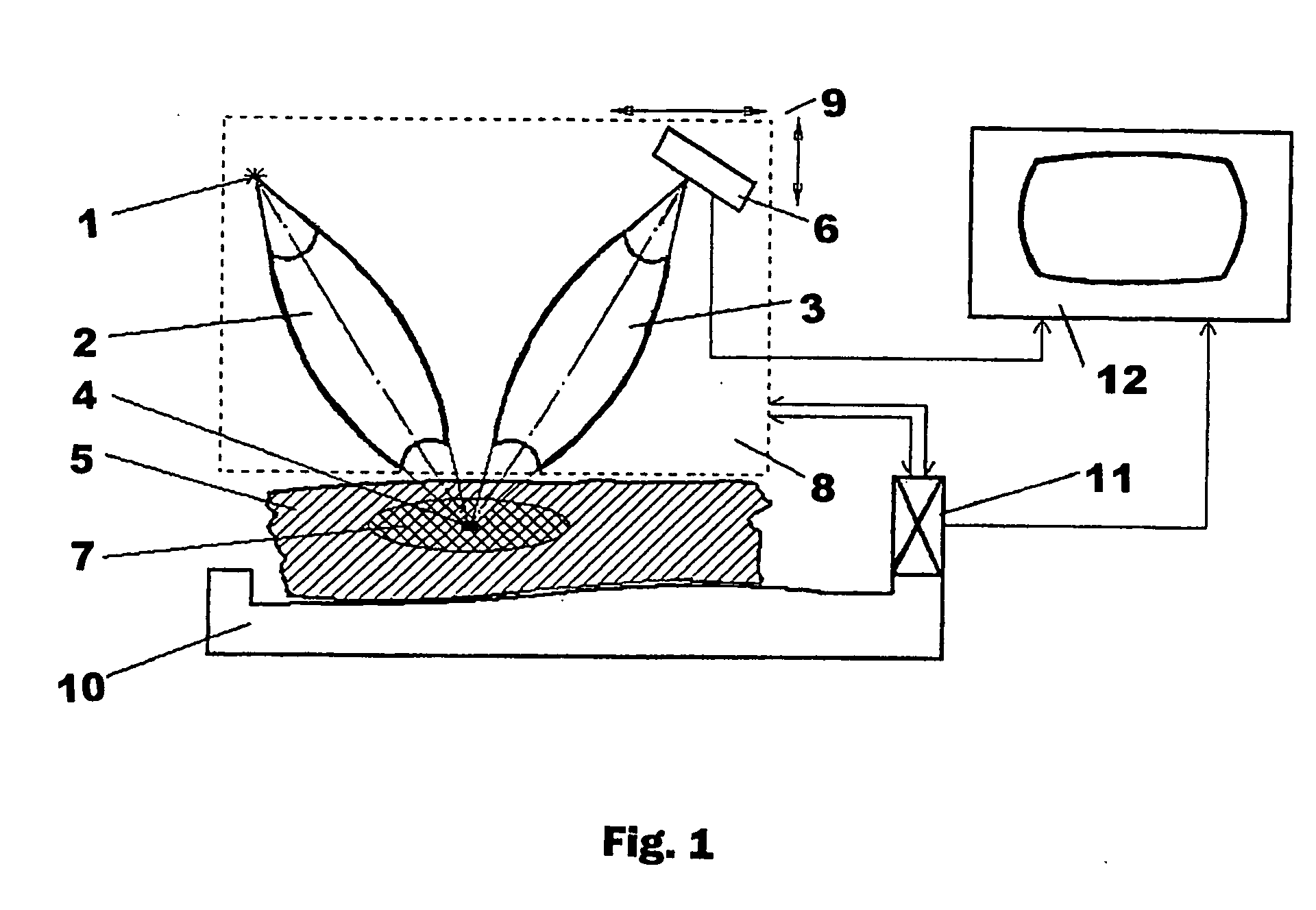
Inventions related to the intra-vision means, designed for production of visually sensed images of the internal structure of an object, in particular, of a biological object, are aimed at higher accuracy of determining the relative density indices of the object's substance in the obtained image together with avoiding complex and expensive engineering; when used for diagnostic purposes in medicine, the dosage of tissues surrounding those that are examined is decreased. X-rays from source 1 is concentrated (for example, using X-ray lens 2) in the zone that includes the current point 4, to which the measurement results are attributed and which is located within the target area 7 of the object 5. Excited in this zone secondary scattered radiation (Compton, fluorescent) is transported (for example, using X-ray lens 3) to one or more detectors 6. By moving the said zone, the target area 7 of object 5 is scanned, and based upon population of the intensity values of the secondary radiation, which are obtained with the help of one or more detectors 6 and which are determined concurrently with coordinates of the current point 6, judgment on the density of the object's substance in this point is made. Density values together with respective coordinate values obtained using sensors 11 are used in the means 12 for data processing and imaging to build up a picture of substance density distribution in the target area of the object.
Owner:KUMAKHOV MURADIN ABUBEKIROVICH
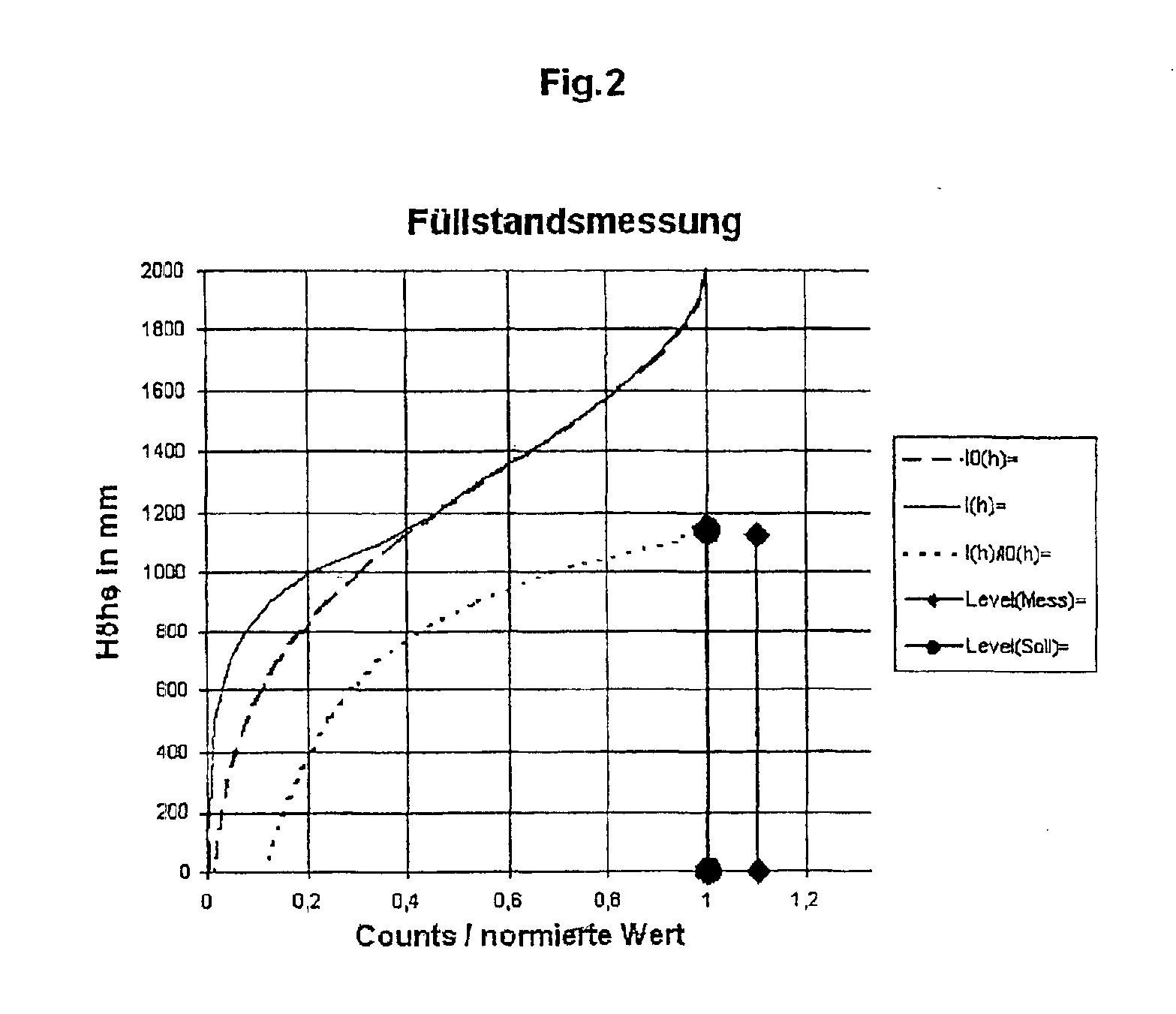
Device for determining and/or monitoring the density and/or the level of a filling material in a container
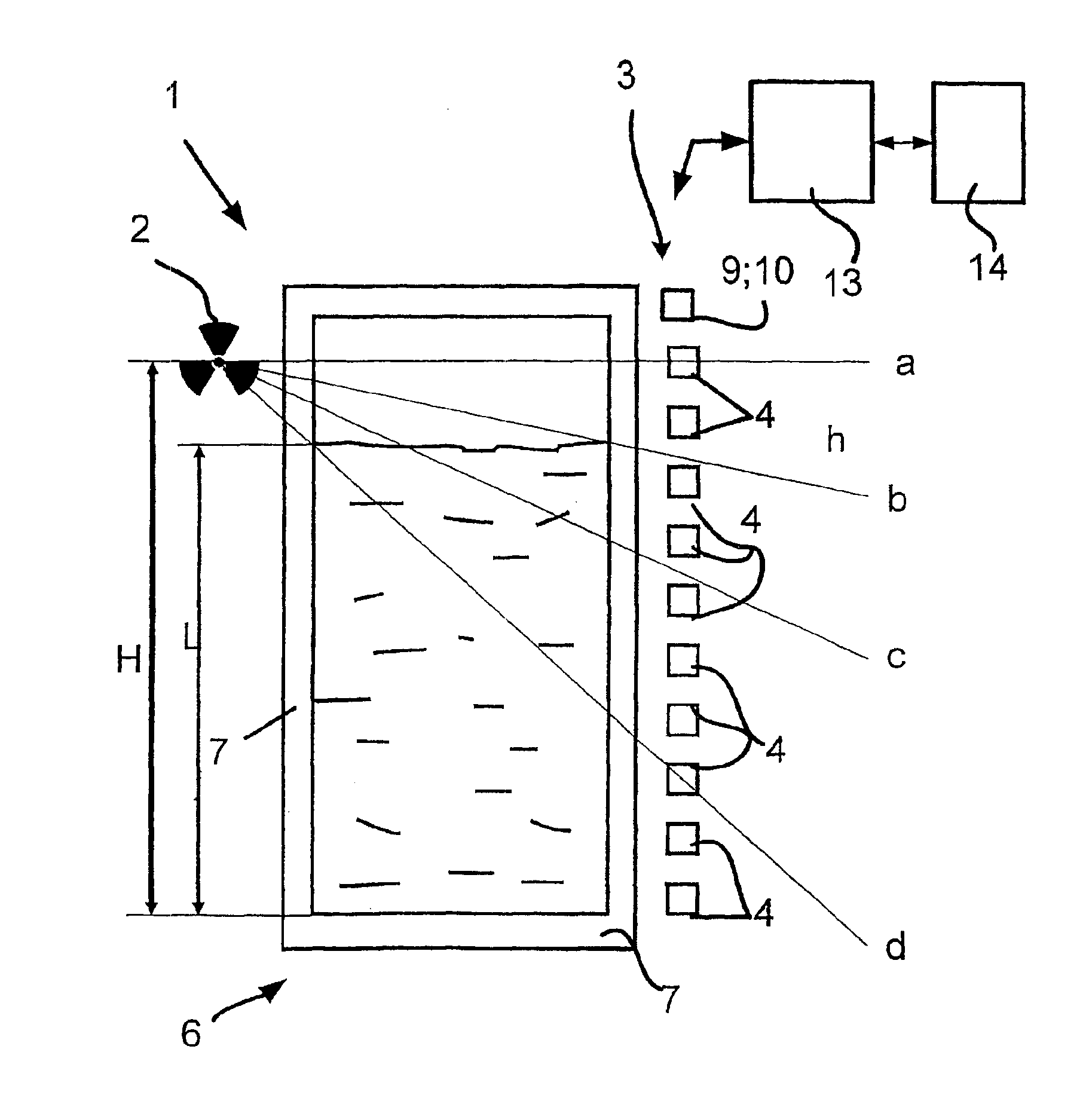
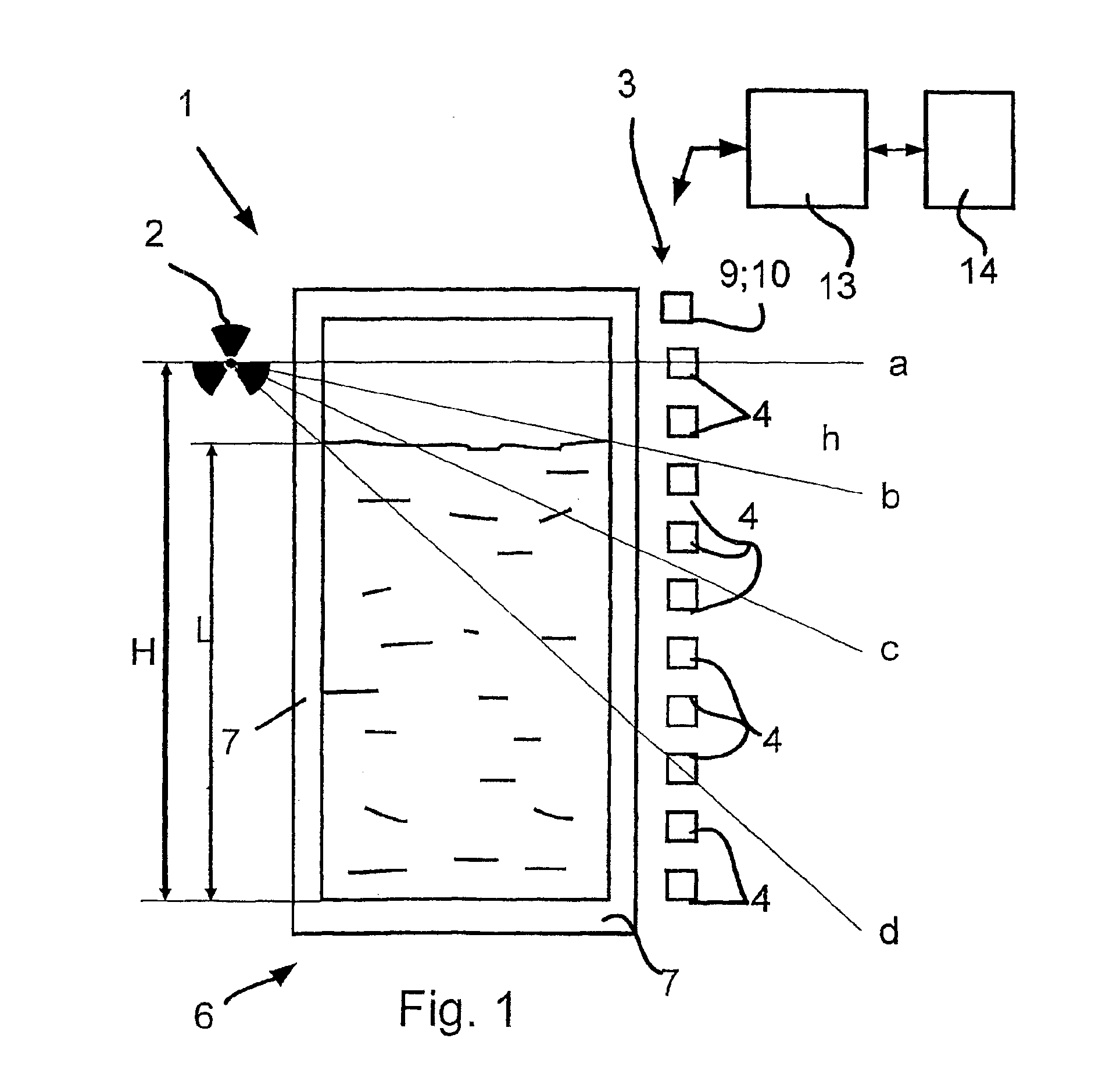
InactiveUS6879425B2Reliable measurementEasy to installMaterial analysis by optical meansMachines/enginesSecondary radiationFilling materials
The invention relates to a device for determining and / or monitoring the density and / or the level (L) of a filling material in a container. A transmitting unit which emits radioactive radiation and a receiving unit which is arranged in such a way that it receives the radioactive radiation or the secondary radiation that is produced by the interaction of the radioactive radiation with the filling material are provided. A regulating / evaluating unit which determines the density and / or the level of the filling material in the container using the measuring data that is supplied by the receiving unit is also provided. The aim of the invention is to provide a device which enables the level or the density of a filling material in a container to be measured reliably. To this end, the receiving unit consists of individual detector units. These detector units are positioned at different distances from the floor of the container, so that each detector unit directly or indirectly, essentially detects the proportion of radiation that passes.
Owner:EHNDRESS KHAUZER GMBKH KO KG
Light emitting diode component
ActiveUS20130099661A1Increase roughnessDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesSecondary radiationReflective layer
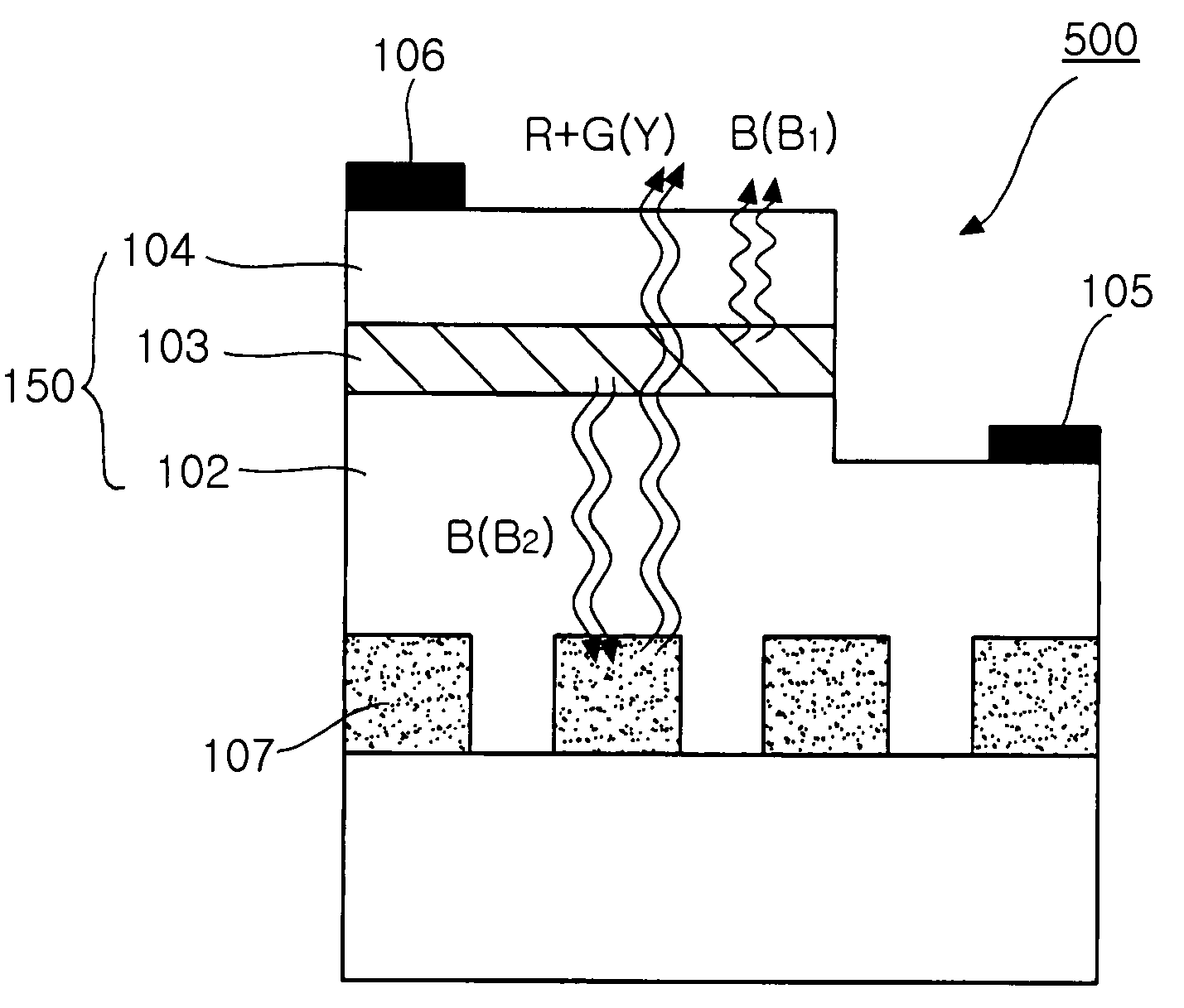
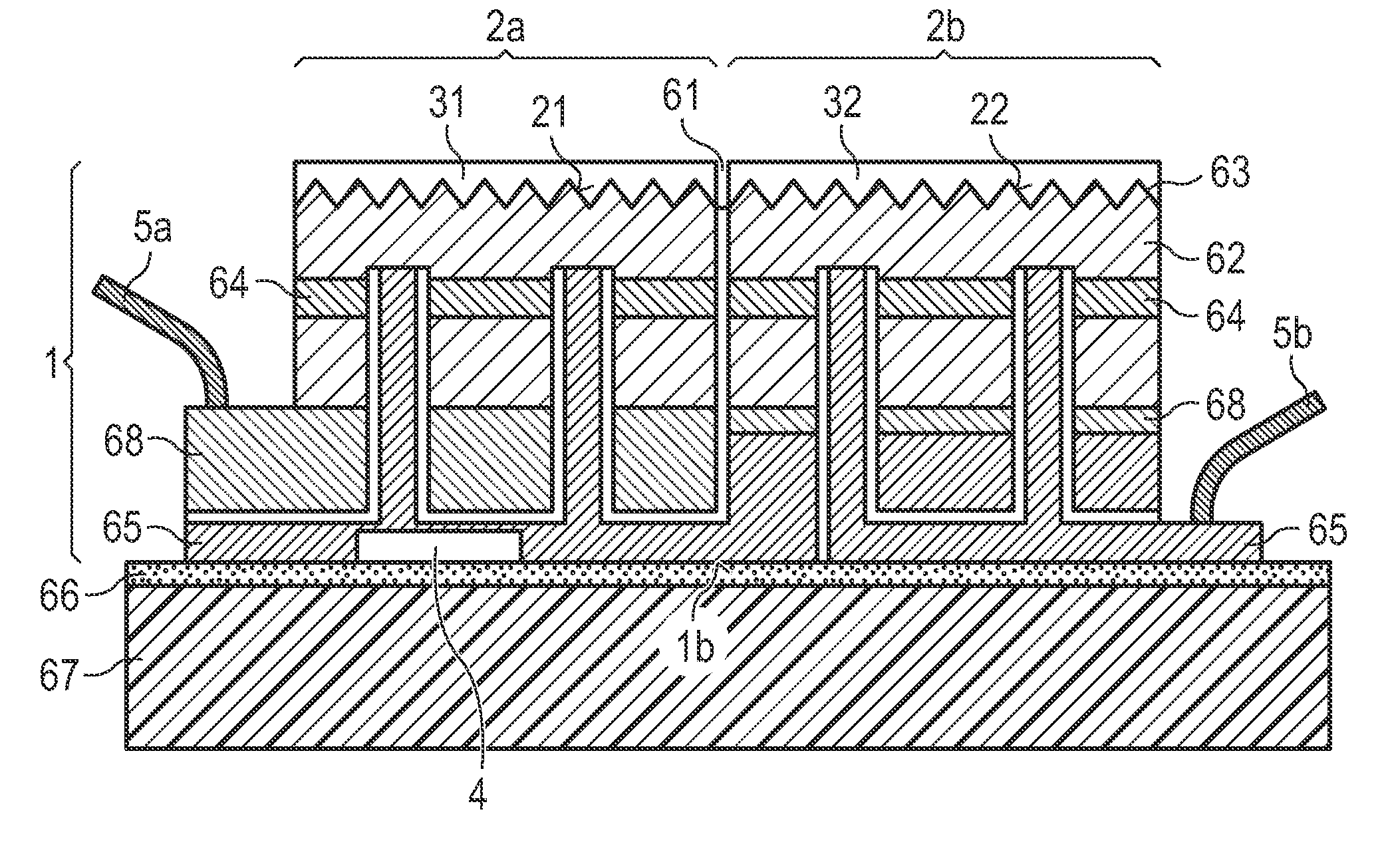
A light-emitting diode component includes a primary source, a conversion layer forming a secondary source configured for absorbing the primary radiation at least in part and emitting a secondary radiation, an encapsulation layer, situated between the primary and secondary sources. The light-emitting diode component also includes a reflection layer (i) situated between the encapsulation layer and the conversion layer and having a face in contact with the encapsulation layer so as to form an interface with the encapsulation layer, the reflection layer (i) and the encapsulation layer being configured so that the interface allows the primary radiation originating from the primary source to pass and reflects the secondary radiation toward the outside of the light emitting diode.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
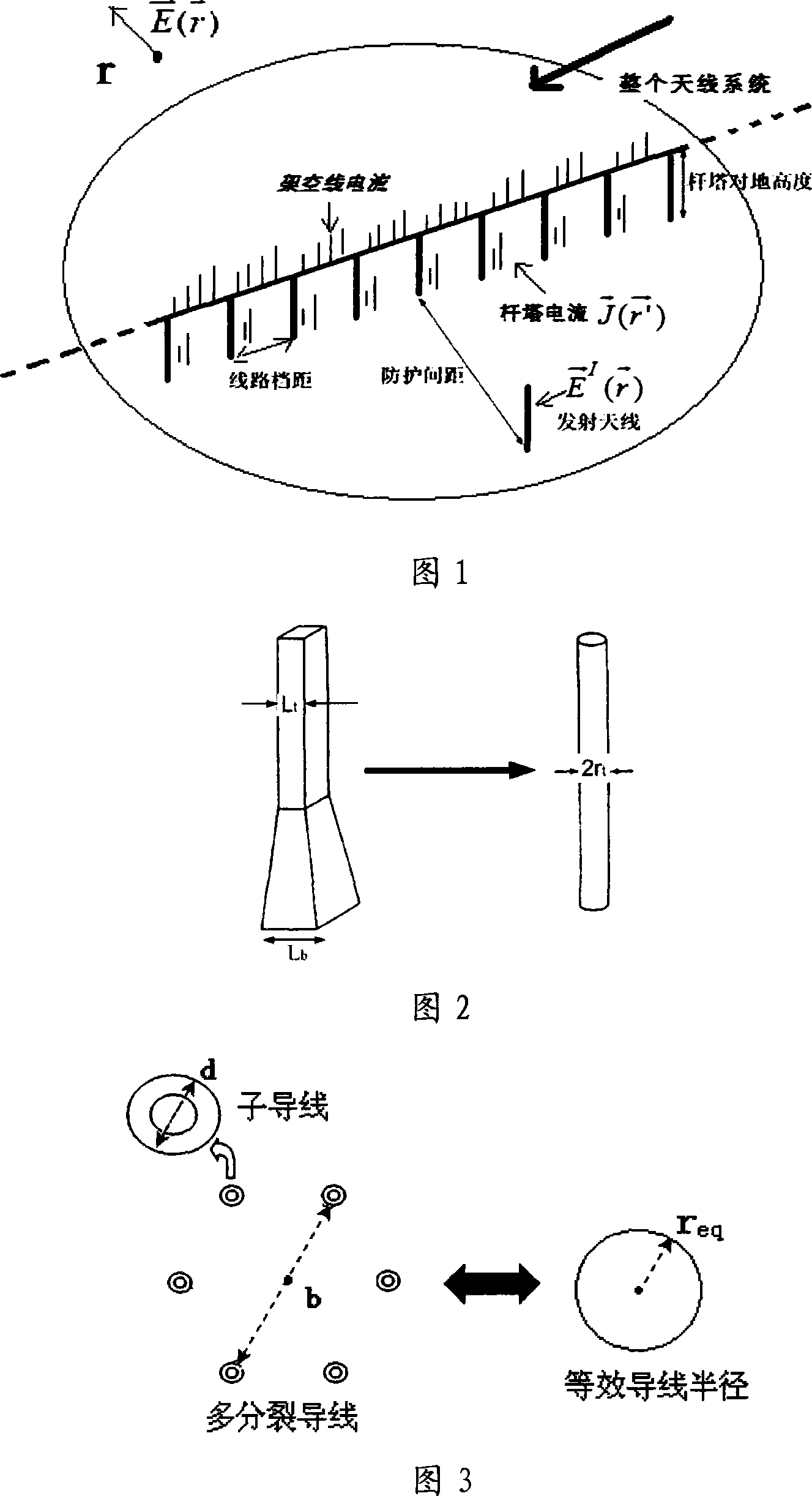
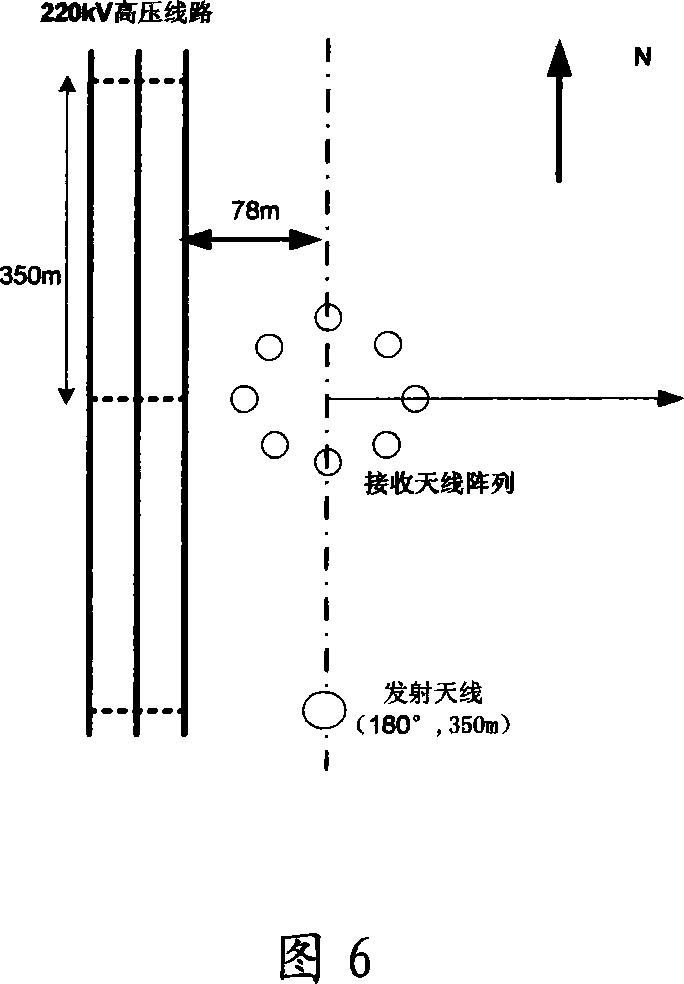
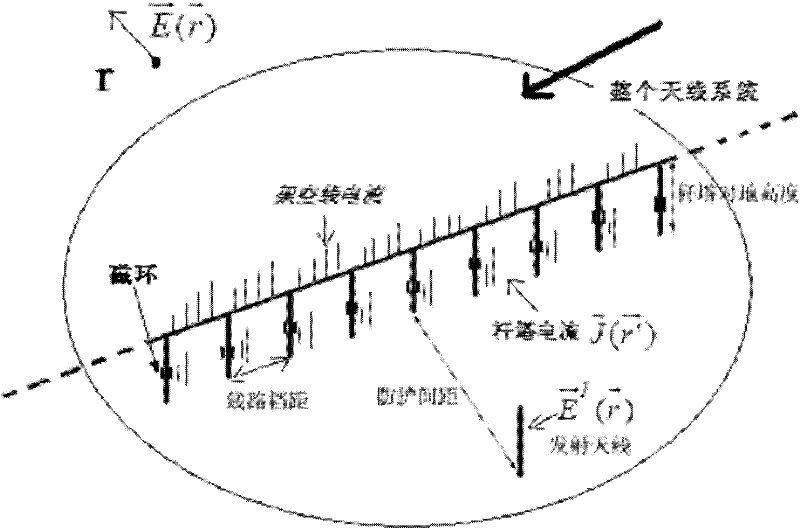
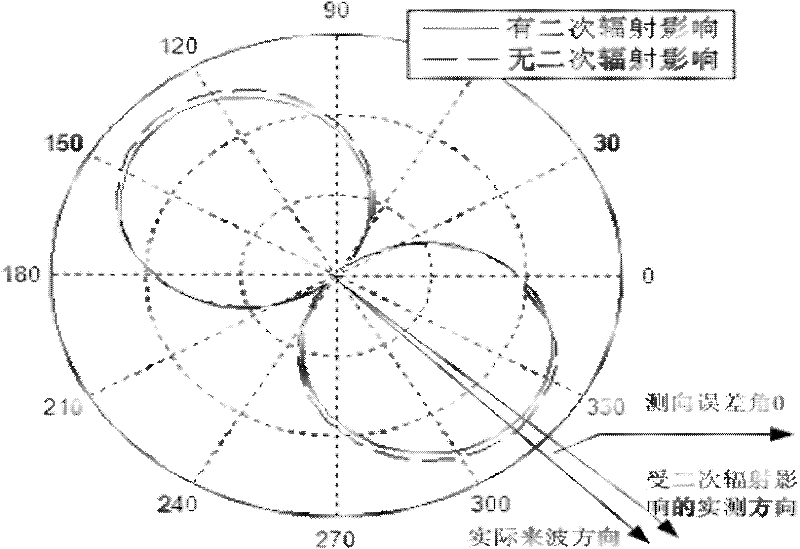
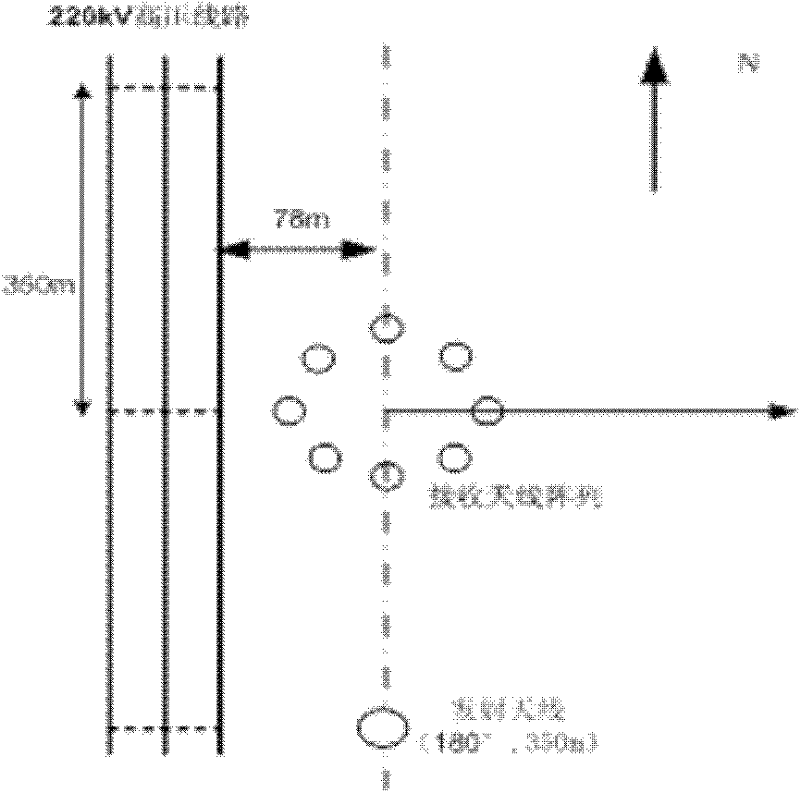
Method for confirming protection distance between extra-high voltage alternating current line and medium wave navigation station
ActiveCN101221204AImprove accuracyElectrical testingElectromagentic field characteristicsReduced modelHigh pressure
The invention relates to a method for determining the protective distance between an AC line with extra-high voltage and a medium wave navigation station, which adopts the method of moments for computing the electric current distribution on the AC transmission line with extra-high voltage and a simplified model of the AC transmission line with extra-high voltage; furthermore, the method comprises the following steps: firstly the method adopts the method of moments and the simplified model of the AC transmission line with extra-high voltage for computing the electric current distribution on the AC transmission line with extra-high voltage, computes a secondary radiation intensity vector which is generated by the induction current according to the acquired induction current distribution on the electric current transmission line, implements the superimposing of the secondary radiation intensity vector and a source radio wave, and computes the interference influence intensity of the AC transmission line with the extra-high voltage of 1000 kilovolts on a medium wave navigation station, thus acquiring the protective distance for the passive jamming between the AC transmission line with extra-high voltage and the medium wave navigation station. The test data comparison acquired from a test proves that the method for determining the protective distance between the AC line with extra-high voltage and the medium wave navigation station has higher accuracy and is applicable for the precise computation of the electromagnetic protective distance between an electric current transmission line with high voltage and an adjacent radio station in the future.
Owner:STATE GRID ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
Method for reducing passive jamming of ultra high voltage alternating current transmission line to radio station
InactiveCN102340357AReduce the effect of passive interferenceImprove accuracyOverhead installationTransmission noise suppressionSecondary radiationUltra high voltage
The invention relates to a method for reducing the passive jamming of an ultra high voltage alternating current transmission line to a radio station. In the method, metal obstacles such as high-voltage overhead lines, iron towers and the like in the vicinity of antennae of the radio station are taken as equivalent receiving antennae, and magnetic rings are arranged on overhead ground wires to control the magnitude of the passive jamming. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a magnetic ring model by adopting Jiles-Atherton, introducing the magnetic ring model into an ultra high voltage alternating current transmission line model to calculate the distribution of current on the ultra high voltage alternating current transmission line, further calculating a secondary radiation intensity vector produced by induced current according to the calculated distribution of the induced current on the transmission line, superposing the secondary radiation intensity vector and original radio waves to calculate the influence degree of the passive jamming of the ultra high voltage alternating current transmission line to the radio station and regulating parameters of the magnetic rings, thereby reducing the passive jamming of the ultra high voltage alternating current transmission line. The method is relatively more highly accurate, and can be applied to the shortening of an electromagnetic protection interval between the ultra high voltage alternating current transmission line and an adjacent radio station in future.
Owner:STATE GRID ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
Electroluminescent device
ActiveCN101405368ASolid-state devicesLuminescent compositionsSecondary radiationVolumetric Mass Density
A conversion element (3) comprising a ceramic material (31) with a multiplicity of pores (32) provided for at least the partial absorption of at least one primary radiation (52) and for transforming the primary radiation (52) into at least one secondary radiation (53), wherein the conversion element (3) has a density greater than or equal to 97% of the theoretical solid-state density of the ceramic material (31), and the pores (32) in the conversion element (3) have a diameter substantially between 200 nm and 5000 nm.
Owner:LUMILEDS HLDG BV
Method and apparatus for real time imaging and monitoring of radiotherapy beams
InactiveUS8049176B1Handling using diaphragms/collimetersMaterial analysis by optical meansHigh energySecondary radiation
A method and apparatus for real time imaging and monitoring of radiation therapy beams is designed to preferentially distinguish and image low energy radiation from high energy secondary radiation emitted from a target as the result of therapeutic beam deposition. A detector having low sensitivity to high energy photons combined with a collimator designed to dynamically image in the region of the therapeutic beam target is used.
Owner:JEFFERSON SCI ASSOCS LLC
Materials and Methods and Systems for Delivering Localized Medical Treatments
InactiveUS20080195223A1Increase temperatureSurgical adhesivesBone implantFilling materialsSecondary radiation
A filler material comprising an energy intercepting element. In an embodiment, an energy intercepting element may attenuate, redirect, concentrate, or otherwise modify the properties of intercepted energy, e.g. the incoming energy flux. In an embodiment an energy intercepting element may be changed, for example generating secondary electrons, and / or secondary radiation, by intercepted energy. Also disclosed is a method comprising introducing a filler material composition into a cavity within a tissue in a patient's body, wherein the filler material includes an energy intercepting element(s) for intercepting energy and directing an energy source at the filler material.
Owner:SANATIS
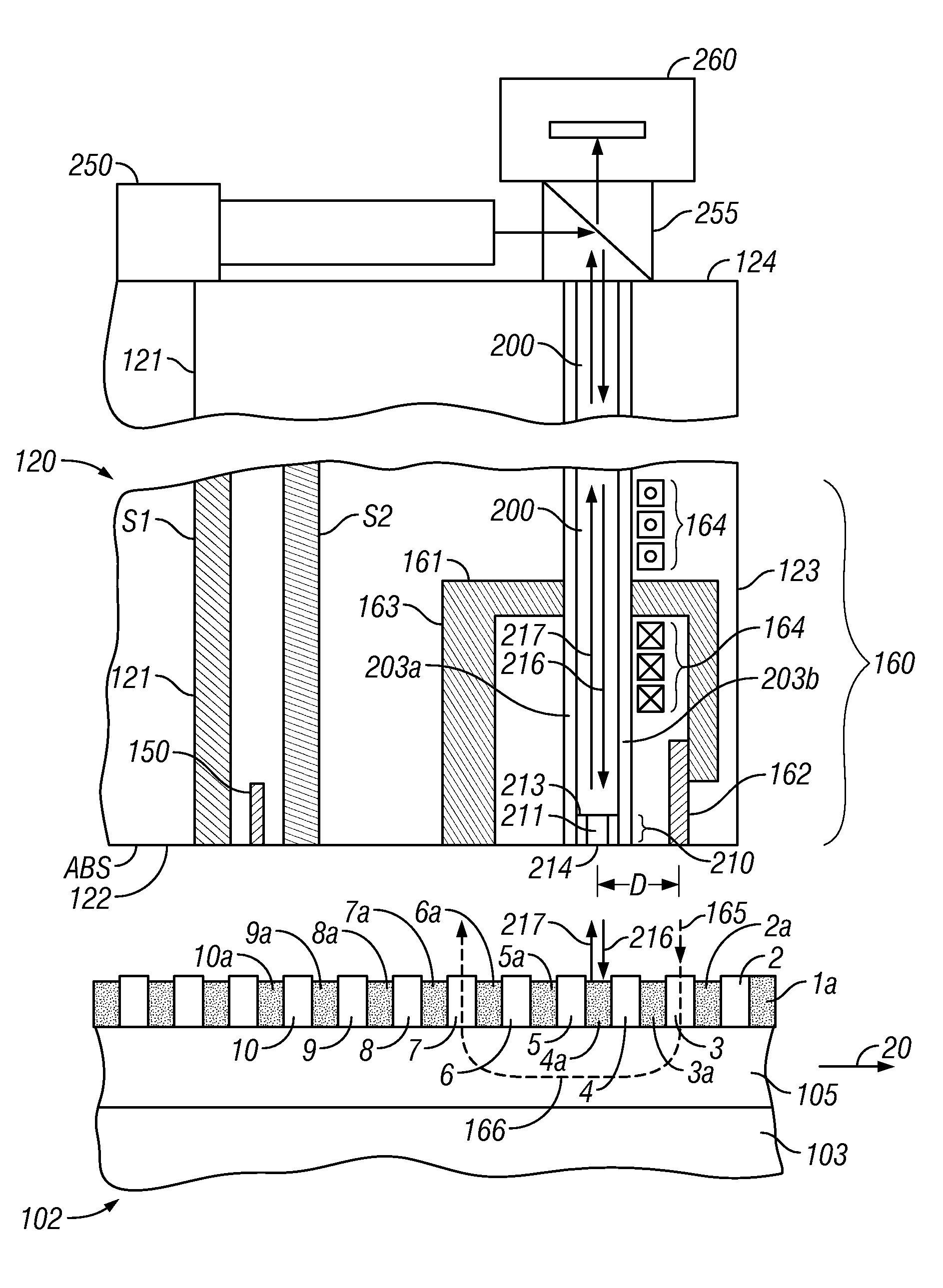
Patterned-media magnetic recording disk with optical contrast enhancement and disk drive using optical contrast for write synchronization
ActiveUS7796353B2Increase contrastCombination recordingPatterned record carriersFluenceSurface plasmon
A patterned-media magnetic recording disk drive uses an optical system for clocking the write data and a patterned-media disk that has discrete magnetizable data islands with nonmagnetic spaces between the islands, wherein the nonmagnetic spaces contain optical contrast material. The optical contrast material may be optically absorptive material, fluorescent material, or a metal layer that generates surface plasmons when excited by radiation of a specific wavelength. Radiation from a primary radiation source is directed to a near-field transducer maintained near the disk surface and a radiation detector detects radiation reflected back from the transducer. If the disk has fluorescent material or a metal layer in the nonmagnetic spaces, then a secondary radiation source irradiates the fluorescent material or metal layer with radiation of a specific wavelength to cause the fluorescent material to emit radiation or the metal layer to generate surface plasmons. As the disk rotates, reflected optical power from the transducer varies depending on whether an island or space is under the transducer. The output signal from the radiation detector output controls the write clock.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Extensible passive addressing LED micro-display device
ActiveCN105914200AGuaranteed stabilityReduce crosstalkStatic indicating devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLow voltageDisplay device
The invention discloses the technical scheme of the structure of an extensible passive addressing LED micro-display device and preparation thereof. The LED micro-display device comprises an LED micro-pixel array and a passive addressing silicon-based driving substrate. Interconnection of the n electrodes of row LED pixel points is realized in the LED array. Interconnection of the P electrodes of column LED pixel points is realized on the silicon-based substrate. Then bonding of the LED array and the silicon-based substrate is realized through the mode of flip-chip welding. Besides, all-band visible light secondary radiation material is coated on the transparent electrodes of the LED pixel points, and red, green and blue alignment distributed pixel point color filters are applied for covering or monochrome secondary radiation material is applied for alignment distributed coating. Blue-violet light radiation is acquired through row and column scanning and addressing of power supply micro LED pixel points, all-band visible light is acquired by stimulating the secondary radiation material, and three primary colors are acquired through the color filters or the three primary colors are acquired by directly stimulating the monochrome secondary radiation material so that the objective of micro-display can be achieved. The micro-display device prepared by the method can achieve the advantages of micro device, low-voltage and low-current driving, color display and long service life.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
System and methods for detecting concealed nuclear material in cargo
InactiveUS20090283690A1Reduce operating costsReduce false alarm rateConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsMaterial analysis by optical meansHigh energyHigh energy photon
A cargo inspection system and active inspection methods for operating the same to confirm or clear a presence of explosives and / or nuclear materials in cargo. The active inspection methods use high-energy photons and / or neutrons to induce fission, and measure prompt neutrons, delayed neutrons, and delayed gamma-rays. Additionally, if one or more suspect objects are identified within the cargo with a preceding radiographic or computed tomography scan, a microprocessor calculates a position that produces optimal active inspection signals. The cargo or one of a primary radiation source, a secondary radiation source, or one or more radiation detectors are moved to this calculated position before fission occurs.
Owner:MORPHO DETECTION INC
Method and apparatus for shielding medical personnel from radiation
ActiveUS20110248193A1Improve sealingAvoid formingSurgical drapesShieldingSecondary radiationRadiation shield
Systems and methods for shielding medical personnel from radiation are provided. A radiation-shielding barrier is positioned between the medical personnel and the radiation source. The radiation-shielding barrier includes an opening such that a portion of the table extends through the opening in the barrier. Medical personnel are protected from secondary radiation transmitted through the patient via a special layering technique of a first, flexible sterile drape, a flexible radiation-resistive drape, and a second flexible sterile drape. The system includes an upper shield and a lower shield of independent movement and a linking mechanism between the two, while maintaining the radiation seal. The system also includes a mechanism for maintaining the radiation barrier between the upper shield and the patient aperture hoop, preventing a radiation gap from forming between the flexible portions of the system (e.g. flexible drapes, curtains, etc.) and the non-flexible portions of the system (e.g. upper shield, lower shield, radiopaque transparent window, etc.).
Owner:ECO CATH LAB SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com