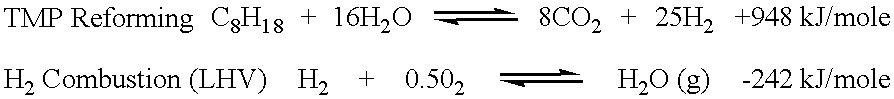Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
15241results about "Chemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
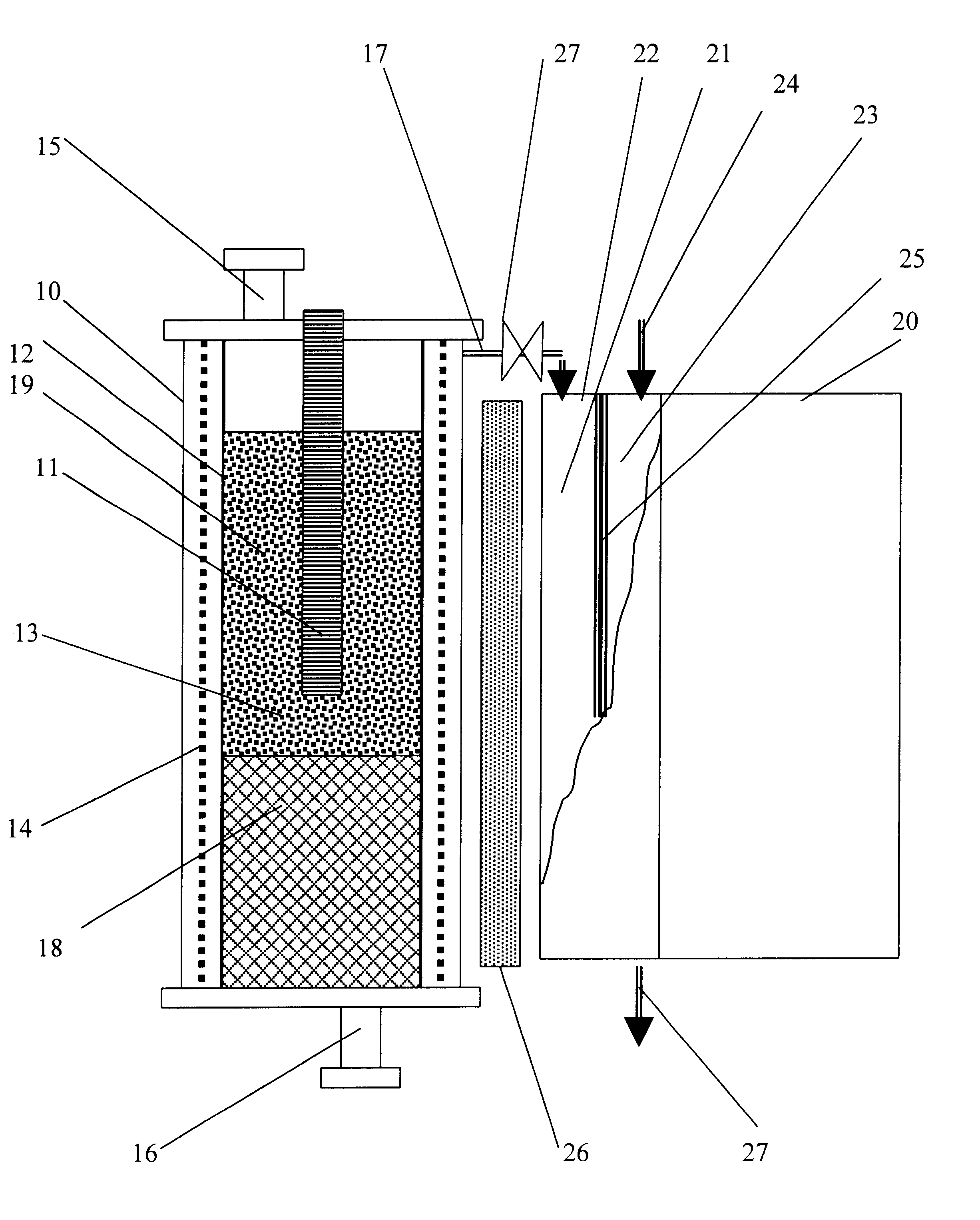
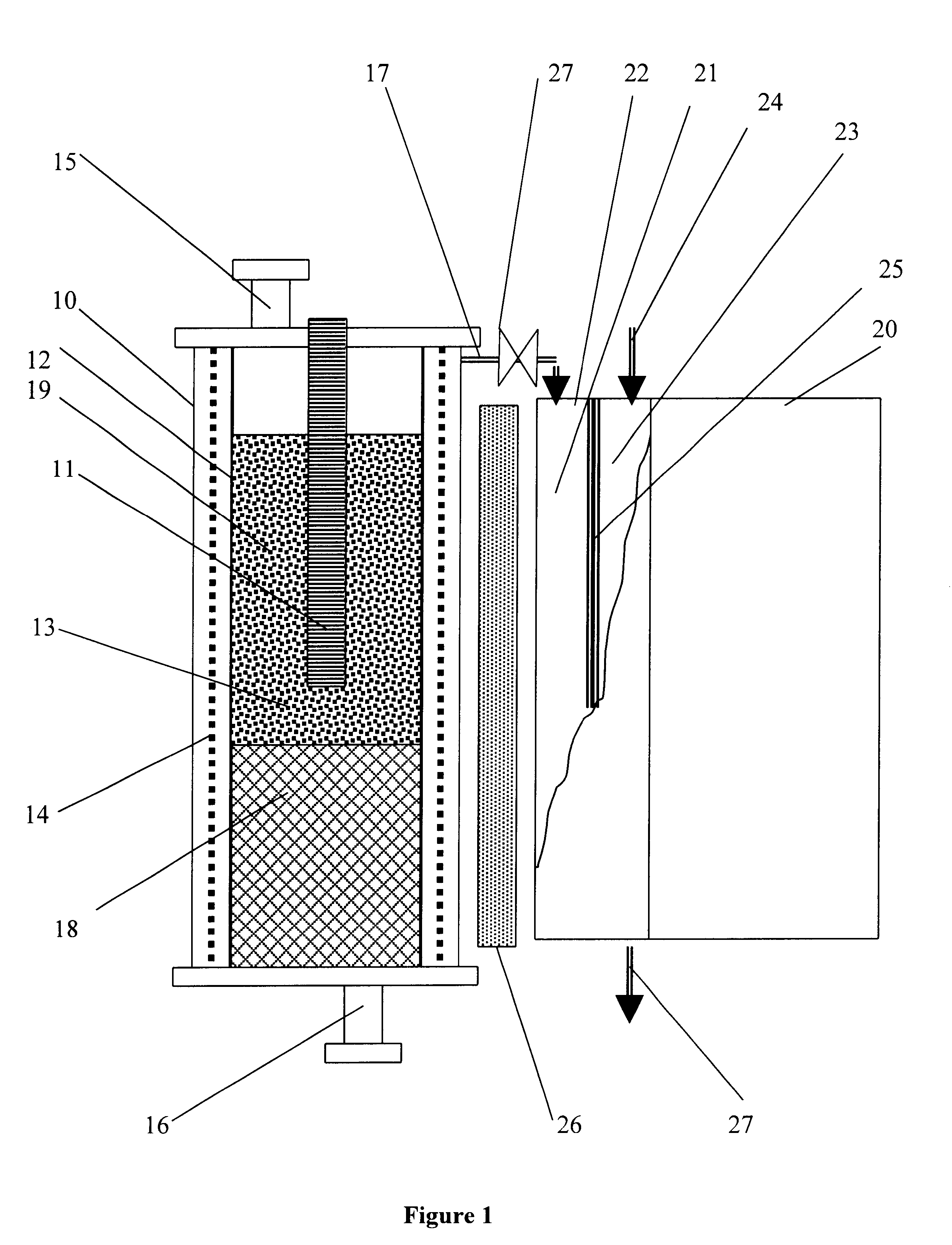
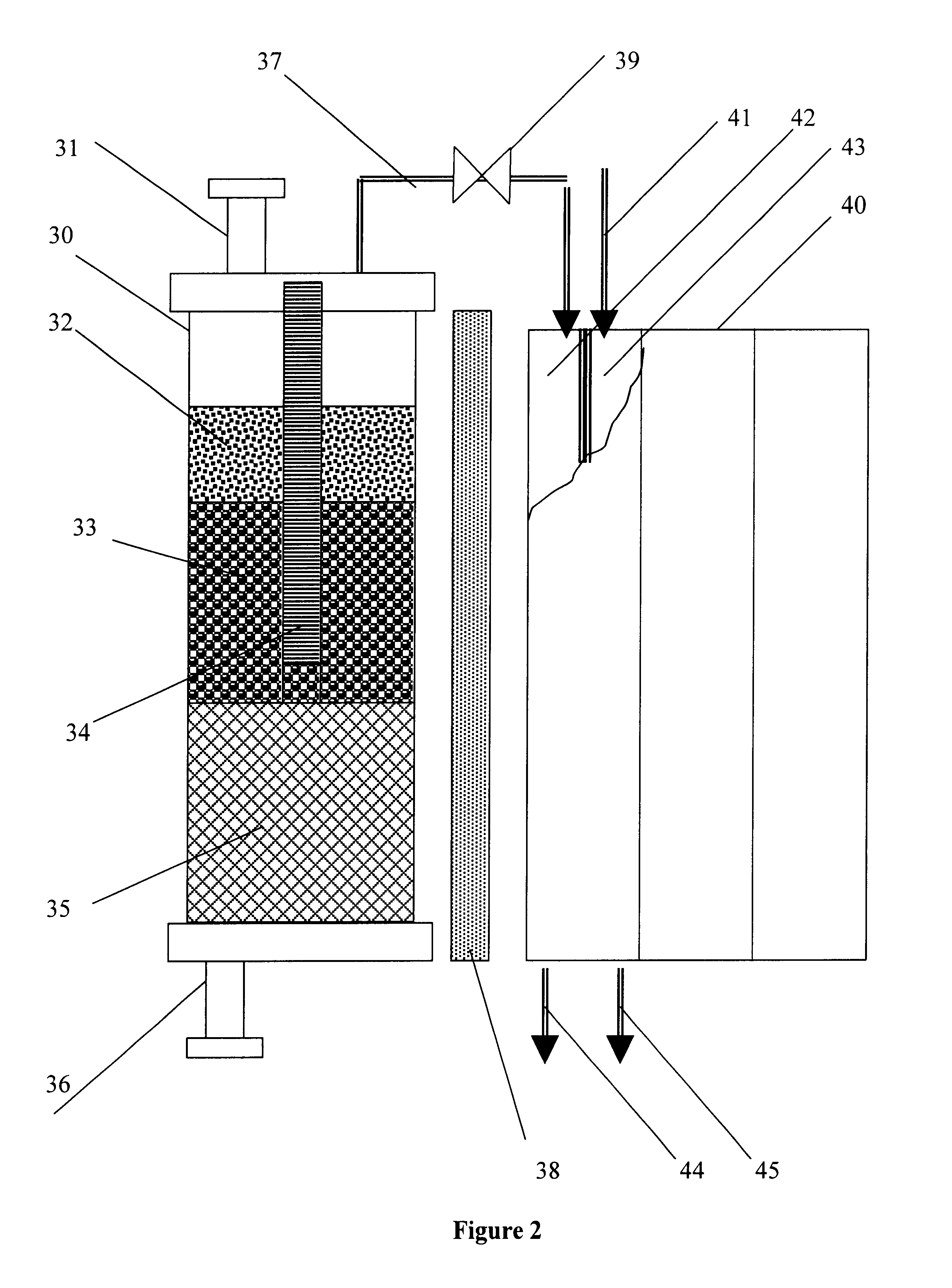
Processes and apparatus for continuous solution polymerization
InactiveUS6881800B2Process control/regulationLiquid-gas reaction as foam/aerosol/bubblesSolution polymerizationProcess plant
The invention relates to processes and plants for continuous solution polymerization. Such plant and processes include a pressure source, a polymerization reactor, downstream of said pressure source, pressure let-down device, downstream of said polymerization reactor, and a separator, downstream of said pressure let-down device, wherein said pressure source is sufficient to provide pressure to said reaction mixture during operation of said process plant to produce a single-phase liquid reaction mixture in said reactor and a two-phase liquid-liquid reaction mixture in said separator in the absence of an additional pressure source between said reactor and said separator.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
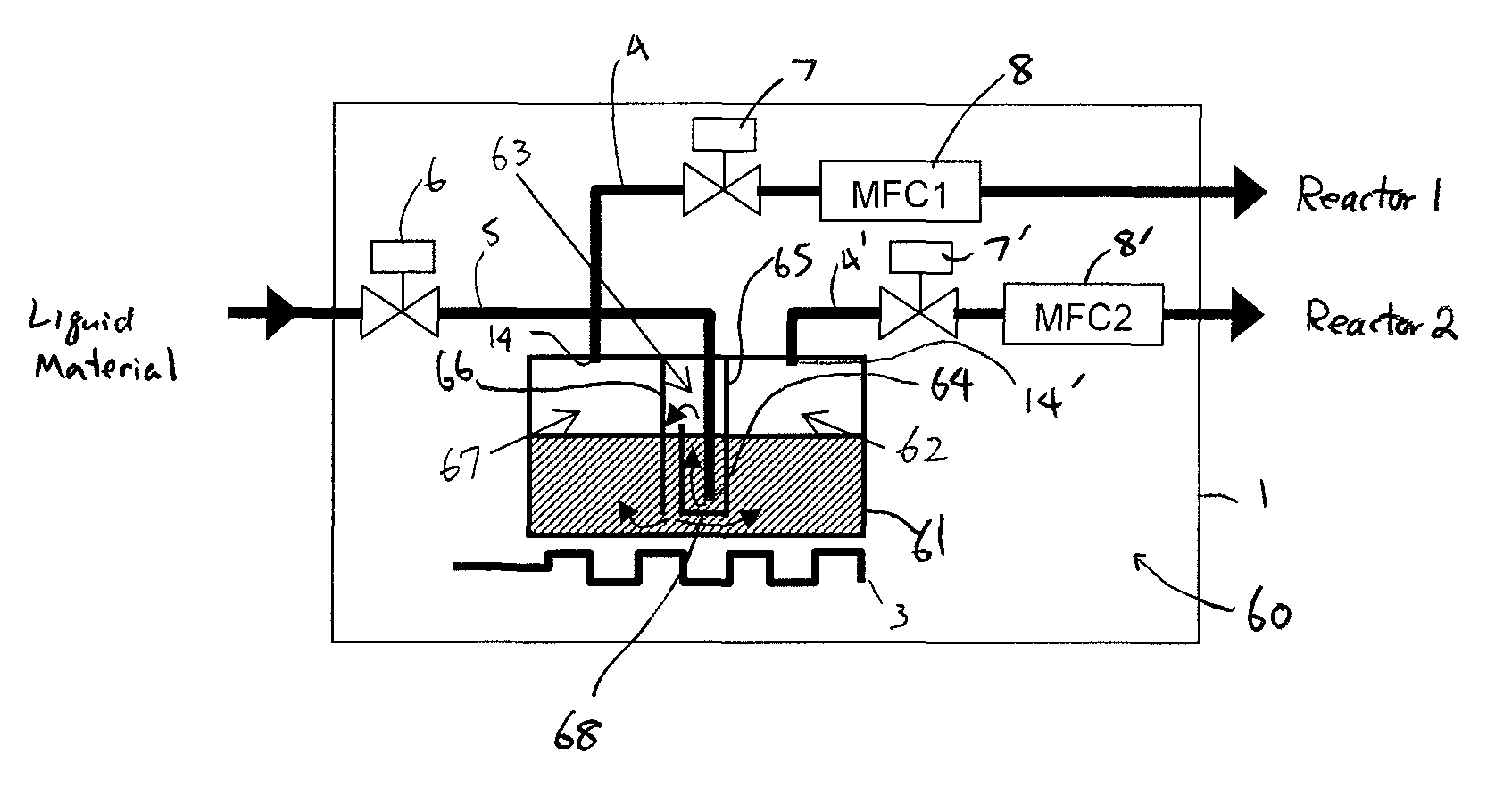
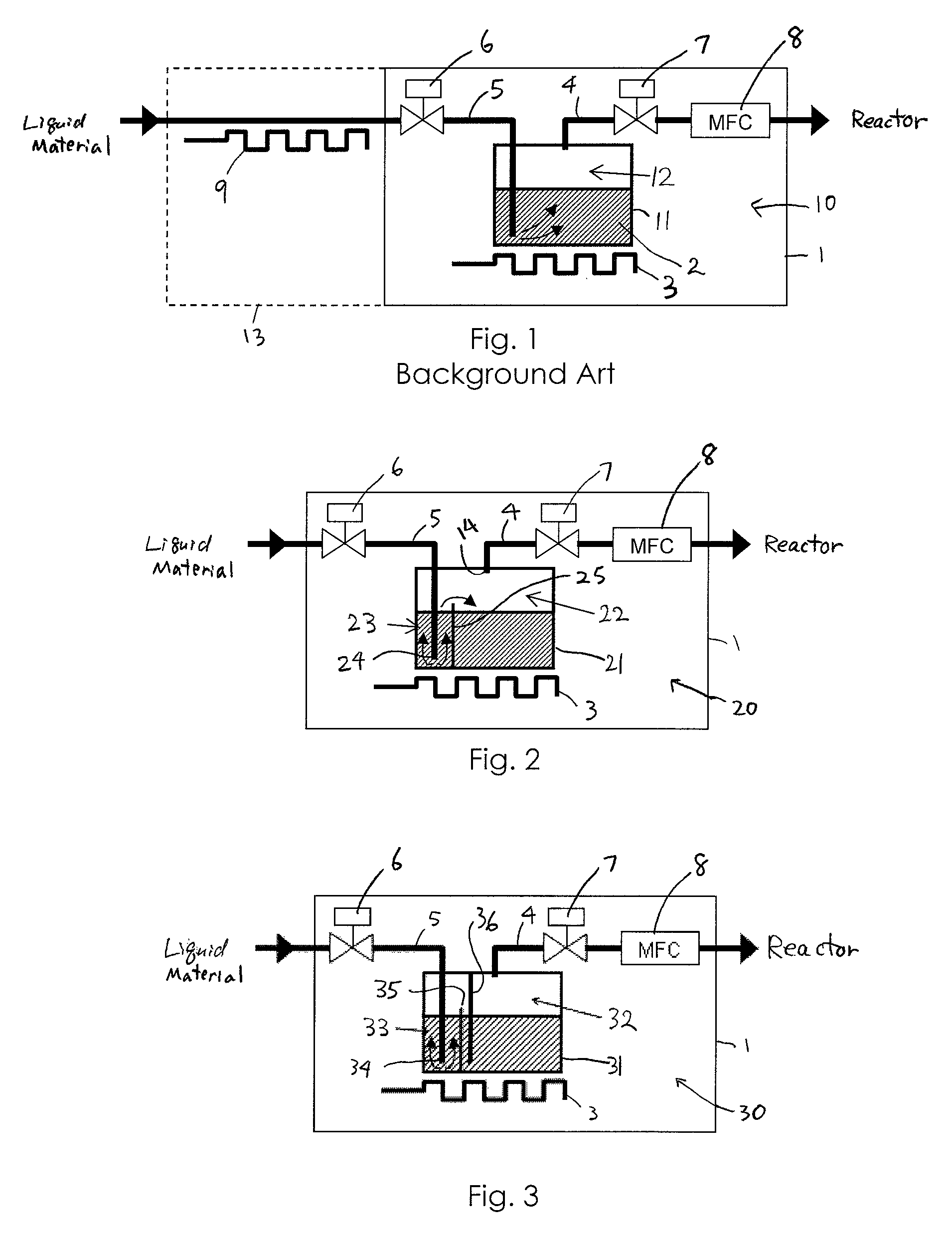
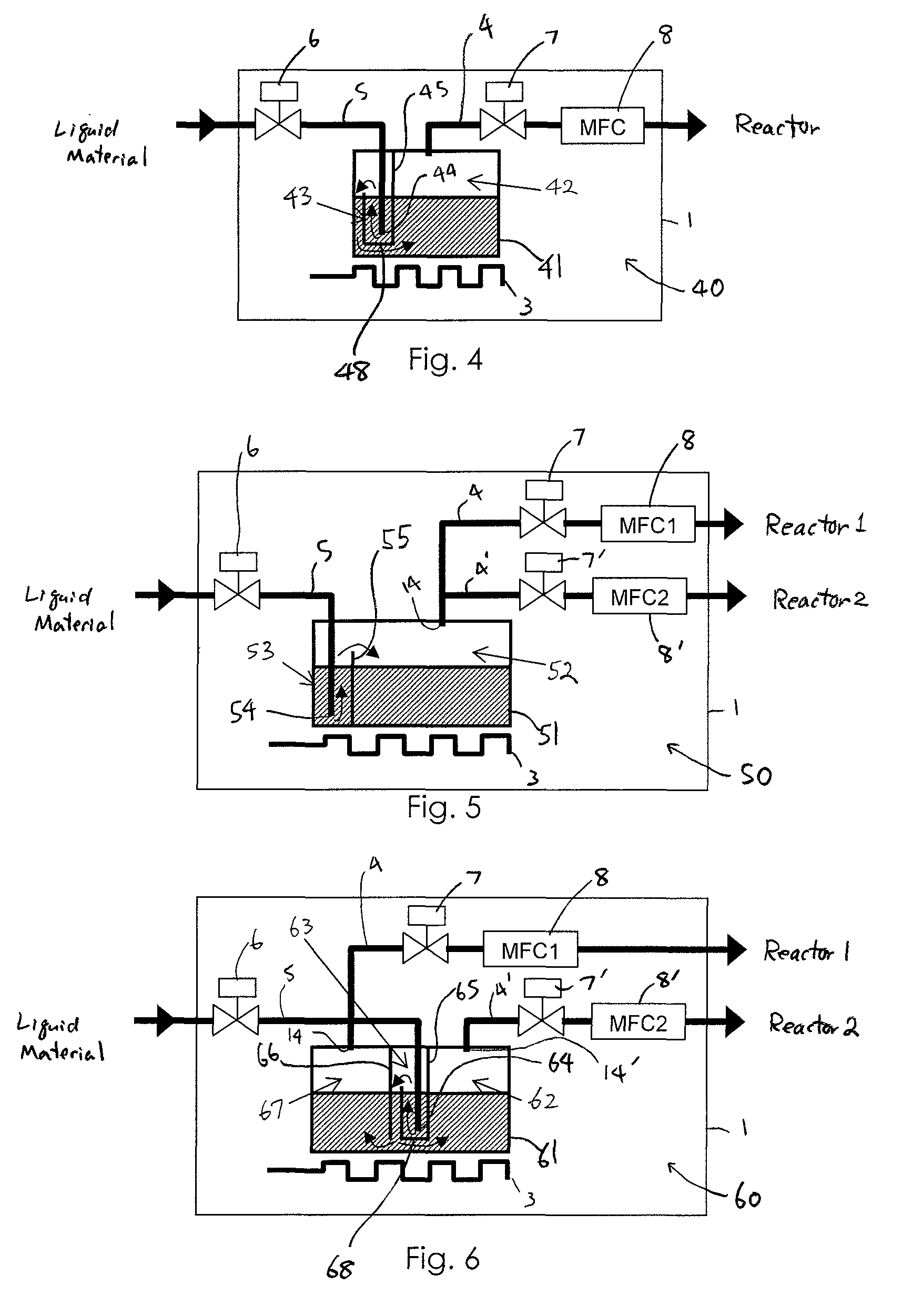
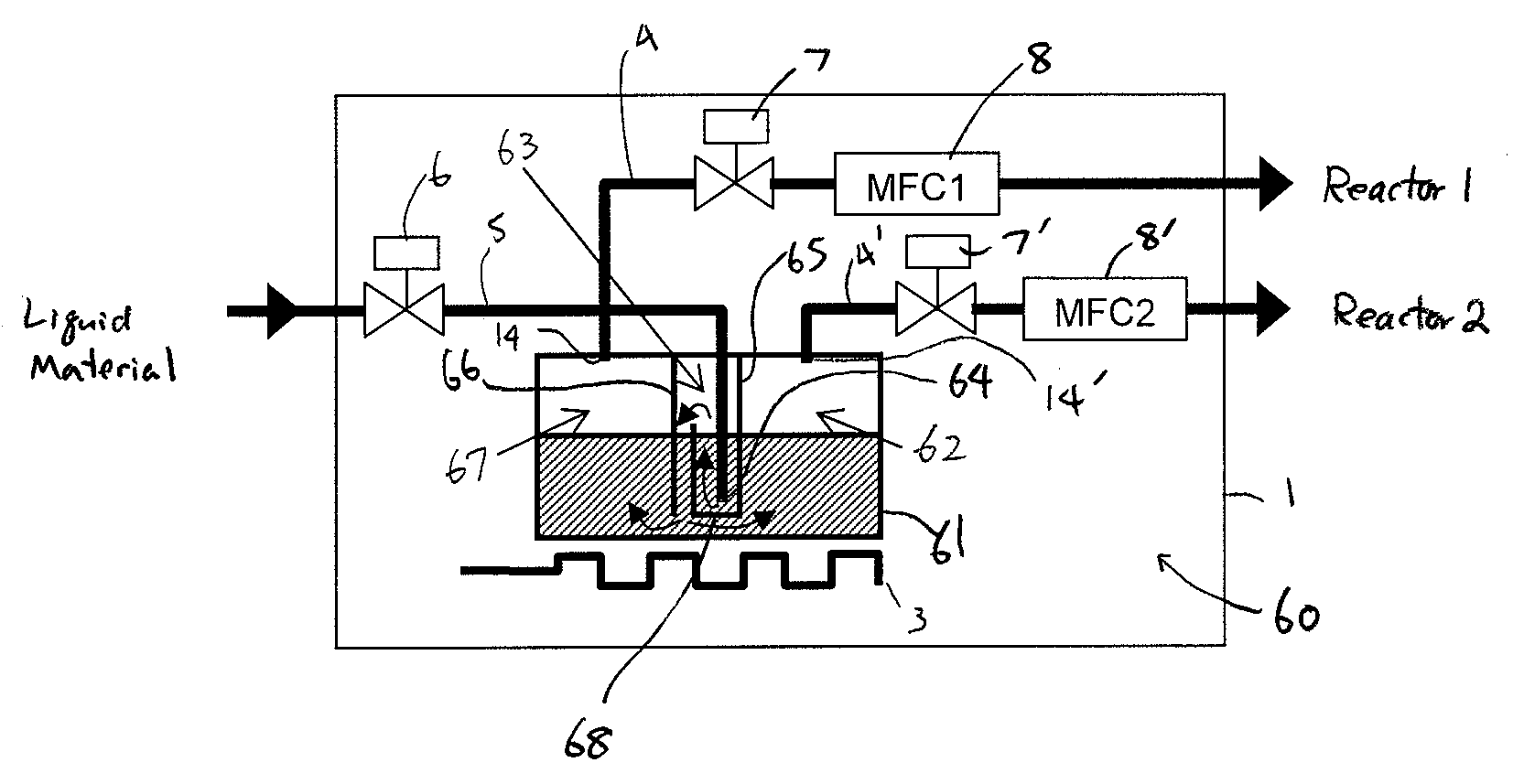
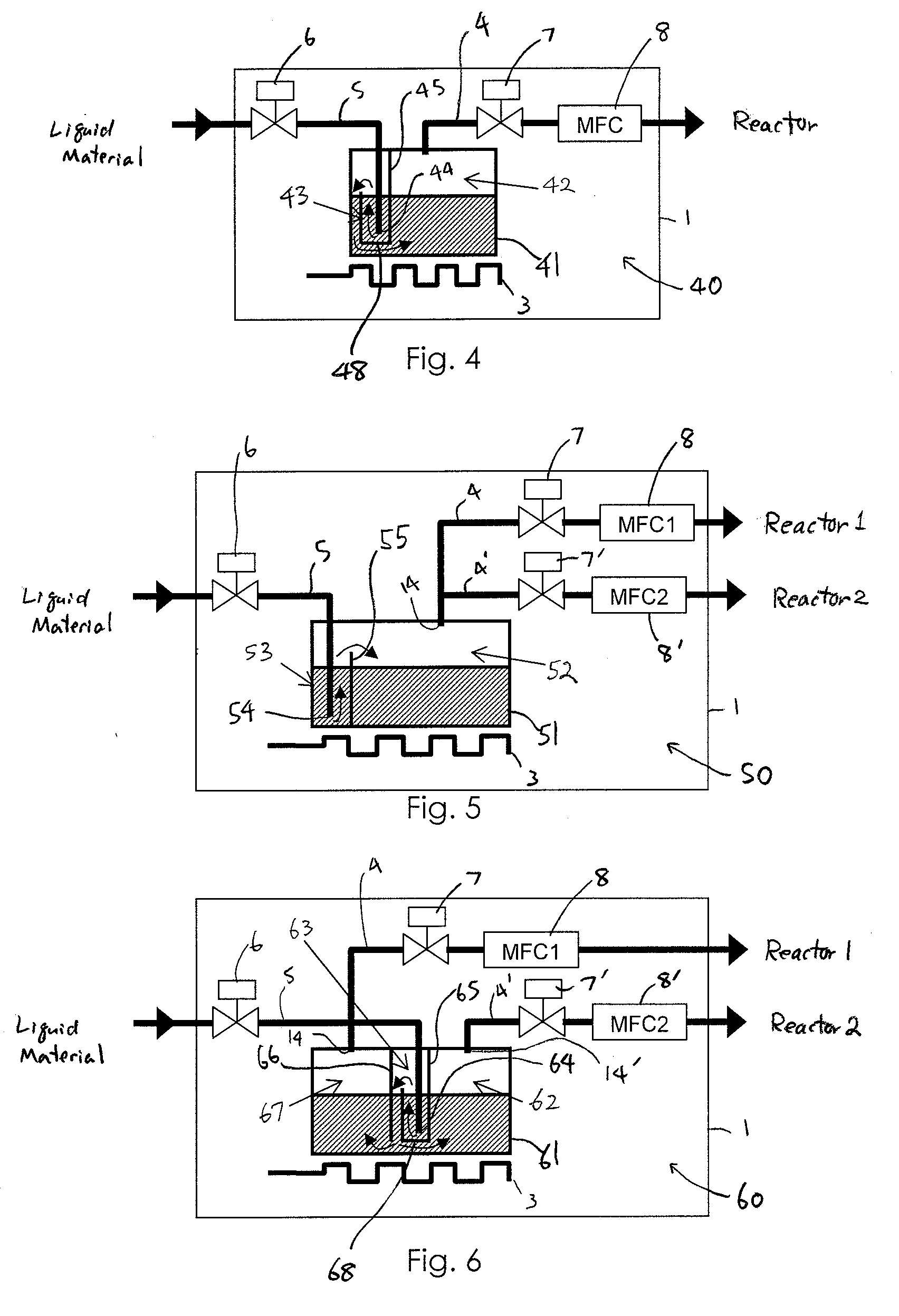
Liquid material vaporization apparatus for semiconductor processing apparatus
ActiveUS7833353B2Reduce the temperatureInhibition is effectiveSteam generation heating methodsSpray nozzlesVaporizationEngineering
A liquid material vaporization apparatus for a semiconductor processing apparatus includes: a vaporization tank; an inner partition wall disposed in the tank for dividing the interior of the tank into a charging compartment and a vaporization compartment which are liquid-communicatable with each other over an upper edge of the inner partition wall. A liquid material charged in the charging compartment overflows over the upper edge of the inner partition wall toward the vaporization compartment to store and vaporize the liquid material in the vaporization compartment.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Liquid material vaporization apparatus for semiconductor processing apparatus
ActiveUS20080173240A1Reduce the temperatureLow thermal conductivitySteam generation heating methodsSpray nozzlesVaporizationEngineering
A liquid material vaporization apparatus for a semiconductor processing apparatus includes: a vaporization tank; an inner partition wall disposed in the tank for dividing the interior of the tank into a charging compartment and a vaporization compartment which are liquid-communicatable with each other over an upper edge of the inner partition wall. A liquid material charged in the charging compartment overflows over the upper edge of the inner partition wall toward the vaporization compartment to store and vaporize the liquid material in the vaporization compartment.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Apparatus and method for combinatorial chemistry synthesis
InactiveUS6045755AOvercome problemsImprove throughputEngagement/disengagement of coupling partsSequential/parallel process reactionsChemical synthesisProcess engineering
In a first embodiment, this invention includes an integrated robot apparatus for performing combinatorial chemistry synthesis protocols and having interchangeable work-stations, robot arm tools, and reaction vessels and reaction vessel arrays. The work-stations and tools are specialized to perform tasks necessary for the synthesis in a plurality of the reaction vessels grouped in a plurality of the reaction vessel arrays. Preferably, these elements function interchangeably because they have standardized sizes and conformation. The work-stations and tools include those for fluid dispensing or aspirating from individual reaction vessels or from all the reaction vessels in an array simultaneously. The reaction vessels can include, alternatively, stackable, ball-sealed reaction vessels, microtitre-like reaction vessel arrays, arrays of independent reaction vessels, valve-sealed reaction vessels, septum-sealed reaction vessels, and syringe reaction vessels. In alternative embodiments, this invention includes these work-stations, tools, reaction vessels and reaction vessel arrays in various combinations or sub-combinations either for use in partially integrated robots or for manual or standalone use.
Owner:LION BIOSCIENCE AG
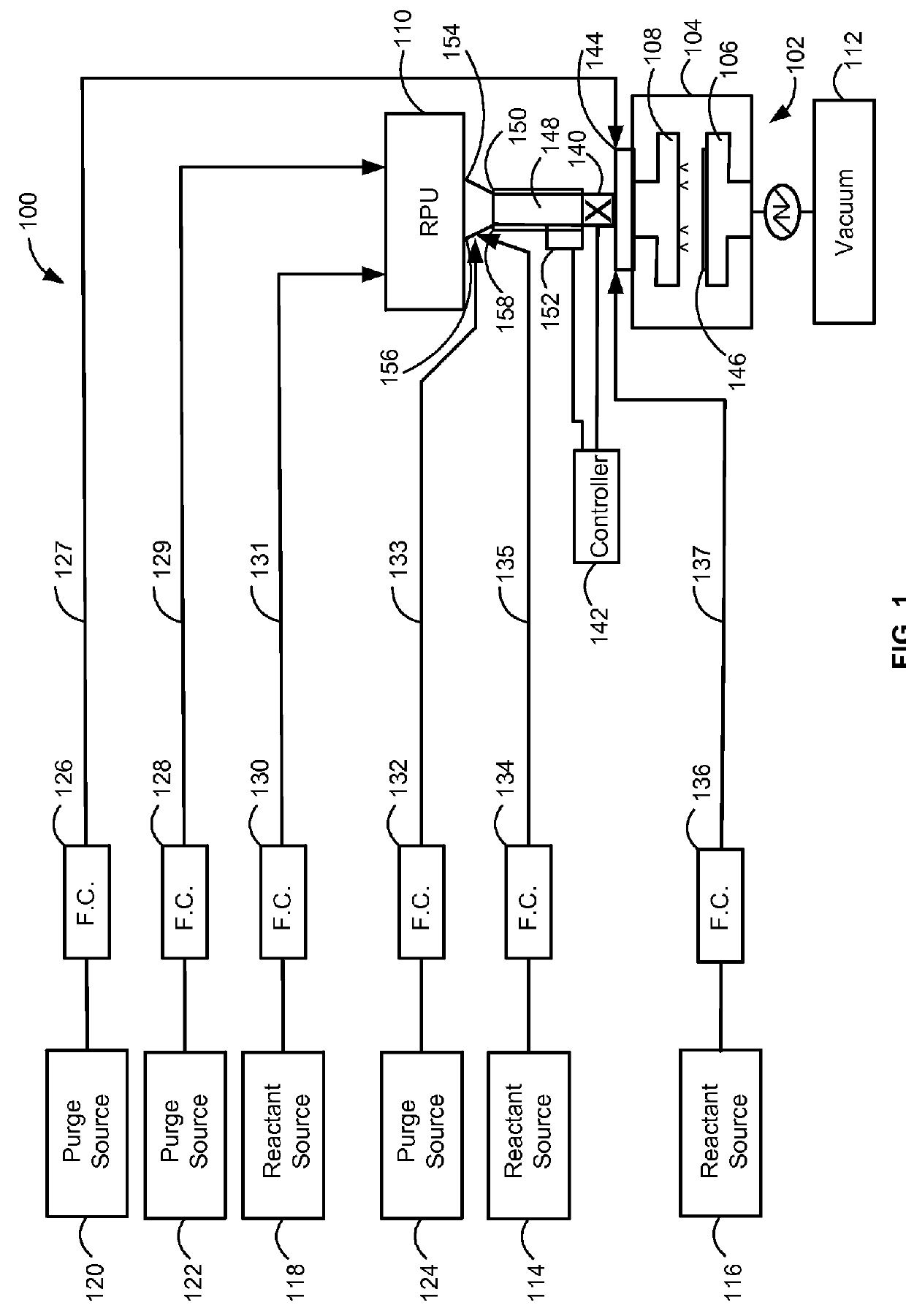
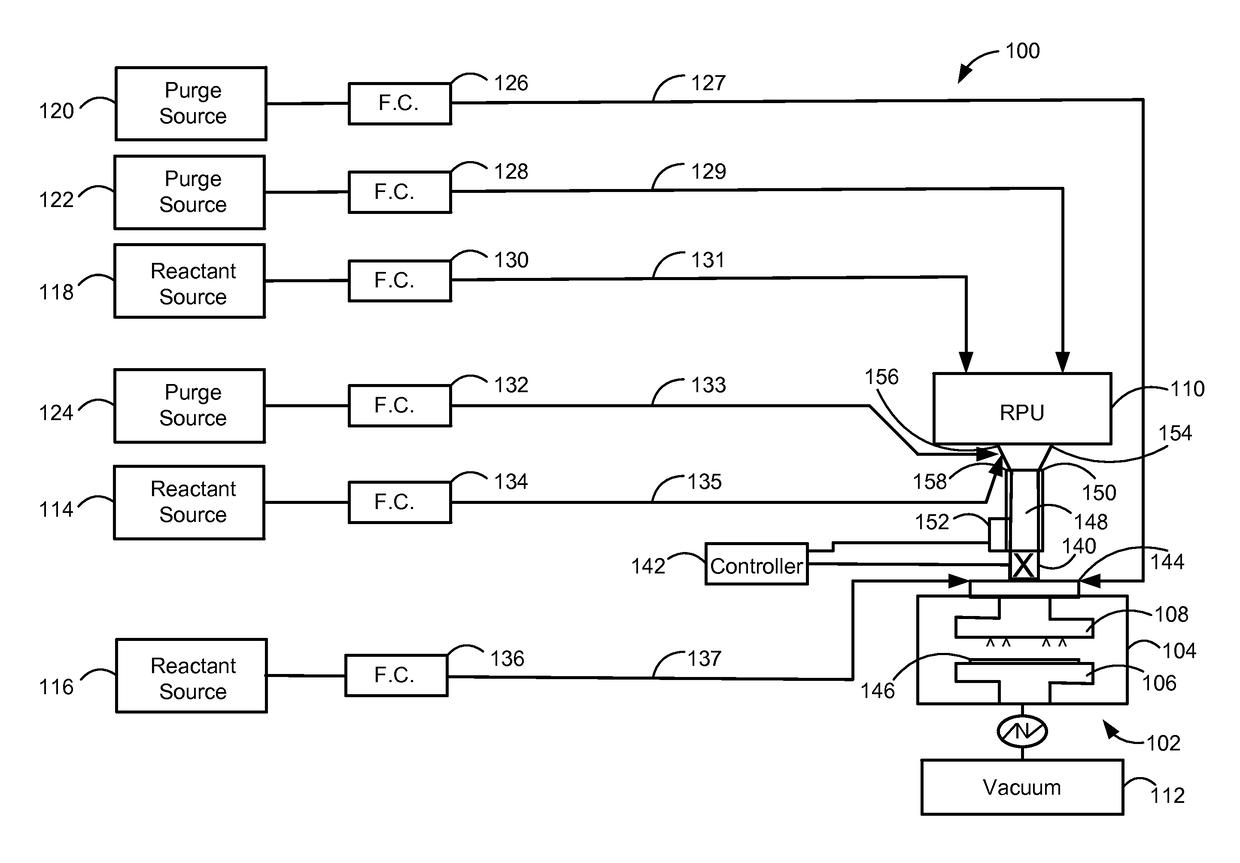
Method and system for in situ formation of gas-phase compounds
ActiveUS20160051964A1Process can be usedProcess control/regulationCell electrodesCompound aGas phase
A system and method for providing intermediate reactive species to a reaction chamber are disclosed. The system includes an intermediate reactive species formation chamber fluidly coupled to the reaction chamber to provide intermediate reactive species to the reaction chamber. A pressure control device can be used to control an operating pressure of the intermediate reactive species formation chamber, and a heater can be used to heat the intermediate reactive species formation chamber to a desired temperature.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method and system for in situ formation of gas-phase compounds
ActiveUS9890456B2Electric discharge tubesChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsCompound aGas phase
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Slurry phase polymerisation process
ActiveUS20100144968A1Avoiding unacceptable reactor foulingReduce energy consumptionChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsPolymer scienceSlurry
A process for controlling a slurry phase (co-) polymerisation process in the presence of a polymerisation catalyst, which comprises maintaining the density SPAN of the polymer powder particles (defined as the absolute value of the density difference in g / cm3 between the average density of the polymer particles exiting the reactor with particle size above D90 and the average density of the material with particle size below D10) below 0.005, preferably below 0.003, more preferably below 0.0026, most preferably below 0.0023.
Owner:INEOS EURO LTD
Method and system for supplying hydrogen for use in fuel cells
InactiveUS6348278B1Reduce hydrogen concentrationImprove concentrationElectricity cogenerationRegenerative fuel cellsHydrogenCombustor
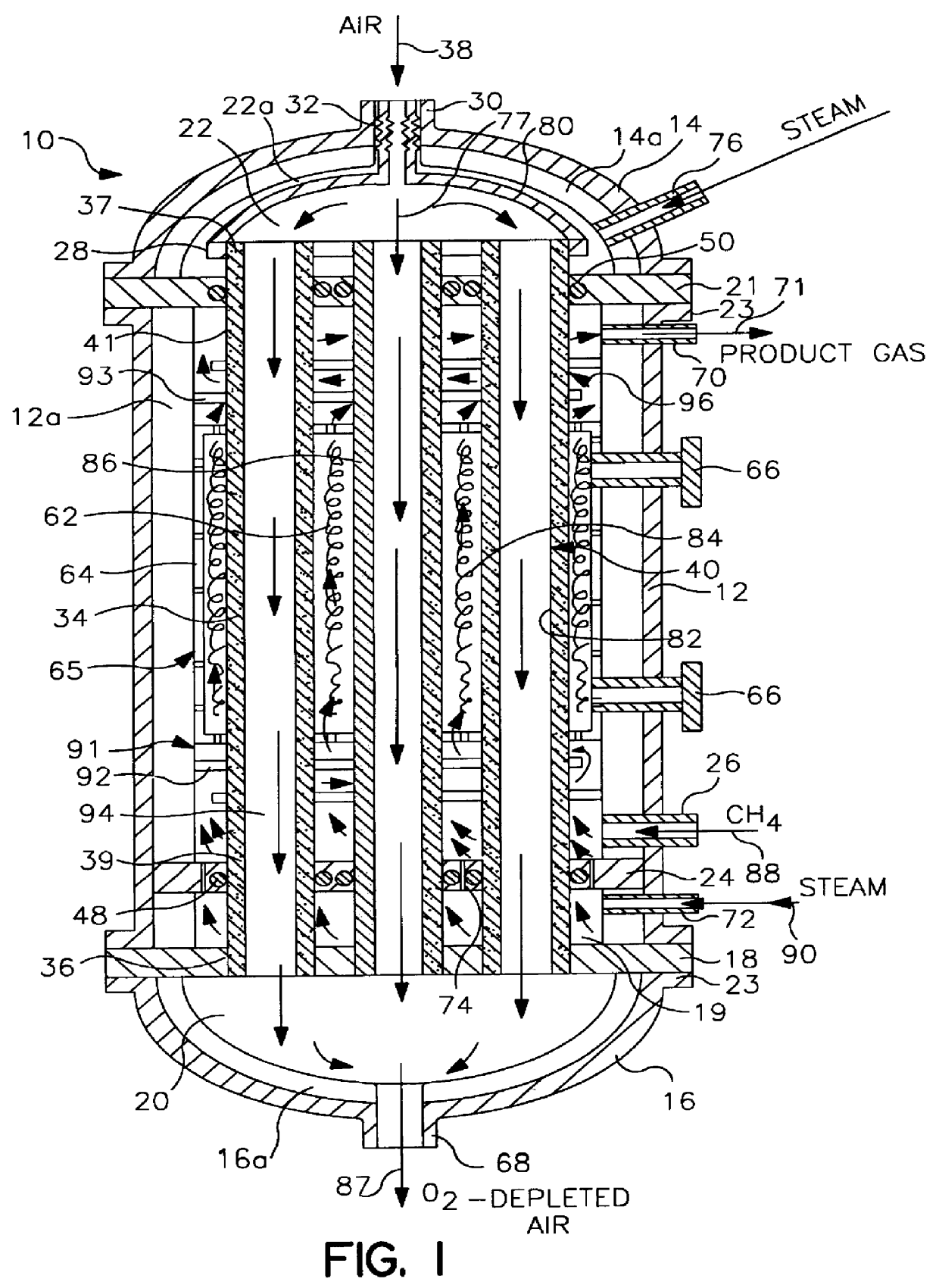
The present invention provides a method and system for efficiently producing hydrogen that can be supplied to a fuel cell. The method and system of the present invention produces hydrogen in a reforming reactor using a hydrocarbon stream and water vapor stream as reactants. The hydrogen produced is purified in a hydrogen separating membrane to form a retentate stream and purified hydrogen stream. The purified hydrogen can then be fed to a fuel cell where electrical energy is produced and a fuel cell exhaust stream containing water vapor and oxygen depleted air is emitted. In one embodiment of the present invention, a means and method is provided for recycling a portion of the retentate stream to the reforming reactor for increased hydrogen yields. In another embodiment, a combustor is provided for combusting a second portion of the retentate stream to provide heat to the reforming reaction or other reactants. In a preferred embodiment, the combustion is carried out in the presence of at least a portion of the oxygen depleted air stream from the fuel cell. Thus, the system and method of the present invention advantageously uses products generated from the system to enhance the overall efficiency of the system.
Owner:MOBIL OIL CORP
Continuous process for the preparation of polytrimethylene ether glycol
InactiveUS6720459B2Liquid-gas reaction as foam/aerosol/bubblesOrganic compound preparationGas phaseEther
The invention is a continuous process for the preparation of polytrimethylene ether glycol from 1,3-propanediol reactant. In addition, the invention is directed to a continuous multi-stage process comprising reacting at least one reactant in a liquid phase in an up-flow column reactor, and forming a gas or vapor phase by-product wherein the gas or vapor phase by-product is continuously removed at the top and at least one intermediate stage.
Owner:DUPONT CA +1
Electrocatalyst powders, methods for producing powders and devices fabricated from same
Electrocatalyst powders and methods for producing electrocatalyst powders, such as carbon composite electrocatalyst powders. The powders have a well-controlled microstructure and morphology. The method includes forming the particles from an aerosol of precursors by heating the aerosol to a relatively low temperature, such as not greater than about 400° C.
Owner:CABOT CORP
Microfluidic Chemical Reaction Circuits
InactiveUS20080281090A1Shaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersTransportation and packagingChemical reactionCompound (substance)
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +3
Pressure swing reforming
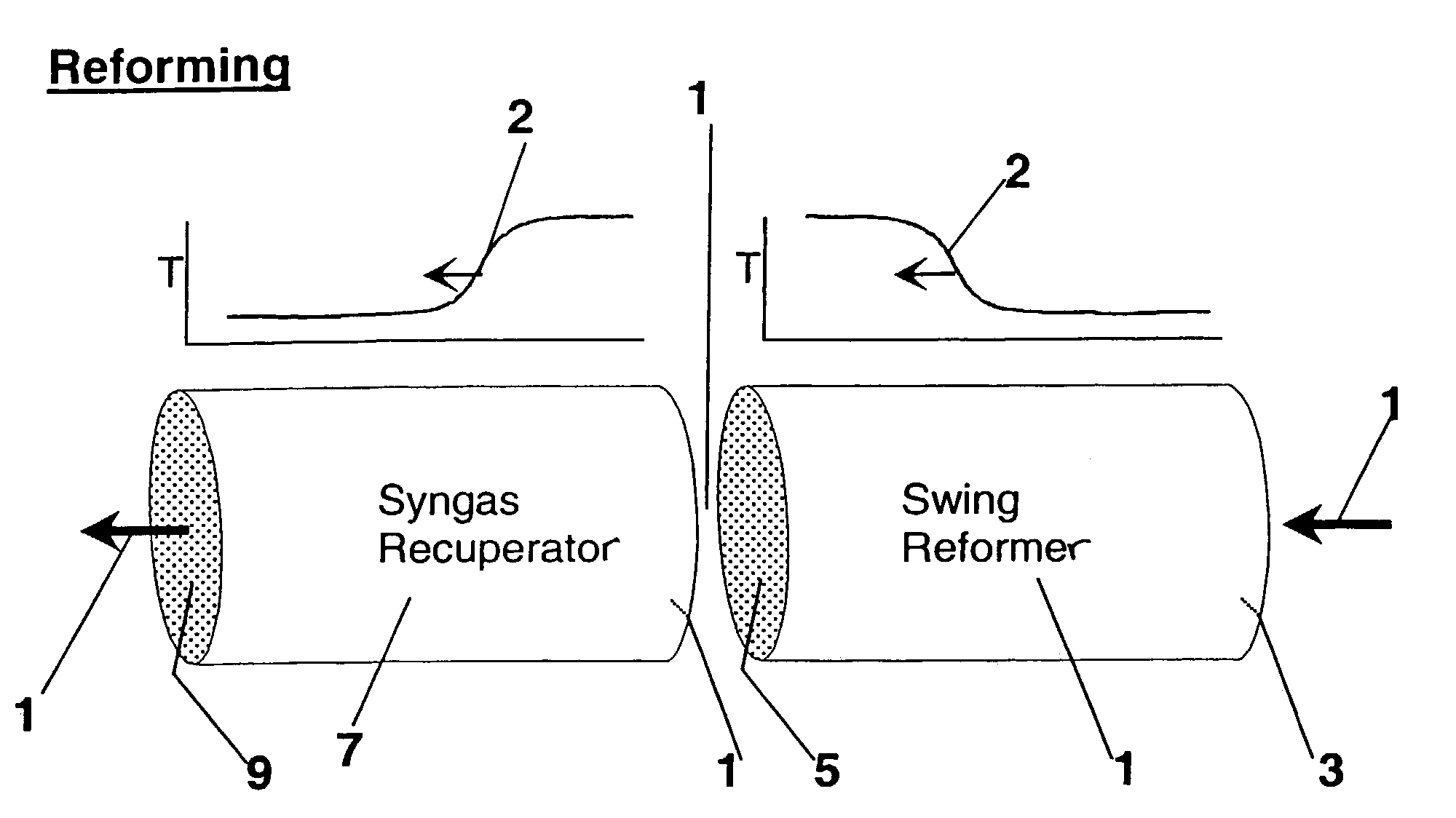
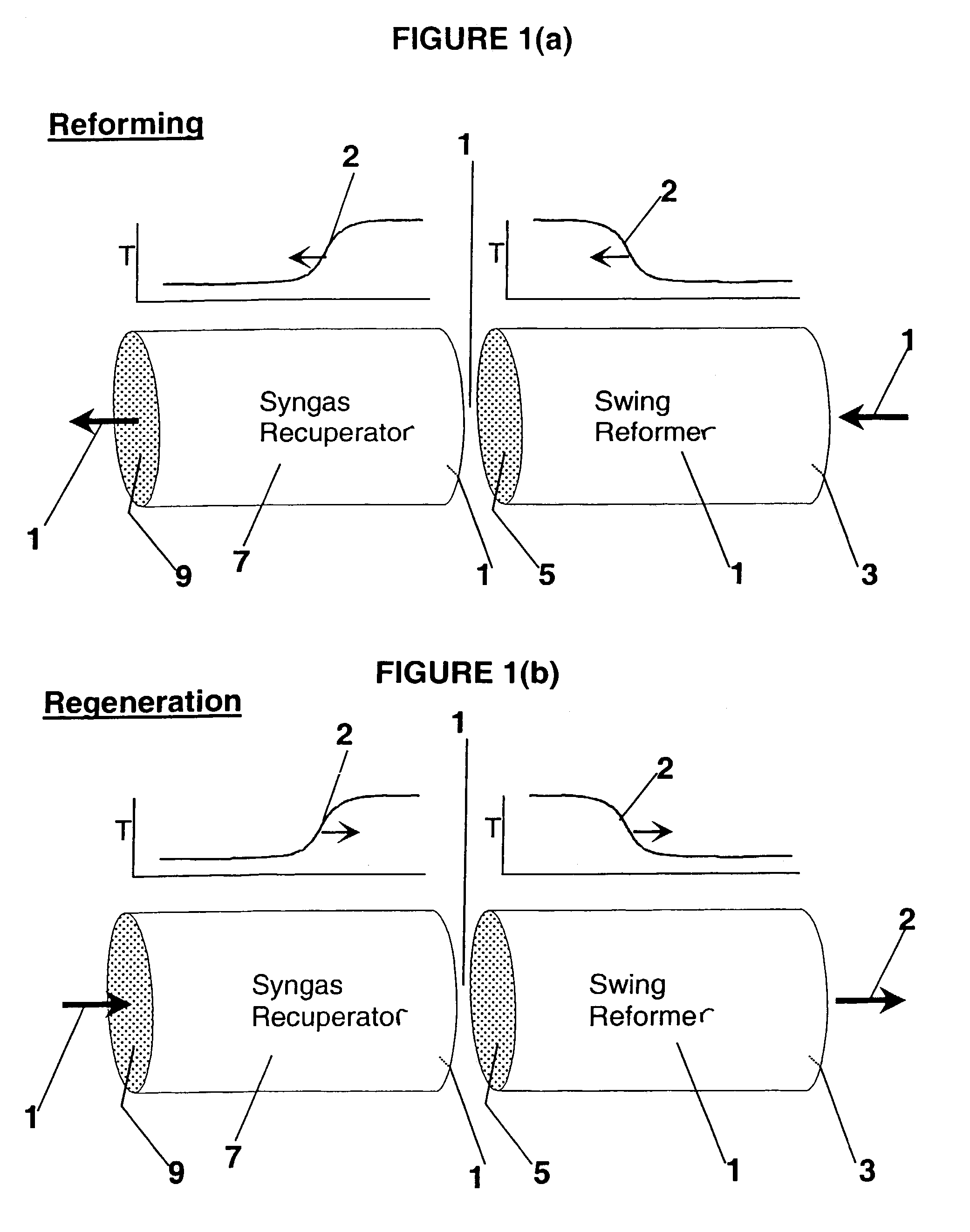
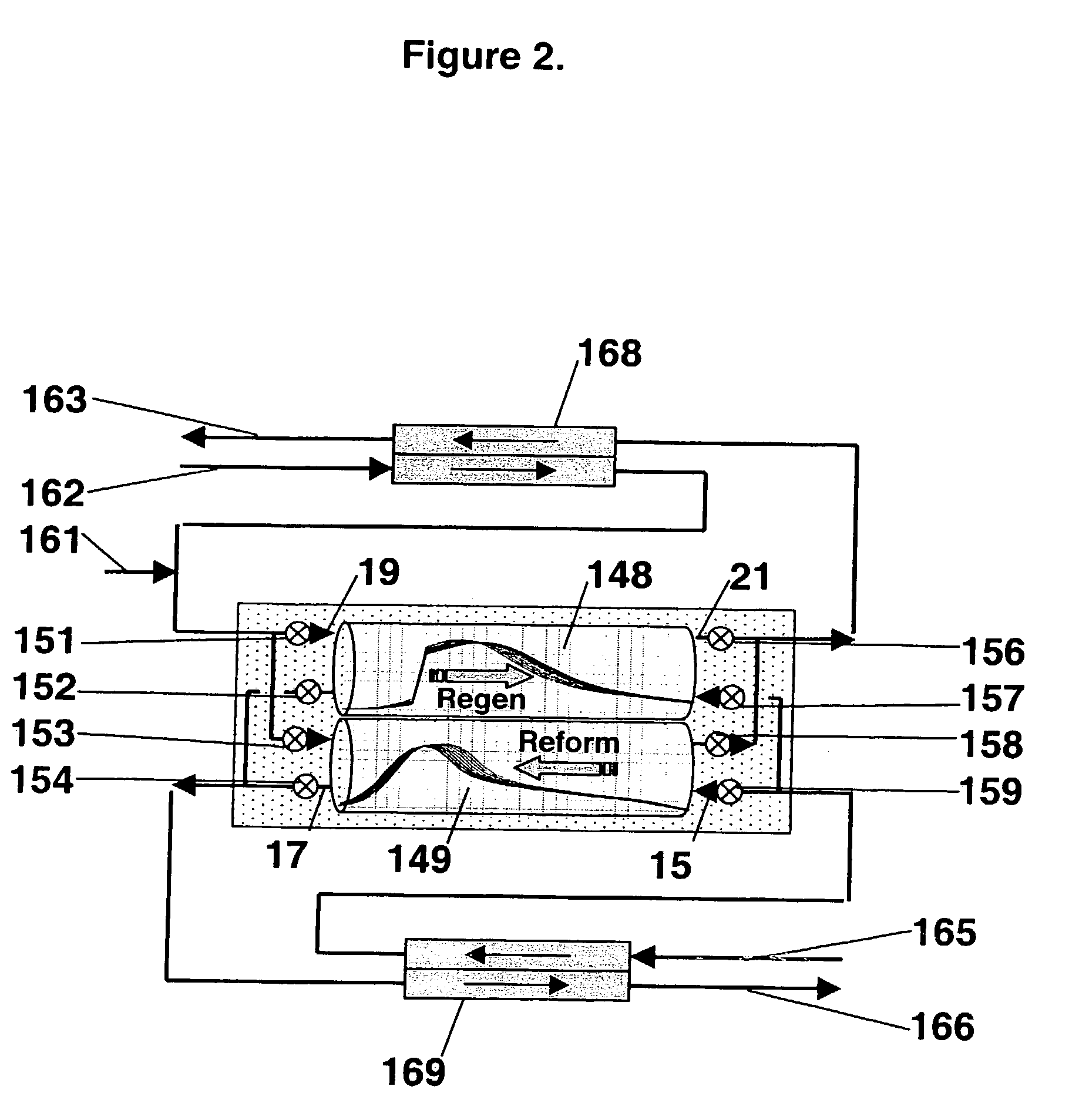
Synthesis gas is produced though a cyclic method where the first step of the cycle includes reforming a hydrocarbon feed over a catalyst to synthesis gas in a first zone of a bed and the second step reheats this first zone. A hydrocarbon feed is introduced to a bed along with CO2 and optionally steam where it is reformed into synthesis gas. The synthesis gas is collected at a second zone of the bed and an oxygen-containing gas is then introduced to this second zone of the bed and combusted with a fuel, thereby reheating the first zone to sufficient reforming temperatures. Additionally, a non-combusting gas can also be introduced to the second zone to move heat from the second zone to the first zone.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
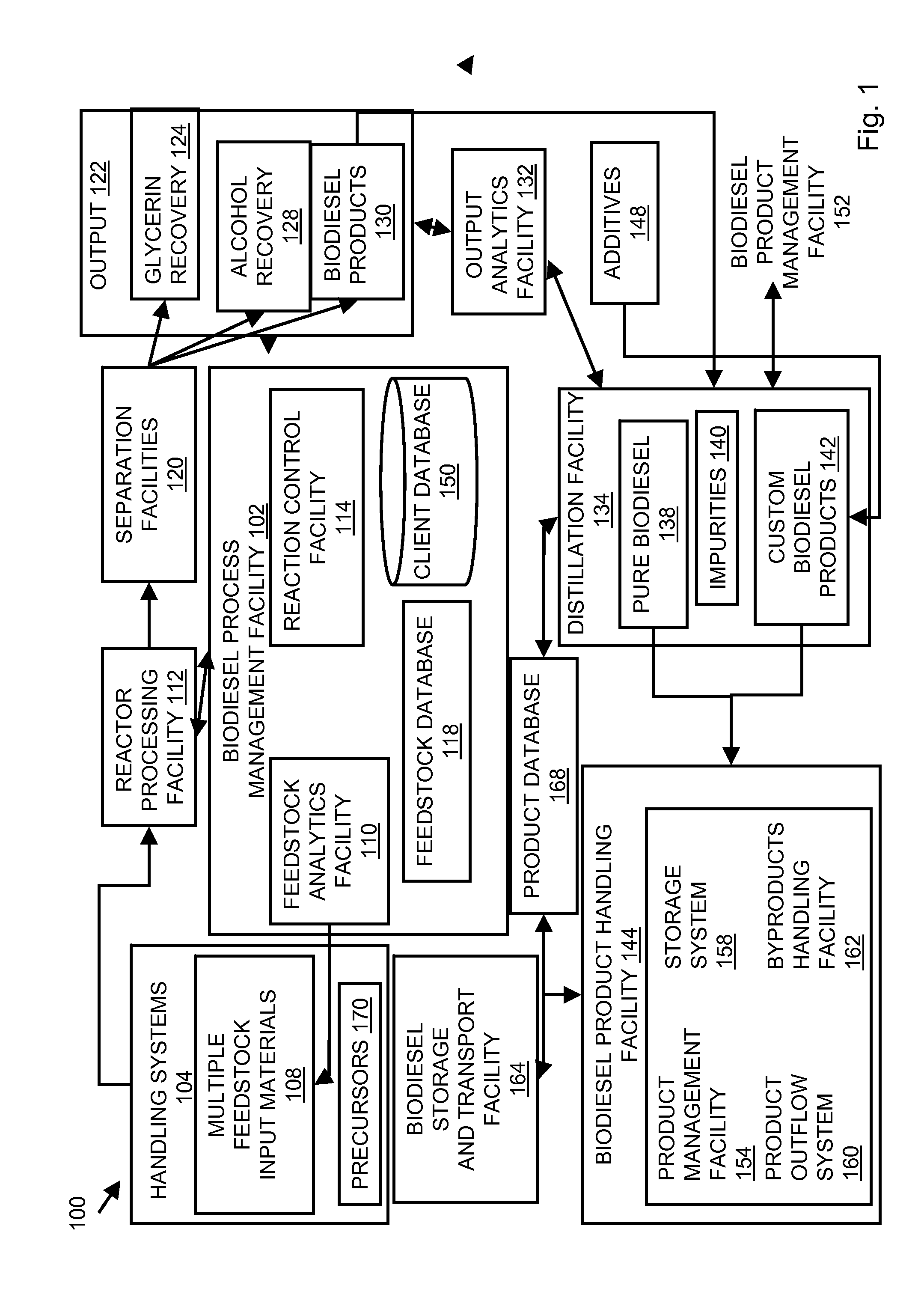
System and process for producing biodiesel
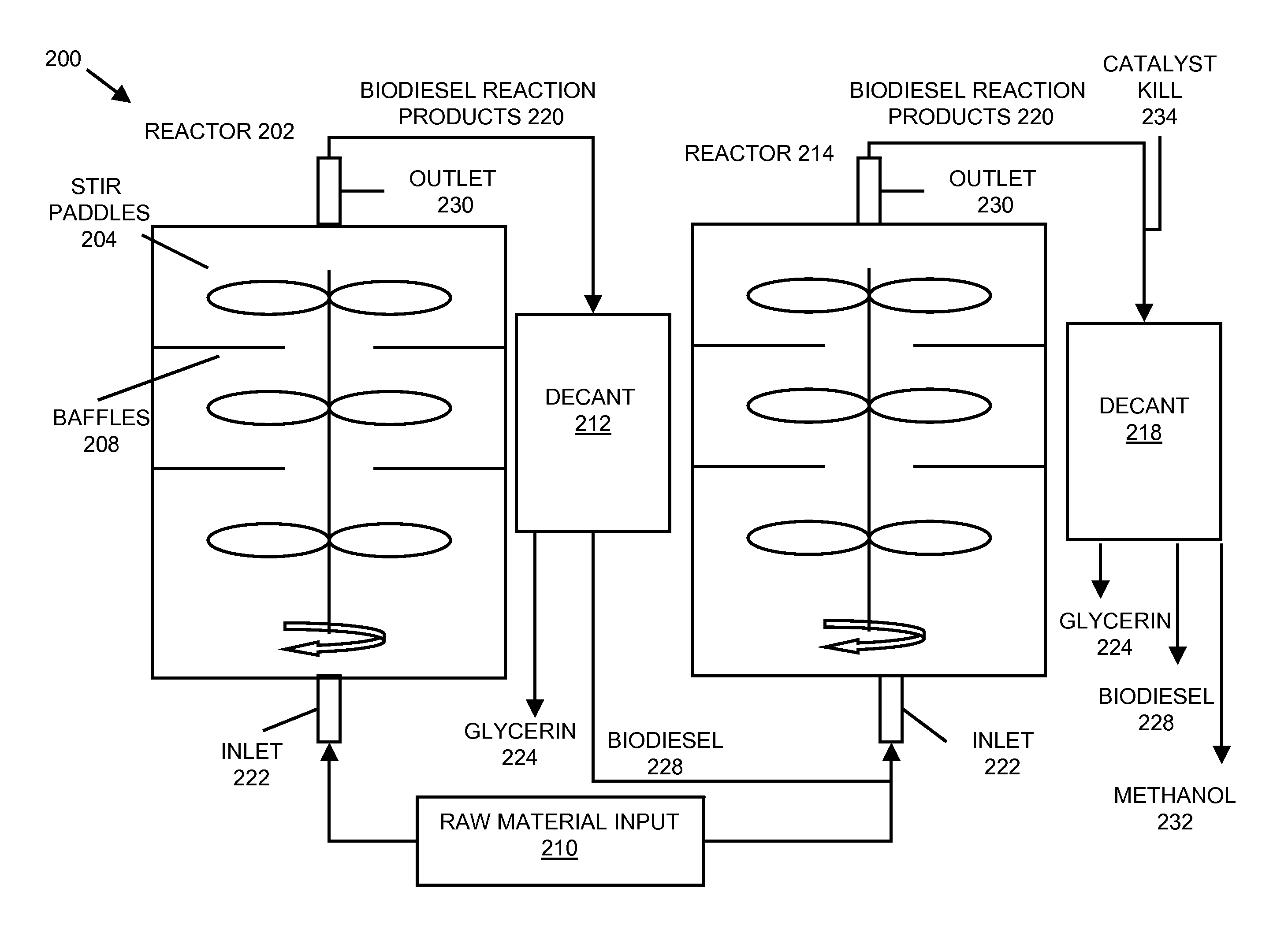
InactiveUS20080282606A1Reducing filter blocking tendencyEnhance biodiesel stabilityFatty acid esterificationFatty acids production/refiningBiodieselDistillation
In embodiments of the present invention, systems for producing a biodiesel product from multiple feedstocks may include a biodiesel reactor, a decanter, a flash evaporator and a distillation column. In other embodiments of the present invention, a process for producing a biodiesel comprises distilling a biodiesel reaction product to remove tocopherols and sterol glucosides and, optionally, adding biodiesel stabilizers to the resultant biodiesel to enhance thermal stability. The components of the system are interrelated so that parameters may be regulated to allow production of a custom biodiesel product.
Owner:IMPERIUM PROCESS TECH
Microwave-based recovery of hydrocarbons and fossil fuels
InactiveUS20070131591A1Organic compounds purification/separation/stabilisationHydrocarbon oil cracking processHydrocotyle bowlesioidesPetroleum
The present invention provides methods for decomposing and extracting compositions for the recovery of petroleum-based materials from composites comprising those petroleum-based materials, comprising subjecting the compositions and / or composites to microwave radiation, wherein the microwave radiation is in the range of from about 4 GHz to about 18 GHz. The present invention also provides for products produced by the methods of the present invention and for apparatuses used to perform the methods of the present invention.
Owner:UNIVERSAL ALTERNATIVE FUELS INC +1
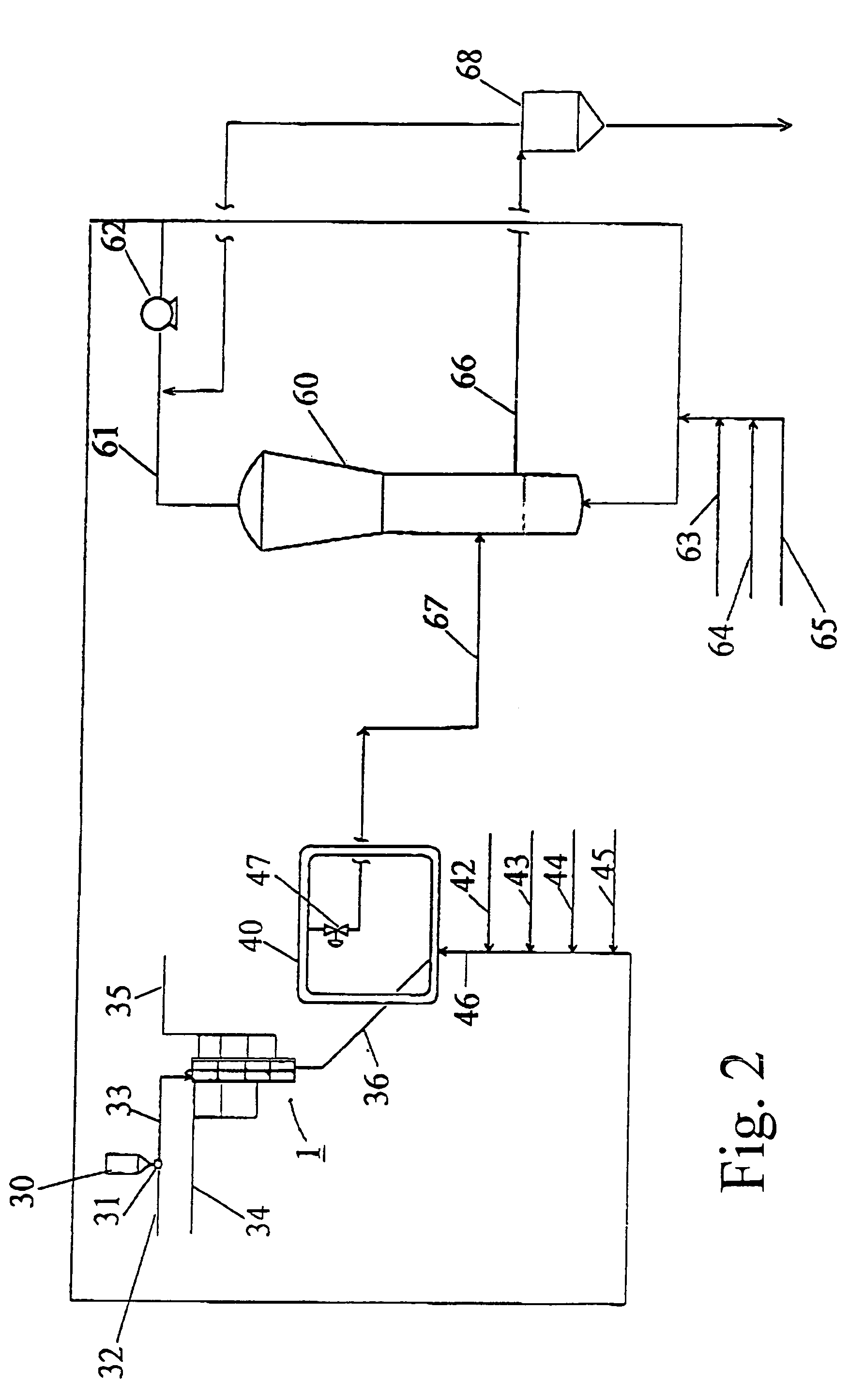
Double loop technology
InactiveUS20050272891A1Constant levelLimited wayControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsExhaust apparatusPolymer sciencePolyolefin
The present invention relates to an apparatus and process for polymerizing olefins. One embodiment comprises polymerizing at least one monomer in a first loop reactor in the presence of a catalyst to produce a first polyolefin fraction. A portion of the first polyolefin fraction is transferred to a second loop reactor, connected in series with the first loop reactor. The process further comprises polymerizing in the second loop reactor at least one monomer in the presence of a catalyst to produce a second polyolefin fraction in addition to the first polyolefin fraction. The combination of the first and second polyolefin fractions can produce a polymer resin fluff having bimodal molecular weight distribution.
Owner:TOTAL RES & TECH FELUY
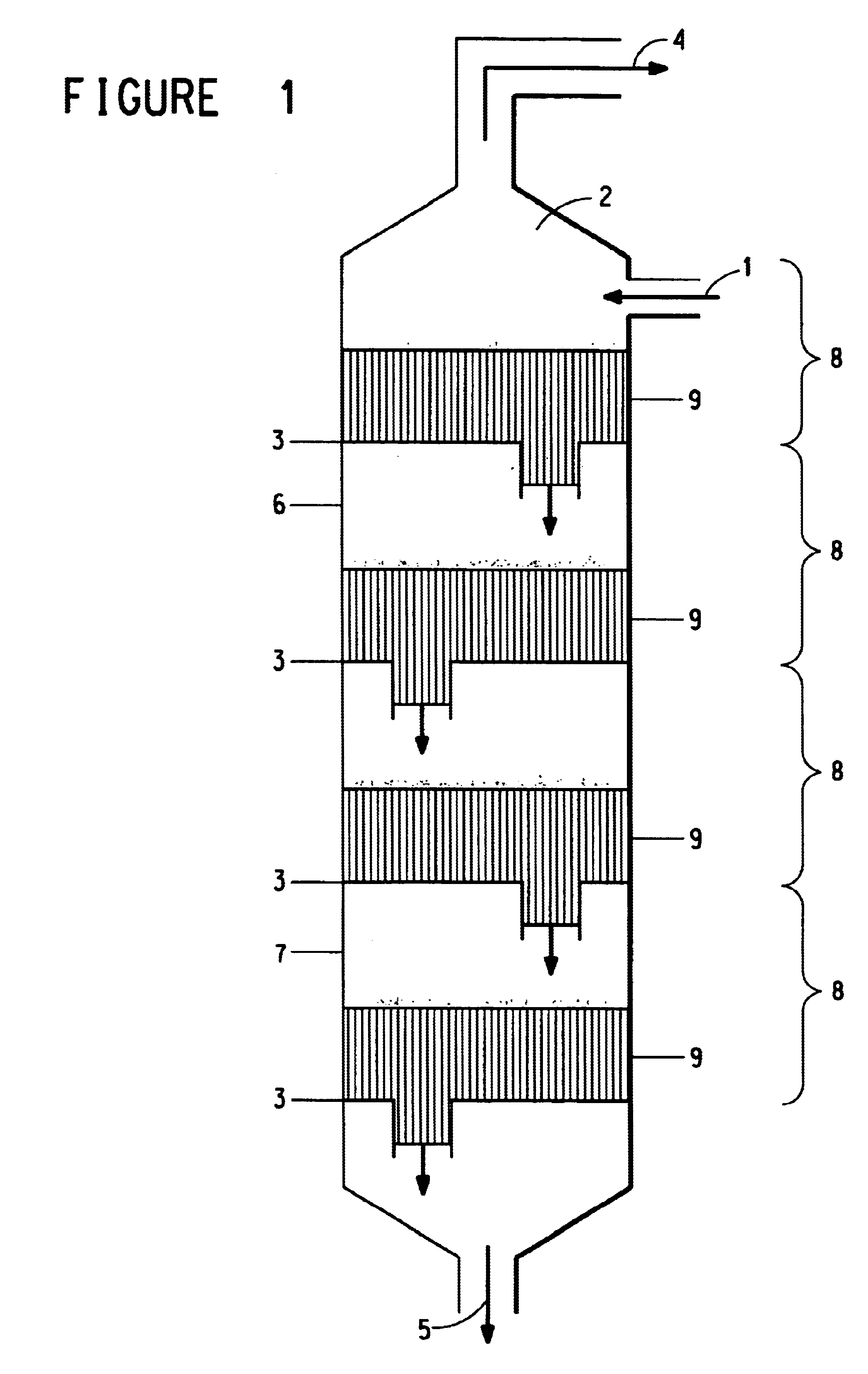
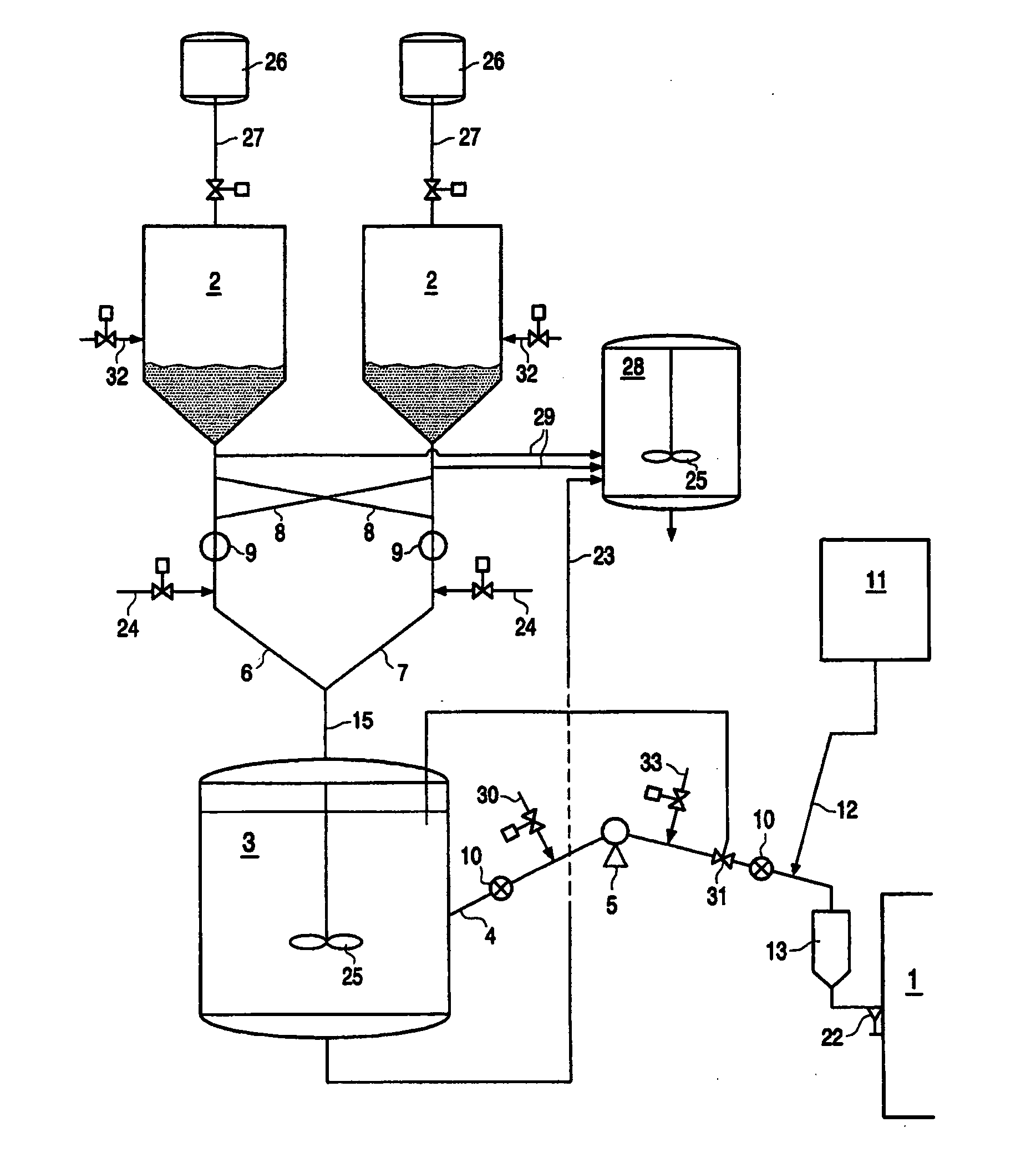
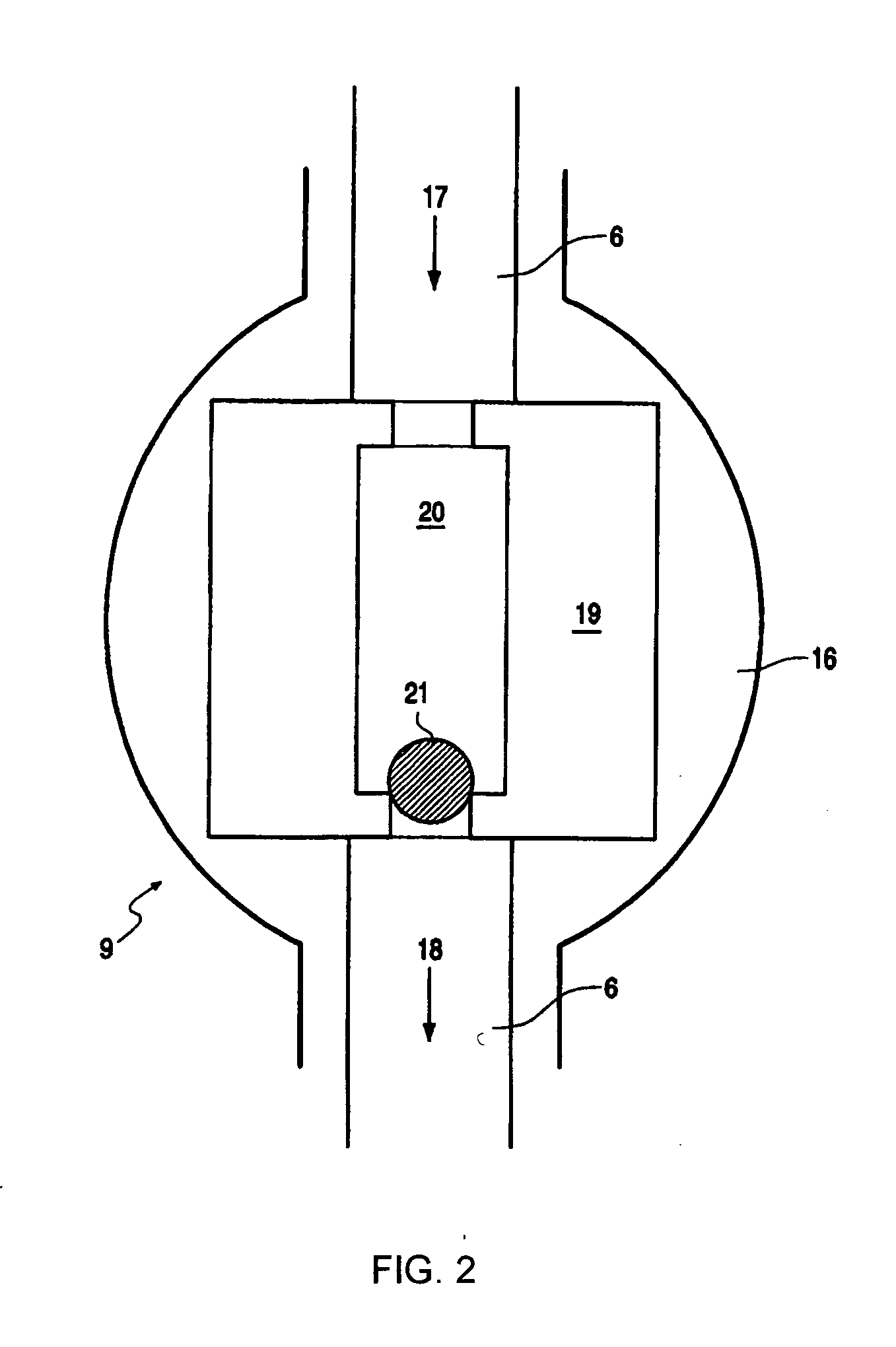
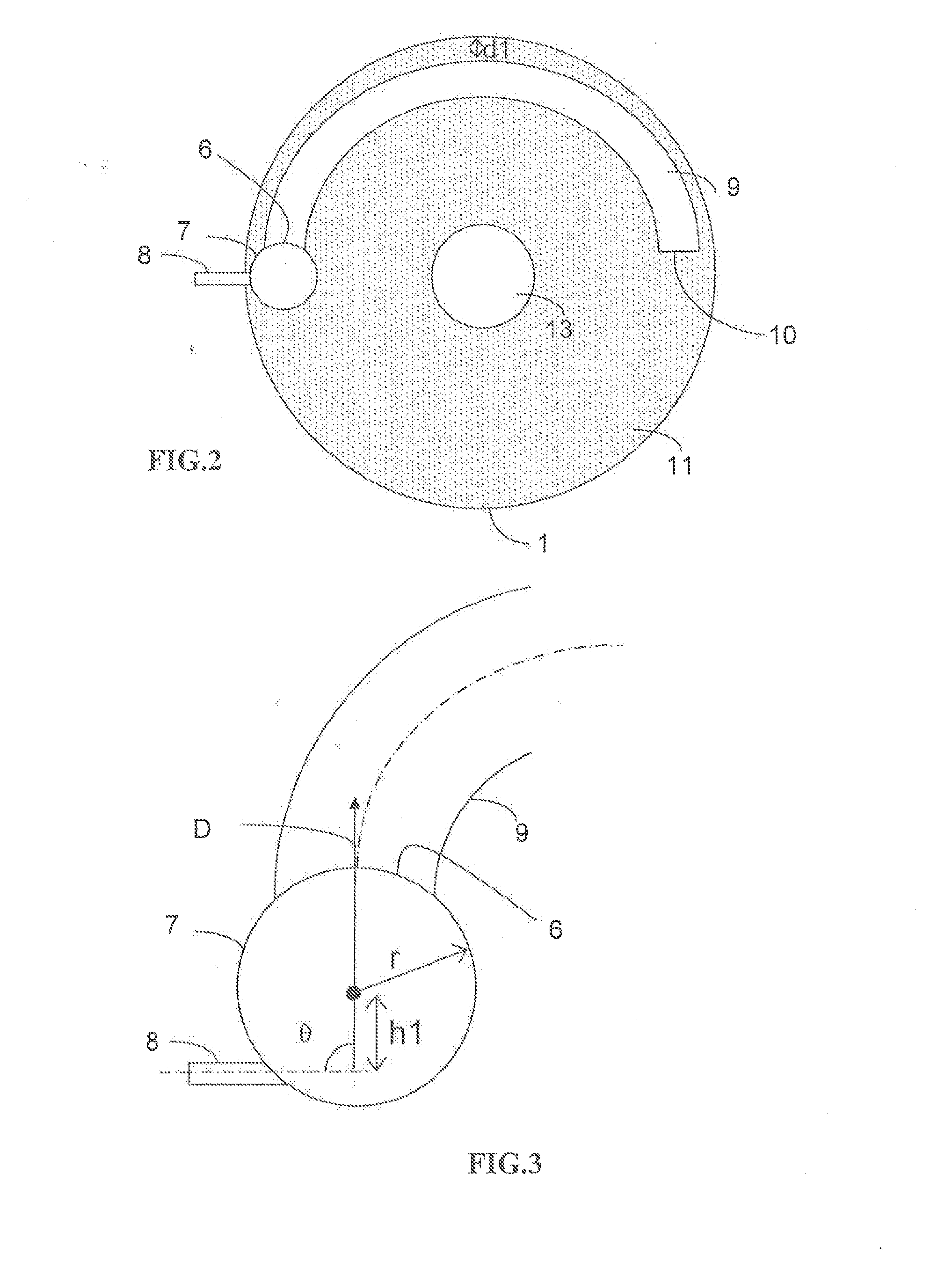
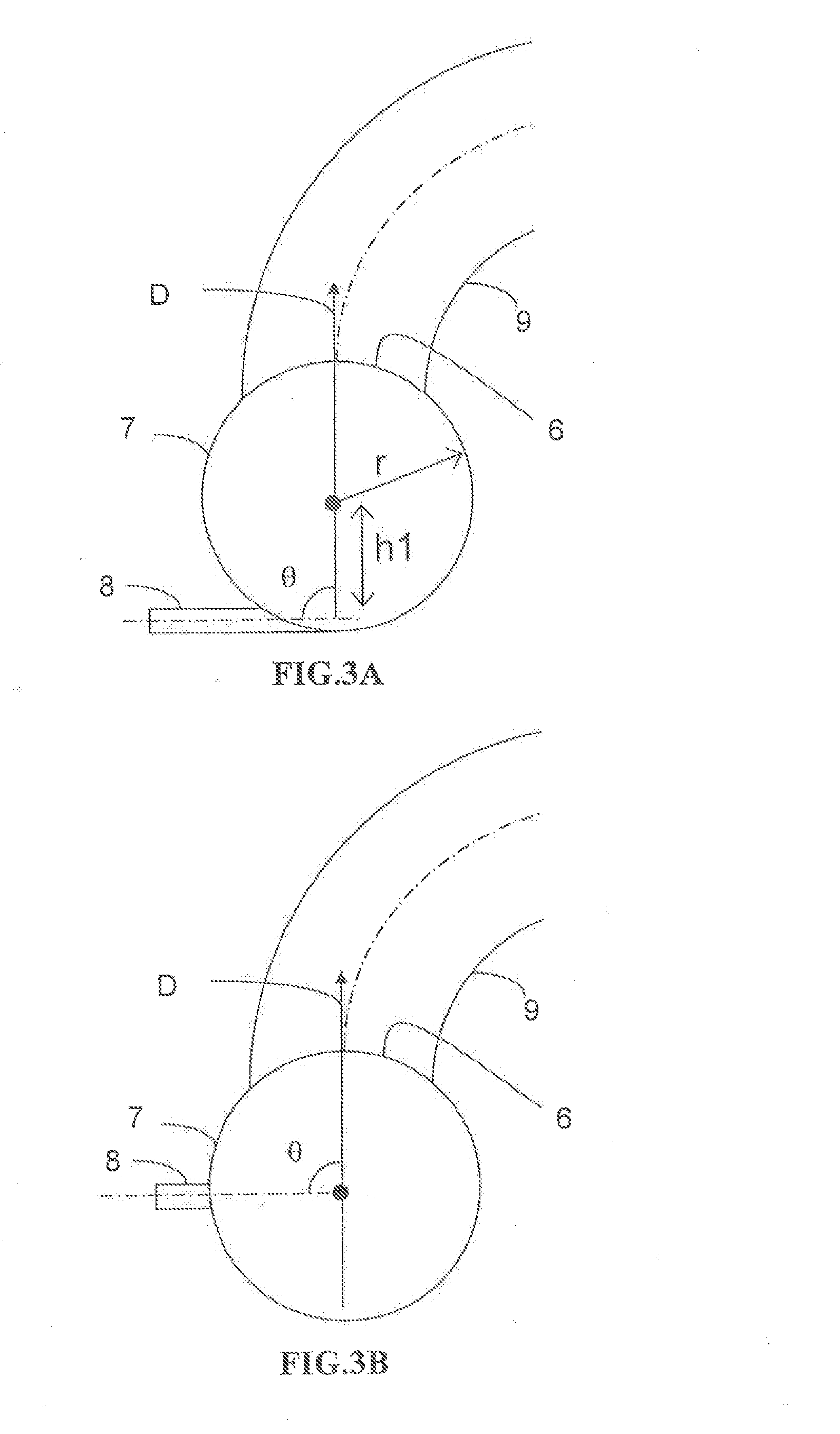
Device for injecting and mixing fluids in a downward-flow reactor
The catalytic reactor with downward flow comprises a chamber (1) containing at least two solid catalyst beds (2; 11) separated by an intermediate zone comprising an essentially horizontal collecting plate (5) communicating with a vertical collecting pipe (7) for receiving fluids collected by the collecting plate, with a means for injecting a quenching fluid (8) emptying into the collecting pipe. An annular mixing chamber (9) is located below the collecting plate (5). A predistribution plate (11) is arranged below the chamber (9).The injection means (8) comprises a tubular portion that empties into the collecting pipe (7) in such a way as to inject quenching fluid in a direction forming an angle θ between 45° and 135° with the direction D from the axis of the mixing chamber measured at its input end.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
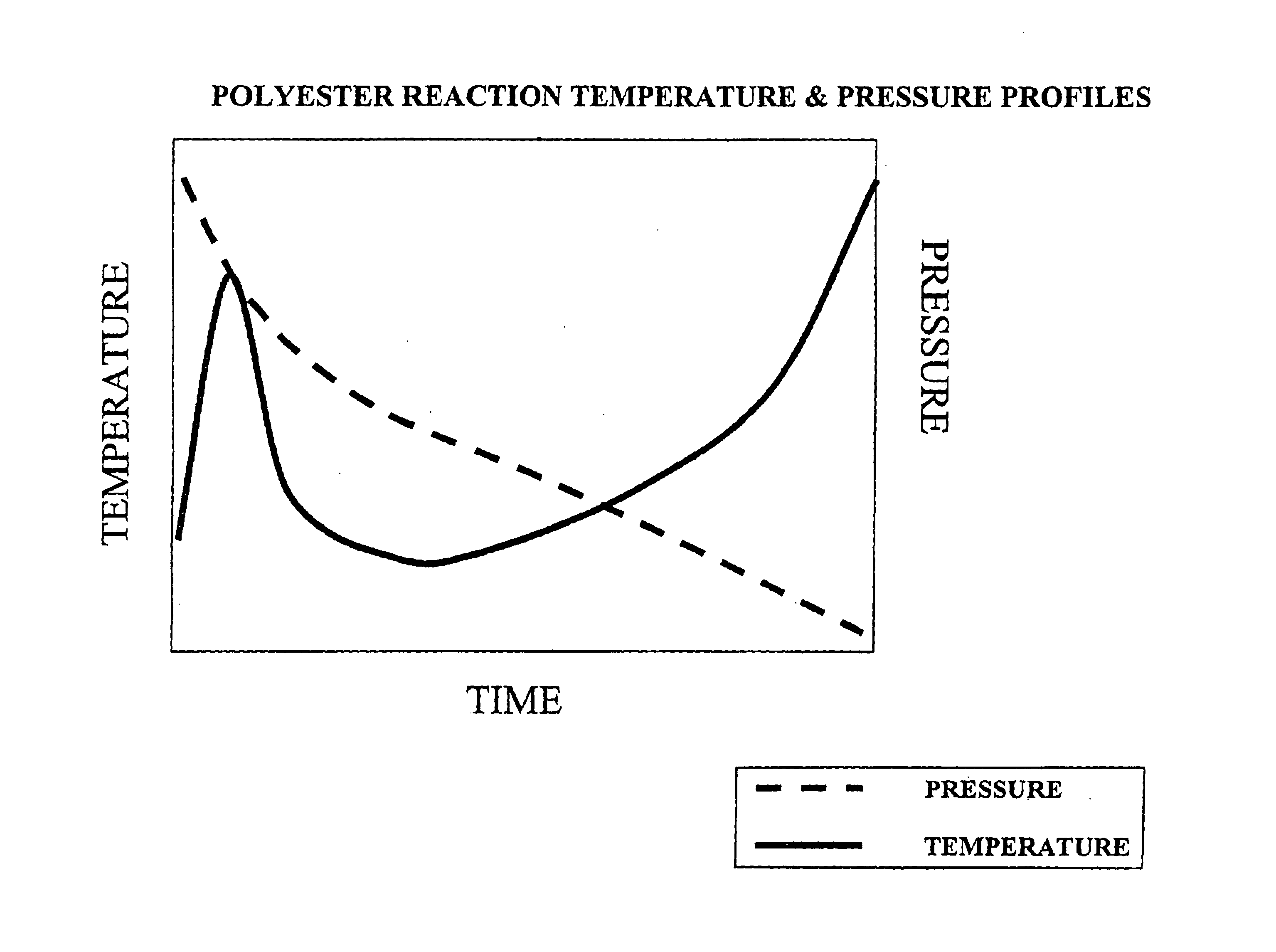
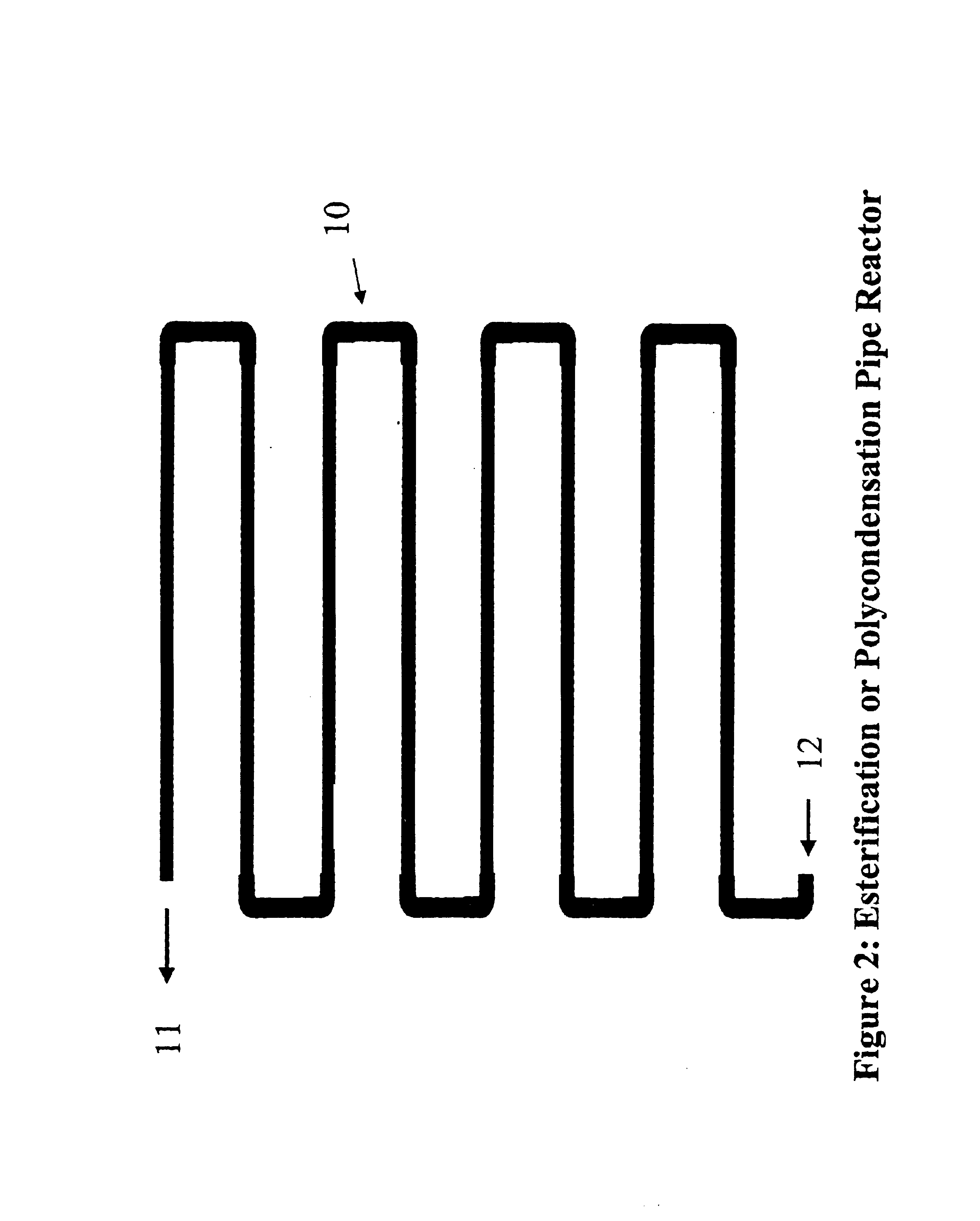
Polyester process using a pipe reactor
InactiveUS6861494B2Reduce pressureEliminate needLiquid degasificationFlow mixersProcess engineeringPolyester resin
Owner:ALPEK POLYESTER SA DE CV
Tube and shell reactor with oxygen selective ion transport ceramic reaction tubes
InactiveUS6139810AIncrease oxygen fluxDecreasing anode side partial oxygen pressureIsotope separationHydrogen/synthetic gas productionPtru catalystElectrical conductor
A reactor comprising: a hollow shell defining a hermetic enclosure; a plurality of tube sheets disposed within said hermetic enclosure, a first one of said plurality of tube sheets defining a first chamber; at least one reaction tube each having a first end and an opposing second end, said first end being fixedly attached and substantially hermetically sealed to one end of said plurality of tube sheets and opening into said first chamber, the second end being axially unrestrained; each of said reaction tubes is comprised of an oxygen selective ion transport membrane with an anode side wherein said oxygen selective ion transport membrane is formed from a mixed conductor metal oxide that is effective for the transport of elemental oxygen at elevated temperatures and at least a portion of said first and second heat transfer sections are formed of metal; each of said reaction tubes includes first and second heat transfer sections and a reaction section, said reaction section disposed between said first and second heat transfer sections; a reforming catalyst disposed about said anode side of said oxygen selective ion transport membrane; a first process gas inlet; a second process gas inlet; and, a plurality of outlets.
Owner:STANDARD OIL CO +1
Fluidics Devices
ActiveUS20080200343A1Reducing and eliminating soluteReducing and eliminating and analytesImmobilised enzymesLibrary screeningFluidicsAnalyte
The invention relates to fluidics as used in medical and diagnostic equipment and relates further to means for purifying, abstracting, filtering, detecting and / or measuring analytes in liquid samples.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC +1
Process and apparatus for production of water-absorbent resin
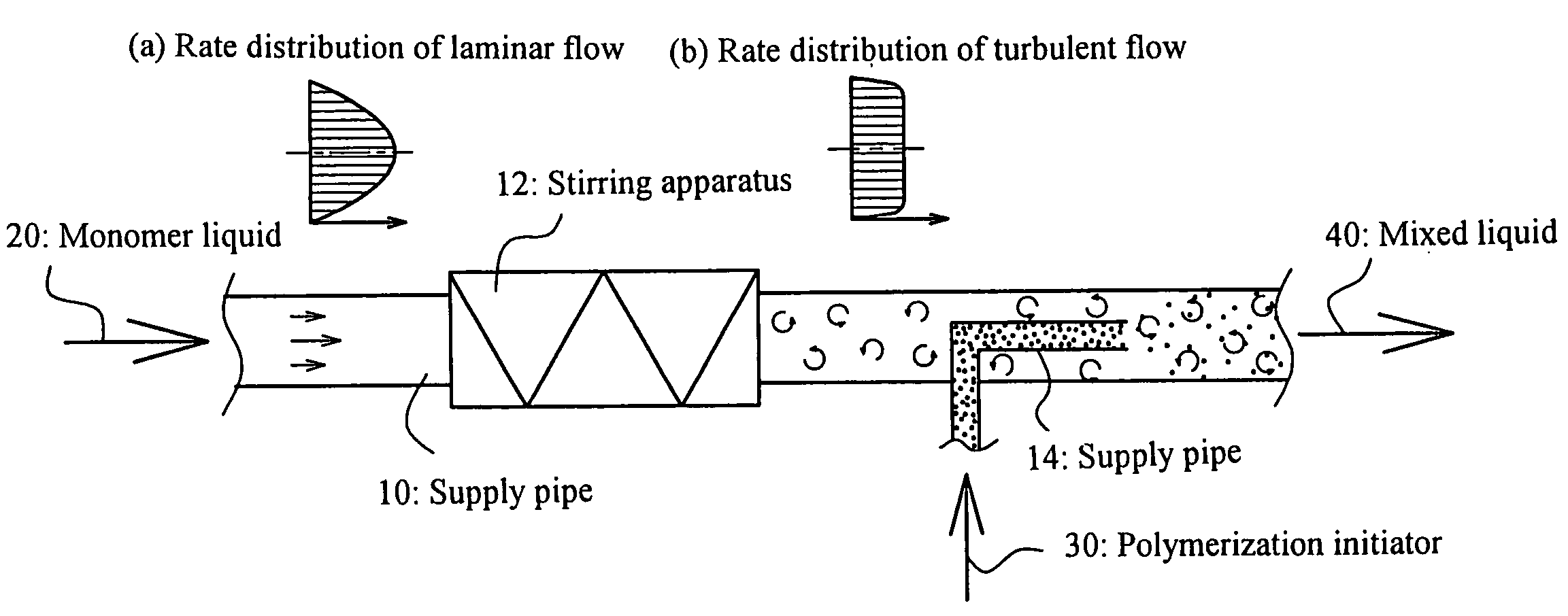
ActiveUS7265190B2Inhibition formationEfficient productionChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsLiquid-liquid reaction processesMonomerPolymerization
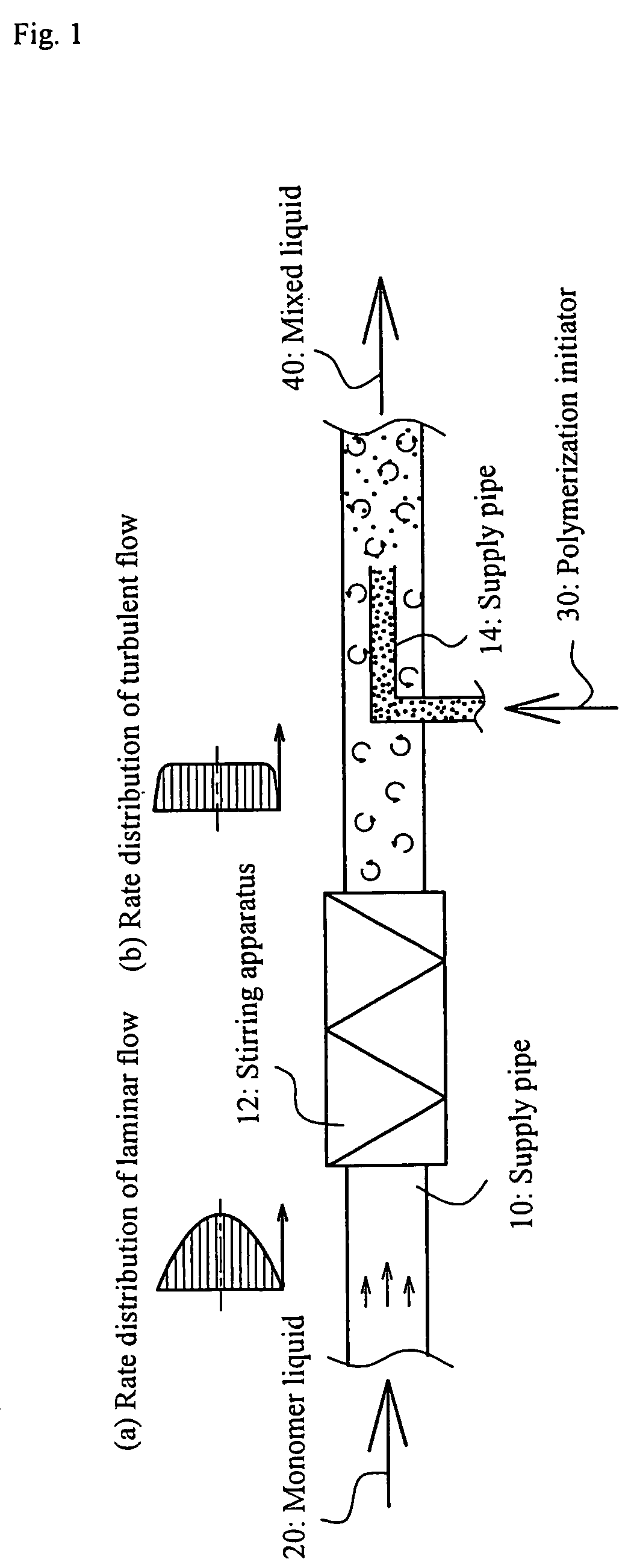
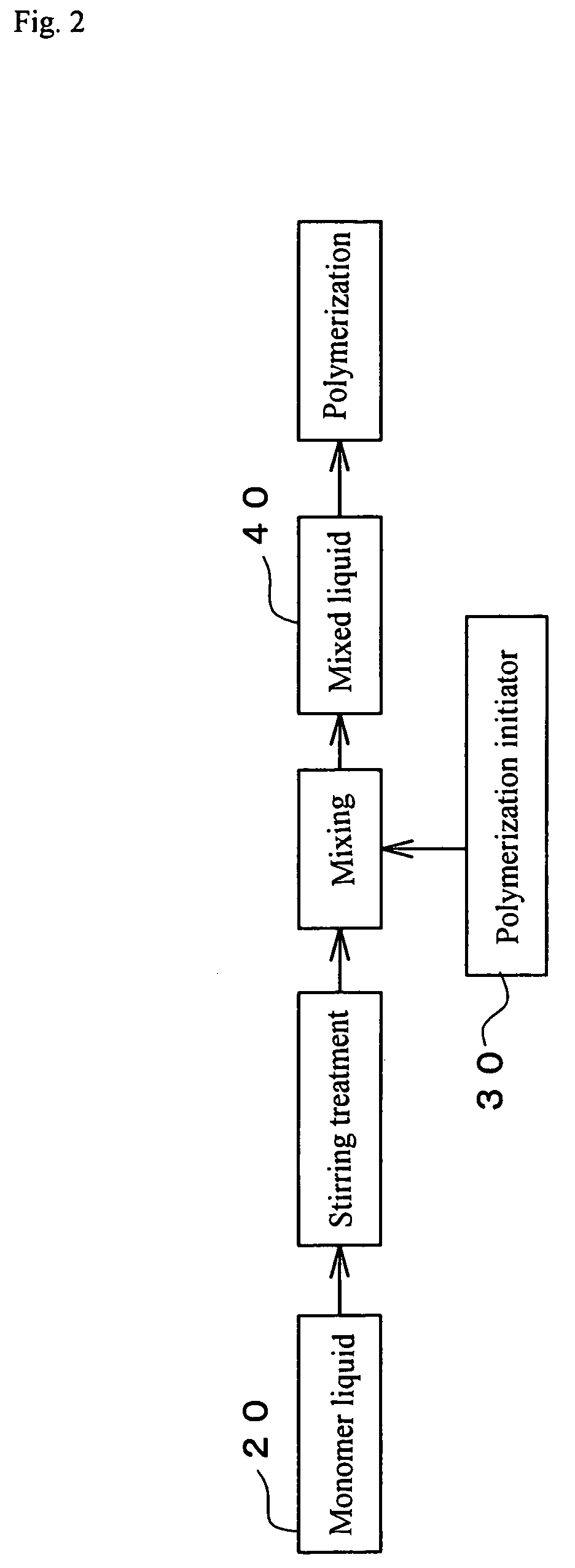
There is disclosed a process to uniformly and rapidly carry out the mixing of a monomer liquid and a polymerization initiator and thus for the resulting polymer not to adhere to the inner surface of the piping or the inside of the apparatus in an art of producing a water-absorbent resin by continuously mixing the monomer liquid and the polymerization initiator together and thereby carrying out polymerization. This process comprises the steps of: (a) continuously supplying a monomer liquid 20 to such as a supply pipe 10 to continuously stir the monomer liquid 20 in the supply pipe 10 with such as a stirring apparatus 12; (b) causing a polymerization initiator 30 to join into a flow of the monomer liquid 20 being in a stirred state, thereby obtaining a mixed liquid 40 of the monomer liquid 20 and the polymerization initiator 30; and (c) continuously supplying the mixed liquid 40 from the supply pipe line 10 to a polymerization apparatus to cause the mixed liquid 40 to run a polymerization reaction.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
Process for high shear gas-liquid reactions
InactiveUS20050033069A1Superior and economical and efficientImprove responseRotary stirring mixersTransportation and packagingGas liquid reactionChemical reaction
A process for performing a chemical reaction between a plurality of chemical reactants in the presence of a catalyst, with at least a first reactant in a liquid phase and at least a second reactant in a gas phase, the first and second reactants mixing at least by interdiffusion. The process comprises supplying the reactants to a passage defined by a first surface and a second surface and optionally moving at least one of the first surface and second surface relative to each other. The reactants their mixture or reaction products form respective boundary layers against the first and second surfaces and the radial spacing between the first surface and second surface is equal to or less than the back-to-back radial thicknesses of the boundary layers.
Owner:323 TRUST +1
High melt strength polypropylene
InactiveUS7365136B2Improve melt strengthHigh viscosityChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsPolymer sciencePtru catalyst
The present invention concerns a high melt strength propylene polymer or copolymer suitable for manufacturing foams and thermoformed product exhibiting a melt strength of at least 3 g and comprising a high molar mass portion and a low or medium molar mass portion. The polymers are produced by subjecting propylene and optionally other olefins to polymerization in a plurality of polymerization reactors connected in series, employing different amounts of hydrogen as a molar mass modifier in at least two of the reactors, and carrying out the polymerization reaction in the presence of a catalyst system capable of catalyzing the formation of a high molar mass polymerization product having a MFR2 of less than 0.1 g / 10 min and a low or medium molar mass polymerization product having a MFR2 of more than 0.5 g / 10 min.
Owner:BOREALIS TECH OY
Multilayered microfluidic DNA analysis system and method
A multilayered microfluidic DNA analysis system includes a cell lysis chamber, a DNA separation chamber, a DNA amplification chamber, and a DNA detection system. The multilayered microfluidic DNA analysis system is provided as a substantially monolithic structure formed from a plurality of green-sheet layers sintered together. The substantially monolithic structure has defined therein a means for heating the DNA amplification chamber and a means for cooling the DNA amplification chamber. The means for heating and means for cooling operate to cycle the temperature of the DNA amplification chamber as required for performing a DNA amplification process, such as PCR.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
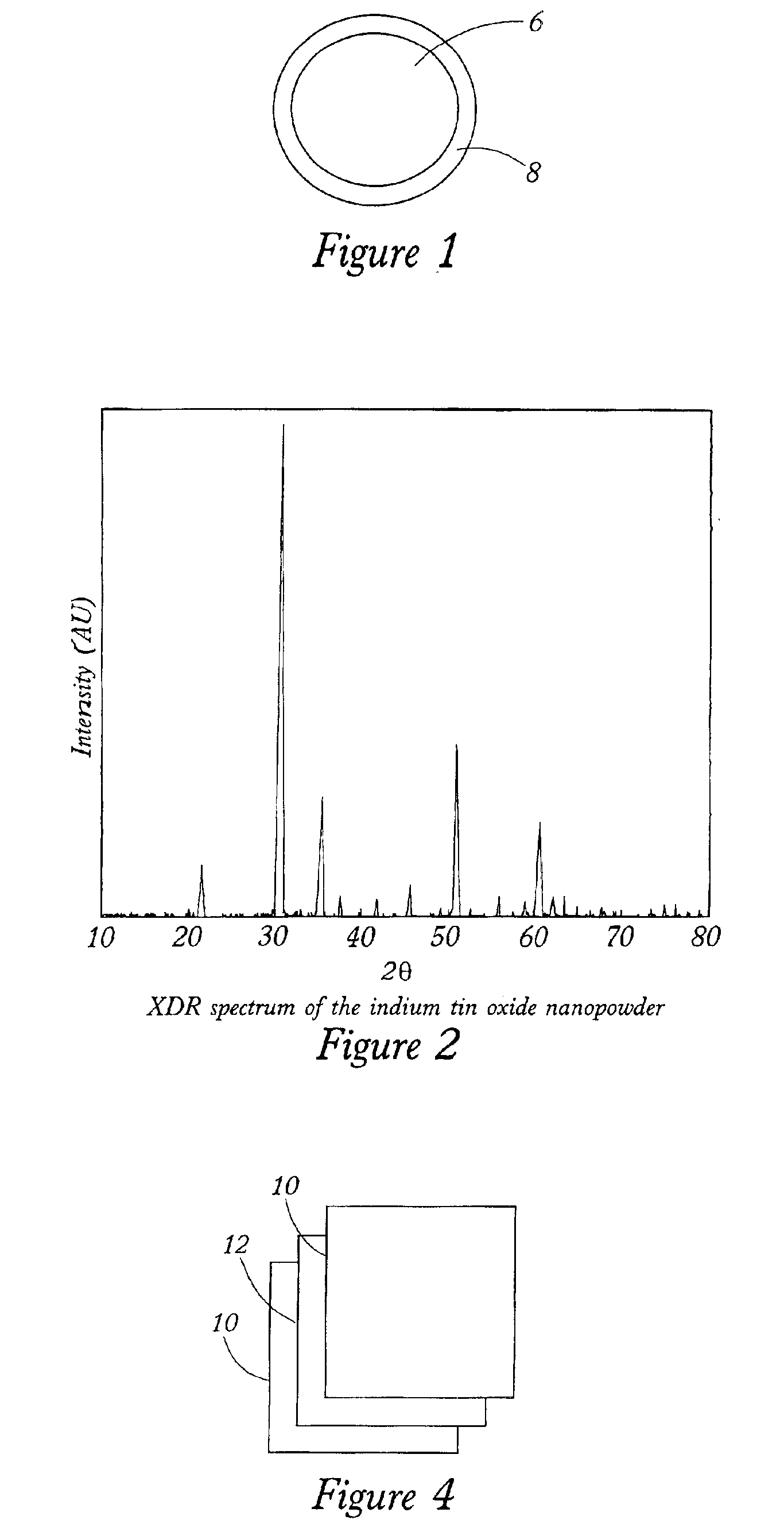
Polymer nanocomposite implants with enhanced transparency and mechanical properties for administration within humans or animals
Polymer nanocomposite implants with nanofillers and additives are described. The nanofillers described can be any composition with the preferred composition being those composing barium, bismuth, cerium, dysprosium, europium, gadolinium, hafnium, indium, lanthanum, neodymium, niobium, praseodymium, strontium, tantalum, tin, tungsten, ytterbium, yttrium, zinc, and zirconium. The additives can be of any composition with the preferred form being inorganic nanopowders comprising aluminum, calcium, gallium, iron, lithium, magnesium, silicon, sodium, strontium, titanium. Such nanocomposites are particularly useful as materials for biological use in applications such as drug delivery, biomed devices, bone or dental implants.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Thermal synthesis apparatus and process
InactiveUS6821500B2Improve efficiencyHigh yieldCarbon monoxideIndirect heat exchangersNuclear engineeringReaction zone
An apparatus for thermal conversion of one or more reactants to desired end products includes an insulated reactor chamber having a high temperature heater such as a plasma torch at its inlet end and, optionally, a restrictive convergent-divergent nozzle at its outlet end. In a thermal conversion method, reactants are injected upstream from the reactor chamber and thoroughly mixed with the plasma stream before entering the reactor chamber. The reactor chamber has a reaction zone that is maintained at a substantially uniform temperature. The resulting heated gaseous stream is then rapidly cooled by passage through the nozzle, which "freezes" the desired end product(s) in the heated equilibrium reaction stage, or is discharged through an outlet pipe without the convergent-divergent nozzle. The desired end products are then separated from the gaseous stream.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
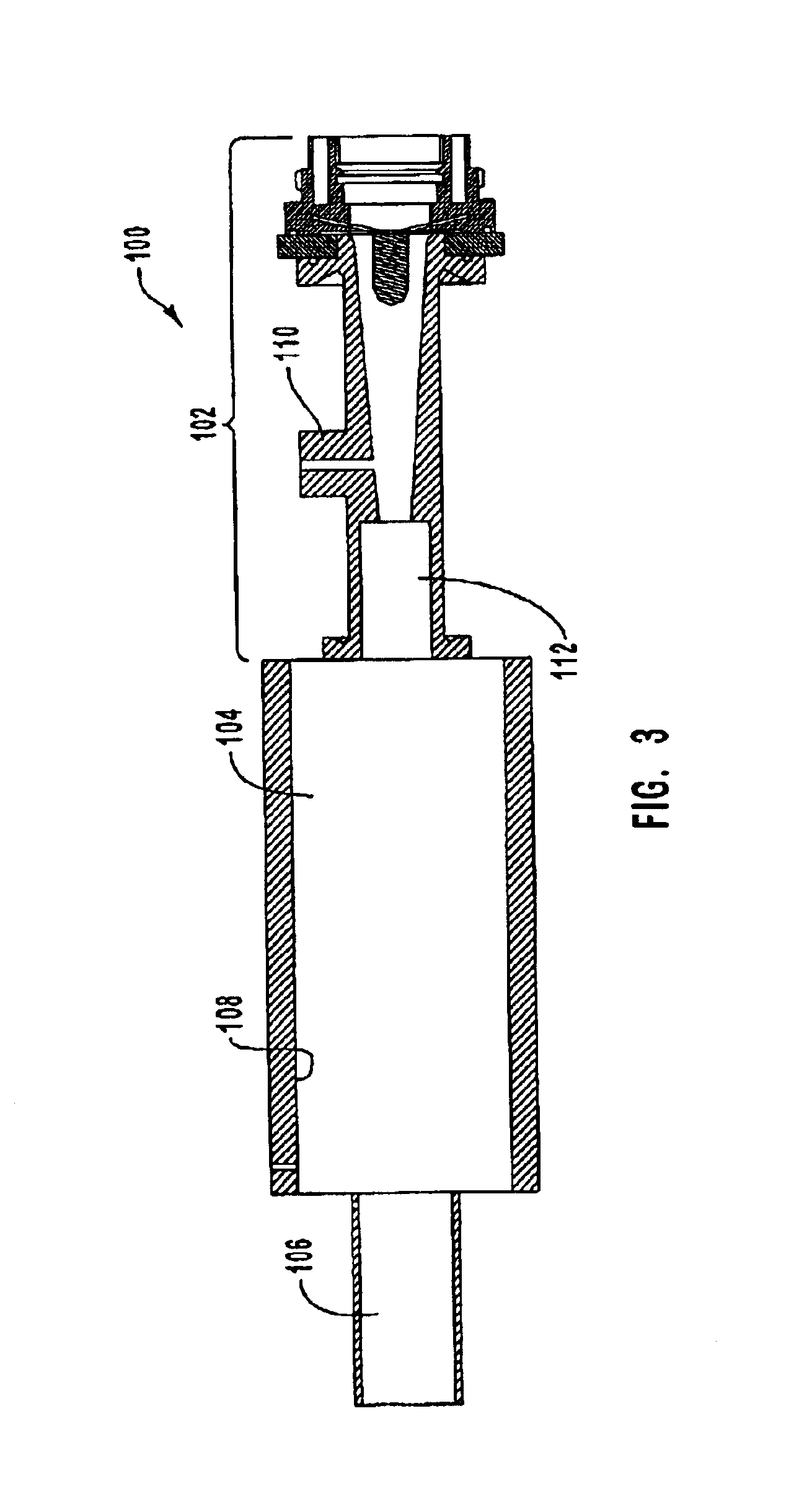
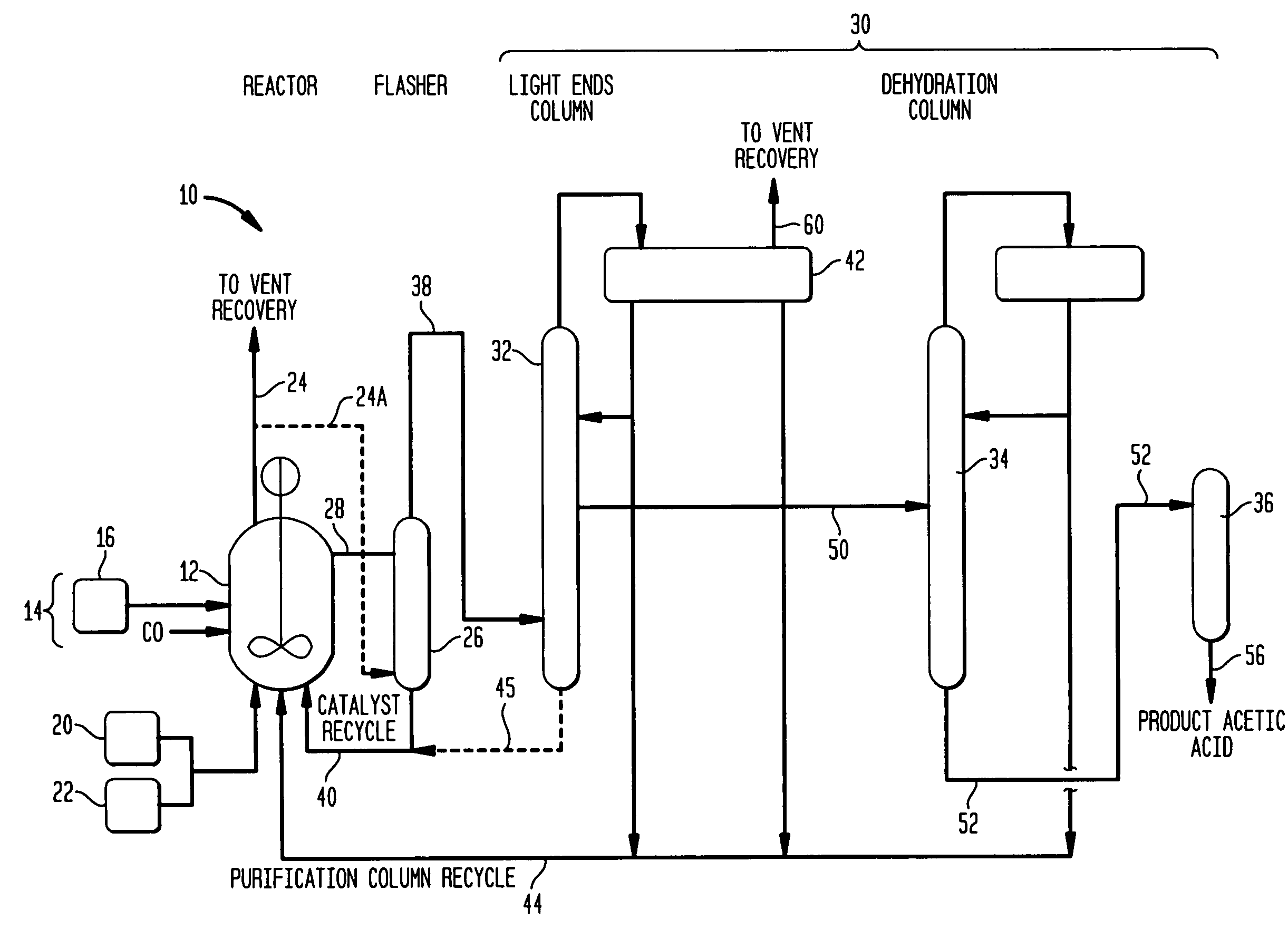
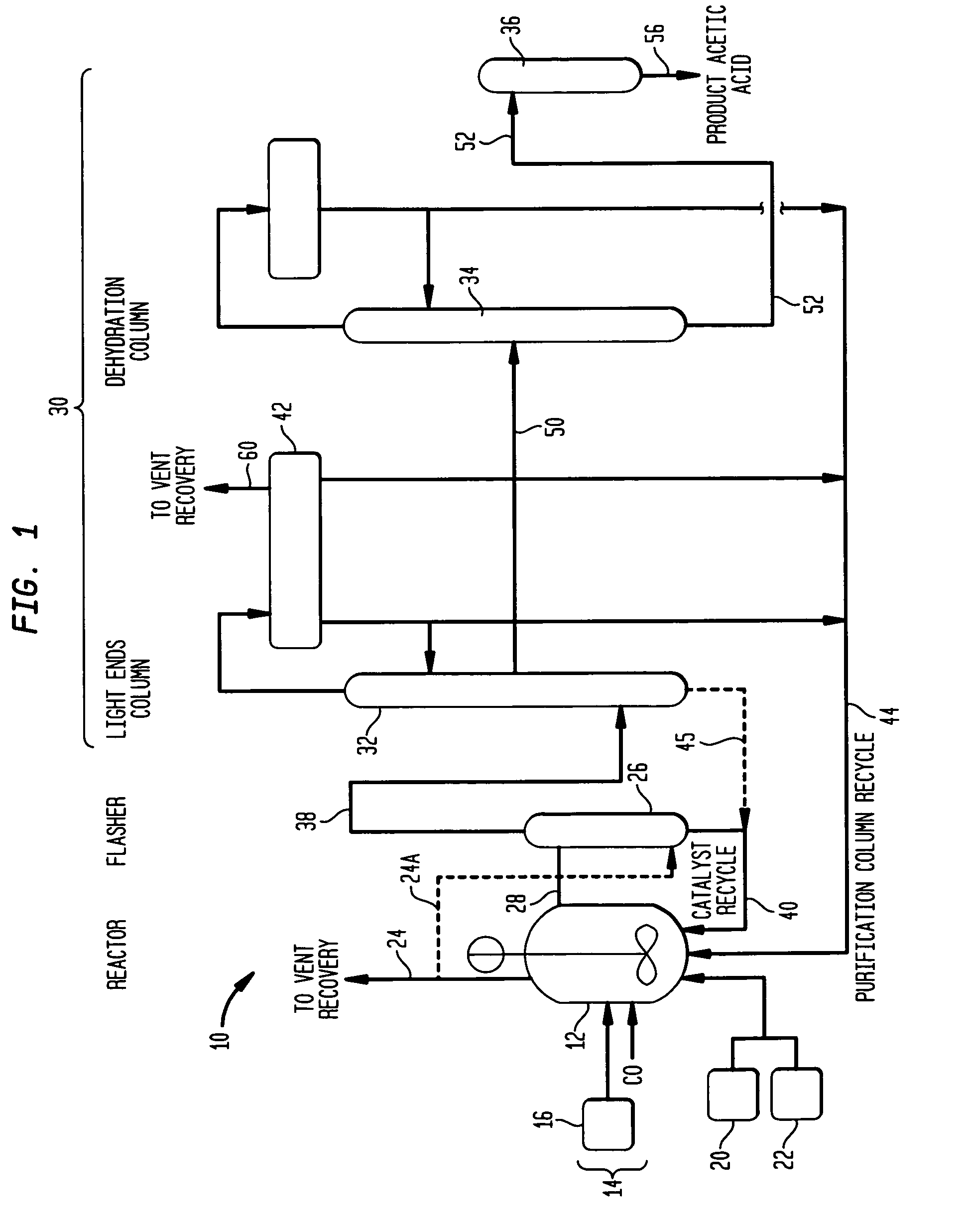
Methanol carbonylation system having absorber with multiple solvent options
A methanol carbonylation system 10 includes an absorber tower 75 adapted for receiving a vent gas stream and removing methyl iodide therefrom with a scrubber solvent, the absorber tower being coupled to first and second scrubber solvent sources 16, 56 which are capable of supplying different first and second scrubber solvents. A switching system including valves 90, 92, 94, 96, 98 alternatively provides first or second scrubber solvents to the absorber tower and returns the used solvent and sorbed material to the carbonylation system to accommodate different operating modes.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Systems and methods for hydrogen generation from solid hydrides
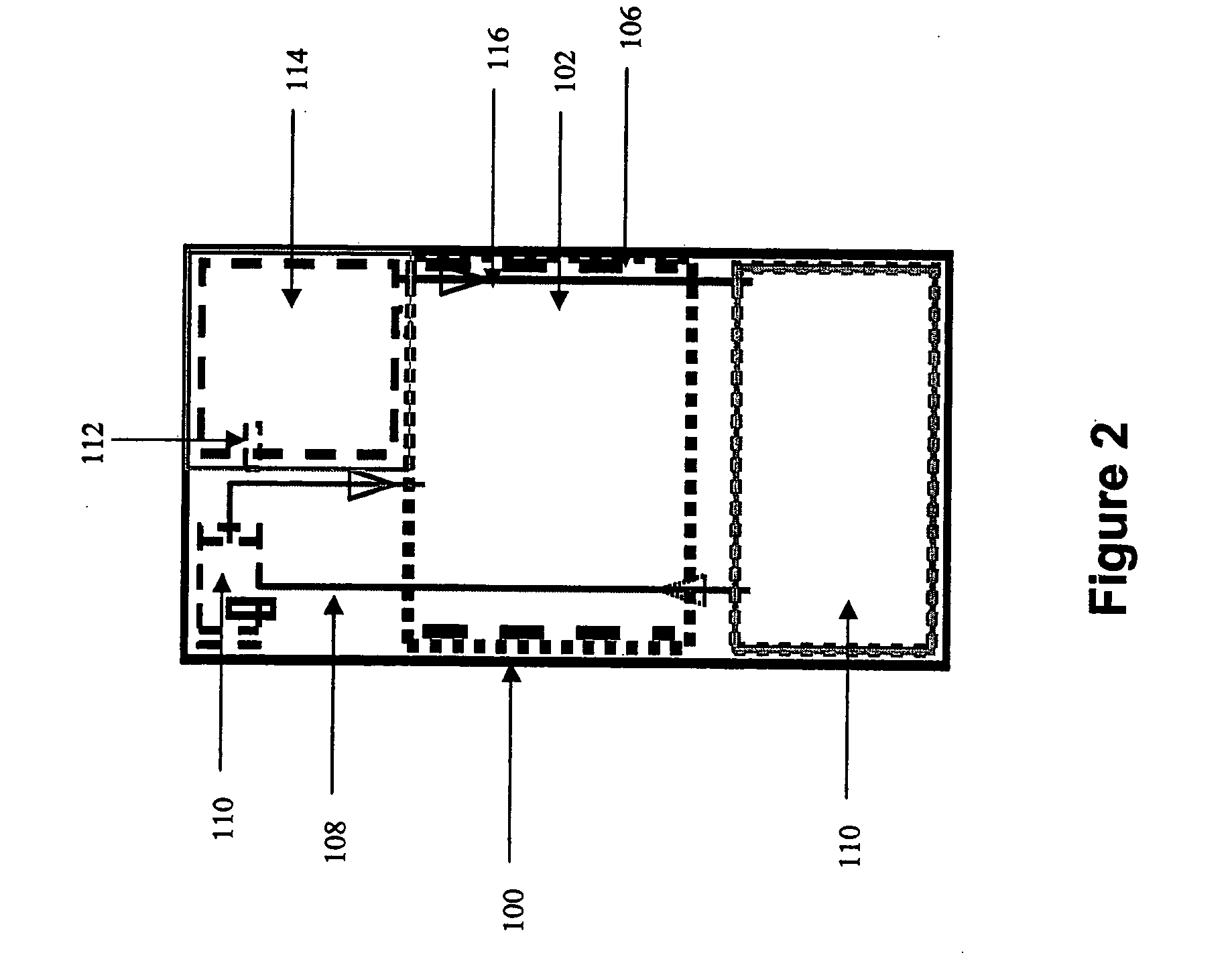
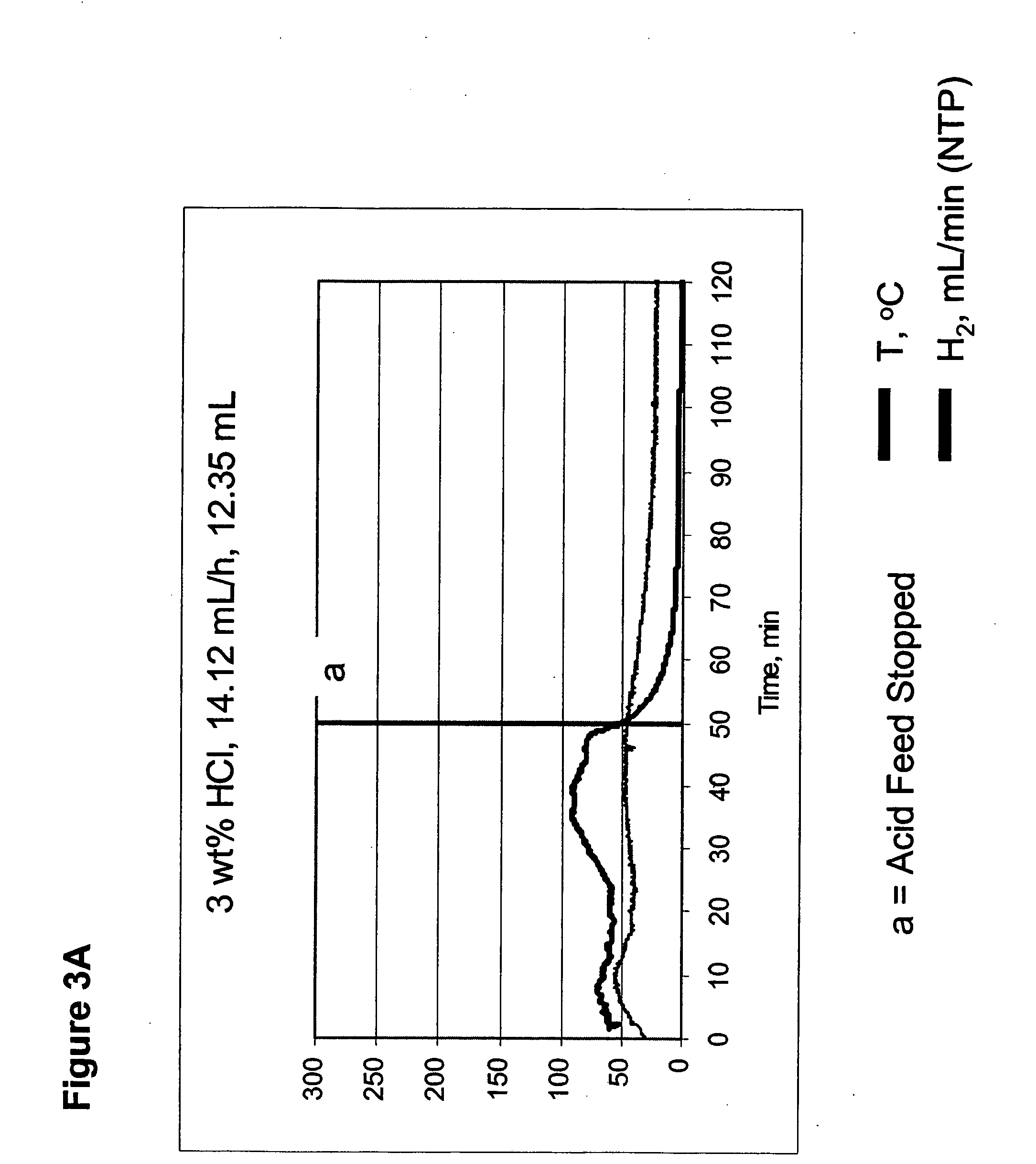
InactiveUS20050238573A1Regulate rateReactant parameters controlHydrogen productionO-Phosphoric AcidAlkaline earth metal
A system is disclosed for hydrogen generation based on hydrolysis of solid chemical hydrides with the capability of controlled startup and stop characteristics wherein regulation of acid concentration, acid feed rate, or a combination of both control the rate of hydrogen generation. The system comprises a first chamber for storing a solid chemical hydride and a second chamber for storing an acidic reagent. The solid chemical hydride is a solid metal borohydride having the general formula MBH4, where M is selected from the group consisting of alkali metal cations, alkaline earth metal cations, aluminum cation, zinc cation, and ammonium cation. The acidic reagent may comprise inorganic acids such as the mineral acids hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, and phosphoric acid, and organic acids such as acetic acid, formic acid, maleic acid, citric acid, and tartaric acid, or mixtures thereof.
Owner:MILLENNIUM CELL
Nanotechnology for drug delivery, contrast agents and biomedical implants
A nanocomposite structure comprising a nanostructured filler or carrier intimately mixed with a matrix, and methods of making such a structure. The nanostructured filler has a domain size sufficiently small to alter an electrical, magnetic, optical, electrochemical, chemical, thermal, biomedical, or tribological property of either filler or composite by at least 20%.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Method and apparatus for producing and treating novel elastomer composites
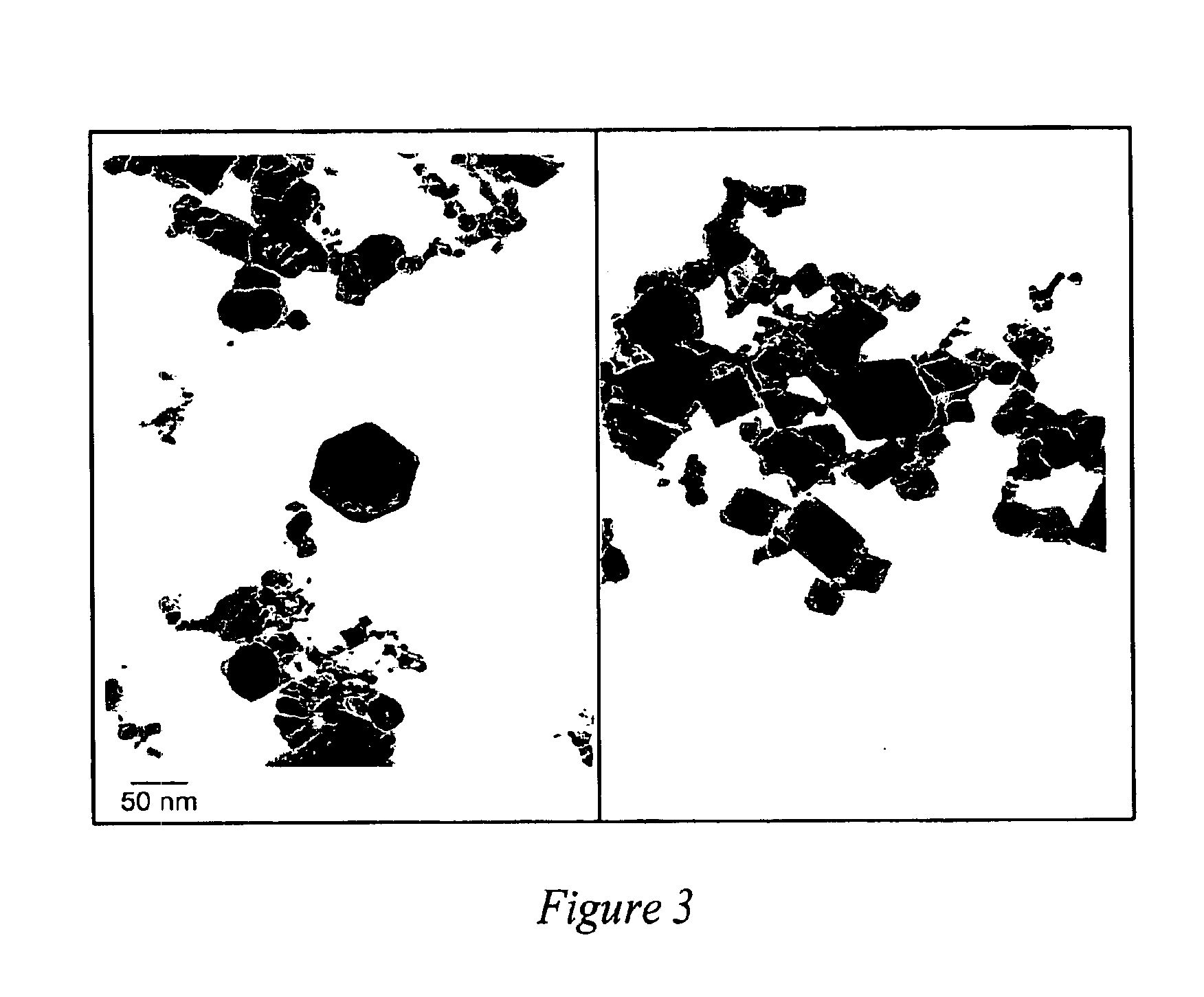
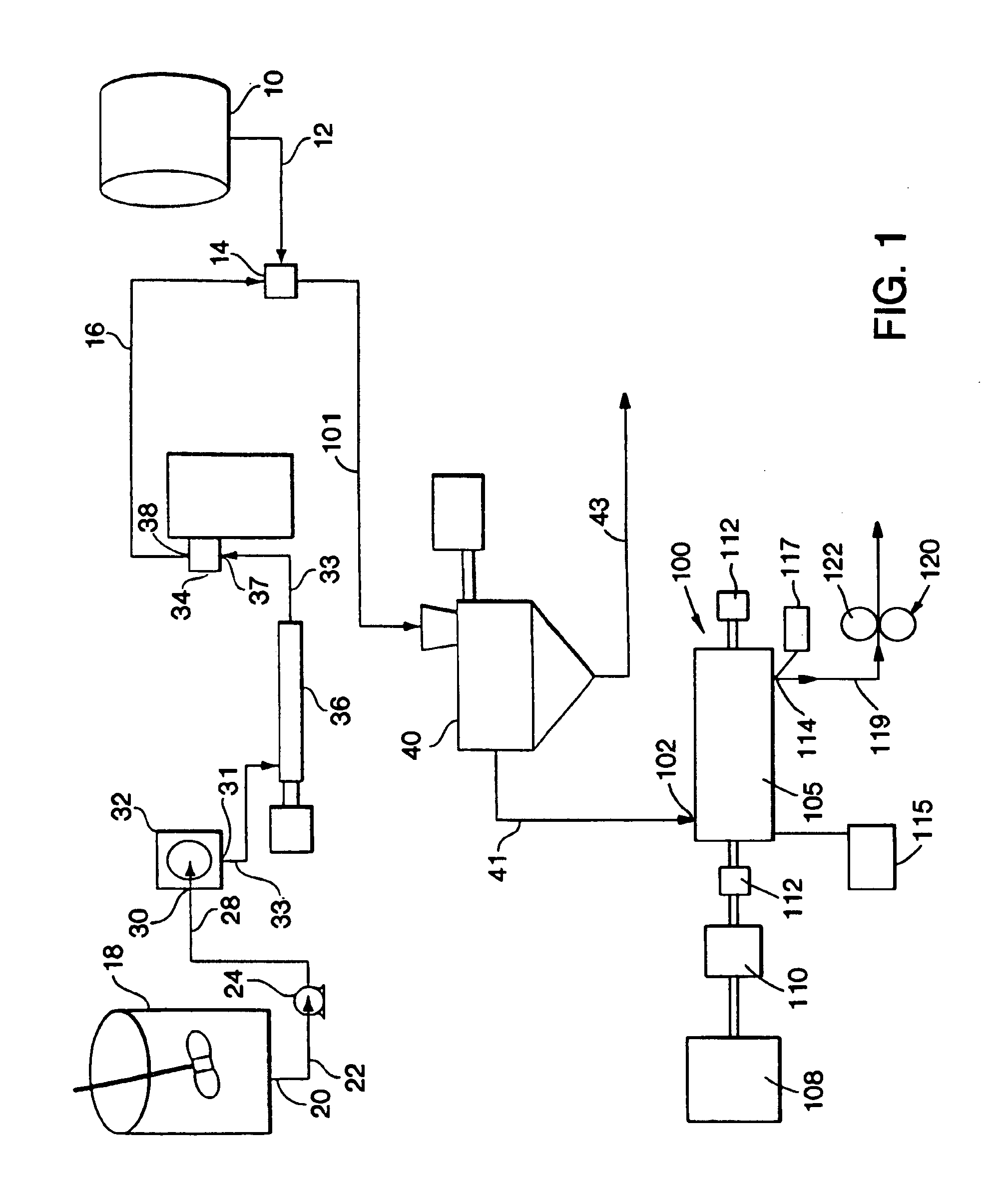
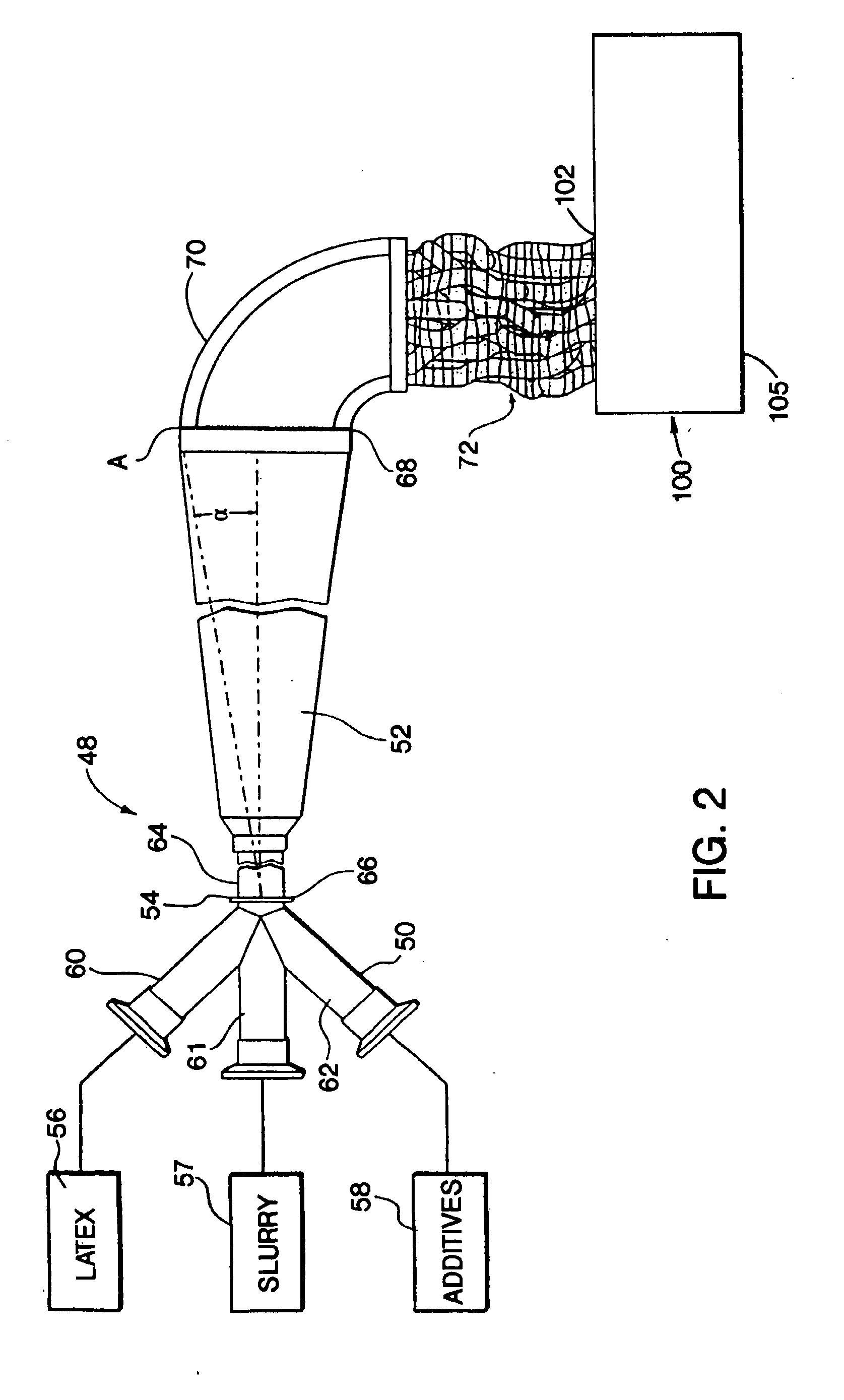
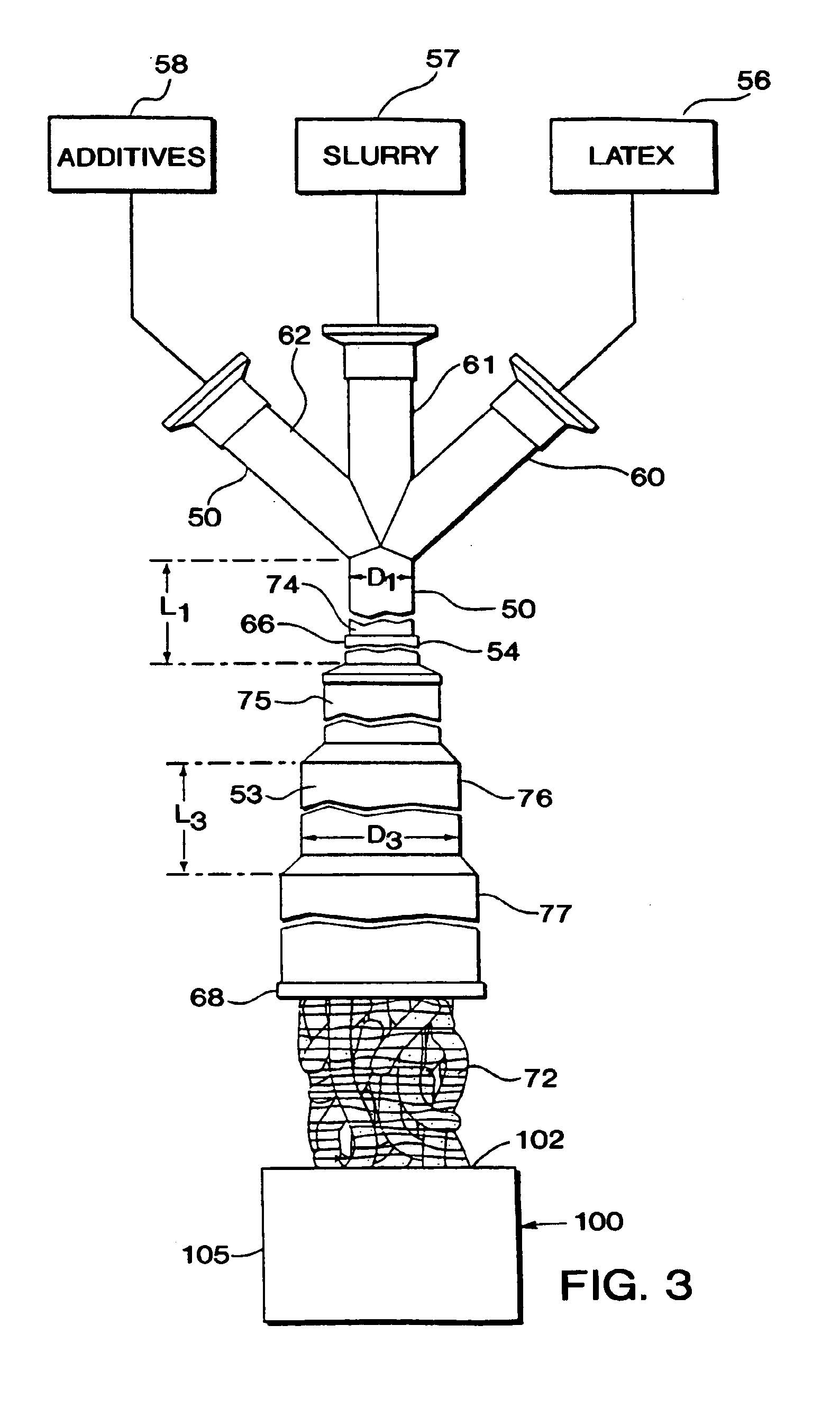
InactiveUS6929783B2Facilitate controlling and changing operating parameterImprove economyLiquid degasificationSpecial tyresParticulatesMasterbatch
Elastomer masterbatch is processed in a continuous compounder having multiple parallel elongate rotors axially oriented in an elongate processing chamber. Optionally, additional materials are compounded into the masterbatch, e.g., additives, other elastomeric compositions, etc. Preferably, the masterbatch then is further processed in an open mill. Excellent control of Mooney Viscosity is achieved.In certain preferred embodiments, elastomer composites are produced by novel continuous flow methods and apparatus in which fluid streams of particulate filler and elastomer latex are fed to the mixing zone of a coagulum reactor to form a coagulated mixture in semi-confined flow continuously from the mixing zone through a coagulum zone to a discharge end of the reactor. The particulate filler fluid is fed under high pressure to the mixing zone, such as to form a jet stream to entrain elastomer latex fluid sufficiently energetically to substantially completely coagulate the elastomer with the particulate filler prior to the discharge end without need of adding acid or salt solution or other coagulation step. The coagulated elastomer and particulate filler composite is fed into the aforesaid continuous compounder for processing and control of its moisture level and Mooney Viscosity. Novel elastomer composites are produced. Such novel elastomer composites combine material properties and characteristics, such as choice of filler, elastomer, level of filler loading, moisture level, Mooney Viscosity, balance between molecular weight and amount of bound rubber, and macro-dispersion not previously achieved.
Owner:CABOT CORP
Portable hydrogen generator-fuel cell apparatus
InactiveUS6653005B1Increase specific energy and overall energy efficiencyHydrogenFuel cell auxillariesKeroseneImpurity
A compact hydrogen generator is coupled to or integrated with a fuel cell for portable power applications. Hydrogen is produced via thermocatalytic decomposition (cracking, pyrolysis) of hydrocarbon fuels in oxidant-free environment. The apparatus can utilize a variety of hydrocarbon fuels, including natural gas, propane, gasoline, kerosene, diesel fuel, crude oil (including sulfurous fuels). The hydrogen-rich gas produced is free of carbon oxides or other reactive impurities, so it could be directly fed to any type of a fuel cell. The catalysts for hydrogen production in the apparatus are carbon-based or metal-based materials and doped, if necessary, with a sulfur-capturing agent. Additionally disclosed are two novel processes for the production of two types of carbon filaments, and a novel filamentous carbon product. The hydrogen generator can be conveniently integrated with high temperature fuel cells to produce an efficient and self-contained source of electrical power.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com