HDPE Films: New Horizons in Agricultural Mulching
HDPE Film Evolution
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) films have undergone significant evolution since their introduction in agricultural mulching applications. Initially developed in the 1960s, these films have transformed from simple plastic sheets to sophisticated, engineered materials tailored for specific agricultural needs.
In the early stages, HDPE films were primarily used as a basic barrier to suppress weed growth and conserve soil moisture. However, as agricultural practices advanced, so did the demands placed on these films. The 1980s saw the introduction of UV-stabilized HDPE films, which significantly extended their lifespan in the field, addressing the issue of premature degradation due to sunlight exposure.
The 1990s marked a turning point in HDPE film technology with the development of multi-layer films. This innovation allowed for the incorporation of different properties within a single film, such as enhanced strength, improved light transmission, and better heat retention. These advancements led to increased crop yields and extended growing seasons in various climates.
As environmental concerns grew in the 2000s, biodegradable HDPE films emerged as a solution to plastic waste in agriculture. These films were designed to break down naturally after the growing season, reducing the environmental impact and labor costs associated with film removal.
The past decade has seen a focus on "smart" HDPE films. These advanced materials incorporate nanotechnology to deliver controlled-release fertilizers, pest repellents, or growth stimulants directly to the soil. Some films are even equipped with sensors to monitor soil conditions, allowing for precise irrigation and nutrient management.
Recent developments have also addressed the challenge of microplastic pollution. New HDPE film formulations are being engineered to degrade into harmless compounds, leaving no persistent plastic residues in the soil. This innovation represents a significant step towards sustainable agriculture.
The evolution of HDPE films has not been limited to material composition alone. Manufacturing processes have also advanced, allowing for the production of thinner yet stronger films. This has resulted in reduced material usage and lower costs for farmers, while maintaining or even improving performance.
Looking ahead, the future of HDPE films in agricultural mulching is likely to focus on further enhancing sustainability and functionality. Research is underway to develop films that can adapt to changing environmental conditions, potentially altering their properties based on temperature or moisture levels to optimize crop growth throughout the season.
Agri-Mulch Market
The agricultural mulch market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for sustainable farming practices and the need to enhance crop yields. This market segment encompasses various types of mulching materials, including plastic films, biodegradable options, and organic mulches. Among these, High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) films have emerged as a prominent player, offering durability and cost-effectiveness for farmers worldwide.
The global agricultural mulch market size was valued at approximately $6.5 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $9.4 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 6.3% during the forecast period. This growth is attributed to several factors, including the rising adoption of modern agricultural techniques, increasing awareness of water conservation, and the need for weed control in crop production.
HDPE films, in particular, have gained traction due to their superior properties such as high tensile strength, chemical resistance, and longevity. These films account for a significant portion of the plastic mulch market, with an estimated market share of 35-40%. The demand for HDPE mulch films is especially strong in regions with intensive agriculture, such as Asia-Pacific, North America, and Europe.
The market dynamics are influenced by several trends and drivers. Climate change and water scarcity have led to increased adoption of mulching techniques to conserve soil moisture and reduce irrigation requirements. Additionally, the push for higher crop yields to meet growing food demand has fueled the use of agricultural mulches, including HDPE films, to create optimal growing conditions.
However, the market also faces challenges, primarily related to environmental concerns. The accumulation of plastic waste from non-biodegradable mulch films has led to stricter regulations in some regions and a growing interest in biodegradable alternatives. This has prompted research and development efforts to improve the recyclability and eco-friendliness of HDPE films used in agriculture.
Despite these challenges, the HDPE film segment within the agricultural mulch market continues to show resilience. Manufacturers are investing in product innovations, such as UV-stabilized and colored HDPE films, to enhance performance and address specific crop needs. The market is also witnessing a trend towards the development of thinner films that maintain strength while reducing material usage and environmental impact.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the agricultural mulch market, accounting for over 40% of the global share. This is largely due to extensive agricultural activities in countries like China and India. North America and Europe follow, with increasing adoption of precision agriculture techniques driving the demand for high-performance mulch films, including HDPE options.
HDPE Film Challenges
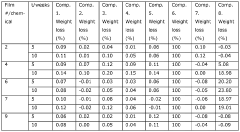
Despite the widespread adoption of HDPE films in agricultural mulching, several significant challenges persist in their application and environmental impact. One of the primary concerns is the degradation of HDPE films under field conditions. While these films are designed to be durable, prolonged exposure to sunlight, temperature fluctuations, and mechanical stress can lead to fragmentation and microplastic formation. This not only reduces the effectiveness of the mulch but also contributes to soil pollution.
The disposal of used HDPE films presents another major challenge. Many farmers struggle with the proper removal and disposal of these films after the growing season. Improper disposal can lead to environmental contamination and visual pollution in agricultural areas. The lack of efficient recycling infrastructure for agricultural plastics exacerbates this issue, as many HDPE films end up in landfills or are incinerated, releasing harmful emissions.
The production of HDPE films also raises sustainability concerns. The manufacturing process relies heavily on fossil fuels, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and depleting non-renewable resources. As global awareness of climate change increases, there is growing pressure to develop more sustainable alternatives or improve the eco-friendliness of HDPE film production.
Another challenge lies in balancing the film's properties for optimal performance. HDPE films must be thick enough to withstand field conditions but thin enough to allow for proper soil gas exchange and water penetration. Achieving this balance while maintaining cost-effectiveness is an ongoing challenge for manufacturers.
The potential for soil ecosystem disruption is a growing concern among researchers and environmentalists. Long-term use of HDPE films may alter soil microbial communities and affect nutrient cycling. This could have cascading effects on soil health and crop productivity, potentially undermining the very benefits that mulching aims to provide.
Lastly, there is the challenge of adapting HDPE films to diverse agricultural conditions. Different crops, climates, and soil types may require variations in film properties, such as thickness, permeability, and additives. Developing a range of specialized HDPE films to meet these varied needs while maintaining economic viability is a complex task for the industry.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, involving innovations in material science, improvements in recycling technologies, and the development of more sustainable agricultural practices. As the agricultural sector continues to seek ways to increase productivity while reducing environmental impact, overcoming these HDPE film challenges remains a critical area of focus for researchers, manufacturers, and policymakers alike.
Current HDPE Solutions
01 Composition and properties of HDPE films
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) films are characterized by their unique composition and properties. These films exhibit high strength, durability, and chemical resistance. The composition can be modified to enhance specific properties such as barrier performance, tear resistance, and thermal stability. Various additives and processing techniques can be employed to tailor the film's characteristics for different applications.- Composition and properties of HDPE films: High-density polyethylene (HDPE) films are characterized by their unique composition and properties. These films exhibit high strength, durability, and chemical resistance. The composition can be modified with additives to enhance specific properties such as UV resistance or barrier properties. HDPE films are widely used in packaging, agriculture, and construction due to their versatility and performance.
- Manufacturing processes for HDPE films: Various manufacturing processes are employed to produce HDPE films, including blown film extrusion, cast film extrusion, and sheet extrusion. These processes involve melting HDPE resin, forming it into a film, and cooling it to achieve the desired thickness and properties. Advanced techniques may incorporate multi-layer co-extrusion or orientation to enhance film performance.
- Surface treatment and modification of HDPE films: Surface treatments and modifications are applied to HDPE films to improve their adhesion, printability, and other surface properties. Common techniques include corona treatment, plasma treatment, and chemical etching. These processes alter the surface energy of the film, making it more receptive to inks, coatings, and adhesives.
- Recycling and sustainability of HDPE films: Recycling and sustainability initiatives for HDPE films are gaining importance in the industry. This includes developing recycling processes specific to HDPE films, incorporating recycled content into new film production, and designing films for easier recyclability. Efforts are also being made to reduce the environmental impact of HDPE film production and use.
- Applications and innovations in HDPE film technology: HDPE films find applications in various industries, with ongoing innovations expanding their use. New developments include enhanced barrier films for food packaging, agricultural films with improved durability and light transmission, and specialized films for medical and pharmaceutical applications. Research is also focused on creating thinner films with improved strength and performance characteristics.
02 Manufacturing processes for HDPE films
The production of HDPE films involves various manufacturing processes, including extrusion, blown film extrusion, and cast film extrusion. These processes can be optimized to control film thickness, orientation, and surface properties. Advanced techniques such as multi-layer co-extrusion and biaxial orientation can be used to create films with enhanced performance characteristics.Expand Specific Solutions03 Surface treatment and modification of HDPE films
Surface treatment and modification techniques can be applied to HDPE films to improve their adhesion properties, printability, and compatibility with other materials. These methods include corona treatment, plasma treatment, chemical etching, and the application of functional coatings. Such modifications can enhance the film's performance in packaging, lamination, and other applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Recycling and sustainability of HDPE films
Recycling and sustainability considerations are increasingly important in the development and use of HDPE films. Innovations in this area focus on improving the recyclability of HDPE films, incorporating recycled content, and developing biodegradable or compostable alternatives. Advanced sorting and recycling technologies are being developed to enhance the circular economy of HDPE film products.Expand Specific Solutions05 Applications and innovations in HDPE film technology
HDPE films find applications in various industries, including packaging, agriculture, construction, and healthcare. Ongoing innovations focus on developing specialized HDPE films with enhanced functionalities such as improved barrier properties, antimicrobial characteristics, and smart packaging features. New applications are being explored in areas such as flexible electronics and renewable energy.Expand Specific Solutions
Key HDPE Producers
The HDPE films market for agricultural mulching is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for sustainable farming practices. The market size is expanding globally, with a projected CAGR of 5-7% over the next five years. Technologically, HDPE films are mature but evolving, with companies like LG Chem Ltd., Borealis AG, and Novamont SpA leading innovation in biodegradable and enhanced-performance films. Emerging players such as TerraVerdae Bioworks and Radical Plastics are focusing on eco-friendly alternatives, while established firms like China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. are leveraging their scale to dominate market share. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of large petrochemical companies and specialized agricultural film manufacturers, with increasing emphasis on sustainability and cost-effectiveness.
Borealis AG
Novamont SpA
HDPE Film Innovations
- A degradable mulch film system comprising a below-ground and above-ground film, co-extruded with additives for controlled biodegradation, allowing for easy integration into soil and reducing environmental impact.
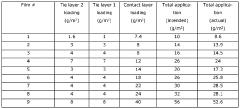
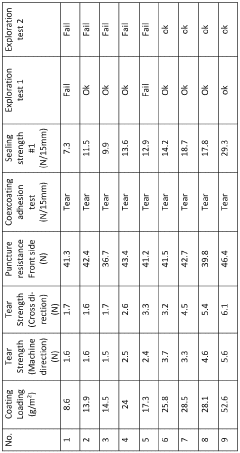
- The use of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) as a contact layer in laminate films, combined with a tie layer and a water/oxygen-resistant base layer, provides a mechanically strong and impermeable packaging solution for agrochemical substances and solvents, ensuring effective sealing and resistance to chemical migration.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of HDPE films in agricultural mulching is a critical consideration as the industry moves towards more sustainable practices. These films, while offering significant benefits in crop yield and water conservation, also present challenges in terms of waste management and ecological effects.
HDPE mulch films contribute to soil pollution when not properly managed. The incomplete removal of these films after use can lead to the accumulation of plastic residues in agricultural soils. Over time, these residues break down into microplastics, which can alter soil structure, affect microbial communities, and potentially enter the food chain. Studies have shown that even small amounts of plastic fragments can impact soil porosity and water holding capacity, potentially affecting long-term soil health and crop productivity.
Water pollution is another concern associated with HDPE mulch films. When fragments of these films are washed away by rain or irrigation, they can enter water systems, contributing to the growing problem of microplastic pollution in aquatic environments. This not only affects marine ecosystems but also poses potential risks to human health through the consumption of contaminated water and seafood.
The production and disposal of HDPE films also contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. The manufacturing process of these films is energy-intensive and typically relies on fossil fuel-based raw materials. Additionally, the improper disposal of used films, often through burning or landfilling, releases harmful emissions into the atmosphere.
However, recent advancements in HDPE film technology are addressing these environmental concerns. Biodegradable and oxo-degradable HDPE films are being developed, which break down more readily in the environment. These innovations aim to reduce the long-term accumulation of plastic in soils and water systems. Furthermore, recycling initiatives for agricultural plastics are gaining traction, with some regions implementing collection and processing systems to turn used HDPE films into new products.
The agricultural industry is also exploring alternatives to traditional HDPE films, such as bio-based mulches made from renewable resources. These alternatives promise reduced environmental impact while maintaining the benefits of plastic mulching. Additionally, precision agriculture techniques are being employed to optimize the use of HDPE films, minimizing waste and improving overall efficiency.
As the agricultural sector continues to prioritize sustainability, the environmental impact of HDPE films remains a key area of focus. Balancing the benefits of these films with their potential ecological drawbacks is crucial for developing sustainable agricultural practices. Ongoing research and innovation in this field are essential to mitigate the negative environmental impacts while harnessing the productivity gains offered by agricultural mulching technologies.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding HDPE films in agricultural mulching is a complex and evolving landscape that significantly impacts the adoption and use of this technology. At the global level, there is a growing emphasis on sustainable agricultural practices and environmental protection, which has led to the development of regulations aimed at minimizing the environmental impact of plastic mulch films.
In the European Union, the European Commission has implemented directives that address the use of plastics in agriculture, including HDPE films. These regulations focus on waste management, recycling, and the reduction of plastic pollution. The EU's Circular Economy Action Plan, for instance, includes measures to promote the use of biodegradable and compostable plastics in agriculture, which may impact the future use of traditional HDPE films.
In the United States, the regulatory approach varies by state, with some states implementing more stringent regulations on plastic mulch use than others. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) provides guidelines on the proper disposal and recycling of agricultural plastics, including HDPE films. Additionally, the USDA's National Organic Program has specific regulations regarding the use of plastic mulches in organic farming systems.
China, as a major producer and consumer of agricultural plastics, has introduced regulations to address the environmental concerns associated with plastic mulch films. The Chinese government has implemented policies to promote the collection and recycling of used films and has set standards for the thickness and degradability of agricultural plastics.
Many countries are also developing or implementing Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) schemes for agricultural plastics. These programs aim to make manufacturers responsible for the entire lifecycle of their products, including collection and recycling after use. This approach is likely to influence the design and production of HDPE films for agricultural mulching in the future.
Regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on the development of standards for biodegradable and oxo-degradable plastics as alternatives to traditional HDPE films. However, there is ongoing debate about the effectiveness and environmental impact of these alternatives, which has led to varying regulatory approaches across different regions.
The regulatory landscape also includes certifications and labeling requirements for agricultural plastics. These standards aim to provide farmers with information about the environmental impact and proper use of mulch films, including HDPE products. Such certifications may become increasingly important in guiding purchasing decisions and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
As concerns about microplastic pollution grow, it is likely that future regulations will address the long-term environmental impacts of HDPE films in soil ecosystems. This may lead to more stringent requirements for film recovery and recycling, as well as potential restrictions on the use of non-biodegradable plastics in certain agricultural applications.