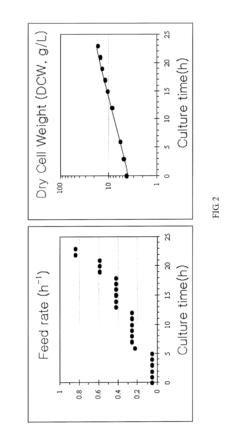
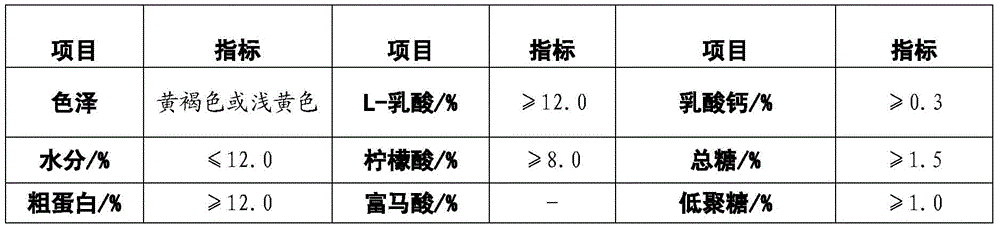
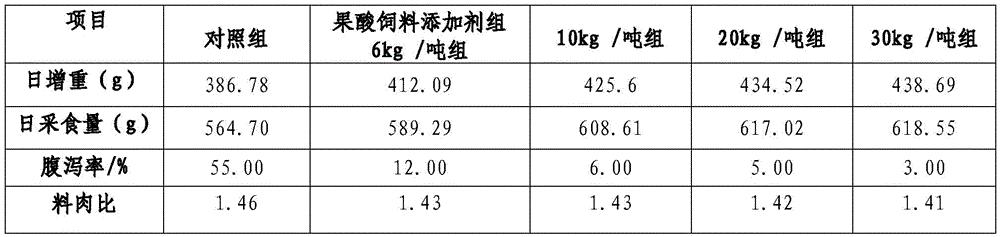
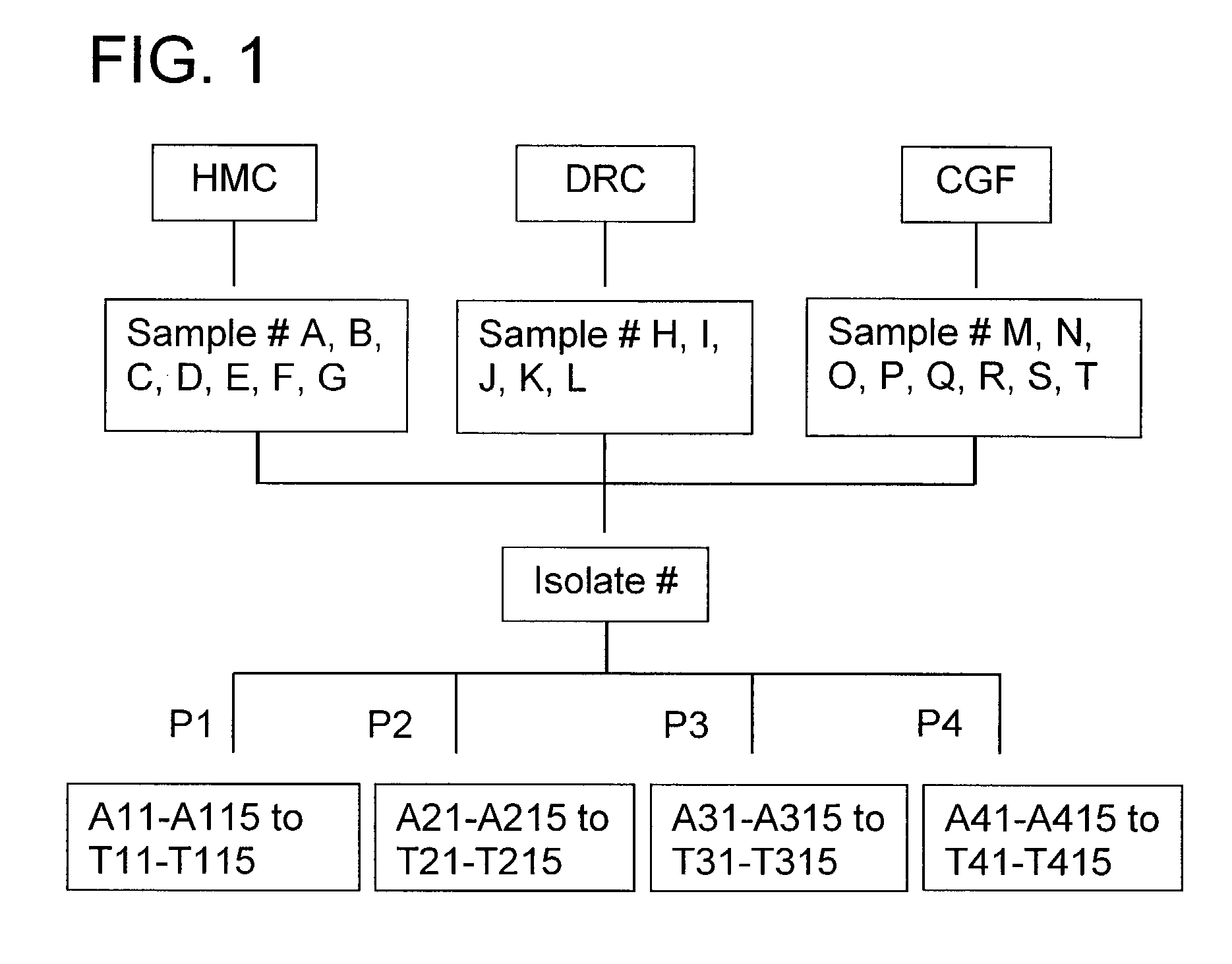
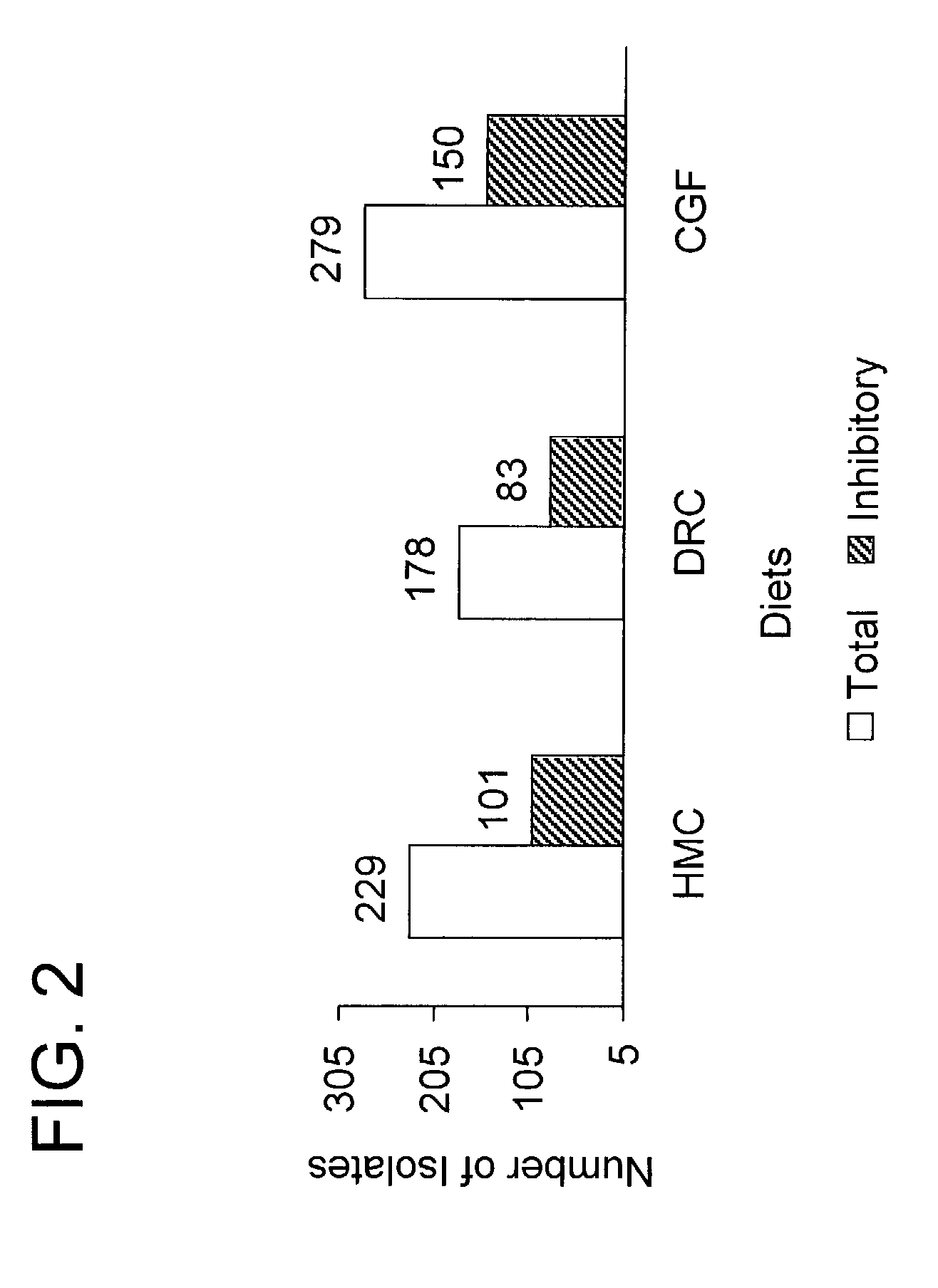
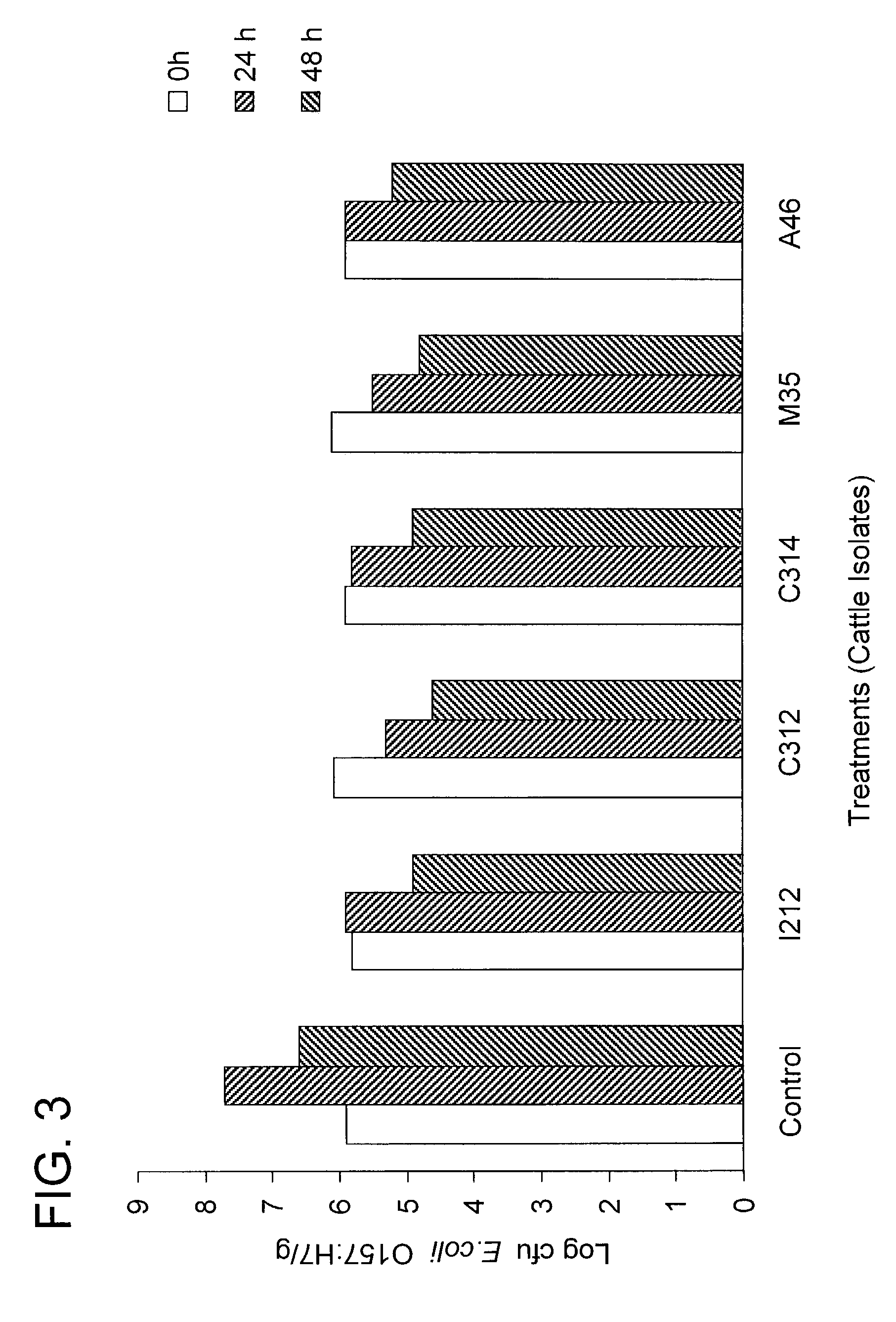
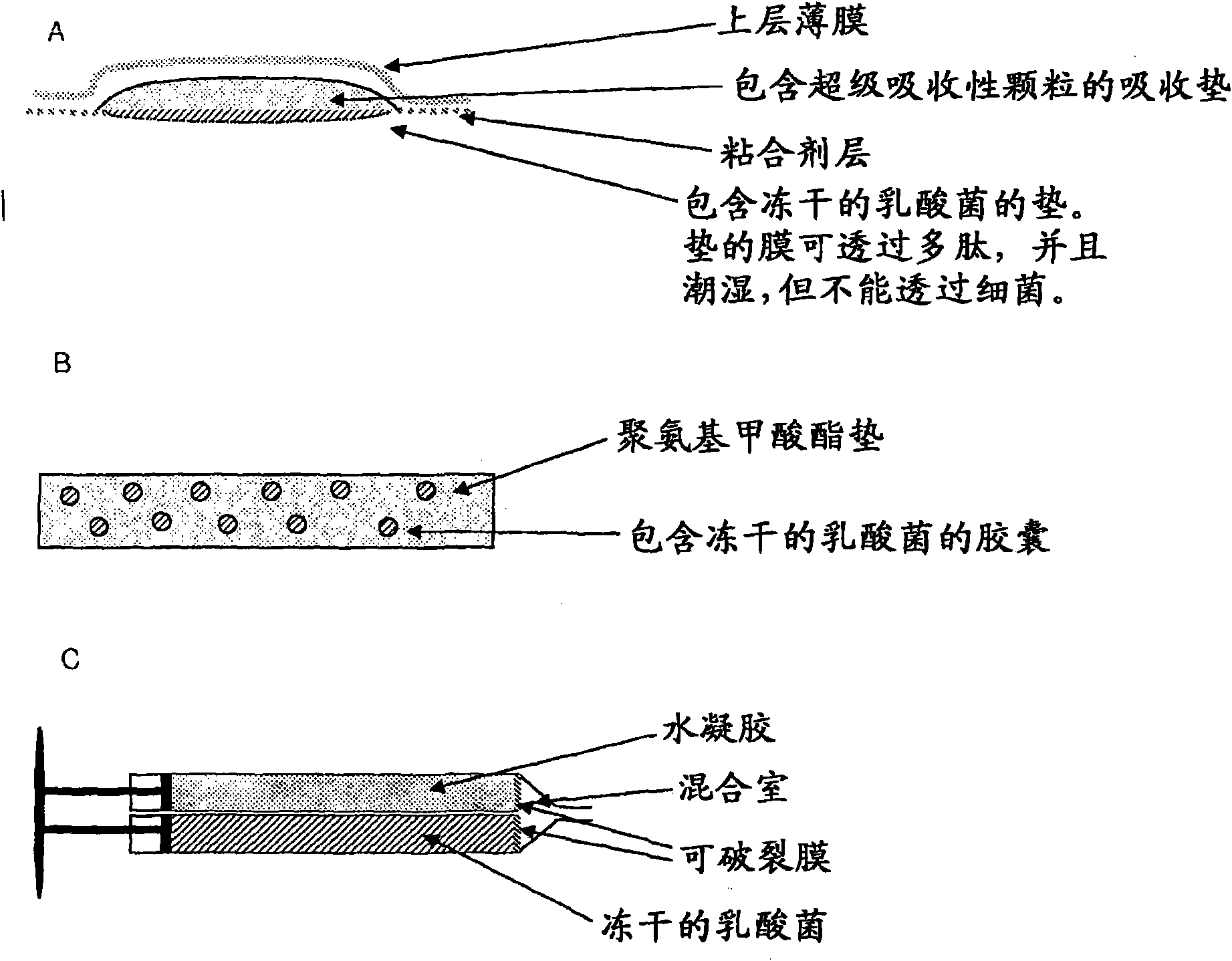
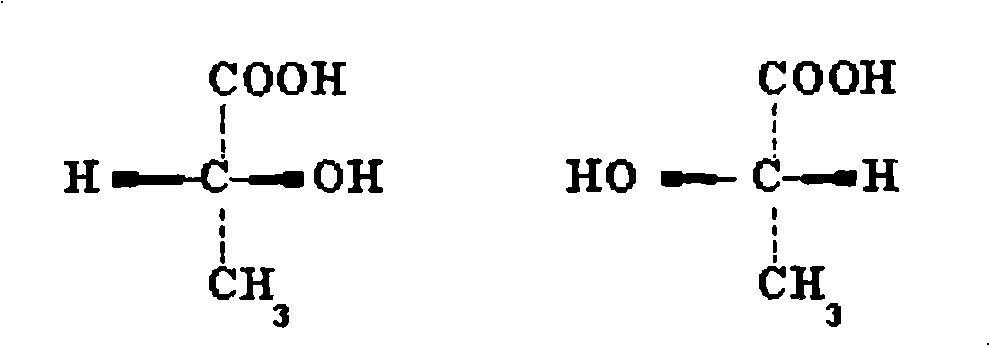Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
103 results about "Lactic acid producing bacteria" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Lactic acid is produced by lactic acid producing bacteria (LAB) such as lactobacillus of which there are all sorts of different strains. This lactobacillus bacteria is present on all fruit, vegetables, in the air on even on your skin.
Probiotic, lactic acid-producing bacteria and uses thereof
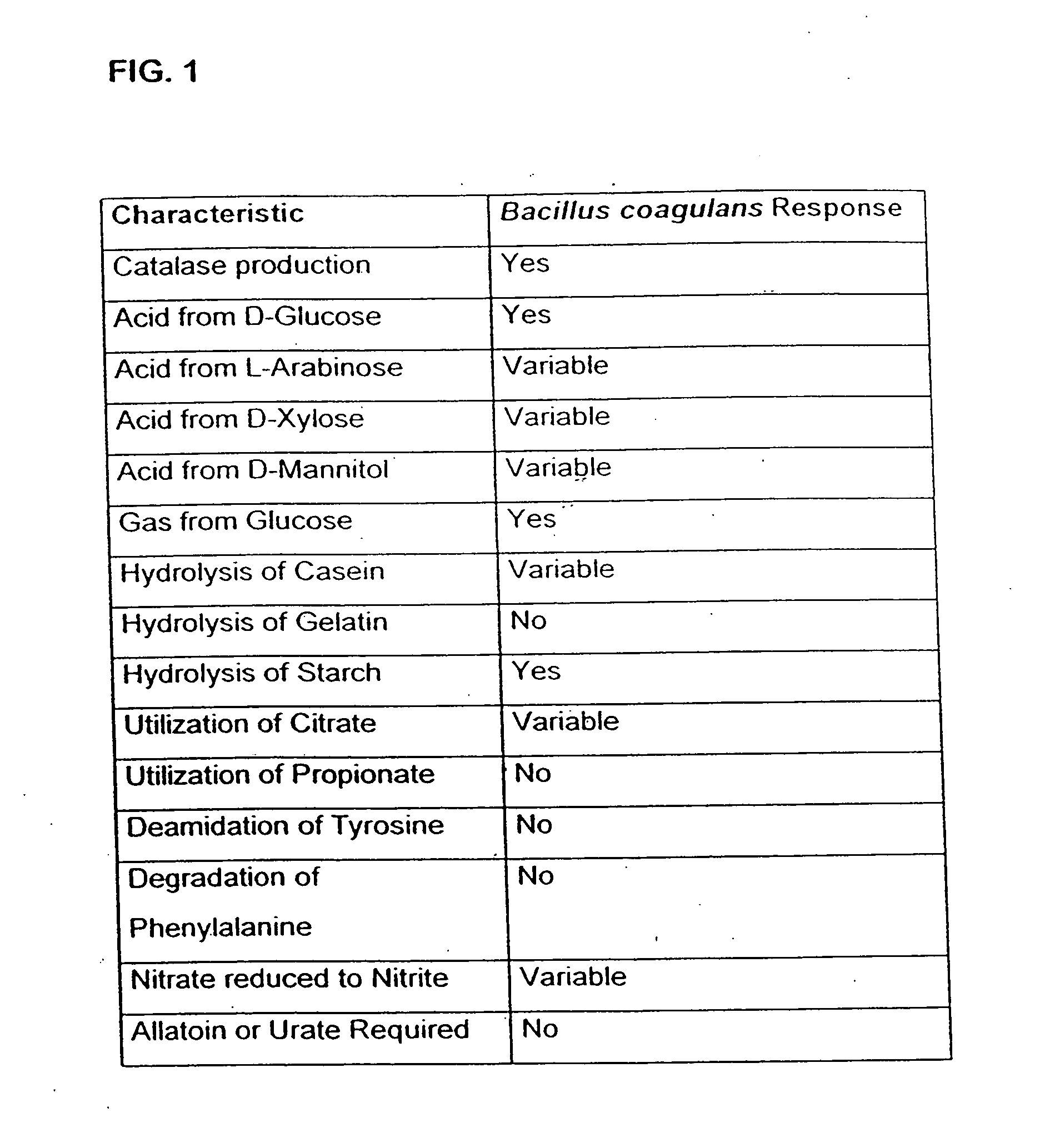
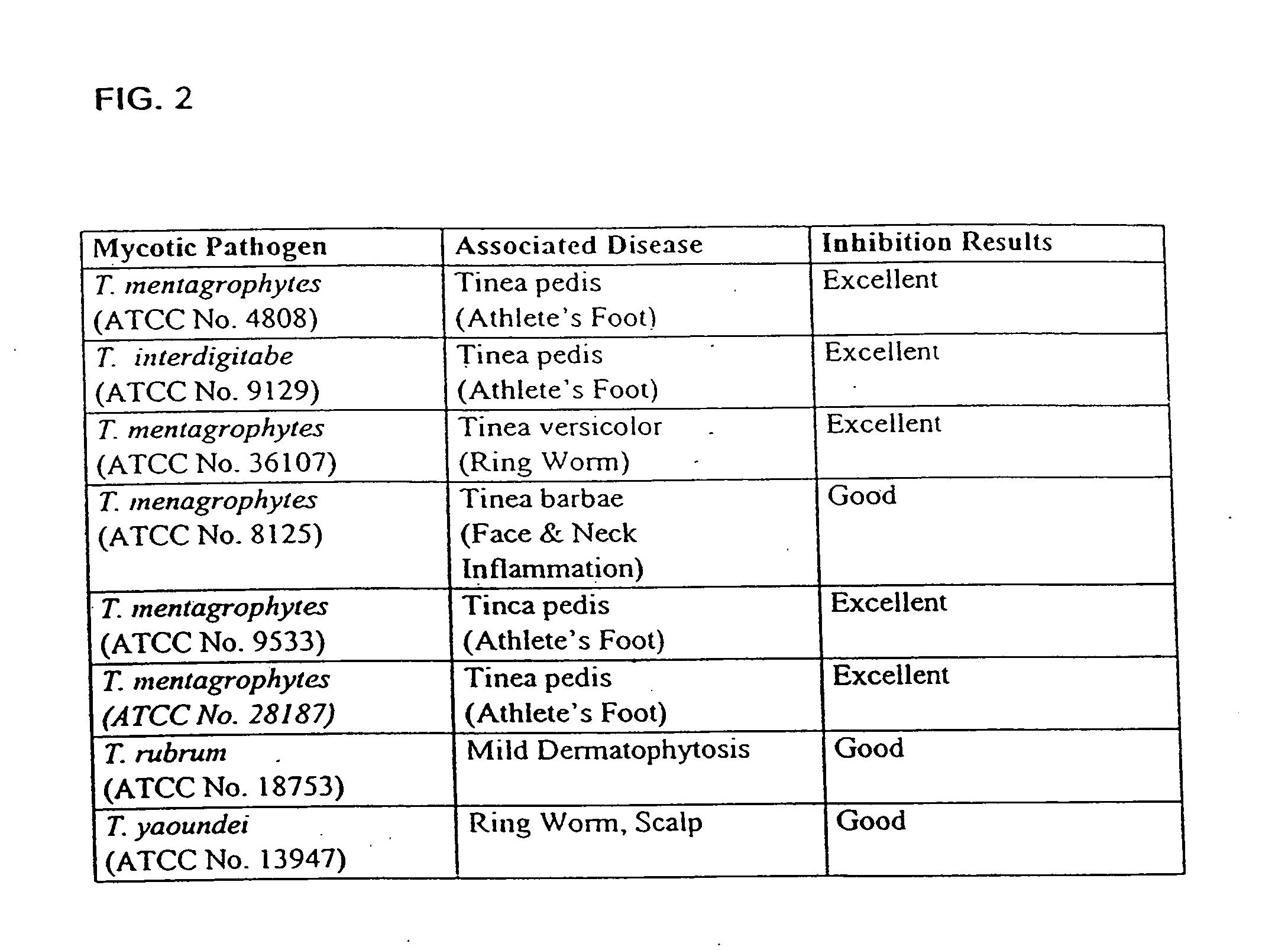
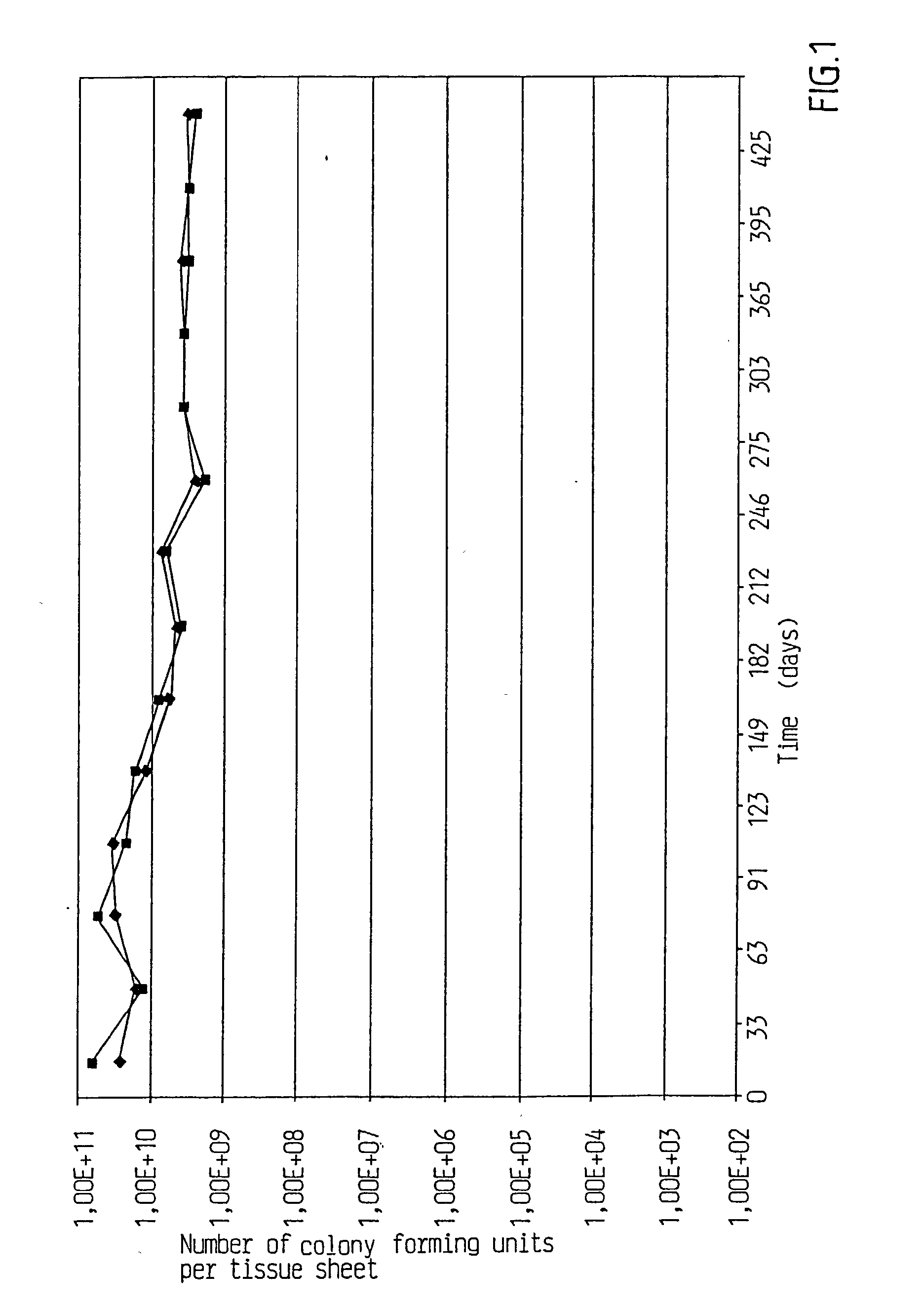
InactiveUS20060099197A1Good curative effectMitigating deleterious side-effectsAntibacterial agentsBiocideMicrobial agentAnti fungal
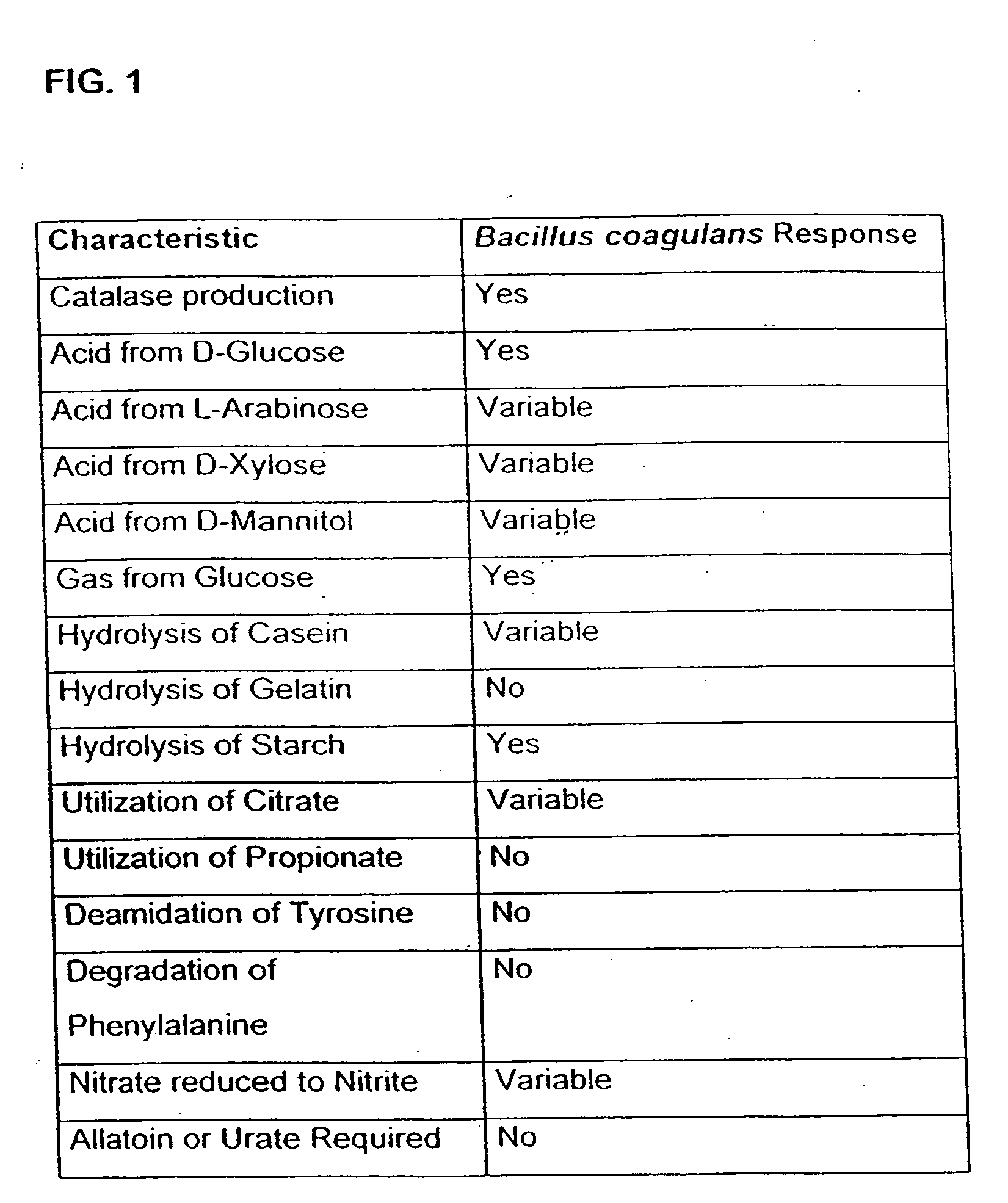
The present invention discloses compositions and methodologies for the utilization of probiotic organisms in therapeutic compositions. More specifically, the present invention relates to the utilization of one or more species or strains of lactic acid-producing bacteria, preferably strains of Bacillus coagulans, for the control of gastrointestinal tract pathogens, including antibiotic-resistant gastrointestinal tract pathogens, and their associated diseases by both a reduction in the rate of colonization and the severity of the deleterious physiological effects of the colonization of the antibiotic-resistant pathogen. In addition, the present invention relates to the utilization of therapeutic compounds comprised of lactic acid—producing bacteria and anti-microbial agents such as antibiotics, anti-fungal compounds, anti-yeast compounds, or anti-viral compounds. The present invention also discloses methodologies for: (i) the selective breeding and isolation of probiotic, lactic acid-producing bacterial strains which possess resistance or markedly decreased sensitivity to anti-microbial agents (e.g., antibiotics, anti-fungal agents, anti-yeast agents, and anti-viral agents); and (ii) treating or preventing bacteria-mediated infections of the gastrointestinal tract by use of the aforementioned probiotic bacterial strains with or without the concomitant administration of antibiotics. While the primary focus is on the treatment of gastrointestinal tract infections, the therapeutic compositions of the present invention may also be administered to buccal, vaginal, optic, and like physiological locations.
Owner:GANEDEN BIOTECH
Probiotic lactic acid bacterium to treat bacterial infections associated with SIDS
Compositions including a non-pathogenic lactic acid-producing bacteria, such as a Bacillus species, spores or an extracellular product of B. coagulans, formulated for oral administration to the intestinal tract for inhibiting bacterial gastrointestinal infections are described. Methods and systems using the compositions for treating gastrointestinal infections, particularly sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) are also disclosed.
Owner:GANEDEN BIOTECH
Process and composition for the manufacture of a microbial-based product
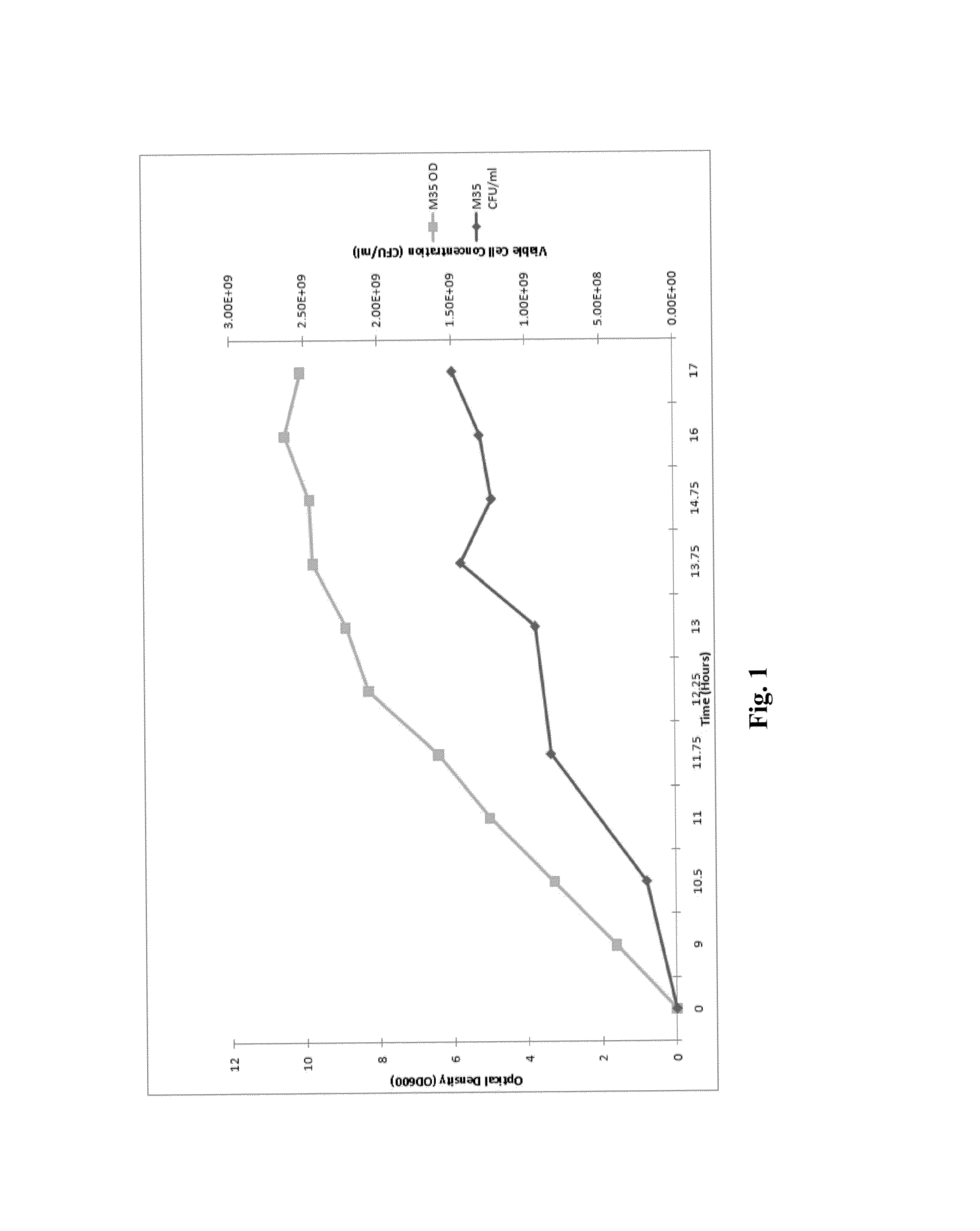
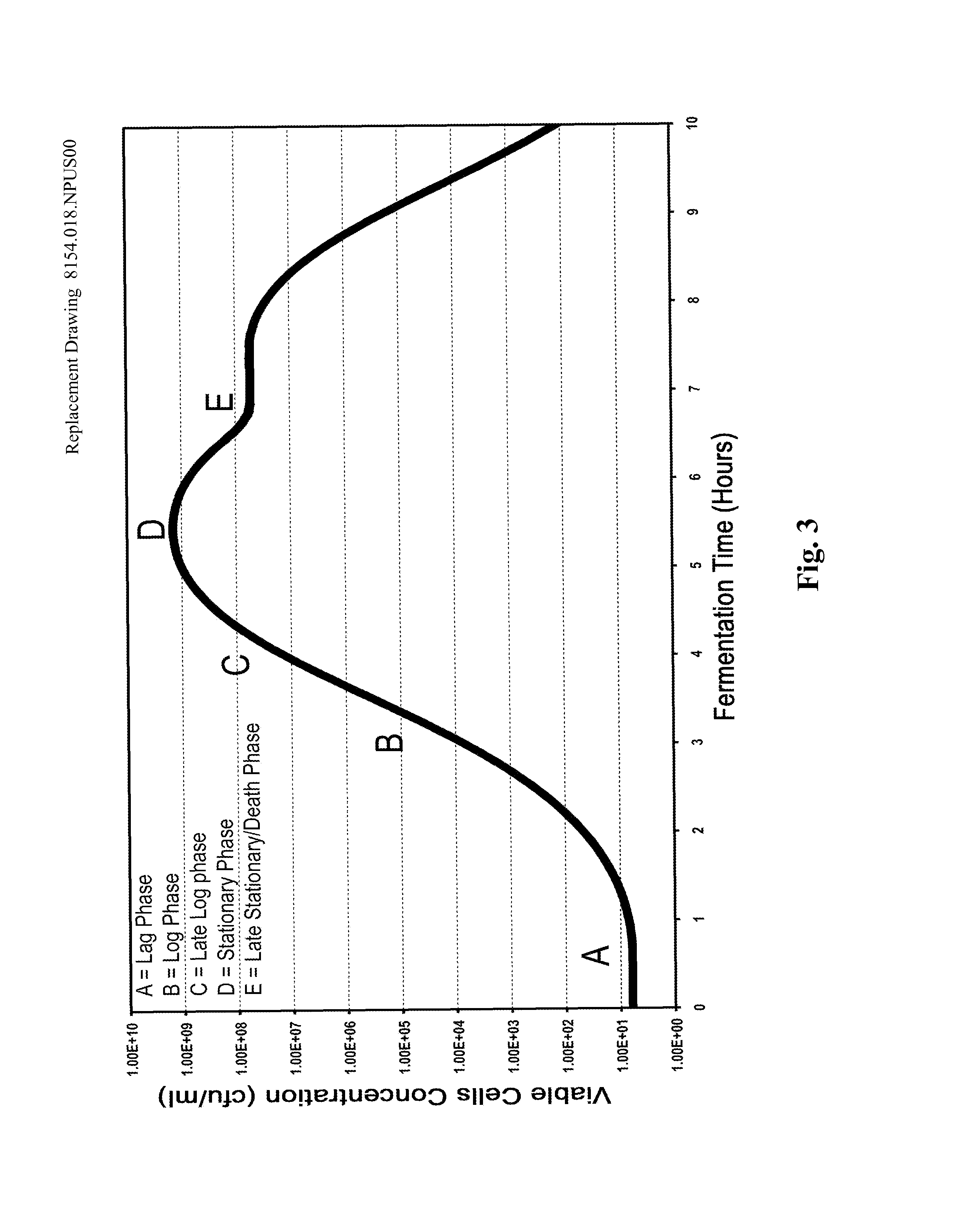
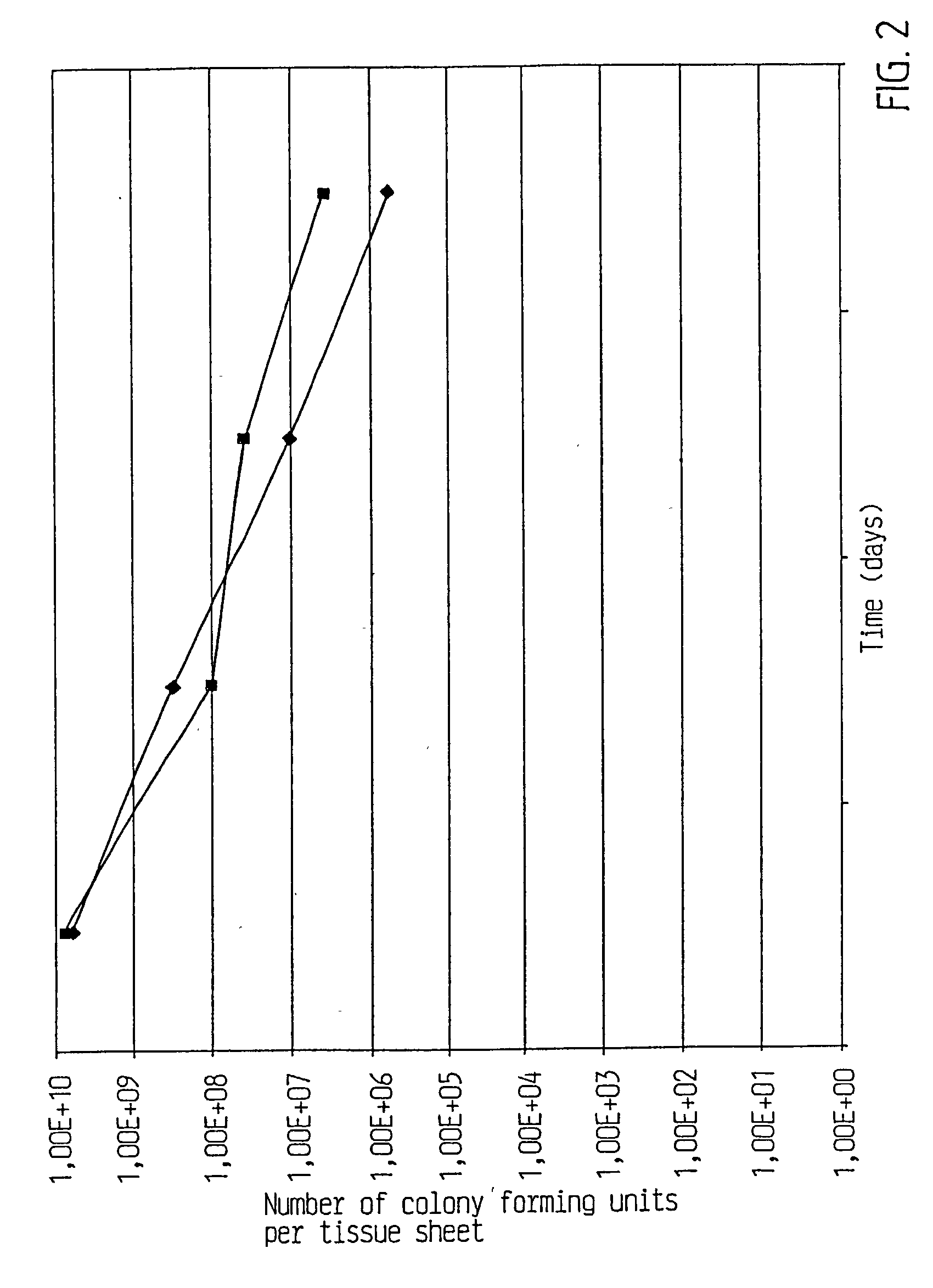
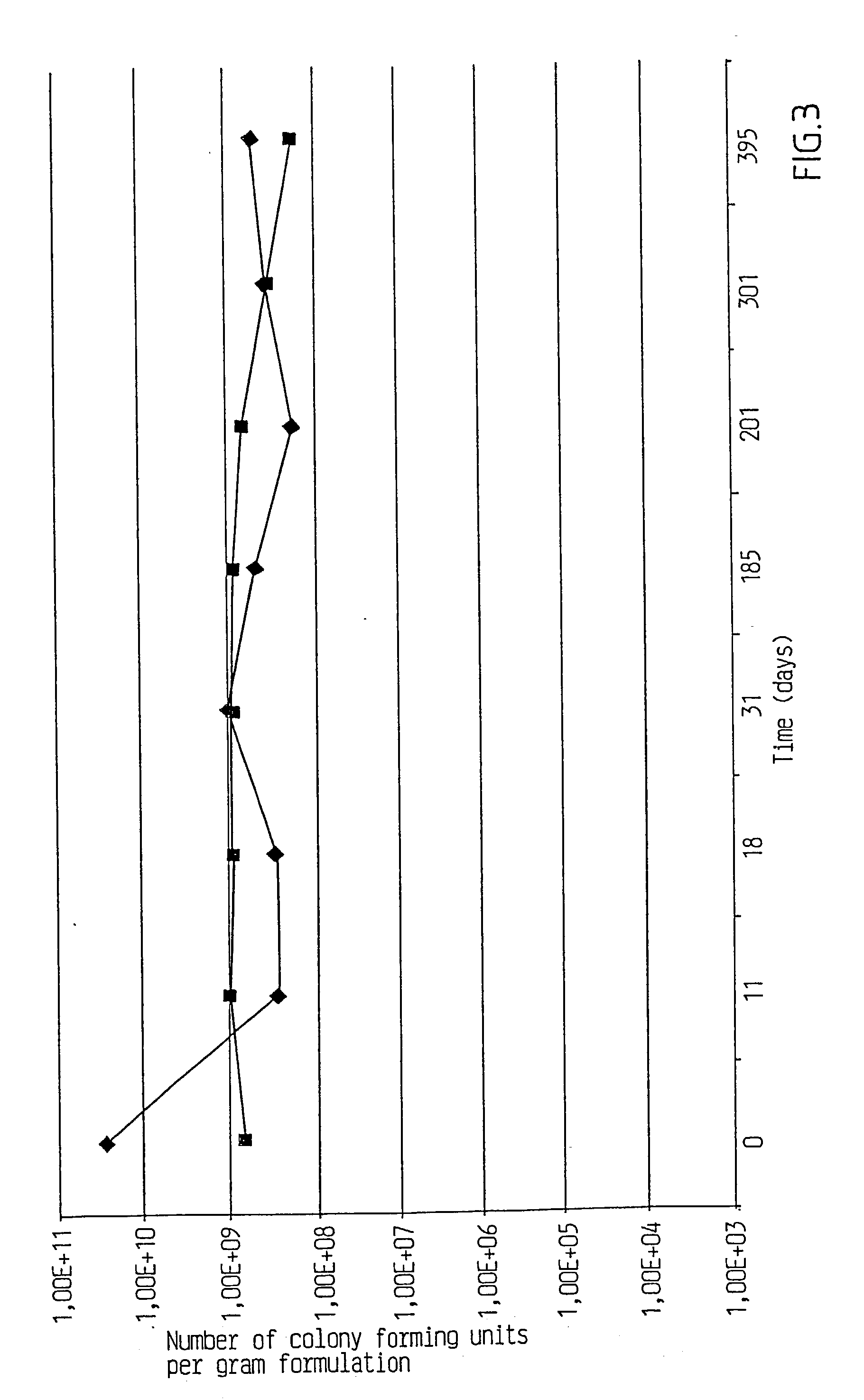
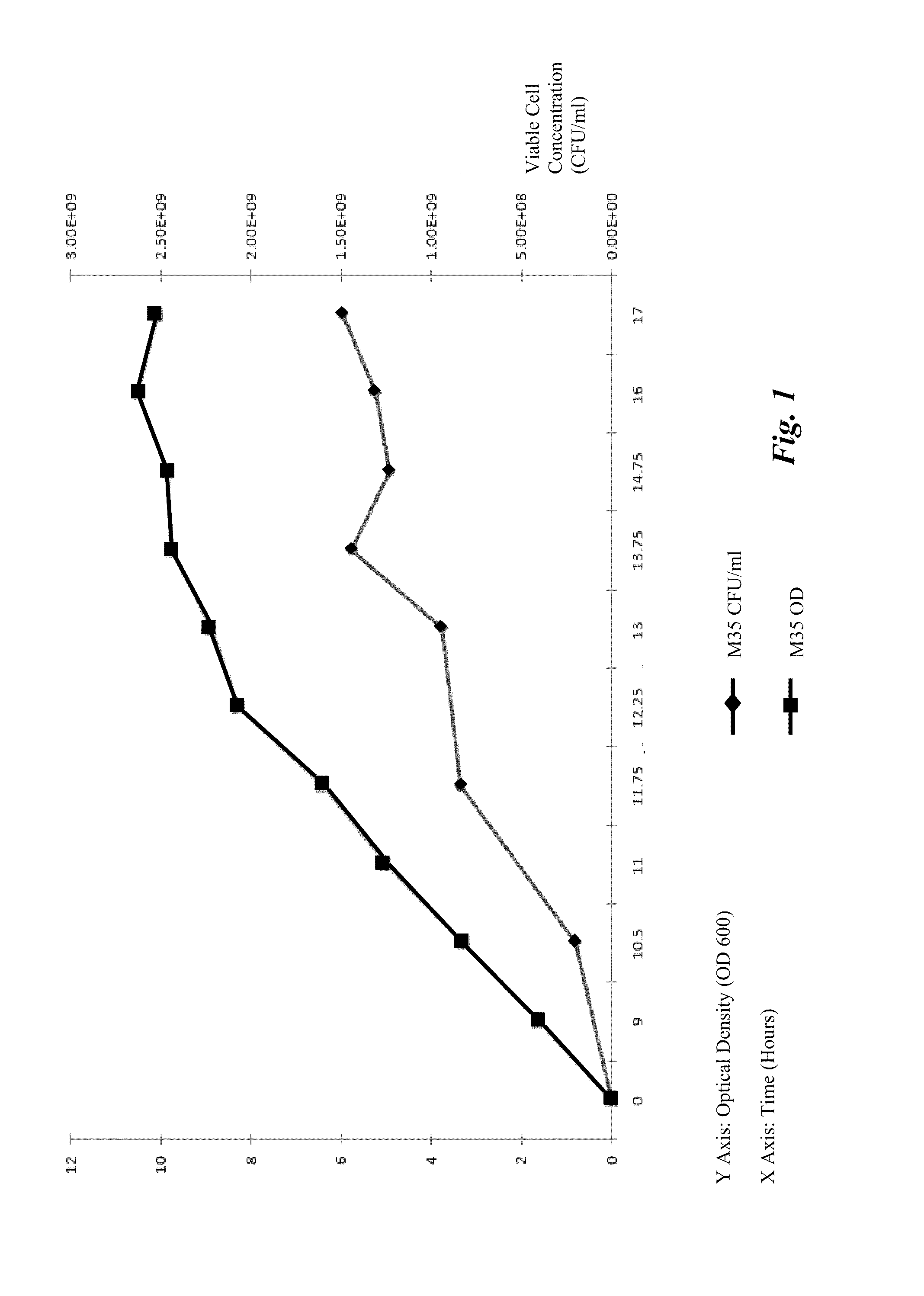
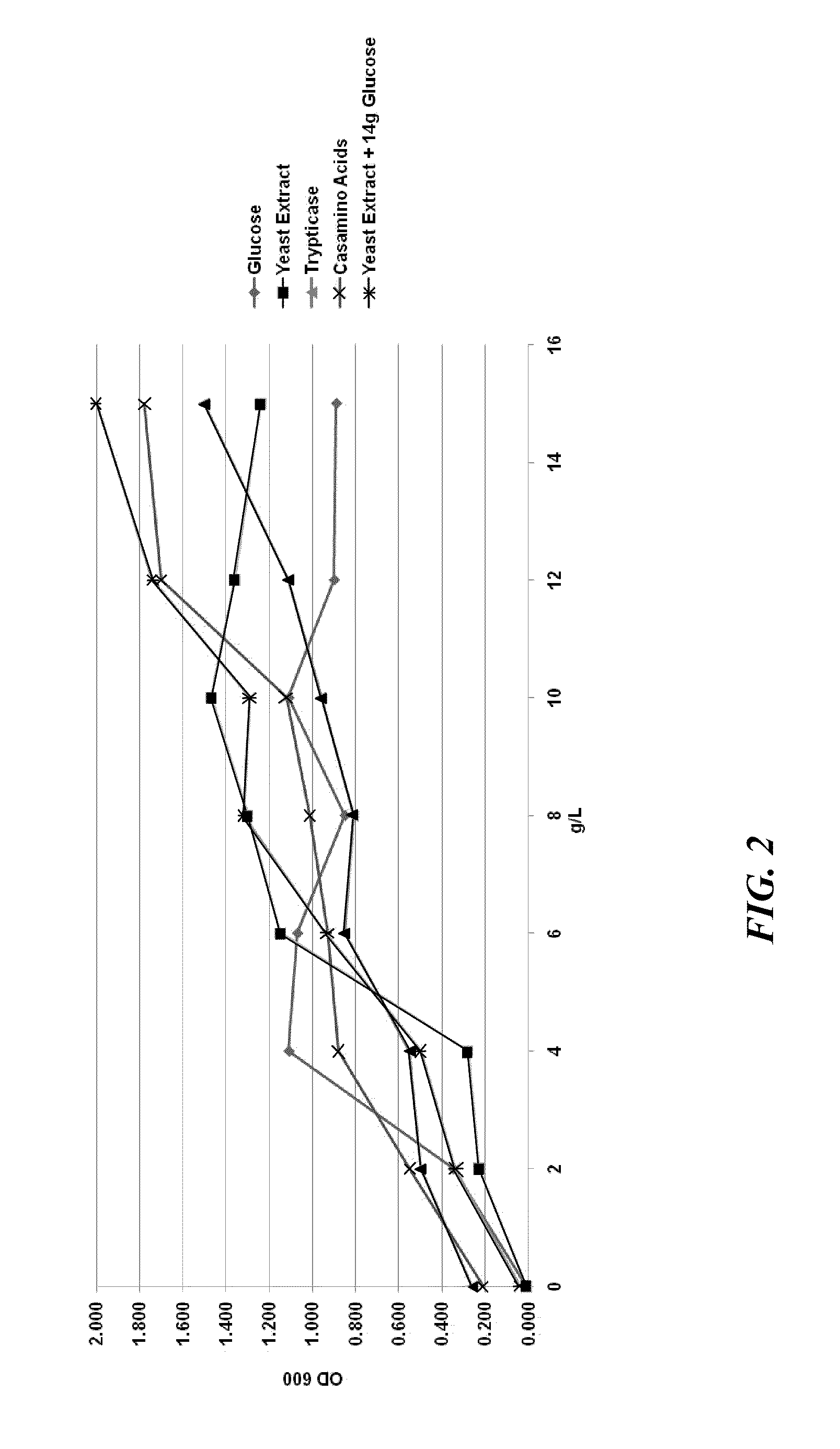
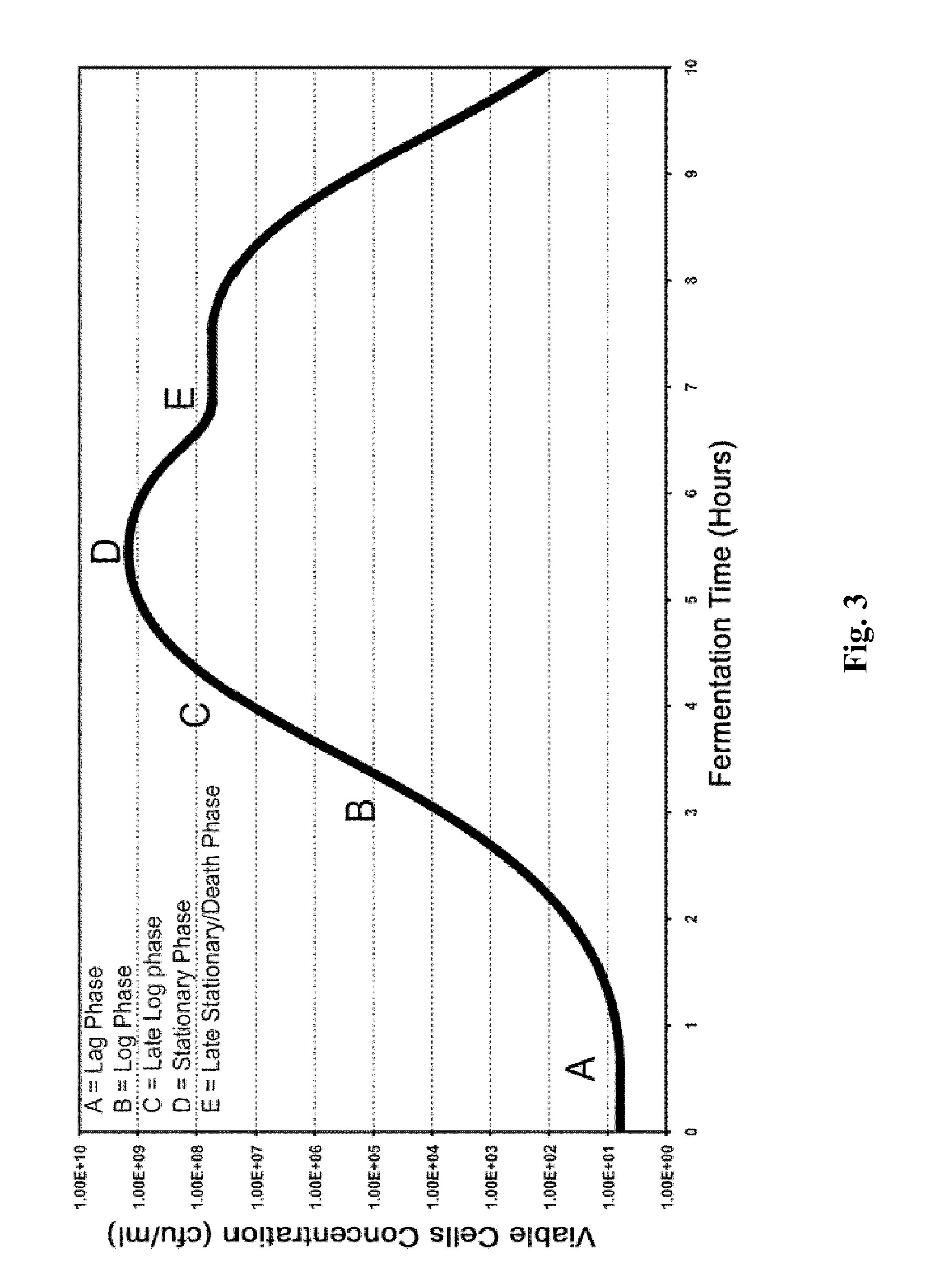
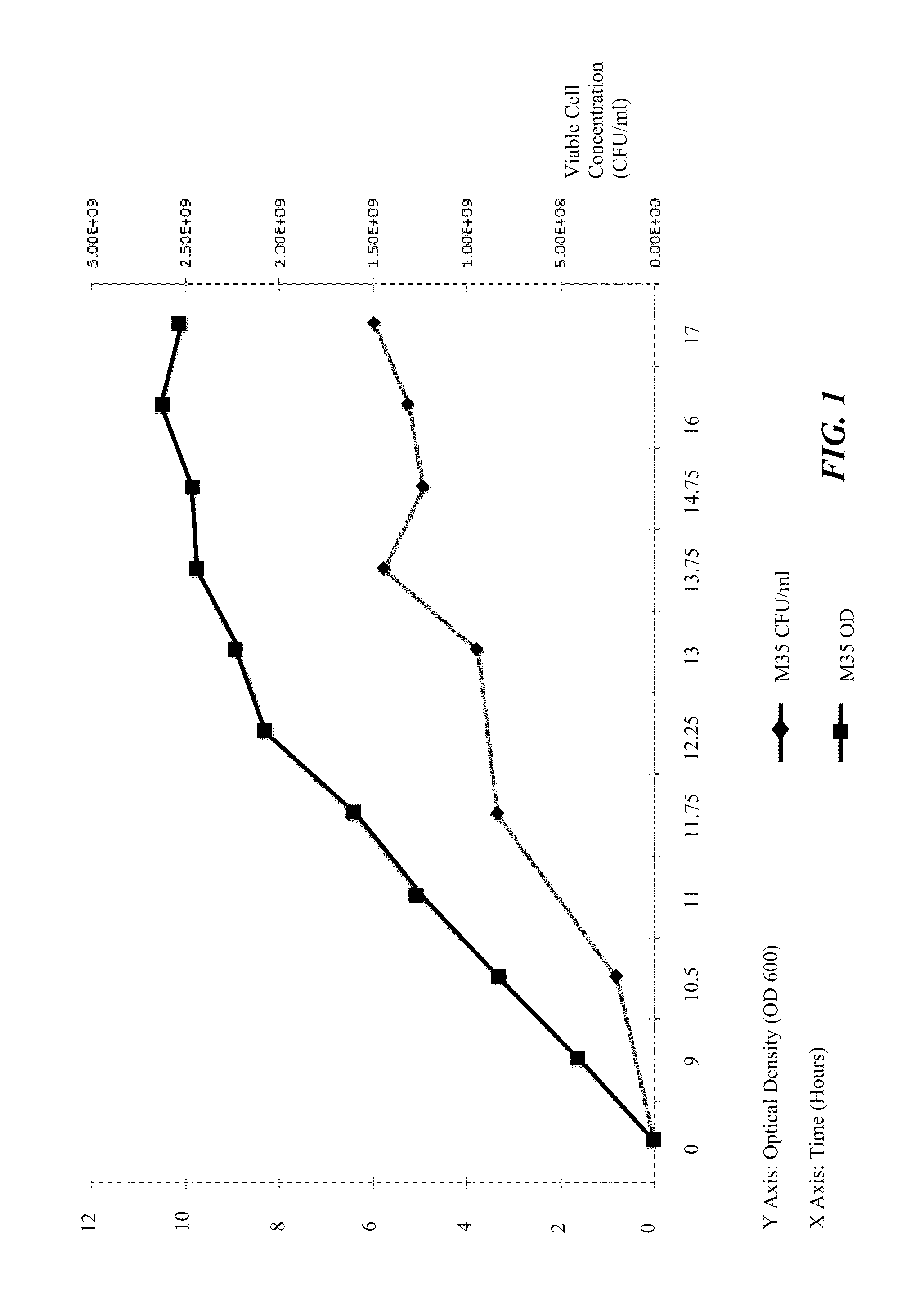
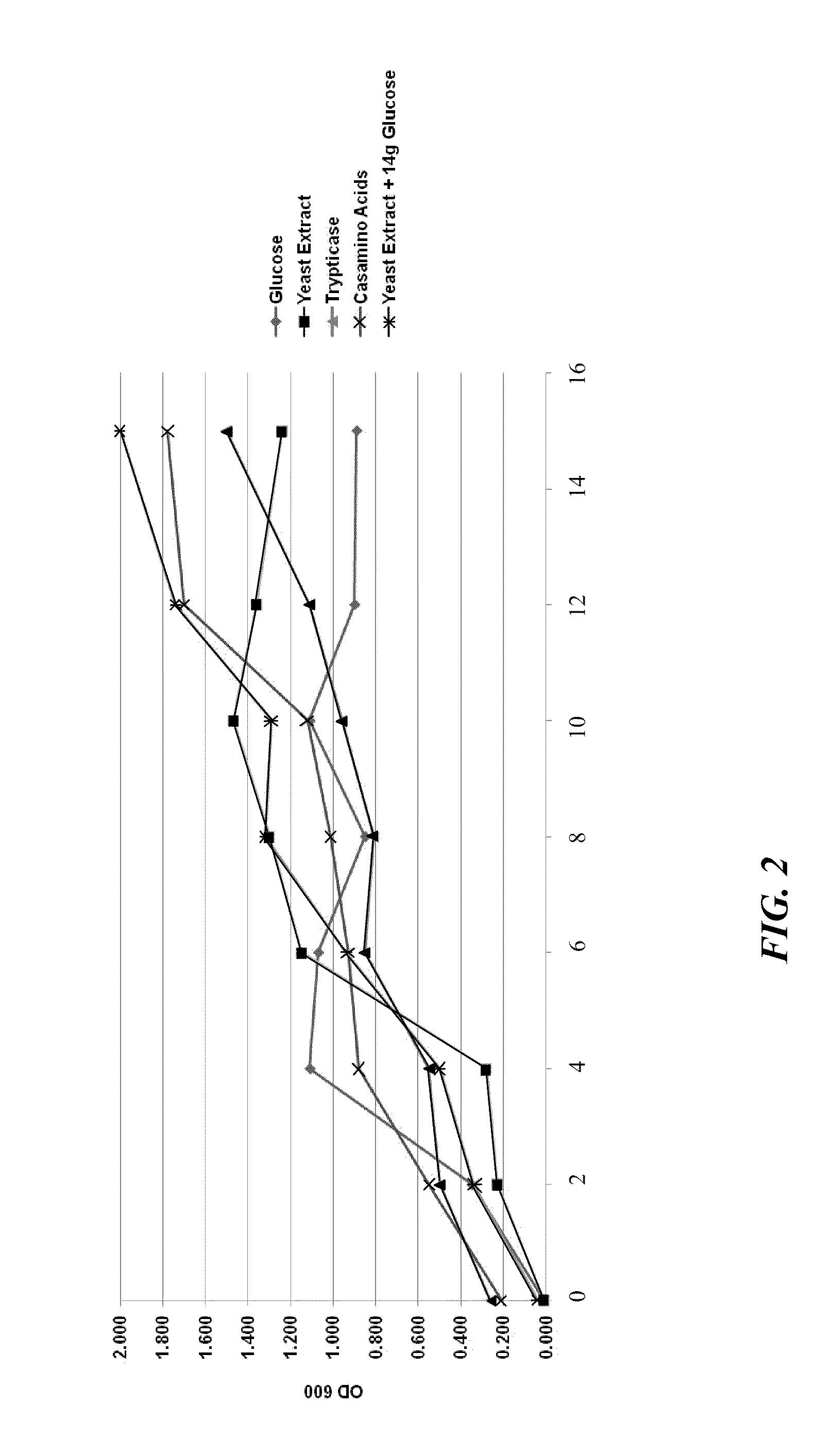
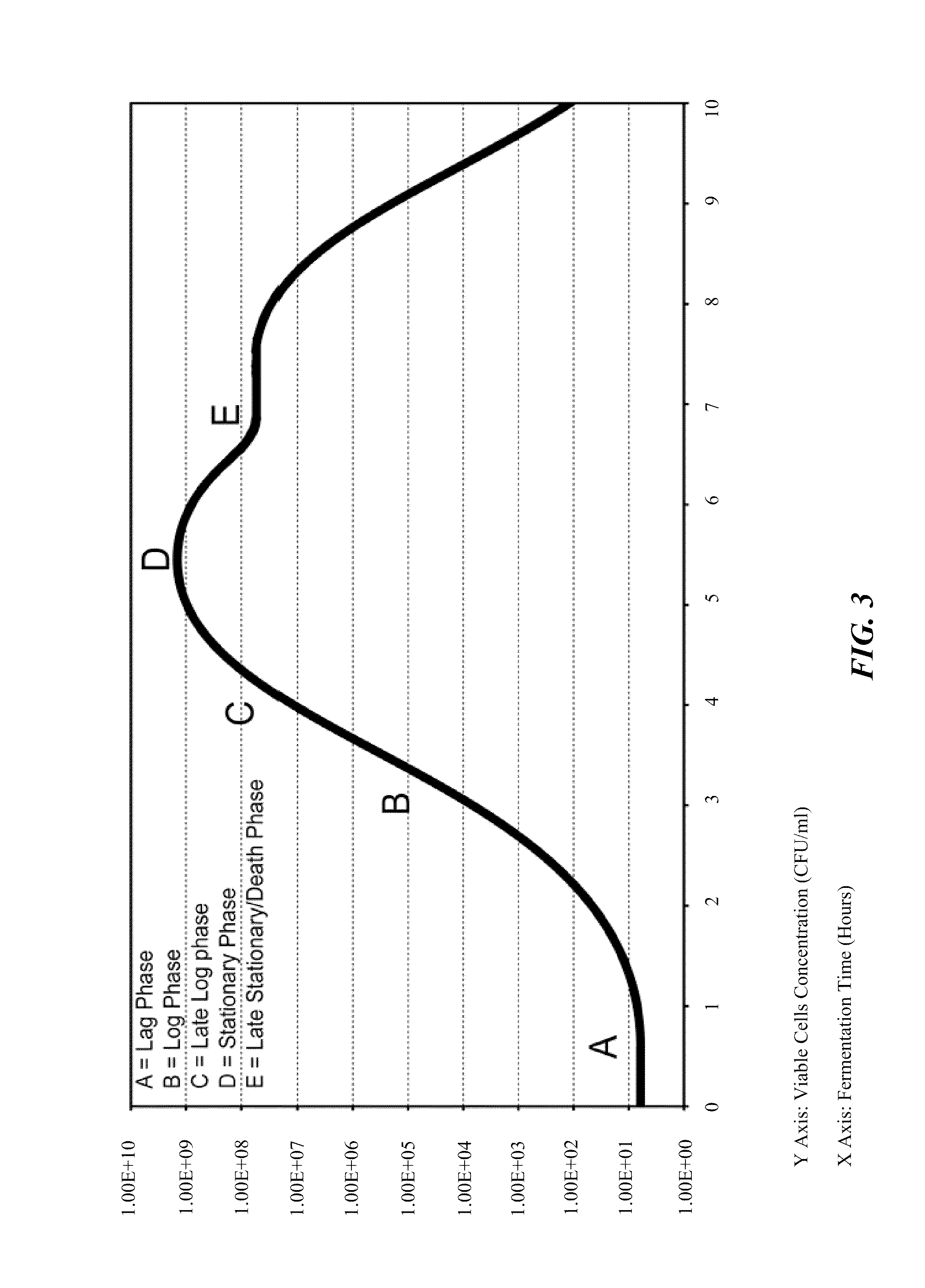
Processes to produce microorganisms that can be incorporated into a microbial-based product that results in high viable cell yields and shelf-stable products are disclosed. These microbial-based products are useful for inhibiting pathogenic growth and as a food additive. A preferred microorganism is the lactic acid producing bacteria, Lactobacillus amylovorus M35. In one embodiment, the process comprises inoculating a lactobacillus fermentation medium with M35 cells, harvesting the M35 cells at mid to late log phase, concentrating the M35 cells, and preserving the M35 cells at a concentration of at least 5×109 cfu / ml.
Owner:MICROBIOS
Probiotic, lactic acid-producing bacteria and uses thereof
InactiveUS7708988B2Good curative effectMitigating deleterious side-effectsAntibacterial agentsBiocideDiseaseMicrobial agent
The present invention discloses compositions and methodologies for the utilization of probiotic organisms in therapeutic compositions. More specifically, the present invention relates to the utilization of one or more species or strains of lactic acid-producing bacteria, preferably strains of Bacillus coagulans, for the control of gastrointestinal tract pathogens, including antibiotic-resistant gastrointestinal tract pathogens, and their associated diseases by both a reduction in the rate of colonization and the severity of the deleterious physiological effects of the colonization of the antibiotic-resistant pathogen. In addition, the present invention relates to the utilization of therapeutic compounds comprised of lactic acid-producing bacteria and anti-microbial agents such as antibiotics, anti-fungal compounds, anti-yeast compounds, or anti-viral compounds. The present invention also discloses methodologies for: (i) the selective breeding and isolation of probiotic, lactic acid-producing bacterial strains which possess resistance or markedly decreased sensitivity to anti-microbial agents (e.g., antibiotics, anti-fungal agents, anti-yeast agents, and anti-viral agents); and (ii) treating or preventing bacteria-mediated infections of the gastrointestinal tract by use of the aforementioned probiotic bacterial strains with or without the concomitant administration of antibiotics. While the primary focus is on the treatment of gastrointestinal tract infections, the therapeutic compositions of the present invention may also be administered to buccal, vaginal, optic, and like physiological locations.
Owner:GANEDEN BIOTECH
Hygiene product with a probiotic composition
InactiveUS20040243076A1Simple preparation processExtended shelf lifeSanitary towelsBaby linensBacterial strainTampon
A hygiene product, such as a sanitary napkin, diaper, panty liner, tampon, incontinence guard, hygiene tissue and the like, includes a probiotic composition having a bacterial preparation of at least one lactic acid producing bacterial strain and a contact sorption drying carrier dispersed in a lipid phase. A method for producing a hygiene product with lactic acid producing bacteria, dried with the aid of contact sorption drying carriers, in a lipid phase is provided. The manufacturing process for the hygiene product has the advantages of economy, simplicity and bacterial survival during manufacturing and subsequent storage.
Owner:SCA HYGIENE PROD AB
Probiotic, lactic acid-producing bacteria and uses thereof
InactiveUS20080233104A1Good curative effectMitigating deleterious side-effectsAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsDiseaseMicrobial agent
The present invention discloses compositions and methodologies for the utilization of probiotic organisms in therapeutic compositions. More specifically, the present invention relates to the utilization of one or more species or strains of lactic acid-producing bacteria, preferably strains of Bacillus coagulans, for the control of gastrointestinal tract pathogens, including antibiotic-resistant gastrointestinal tract pathogens, and their associated diseases by both a reduction in the rate of colonization and the severity of the deleterious physiological effects of the colonization of the antibiotic-resistant pathogen. In addition, the present invention relates to the utilization of therapeutic compounds comprised of lactic acid-producing bacteria and anti-microbial agents such as antibiotics, anti-fungal compounds, anti-yeast compounds, or anti-viral compounds. The present invention also discloses methodologies for: (i) the selective breeding and isolation of probiotic, lactic acid-producing bacterial strains which possess resistance or markedly decreased sensitivity to anti-microbial agents (e.g., antibiotics, anti-fungal agents, anti-yeast agents, and anti-viral agents); and (ii) treating or preventing bacteria-mediated infections of the gastrointestinal tract by use of the aforementioned probiotic bacterial strains with or without the concomitant administration of antibiotics. While the primary focus is on the treatment of gastrointestinal tract infections, the therapeutic compositions of the present invention may also be administered to buccal, vaginal, optic, and like physiological locations.
Owner:GANEDEN BIOTECH
Hygiene tissue
InactiveUS20030143262A1Easy to useEfficient transferBiocideCosmetic preparationsMicroorganismLactobacillus
A hygiene tissue to be used for cleaning and caring of the skin and the urogenital area, simultaneously delivers lactic acid producing bacteria, thereby establishing and maintaining a healthy microbial flora in these areas. The hygiene tissue is impregnated with a composition including a lactic acid producing bacterium / bacteria suspended in a lipid and optionally additional components. Encapsulating the lactic acid producing bacterium in a lipid provides a moisturefree environment enhancing the survival of the bacterium and keeping the bacterium fit for growth after delivery to the skin. By this approach, hygiene tissues, including lactic acid producing bacteria can be stored for long time periods. Also, the hygiene tissue improves the efficiency of transfer of the lactic acid producing bacterium to the skin and urogenital area. In addition, the lipid provides a cleaning function, so that the skin is cleaned simultaneously as the lactic acid bacteria is delivered.
Owner:SCA HYGIENE PROD AB
Process and composition for the manufacture of a microbial-based product
Processes to produce microorganisms that can be incorporated into a microbial-based product that results in high viable cell yields and shelf-stable products are disclosed. These microbial-based products are useful for inhibiting pathogenic growth and as a food additive. A preferred microorganism is a lactic acid producing bacteria. In one embodiment, the process comprises inoculating a lactobacillus fermentation medium with lactic acid producing bacterial cells, harvesting the lactic acid producing bacterial cells at mid to late log phase, concentrating the lactic acid producing bacterial cells, and preserving the lactic acid producing bacterial cells at a concentration of at least 5×109 cfu / ml.
Owner:MICROBIOS
Polymer matrix with lactic acid producing bacteria
InactiveUS20040241151A1Increasing bacterial survivalSpeed up the transfer processBiocideBacteriaPolymer scienceMoisture
Owner:SCA HYGIENE PROD AB
Process and composition for the manufacture of a microbial-based product
Processes to produce microorganisms that can be incorporated into a microbial-based product that results in high viable cell yields and shelf-stable products are disclosed. These microbial-based products are useful for inhibiting pathogenic growth and as a food additive. A preferred microorganism is the lactic acid producing bacteria, Lactobacillus amylovorus M35. In one embodiment, the process comprises inoculating a lactobacillus fermentation medium with M35 cells, harvesting the M35 cells at mid to late log phase, concentrating the M35 cells, and preserving the M35 cells at a concentration of at least 5×109 cfu / ml.
Owner:MICROBIOS
Methods for inhibiting microbial infections associated with sanitary products and for enhancing sanitary product degradation, systems and compositions
InactiveUS20060177429A1Prevent and inhibit infectionGrowth inhibitionBiocideBacteria material medical ingredientsBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The present invention describes compositions and methods for inhibiting microbial infections associated with the use of sanitary products, such as diapers, bandages, sanitary napkins, tampons, and the like. The present invention comprises providing for use a sanitary product containing an effective amount of a viable, non-pathogenic, lactic acid-producing bacteria, such as Bacillus coagulans, or an extracellular product thereof, useful for inhibiting growth of parasites and pathogens on the epithelial tissue in contact with the sanitary product during use of the product. The present invention also provides for enhancing biodegradation of sanitary products after use and disposal. Also described herein are methods using the product and systems containing the compositions.
Owner:GANEDEN BIOTECH
Methods for reducing cholesterol using Bacillus coagulans spores, systems and compositions
The invention describes therapeutic compositions including a lactic acid-producing bacteria, such as isolated Bacillus coagulans, in combination with a bifidogenic oligosaccharides or other cholesterol-reducing agents for use in reducing LDL cholesterol and serum triglycerides. Also described are therapeutic methods using the compositions and systems containing the therapeutic compositions.
Owner:GANEDEN BIOTECH
Compositions containing probiotics and polysaccharides and methods of use
InactiveUS20050186188A1Simple compositionImproved host defenseBiocideOrganic active ingredientsMicroorganismPathogenic bacteria
Compositions and methods are provided for improving GI tract health by reducing the level of pathogenic bacteria present. The compositions comprise probiotic microorganisms, such as a lactic acid producing bacteria or a yeast and mannanoligosaccharide. Optionally, the compositions may further comprise fructooligosaccharide. Methods for administering the composition to improve GI tract health are also provided.
Owner:JARROW FORMULAS INC
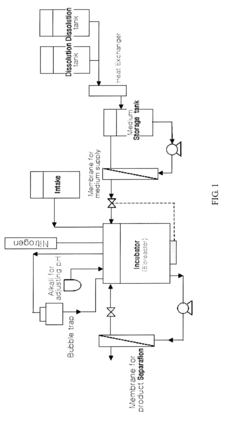
Method for producing high concentrate lactic acid bacteria with membrane bioreactor and freeze-dried, lactic acid bacteria powder
InactiveUS20120064606A1Good chemical stabilityImprove physical stabilityBacteriaUnicellular algaeHigh concentrationLactic acid bacterium
The present invention relates to a method for producing lactic acid bacteria of a high concentration continuously using a membrane bioreactor. Specifically, the present invention relates to a method for producing lactic acid bacteria of a high concentration in a membrane bioreactor that comprises the steps of cultivating lactic acid bacteria in a membrane bioreactor including a membrane for product separation and a medium supply apparatus; supplying culture media to the bioreactor through the medium supply apparatus; continuously separating and discharging culture filtrate through the membrane for product separation; and recycling lactic acid bacteria continuously to the bioreactor. Additionally, the present invention relates to a method for producing lactic acid bacteria powder by freeze drying the bacteria produced in the membrane bioreactor using a freeze drying preservative composition. The lactic acid bacteria obtained through the membrane bioreactor is obtained in pellet form with a centrifugal separator, and is subjected to freeze-drying using the composition for freeze drying preservative containing certain amounts of trehalose, maltodextrin, starch and sodium carboxy methyl cellulose to form lactic acid powder. The lactic acid bacteria that have been converted into powder by such method exhibit superior stability chemically and physically compared to lactic acid bacteria powder that has been subjected to simple freeze drying.
Owner:LACTOMASON CO LTD
Preparation method of livestock and poultry acidification and glycolysis feed
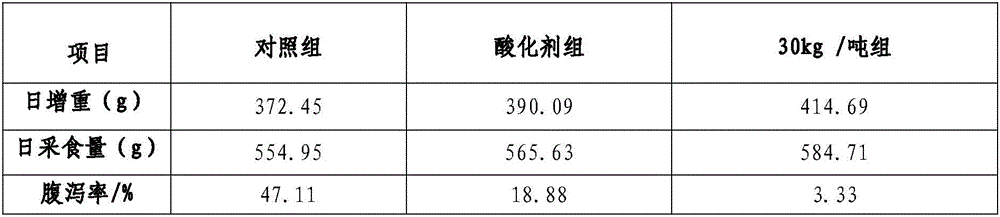
InactiveCN105639090ALow digestibilityLow in Anti-Nutritional FactorsAnimal feeding stuffNutrientLactic acid fermentation
The invention relates to a preparation method of a livestock and poultry acidification and glycolysis feed. The method comprises the following steps: crushing a starch-containing product, mashing the crushed starch-containing product, carrying out enzymatic hydrolysis to prepare a residue-containing saccharification liquid or carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain a residue-free saccharification liquid; inoculating the residue-containing saccharification liquid to citric acid producing strains, and carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain acid residues and a citric acid fermentation liquid; inoculating the residue-free saccharification liquid to lactic acid production strains, fermenting the inoculated saccharification liquid, and acidifying the fermented saccharification liquid to prepare a lactic acid fermentation liquid; concentrating one or more of the lactic acid fermentation liquid and the citric acid fermentation liquid to prepare an organic acid concentrate liquid; mixing one or more of sugar residues and acid residues with a feed raw material, a composite strain liquid and a compound enzyme, and carrying out enzymatic hydrolysis fermentation to prepare glycolysis residue meal; and mixing the organic acid concentrate liquid and the glycolysis residue meal with one or more of feeding inorganic acids, organic acid salts, carbohydrates and grease to prepare the livestock and poultry acidification and glycolysis feed. The livestock and poultry acidification and glycolysis feed prepared in the invention is rich in organic acids, small peptides, oligosaccharides, probiotics and other nutrients, and has the characteristics of diarrhea resistance, good palatability and easy digestion.
Owner:FLSUGARPEPTIDE BIOLOGY ENG
Methods for reducing cholesterol using Bacillus coagulans spores, systems and compositions
The invention describes therapeutic compositions including a lactic acid-producing bacteria, such as isolated Bacillus coagulans, in combination with a bifidogenic oligosaccharides or other cholesterol-reducing agents for use in reducing LDL cholesterol and serum triglycerides. Also described are therapeutic methods using the compositions and systems containing the therapeutic compositions.
Owner:GANEDEN BIOTECH
Lactic acid bacteria cultures that inhibit food-borne pathogens
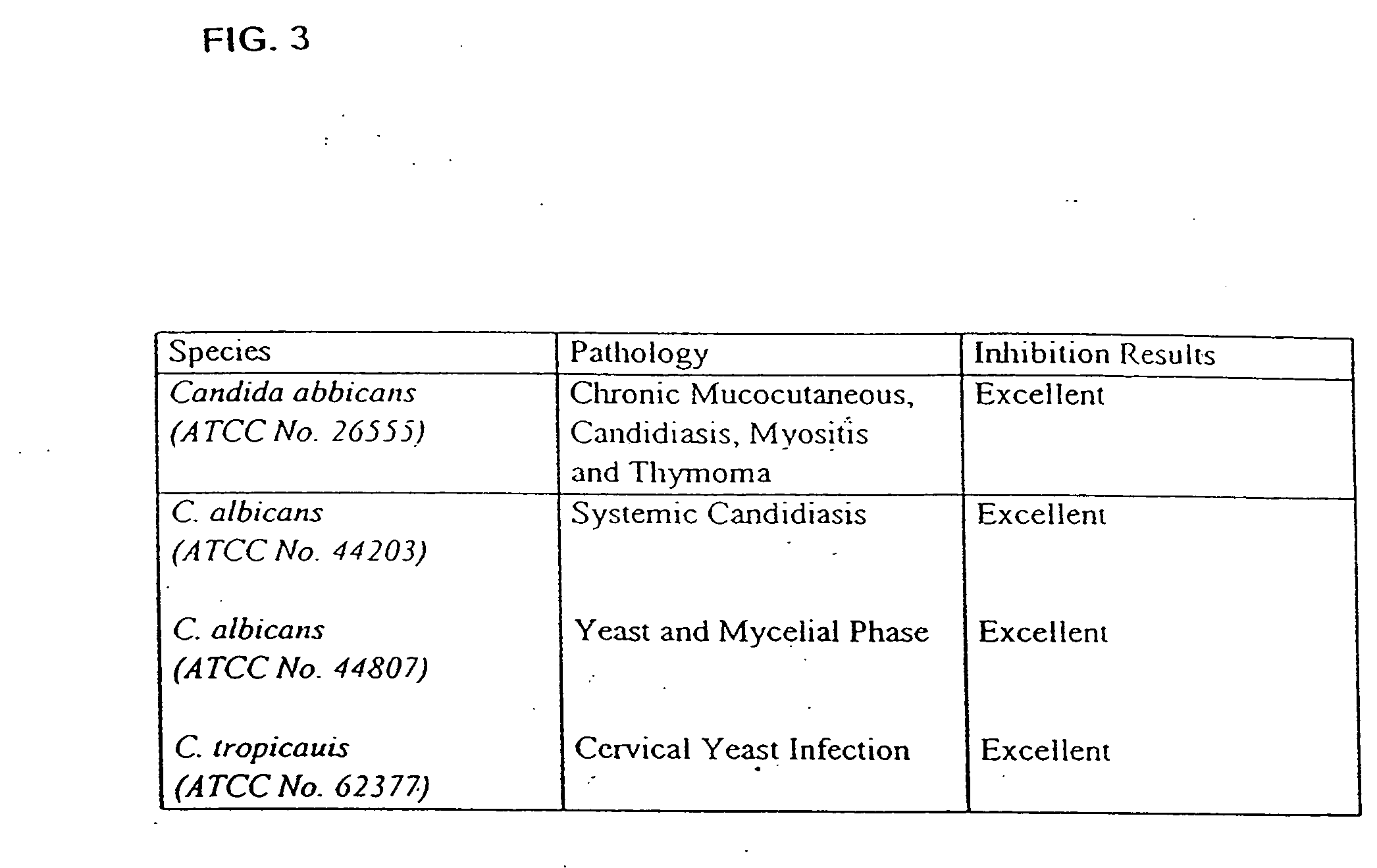
The present invention provides methods and compositions for preventing or inhibiting human food-borne pathogens in animals, and methods for increasing feed efficiency in animals by administering to the animal effective amounts of probiotic lactic acid producing bacteria. Further provided are feed compositions comprising probiotic lactic acid producing bacteria. A preferred probiotic lactic acid producing bacteria is Lactobacillus acidophilus strain ATCC accession number PTA-5249. This bacterial strain inhibits nalidixic acid-resistant Escherichia coli 0157:H7.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF NEBRASKA
Wound or tissue dressing comprising lactic acid bacteria
InactiveCN101641121ARelieve symptomsReduce the severity of the diseaseAbsorbent padsBandagesVagococcusBacteroides
The present invention is directed to a wound or tissue dressing comprising a bacteria having the property of producing lactic acid from sugars by fermentation of the sugars. The bacteria preferably belongs to the family of lactic acid bacteria. The family of lactic acid bacteria refers to any bacteria belonging to a genus selected from the group consisting of Carnobacterium, Enterococcus, Lactobacillus, Lactococcus, Leuconostoc, Oenococcus, Pediococcus, Streptococcus, Tetragenococcus, Vagococcus and Weissella. There is also provided a wound or tissue dressing comprising an absorbent compound for absorbing wound exudate, wherein said wound or tissue dressing is attached to or comprises a lactic acid bacterium. The utility of the present invention is demonstrated by use of the wound or tissue dressings in methods for treating a wound or damaged tissue in an individual, said method comprising the steps of contacting said wound or damaged tissue with the wound or tissue dressing accordingto the invention, thereby treating the wound or damaged tissue. The treatment results in healing of the wound or in accelerated healing of the wound. There is also provided the use of a lactic acid bacteria in the manufacture of a wound or tissue dressing for treating or accelerating the healing of a wound in an individual.
Owner:FERROSAN MEDICAL DEVICES
Improved meat slurry methods of production and compositions
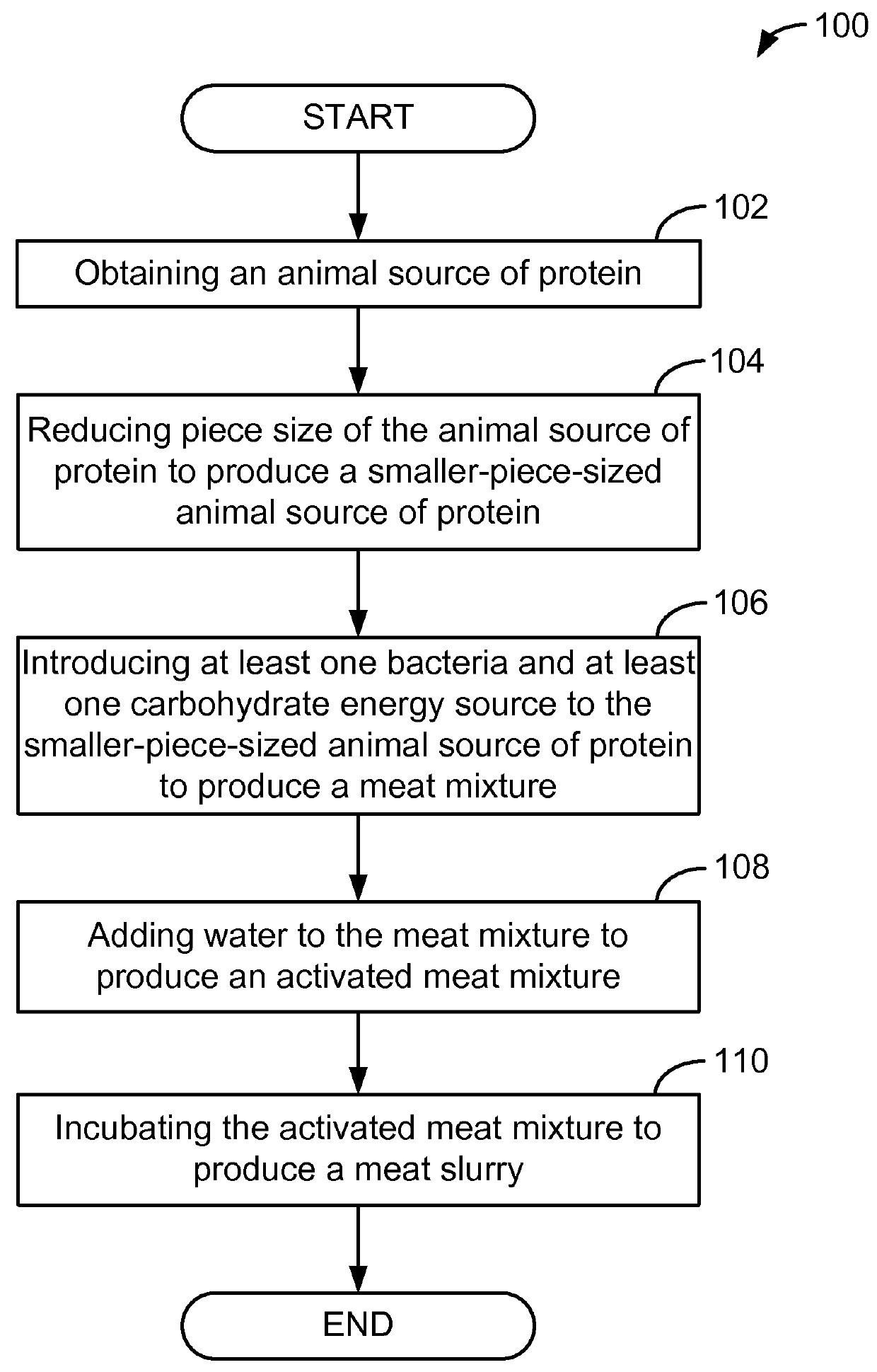
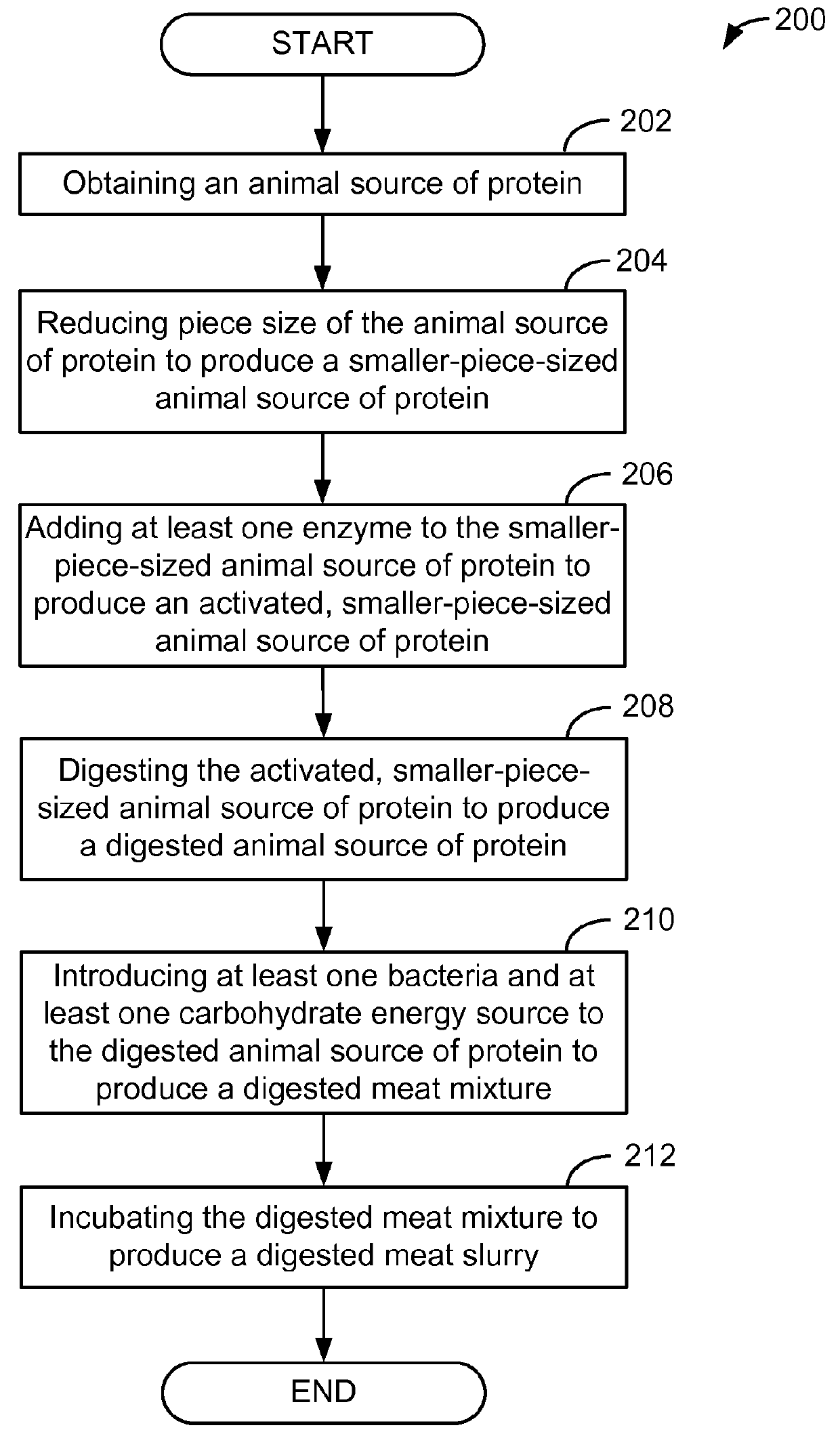
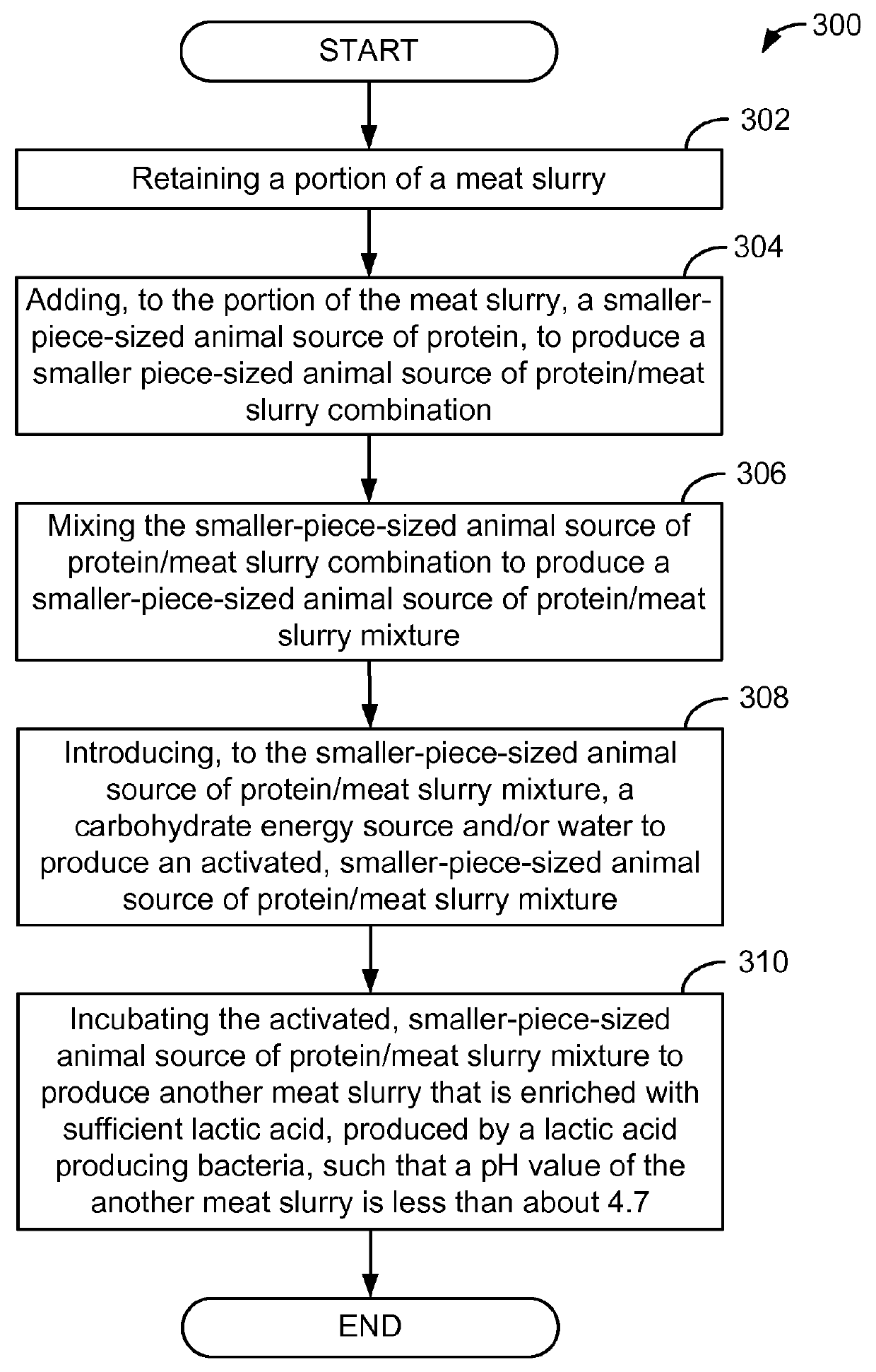
InactiveUS20160029667A1Sufficient amountSmall sizeMilk preparationAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyAnimal protein
A process for producing a meat slurry is described. The process includes: (i) obtaining an animal source of protein; (ii) reducing piece size of the animal source of protein to produce a smaller-piece-sized animal source of protein; (iii) introducing one or more types of lactic acid producing bacteria and at least one carbohydrate energy source to the smaller-piece-sized animal source of protein to produce a meat mixture; (iv) adding water to the meat mixture to produce an activated meat mixture; (v) incubating the activated meat mixture to produce a meat slurry; and wherein the activated meat mixture has a pH value that is greater than about 5.0, and wherein prior to incubating, the lactic acid producing bacteria is present on the meat mixture in an amount that is at least about 1×107 colony forming units (“CFU”) of lactic acid producing bacteria per gram of said meat mixture, and wherein after incubating, the lactic acid producing bacteria produces lactic acid in an amount that is sufficient to maintain a pH of the meat slurry at a value that is no greater than about 4.7.
Owner:MICRO NATURE
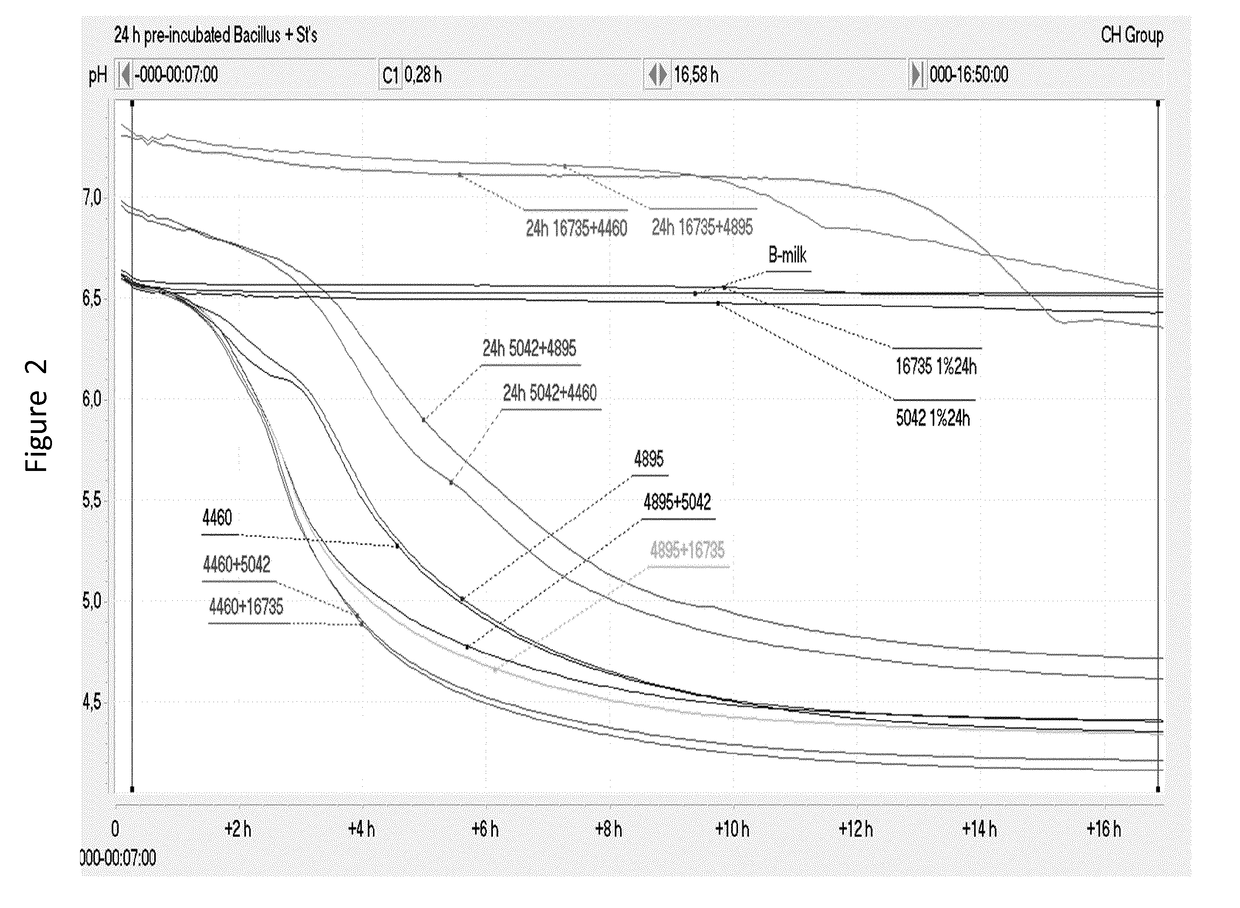
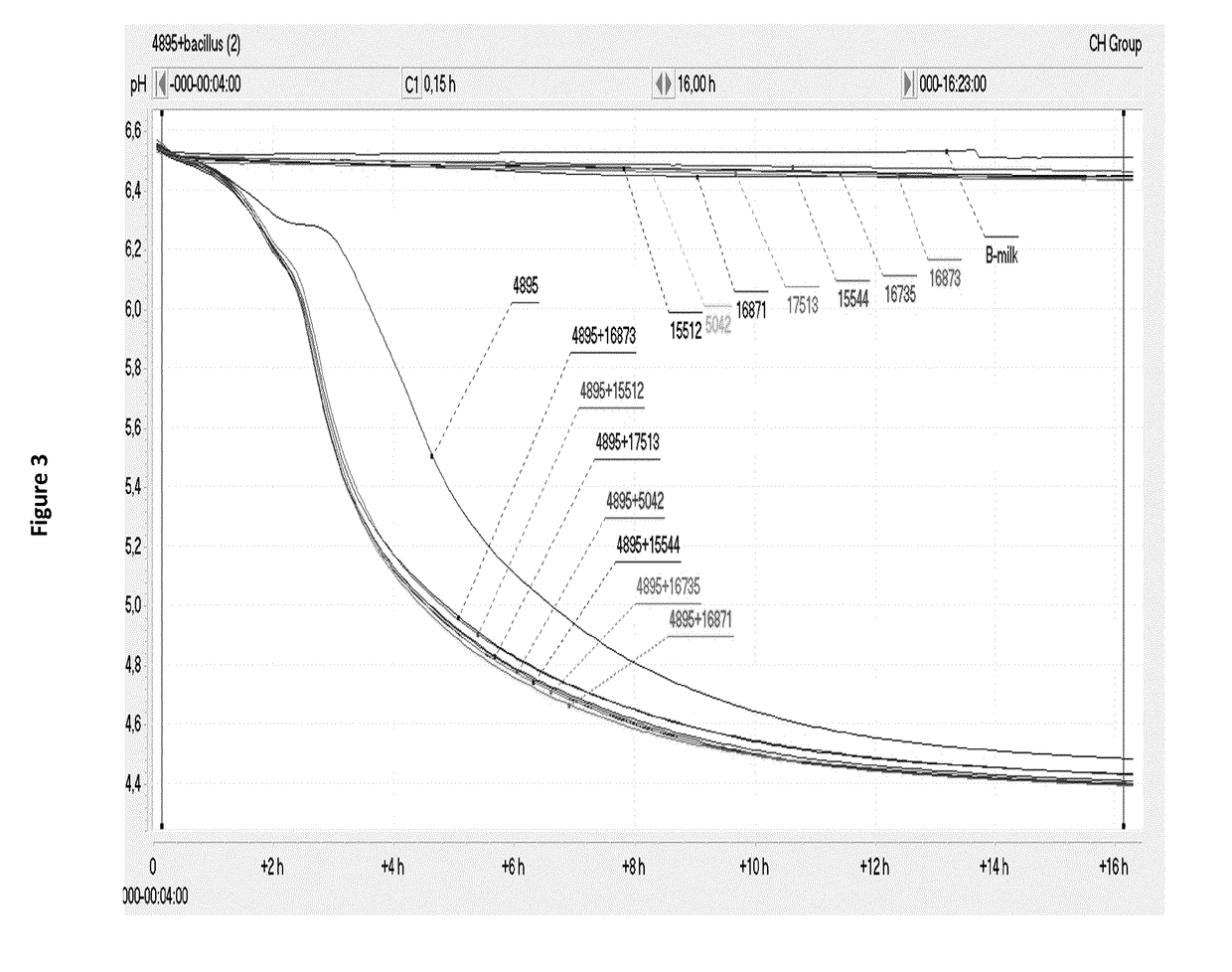
Fermented milk inoculated with both lactic acid bacteria (LAB) and bacillus
ActiveUS20180199582A1Reduce the amount of solutionImprove propertiesMilk preparationLactobacillusLactic acid bacteriumBiotechnology
A method for producing a lactic acid bacteria fermented milk product comprising fermenting milk with both inoculated lactic acid bacteria (LAB) and inoculated Bacillus bacteria.
Owner:CHR HANSEN AS
Bacteriocins and novel bacterial strains
InactiveUS7132102B2Reducing level of colonizationDecrease in levelAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacteroidesBacterial strain
Novel bacteriocins and / or the novel lactic acid-producing strains are used for at least reducing the levels of colonization by at least one target bacteria in animals, especially poultry.
Owner:US SEC AGRI +1
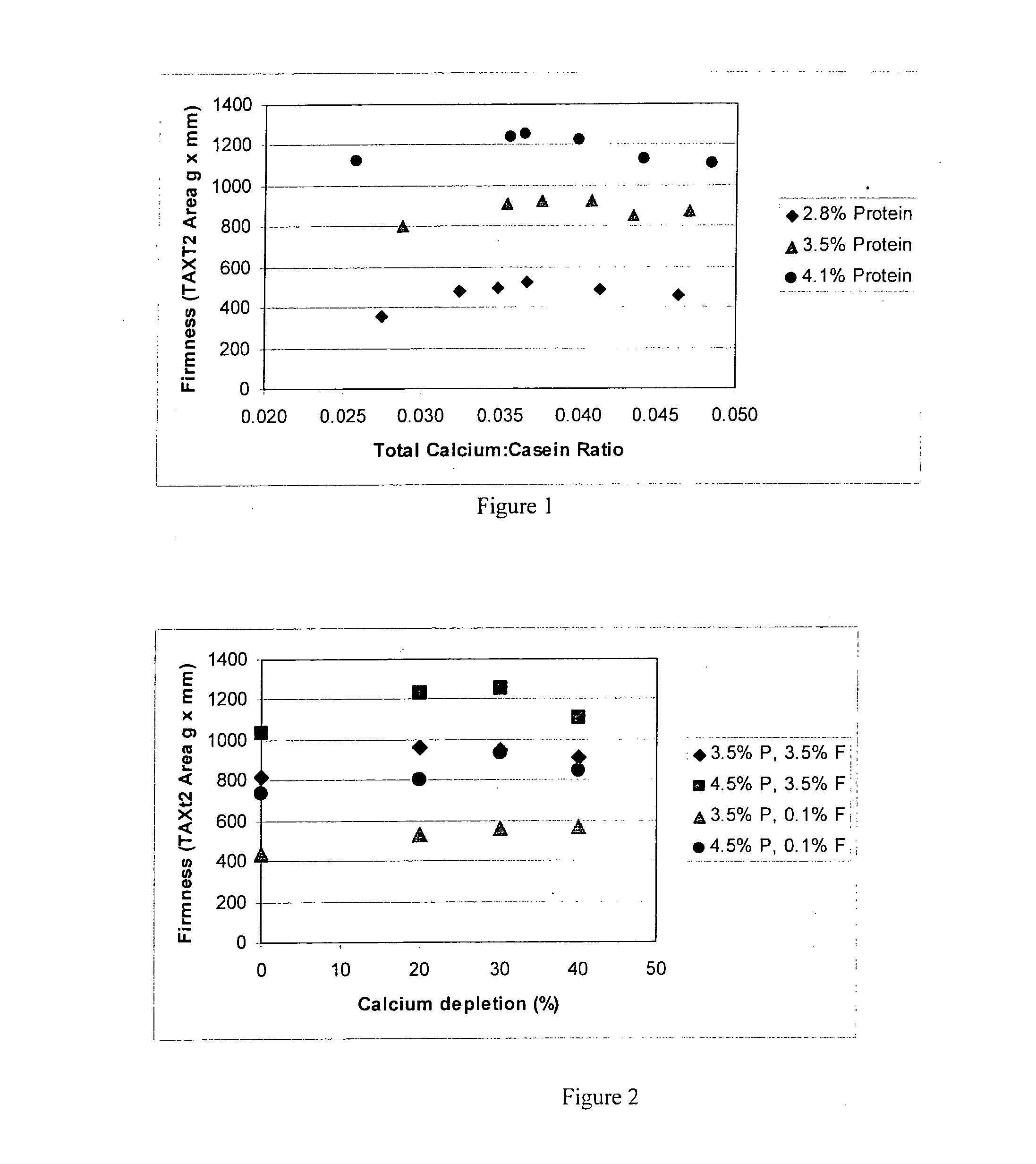
Dairy Product and Process
InactiveUS20100143538A1Reduce syneresis)Increase textural firmnessMilk preparationCheese manufactureAdditive ingredientPotassium
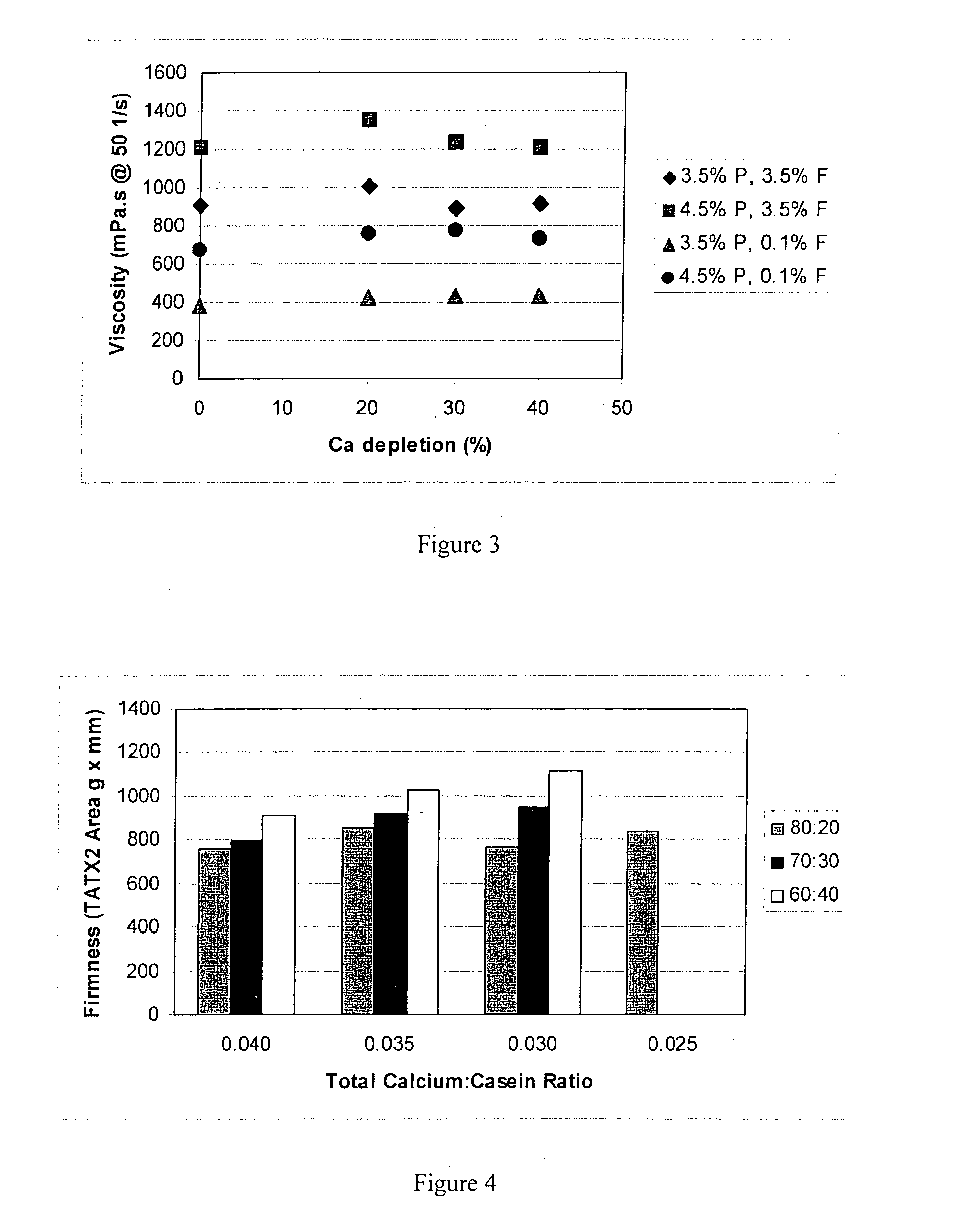
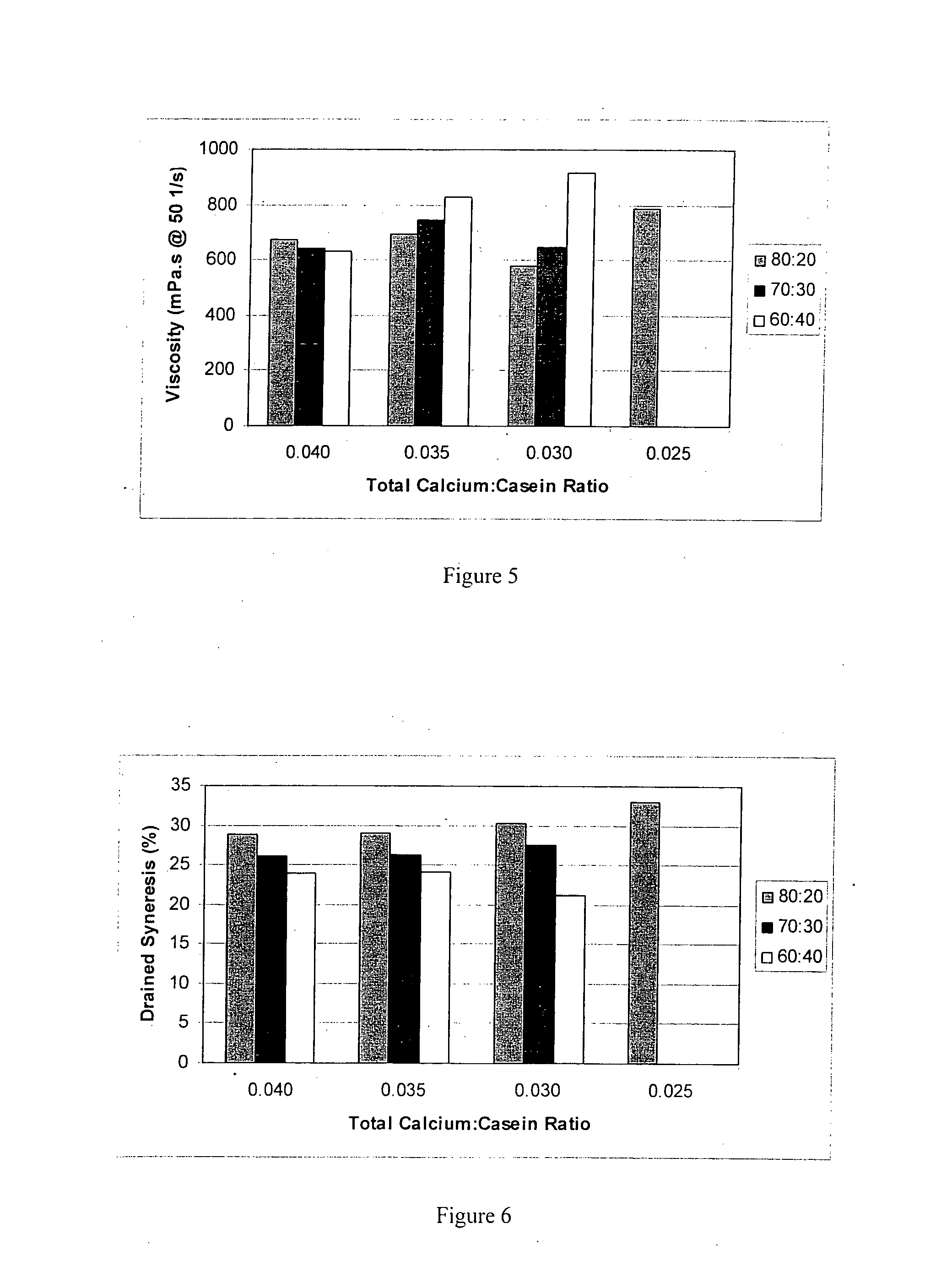
A method for preparing a yoghurt is provided. The method comprises (a) preparing a calcium-depleted milk composition comprising either (i) calcium-depleting a starting milk composition, or (ii) including within a starting milk composition a calcium-depleted milk ingredient selected from milk, fat standardised milk, skim milk, or milk concentrate; and (b) acidifying the calcium-depleted milk composition with chemical acidification or lactic acid producing bacteria, to prepare a yoghurt, wherein the calcium depletion is by contacting the milk composition or ingredient with a cation exchanger to replace calcium in the composition or ingredient with sodium or potassium.
Owner:FONTERRA COOP GRP LTD
Preparing method for livestock and poultry acidified calcium salt glycolysis feed
InactiveCN106260543AHigh calcium absorptionAntidiarrhealFood processingAnimal feeding stuffDiarrheaFermentation
The invention relates to a preparing method for livestock and poultry acidified calcium salt glycolysis feed. The preparing method comprises the steps that starch substances are prepared into pulp and subjected to enzymolysis and saccharification, then a lactic acid producing strain is inoculated for fermentation, calcium hydroxide is fed in batches for fermentation, calcium lactate fermentation liquor including the thalli and lactic acid is obtained, solid-liquid separation and concentration are carried out, and then a thallus acid residue wet base and concentrated calcium lactate liquor containing lactic acid are obtained; after starch substances are prepared into pulp and subjected to enzymolysis and saccharification, a citric acid producing strain is inoculated for fermentation, solid-liquid separation and concentration are carried out, and then a citric acid residue wet base and concentrated citric acid liquor are obtained; one or more of a sugar residue wet base, the thallus acid residue wet base and the citric acid residue wet base are mixed with feed raw materials, clean water, compound bacteria and a complex enzyme, then glycolysis is carried out, and a glycolysis residue wet base is obtained; the concentrated calcium lactate liquor, the concentrated citric acid liquor and the glycolysis residue wet base are mixed, and the livestock and poultry acidified calcium salt glycolysis feed is obtained. The feed prepared with the method contains rich citric acid, calcium lactate, lactic acid, small peptide, oligosaccharide and other nutritional ingredients, and has the advantages of being high in calcium absorbing rate, capable of resisting diarrhea, good in palatability and the like.
Owner:FLSUGARPEPTIDE BIOLOGY ENG
Sanitary article comprising lactobacilli in a hydrophilic carrier
InactiveUS20100136210A1Satisfactory storage stabilityGuaranteed water absorptionCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsPolymer scienceWater activity
A sanitary article such as a sanitary napkin, a panty liner, an incontinence protector, a diaper, an incontinence pad, a feminine insert, a tampon, hygiene tissue or the like, includes lactic acid producing bacteria being dispersed in a carrier. The dispersion is applied on or in parts of the final sanitary article. The carrier is a hydrophilic carrier and the dispersion has a viscosity of 110 Pa·s or lower, at a temperature of 35° C., and a water activity below 0.2.
Owner:SCA HYGIENE PROD AB
Lactic Acid Bacteria And Their Use As Dietary Supplementals For Poultry
InactiveUS20140328815A1Reducing pathogenic infectionImprove feeding efficiencyBiocideBacterial antigen ingredientsLactobacillusFowl
Methods and compositions are hereby disclosed for enhancing weight gain and feed efficiency in a bird, such as a chicken, a turkey, or a laying hen, among others. The methods include administering to the bird a lactic acid producing bacterium (LAB) or combination of LABs. The disclosed methods and compositions also help reduce pathogen infection in the bird and reduce incidence of pathogen contamination in eggs produced by laying hens.
Owner:CHR HANSEN AS
Potato starch processing juice lactic acid beverage and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106107335AStability impactImprove filtration efficiencyFood ingredient as antioxidantPotato starchSolanum tuberosum
The invention provides a preparation method of potato starch processing juice lactic acid beverage. According to the method, potato starch processing juice is subjected to enzymolysis, and then odor-free potato starch processing juice lactic acid beverage with mild sour and sweet taste and good stability and without whey separation is obtained by taking Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus reuteri and Streptococcus thermophilus as fermentation strains through bio-fermentation engineering. The yogurt beverage product not only contains lactic acid bacteria of the existing commercially available similar products available in the market and has the beneficial function of adjusting the bacteria flora of intestinal tract and promoting absorption in nutrient of lactic acid bacteria, but also contains functional active substances, capable of resisting against oxidation, resisting against cancer and controlling blood sugar, in potatoes, thus being suitable for being consumed and drank by all kinds of people; and the preparation method is simple in process, suitable for scale application and good in market prospect.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Compositions and methods for brewing sour beer
The present invention relates to the unexpected discovery of a new strain of yeast, dubbed GY7B, which is related to, but genetically and phenotypically distinct from, Lachancea thermotolerans. The invention provides methods of brewing sour beer using GY7B, wherein the methods do not require use of lactic acid or lactic acid producing bacteria.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF THE SCIENCES
Method for cultivating lactobacillus and producing live lactobacillus feed by utilizing scum
InactiveCN101822310ALow costLow live bacteria contentBacteriaAnimal feeding stuffAgricultural scienceAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to a method for cultivating lactobacilli and producing live lactobacillus feed by utilizing scum, which belongs to the field of biological engineering. The method comprises the following steps: using the scum which is a byproduct of a cornstarch sugar manufacturing industry as a main raw material, using feeding lactobacilli as starting bacteria, and carrying out solid state cultivation of the lactobacilli to prepare feed containing live lactobacilli; and cultivating the lactobacilli through liquid state fermentation to prepare a live lactobacillus preparation. In the invention, the scum is used as the main raw material, the optimization of culture medium components and the optimization of cultural conditions are researched in details to obtain optimization process parameters, the feeding lactobacilli are cultivated at high density by adopting the modes of solid state batching, liquid state batching or liquid state supplementation, high-grade feed rich in the live lactobacilli is cultivated through solid state or liquid state fermentation, the content of the live lactobacilli through liquid state cultivation can reach more than 109cfu / mL, and the content of the live lactobacilli through solid state cultivation can reach more than 108cfu / g. In the invention, the scum is used as the main raw material for cultivating the feeding lactobacilli, so that waste is changed into resources, and the cost for producing the lactobacilli is lowered.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Nutritional composition for infants delivered via caesarean section
InactiveUS20110117077A1Fast colonisationInduce toleranceOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsBiotechnologyPhysiology
The present invention relates to methods for feeding of infants delivered via caesarean section and to compositions to be administered to infants delivered via caesarean section and in particular to the use of a product obtained by fermentation of milk, whey, whey protein, whey protein hydrolysate, casein, casein hydrolysate and / or lactose by lactic acid producing bacteria. Thereby it is possible to stimulate a fast colonisation of the intestinal microbiota of said infants.
Owner:NV NUTRICIA
Method for largely and rapidly reproducing lactic acid bacteria
ActiveCN102311929ASimple productivitySimple conditionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesLactic acid bacteriumNutrient solution
The invention relates to a method for largely and rapidly reproducing lactic acid bacteria, which comprises the following steps: (1) mixing wormwood or tea-leaf, molasses with common salt in the proportion of 16:8:2 in percentage by weight; (2) filling the mixed wormwood or tea-leaf, molasses and common salt into a plastic film bag, tightening the mouth of the plastic film bag, and spontaneously fermenting at normal temperature; (3) fetching 60kg of molasses and 1kg of common salt and adding 300L of water to stir and dissolve the molasses and the common salt, and then, adding the water into a plastic tank of which the capacity is 3000L to 3000L to prepare a nutrient solution for reproducing the lactic acid bacteria through the suction of a pump; and (4) after 7 days of spontaneous fermentation, taking out a fermentation solution, i.e. a lactic acid bacteria strain stock solution, adding 100L of lactic acid bacteria strain stock solution into the plastic tank, and then adding the nutrient solution of the lactic acid bacteria to 3000L. The invention has the advantages as follows: the technology and the method for largely and rapidly reproducing the lactic acid bacteria by fermenting the wormwood or the tea-leaf are at least 100 times higher than a traditional lactic acid bacteria production technology in speed, and the cost price is only 1 / 100 the cost price of the traditional lactic acid bacteria production technology.
Owner:黄家总
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com