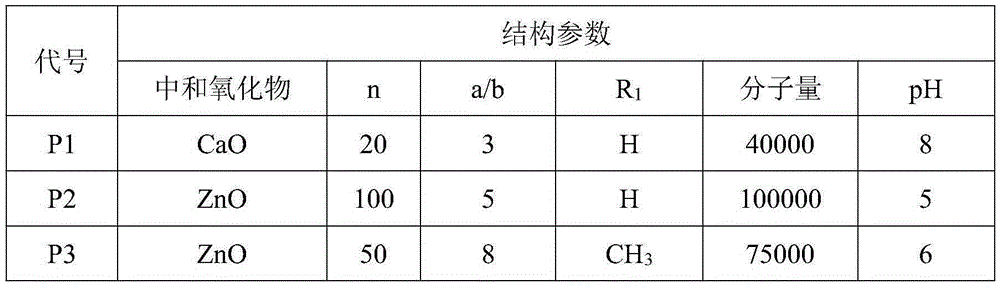
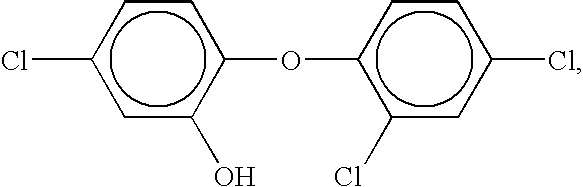
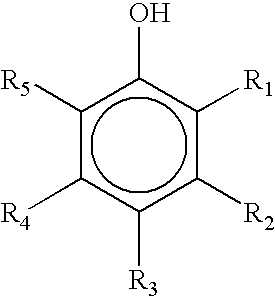
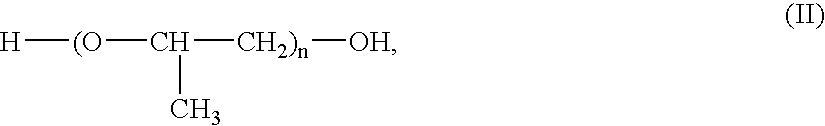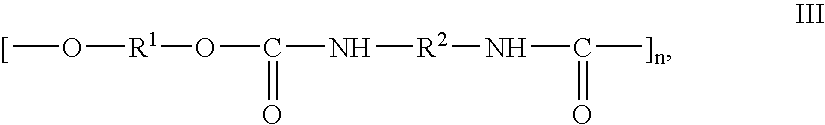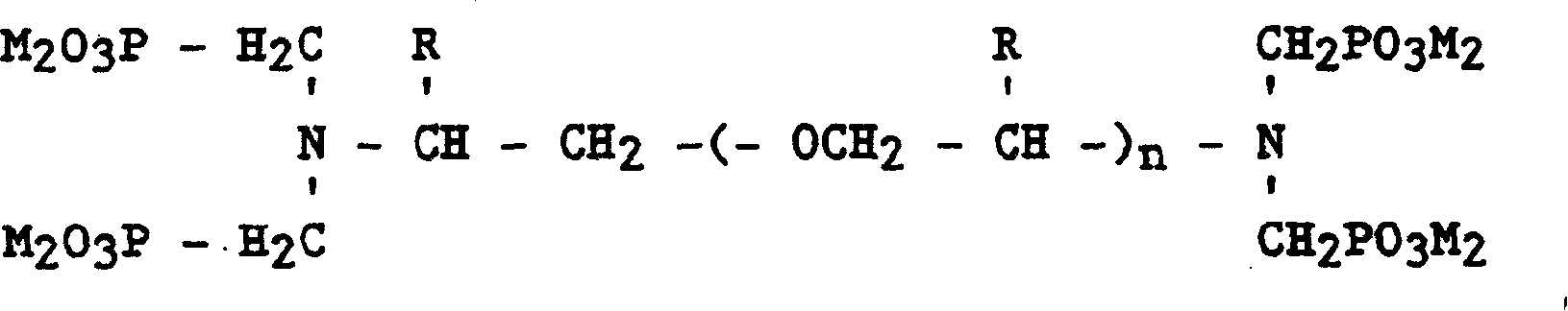Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4304 results about "Zinc salts" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Zinc salts are a group of chemical substances that are each individually formed by the reaction of zinc with a non-metal element. Zinc salts are used because zinc is a corrosion resistant element in most naturally occurring environments.
Zinc salt compositions for the prevention of dermal and mucosal irritation
InactiveUS20040102429A1Minimize and prevent irritationReduce transmissionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsHigh concentrationFungicide
The addition of low concentrations of combinations of water-soluble organic salts of zinc to gels, creams, lotions or ointments can increase the ability of these products to reduce or prevent exogenous irritants from causing irritation of the underlying substrate. The addition of low concentrations of combinations of water-soluble organic zinc salts to these gels, creams, lotions or ointments also can reduce the irritation of skin or mucous membranes caused by the addition of potentially-irritating substances such as spermicides, microbicides, fungicides or other therapeutic agents to the gel, cream, lotion or ointment. The advantages of this anti-irritant approach over others, which generally employ high concentrations of single zinc salts, are the reduced potential for zinc toxicity, the reduced potential for toxicity related to zinc itself, and the preservation of the desirable biological properties of potentially-irritating therapeutic substances added to the gel, cream, lotion or ointment.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Composition, method of making, and treatment of wood with an injectable wood preservative slurry having biocidal particles
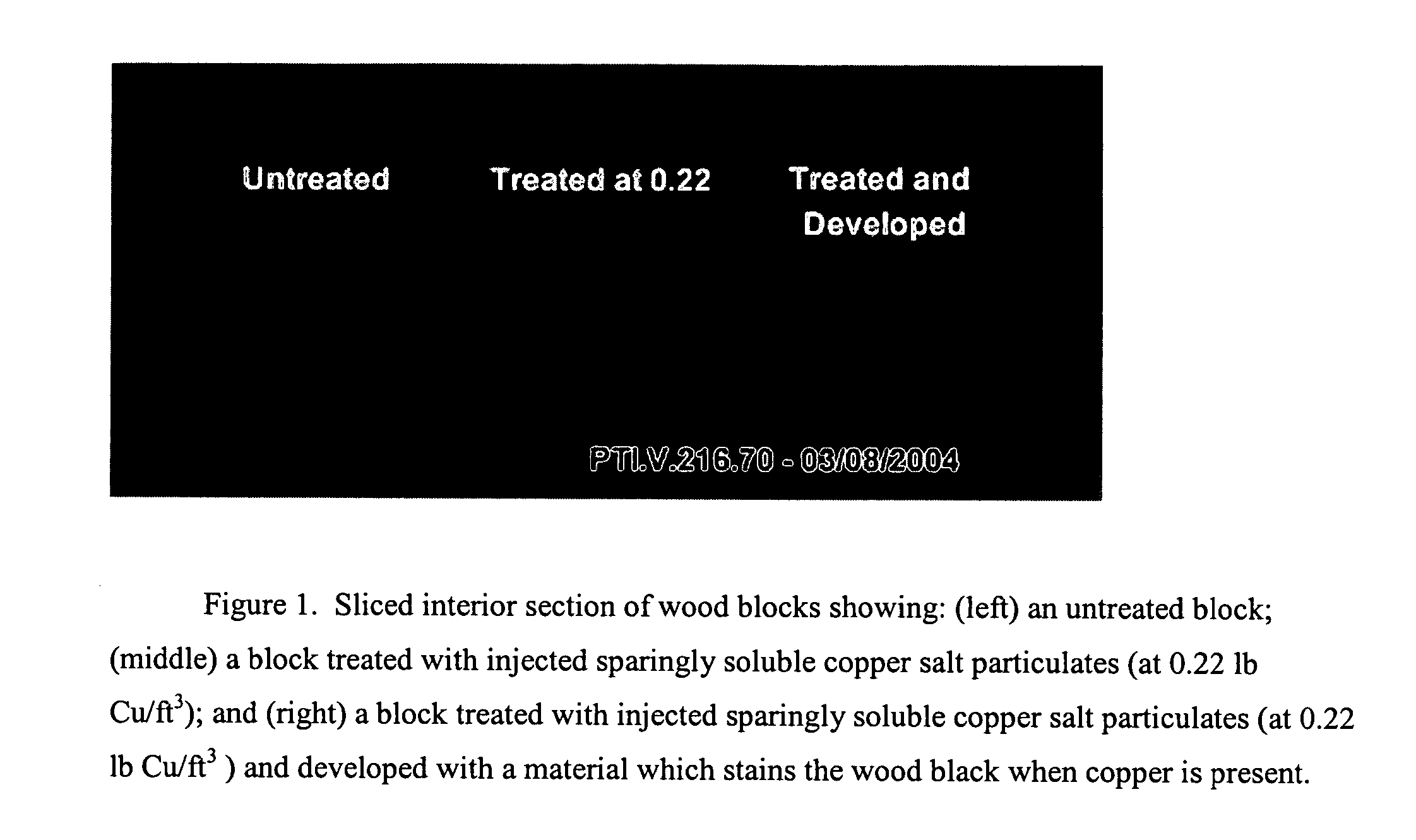
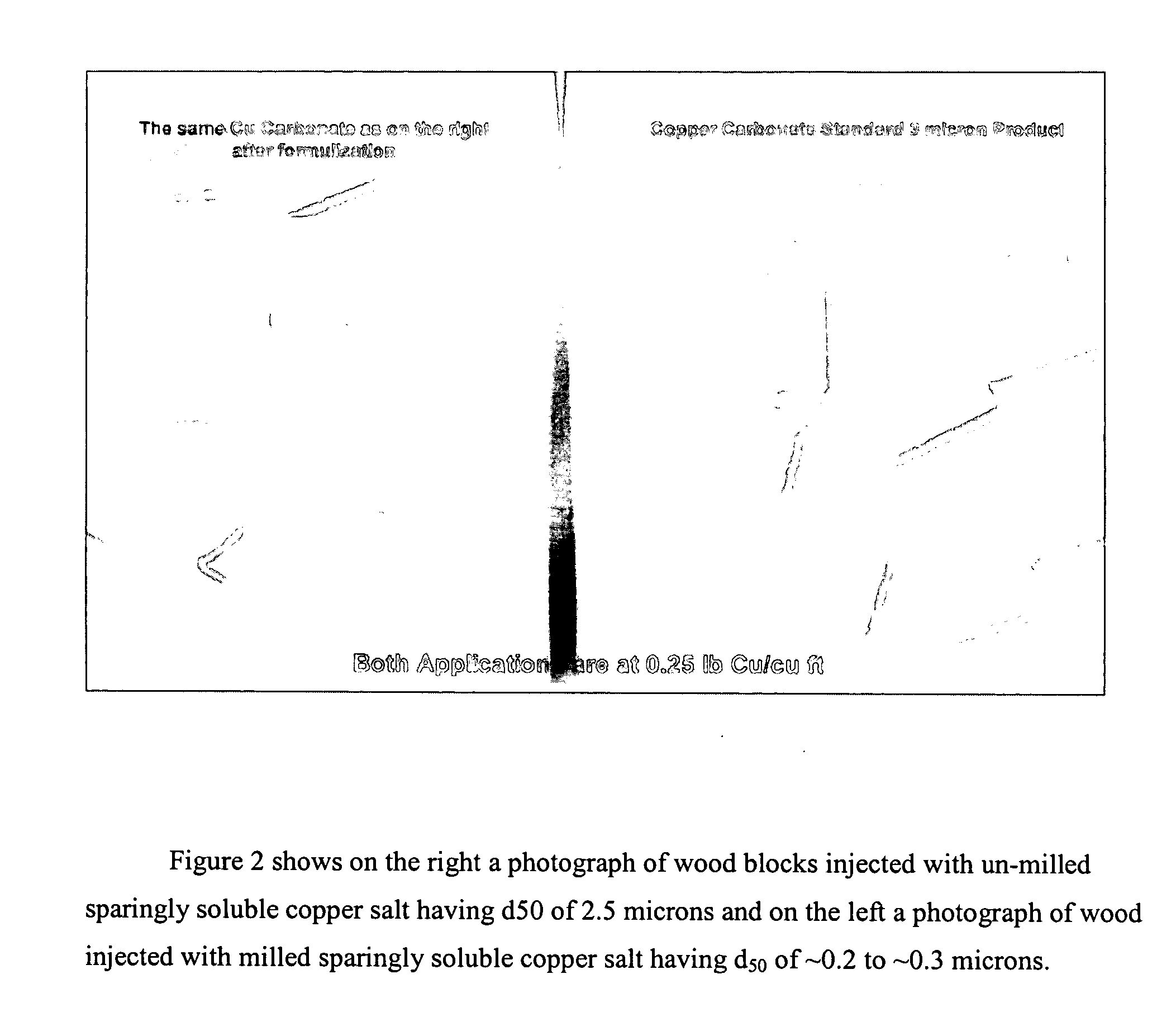
A method of preserving wood includes injecting into the wood an effective amount of a aqueous wood-injectable biocidal slurry, said a wood-injectable biocidal slurry containing dispersants and sub-micron biocidal particles selected from at least one of the following classes: 1) a plurality of particles containing at least 25% by weight of a solid phase of sparingly soluble salts selected from copper salts, nickel salts, tin salts, and / or zinc salts; 2) a plurality of particles containing at least 25% by weight of a solid phase of sparingly soluble metal hydroxides selected from copper hydroxide, nickel hydroxide, tin hydroxide, and / or zinc hydroxide; 3) a plurality of particles containing at least 25% by weight of a solid phase comprising a substantially-insoluble organic biocide selected from triazoles, chlorothalonil, iodo-propynyl butyl carbamate, copper-8-quinolate, fipronil, imidacloprid, bifenthrin, carbaryl, strobulurins, and indoxacarb; 4) a plurality of particles containing on the outer surface thereof a substantially-insoluble organic biocide; 5) a plurality of particles containing a solid phase of a biocidal, partially or fully glassified composition comprising at least one of Zn, B, Cu, and P. The particles may advantageously contain metallic copper, a leachability barrier, pigments, dyes, or other adjuvants disposed on the outer surface thereof.
Owner:OSMOSE
Zinc salt compositions for the prevention of dermal and mucosal irritation
InactiveUS20050238602A1Minimize and prevent irritationReduce transmissionCosmetic preparationsBiocideMedicineIrritation
The present invention provides for compositions and methods that may offer protection from irritants, as well as antimicrobial protection. Preferred embodiments of the invention include topical antimicrobial compositions comprising two or more water-soluble zinc salts in low concentrations.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Stable solution of zinc ions and bicarbonate and/or carbonate ions
InactiveUS6015547APrevention and counteractingInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsBiocideZinc ionBicarbonate Ion
A storage stable aqueous solution or aqueous gel of zinc ions in the presence of bicarbonate ions is disclosed. The solution comprises: (a) a source of zinc ion, (b) a source of a stabilizing anion which can stabilize soluble zinc and bicarbonate and / or carbonate in solution; (c) a source of bicarbonate ion; and (d) a solvent therefor. The solvent comprises a major proportion of water. The zinc salt is present in an amount suitable for the intended purpose; the stabilizing anion in an amount B of at least 1.2 equivalents per equivalent of zinc ion; and the bicarbonate ion cannot exceed certain levels which are related to the level of the stabilizing anion.
Owner:CHURCH & DWIGHT CO INC
Co-N-C@RGO composite material, preparation method and application to modification of lithium-sulfur battery diaphragms
ActiveCN106784525AIncrease the areaHigh porosityLi-accumulatorsCell component detailsPorous carbonElectrical battery
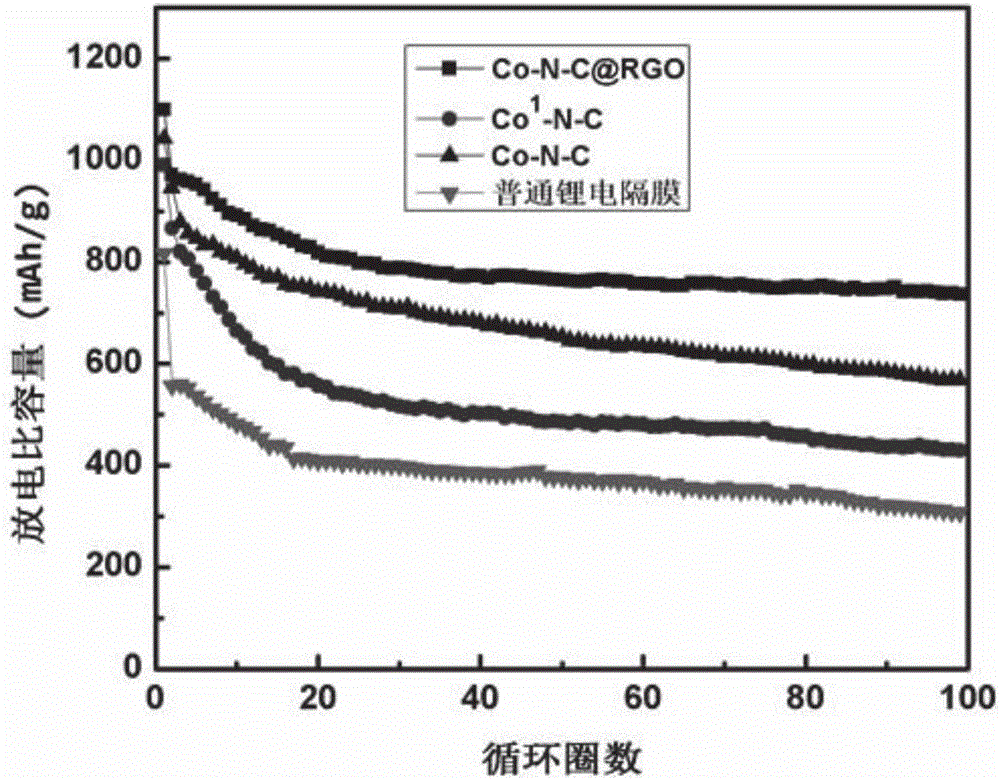
The invention discloses a method for preparing porous carbon@graphene composite material by taking a bimetal organic framework material as a precursor and application to modification of lithium-sulfur battery diaphragms thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: taking zinc salt and cobalt salt in a certain ratio as the raw materials, synthesizing a zinc / cobalt-bimetal organic framework@graphene composite material through a room-temperature liquid phase method, taking the zinc / cobalt-bimetal organic framework@graphene composite material as the precursor, carrying out high-temperature reaction under inert atmosphere, pickling and drying to obtain a cobalt / nitrogen double-doped porous carbon@graphene (Co-N-C@RGO) composite material. Co-N-C@RGO has high conductivity; the specific surface area of Co-N-C@RGO reaches up to 750-1000m<2> / g; the content of Co is 2-4At%; the content of N is 10-20At%. When the material is applied to the modification of the lithium-sulfur battery diaphragms, the material has the function of obviously inhibiting polysulfide shuttle effect and is capable of greatly improving actual specific capacity and cyclic performance of the lithium-sulfur batteries; meanwhile, the raw materials needed for synthesizing the material are simple; the operation is convenient; the large-scale production can be achieved; the material has certain promoting effect on commercialization of lithium-sulfur battery systems.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Non-phosphorus compound scale and corrosion inhibitor for treatment of circulating cooling water
ActiveCN1621362AEasy to useIncrease the concentration factorScale removal and water softeningPhosphateTungstate
The composite phosphate-free scale inhibiting corrosion inhibitor for treating circular cooling water consists of scale inhibitor and corrosion inhibitor. The scale inhibitor consists of one or several of PASP, PVA, oxidized starch, polyacrylic acid, acrylic acid / acrylate copolymer and acrylic acid / acrylate copolymer with sulfo radical. The corrosion inhibitor consists of one or several of sodium salt / potassium salt / ammonium salt of organic salt, sodium / potassium / ammonium borate, nitrous organic matter, soluble molybdenate, soluble tungstate, soluble nitrate, soluble nitrite and soluble zinc salt. The composite scale inhibiting corrosion inhibitor has excellent scale inhibiting and corrosion inhibiting performance, is environment friendly, and is especially the treatment of hard circulation water with high calcium and high alkali content.
Owner:BEIJING YANHUA XINGYE TECH DEV +1
Antimicrobial/preservative compositions comprising botanicals
InactiveUS20120201902A1Promote wound healingGood antifungal activityAntibacterial agentsBiocideMedicinePreservative
The present invention relates to a preservative or antimicrobial compositions which comprise low concentrations of botanical extracts, in synergistic combinations with alkanediols in a solvent system, optionally with fruit acids. Additionally, the present invention relates to a preservative or antimicrobial compositions which comprise a silver compound, an essential oil or individual constituent, one or more zinc salts, and one or more alkanediol. The compositions of the invention may be used in personal care products including wound care products or in veterinary use. Preferably, the compositions of the invention have little or no human-detectable fragrance.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Nutrition bar
InactiveUS20050181019A1Stable and goodExtended shelf lifeBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsRice proteinIngested food
A nutrition bar comprising about 10% wt or more of soy and / or rice protein, at least one transition metal or transition metal compound, and about 2% wt or more of a humectant, and wherein the at least one transition metal or transition metal compound is in a substantially water insoluble form at 20° C. or the nutrition bar has an Aw of 0.45 or less or about 1% wt or more of the soy and / or rice protein is in the form of nuggets and the humectant is selected from polyols. The bars have elevated levels of soy and / or rice protein, yet do not suffer unacceptable from a deterioration in taste or other organoleptic properties over time. In other aspects, a nutrition bar or other food which incorporates pro-oxidants and / or polyunsaturated fatty acids or their sources in encapsulated form, especially as microcapsules. The pro-oxidants may be metal salts such as copper, manganese, iron and / or zinc salts. Sources of omega-3 fatty acids include fish oil. Processes for preparing the polyunsaturated fatty acid capsules are also disclosed. The polyunsaturated fatty acid capsules / microcapsules are prepared by forming an emulsion of the unsaturated fatty acid with a carrier, spray drying the emulsion to form a powder and encapsulating powder, especially with a fluid bed. The invention is especially useful for encapsulating polyunsaturated fatty acids, or oil sources thereof, most preferably omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, such as arachidonic acid, docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), lineoleic acid, linolenic acid (alpha linolenic acid), and gamma-linolenic acids, fish oil, and oil sources of C18:2 and C18:3 fatty acids such as canola oil, soybean oil or blends thereof.
Owner:SLIM FAST FOODS COMPANY A DIV OF CONOPCO
Non-irritating compositions containing zinc salts
InactiveUS20070020342A1Minimize prevent irritationPromoting rapid killBiocideCosmetic preparationsIrritationMedicine
The present invention relates to methods and compositions which employ low concentrations of combinations of zinc salts to prevent the irritation of skin or mucous membranes that may be caused by therapeutic agents, by personal hygiene products, by articles such as gloves or condoms, or by various physical, chemical, mechanical, or biological irritants.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Zinc salt compositions for the prevention of dermal and mucosal irritation
InactiveUS20050281762A1Minimize and prevent irritationReduce transmissionBiocideCosmetic preparationsMedicineIrritation
The present invention relates to methods and compositions which employ low concentrations of combinations of zinc salts to prevent the irritation of skin or mucous membranes that may be caused by therapeutic agents, by personal hygiene products, or by various physical, chemical, mechanical, or biological irritants, including infectious agents.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Dishwasher detergent with improved protection against glass corrosion
InactiveUS20050075258A1Organic detergent compounding agentsSurface-active detergent compositionsOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATEOrganic acid
A dishwasher detergent containing a builder and one or more magnesium and / or zinc salt(s) of at least one monomeric and / or polymeric organic acid, excluding zinc ricinoleate, zinc abietate, and zinc oxalate. A method of inhibiting glass corrosion by treatment with one or more salts of magnesium and / or zinc with organic acids, excluding formic acid, acetic acid, gluconic acid, and oxalic acid.
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
Composite scale resistant corrosion inhibitor and its use in reusing ammonia-nitrogen containing waste water in circulating cooling water
The present invention features that while reusing sewage containing ammonia nitrogen as circulating cooling water, acid is added into water to control pH value in 6.5-8.5, and composite scale and corrosion inhibitor and bactericide are used unitedly to control the corrosion, scaling and bacteria growth during reusing sewage. The composite scale and corrosion inhibitor includes phosphate, polyphosphate, organic phosphonic acid, carboxy radical containing copolymer, zinc salt, etc.
Owner:中国石油化工股份有限公司北京燕山分公司研究院
Zinc salt compositions for the prevention of dermal and mucosal irritation
ActiveUS20050048139A1Minimize and prevent irritationReduce transmissionCosmetic preparationsBiocideIrritationMedicine
The present invention provides for compositions and methods that may offer protection from irritants as well as antimicrobial protection. Preferred embodiments of the invention include topical antimicrobial compositions that lack conventional antibiotics or preservatives, wherein the antimicrobial benefit is created by essential oils (or their active ingredients), emollient solvents and, in some instances, anti-inflammatory agents.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
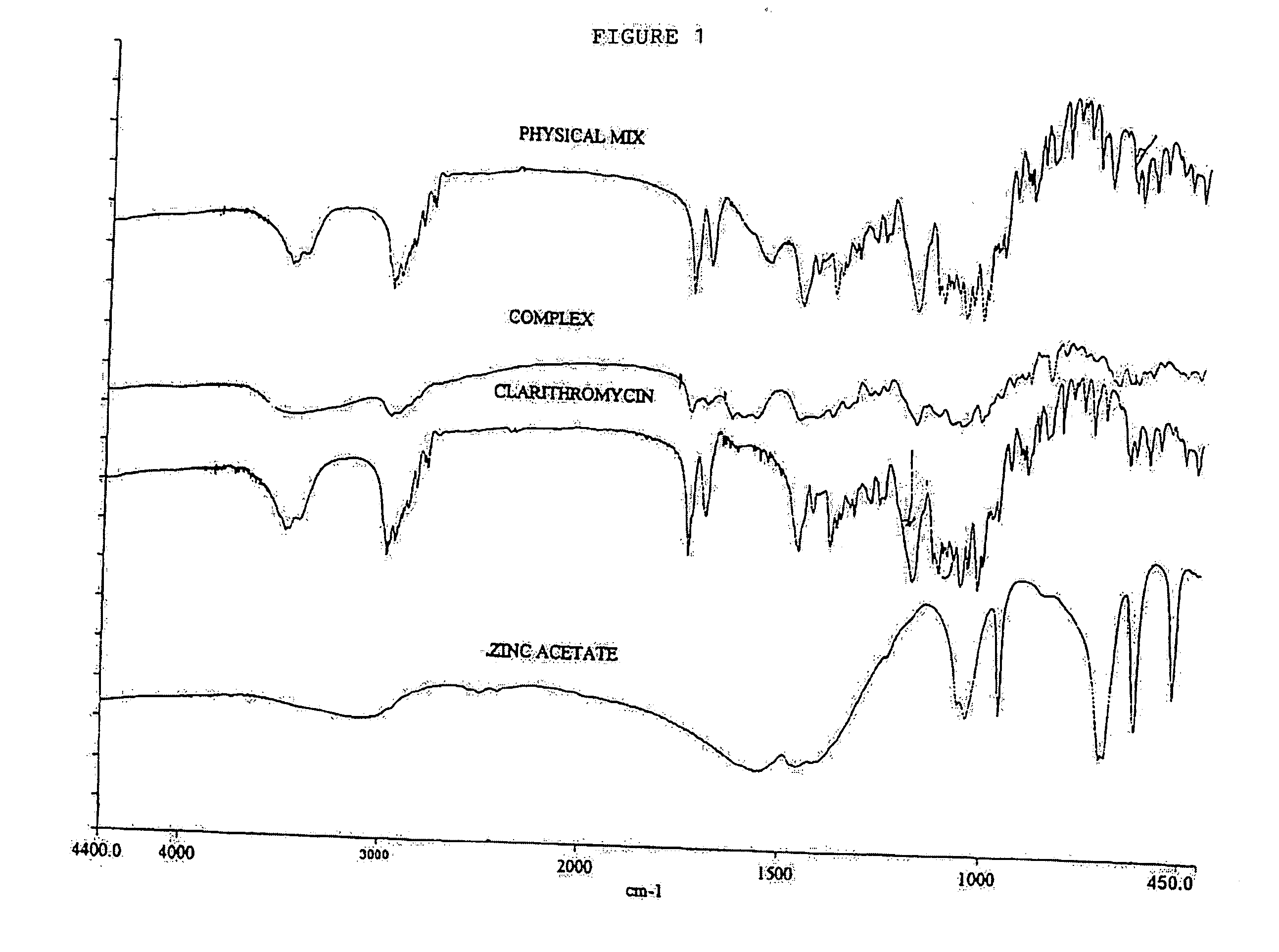
Clear, stable topical compositions of clarithromycin and processes for their preparation
The invention relates to clear, stable topical compositions of clarithromycin for the treatment of acne and processes for their preparation. The transparent topical compositions include clarithromycin, a zinc salt, a pharmaceutically acceptable vehicle and may include gelling agents.
Owner:RANBAXY LAB LTD
Corrosion and scale inhibitor for cooling water in petrochemical industry
ActiveCN102603086AStrong targetingLow phosphine contentScale removal and water softeningChemical industryPetrochemical
The invention belongs to the technical field of chemical industry, and relates to a cooling water corrosion inhibitor, in particular to an efficient composite corrosion and scale inhibitor which can remarkably reduce corrosion and scaling phenomena of the cooling water of a petrochemical system. The corrosion and scale inhibitor is prepared by evenly mixing organic phosphine carboxylic acid corrosion inhibitor, organic multi-element phosphine acid corrosion and scale inhibitor, polymer scale inhibitor, metal ion succimer, surface active agent, zinc salt, functionality additive and water. The corrosion and scale inhibitor prepared from the components has low phosphine content and excellent corrosion and scale inhibition performance, can prolong the service life of devices, improve the repeated utilization rate of cooling water and reduce the water resource consumption.
Owner:山东京博众诚清洁能源有限公司
Preparation method of zinc oxide nano-rod film on fibre product
InactiveCN101012621ASmall granularityHigh purityFibre treatmentLiquid/gas/vapor textile treatmentFiberChemical solution
The invention relates to a manufacturing method for nanometer rod film of zinc oxide on fiber product, comprising (1) by sol-gel method ZnO nano-crystal grain is prepared and a great deal of ZnO seed crystal is deposited on the surface of fiber product, molar concentrations of zinc salt and alkaline agent are all 0.001M-0.75M; (2) by hydrothermal method or precipitation of chemical solution pool, nanometer rod film of zinc oxide grows on fiber product, molar concentrations of zinc salt solution and complexing agent solution are all 0.001M-0.05M; ZnO nanometer rod film with equal surface and good directivity is obtained. The manufacturing method is provided with simple method and low cost. It is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Sugar alcohol calcium magnesium zinc boron compound liquid fertilizer and preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN103588564AAvoid reactionAchieve preparationFertilizer mixturesHigh concentrationMagnesium salt
The invention belongs to the field of agricultural production and discloses a sugar alcohol calcium magnesium zinc boron compound liquid fertilizer and a preparation method and application thereof. The liquid fertilizer is prepared from various mother solutions, a chelating agent, a plant growth regulator and surface active materials. The preparation method comprises the following steps: causing sugar alcohol to respectively react with calcium salt, magnesium salt, zinc salt and boric acid to prepare calcium, magnesium, zinc and boron mother solutions, then mixing the mother solutions according to a certain ratio, and adding the chelating agent to cause the mother solutions to carry out secondary chelating reaction; after a while, adding the plant growth regulator and the surface active materials into reaction liquid, uniformly mixing, and cooling to the room temperature to obtain the high-concentration, stable and good-effect compound liquid fertilizer. The prepared liquid fertilizer provides adequate calcium, magnesium, zinc and boron and other nutrients for plants and can also carry out mixing of different elements and proportions according to the needs of different plants and different growth stages of plants.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV +1
Green environment-protective composite slow-corrosion scale resistor for circulated cooling-water treatment
InactiveCN1850661AGood scale inhibition and dispersibilityObvious synergistic effect of corrosion inhibitionTreatment using complexing/solubilising chemicalsGreen environmentWater quality
The invention belongs to the environmental protection field, concretely relating to a green environmental-protection composite corrosion inhibition antifouling agent for water circulating cooling, compounded of antifouling dispersants and corrosion inhibitors: polyepoxy sodium succinate, polymerized sodium aspartate, hydrolyzed polymaleic anhydride, sodium gluconate, zinc salt, in the mass ratio of 1-6 to 1-4 to 2-6 to 1-2 to 1-2. And it has characters of no phosphorus and biodegradability, an environment-friendly water quality stabilizer, used in a water-circulating cooling system to play the role in corrosion inhibition and antifouling.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Non-Phosphorus composite anti incrustation eorrosion snhibiter and its application in water treatment
ActiveCN1785853AImprove performanceExcellent resistance to CaCO
<sub>3</sub>
Dirt performanceScale removal and water softeningMolybdatePolyaspartic acid
The present invention relates to a phosphorus-free composite antiincrustation corrosion inhibitor. It includes polyaspartic acid and / or polyepoxysuccinic acid and at least one kind of scale inhibition and dispersion agent, in which the scale inbibition and dispersion agent is polymer containing carboxylic acid group, or it includes polyaspartic acid and / or polyepoxysuccinic acid, zinc salt, molybdate or tungstate and polymer containing carboxylic acid group. Said invention is applicable to treatment of circulating cooling water.
Owner:BEIJING YANHUA PETRO CHEM
Method for preparing concavo-convex rod soil/zinc oxide nanometer composite material
The invention discloses a method for preparing concavo-convex rod soil / zinc oxide nanometer composite materials, which comprises the following steps: purifying and dispersing the concavo-convex rod soil in water to prepare concavo-convex rod soil dispersion liquid; then adjusting the temperature of the concavo-convex rod soil dispersion liquid to 30 to 100 DEG C; agitating the concavo-convex rod soil dispersion liquid dispersion liquid and while adding zinc salt aqueous solution with the concentration of 0.3 to 3 mol.L<-1> and carbonate aqueous solution with the concentration of 0.3 to 2 mol.L<-1> to the concavo-convex rod soil dispersion liquid dispersion liquid; and keeping the pH value of mixed liquid within the range of 6.0 to 8.0. The prepared mixed serous fluid comprising the prepared nanometer concavo-convex rod soil and basic zinc carbonate is filtered; and a filter cake is washed by deionized water; when the electrical conductivity of filtrate is less than 300 MuS.cm<-1>, the washing is finished; and the filter bake obtained is dried at the temperature of below 100 DEG C, then baked for 1 to 10 hours at the temperature of 300 to 600 DEG C, and finally crushed. The invention is simple and has the advantages of low energy consumption and high safety; the load of the adsorbing material prepared is uniform and has good dispersibility, strong adsorbability and remarkable photo-catalyzed degradation property.
Owner:JIANGSU POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY +1
Phosphorus-free corrosion and scale inhibitor
InactiveCN101607763AReduce dosagePlay a role in corrosion inhibitionTreatment using complexing/solubilising chemicalsChelationPrecipitation types
The invention relates to a phosphorus-free corrosion and scale inhibitor, which is prepared from sodium molybdate, zinc salt, citrate, triethanolamine, benzotriazole (BTA), polyaspartic acid (PASP), polyepoxysuccinic acid (PESA), AA / AMPS terpolymer, solid alkali and water. The phosphorus-free corrosion and scale inhibitor inhibits corrosion of metals by forming oxidization type and precipitation type films on the surfaces of the metals, has the effect of inhibiting scale through chelation and dispersive action on salts causing scale in cooling water, is non-toxic and phosphorus-free, has easily biodegradable major organic compositions, does not cause environmental pollution and is not limited by phosphorus in emission.
Owner:SHANGHAI WEILAI ENTERPRISE
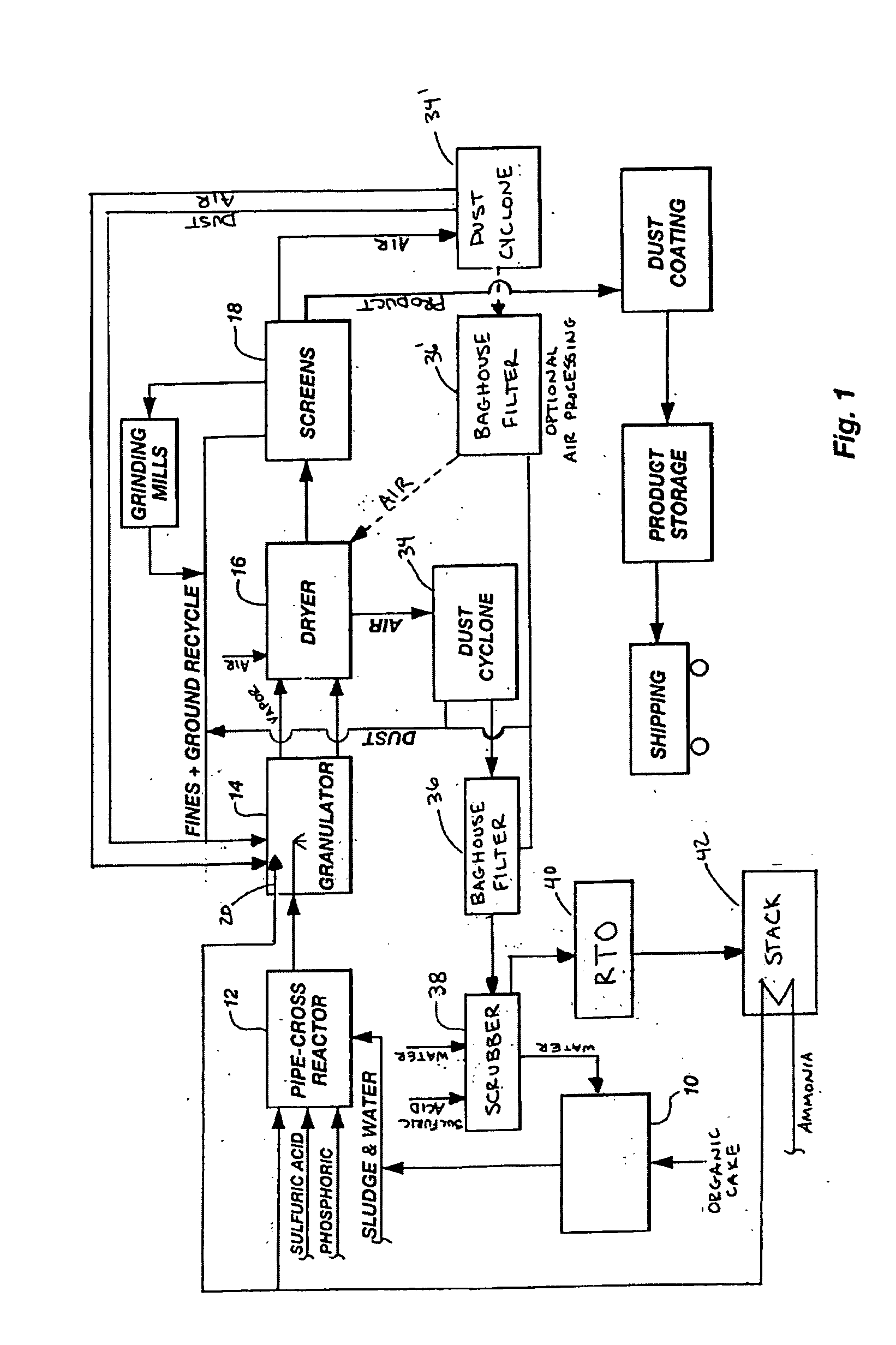
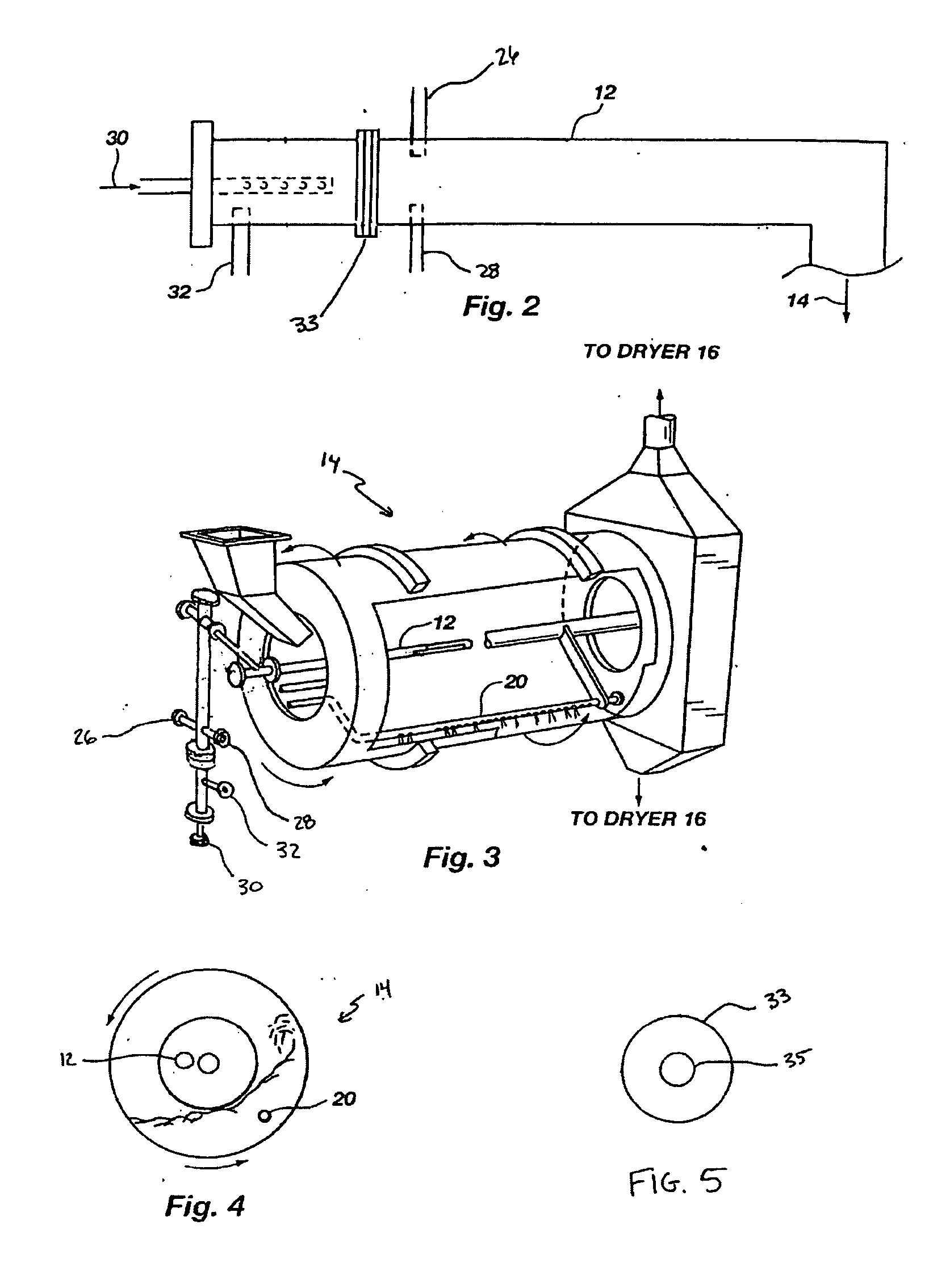
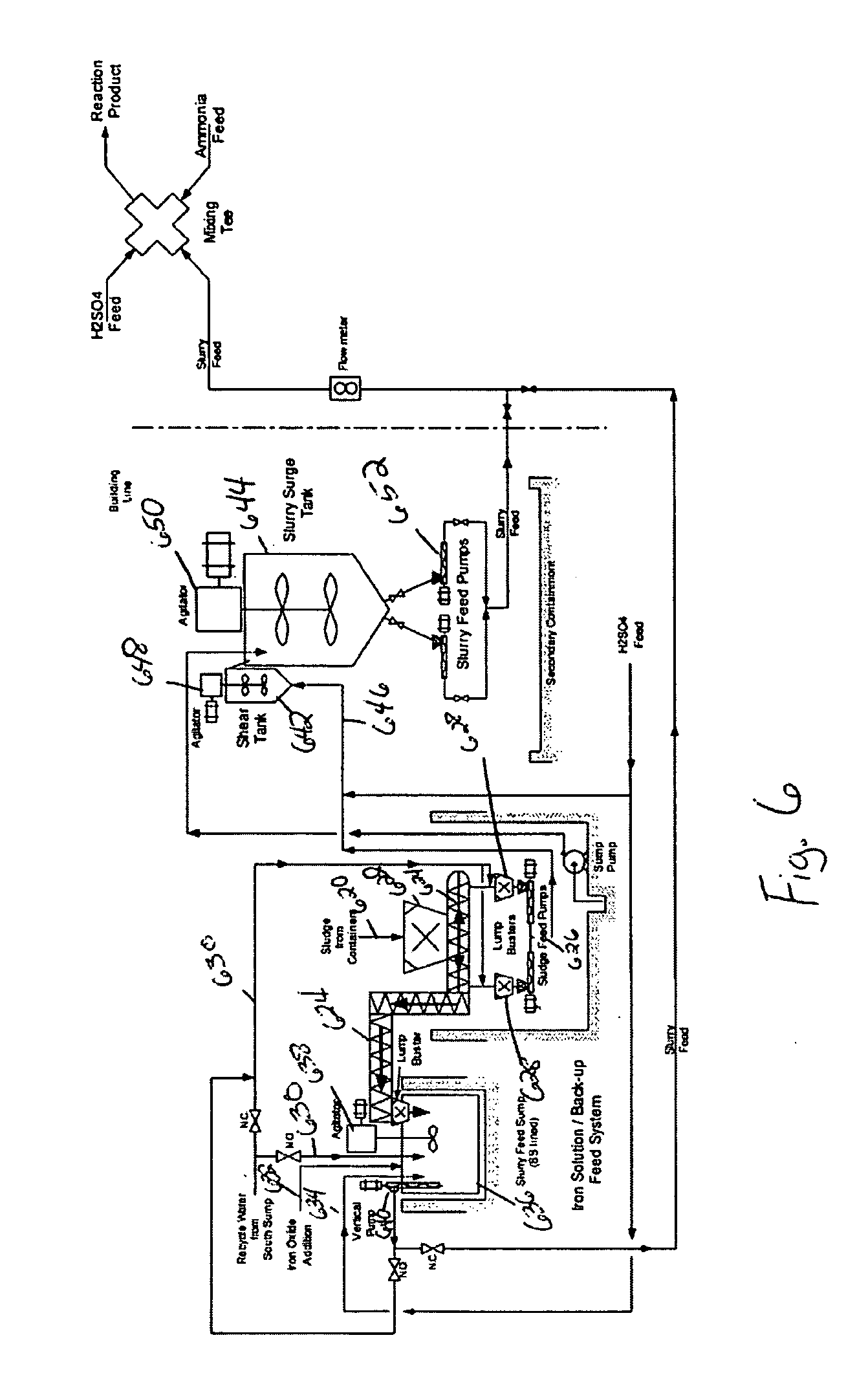
Organic recycling with metal addition
InactiveUS20050039508A1Reduce slurry viscosityAvoid flowAnimal corpse fertilisersAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserSolubilityIron sulfate
The invention is directed to methods for producing a granular nitrogen fertilizer from an organic material comprising adding a metallic salt to said organic material to form a slurry. Preferably the organic material comprises dewatered biosolids and contains water from a scrubber. Metallic salts that can be used comprise a salt of iron, zinc, or a mixture thereof. Preferred iron salts comprises ferric sulfate or ferric oxide, and preferred zinc salts comprises zinc sulfate or zinc oxide. Preferably, the metallic salt is mixed with an acid such as sulfuric acid to form an acidified metal salt. Slurry pH ranges from approximately 2-2.5. The acidified metal salt is added to the organic material in sufficient quantity to lower viscosity of the slurry such that the resulting fluid does not hinder fluid flow during operation. When the metallic salt comprises acidified ferric sulfate or ferrous sulfate, sufficient iron can be present to produce a fertilizer product with 0.1 weight percent to 10 weight percent iron sulfate calculated on a dry weight basis. The invention is also directed to fertilizer products made by the methods of the invention. Preferred products are granules and the metallic salt increases product hardness. Fertilizer granules preferably contain metal that is bioavailable to a plant when used as a fertilizer. Solubility of the metal of the product in water is enhanced, and the product is low staining.
Owner:UNIFIED ENVIRONMENTAL SERVICES GROUP +1
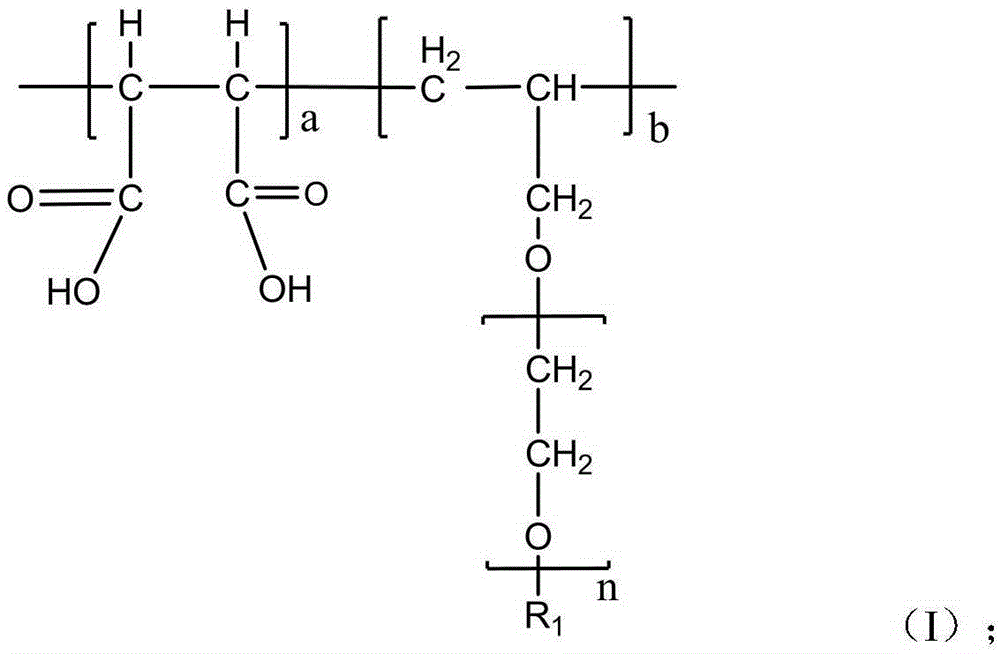
Nano suspension liquid concrete early strength agent and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a nano suspension liquid concrete early strength agent and a preparation method thereof. The nano suspension liquid concrete early strength agent is prepared from transition metal element doped nano calcium metasilicate suspension liquid, the suspension liquid is mainly composed of nanometer silicon particles, the chemical structure of the nanometer silicon particles is aCaO.bAl2O3.cZnO.SiO2.6H2O, 1<=a<=2, 0.50<=b<=1, and 0.25<=c<=0.50. The nanometer silicon particles are prepared from soluble calcium salt, soluble silicate, soluble aluminum salt, soluble zinc salt and a high polymer dispersing agent. On the one hand, the early strength agent contains no chlorine salt and has no corroding function on steel bars in concrete; on the other hand, an extremely stable suspension liquid system is achieved, adding is facilitated, and the early strength agent can be evenly dispersed easily in the concrete preparation process. The early strength of concrete can be remarkably improved, the early strength effect on concrete adopting highly-doped mineral admixtures is especially obvious, the early strength agent is especially suitable for production of precast concrete components, and a steam maintenance process can be effectively reduced and even omitted.
Owner:JIANGSU SOBUTE NEW MATERIALS
Rubber composition for base tread and tire
InactiveUS7919553B2Improve production efficiencyHigh mechanical strengthFibre treatmentSpecial tyresPolymer scienceCarboxylic acid
The present invention aims to produce a rubber composition for a base tread, which suppresses reversion and achieves excellent mechanical strength, fuel economy and processability, and a tire using the rubber composition, with high efficiency to provide them to customers at low prices. The present invention relates to a rubber composition for a base tread, containing: a rubber component; and a mixture of a zinc salt of an aliphatic carboxylic acid and a zinc salt of an aromatic carboxylic acid, wherein the rubber component contains natural rubber and butadiene rubber, the butadiene rubber content being 10 to 90% by mass per 100% by mass of the rubber component, and the mixture of a zinc salt of an aliphatic carboxylic acid and a zinc salt of an aromatic carboxylic acid is contained in an amount of 1 to 10 parts by mass per 100 parts by mass of the rubber component.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Zinc salt compositions for the prevention of dermal and mucosal irritation
InactiveUS7563461B2Minimize and prevent irritationReduce transmissionCosmetic preparationsBiocideIrritationMedicine
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Method of electroplating zinc, nickel, molybdenum and their alloys by using ionic liquid
The invention discloses a novel cleaning plating technology by using an ionic liquid which is a non-aqueous media as an electroplate liquid. Through using the technology, problems of bad environment and unstable qualities of electroplates existing in the condition of electroplating zinc, nickel, molybdenum and their alloys in an aqueous system can be solved. Qualities of coatings generated by using the technology are better than the qualities of coatings generated in the traditional system. The technology comprises the following steps: dissolving zinc salts, nickel salts and molybdate salt into the ionic liquid which is regarded as an electrolyte to prepare the electroplate liquid; electroplating at a current density of 1-30mA / cm2, wherein metallic zinc, nickel, molybdenum and their alloys are taken as soluble anode or graphite, complex carbon, glassy carbon, metal tungsten and titanium base plating platinum are taken as insoluble anode, and components which are needed to be electroplated are taken as cathode. Needed depth of coating can be obtained through controlling the current density and electroplating time.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Composite corrosion-retarding antisludging agent for treating high-concentration multiple circulating water
InactiveCN101125715AGrowth inhibitionLimit metabolismScale removal and water softeningHigh concentrationCarboxylic acid
A compound inhibition antisludging agent is used for treating high-concentration circulation water, comprising a liquid part and a solid part. Based on that the total weight of the liquid part is deemed to be 100 percent, percentages of each component by weight are: organic phosphonic acid 5-40 percent, organic carboxylic acid 5-40 percent and water 20-90 percent; and based on that the total weight of the solid part is deemed to be 100 percent, percentages of each component by weight are: polymer with antisludging effect 5-35 percent, alkaline agent 45-80 percent, azoles 1-10 percent and zinc salt 1-10 percent. The concentrations of the liquid part and the solid part in the circulating water are that: the solid part: the dosage of the agent added into make-up water is 20-200mg / L; the liquid part: total phosphine kept in the circulating water system is 10-15mg / L. The invention has effects of inhibition, antisludging, sterilization and algae removal upon meeting the requirements of the state, can promote the concentration multiple of the circulating water system up to 7.5 or more and can be operated at normal temperature with good effect and without pre-membrane treatment.
Owner:上海潓溱环保科技股份有限公司
Compositions Having A High Antiviral And Antibacterial Efficacy
InactiveUS20080138438A1Effective contactShorten the construction periodBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsOrganic acidAlcohol
Antimicrobial compositions having a rapid and persistent antiviral and antibacterial effectiveness are disclosed. The antimicrobial compositions contain (a) a divalent zinc salt, (b) an optional disinfecting alcohol, (c) an optional antimicrobial agent, and (d) an optional organic acid, wherein the composition has a pH of about 5 or less.
Owner:DIAL CORPORATION
Dirty blocking inhibitor and application in water treatment thereof
ActiveCN101172719AGood dispersionGood corrosion inhibition effectScale removal and water softeningSludgeWater quality
The invention provides anti-sludge inhibiter and the application method thereof. The inhibiter comprises multi-amino multi-ether methene phosphonic acid, poly-aspartic acid and acrylic polymer which comprises sulfonic groups, and at least one of other organic phosphonic acid, as well as zinc salt, inorganic acid, manganese salt and copper inhibiter. The inhibiter is applicable to the water quality with high rigidity, high alkaline and high salt. The sum of the rigidity the calcium and total alkalinity in water reaches 1500mg per liter, wherein, the inhibiter has excellent anti-sludge and corrosion inhibition effect when the rigidity of the calcium (counting in accordance with calcium carbonate ) is 1000mg per liter. The invention can be used in the circulated cooling water system of the industries such as petroleum chemical, as well as power and paper making plant. The invention can also be used in the water treatment process of poor water quality conditions such as seawater desalination and reverse osmosis.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Water system high-voltage mixed ion secondary battery based on zinc-lithium ferric manganese phosphate
InactiveCN105826520AIncrease capacityExcellent rate performanceCell electrodesSecondary cellsElectrolytic agentElectrical battery
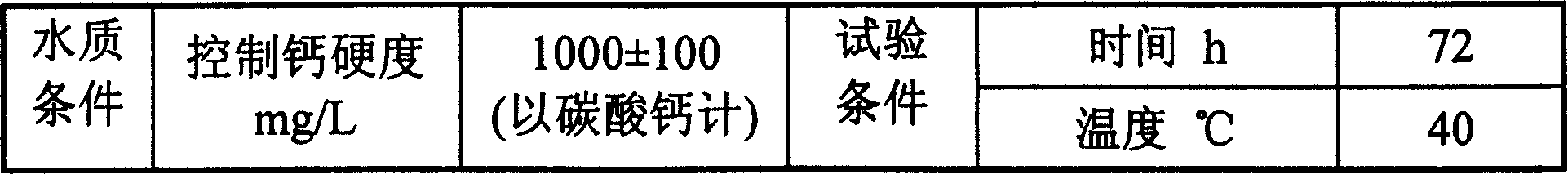
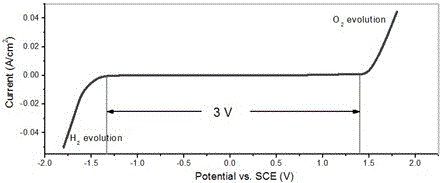
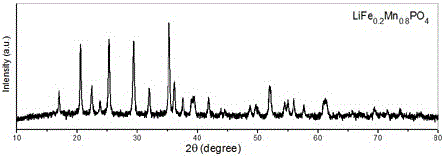
The invention relates to a water system high-voltage mixed ion secondary battery. A positive pole material of the battery is a high-voltage battery positive pole material, namely zinc-lithium ferric manganese phosphate (LiFe1-xMnxPO4), the element zinc serves as the majority of a negative pole material, and electrolyte is a liquid-state or gel-state material which is formed by lithium bis(trifluoromethane sulfonimide) (LiTFSI) and soluble zinc salt as solute and water as solvent and has ionic conductivity. The battery is based on the energy storage mechanisms of a dissolution-out / deposition reaction of zinc ions (Zn2+) on a negative pole and a reversible embedding / ejection reaction of the zinc ions (Zn2+) on a positive pole, meanwhile, through the water-in-salt electrolyte formed by high-concentration LiTFSI, the electrochemical water decomposition process is inhibited, a potential window of the water system electrolyte is remarkably broadened, the zinc-lithium mixed ion secondary battery has the advantages of being high in capacity, long in cycling life, safe, environmentally friendly, low in cost and the like, and the battery can be applied to the fields such as consumer electronic equipment, electromobiles and large-scale energy storage.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com