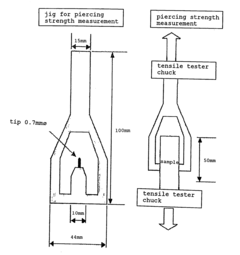
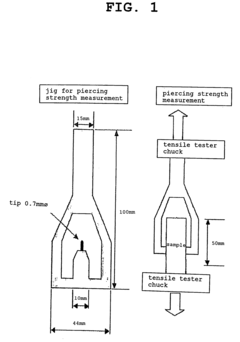
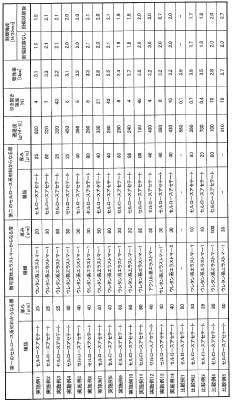
How to Attain High Tear Resistance in Cellophane Films?
JUL 9, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Cellophane Film Evolution
Cellophane film, a transparent and flexible material derived from regenerated cellulose, has undergone significant evolution since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially developed as a waterproof coating for tablecloths, cellophane quickly found its way into various applications due to its unique properties.
The evolution of cellophane films can be traced back to 1908 when Jacques E. Brandenberger, a Swiss textile engineer, invented the first machine to produce transparent sheets of regenerated cellulose. This breakthrough laid the foundation for the commercial production of cellophane, which began in the 1920s.
Throughout the mid-20th century, cellophane experienced rapid growth and technological advancements. The introduction of moisture-proof coatings in the 1930s significantly expanded its use in food packaging. This innovation allowed cellophane to maintain its clarity while providing an effective barrier against moisture and gases, thereby extending the shelf life of packaged products.
The 1950s and 1960s saw further improvements in cellophane production techniques, leading to enhanced mechanical properties and increased versatility. During this period, researchers focused on optimizing the film's strength, flexibility, and barrier properties, making it suitable for a wider range of applications beyond food packaging.
In the latter part of the 20th century, the evolution of cellophane films faced challenges from the emergence of synthetic polymers. However, the growing environmental concerns and the push for sustainable materials have led to a renewed interest in cellophane as a biodegradable alternative to petroleum-based plastics.
Recent developments in cellophane film technology have centered on improving its tear resistance, a critical property for many applications. Researchers have explored various approaches, including the incorporation of reinforcing agents, optimization of the cellulose regeneration process, and the development of multi-layer structures.
The quest for high tear resistance in cellophane films has driven innovations in both material composition and manufacturing processes. Scientists have investigated the use of nanocomposites, cross-linking agents, and surface modifications to enhance the film's mechanical properties without compromising its transparency or biodegradability.
As environmental regulations become more stringent and consumer demand for sustainable packaging grows, the evolution of cellophane films continues to focus on balancing performance with eco-friendliness. Current research efforts are directed towards developing cellophane films with improved tear resistance while maintaining their inherent biodegradability and compostability.
The ongoing evolution of cellophane films demonstrates the material's adaptability and enduring relevance in the face of changing market demands and technological advancements. As the industry strives to address the challenge of attaining high tear resistance, cellophane remains a promising material for sustainable packaging solutions in the 21st century.
The evolution of cellophane films can be traced back to 1908 when Jacques E. Brandenberger, a Swiss textile engineer, invented the first machine to produce transparent sheets of regenerated cellulose. This breakthrough laid the foundation for the commercial production of cellophane, which began in the 1920s.
Throughout the mid-20th century, cellophane experienced rapid growth and technological advancements. The introduction of moisture-proof coatings in the 1930s significantly expanded its use in food packaging. This innovation allowed cellophane to maintain its clarity while providing an effective barrier against moisture and gases, thereby extending the shelf life of packaged products.
The 1950s and 1960s saw further improvements in cellophane production techniques, leading to enhanced mechanical properties and increased versatility. During this period, researchers focused on optimizing the film's strength, flexibility, and barrier properties, making it suitable for a wider range of applications beyond food packaging.
In the latter part of the 20th century, the evolution of cellophane films faced challenges from the emergence of synthetic polymers. However, the growing environmental concerns and the push for sustainable materials have led to a renewed interest in cellophane as a biodegradable alternative to petroleum-based plastics.
Recent developments in cellophane film technology have centered on improving its tear resistance, a critical property for many applications. Researchers have explored various approaches, including the incorporation of reinforcing agents, optimization of the cellulose regeneration process, and the development of multi-layer structures.
The quest for high tear resistance in cellophane films has driven innovations in both material composition and manufacturing processes. Scientists have investigated the use of nanocomposites, cross-linking agents, and surface modifications to enhance the film's mechanical properties without compromising its transparency or biodegradability.
As environmental regulations become more stringent and consumer demand for sustainable packaging grows, the evolution of cellophane films continues to focus on balancing performance with eco-friendliness. Current research efforts are directed towards developing cellophane films with improved tear resistance while maintaining their inherent biodegradability and compostability.
The ongoing evolution of cellophane films demonstrates the material's adaptability and enduring relevance in the face of changing market demands and technological advancements. As the industry strives to address the challenge of attaining high tear resistance, cellophane remains a promising material for sustainable packaging solutions in the 21st century.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for high tear-resistant cellophane films has been steadily increasing across various industries. This growth is primarily driven by the packaging sector, where cellophane films are extensively used for food packaging, consumer goods, and industrial applications. The need for improved tear resistance stems from the desire to enhance product protection, extend shelf life, and reduce material waste.
In the food packaging industry, there is a growing trend towards sustainable and eco-friendly packaging solutions. Cellophane films, being biodegradable and derived from renewable resources, align well with this trend. However, the demand for higher tear resistance in these films is crucial to ensure the integrity of packaged products during transportation, handling, and storage. This is particularly important for perishable goods and products with extended shelf lives.
The consumer goods sector, including personal care and household products, also contributes significantly to the demand for high tear-resistant cellophane films. Manufacturers are seeking packaging materials that can withstand the rigors of distribution and consumer handling while maintaining an attractive appearance on store shelves. The ability to resist tearing helps prevent product contamination and maintains brand image.
In the industrial sector, cellophane films with enhanced tear resistance find applications in protective packaging for delicate components, electronics, and automotive parts. The demand in this sector is driven by the need for lightweight yet durable packaging solutions that can safeguard products during shipping and handling.
The pharmaceutical industry represents another key market for high tear-resistant cellophane films. With stringent regulations on drug packaging and the need to maintain product integrity, there is a growing demand for films that can withstand punctures and tears while providing an effective barrier against moisture and contaminants.
Market analysis indicates that the global cellophane film market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 4% in the coming years. The demand for high tear-resistant variants is projected to outpace the overall market growth, driven by the increasing emphasis on product protection and sustainability.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific region leads the market demand for cellophane films, followed by North America and Europe. The rapid industrialization and growing consumer markets in countries like China and India are major contributors to this demand. However, the push for high tear resistance is more pronounced in developed markets where stringent packaging regulations and consumer expectations drive innovation.
As environmental concerns continue to shape consumer preferences and regulatory landscapes, the demand for biodegradable packaging solutions is expected to further boost the market for cellophane films. This trend, coupled with the ongoing need for improved mechanical properties such as tear resistance, presents significant opportunities for innovation and market growth in the cellophane film industry.
In the food packaging industry, there is a growing trend towards sustainable and eco-friendly packaging solutions. Cellophane films, being biodegradable and derived from renewable resources, align well with this trend. However, the demand for higher tear resistance in these films is crucial to ensure the integrity of packaged products during transportation, handling, and storage. This is particularly important for perishable goods and products with extended shelf lives.
The consumer goods sector, including personal care and household products, also contributes significantly to the demand for high tear-resistant cellophane films. Manufacturers are seeking packaging materials that can withstand the rigors of distribution and consumer handling while maintaining an attractive appearance on store shelves. The ability to resist tearing helps prevent product contamination and maintains brand image.
In the industrial sector, cellophane films with enhanced tear resistance find applications in protective packaging for delicate components, electronics, and automotive parts. The demand in this sector is driven by the need for lightweight yet durable packaging solutions that can safeguard products during shipping and handling.
The pharmaceutical industry represents another key market for high tear-resistant cellophane films. With stringent regulations on drug packaging and the need to maintain product integrity, there is a growing demand for films that can withstand punctures and tears while providing an effective barrier against moisture and contaminants.
Market analysis indicates that the global cellophane film market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 4% in the coming years. The demand for high tear-resistant variants is projected to outpace the overall market growth, driven by the increasing emphasis on product protection and sustainability.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific region leads the market demand for cellophane films, followed by North America and Europe. The rapid industrialization and growing consumer markets in countries like China and India are major contributors to this demand. However, the push for high tear resistance is more pronounced in developed markets where stringent packaging regulations and consumer expectations drive innovation.
As environmental concerns continue to shape consumer preferences and regulatory landscapes, the demand for biodegradable packaging solutions is expected to further boost the market for cellophane films. This trend, coupled with the ongoing need for improved mechanical properties such as tear resistance, presents significant opportunities for innovation and market growth in the cellophane film industry.
Technical Challenges
The development of high tear-resistant cellophane films faces several significant technical challenges. One of the primary obstacles is the inherent brittleness of cellophane, which makes it prone to tearing under stress. This characteristic is due to the molecular structure of cellulose, the main component of cellophane, which forms strong hydrogen bonds between polymer chains, resulting in a rigid and inflexible material.
Another major challenge lies in maintaining the transparency and optical properties of cellophane while enhancing its tear resistance. Traditional methods of improving tear strength often involve the addition of reinforcing agents or the modification of the film structure, which can compromise the film's clarity and light transmission capabilities. Balancing these properties is crucial for preserving cellophane's desirable visual characteristics.
The manufacturing process of cellophane also presents technical hurdles in achieving high tear resistance. The regeneration of cellulose from viscose solution and subsequent film formation involve complex chemical reactions and physical transformations. Controlling these processes to optimize the film's mechanical properties without sacrificing other essential qualities requires precise engineering and advanced process control systems.
Environmental concerns and regulatory requirements pose additional challenges. As the demand for sustainable and biodegradable packaging materials increases, the development of tear-resistant cellophane must align with eco-friendly standards. This necessitates the use of environmentally benign additives and processing methods, which can limit the available options for enhancing tear strength.
The scalability of production techniques for high tear-resistant cellophane is another significant challenge. Laboratory-scale successes in improving tear resistance often face difficulties when translated to industrial-scale manufacturing. Ensuring consistent quality and properties across large production volumes while maintaining cost-effectiveness is a complex task that requires substantial research and development efforts.
Furthermore, the compatibility of tear-resistant cellophane with existing packaging equipment and processes presents a technical challenge. Any modifications to the film's properties must not compromise its ability to be sealed, printed, or otherwise processed using standard packaging machinery. This requirement adds another layer of complexity to the development of improved cellophane films.
Lastly, the long-term stability and performance of tear-resistant cellophane under various environmental conditions remain a concern. Factors such as humidity, temperature fluctuations, and exposure to UV light can affect the film's mechanical properties over time. Developing formulations and structures that maintain high tear resistance throughout the product's lifecycle is an ongoing challenge for researchers and manufacturers in this field.
Another major challenge lies in maintaining the transparency and optical properties of cellophane while enhancing its tear resistance. Traditional methods of improving tear strength often involve the addition of reinforcing agents or the modification of the film structure, which can compromise the film's clarity and light transmission capabilities. Balancing these properties is crucial for preserving cellophane's desirable visual characteristics.
The manufacturing process of cellophane also presents technical hurdles in achieving high tear resistance. The regeneration of cellulose from viscose solution and subsequent film formation involve complex chemical reactions and physical transformations. Controlling these processes to optimize the film's mechanical properties without sacrificing other essential qualities requires precise engineering and advanced process control systems.
Environmental concerns and regulatory requirements pose additional challenges. As the demand for sustainable and biodegradable packaging materials increases, the development of tear-resistant cellophane must align with eco-friendly standards. This necessitates the use of environmentally benign additives and processing methods, which can limit the available options for enhancing tear strength.
The scalability of production techniques for high tear-resistant cellophane is another significant challenge. Laboratory-scale successes in improving tear resistance often face difficulties when translated to industrial-scale manufacturing. Ensuring consistent quality and properties across large production volumes while maintaining cost-effectiveness is a complex task that requires substantial research and development efforts.
Furthermore, the compatibility of tear-resistant cellophane with existing packaging equipment and processes presents a technical challenge. Any modifications to the film's properties must not compromise its ability to be sealed, printed, or otherwise processed using standard packaging machinery. This requirement adds another layer of complexity to the development of improved cellophane films.
Lastly, the long-term stability and performance of tear-resistant cellophane under various environmental conditions remain a concern. Factors such as humidity, temperature fluctuations, and exposure to UV light can affect the film's mechanical properties over time. Developing formulations and structures that maintain high tear resistance throughout the product's lifecycle is an ongoing challenge for researchers and manufacturers in this field.
Current Solutions
01 Polymer blending for improved tear resistance
Blending different polymers can enhance the tear resistance of cellophane films. This approach combines the beneficial properties of multiple materials to create a more robust film structure. The resulting composite films often exhibit improved mechanical properties, including higher tear strength and durability.- Polymer blending for improved tear resistance: Blending different polymers can enhance the tear resistance of cellophane films. This approach combines the beneficial properties of multiple materials to create a more robust film structure. The resulting composite films often exhibit improved mechanical properties, including higher tear strength and durability.
- Surface treatment and coating techniques: Applying various surface treatments or coatings to cellophane films can significantly improve their tear resistance. These methods may include chemical modifications, plasma treatments, or the application of specialized coatings that enhance the film's mechanical properties and reduce its susceptibility to tearing.
- Reinforcement with fibers or particles: Incorporating fibers or particles into the cellophane film matrix can greatly enhance its tear resistance. These reinforcing elements can be natural or synthetic materials that provide additional strength and structural integrity to the film, making it more resistant to tearing forces.
- Orientation and stretching techniques: Employing specific orientation and stretching techniques during the film production process can improve the tear resistance of cellophane films. These methods align the polymer chains in specific directions, enhancing the overall strength and tear resistance of the resulting film.
- Multilayer film structures: Creating multilayer film structures by combining cellophane with other materials can significantly enhance tear resistance. This approach allows for the incorporation of layers with complementary properties, resulting in a composite film with improved overall performance and durability.
02 Surface treatment techniques
Various surface treatment methods can be applied to cellophane films to improve their tear resistance. These techniques may include chemical modifications, plasma treatments, or the application of specialized coatings. Such treatments can alter the surface properties of the film, enhancing its resistance to tearing and other forms of mechanical damage.Expand Specific Solutions03 Reinforcement with fibers or particles
Incorporating fibers or particles into cellophane films can significantly increase their tear resistance. These reinforcing elements can be natural or synthetic materials that are dispersed throughout the film matrix. The added components help to distribute stress and prevent tear propagation, resulting in a more robust film structure.Expand Specific Solutions04 Multilayer film structures
Creating multilayer film structures can enhance the tear resistance of cellophane films. By combining layers with different properties, such as a tough outer layer with a more flexible inner layer, the overall tear resistance of the film can be improved. This approach allows for the optimization of various film characteristics while maintaining the desired tear resistance.Expand Specific Solutions05 Molecular orientation and crystallinity control
Controlling the molecular orientation and crystallinity of cellophane films during production can lead to improved tear resistance. This can be achieved through various processing techniques, such as stretching or annealing. By optimizing these parameters, the film's molecular structure can be tailored to enhance its mechanical properties, including tear resistance.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The market for high tear resistance cellophane films is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand in packaging and industrial applications. The global market size is estimated to be in the billions of dollars, with steady annual growth projected. Technologically, the field is moderately mature but continues to evolve with innovations in material science and manufacturing processes. Key players like Toyobo, FUJIFILM, and Mitsubishi Kasei are at the forefront, investing heavily in R&D to improve film properties. Companies such as 3M, Nitto Denko, and Daicel are also significant contributors, leveraging their expertise in advanced materials to develop high-performance cellophane films. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established chemical conglomerates and specialized film manufacturers, with ongoing efforts to enhance tear resistance while maintaining other desirable film properties.
Toyobo Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Toyobo has developed a high-performance cellophane film with enhanced tear resistance through a proprietary cross-linking technology. The process involves introducing chemical bonds between cellulose molecules, creating a more robust network structure. This cross-linked cellophane exhibits up to 50% higher tear strength compared to conventional films[1]. Additionally, Toyobo has implemented a multi-layer film structure, incorporating tear-resistant polymers like polyethylene or polypropylene as reinforcing layers. This composite approach allows for a balance between transparency, barrier properties, and tear resistance[3]. The company has also explored the use of nanocellulose fibers as reinforcing agents, which can significantly improve the mechanical properties of the film without compromising its transparency[5].
Strengths: Superior tear resistance, maintained transparency, and improved barrier properties. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs and complexity in manufacturing process.
FUJIFILM Corp.
Technical Solution: FUJIFILM has developed an innovative approach to enhance tear resistance in cellophane films through a combination of material science and nanotechnology. Their method involves incorporating specially designed nanoparticles into the cellulose matrix during film formation. These nanoparticles, typically made of silica or alumina, create a network of strong interactions within the film structure, significantly improving its mechanical properties[2]. The company has also implemented a controlled orientation process during film production, aligning cellulose molecules to maximize strength in multiple directions. This orientation technique has been reported to increase tear resistance by up to 40% compared to standard cellophane[4]. Furthermore, FUJIFILM has developed a surface treatment technology that applies a thin, flexible coating to the cellophane, which not only enhances tear resistance but also improves moisture barrier properties[6].
Strengths: High tear resistance, improved moisture barrier, and versatility in applications. Weaknesses: Potential increase in production costs and possible alterations to film transparency.
Innovative Patents
Polyester Resin Film and Process for Producing the Same
PatentInactiveUS20080193783A1
Innovation
- A production method involving mixing two polyester resin starting materials with different melting points, extruding the mixture, and stretching it in the monoaxial direction followed by heat treatment at a temperature 3°C lower than the lowest melting point, ensuring a resin proportion of 20-65 wt% with a melting point difference of at least 15°C, to achieve superior hand-tearability and twistability.
Film and method for producing the same
PatentActiveJP2020078909A
Innovation
- A film structure comprising layers of cellulose acetate and a thermoplastic elastomer, with specific thickness ranges for each layer, enhancing tear strength and moisture permeability.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of cellophane films with high tear resistance is a crucial consideration in the development and application of these materials. As the demand for durable packaging solutions increases, it is essential to evaluate the ecological footprint of enhanced cellophane films throughout their lifecycle.
The production process of high tear-resistant cellophane films often involves additional chemical treatments or the incorporation of synthetic polymers. These modifications can lead to increased energy consumption and the use of potentially harmful substances. However, advancements in green chemistry and sustainable manufacturing practices are mitigating some of these concerns, with researchers exploring bio-based additives and environmentally friendly processing methods.
One significant environmental advantage of cellophane films is their biodegradability. Even with improved tear resistance, cellophane remains fundamentally a cellulose-based material, which can decompose naturally in the environment. This characteristic sets it apart from many synthetic plastic alternatives, potentially reducing long-term environmental pollution. However, the rate of biodegradation may be affected by the additives used to enhance tear resistance, necessitating careful consideration of the overall environmental impact.
The improved durability of high tear-resistant cellophane films can contribute to waste reduction by extending the lifespan of packaging materials and reducing the need for double packaging or excessive material use. This can lead to a decrease in overall material consumption and, consequently, a reduction in the carbon footprint associated with packaging production and disposal.
Recycling considerations are also paramount when assessing the environmental impact of these enhanced films. While cellophane is generally recyclable, the additives used to improve tear resistance may complicate the recycling process. It is crucial to develop tear-resistant formulations that do not compromise the material's recyclability or introduce contaminants into the recycling stream.
The potential for reduced food waste is another environmental benefit of high tear-resistant cellophane films. By providing more robust packaging for perishable goods, these films can help extend shelf life and minimize food spoilage, thereby addressing one of the significant contributors to global greenhouse gas emissions.
In conclusion, while the environmental impact of high tear-resistant cellophane films presents both challenges and opportunities, ongoing research and development in this field are focused on optimizing the balance between performance and sustainability. The goal is to create packaging solutions that offer enhanced durability without compromising the environmental benefits inherent to cellophane-based materials.
The production process of high tear-resistant cellophane films often involves additional chemical treatments or the incorporation of synthetic polymers. These modifications can lead to increased energy consumption and the use of potentially harmful substances. However, advancements in green chemistry and sustainable manufacturing practices are mitigating some of these concerns, with researchers exploring bio-based additives and environmentally friendly processing methods.
One significant environmental advantage of cellophane films is their biodegradability. Even with improved tear resistance, cellophane remains fundamentally a cellulose-based material, which can decompose naturally in the environment. This characteristic sets it apart from many synthetic plastic alternatives, potentially reducing long-term environmental pollution. However, the rate of biodegradation may be affected by the additives used to enhance tear resistance, necessitating careful consideration of the overall environmental impact.
The improved durability of high tear-resistant cellophane films can contribute to waste reduction by extending the lifespan of packaging materials and reducing the need for double packaging or excessive material use. This can lead to a decrease in overall material consumption and, consequently, a reduction in the carbon footprint associated with packaging production and disposal.
Recycling considerations are also paramount when assessing the environmental impact of these enhanced films. While cellophane is generally recyclable, the additives used to improve tear resistance may complicate the recycling process. It is crucial to develop tear-resistant formulations that do not compromise the material's recyclability or introduce contaminants into the recycling stream.
The potential for reduced food waste is another environmental benefit of high tear-resistant cellophane films. By providing more robust packaging for perishable goods, these films can help extend shelf life and minimize food spoilage, thereby addressing one of the significant contributors to global greenhouse gas emissions.
In conclusion, while the environmental impact of high tear-resistant cellophane films presents both challenges and opportunities, ongoing research and development in this field are focused on optimizing the balance between performance and sustainability. The goal is to create packaging solutions that offer enhanced durability without compromising the environmental benefits inherent to cellophane-based materials.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance plays a crucial role in the development and production of high tear-resistant cellophane films. As these films are widely used in packaging applications, particularly for food and consumer goods, adherence to strict regulatory standards is essential to ensure product safety and market acceptance.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates cellophane films used in food packaging under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. Manufacturers must ensure that their cellophane films comply with FDA regulations, including 21 CFR 177.1200, which specifies the requirements for cellophane intended for food contact. This regulation outlines the permissible raw materials, additives, and manufacturing processes for cellophane production.
The European Union has its own set of regulations governing food contact materials, including Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004 on materials and articles intended to come into contact with food. Cellophane films must comply with these regulations, which include specific migration limits for various substances and overall migration limits to ensure the safety of packaged food products.
In addition to food safety regulations, environmental considerations are becoming increasingly important in the regulatory landscape. Many countries have implemented or are in the process of implementing regulations aimed at reducing plastic waste and promoting sustainable packaging solutions. For instance, the EU's Single-Use Plastics Directive aims to reduce the environmental impact of certain plastic products, including some types of packaging films.
To achieve high tear resistance in cellophane films while maintaining regulatory compliance, manufacturers must carefully select additives and processing methods that are approved for use in food contact materials. This may involve using approved strengthening agents or modifying the cellulose structure through approved chemical treatments. Any new additives or processes developed to enhance tear resistance must undergo rigorous testing and approval processes before they can be used in commercial products.
Manufacturers must also consider regulations related to chemical substances, such as the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation in the EU. This regulation requires manufacturers to register and assess the safety of chemical substances used in their products, including those used in cellophane film production.
As sustainability becomes a greater focus in regulatory frameworks, manufacturers of high tear-resistant cellophane films must also consider end-of-life scenarios for their products. This includes compliance with recycling and composting standards, as well as potential future regulations on biodegradability and environmental impact.
Staying abreast of evolving regulations and ensuring compliance across different markets is a significant challenge for manufacturers. It requires ongoing monitoring of regulatory changes, investment in research and development to find compliant solutions, and regular testing and certification of products to demonstrate adherence to applicable standards.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates cellophane films used in food packaging under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. Manufacturers must ensure that their cellophane films comply with FDA regulations, including 21 CFR 177.1200, which specifies the requirements for cellophane intended for food contact. This regulation outlines the permissible raw materials, additives, and manufacturing processes for cellophane production.
The European Union has its own set of regulations governing food contact materials, including Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004 on materials and articles intended to come into contact with food. Cellophane films must comply with these regulations, which include specific migration limits for various substances and overall migration limits to ensure the safety of packaged food products.
In addition to food safety regulations, environmental considerations are becoming increasingly important in the regulatory landscape. Many countries have implemented or are in the process of implementing regulations aimed at reducing plastic waste and promoting sustainable packaging solutions. For instance, the EU's Single-Use Plastics Directive aims to reduce the environmental impact of certain plastic products, including some types of packaging films.
To achieve high tear resistance in cellophane films while maintaining regulatory compliance, manufacturers must carefully select additives and processing methods that are approved for use in food contact materials. This may involve using approved strengthening agents or modifying the cellulose structure through approved chemical treatments. Any new additives or processes developed to enhance tear resistance must undergo rigorous testing and approval processes before they can be used in commercial products.
Manufacturers must also consider regulations related to chemical substances, such as the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation in the EU. This regulation requires manufacturers to register and assess the safety of chemical substances used in their products, including those used in cellophane film production.
As sustainability becomes a greater focus in regulatory frameworks, manufacturers of high tear-resistant cellophane films must also consider end-of-life scenarios for their products. This includes compliance with recycling and composting standards, as well as potential future regulations on biodegradability and environmental impact.
Staying abreast of evolving regulations and ensuring compliance across different markets is a significant challenge for manufacturers. It requires ongoing monitoring of regulatory changes, investment in research and development to find compliant solutions, and regular testing and certification of products to demonstrate adherence to applicable standards.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!