High Density Polyethylene in Furniture Design: Trends and Benefits
HDPE Furniture Evolution
The evolution of High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) in furniture design represents a significant shift in material usage and manufacturing processes within the industry. Initially introduced in the mid-20th century, HDPE's application in furniture was limited due to its perceived lack of aesthetic appeal and durability concerns. However, advancements in polymer science and manufacturing techniques have dramatically transformed HDPE's role in furniture design over the past few decades.
In the 1960s and 1970s, HDPE was primarily used for outdoor furniture, particularly in garden and patio settings. Its weather-resistant properties made it an attractive alternative to traditional materials like wood and metal. The early designs were simple and functional, often featuring monochromatic color schemes and basic shapes.
The 1980s and 1990s saw a significant leap in HDPE furniture design. Improved molding techniques allowed for more complex shapes and structures, expanding the material's application to indoor furniture. Designers began experimenting with color variations and textures, challenging the perception of plastic furniture as cheap or disposable. This period also marked the beginning of HDPE's use in children's furniture, capitalizing on its durability and safety features.
The turn of the millennium brought about a renewed focus on sustainability in design, propelling HDPE to the forefront of eco-friendly furniture solutions. Recycled HDPE became increasingly popular, addressing environmental concerns while maintaining the material's desirable properties. This shift not only improved the material's public image but also opened up new design possibilities.
In recent years, technological advancements have further revolutionized HDPE furniture design. 3D printing and advanced molding techniques have enabled the creation of intricate patterns and structures previously impossible with traditional manufacturing methods. This has led to a new wave of innovative designs that blur the lines between art and functionality.
The current trend in HDPE furniture design emphasizes versatility and modularity. Designers are creating pieces that can be easily reconfigured or adapted to different spaces and uses, reflecting the changing needs of modern consumers. Additionally, there's a growing interest in combining HDPE with other materials, such as metal or wood, to create hybrid designs that leverage the strengths of each material.
Looking forward, the evolution of HDPE in furniture design is likely to continue along the paths of sustainability, technological innovation, and aesthetic refinement. As manufacturing processes become more sophisticated and designers push the boundaries of what's possible with the material, HDPE furniture is poised to play an increasingly significant role in both residential and commercial spaces.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) in furniture design has been steadily increasing over the past decade. This growth is driven by several factors, including the material's durability, versatility, and eco-friendly characteristics. HDPE furniture has gained popularity in both residential and commercial settings, with a particular emphasis on outdoor and children's furniture.
In the residential sector, homeowners are increasingly seeking low-maintenance, weather-resistant outdoor furniture options. HDPE meets these requirements perfectly, offering resistance to UV rays, moisture, and temperature fluctuations. The material's ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions without fading, cracking, or warping has led to a surge in demand for HDPE patio sets, loungers, and garden furniture.
Commercial applications of HDPE furniture have also seen significant growth. Hotels, resorts, and restaurants are adopting HDPE furniture for their outdoor spaces due to its longevity and ease of maintenance. The material's resistance to stains and chemicals makes it ideal for high-traffic areas and frequent cleaning, which is particularly valuable in the hospitality industry.
The children's furniture market has embraced HDPE due to its safety features and durability. Parents and educational institutions are drawn to HDPE furniture for its non-toxic nature, rounded edges, and ability to withstand rough handling. This has led to an increased demand for HDPE tables, chairs, and play structures in homes, schools, and daycare centers.
Sustainability concerns are also driving market demand for HDPE furniture. As consumers become more environmentally conscious, they are seeking products made from recyclable materials. HDPE's recyclability and the growing trend of furniture made from recycled ocean plastics have positioned it as an eco-friendly choice in the furniture industry.
The global HDPE furniture market is expected to continue its growth trajectory. Emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are showing increased adoption of HDPE furniture, particularly in outdoor and commercial applications. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated this trend, with a heightened focus on outdoor living spaces and easy-to-clean furniture solutions.
Innovation in HDPE furniture design is also fueling market demand. Manufacturers are exploring new techniques to improve the aesthetic appeal of HDPE furniture, including textured finishes, color blending, and innovative shapes. This has expanded the material's appeal beyond traditional outdoor settings, with some designers incorporating HDPE into contemporary indoor furniture pieces.
HDPE Challenges
While High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) offers numerous advantages in furniture design, it also presents several challenges that manufacturers and designers must address. One of the primary concerns is the material's susceptibility to UV degradation. When exposed to prolonged sunlight, HDPE can experience color fading, brittleness, and reduced structural integrity. This limitation necessitates the incorporation of UV stabilizers or protective coatings, which can increase production costs and complexity.
Another significant challenge lies in HDPE's thermal expansion properties. The material expands and contracts with temperature fluctuations, potentially leading to warping or distortion in furniture pieces. This characteristic requires careful consideration in design and assembly processes to ensure long-term stability and functionality, particularly for outdoor furniture applications.
The surface finish of HDPE can also pose difficulties. While the material is naturally smooth, achieving high-quality, aesthetically pleasing surfaces that meet consumer expectations can be challenging. Advanced molding techniques or post-processing methods may be required to enhance the visual appeal of HDPE furniture, adding to production time and costs.
Recycling and sustainability present both opportunities and challenges for HDPE in furniture design. While HDPE is recyclable, the process of separating it from other materials in furniture pieces can be complex. Additionally, ensuring the purity of recycled HDPE for high-quality furniture production remains a technical hurdle.
The joining and assembly of HDPE components in furniture design also present challenges. Traditional fastening methods may not be as effective due to the material's properties, necessitating specialized techniques such as heat welding or the use of compatible adhesives. This can complicate the manufacturing process and impact the ease of furniture assembly or disassembly.
HDPE's relatively low heat resistance compared to some other materials used in furniture manufacturing limits its applications in certain environments. This characteristic requires careful consideration in design and material selection for furniture intended for use in high-temperature settings or near heat sources.
Lastly, while HDPE offers good chemical resistance, it may still be susceptible to certain solvents and oils. This can lead to potential staining or degradation in specific use cases, requiring the development of protective treatments or careful material selection for different furniture applications.
Addressing these challenges requires ongoing research and development efforts in material science, manufacturing processes, and design techniques. As the furniture industry continues to explore the potential of HDPE, innovative solutions to these challenges will likely emerge, further expanding the material's applications and benefits in furniture design.
Current HDPE Solutions
01 Composition and properties of HDPE
High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is a thermoplastic polymer with a high strength-to-density ratio. It is characterized by its long linear chains with minimal branching, resulting in higher tensile strength, stiffness, and chemical resistance compared to other polyethylene types. HDPE's properties make it suitable for various applications in packaging, construction, and automotive industries.- Composition and properties of HDPE: High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is a thermoplastic polymer with a high strength-to-density ratio. It is characterized by its long linear chains with minimal branching, resulting in higher tensile strength and improved chemical resistance compared to other polyethylene types. HDPE's properties make it suitable for various applications, including packaging, pipes, and containers.
- HDPE blends and composites: HDPE can be blended with other materials or reinforced with additives to enhance its properties. These blends and composites often aim to improve mechanical strength, thermal stability, or specific functional characteristics. Common additives include other polymers, fibers, nanoparticles, or mineral fillers, resulting in materials with tailored properties for specific applications.
- HDPE processing techniques: Various processing techniques are employed to manufacture HDPE products. These include injection molding, extrusion, blow molding, and rotational molding. Each technique offers specific advantages and is suited for different product types. Advancements in processing technology focus on improving efficiency, reducing cycle times, and enhancing product quality.
- Recycling and sustainability of HDPE: HDPE is widely recycled due to its thermoplastic nature, allowing it to be melted and reformed multiple times. Recycling processes for HDPE include mechanical recycling, chemical recycling, and energy recovery. Efforts are being made to improve recycling efficiency, develop new recycling technologies, and increase the use of recycled HDPE in various applications to promote sustainability.
- HDPE applications and innovations: HDPE finds applications in diverse industries due to its versatile properties. It is commonly used in packaging, construction, automotive, and healthcare sectors. Ongoing research focuses on developing new HDPE grades with enhanced properties, such as improved barrier characteristics, antimicrobial properties, or better processability. Innovations also include the development of HDPE-based composites for specialized applications.
02 HDPE blends and composites
HDPE can be blended with other materials or reinforced with fillers to enhance its properties. These blends and composites often aim to improve mechanical strength, thermal stability, or specific functional characteristics. Common additives include other polymers, natural fibers, or inorganic particles, resulting in materials with tailored properties for specific applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 HDPE processing techniques
Various processing techniques are employed to manufacture HDPE products, including injection molding, extrusion, and blow molding. These methods allow for the production of a wide range of items, from bottles and containers to pipes and automotive parts. Advancements in processing technology focus on improving efficiency, reducing cycle times, and enhancing product quality.Expand Specific Solutions04 Recycling and sustainability of HDPE
HDPE is highly recyclable, making it an environmentally friendly option in many applications. Recycling processes for HDPE involve collection, sorting, cleaning, and reprocessing into new products. Innovations in this area focus on improving recycling efficiency, developing new applications for recycled HDPE, and creating closed-loop systems to minimize waste and environmental impact.Expand Specific Solutions05 HDPE applications in specialized fields
HDPE finds applications in various specialized fields due to its unique properties. These include use in medical devices, food packaging, water treatment systems, and geomembranes for environmental protection. Research in this area focuses on developing HDPE grades with enhanced properties for specific applications, such as improved barrier properties for packaging or increased durability for outdoor use.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The high-density polyethylene (HDPE) market in furniture design is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for durable, lightweight, and eco-friendly materials. The industry is in a mature stage, with a global market size expected to reach $84.79 billion by 2028. Technological advancements have improved HDPE's properties, making it more suitable for furniture applications. Major players like Dow Global Technologies, ExxonMobil Chemical Patents, and SABIC Global Technologies are leading innovation in HDPE formulations. Companies such as Zhejiang Lifan Furniture and Zhejiang Senchuan Furniture are integrating HDPE into their product lines, showcasing the material's versatility and market acceptance in the furniture sector.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Borealis AG
HDPE Design Innovations
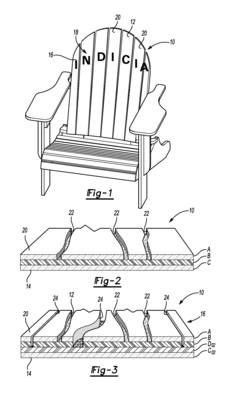
- A method involving a three-layer construction of HDPE (High Density Polyethylene) where the outer layers are the same color and the inner layer is different, with a router used to expose the inner layer to create a multi-color, three-dimensional design that lasts the life of the furniture.
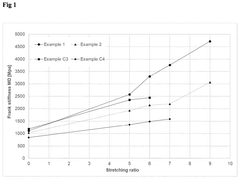
- A polyethylene composition with a density of 955-965 kg/m3, a melt index of 0.1-2 g/10 min, and specific rheological properties is developed, allowing for high stretching ratios in the machine direction, resulting in films with enhanced stiffness and low shrinkage, suitable for replacing polyethylene terephthalate (PET) layers in multilayer films.
Sustainability Impact
The integration of High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) in furniture design has significant implications for sustainability. HDPE, being a recyclable material, contributes to the circular economy by reducing waste and conserving resources. When used in furniture production, it offers a more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional materials like wood or metal.
One of the primary sustainability benefits of HDPE furniture is its durability and longevity. HDPE products can withstand harsh weather conditions, resist fading, and maintain their structural integrity for extended periods. This longevity reduces the need for frequent replacements, thereby minimizing resource consumption and waste generation over time.
The recyclability of HDPE furniture is another crucial aspect of its sustainability impact. At the end of its lifecycle, HDPE can be easily recycled and repurposed into new products, reducing the burden on landfills and conserving raw materials. This closed-loop system aligns with the principles of a circular economy, where materials are reused and recycled rather than discarded.
Furthermore, the production process of HDPE furniture often requires less energy compared to traditional materials. The manufacturing of HDPE involves lower temperatures and fewer processing steps, resulting in reduced energy consumption and lower carbon emissions. This energy efficiency contributes to the overall reduction of the carbon footprint associated with furniture production.
HDPE furniture also offers advantages in terms of transportation and distribution. Its lightweight nature compared to traditional materials like wood or metal means that more units can be transported in a single shipment, reducing fuel consumption and associated emissions. This efficiency in logistics further enhances the sustainability profile of HDPE furniture.
The use of HDPE in furniture design also promotes the concept of upcycling. Many manufacturers are now using recycled HDPE from post-consumer waste, such as plastic bottles, to create new furniture pieces. This practice not only diverts plastic waste from landfills and oceans but also reduces the demand for virgin plastic production, contributing to resource conservation and pollution reduction.
In terms of maintenance, HDPE furniture requires minimal upkeep and does not need harmful chemical treatments or paints to maintain its appearance. This reduces the use of potentially toxic substances and minimizes the environmental impact associated with furniture maintenance over its lifetime.
Manufacturing Processes
The manufacturing processes for High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) furniture have evolved significantly, offering innovative solutions for designers and manufacturers alike. The primary methods used in HDPE furniture production include injection molding, rotational molding, and extrusion.
Injection molding is widely employed for creating complex shapes and intricate details in HDPE furniture components. This process involves heating HDPE pellets until molten, then injecting the material into a mold under high pressure. Once cooled and solidified, the part is ejected. Injection molding allows for high-volume production with consistent quality and minimal waste.
Rotational molding, or rotomolding, is particularly suitable for producing large, hollow HDPE furniture pieces. The process begins by placing HDPE powder into a mold, which is then heated and rotated simultaneously. As the mold rotates, the melted plastic coats the interior surfaces, creating a uniform thickness. This method is ideal for manufacturing items like outdoor chairs, tables, and storage containers.
Extrusion is another key manufacturing process used in HDPE furniture production, especially for creating long, continuous profiles such as planks or tubes. In this process, HDPE pellets are melted and forced through a die with a specific cross-sectional shape. The extruded material is then cooled and cut to the desired length. This method is commonly used for producing components like table edges, chair slats, and structural elements.
Recent advancements in manufacturing technologies have led to improved efficiency and sustainability in HDPE furniture production. Computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) systems have streamlined the design-to-production process, allowing for rapid prototyping and iterative design improvements. Additionally, the integration of robotics and automation in manufacturing lines has enhanced precision and reduced production times.
Sustainability considerations have also influenced HDPE furniture manufacturing processes. Many manufacturers now incorporate recycled HDPE into their production, reducing the demand for virgin materials. Advanced recycling technologies have made it possible to process post-consumer HDPE into high-quality raw materials suitable for furniture production. This circular approach not only reduces waste but also appeals to environmentally conscious consumers.
The durability and weather resistance of HDPE have made it an increasingly popular choice for outdoor furniture. Manufacturers have developed specialized UV-stabilization processes to enhance the material's resistance to sun damage and color fading. This involves incorporating UV-resistant additives during the manufacturing process, ensuring the longevity of HDPE furniture in outdoor settings.